Performance Comparisons on Parallel Optimization of Atmospheric and Ocean Numerical Circulation Models Using KISTI Supercomputer Nurion System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Configuration
3. Performance Evaluation of WRF
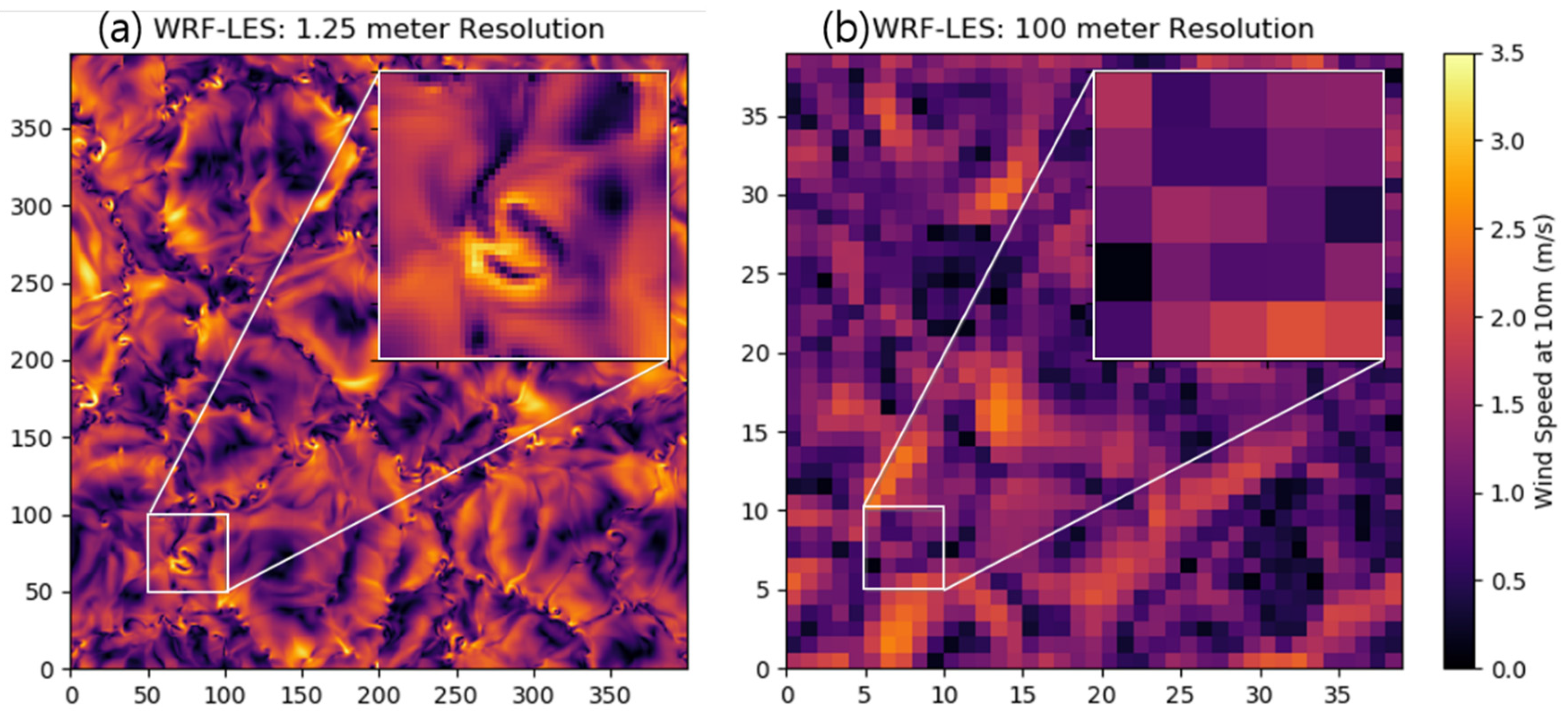
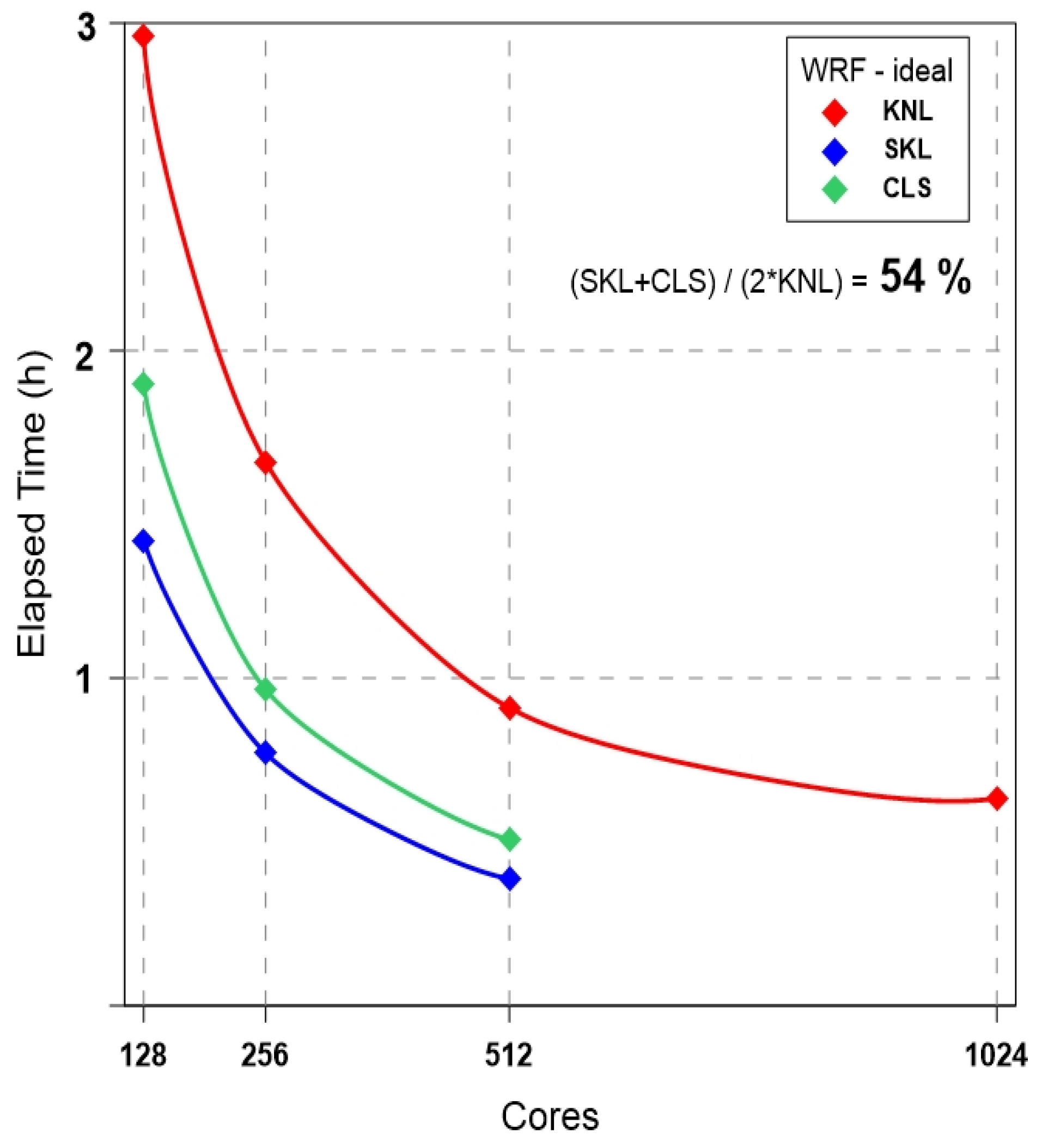
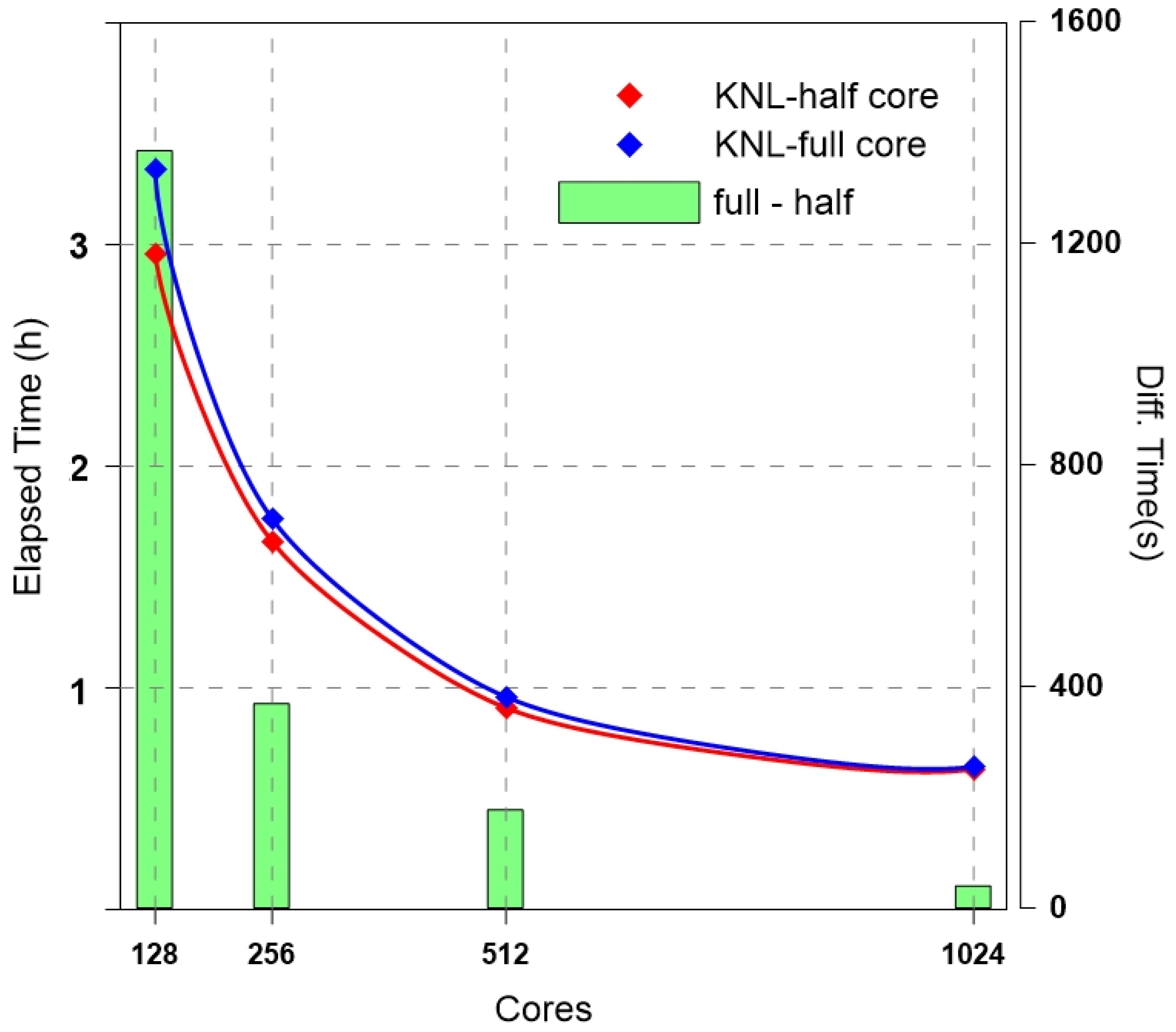
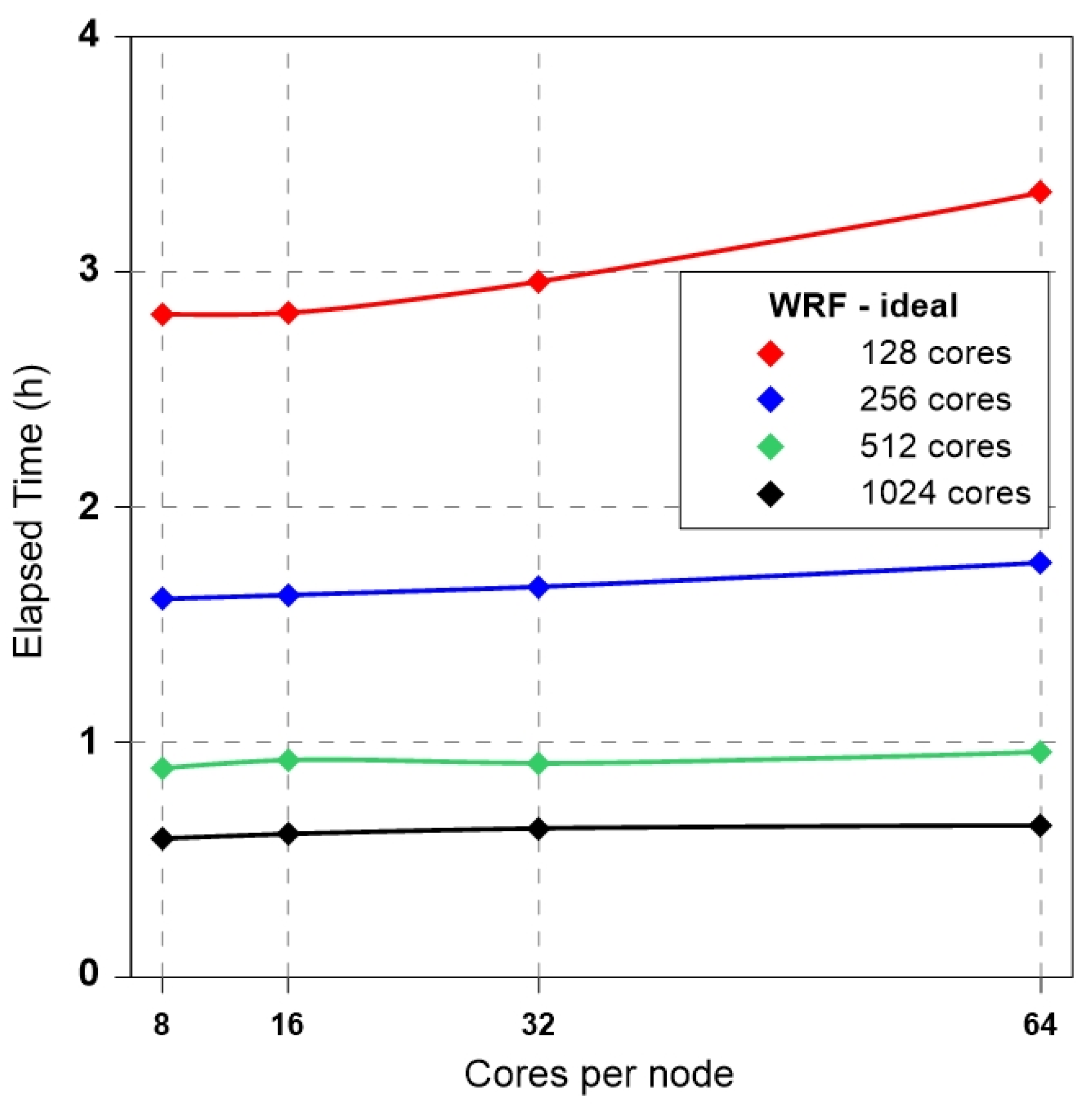
3.1. Ideal Experiment: WRF-LES
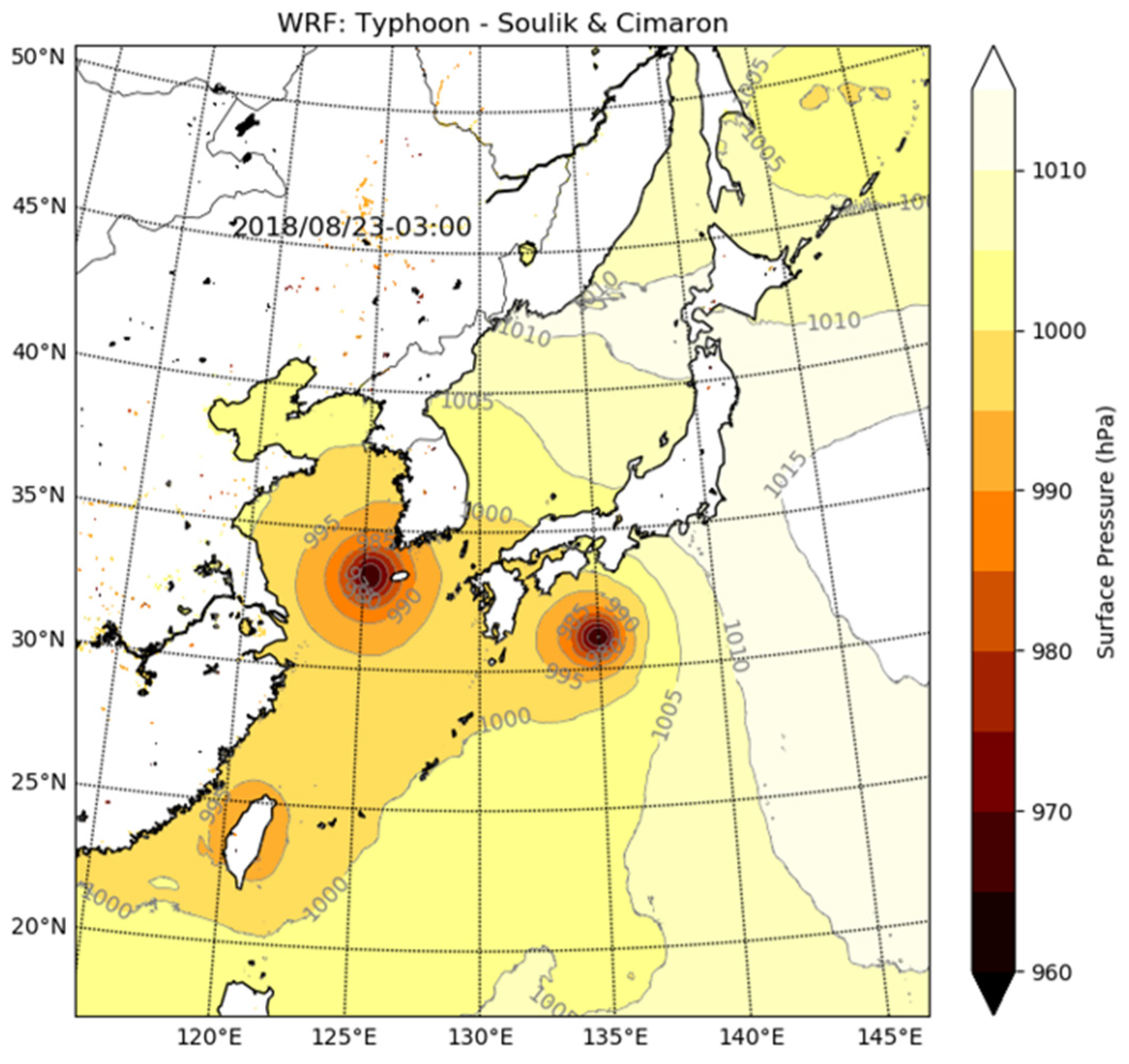
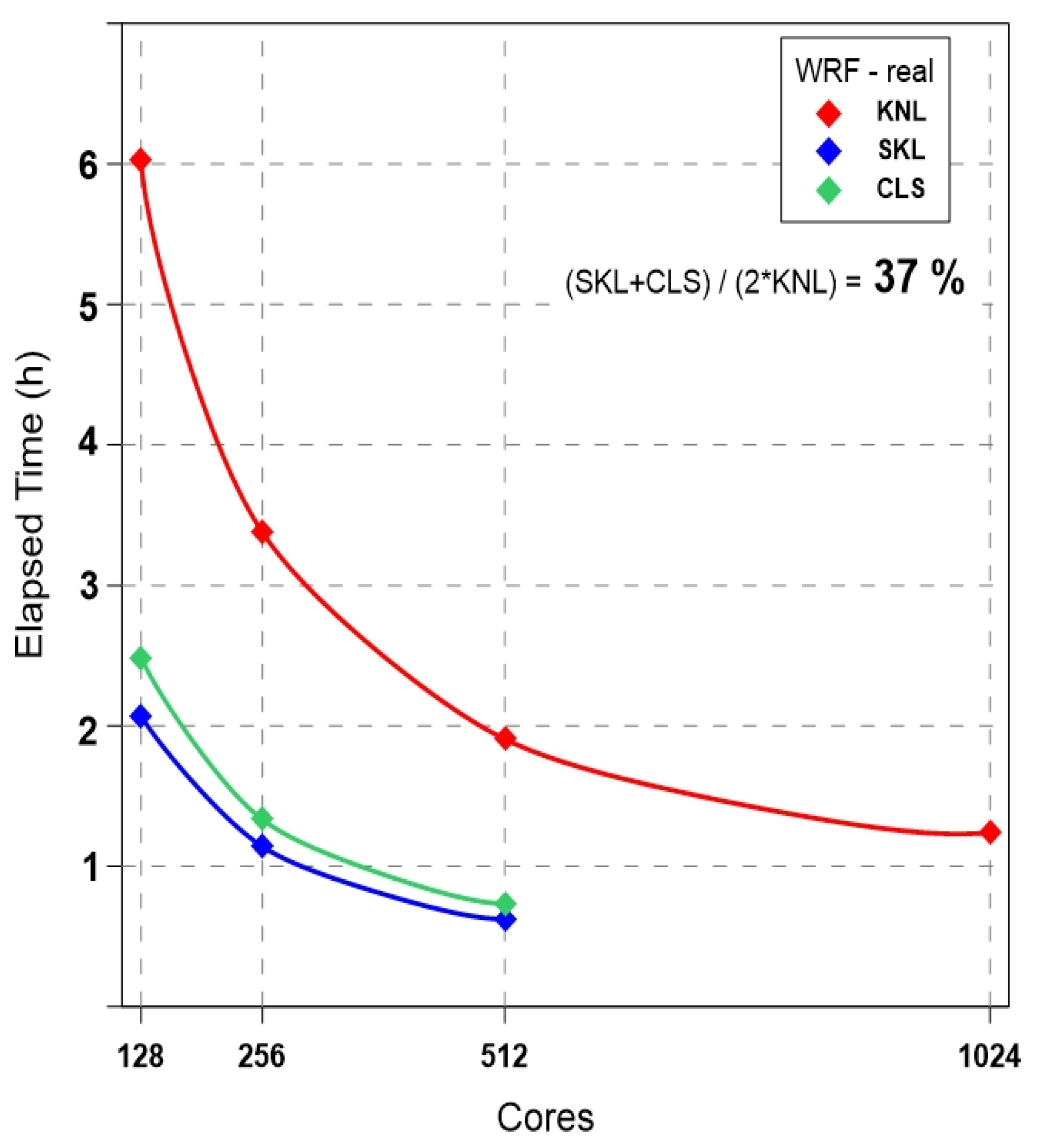
3.2. Real Experiment: WRF-NWP
4. Performance Evaluation of ROMS
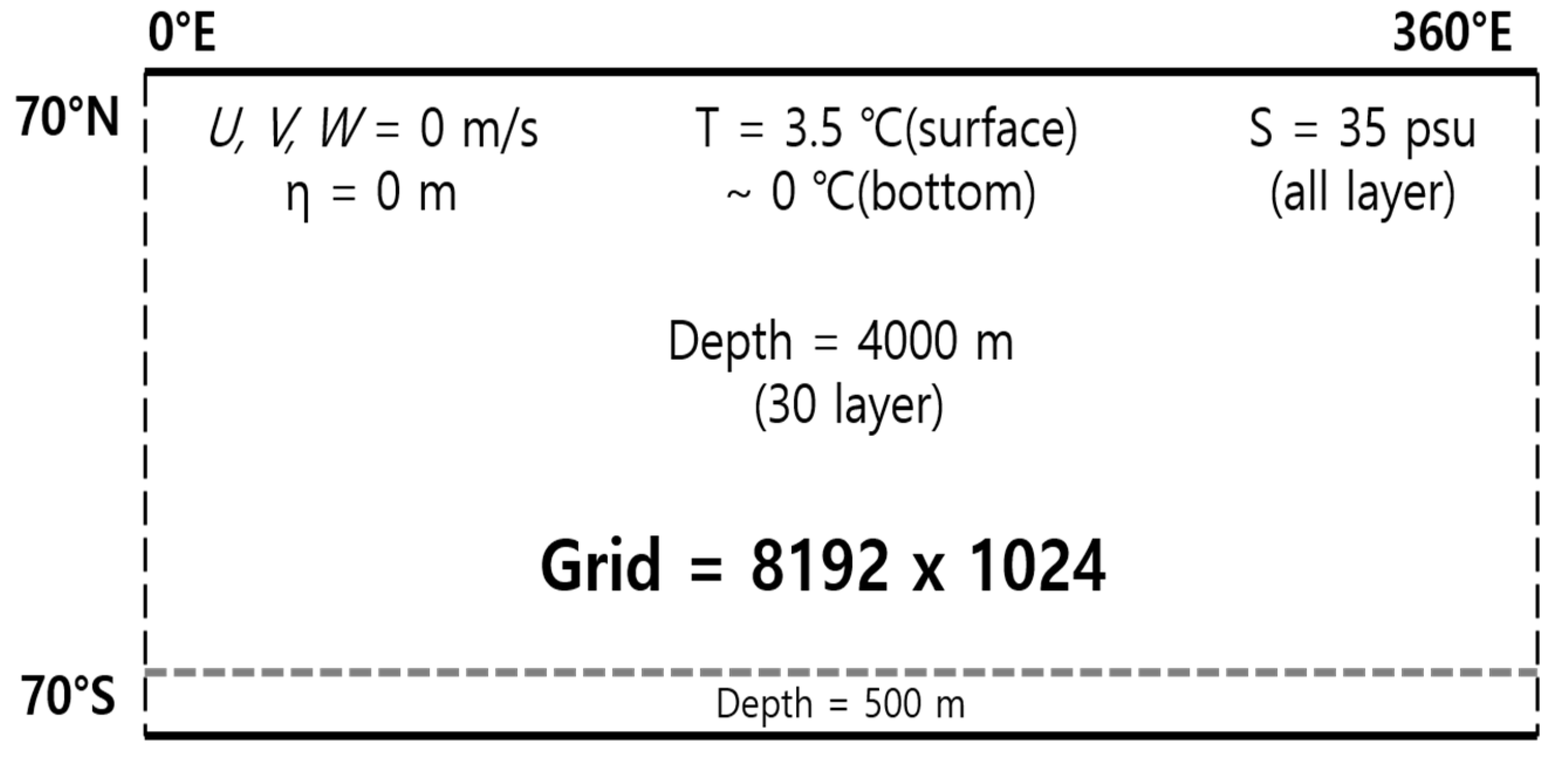
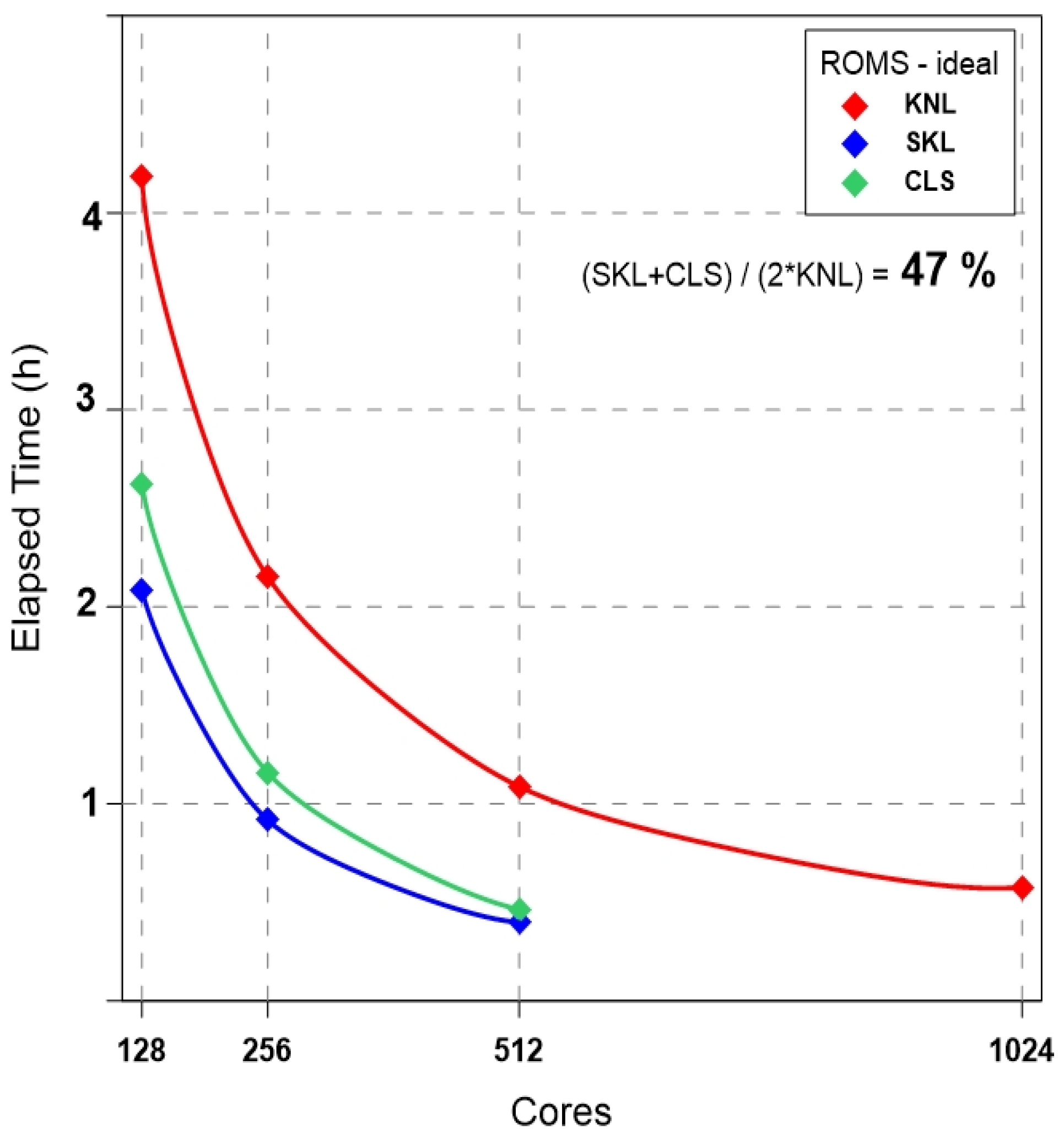
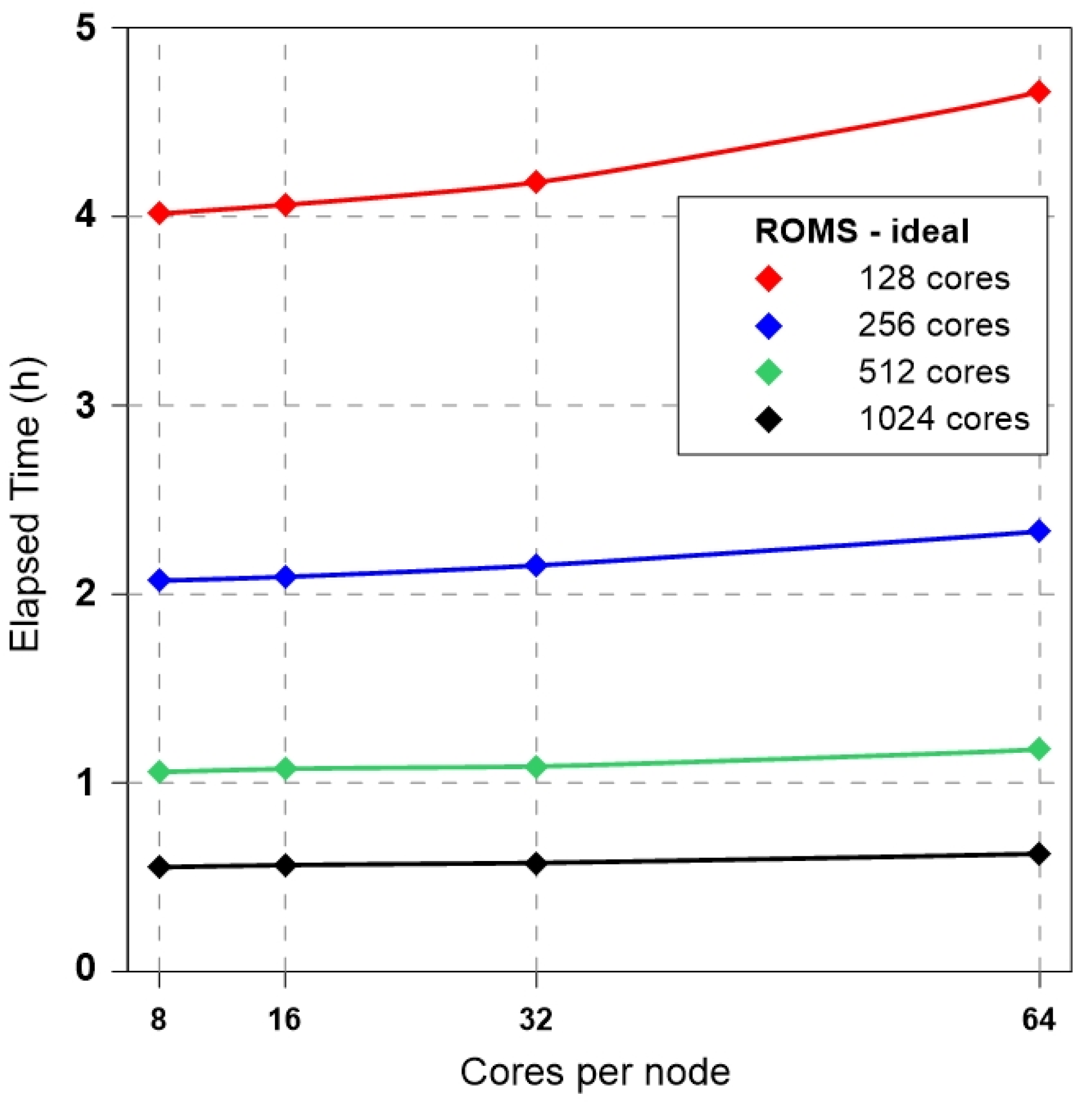
4.1. Ideal Experiment: ROMS-Benchmark
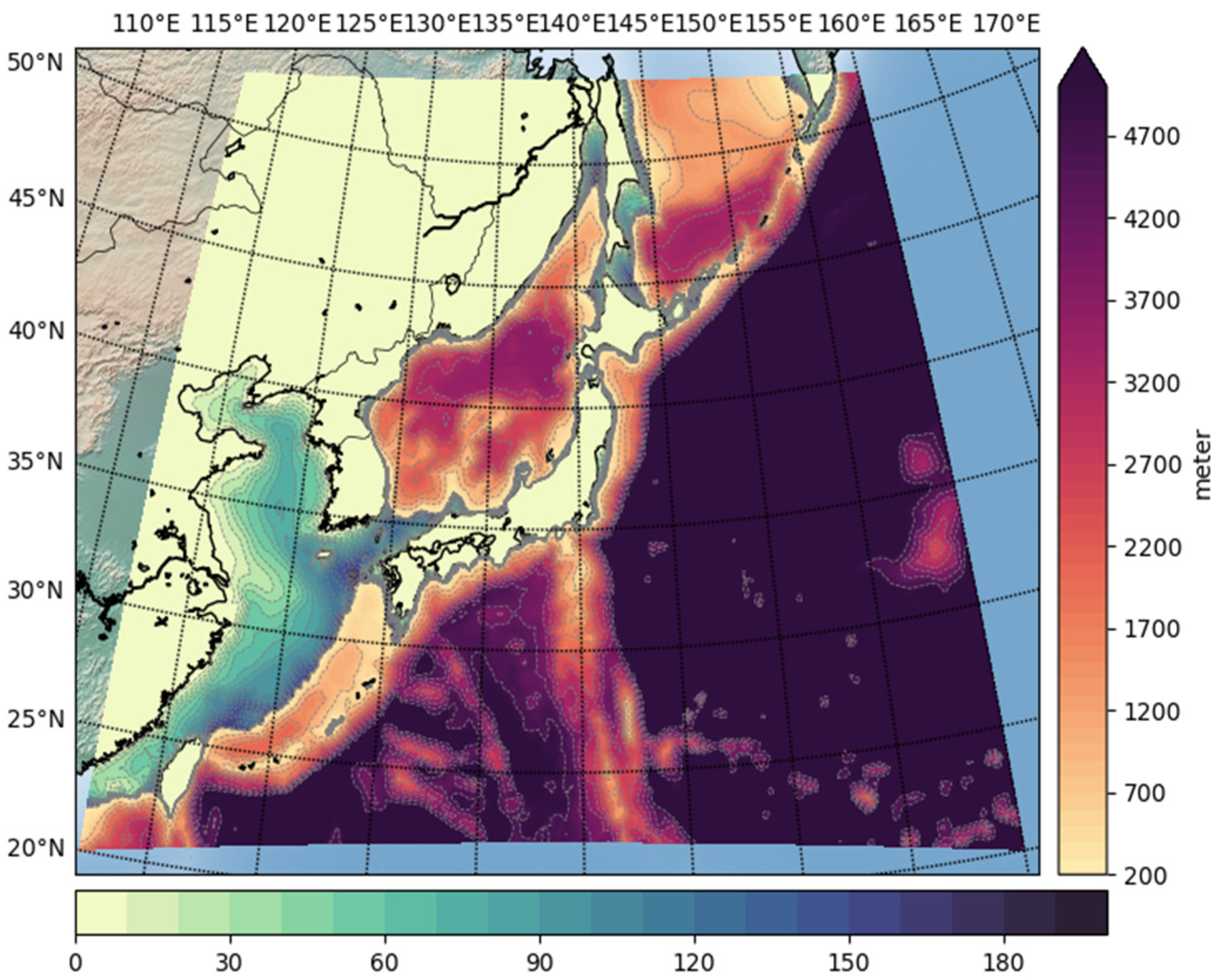
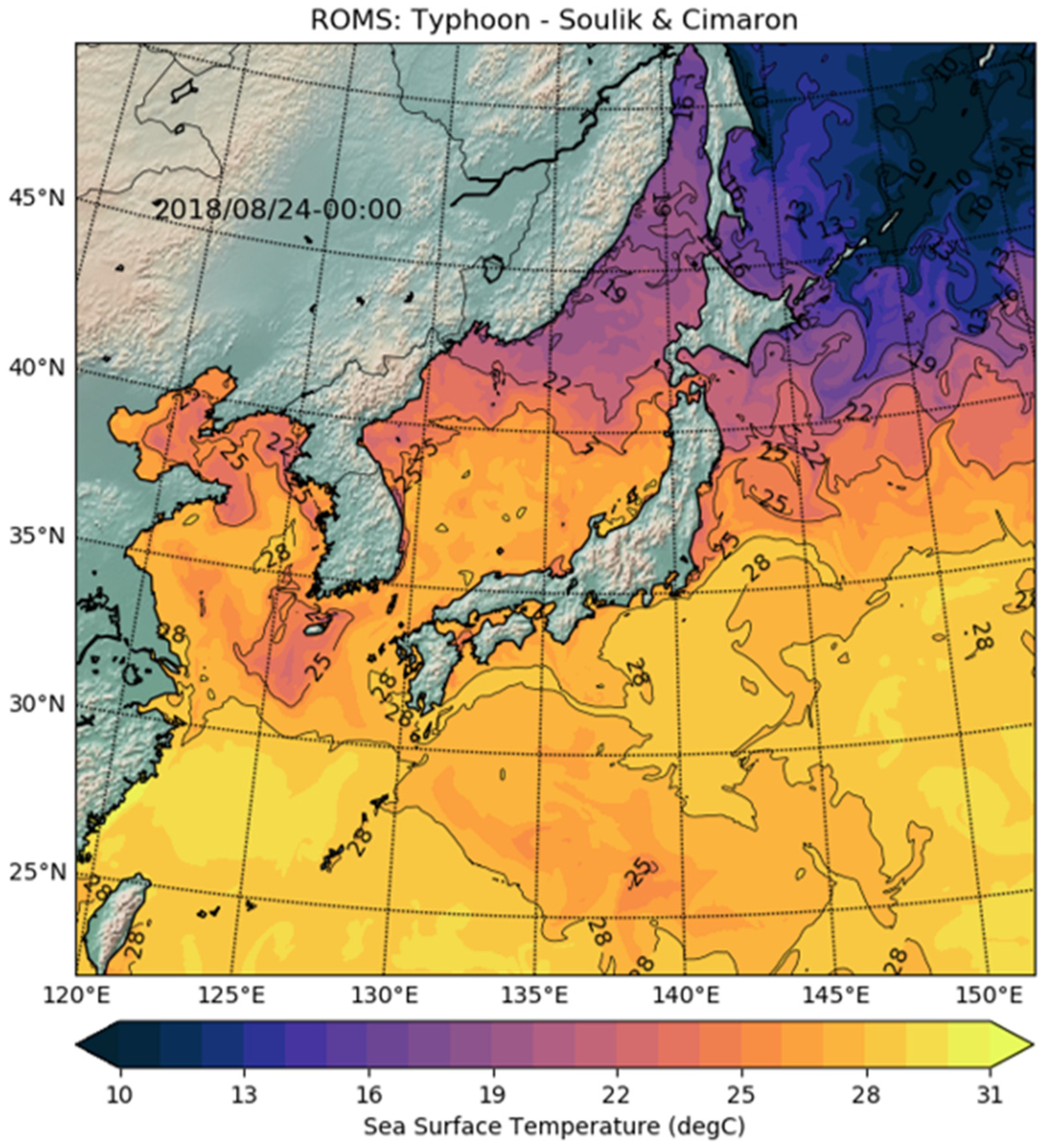
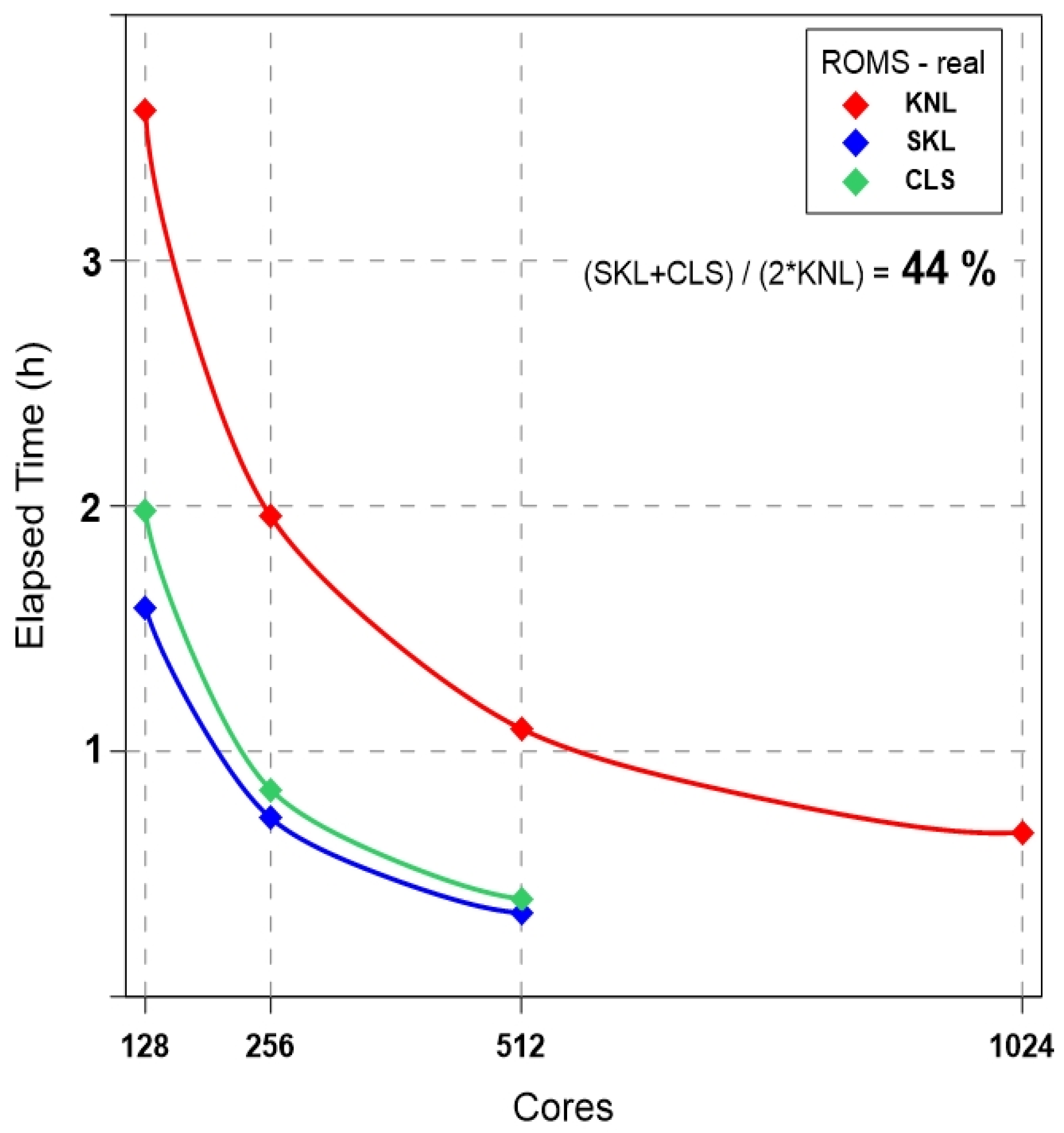
4.2. Real Experiment: ROMS-NWP
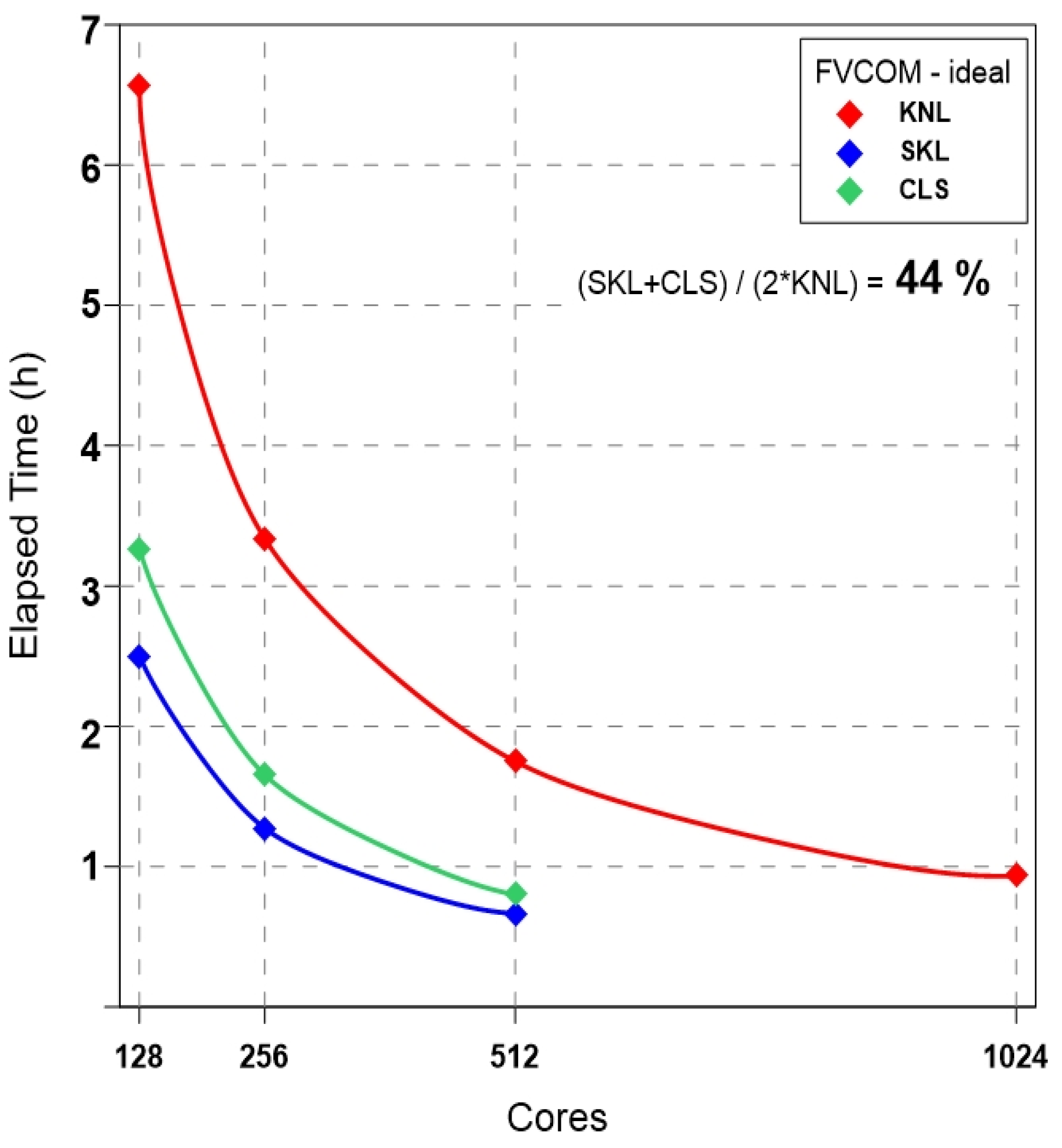
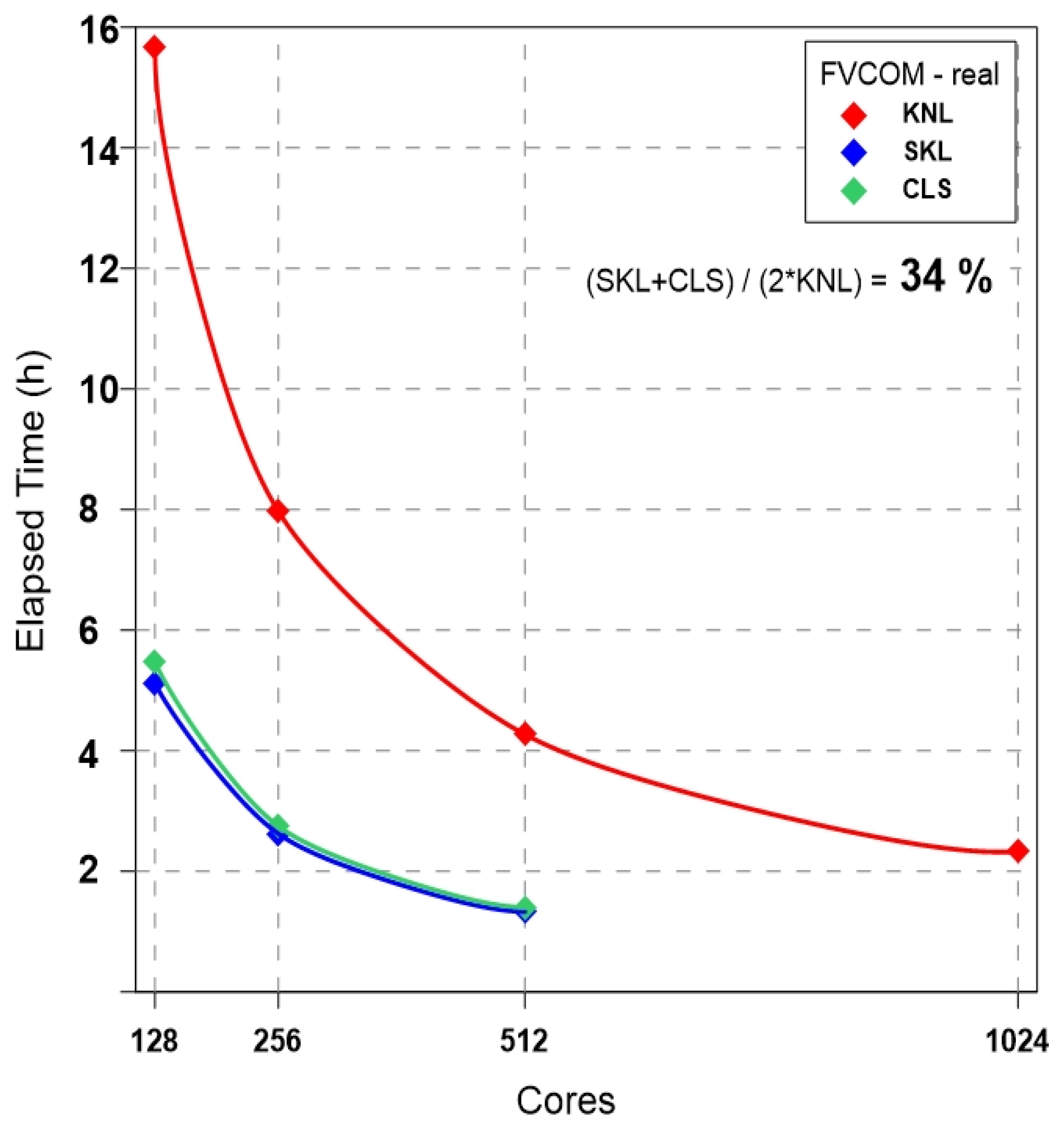
5. Performance Evaluation of FVCOM
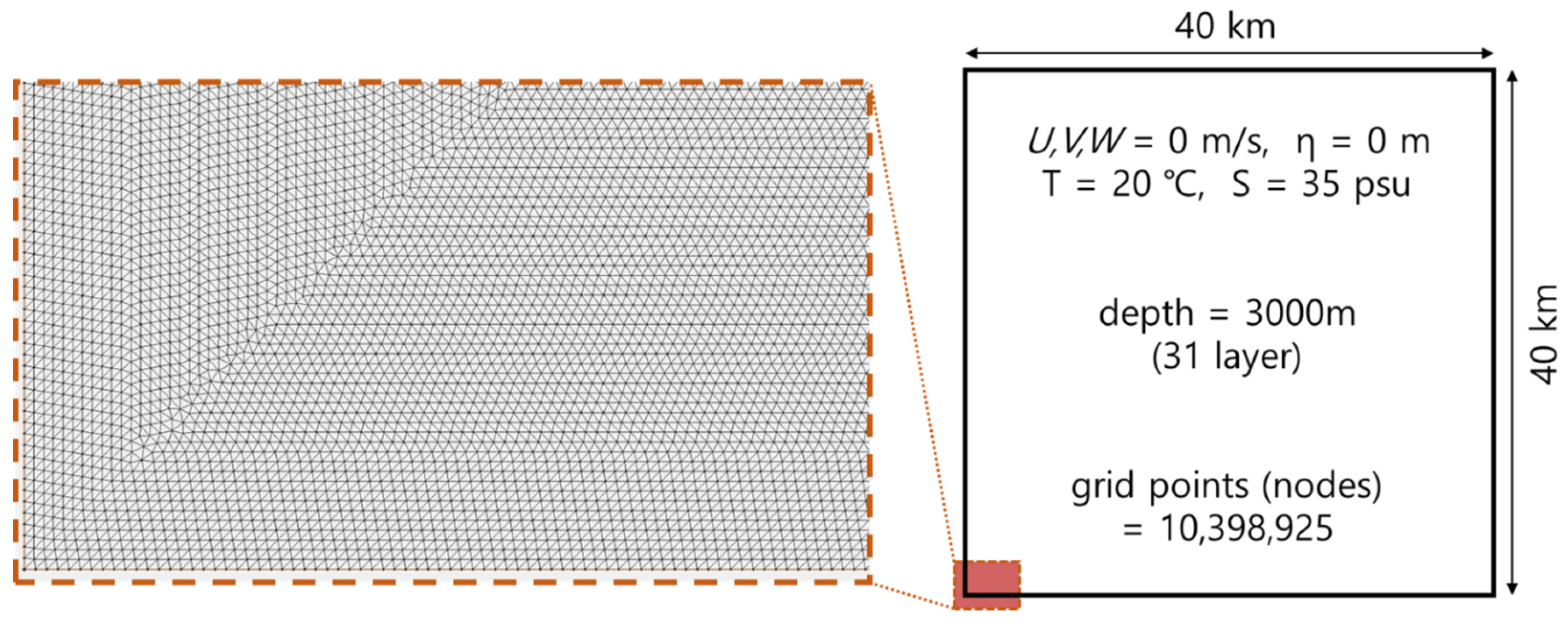
5.1. Ideal Experiment: FVCOM-Benchmark
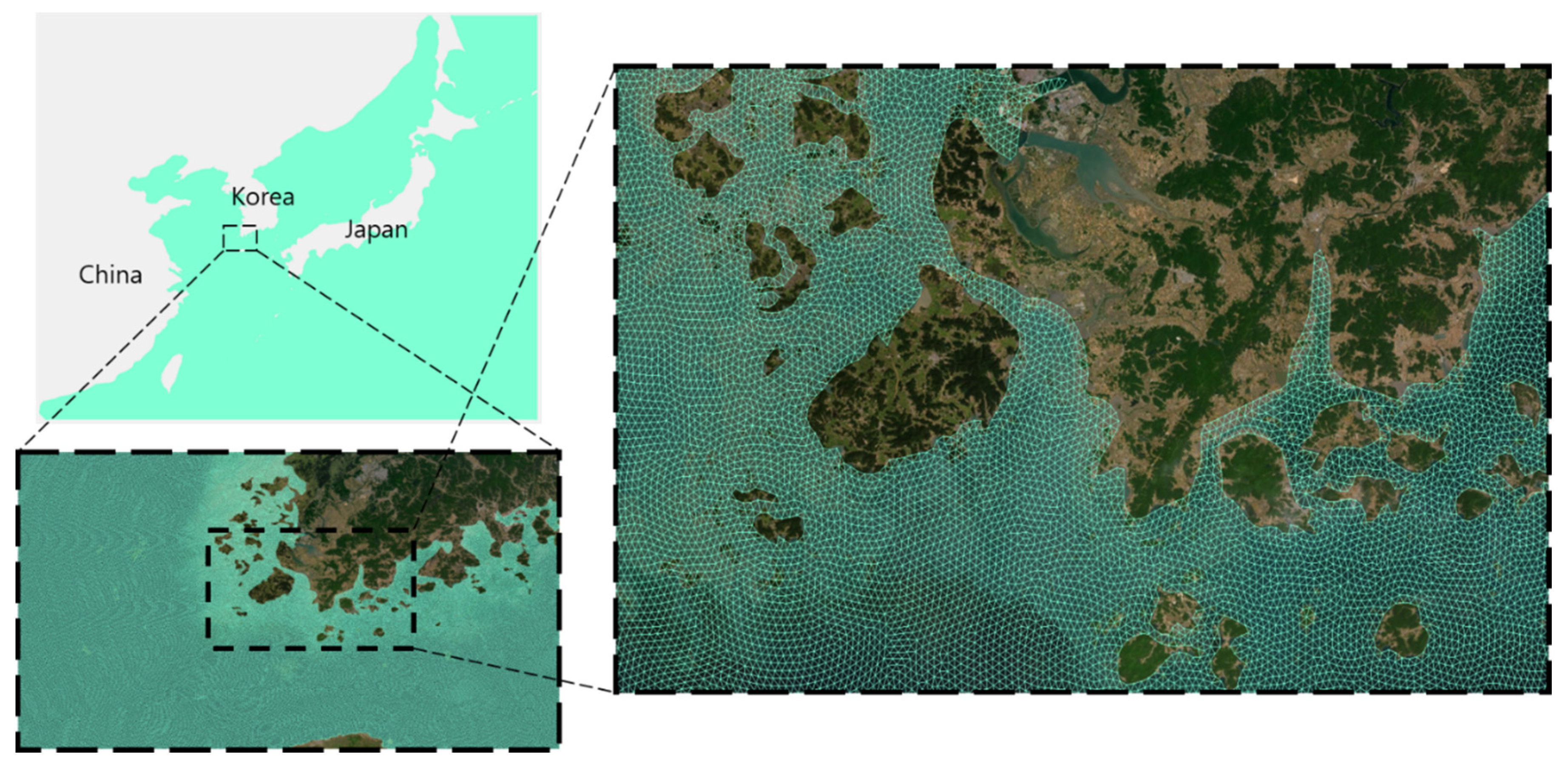
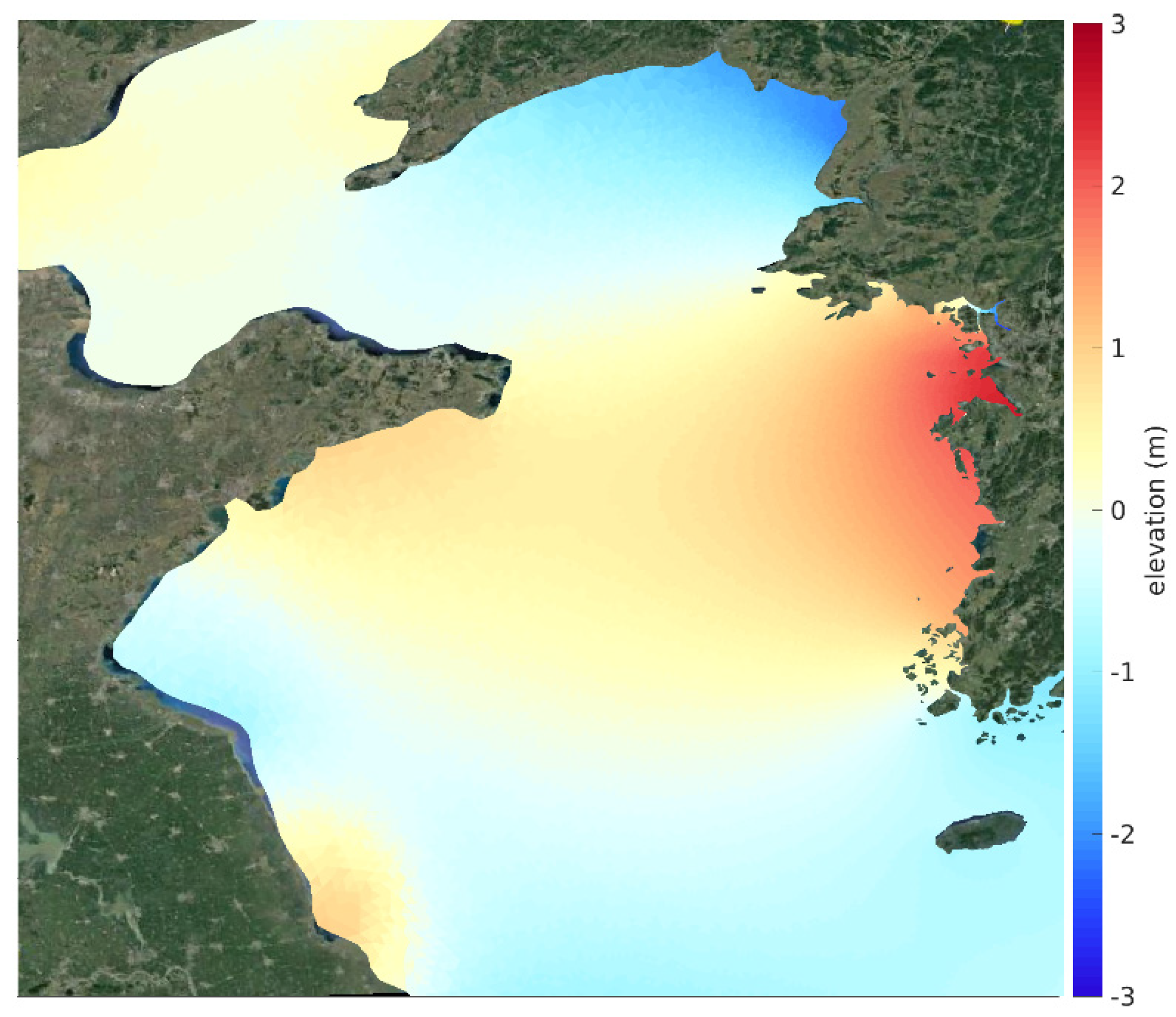
5.2. Real Experiment: FVCOM-NWP
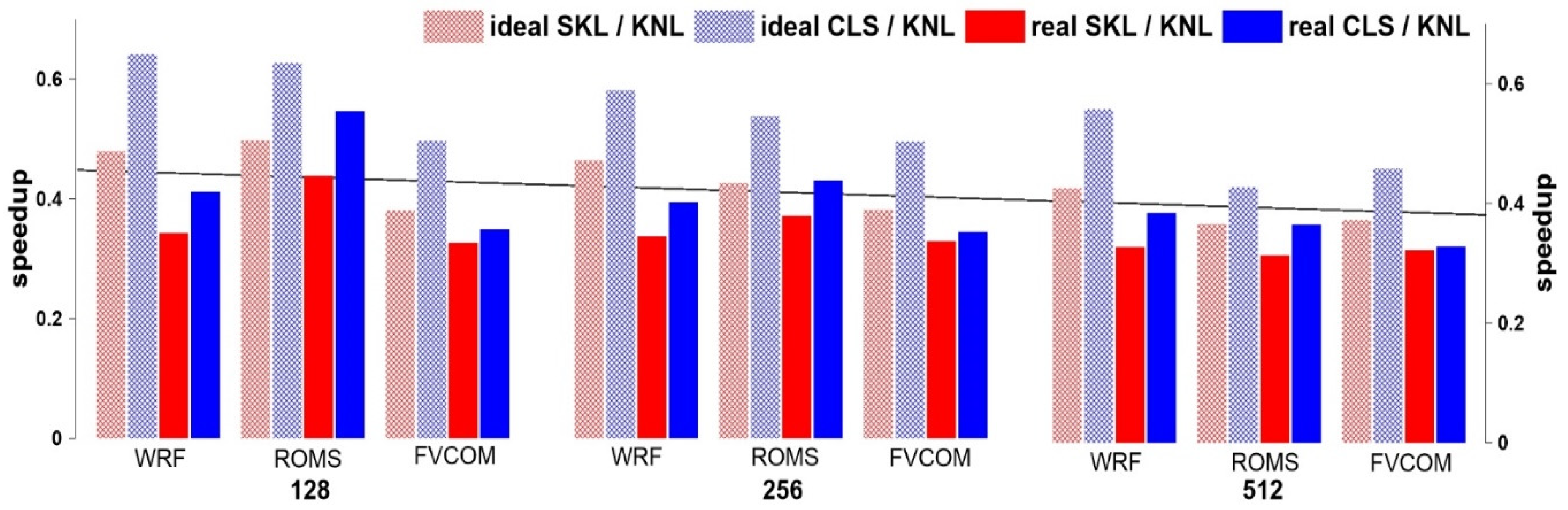
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sodani, A. Knights Landing (KNL): 2nd Generation Intel Xeon Phi Processor. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Hot Chips, Cupertino, CA, USA, 22–25 August 2015; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Dell EMC Solutions. Application Performance of Intel Skylake and Intel Knights Landing Processors on Stampede2; Dell EMC Solutions: Round Rock, TX, USA, 2018; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.-Y.; Jin, H.-W.; Nam, D. Using the On-Package Memory of Manycore Processor for Improving Performance of MPI Intra-Node Communication. J. Kiise 2017, 44, 124–131, (In Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, N.; Oliver, S.L.; Berry, J.; Hammond, S.D.; Kogge, P.M. Optimizing for KNL Usage Modes When Data Doesn’t Fit in MCDRAM. In Proceedings of the 47th International Conference on Parallel Processing, Eugene, OR, USA, 13–16 August 2018; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Rho, S.; Kim, S.; Nam, D.; Park, D.; Kim, J.-S. Enhancing the Performance of Multiple Parallel Applications using Heterogeneous Memory on the Intel’s Next-Generation Many-core Processor. J. Kiise 2017, 44, 878–886, (In Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.W.; Song, U.-S. System Characteristics and Performance Analysis in Multi and Many-core Architectures. J. Digit. Contents Soc. 2019, 22, 597–603, (In Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooyama, K.V. A thermodynamic foundation for modeling the moist atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 1990, 47, 2580–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Barker, D.M.; Duda, M.G.; Huang, X.Y.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Version 3. NCAR Technical Note NCAR/TN/475+STR. 2008. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.5065/D68S4MVH (accessed on 1 July 2019).
- Smagorinsky, J. General circulation experiments with the primitive equations. I. The basic experiment. Mon. Weather Rev. 1963, 91, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deardorff, J.W. Three-dimensional numerical study of turbulence in an entraining mixed layer. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1974, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, F.; Moeng, C.-H. Large-Eddy Simulation of the Daytime Boundary Layer in an Idealized Valley Using the Weather Research and Forecasting Numerical Model. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2010, 137, 49–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeng, C.-H.; Dudhia, J.; Klemp, J. Examining Two-Way Nesting for Large Eddy Simulation of the PBL Using the WRF Model. Mon. Weather Rev. 2007, 135, 2295–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchepetkin, A.F.; McWilliams, J.C. The regional oceanic modeling system (ROMS): A split explicit, free surface, topography following coordinate oceanic model. Ocean Model. 2005, 9, 347–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA. ETOPO2, 2-Minute Gridded Global Relied Data; National Geophysical Data Center; NOAA: Boulder, CO, USA, 2006. Available online: http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/mgg/global/etopo2.html (accessed on 1 July 2019).
- Chen, C.; Beardsley, R.C.; Cowles, G. An unstructured grid, finite-volume coastal ocean model (FVCOM) system. Oceanography 2006, 19, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.-N. Digital 30 sec gridded bathymetric data of Korea marginal seas—KorBathy30s. J. Korean Soc. Coast. Ocean Eng. 2008, 20, 110–120, (In Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Amante, C.; Eakins, B. ETOPO1 1 Arc-Minute Global Relief Model: Procedures, Data Sources and Analysis; Technical Memorandum NESDIS NGDC-24; NOAA: Boulder, CO, USA, 2009. Available online: http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/mgg/global/global.html (accessed on 1 July 2019).


| Category | KNL | SKL | CLS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer and model | Intel Xeon Phi 7250 KnightsLanding | Intel Xeon 6148 Skylake | Intel Xeon Gold 6140 |
| Number of nodes | 8305 | 132 | 16 |
| CPU × cores per node | 1 × 68 = 68 | 2 × 20 = 40 | 2 × 18 = 36 |
| Clock speed | 1.4 GHz | 2.4 GHz | 2.3 GHz |
| Main Memory | 16 GB (MCDRAM), 96 GB | 192 GB | 252 GB |
| File System | Lustre | Lustre | Lustre |
| Compiler | Intel v17.0.5 Intel v19.0.4 | Intel v17.0.5 Intel v19.0.4 | Intel 18.0.4 |
| MPI Library | openmpi v3.1.0 impi v19.0.4 | openmpi v3.1.0 impi v19.0.4 | openmpi v3.1.1 |
| NetCDF Library | netcdf v4.6.1 | netcdf v4.6.1 | netcdf v4.4.4 |
| Compiler Options | -fp-model consistent -ip–O3–no–prec–div -static-intel -xMIC-AVX512 | -fp-model consistent -ip–O3–no–prec–div -static-intel -xCORE-AVX512 | -fp-model consistent -ip–O3–no–prec–div -static -intel |
| Ideal Experiments (Case: Grid Resolution) | Real Experiments | |
|---|---|---|
| WRF | Large Eddy Simulation : (3200 × 3200) grids × 10 layers | NWP, Typhoon Soulik and Cimaron : (2048 × 2048) grids × 33 layers |
| ROMS | Benchmark : (8192 × 1024) grids × 30 layers | NWP, Typhoon Soulik and Cimaron : (2048 × 2048) grids × 33 layers |
| FVCOM | Benchmark : 10,398,925 nodes × 31 layers | NWP, Tide case : 8,369,391 nodes × 10 layers |
| Experiment | KNL | CLS | SKL |
|---|---|---|---|
| 128 cores | 16n × 8c (W-ir), 8n × 16c (W-ir) 4n × 32c (R&F-r), 2n × 64c (W-ir, R&F-i) | 4n × 32c (W&R&F-ir) | 4n × 32c (W&R&F-ir) |
| 256 cores | 32n × 8c (W-ir), 16n × 16c (W-ir) 8n × 32c (R&F-r), 4n × 64c (W-ir, R&F-i) | 8n × 32c (W&R&F-ir) | 8n × 32c (W&R&F-ir) |
| 512 cores | 64n × 8c (W-ir), 32n × 16c (W-ir) 16n × 32c (R&F-r), 8n × 64c (W-ir, R&F-i) | 16n × 32c (W&R&F-ir) | 16n × 32c (W&R&F-ir) |
| 1024 cores | 128n × 8c (W-ir), 64n × 16c (W-ir) 32n × 32c (R&F-r), 16n × 64c (W-ir, R&F-i) | - | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, C.; Kim, D.-H.; Woo, S.-B.; Joh, M.; An, J.; Moon, I.-J. Performance Comparisons on Parallel Optimization of Atmospheric and Ocean Numerical Circulation Models Using KISTI Supercomputer Nurion System. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10082883
Lim C, Kim D-H, Woo S-B, Joh M, An J, Moon I-J. Performance Comparisons on Parallel Optimization of Atmospheric and Ocean Numerical Circulation Models Using KISTI Supercomputer Nurion System. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(8):2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10082883
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Chaewook, Dong-Hoon Kim, Seung-Buhm Woo, Minsu Joh, Jooneun An, and Il-Ju Moon. 2020. "Performance Comparisons on Parallel Optimization of Atmospheric and Ocean Numerical Circulation Models Using KISTI Supercomputer Nurion System" Applied Sciences 10, no. 8: 2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10082883
APA StyleLim, C., Kim, D.-H., Woo, S.-B., Joh, M., An, J., & Moon, I.-J. (2020). Performance Comparisons on Parallel Optimization of Atmospheric and Ocean Numerical Circulation Models Using KISTI Supercomputer Nurion System. Applied Sciences, 10(8), 2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10082883







