Abstract
In this work, diatomaceous earth (DE) or diatoms are modified with Mg–Al-layered double hydroxide (DE-LDH) using the facile co-precipitation method to demonstrate their application for the removal of toxic dyes such as Congo Red (CR), which was used as a model. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) characterization confirms the successful modification of diatom microcapsules structures, showing their surface decorated with LDH nano patches with sheet-like morphologies. The surface area of the DE was enhanced from 28 to 51 m2/g after modification with LDH. The adsorption studies showed that the maximum CR removal efficiency of DE and DE-LDH was ~15% and ~98%, respectively at pH 7, which is a significant improvement compared with unmodified DE. The maximum adsorption capacities of DE-LDH were improved ten times (305.8 mg/g) compared with the bare DE (23.2 mg/g), showing very high adsorption performances. The recyclability study of DE-LDH up to five cycles, after desorbing CR either by methanol or by NaOH, showed the efficient removal of the CR by up to three cycles via adsorption. The presented study suggests the promising application of DE-LDH as an effective material for application in the removal of CR from aqueous solutions for industrial wastewater treatment.
1. Introduction
The purity of water, due to extensive industrialization, urbanization and agriculture, is critically diminished in many countries due contaminations by dye-based industries such as textiles, paint, plastics, paper, leather and so on. The untreated wastewater containing dyes from these industries are posing a very serious threat to human health and the environment. Therefore, the dye-contaminated wastewater should be treated and dyes removed before releasing it into the environment or reusing it. Among many dyes used in these industries, water-soluble Congo Red (CR) is particularly hazardous and used at high concentrations in textile and biochemistry based industries [1]. This benzidine based dye is very toxic, highly carcinogenic and can lead to serious health issues such as diarrhoea, vomiting and nausea [2]. Many water purification technologies have been developed and are commercially available for the removal of organic dyes from water, including membranes, coagulation, catalysis, ozonation, and adsorption [3,4,5]. Among them, the adsorption process is commonly used as it is a very simple, cost-effective, reproducible and effective process for the removal of dyes from water [6]. Many efficient adsorbents such as activated carbons, polymers and clays were explored and some of them were commercially used for dye removal from water, including CR. However, there is still a strong demand to develop new adsorbents that are environmentally friendly, low cost and, more specifically, efficient for dye adsorption [7]. One such environmental friendly naturally available low-cost material known as diatomaceous earth or diatom (DE) has been well-recognized as an excellent candidate for dye removal applications, with an attractive ability to tune the surface properties of dye and significantly increase its adsorption efficiency.
Naturally, available DE materials originating from single-cell algae are found in fresh and sea waters in large quantities. These single cell algae are protected by a unique porous silica shell called the frustule. These hollow DE silica structures have a unique pattern of pores with pore sizes from 100 to 900 nm; also, the size of the DE varies between 1 and 500 µm. DE is an amorphous silica and is considered non-toxic and biocompatible. It has a high porosity and is lightweight, with high thermal stability and is hydrophilic in nature. These properties make DE as an ideal candidate for the various applications such as waste and drinking water purification, as an additive for composites, drug delivery, pest control, sensors, etc. [8,9,10,11,12,13]. However, the fact that bare DE showed less adsorption capacity in the removal of organic dyes could be the reason for the smaller surface area [14] and less hydroxyl groups (-OH) on their surfaces. Therefore, the surface of DE needs further surface modification for better efficiency for the removal of dyes and other pollutants and has been explored by several groups [15,16,17].
In the current work, we present a new concept to modify DE material with Mg–Al-layered double hydroxide (DE-LDH) to enhance the dye removal efficiency and adsorption capacity of DE. Layered double hydroxide (LDH) is a mixed-metal hydroxide clay that consists of octahedral double hydroxyl layers with high positive charges, negatively charged interlayers and water molecules [18]. LDH has some advantages such as its low cost, non-toxicity, simplicity, higher adsorption capacity, and has a high thermal stability [19]. Thus, the LDHs are ideal candidates for the removal of organic and inorganic pollutants from water [19,20,21,22]. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report where DE-LDH has been used for the efficient removal of CR from aqueous media. To study the DE and DE-LDH adsorbents, isotherms were used in the batch adsorption, and kinetic studies were carried out for CR removal. In addition, the obtained maximum adsorption capacity (qm) of DE-LDH has been compared with earlier reported adsorbents. Figure 1a,b shows a schematic illustration of DE-LDH synthesis, and its removal of CR from the aqueous solution by the adsorption process.
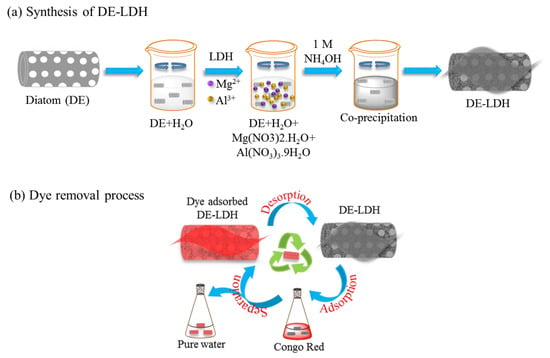
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration for the synthesis of diatomaceous earth Mg–Al-layered double hydroxide (DE-LDH) (a) and its application in Congo Red (CR) removal (b).
2. Experimental
2.1. Material and Methods
DE was received in the form of a rock-solid material from Mount Sylvia Pvt. Ltd., Australia and its purification process was carried out using an earlier reported procedure [23]. Magnesium nitrate (Mg(NO3)2·6H2O) and aluminum nitrate (Al(NO3)3·9H2O) were obtained from S. D. Fine-Chem Ltd., India. CR dye (Figure S1, Supplementary Materials) was received from Avra Synthesis Pvt. Ltd., India. The sodium hydroxide was received from Avantor Performance Materials India, Ltd. The hydrochloric acid, and ammonium hydroxides were received from Spectrochem Pvt. Ltd., India. The obtained solvents and chemicals were all used without further purification processes. The characterization of DE and DE-LDH before and after CR adsorption was done using X-ray diffraction (XRD, Rigaku Ultima IV, Japan), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM, JEOL, JSM-7100F, Japan), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR, Perkin Elmer, Spectrum two, USA), and a Brunauer–Emmett–Teller surface area analyzer (BELSORP-max, MicrotracBEL, Japan). Furthermore, the concentrations of CR were recorded by UV-visible spectrometer (UV-1800, Shimadzu, Japan). The zeta potential measurement was performed using Litesizer 500, Anton Paar.
2.2. Synthesis of Mg–Al LDH Modified Diatom
The purified 250 mg DE was dispensed in 25 mL water in the 100 mL beaker with constant stirring. A total of 25 mL each of 0.1 M Mg(NO3)2·6H2O and 0.05 M Al(NO3)3·9H2O were added to the above dispersion and stirred for 30 min [24]. Furthermore, 1 M of NH4OH was added drop by drop to adjust the solutions at pH 10. The obtained precipitate was stirred for 12 h and then sonicated for about 30 min. The particles were collected via centrifugation and washed with water four times in order to remove unreacted salts. Finally, the particles were dried in a hot air oven at 80 °C to obtain the Mg–Al LDH modified diatom (DE-LDH).
2.3. Adsorption Experiment
The CR removal studies were carried out by adjusting the parameters, such as solution pH, dosage, the concentration of dye and time studies. The adsorption isotherm studies were performed in concentrations ranging from 50 to 1000 mg/L. The required 40 mg dosage of DE and DE-LDH was dispersed in various concentrations of CR solutions at pH 7 in a 100 mL volume conical flask with constant shaking for around 1 h at room temperature. The CR adsorbed adsorbents were centrifuged and the absorbance of the CR supernatant was recorded using a UV-visible spectrometer. The final concentration of CR was investigated from the standard calibration linear curve plotted at λmax = 497 nm. The dye removal efficiency, R (%) and the adsorption capacity, qe (mg/g) were calculated by using Equations (1) and (2), respectively.
where C0 and Ce are represented as the initial and final concentrations of CR solutions, respectively.
where V and M are represented as the volume of CR solutions in litres and the quantity of adsorbents used in grams, respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural and Chemical Characterization
To study the surface morphology of DE and DE-LDH before and after CR adsorption, FESEM with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (FESEM-EDX) images were obtained and shown in Figure 2a–d. The bare DE shows a well-arranged porous structure, its surface is well purified and there is no contamination on the surface. The chemical composition for DE was analyzed by EDX which showed silicon (Si) and oxygen (O) as major components, which confirms that DE consists of SiO2. After modification with LDH, the surface of DE showed LDH formation with sheet-like morphology and the pores of DE were almost wrapped with LDH. The composition of DE-LDH showed additional elements such as magnesium (Mg) and aluminum (Al) and it was confirmed that Mg–Al LDH was formed on the DE surface. Furthermore, the morphology of prepared adsorbents was analyzed after dye adsorption to confirm any morphological changes and it was observed that there were not many morphological changes even after dye adsorption.
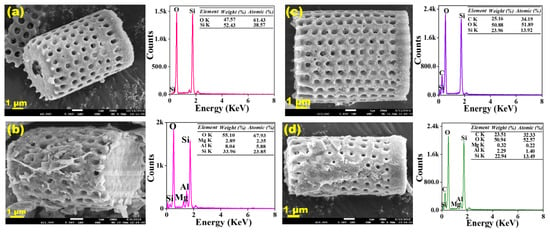
Figure 2.
Field emission scanning electron microscopy-energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (FESEM-EDX) images of before adsorption (a) DE, (b) DE-LDH and after dye adsorption (c) DE-Congo Red (CR) and (d) DE-LDH-CR.
Figure 3a shows the XRD pattern of DE and DE-LDH before and after dye adsorption. The broad spectrum of DE shows the amorphous structure of SiO2 diffraction peaks which matches Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards (JCPDS) file no. 89-3435. After modification with LDH, the XRD pattern was obtained for the both DE and LDH diffraction peaks (JCPD file no. 89-0460). The presence of LDH diffraction peaks shows a hydrotalcite structure and these peaks evidenced that LDH was modified on DE. Additionally, there is a slight impurity observed at around 18–20° (JCPDS file no. 77-0114) in the XRD pattern of DE-LDH due to the presence of Al(OH)3 which has low solubility compared with Mg(OH)2 in water and, hence, there could be undissolved Al(OH)3 present during the synthesis [20]. Similarly, the same adsorbents were recorded after dye adsorption using XRD (Figure 3a). The peaks of DE-CR and DE-LDH-CR did not change, which shows the stability of the adsorbents [25] during the whole adsorption process. This study revealed that the adsorbent can be further regenerated and reused in the dye adsorption process.
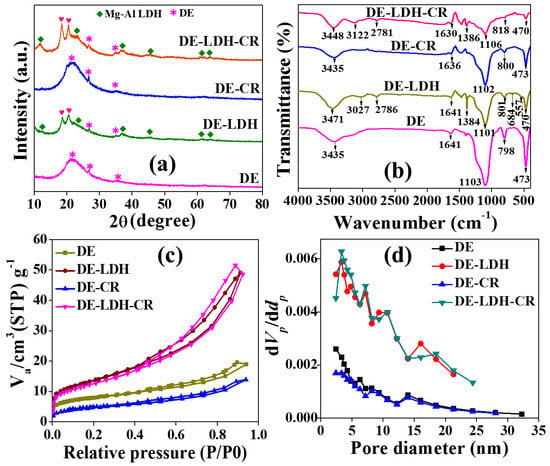
Figure 3.
Characterization of DE and DE-LDH (before dye adsorption) and DE-CR and DE-LDH-CR (after dye adsorption) by (a) XRD pattern, (b) Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectra (c) N2 adsorption–desorption at 77 K and (d) pore size distribution plot using the Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) method.
Furthermore, DE and DE-LDH before and after dye adsorption were analyzed by FTIR, the results of which are shown in Figure 3b. DE showed a broad peak at 3435 cm−1 because of the presence of -OH on its surface. The characteristic peak at 1641 cm−1 was found to be bending vibration of the water molecules on DE. The characteristic peaks at 1103, 798 and 473 cm−1 are found to be asymmetric and symmetric stretching vibrations of the Si–O–Si bond and Si–O bending vibration of siloxane, respectively [26]. For DE-LDH, the broad peak at 3471 cm−1 is due to the -OH stretching vibration. The peaks at 3027 and 2786 cm−1 are because of the C-H stretching of LDH [27]. The sharp peak at 1384 cm−1 was attributed to the stretching vibration of the NO3− ions of LDH [18]. Furthermore, the peaks from 500 to 800 cm−1 denoted the M-O lattice vibration of LDH (M=Mg and Al) [19]. After the dye adsorption, additional peaks were not observed for DE-CR, which is due to the reduced adsorption of CR. On the other hand, DE-LDH-CR showed major changes by showing the shift of hydroxyl peaks from 3471 to 3448 and 3027 to 3122 cm−1 due to the hydrogen bond between DE-LDH and CR. Furthermore, an additional peak was found at 1020 cm−1, attributed to the symmetric stretching of the sulfonate group (-SO3−) present in CR dye (Figure S2, Supplementary Materials) [28].
Figure 3c,d shows the N2 adsorption–desorption isotherm and BJH pore size distribution for DE and DE-LDH before and after dye adsorption. The bare DE showed a Type II isotherm curve with a porous nature according to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) classification. The surface area of DE was found to be 28 m2/g with the sizes of the pore diameters and pore volumes being 2.44 nm and 0.0225 cm3/g (Table 1), respectively. After modification with LDH, the isotherm curve was Type II, suggesting the porous nature of DE-LDH. There is an increase in the surface area, pore volumes, and pore diameter from 28 to 51 m2/g, 0.022 to 0.069 cm3/g, and 2.44 to 3.33 nm, respectively. Therefore, the change in the various Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) parameters endorses that LDH was modified on DE. Further, investigations on surface area of adsorbents after dye adsorption were studied. As expected, the surface areas of DE-CR (18 m2/g) and DE-LDH-CR (44 m2/g) were decreased after the dye adsorption which indicates that the dye molecules were adsorbed on the available pores of the adsorbent surface. From the BJH method, the pore size distribution curve was not affected after the dye adsorption by the adsorbents (Figure 3d).

Table 1.
Surface area and porosity measurement of adsorbents.
The surface charge of the adsorbents is known to affect the removal process of charged dye molecules from aqueous solution. Thus, the surface charge characteristics of adsorbents were measured by zeta potential. The zeta potential was calculated between pH 2 and 12 for DE and DE-LDH (Figure 4), which showed that the zero-point charge (pHzpc) of DE-LDH is 10.9. However, DE showed a negative charge on its surface at all the pH levels studied. This measurement showed that the DE-LDH is positively charged below pH 10.9 and, thus, negatively charged CR dye molecules can adsorb with high efficiency below pH 10.9. The DE, on the other hand, being negatively charged, electrostatically repels the negatively charged CR dye at a wide range of pH levels.
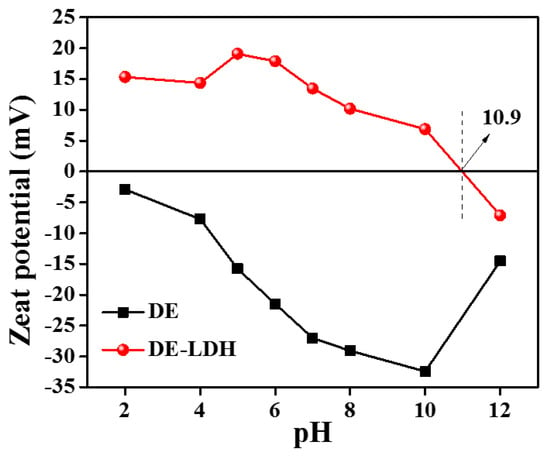
Figure 4.
The zeta potential measurement of DE and DE-LDH.
3.2. Adsorption Performances of DE and DE-LDH
3.2.1. Effect of pH
The dye removal efficiency could be influenced by the adjustment of the pH of the solution and it is important to investigate the CR removal efficiency of DE and DE-LDH at various pH levels. However, the CR is not stable below pH 5. Thus, current study was carried out by varying the pH from 5 to 10 to remove 25 mL of 50 mg/L CR using 20 mg of adsorbent (Figure 5a). DE shows that the dye removal efficiency was gradually decreased from 8.2% to 0.55% with increasing pH from 5 to 10 [29]. This decrease in the dye removal efficiency is evident as the surface of DE becomes highly negative (−2.9 to −32 mV when the pH varied from 2 to 10 as shown in Figure 4). This negative charge on the surface of DE electrostatically repels negatively charged CR. On the other hand, the zero-point charge of DE-LDH was found to be 10.9. Thus, the surface of DE-LDH is positively charged (OH2+) below pH 10.9 and it electrostatically attracts negatively charged -SO3− groups of anionic CR. Therefore, DE-LDH showed maximum dye removal efficiency (93.3%) at pH 5 where it had an efficiency of 19.1 mV. The dye removal efficiency is decreased after pH 10 as the surface of DE-LDH becomes negatively charged, which electrostatically repels the negatively charged dye. However, the dye removal efficiency of DE-LDH did not vary much between pH 5–9. Thus, pH 7 was selected and we carried out all further experiments at pH 7. The removal efficiency was higher for DE-LDH compared to DE due to the surface area and surface functional groups of LDH that were present on DE, which played a vital role in the effect of pH.
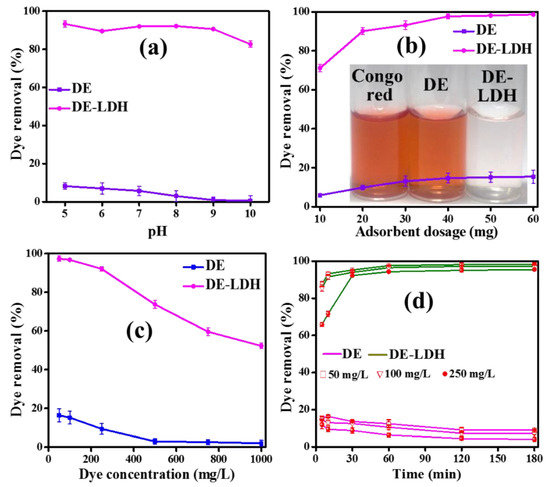
Figure 5.
The CR removal efficiency with respect to effect of (a) pH, (b) adsorbent dosage (inset: photograph of CR supernatant solutions before and after adsorption at pH 7), (c) dye concentration and (d) contact time.
3.2.2. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
The influence of adsorbent dosage on dye removal experiments were carried out by adjusting the adsorbent dosage from 10 to 60 mg at optimized pH (Figure 5b). From the results, the CR removal efficiency was improved from 6% to 15.5% for DE and 71% to 98.6% for DE-LDH when the dosage was increased from 10 to 60 mg. However, there was no observable change in the removal efficiency after 40 mg of adsorbent dosage, suggesting that it had reached its saturation level as there were no dye molecules available to be adsorbed at higher dosages [30]. Thus, the 40 mg of adsorbent dosage was optimized and selected for further experiments. The dye removal efficiency of DE-LDH is higher than that of DE due to the larger surface area and higher protonation. DE has less surface area and less hydroxyl groups (low protonation) which leads to much lower dye adsorption. The supernatant solution of CR before and after dye adsorption confirms that 40 mg of DE-LDH is a reasonable dosage for the removal of CR (Figure 5b, inset). However, it is obvious that the dye removal efficiency increases with the increase in adsorbent dosage due to the availability of active adsorbent sites. In addition, the removal efficiency also depends on the surface area and surface functional groups of adsorbents, which play important roles in the removal of dye.
3.2.3. Effect of Dye Concentration
The concentration of CR molecules plays a critical role in adsorption and it is an important parameter to evaluate the ability of adsorbents and to find the maximum removal concentration at an optimized dosage and pH. The concentration range of CR from 50 to 1000 mg/L has been selected for this study (Figure 5c). The CR removal efficiency of adsorbent DE gradually decreased from 16.3% to 2.9% with the increase in CR concentrations from 50 to 1000 mg/L. DE-LDH showed a decrease in its dye removal efficiency from 97.3% to 52.2% with an increase in the concentration of dye from 50 to 1000 mg/L. From the results, DE-LDH exhibited a higher removal efficiency compared to the DE even at 1000 mg/L. The dye removal efficiency decreases with the increase in concentration due to the unavailability of active sites on the DE and DE-LDH surfaces. However, DE-LDH adsorbent has shown higher removal efficiency than DE due to its larger surface area.
3.2.4. Effect of Contact Time
The adsorption dependency on the contact time of the adsorbate and adsorbent was studied by varying the contact time to find out the equilibrium time required for the adsorption. The removal efficiency of CR with different concentrations 50, 100 and 250 mg/L for DE and DE-LDH was performed as a function of the contact time, adjusting this from 5 to 180 min (Figure 5d). The adsorption rate of dye on DE-LDH was rapid in the beginning due to the availability of freely accessible active sites with larger surface areas, and attained saturation after 30 min as there were no dye molecules present to adsorb on to DE-LDH. On the other hand, DE showed slow adsorption kinetics and the removal efficiency decreased with the increase in contact time adjusted from 10 to 180 min for all the dye concentrations. This decrease was attributed to the very weak adsorption on DE surfaces due to the smaller surface area and weakly adsorbed dye molecules which could easily be detached from DE as the contact time increased. Thus, it is evident that even by increasing the contact time it is difficult for dye molecules to adsorb on DE surfaces. Obviously, DE-LDH showed enhanced CR adsorption at higher concentrations, which required only 30 min when compared to DE. Figure 6a–c shows photographs of the supernatant of CR at various concentrations (50, 100 and 250 mg/L) before and after adsorption on DE and DE-LDH, and its corresponding UV-visible spectra. This confirms DE-LDH could absorb higher amounts of CR compared to DE.

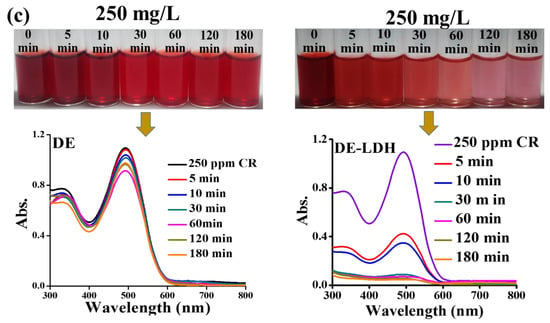
Figure 6.
Supernatant of CR before and after adsorption on DE and DE-LDH with respect to contact time and corresponding UV-visible spectra (a) 50 mg/L (b) 100 mg/L and (c) 250 mg/L (adsorbent dosage: 40 mg, pH: 7, volume: 25 mL, temperature: 30 °C).
3.2.5. Adsorption Isotherms
Adsorption isotherms were analyzed to study the maximum adsorption capacity (qm) of the adsorbent and to investigate the nature of adsorption of CR onto the adsorbent surface. Figure 7a,b,d,e show the adsorption isotherm parameters of adsorbents analyzed by the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm linear fitting models using Equations (S1) and (S3) (Supplementary Materials) and the values are presented in Table 2. DE adsorption isotherms showed that correlation coefficients (R2) for the Freundlich isotherm was well fitted when compared to the Langmuir isotherm, confirming the multilayer adsorption of CR on DE. The maximum adsorption capacity (qm) of DE was 23.2 mg/g. Similarly, adsorption isotherms were analyzed for DE-LDH, which showed that the R2 value of the Langmuir isotherm was higher than that of the Freundlich isotherm. Therefore, the adsorption of CR occurred in the monolayer on the surface of DE-LDH and its maximum adsorption capacity was found to be 305.8 mg/g. The separation factor (RL) values were calculated using Equation (S2) (Supplementary Materials) and the obtained values are between zero and one (Table 2), revealing that the adsorption process is favorable. On the other hand, high KL values depict an admirable adsorption process and these values showed a higher affinity between CR and DE-LDH surfaces, but a lower affinity between DE and CR. Moreover, the adsorption coefficient and KF values of adsorbents depict that the amount of CR adsorbed on DE-LDH (42.1 mg/g) is higher than that of DE (0.54 mg/g). In addition, the non-linear plot Ce vs. qe showed that the Freundlich isotherm is finely fitted with the experimental value for DE, and the Langmuir isotherm is finely fitted with the experimental value for DE-LDH (Figure 7c,f).
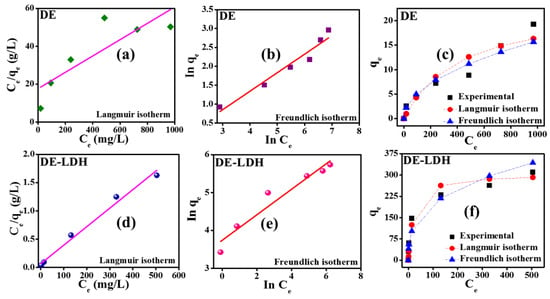
Figure 7.
Adsorption isotherm plots of CR on DE and DE-LDH.

Table 2.
Adsorption isotherm parameters for adsorption of CR onto DE and DE-LDH.
3.2.6. Adsorption Kinetics
In the adsorption process, the adsorption kinetics are the keys to understanding the mechanism of sorption. To study the kinetics, the equations such as pseudo-first order kinetics, second-order kinetics and intra-particle diffusion models were plotted (Equations (S5)–(S7)) (Supplementary Materials) and tabulated for dye concentrations of 50, 100 and 250 mg/L (Figure 8 and Table 3). From the results, the pseudo-second order is well fitted with the data compared to the pseudo-first order model. The correlation coefficient was higher (R2 = 0.999) for the pseudo-second order compared to the first order model. The values of qe,cal obtained from the pseudo-second order model were well matched with the qe,exp values obtained from the experiment studies. Therefore, based on fine data fittings with the pseudo-second order kinetic model of the CR adsorption on the adsorbent, it is understood that the sorption is a chemisorption.
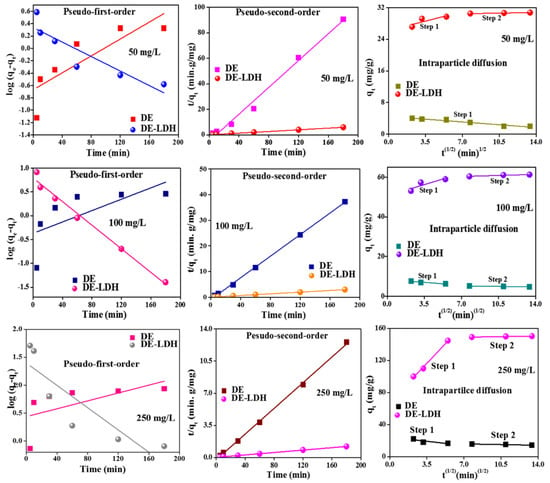
Figure 8.
Adsorption kinetic plots for different concentration of CR onto DE and DE-LDH.

Table 3.
Adsorption kinetic values for adsorption of CR onto DE and DE-LDH.
The rate controlling steps of CR adsorption in the adsorption process can be analyzed through Weber’s intra-particle diffusion model and this could be used to understand the rate of adsorption at various concentrations (50, 100 and 250 mg/L) of CR onto the adsorbents (DE and DE-LDH). From the contact time studies, the removal efficiency of DE decreases with an increase in the time due to the smaller surface area and weak adsorption which leads to lesser adsorption; furthermore, increasing the time of contact could lead to the leaching of the dye from the surface. Based on time studies, an intra-particle diffusion model could not be used to describe the diffusion of the dye molecules onto DE surfaces. From Figure 8, the diffusion plot of DE decreases with the increase in time for all the concentrations. Therefore, intra-particle diffusion was applied only for DE-LDH. The linear plot does not pass through the origin, suggesting that the intra-particle diffusion model is not a rate-limiting step. Two stages of the process were observed; the first step is attributed to the boundary layer diffusion, i.e., the diffusion of CR molecules from the bulk solution to the external surface of DE-LDH. The second step was due to the fast diffusion of dye molecules into the pores of DE-LDH. From Table S1 (Supplementary Materials), the diffusion rate constant Kint1 values are higher than Kint2, which reveals that the dye diffusion in the first step was quicker than the diffusion in the second step, as the surface of DE-LDH was freely accessible at the initial stage. Moreover, the diffusion rate constant (Kint) increases with an increase in dye concentration due to the higher dye concentration, which could rush the dye molecules from the bulk solution to the adsorbent surface. The boundary layer thickness (C) values increased from C1 to C2 due to the diffusion of dye molecules which occupy the surface, leading to low values of C1 and, later dye, molecules quickly entered the pores, leading an increase in the thickness of the boundary layer to C2. The C values increase with increasing dye concentration, which indicates that, at higher concentrations of dye, the adsorption rate is also high and this phenomenon is attributed to the increase in the boundary layer of the pores on the adsorbent surfaces.
3.2.7. Mechanism of CR Adsorption on DE-LDH
The possible mechanisms and the surface interactions of DE-LDH with the CR dye molecules were investigated by XRD, FTIR and BET. Figure 3a shows the XRD patterns of adsorbent DE-LDH before and after CR adsorption. There were few changes observed in the XRD pattern after adsorption, which indicates that the crystallinity of DE-LDH is stable even after dye adsorption; only a slight shift of the peaks due to crystallinity was observed after dye adsorption. Figure 3b shows FTIR spectra of DE-LDH before and after dye adsorption: it was noted that many new peaks (400–1000 cm−1) were observed after CR adsorption on the DE-LDH surface (Figure S2, Supplementary Materials) and the major hydroxyl group (-OH) shifted from 3471 to 3448 cm−1 due to hydrogen bonding between one of the functional groups of CR (-N=N-) and the -OH of DE-LDH. After the dye adsorption, the peak at 1020 cm−1 was found to be due to the symmetric stretching of the sulfonate group (-SO3−) of CR [28]. The FTIR spectra indicates that the high CR adsorption on DE-LDH is strongly dependent on the hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interaction. Furthermore, Table 1 evidently shows that the surface area of DE-LDH (51 to 44 m2/g) decreases after adsorption. Thus, the above results suggest that CR was strongly adsorbed on the pores of DE-LDH. Figure 9 shows a schematic representation of the adsorption mechanism of CR onto DE-LDH.
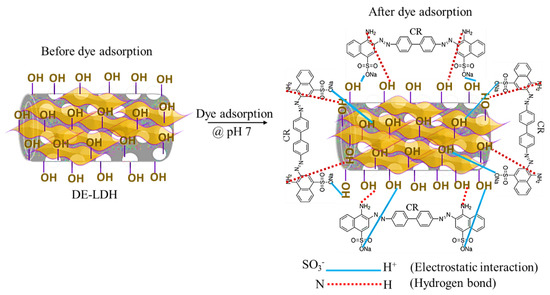
Figure 9.
Schematic representation of CR adsorption mechanism onto DE-LDH.
3.2.8. Selectivity Studies for Removal of CR
It is important to perform the selective removal of CR over other toxic dyes in aqueous solution. Thus, the adsorbent DE-LDH was studied for the selective removal of CR in the mixture with various organic dyes such as Eriochrome Black T (EBT) and Rhodamine B (RB), shown in Figure 10. The mixture of dyes was soaked with DE-LDH and the extracted supernatant solutions were recorded using a UV-visible spectrometer. From the UV-visible spectrum, the DE-LDH was able to selectively remove the CR in a mixture of various dye solutions. It is worth noting here that the absorbance spectrum of CR entirely disappeared, whereas the spectra of EBT and RB dyes were observable. This study shows the selective removal of CR dye is based on its chemical structure and interaction. The positively charged DE-LDH surfaces adsorbed the CR molecules by electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonding due to the functional SO3− and -NH2 groups, respectively. Though the other dyes, EBT and RB, have nitro and hydroxyl (NO2 and -OH) groups and tertiary amine and carboxyl (=N(C2H5)2 and -COOH) groups, respectively, the adsorption is more prominent in the case of the CR dye due to the stronger interaction between the readily available functional groups of CR and the adsorbent surface. Thus, these dyes were removed to a lesser extent compared to CR by DE-LDH.
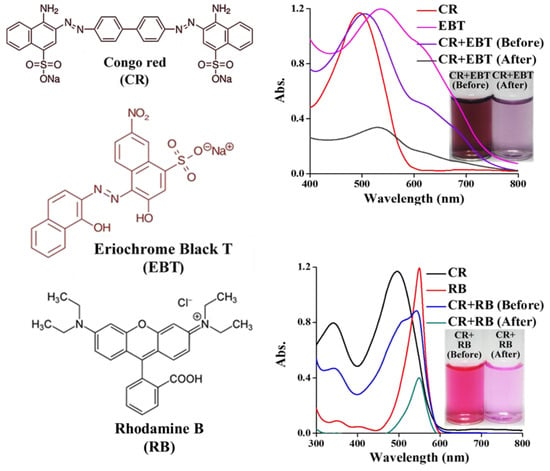
Figure 10.
The selective removal of CR dye with other organic dyes under pH 7.
3.2.9. Effect of Salt
Industrial wastewater generally contains water soluble inorganic salts at higher concentrations. Thus, the effect of salts and the study of ionic strength are important parameters in the dye adsorption process. Figure 11 shows the effect of different concentrations of NaCl, Na2SO4 and Na2CO3 salts on the removal efficiency of CR by DE-LDH. From the results, it is evident that the presence of salts in the dye solution slightly decreases the CR adsorption onto DE-LDH. This initial decrease in the efficiency justifies anion deposition on the surface of DE-LDH from 0.1 to 0.3 M concentrations. However, by increasing the salt concentration from 0.5 to 0.9 M, the dye removal efficiency was slightly increased. This observation is attributed to the salt effect on the CR. Thus, the presence of salt at higher concentrations enhances the solubility of CR, which increases the adsorption.
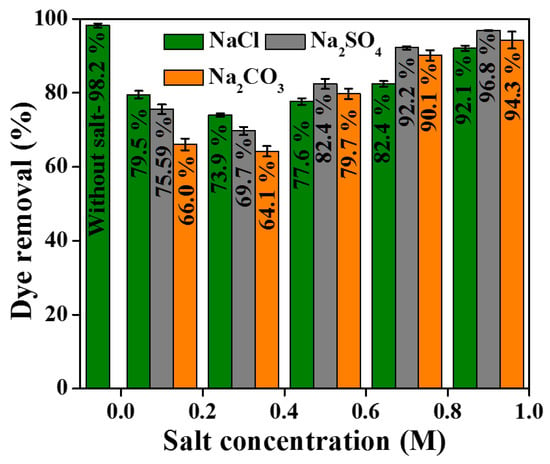
Figure 11.
Effect of salt concentration on adsorption of CR onto DE-LDH (dye concentration: 50 mg/L, dosage: 40 mg, pH: 7 and time: 1 h).
3.2.10. Reusability Study
To reduce the solid wastage after adsorption on an industrial scale, the reusability of DE-LDH was examined. The desorption was carried out using desorption media such as methanol and 0.1 M NaOH for 30 min and the dye desorbed adsorbent was washed with double-distilled water. This was repeated for up to five cycles of adsorption, which showed that the removal efficiency of the adsorbent severely decreased from 43.6% (first cycle) to 18% (fifth cycle) when methanol was used as the desorbing media (Figure 12). Similarly, when 0.1 M NaOH was used to desorb the CR from DE-LDH, the dye removal efficiency of this adsorbent gradually decreased from the first to the fifth cycle (from 70.6% to 24%). This study indicates that the reusability of DE-LDH is dependent on the desorption media. From the results, NaOH acts as a better desorption media compared to methanol. This decrease in removal efficiency with the increase in the cycle process is due to the presence of strongly bound CR on the adsorbent surface. This study reveals that the reusability of DE-LDH is capable for up to two to three cycles for the adsorption of CR (upon desorbing the dye either with methanol or NaOH).
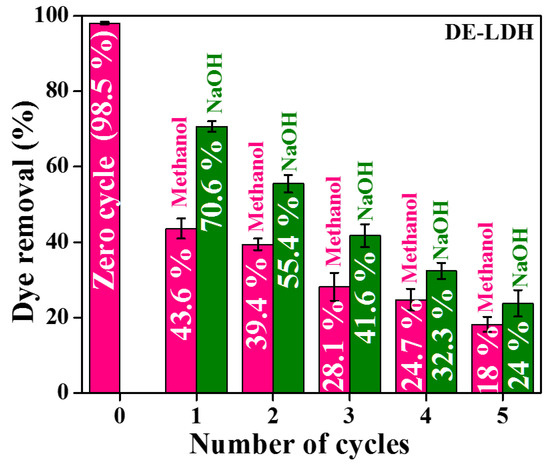
Figure 12.
Reusability of DE-LDH for the adsorption of CR.
3.2.11. Comparison with Other Adsorbents
The present study of maximum adsorption capacity has been compared with earlier reports for CR (Table 4). From this table, DE-LDH was either identical to or was a better adsorbent than earlier reported adsorbents for the adsorption of CR [2,28,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38]. Moreover, all the adsorption data were obtained at pH 7, indicating the possibilities for practical applications on an industrial scale.

Table 4.
Comparison of DE-LDH with reported different adsorbent in the adsorption of CR.
4. Conclusions
In summary, the development of new adsorbents for the adsorption of CR with high selectivity and high adsorption capacity on the modified DE by using LDH is demonstrated. The current work reveals a simple and scalable preparation process that can provide low-cost adsorbent DE-LDH for the removal of anionic CR dye. The maximum removal of CR dye (50 mg/L) from 15% for unmodified DE to 98% for modified DE-LDH was achieved, showing an outstanding improvement in efficiency. The maximum adsorption capacity for DE-LDH was scientifically high (305.8 mg/g) compared to only 23.2 mg/g for DE, showing an excellent adsorption performance as result of LDH modification. Further, the high selectivity removal of CR was achieved during the selectivity study, using other dyes such as EBT and RB by DE-LDH. These results are explained by the chemical binding mechanism between CR and LDH. Desorption studies were carried out using different desorption agents and it showed that the removal of CR by DE-LDH was found to be better using NaOH when the DE-LDH-CR was desorbed than using methanol. Clearly, the current study suggests that DE-LDH can be used as reliable and an efficient adsorbent for the removal of CR from aqueous solutions and it can be a superior adsorbent for wastewater treatment.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/10/7/2285/s1, Figure S1: Structure of Congo Red., Figure S2. FTIR spectra of after CR adsorption for DE and DE-LDH, Table S1. Intraparticle diffusion constants of Congo red adsorption onto DE and DE-LDH.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: D.L., M.D.K. and M.K., methodology: G.S. and U.T.U. formal analysis/investigation: G.S. and U.T.U., resources: H.-Y.J., D.L., M.D.K. writing—original draft preparation: G.S. and U.T.U., writing—review and editing: D.L., M.D.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Department of Science and Technology (DST), India (DST/BDTD/EAG/2019), DST, India (DST-TM-WTI-2K14-213), and DST Nanomission, India (SR/NM/NS-20/2014), for the financial assistance for this work. Ho-Yong Jung would like to acknowledge Chonnam National University (Grant number: 2018-3274), South Korea for the financial assist. D.L. acknowledges the support from ARC Research Hub for Graphene-Enabled Industry Transformation; funding was given under Industrial Transformation Research Hub IH150100003.
Acknowledgments
We also thank Jain (Deemed-to-be University), India for providing the infrastructure and other valuable facilities.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Aliabadi, R.S.; Mahmoodi, N.O. Synthesis and characterization of polypyrrole, polyaniline nanoparticles and their nanocomposite for removal of azo dyes; sunset yellow and Congo red. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 179, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miandad, R.; Kumar, R.; Barakat, M.A.; Basheer, C.; Aburiazaiza, A.S.; Nizami, A.S.; Rehan, M. Untapped conversion of plastic waste char into carbon-metal LDOs for the adsorption of Congo red. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 511, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikrant, K.; Giri, B.S.; Raza, N.; Roy, K.; Kim, K.H.; Rai, B.N.; Singh, R.S. Recent advancements in bioremediation of dye: Current status and challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 253, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katheresan, V.; Kansedo, J.; Lau, S.Y. Efficiency of various recent wastewater dye removal methods: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4676–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimifard, S.; Moghaddam, M.R. Application of response surface methodology in physicochemical removal of dyes from wastewater: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 772–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, G.; Uthappa, U.T.; Rego, R.M.; Kigga, M.; Kumeria, T.; Jung, H.Y.; Kurkuri, M.D. Ceria decorated porous diatom-xerogel as an effective adsorbent for the efficient removal of Eriochrome Black T. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadegh, H.; Ali, G.A.; Gupta, V.K.; Makhlouf, A.S.; Shahryari-ghoshekandi, R.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Sillanpää, M.; Megiel, E. The role of nanomaterials as effective adsorbents and their applications in wastewater treatment. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiri, S.; Kurkuri, M.D.; Kumeria, T.; Losic, D. Frit-free PDMS microfluidic device for chromatographic separation and on-chip detection. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 15276–15280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bariana, M.; Aw, M.S.; Kurkuri, M.; Losic, D. Tuning drug loading and release properties of diatom silica microparticles by surface modifications. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 443, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthappa, U.T.; Sriram, G.; Brahmkhatri, V.; Kigga, M.; Jung, H.Y.; Altalhi, T.; Neelgund, G.M.; Kurkuri, M.D. Xerogel modified diatomaceous earth microparticles for controlled drug release studies. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 11964–11971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthappa, U.T.; Brahmkhatri, V.; Sriram, G.; Jung, H.Y.; Yu, J.; Kurkuri, N.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Altalhi, T.; Neelgund, G.M.; Kurkuri, M.D. Nature engineered diatom biosilica as drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2018, 281, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uthappa, U.T.; Kigga, M.; Sriram, G.; Ajeya, K.V.; Jung, H.Y.; Neelgund, G.M.; Kurkuri, M.D. Facile green synthetic approach of bio inspired polydopamine coated diatoms as a drug vehicle for controlled drug release and active catalyst for dye degradation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 288, 109572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, I.; Terracciano, M.; De Stefano, L. Synthetic vs. Natural: Diatoms Bioderived Porous Materials for the Next Generation of Healthcare Nanodevices. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Zhang, J.; Shi, H.; Li, N.; Ping, Q. Adsorption of Malachite Green by Diatomite: Equilibrium Isotherms and Kinetic Studies. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2016, 37, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.; Bhat, M.P.; Gatti, M.G.; Kabiri, S.; Altalhi, T.; Jung, H.Y.; Losic, D.; Kurkuri, M. Chemodosimeter functionalized diatomaceous earth particles for visual detection and removal of trace mercury ions from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 327, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, G.; Uthappa, U.T.; Kigga, M.; Jung, H.Y.; Altalhi, T.; Brahmkhatri, V.; Kurkuri, M.D. Xerogel activated diatoms as an effective hybrid adsorbent for the efficient removal of malachite green. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 3810–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, G.; Bhat, M.P.; Kigga, M.; Uthappa, U.T.; Jung, H.Y.; Kumeria, T.; Kurkuri, M.D. Amine activated diatom xerogel hybrid material for efficient removal of hazardous dye. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 235, 121738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.H.; Tzou, Y.M.; Wang, M.K.; Liu, C.H.; Chiang, P.N. Removal of 2-Chlorophenol from Aqueous Solution by Mg/Al Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH) and Modified LDH. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 3813–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Zhang, C.; Meng, L. Adsorption of Methyl Orange from Aqueous Solution on Hydrothermal Synthesized Mg–Al Layered Double Hydroxide. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 4217–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Gunawan, P.; Xu, R. Self-assembled Fe3O4-layered double hydroxide colloidal nanohybrids with excellent performance for treatment of organic dyes in water. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somosi, Z.; Muráth, S.; Nagy, P.; Sebők, D.; Szilagyi, I.; Douglas, G. Contaminant removal by efficient separation of in situ formed layered double hydroxide compounds from mine wastewaters. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, B.; Ho, W. Hierarchical porous Ni/Co-LDH hollow dodecahedron with excellent adsorption property for Congo red and Cr(VI) ions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 478, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, M.S.; Simovic, S.; Addai-Mensah, J.; Losic, D. Silica microcapsules from diatoms as new carrier for delivery of therapeutics. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 1159–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wang, P.; Lim, T.T.; Liu, L.; Liu, S.; Xu, R. A facile synthesis of monodispersed hierarchical layered double hydroxide on silica spheres for efficient removal of pharmaceuticals from water. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 3877–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yao, Q.; Lu, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, W. Layered double hydroxide-carbon dot composite: High-performance adsorbent for removal of anionic organic dye. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 20225–20233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprynskyy, M.; Pomastowski, P.; Hornowska, M.; Król, A.; Rafińska, K.; Buszewski, B. Naturally organic functionalized 3D biosilica from diatom microalgae. Mater. Des. 2017, 132, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Yu, S.; Wang, J.; Zou, Y.; Lu, S.; Ai, Y.; Alharbi, N.S.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X. Enhanced removal of methyl orange on calcined glycerol-modified nanocrystallined Mg/Al layered double hydroxides. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xu, D.; Zhu, B.; Cheng, B.; Jiang, C. Adsorptive removal of an anionic dye Congo red by flower-like hierarchical magnesium oxide (MgO)-graphene oxide composite microspheres. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 435, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.H.; Chen, J.; Li, M.; Feng, L.; Losic, D.; Dong, F.; Zhang, Y.X. Synergistic effect of manganese dioxide and diatomite for fast decolorization and high removal capacity of methyl orange. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 484, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayunigari, M.K.; Das, R.; Maity, A.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K. Folic acid modified cross-linked cationic polymer: Synthesis, characterization and application of the removal of Congo red dye from aqueous medium. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 227, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, M.; Mao, L.; Xu, D.; Zeng, G.; Huang, H.; Jiang, R.; Deng, F.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. Surface functionalized SiO2 nanoparticles with cationic polymers via the combination of mussel inspired chemistry and surface initiated atom transfer radical polymerization: Characterization and enhanced removal of organic dye. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 499, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.H. Excellent adsorption performance for Congo red on hierarchical porous magnesium borate microsphere prepared by a template-free hydrothermal method. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 86, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munagapati, V.S.; Kim, D.S. Equilibrium isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamics studies for congo red adsorption using calcium alginate beads impregnated with nano-goethite. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 141, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Jin, W.; Pei, Y.; Tang, K. Efficient removal of anionic dye (Congo red) by dialdehyde microfibrillated cellulose/chitosan composite film with significantly improved stability in dye solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafi, R.; Charradi, K.; Djebbi, M.A.; Amara, A.B.; Hafiane, A. Adsorption study of Congo red dye from aqueous solution to Mg–Al–layered double hydroxide. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkhami, A.; Moosavi, R. Adsorptive removal of Congo red, a carcinogenic textile dye, from aqueous solutions by maghemite nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorai, S.; Sarkar, A.K.; Panda, A.B.; Pal, S. Effective removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution using modified xanthan gum/silica hybrid nanocomposite as adsorbent. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Ling, Y.; Fan, J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xie, Z. Preparation of ionic liquid-functionalized layered double hydroxide via thiol-ene click chemistry for highly efficient removal of azo dyes during broad pH range. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).