Analysis and Design of Rateless Two-way Relay Networks Based on a Multiply-and-Forward Scheme
Abstract
1. Introduction
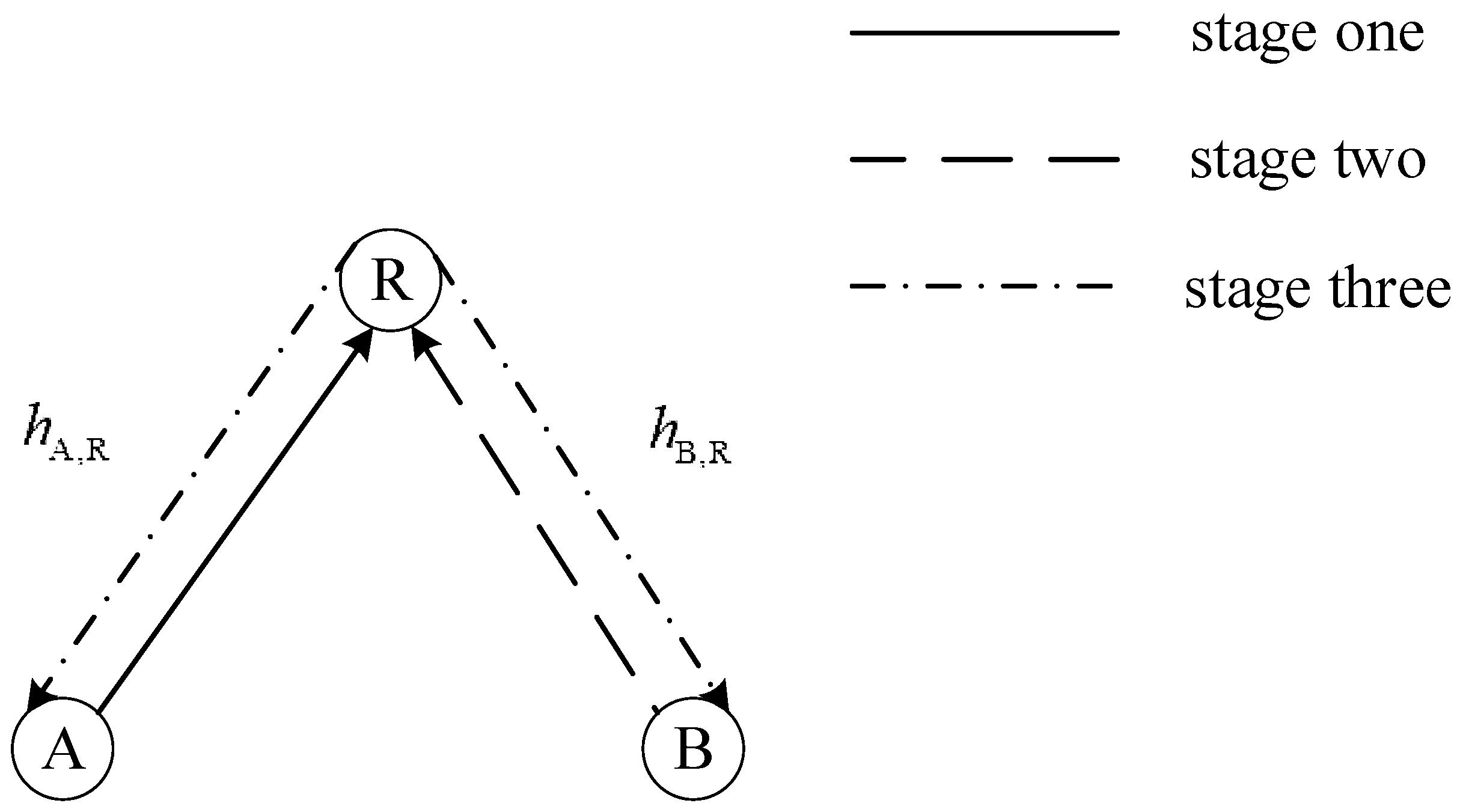
2. System Model
- a)
- node A sends modulated symbols to node R and the received signal vector is given by
- b)
- node B sends modulated symbols to node R and the received signal vector is given by
- c)
- node R processes the signals received from A and B and broadcasts to nodes A and B with the signalwhere is a factor to ensure power normalization and function represents the processing of received signals at node R, such as DF and AF. Then, the received signals at nodes A and B can be represented asand
3. Analysis on Uncoded TWRN
3.1. AF Scheme
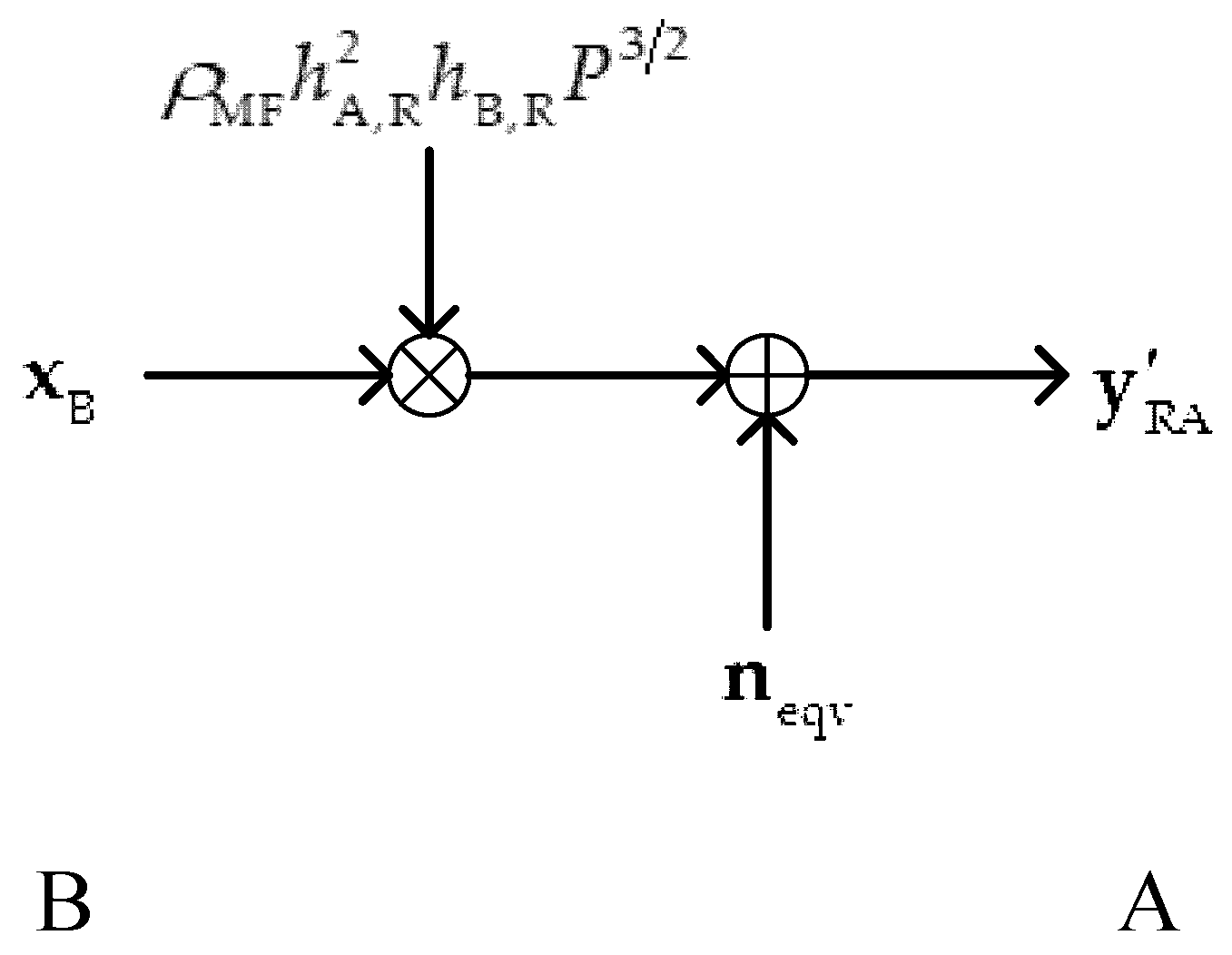
3.2. MF Scheme
4. Fountain-coded MF-TWRN
4.1. Asymptotic Analysis
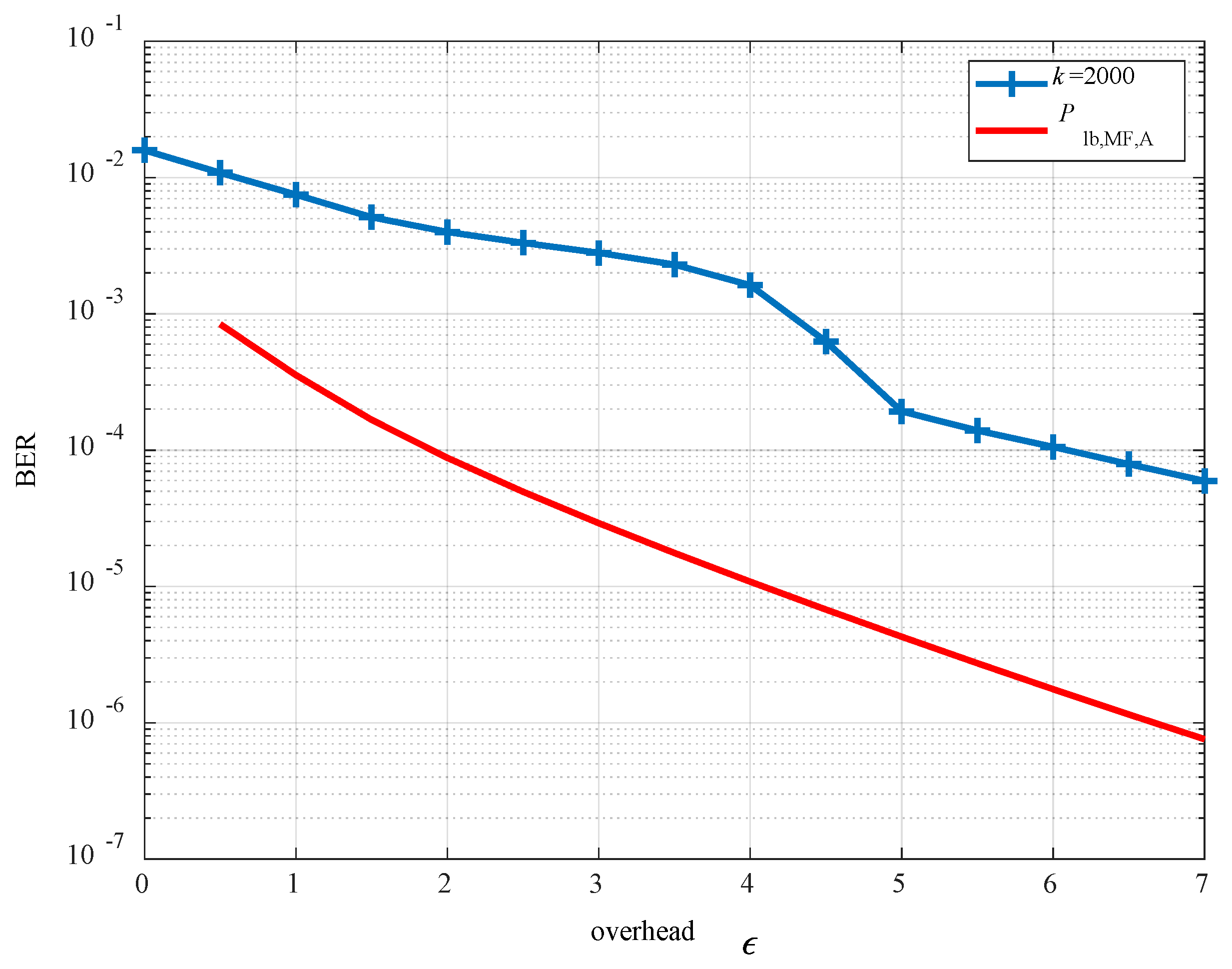
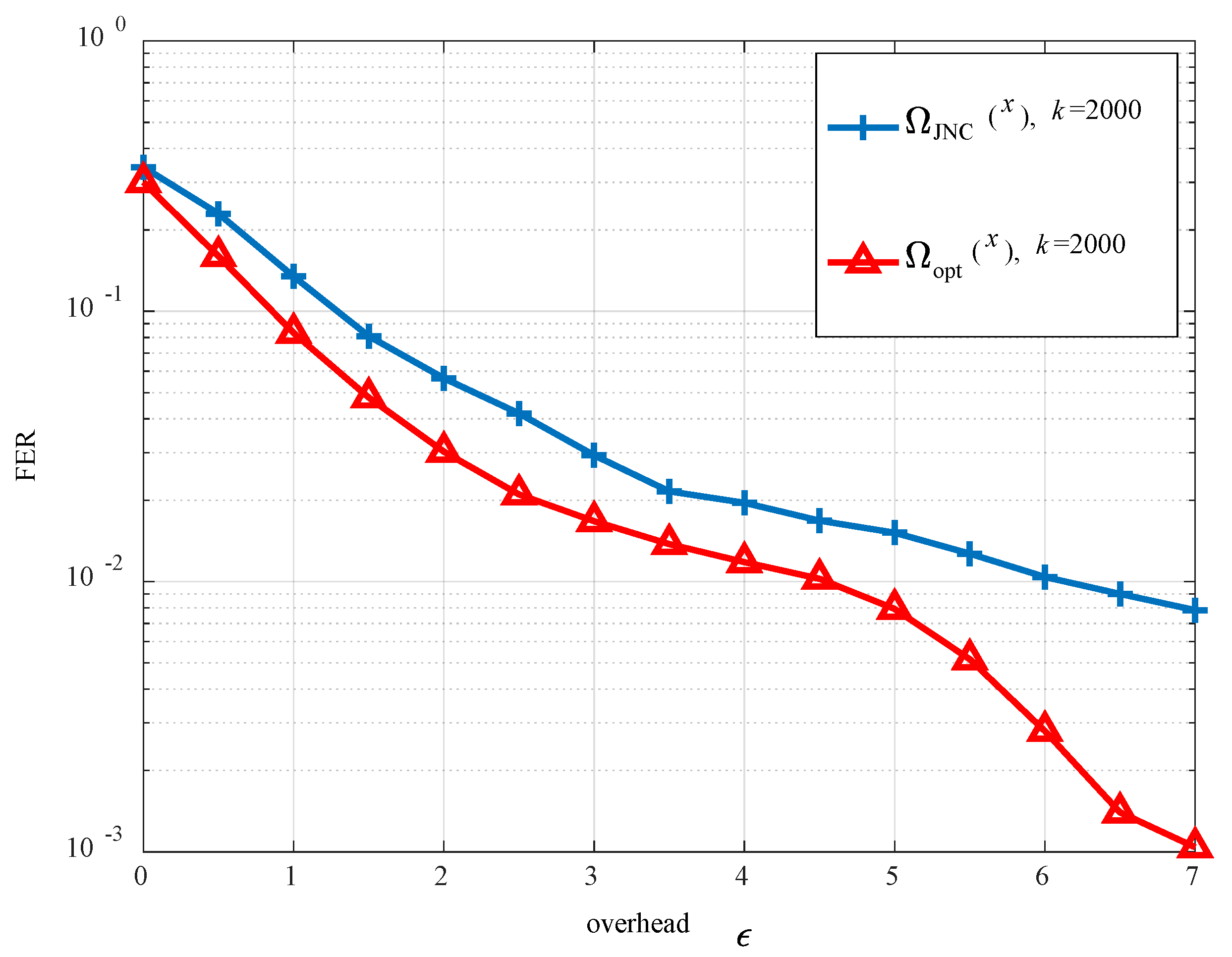
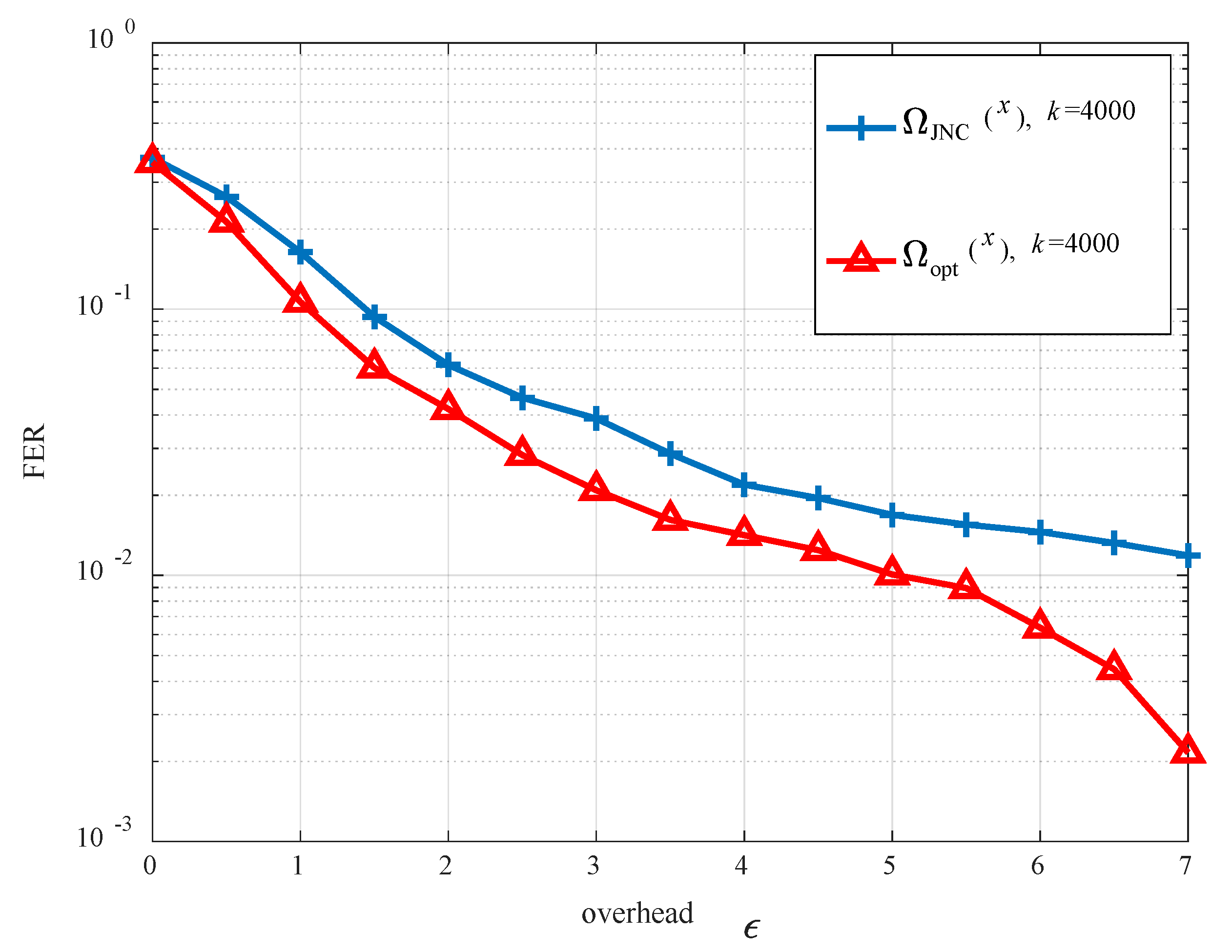
4.2. Optimization Design
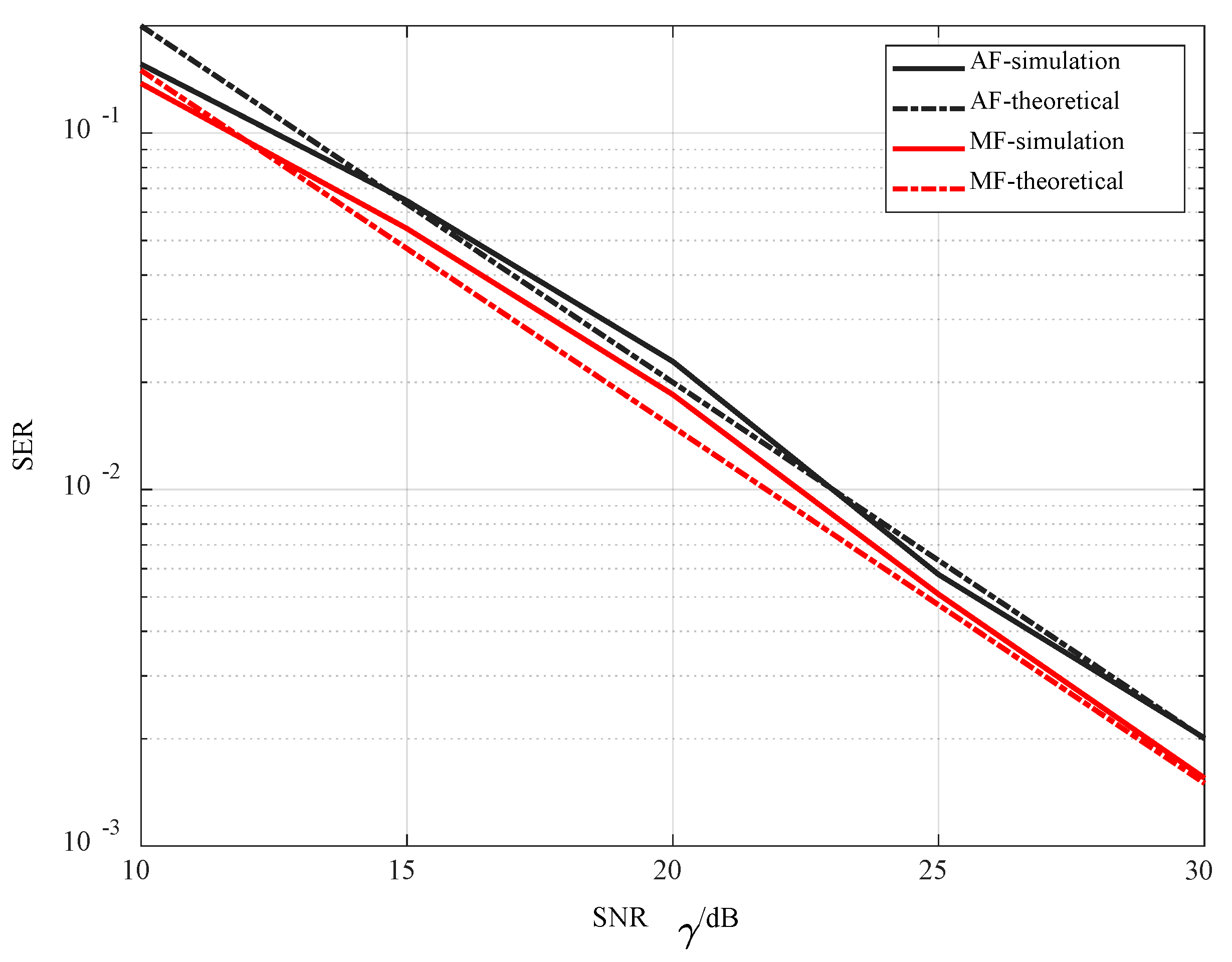
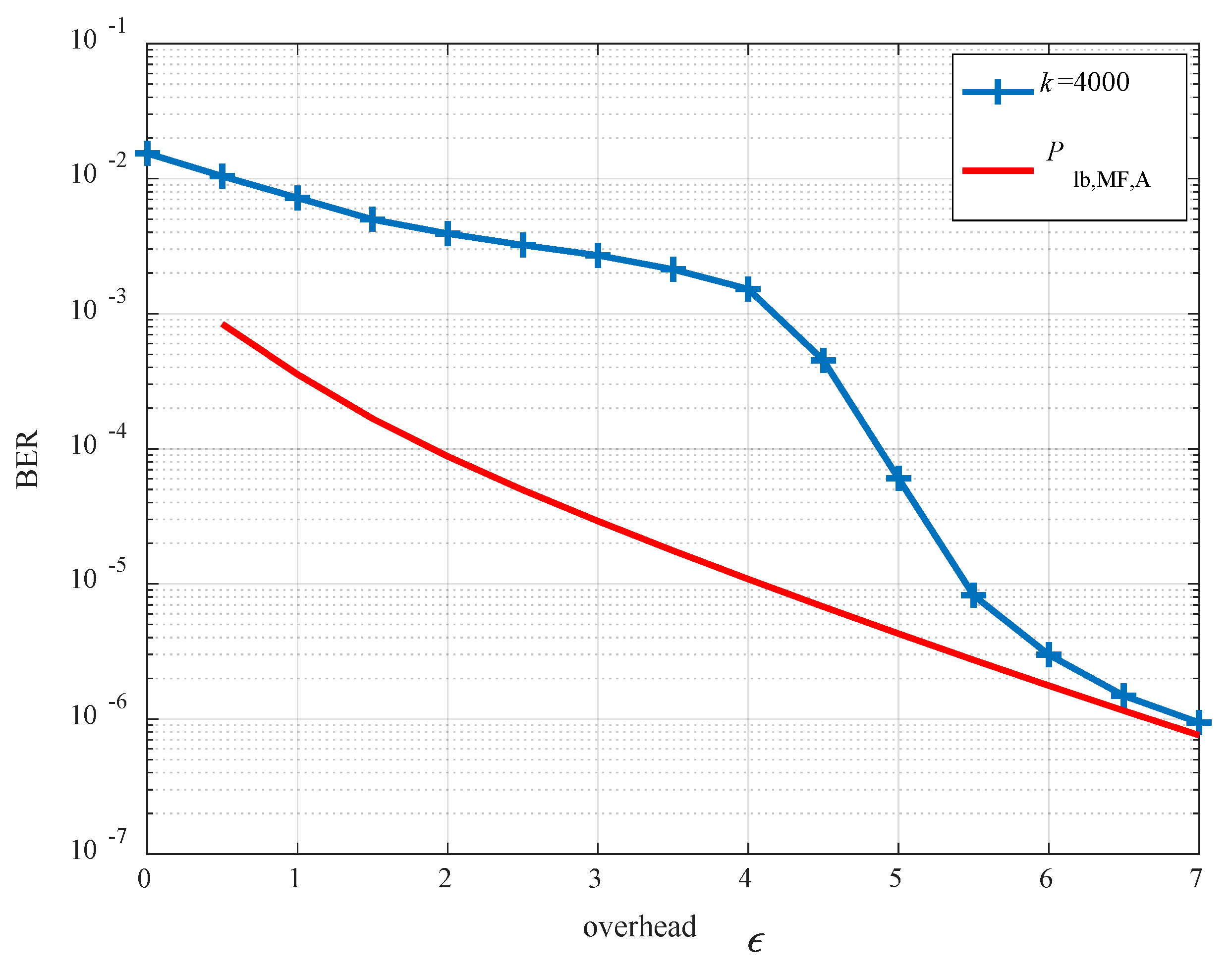
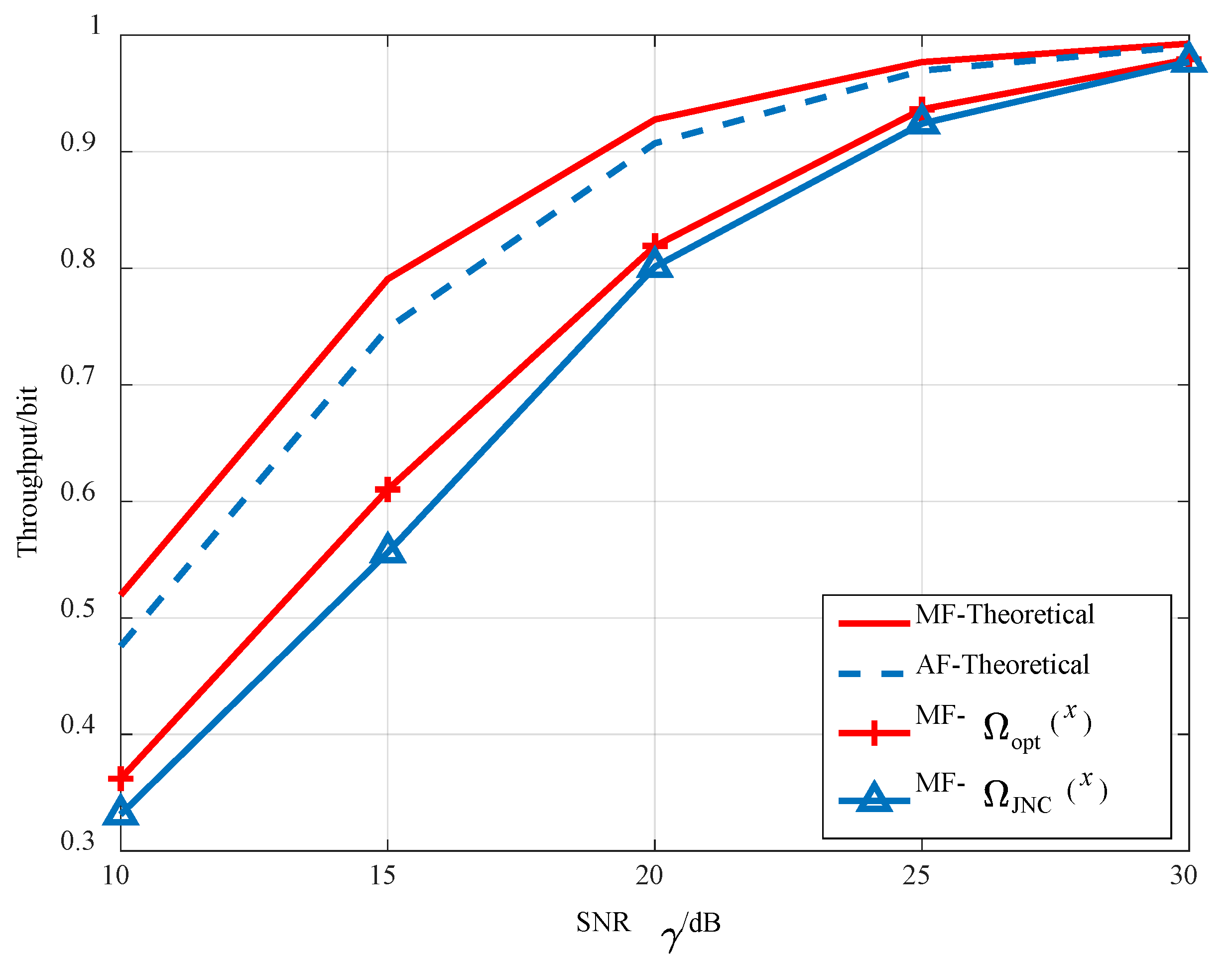
5. Simulation Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Source Vector | |
|---|---|
| received vector | |
| channel fading coefficient | |
| distance between source and relay node | |
| path loss exponent | |
| signal-to-noise ratio | |
| transmit power | |
| power normalization factor | |
| Gaussian density with mean and variance | |
| mathematical expectation | |
| degree distribution | |
| Moment generating function of | |
| Hadamard product of vectors and |
Appendix B
| 1 | 0.0853 | 42 | 0.0002 | 74 | 0.0002 | 106 | 0.0002 |
| 2 | 0.2421 | 43 | 0.0002 | 75 | 0.0002 | 107 | 0.0002 |
| 3 | 0.0917 | 44 | 0.0002 | 76 | 0.0002 | 108 | 0.0002 |
| 4 | 0.1955 | 45 | 0.0002 | 77 | 0.0002 | 109 | 0.0002 |
| 5 | 0.0616 | 46 | 0.0002 | 78 | 0.0002 | 110 | 0.0002 |
| 6 | 0.0522 | 47 | 0.0002 | 79 | 0.0002 | 111 | 0.0002 |
| 7 | 0.0459 | 48 | 0.0002 | 80 | 0.0002 | 112 | 0.0002 |
| 8 | 0.0761 | 49 | 0.0002 | 81 | 0.0002 | 113 | 0.0002 |
| 9 | 0.0333 | 50 | 0.0002 | 82 | 0.0002 | 114 | 0.0002 |
| 10 | 0.0270 | 51 | 0.0002 | 83 | 0.0002 | 115 | 0.0002 |
| 11 | 0.0207 | 52 | 0.0002 | 84 | 0.0002 | 116 | 0.0002 |
| 12 | 0.0144 | 53 | 0.0002 | 85 | 0.0002 | 117 | 0.0002 |
| 13 | 0.0081 | 54 | 0.0002 | 86 | 0.0002 | 118 | 0.0002 |
| 14 | 0.0203 | 55 | 0.0002 | 87 | 0.0002 | 119 | 0.0002 |
| 24 | 0.0001 | 56 | 0.0002 | 88 | 0.0002 | 120 | 0.0002 |
| 25 | 0.0001 | 57 | 0.0002 | 89 | 0.0002 | 121 | 0.0002 |
| 26 | 0.0001 | 58 | 0.0002 | 90 | 0.0002 | 122 | 0.0002 |
| 27 | 0.0001 | 59 | 0.0002 | 91 | 0.0002 | 123 | 0.0002 |
| 28 | 0.0001 | 60 | 0.0002 | 92 | 0.0002 | 124 | 0.0002 |
| 29 | 0.0001 | 61 | 0.0002 | 93 | 0.0002 | 125 | 0.0001 |
| 30 | 0.0005 | 62 | 0.0002 | 94 | 0.0002 | 126 | 0.0001 |
| 31 | 0.0001 | 63 | 0.0002 | 95 | 0.0002 | 127 | 0.0001 |
| 32 | 0.0001 | 64 | 0.0002 | 96 | 0.0002 | 128 | 0.0001 |
| 33 | 0.0011 | 65 | 0.0002 | 97 | 0.0002 | 129 | 0.0001 |
| 34 | 0.0001 | 66 | 0.0002 | 98 | 0.0002 | 130 | 0.0001 |
| 35 | 0.0001 | 67 | 0.0002 | 99 | 0.0002 | 131 | 0.0001 |
| 36 | 0.0002 | 68 | 0.0002 | 100 | 0.0002 | 132 | 0.0001 |
| 37 | 0.0002 | 69 | 0.0002 | 101 | 0.0002 | 133 | 0.0001 |
| 38 | 0.0002 | 70 | 0.0002 | 102 | 0.0002 | 134 | 0.0001 |
| 39 | 0.0002 | 71 | 0.0002 | 103 | 0.0002 | 135 | 0.0001 |
| 40 | 0.0002 | 72 | 0.0002 | 104 | 0.0002 | 136 | 0.0001 |
| 41 | 0.0002 | 73 | 0.0002 | 105 | 0.0002 | 200 | 0.0008 |
References
- Waheed, M.; Ahmad, R.; Ahmed, W.; Drieberg, M.; Alam, M.M. Towards Efficient Wireless Body Area Network Using Two-Way Relay Cooperation. Sensors 2018, 18, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieu, T.D.; Duy, T.T.; Dung, L.T.; Choi, S.G. Performance Evaluation of Relay Selection Schemes in Beacon-Assisted Dual-Hop Cognitive Radio Wireless Sensor Networks under Impact of Hardware Noises. Sensors 2018, 18, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, P.; Johansson, N.; Sunell, K.E. Coded bi-directional relaying. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE 63rd Vehicular Technology Conference, Melbourne, VICAustralia, 7–10 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.J.; Mitran, P.; Tarokh, V. Performance bounds for bi-directional coded cooperation protocols. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2008, 54, 5235–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankov, B.; Wittneben, A. Spectral efficient protocols for half-duplex fading relay channels. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2007, 25, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Li, F.; Liu, H.; Wang, G. Outage-Based Resource Allocation for DF Two-Way Relay Networks with Energy Harvesting. Sensors 2018, 18, 3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovski, P.; Yomo, H. Wireless network coding by amplify-and- forward for bi-directional traffic flows. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2007, 11, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ting, S.H.; Ho, C.K.; Chin, W.H. Performance bounds for two-way amplify-and-forward relaying. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2009, 8, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, J.; Ting, S.H. Rate performance of AF two-way relaying in low SNR region. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2009, 13, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liang, Y.C.; Chai, C.C.; Cui, S. Optimal beamforming for two-way multi-antenna relay channel with analogue network coding. IEEE J. Sel. Area Commun. 2009, 27, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.; Kuhn, M.; Wittneben, A. Recent advances in amplify-and-forward two-hop relaying. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2009, 47, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roemer, F.; Haardt, M. Algebraic norm-maximizing (ANOMAX) transmit strategy for two-way relaying with MIMO amplify and forward realys. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. Lett. 2009, 16, 909–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahajwani, M.; Jain, A.; Gamad, R. Log Likelihood Ratio Based Relay Selection Scheme for Amplify and Forward Relaying with Three State Markov Channel. Future Internet 2018, 10, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Xu, D.; Zhang, X.; Shao, H. Two-way relay networks based on product relay. Electron. Lett. 2015, 51, 429–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.T.; Choi, K.W.; Hasan, S.F.; Chung, M.Y. Energy harvesting and information processing in two-way multiplicative relay networks. Electron. Lett. 2016, 52, 751–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chu, X.; Zhang, H. Dynamic asymmetric power splitting scheme for SWIPT based two-way multiplicative AF relaying. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 25, 1014–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, H. Dynamic power splitting for three-step two-way multiplicative AF relay networks. In Proceedings of the 86th IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference, Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–27 September 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- MacKay, D.J.C. Fountain codes. IEEE Proc. Commun. 2005, 152, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luby, M. LT codes. In Proceedings of the 43rd Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 16–19 November 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Shokrollahi, A. Raptor codes. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 2551–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanki, R.; Yedidia, J.S. Rateless codes on noisy channels. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Information Theory, Chicago, IL, USA, 27 June–2 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Etesami, O.; Shokrollahi, A. Raptor codes on binary memoryless symmetric channels. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 2033–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Yang, L.L.; Ng, S.X.; Hanzo, L. An optimal degree distribution design and a conditional random integer generator for the systematic Luby transform coded wireless Internet. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 31 March–3 April 2008; pp. 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Xu, D. Optimization design and asymptotic analysis of systematic Luby transform codes over BIAWGN channels. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2016, 64, 3160–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, R.; Yu, G.; Wang, W. Joint network-channel coding with rateless code in two-way relay systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2013, 12, 3158–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.K.; Alouini, M.S. Digital Communication over Fading Channels–A Unified Approach to Performance Analysis, 1st ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Su, W.; Sadek, A.K.; Liu, K.J.R. Cooperative communication protocols in wireless networks: Performance analysis and optimum power allocation. Wireless Pers. Commun. 2008, 44, 181–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, W.; Xu, S.; Huang, D.; Xu, C. Analysis and Design of Rateless Two-way Relay Networks Based on a Multiply-and-Forward Scheme. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2389. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072389
Han W, Xu S, Huang D, Xu C. Analysis and Design of Rateless Two-way Relay Networks Based on a Multiply-and-Forward Scheme. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(7):2389. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072389
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Wei, Shengkai Xu, Daqing Huang, and Cheng Xu. 2020. "Analysis and Design of Rateless Two-way Relay Networks Based on a Multiply-and-Forward Scheme" Applied Sciences 10, no. 7: 2389. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072389
APA StyleHan, W., Xu, S., Huang, D., & Xu, C. (2020). Analysis and Design of Rateless Two-way Relay Networks Based on a Multiply-and-Forward Scheme. Applied Sciences, 10(7), 2389. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072389




