Wireless Epidermal Six-Axis Inertial Measurement Units for Real-Time Joint Angle Estimation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
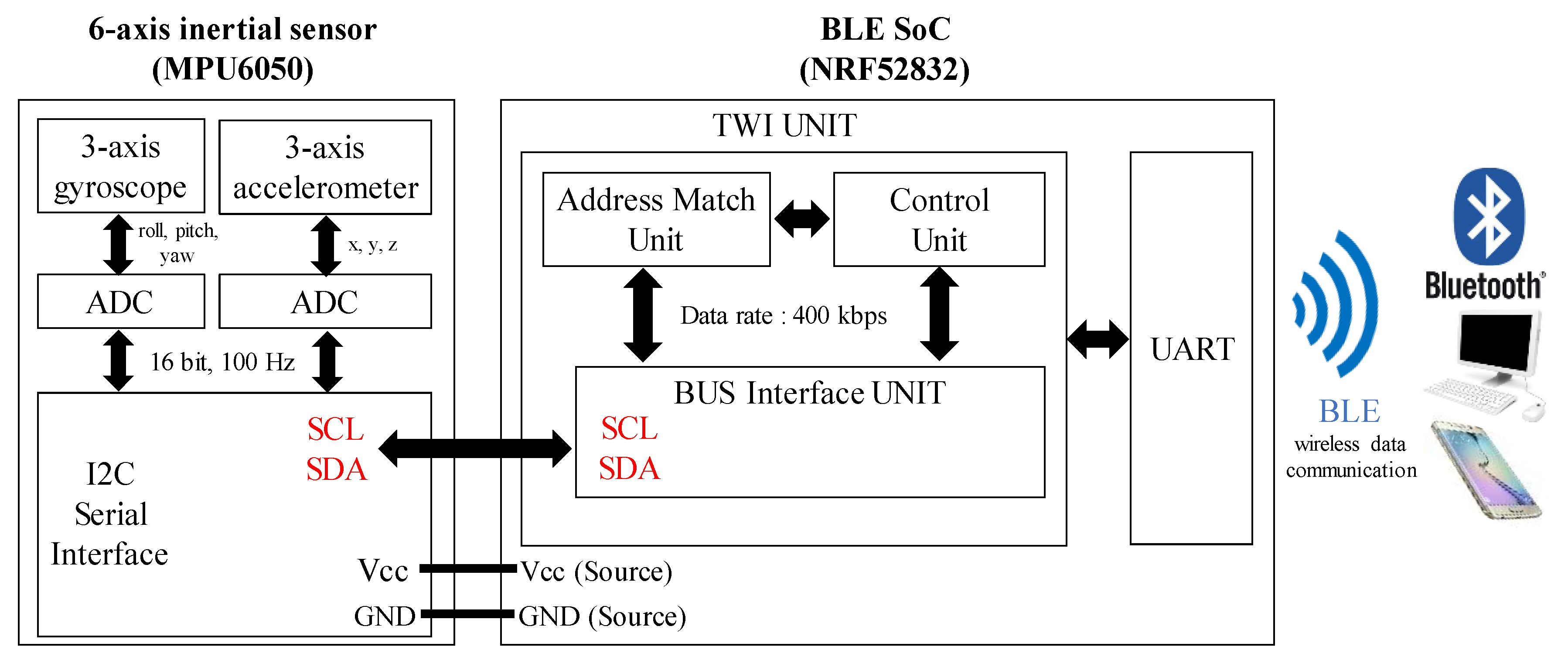
2.1. Design
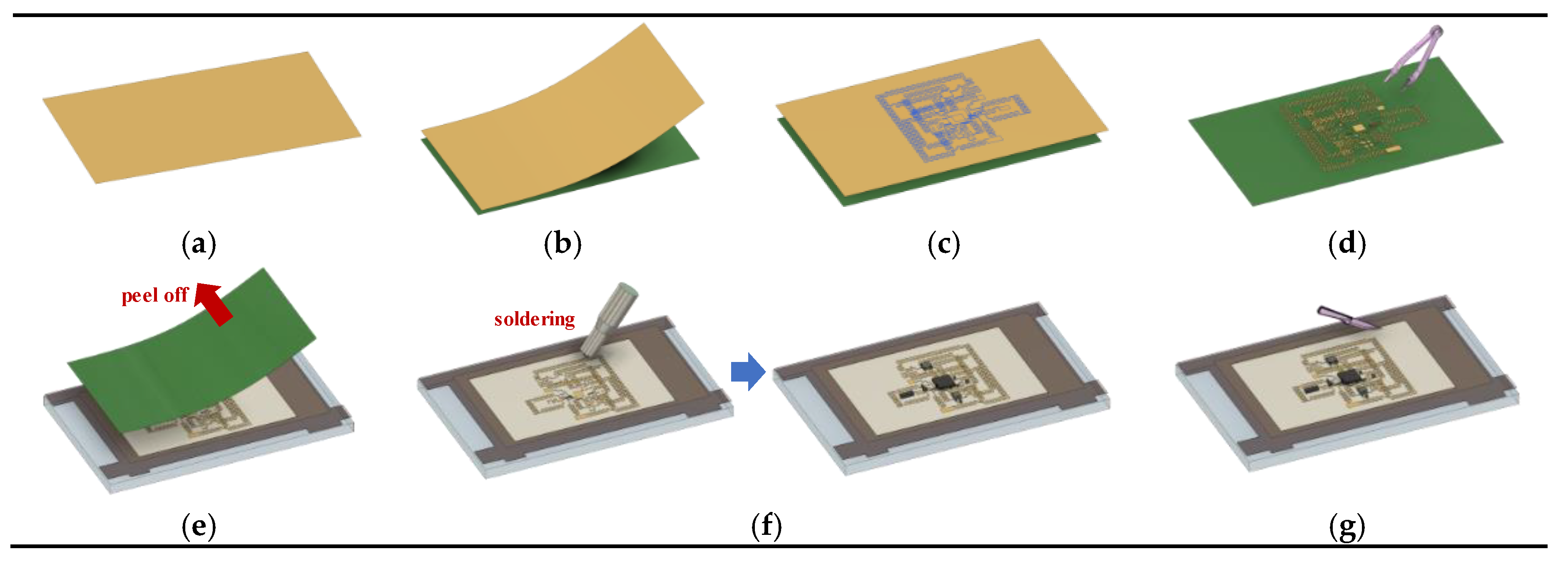
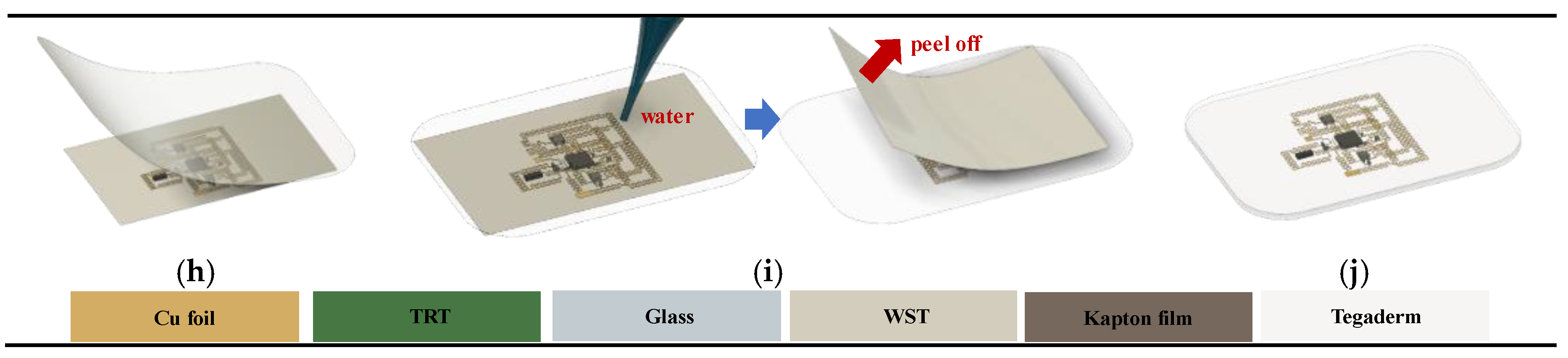
2.2. Manufacturing Process
3. Results
3.1. Implementation Results
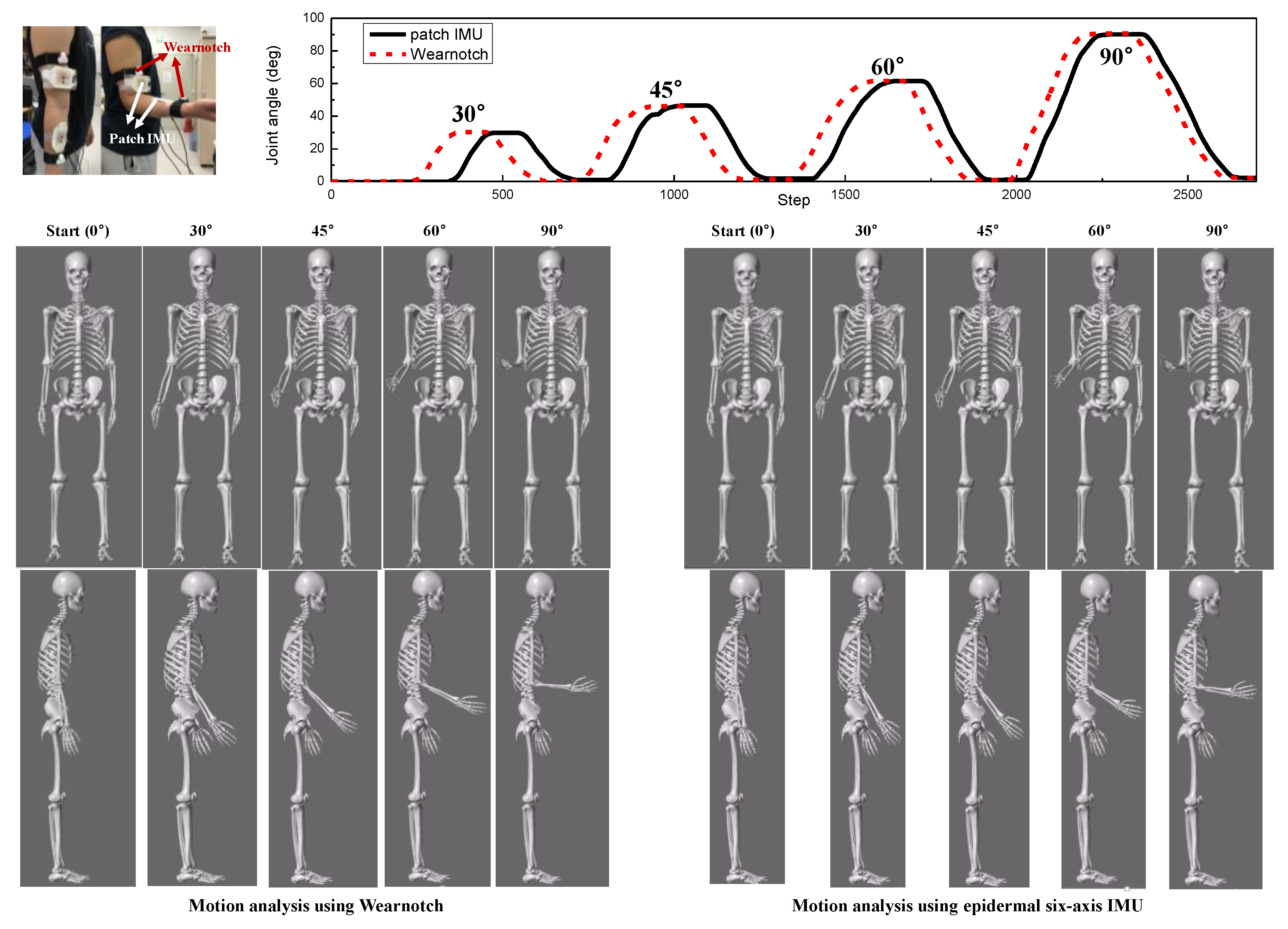
3.2. Performance Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, D.; Lu, N.; Ma, R.; Kim, Y.; Kim, R.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Won, S.M.; Tao, H.; Islam, A.; et al. Epidermal electronics. Science 2011, 333, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Choi, T.K.; Lee, Y.B.; Cho, H.R.; Ghaffari, R.; Wang, L.; Choi, H.J.; Chung, T.D.; Lu, N.; Hyeon, T.; et al. A Graphene-Based Electrochemical Device with Thermoresponsive Microneedles for Diabetes Monitoring and Therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, A.; Lee, S.; Cooray, N.F.; Lee, S.; Mori, M.; Matsuhisa, N.; Jin, H.; Yoda, L.; Yokota, T.; Itoh, A.; et al. Inflammation-Free, Gas-Permeable, Lightweight, Stretchable On-Skin Electronics With Nanomeshes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvo, P.; Pingitore, A.; Barbini, A.; Di Francesco, F. A Wearable Sweat Rate Sensor to Monitor the Athletes’ Performance during Training. Sci. Sports 2017, 33, e51–e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Ota, H.; Kiriya, D.; Takei, K.; Javey, A. Flexible Electronics Toward Wearable Sensing. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Norton, J.J.S.; Qazi, R.; Zou, Z.; Ammann, K.R.; Liu, H.; Yan, L.; Tran, P.L.; Jang, K.; Lee, J.W.; et al. Epidermal Mechano-Acoustic Sensing Electronics for Cardiovascular Diagnostics and Human-Machine Interfaces. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1601185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, Z.; Guo, C.F. Flexible Electronics: Stretchable Electrodes and Their Future. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1805924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Son, D.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.B.; Song, J.; Choi, S.; Lee, D.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.; Hyeon, T.; et al. Wearable Electronics: Transparent and Stretchable Interactive Human Machine Interface Based on Patterned Graphene Heterostructures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 25, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teufl, W.; Lorenz, M.; Miezal, M.; Taetz, B.; Frohlich, M.; Bleser, G. Towards Inertial Sensor Based Mobile Gait analysis: Event-Detection and Spatio-Temporal Parameters. Sensors 2019, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Y.-C.; Kuo, Y.-C.; Lin, H.-C. Personalized Rehabilitation Recognition Model upon ANFIS. Proc. Eng. Technol. Innov. 2020, 14, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Shull, P.B.; Jirattigalachote, W.; Hunt, M.A.; Cutkosky, M.R.; Delp, S.L. Quantified Self and Human Movement: A Review on the Clinical Impact of Wearable Sensing and Feedback for Gait Analysis and Intervention. Gait Posture 2014, 40, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, D.; Riener, R. A Survey of Sensor Fusion Methods in Wearable Robotics. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2015, 73, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casson, A.J. Wearable EEG and Beyond. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2019, 9, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurelbaatar, T.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.H. Consistent Accuracy in Whole-Body Joint Kinetics During Gait Using Wearable Inertial Motion Sensors and In-Shoe Pressure Sensors. Gait Posture 2015, 42, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Kim, J.S.; Purevsuren, T.; Khuyagbaatar, B.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.H. New Method to Evaluate Three-Dimensional Push-off Angle during Short-Track Speed Skating Using Wearable Inertial Measurement Unit Sensors. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2019, 233, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purevsuren, T.; Khuyagbaatar, B.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.H. Biomechanical Factors Leading to High Loading in the Anterior Cruciate Ligament of the Lead Knee During Golf Swing. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2020, 21, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bogert, A.J.; Geijtenbeek, T.; Even-Zohar, O.; Steenbrink, F.; Hardin, E.C. A Real-Time System for Biomechanical Analysis of Human Movement and Muscle Function. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2013, 51, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kun, L.; Inoue, Y.; Shibata, K.; Enguo, C. Ambulatory Estimation of Knee-Joint Kinematics in Anatomical Coordinate System Using Accelerometers and Magnetometers. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Lee, S. Implementation of Six-Axis Inertial Measurement Unit on a Stretchable Platform Using “Cut-and-Paste” Method for Biomedical Applications. Sens. Mater. 2019, 31, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Kim, K.; Lee, S. Stretchable, Patch-Type, Wireless, 6-axis Inertial Measurement Unit for Mobile Health Monitoring. Proc. Eng. Technol. Innov. 2020, 14, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; Soh, C.B.; Gunawan, E.; Low, K.S.; Maskooki, A. A Novel Approach to Joint Flexion/Extension Angles Measurement Based on Wearable UWB Radios. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inf. 2014, 18, 300–308. [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher, A.J.; Ni Anniadh, A.; Bruyere, K.; Otténio, M.; Xie, H.; Gilchrist, M.D. Dynamic Tensile Properties of Human Skin. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Research Council on the Biomechanics of Injury Conference, Dublin, Ireland, 12–14 September 2012; Volume 40, pp. 494–502. [Google Scholar]
- Euston, M.; Coote, P.; Mahony, R.; Kim, J.; Hamel, T. A Complementary Filter for Attitude Estimation of a Fixed-Wing UAV. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Nice, France, 22–26 September 2008; pp. 340–345. [Google Scholar]
- Notch Docs. Available online: https://docs.wearnotch.com (accessed on 28 February 2020).
- Qi, Y.; Soh, C.B.; Gunawan, E.; Low, K.-S.; Thomas, R. Lower Extremity Joint Angle Tracking with Wireless Ultrasonic Sensors during a Squat Exercise. Sensors 2015, 15, 9610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Center of Rotation Plate | End of Rotation Plate (30 cm from Center) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axes | x | y | z | x | y | z |
| Maximum RMS error | 1.41° (X-axis rotation) | 1.60° (Y-axis rotation) | 1.84° (Z-axis rotation) | 1.94° (X-axis rotation) | 3.31° (Y-axis rotation) | 2.91° (Z-axis rotation) |
| Maximum angle difference | 3.06° (X-axis rotation) | 0.78° (X-axis rotation) | 0.27° (X-axis rotation) | 2.25° (X-axis rotation) | 1.10° (X-axis rotation) | 1.07° (X-axis rotation) |
| 0.97° (Y-axis rotation) | 2.71° (Y-axis rotation) | 1.05° (Y-axis rotation) | 1.02° (Y-axis rotation) | 3.79° (Y-axis rotation) | 1.23° (Y-axis rotation) | |
| 0.67° (Z-axis rotation) | 0.79° (Z-axis rotation) | 2.39° (Z-axis rotation) | 1.63° (Z-axis rotation) | 1.53° (Z-axis rotation) | 3.38° (Z-axis rotation) | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.K.; Han, S.J.; Kim, K.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, S. Wireless Epidermal Six-Axis Inertial Measurement Units for Real-Time Joint Angle Estimation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072240
Lee JK, Han SJ, Kim K, Kim YH, Lee S. Wireless Epidermal Six-Axis Inertial Measurement Units for Real-Time Joint Angle Estimation. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(7):2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072240
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jae Keun, Seung Ju Han, Kangil Kim, Yoon Hyuk Kim, and Sangmin Lee. 2020. "Wireless Epidermal Six-Axis Inertial Measurement Units for Real-Time Joint Angle Estimation" Applied Sciences 10, no. 7: 2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072240
APA StyleLee, J. K., Han, S. J., Kim, K., Kim, Y. H., & Lee, S. (2020). Wireless Epidermal Six-Axis Inertial Measurement Units for Real-Time Joint Angle Estimation. Applied Sciences, 10(7), 2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072240






