Optimization of the Secondary Optical Element of a Hybrid Concentrator Photovoltaic Module Considering the Effective Absorption Wavelength Range
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Simulation Setup
3. Simulations
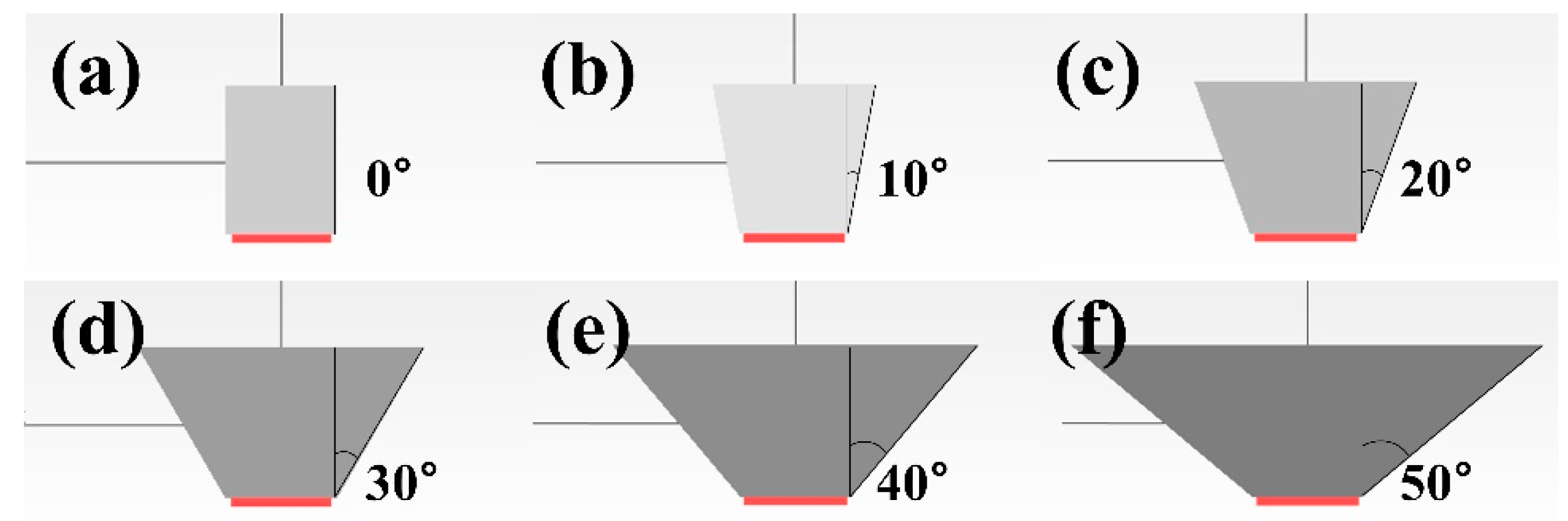
3.1. Optimization of SOE Design
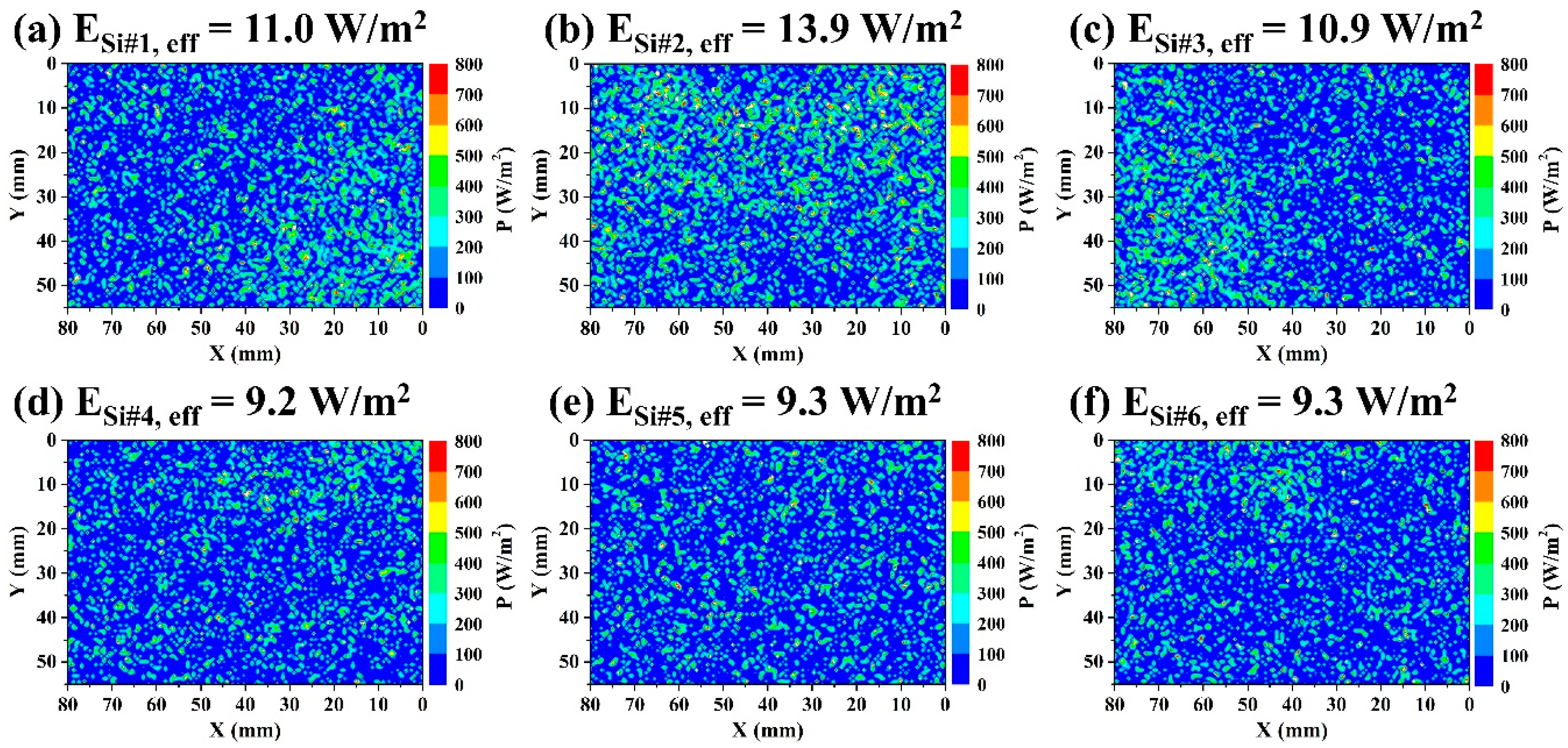
3.2. Irradiance Distributions
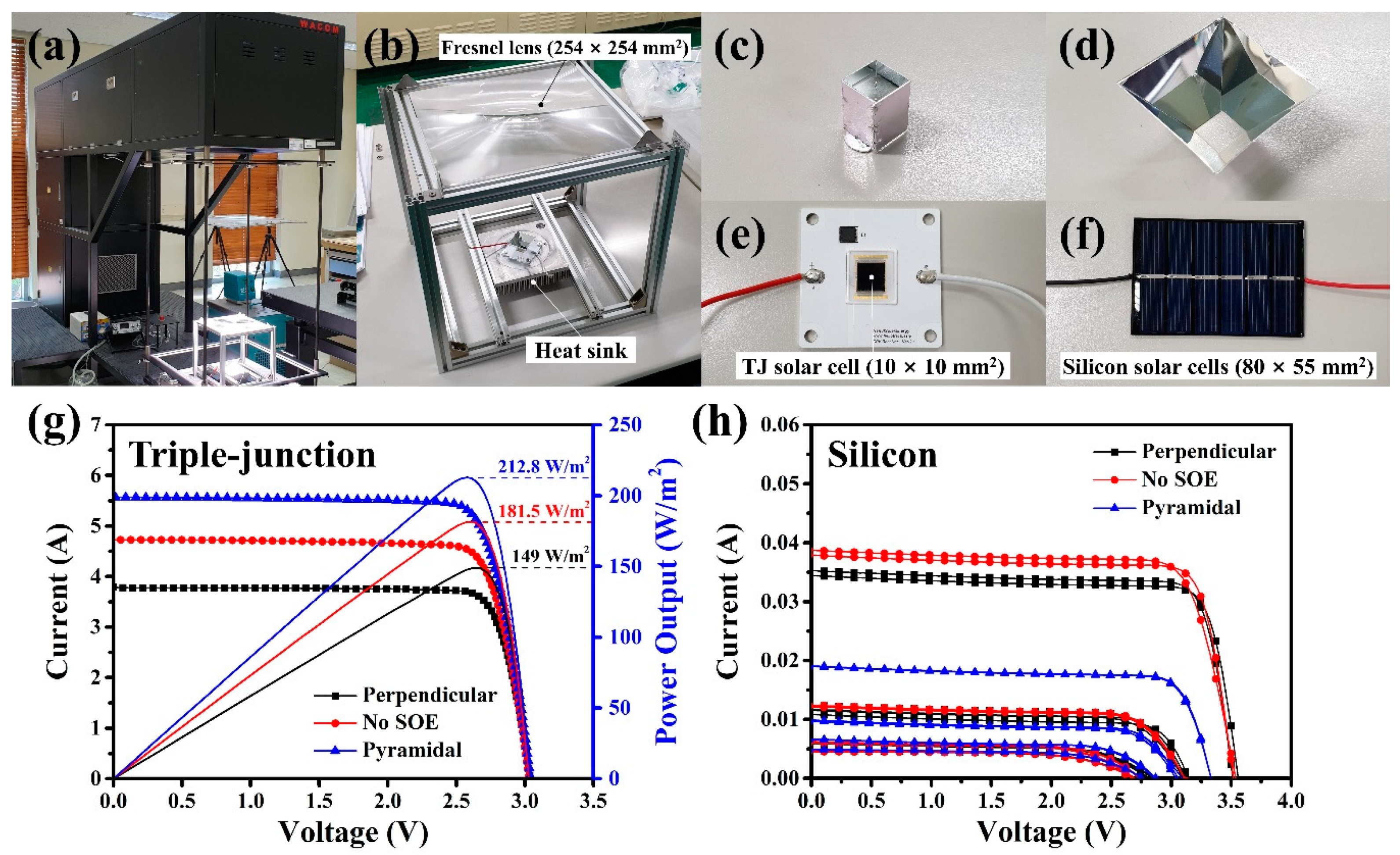
4. Experimental Measurements
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McDaniels, D.K.; Lowndes, D.H.; Mathew, H.; Reynolds, J.; Gray, R. Enhanced solar energy collection using reflector-solar thermal collector combinations. Sol. Energy 1975, 17, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.; McDaniels, D.K.; Kaehn, H.D.; Lowndes, D.H. Time integrated calculation of the insolation collected by a reflector-collector system. Sol. Energy 1978, 20, 415–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenta, C.; Vorobieff, P.; Mammoli, A. Summer off-peak performance enhancement for rows of fixed solar thermal collectors using flat reflective surfaces. Sol. Energy 2011, 85, 2041–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, O.Z.; Orhan, M.F. Concentrated photovoltaic thermal (CPVT) solar collector systems: Part I—Fundamentals, design considerations and current technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 1500–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, R.; Victoria, M.; Domínguez, C.; Askins, S.; Antón, I.; Sala, G. Concentration photovoltaic optical system irradiance distribution measurements and its effect on multi-junction solar cells. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2012, 20, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.M.; Feuermann, D.; Young, P. Unfolded aplanats for high-concentration photovoltaics. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 1114–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansoni, P.; Fontani, D.; Francini, F.; Jafrancesco, D.; Pierucci, G.; Lucia, M.D. Technique for outdoor test on concentrating photovoltaic cells. Int. J. Photoenergy 2015, 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yin, B.; Xiang, H.; Huang, Q. Direct liquid-immersion cooling of concentrator silicon solar cells in a linear concentrating photovoltaic receiver. Energy 2014, 65, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimman, K.; Selvarasan, I. Design construction and analysis of solar ridge concentrator photovoltaic (PV) system to improve battery charging performance. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 127, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, A.; Chen, Z.; Sze, J. Planar solar concentrator with a v-groove array for a side-absorption concentrated photovoltaic system. Optik 2016, 127, 10858–10867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chiang, H. Design of the secondary optical elements for concentrated photovoltaic units with Fresnel Lenses. Appl. Sci. 2015, 5, 770–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, M.; Yamada, N. Characterization of core-shell spherical lens for microtracking concentrator photovoltaic system. Energies 2019, 12, 3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, N.; Hirai, D. Maximization of conversion efficiency based on global normal irradiance using hybrid concentrator photovoltaic architecture. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2016, 24, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.T.; Yao, Y.; He, J.; Fisher, B.; Sheng, X.; Lumb, M.; Xu, L.; Anderson, M.A.; Scheiman, D.; Han, S.; et al. Concentrator photovoltaic module architectures with capabilities for capture and conversion of full global solar radiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E8210–E8218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, N.; Okamoto, K. Experimental measurements of a prototype high concentration Fresnel lens CPV module for the harvesting of diffuse solar radiation. Opt. Express 2014, 22, A28–A34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araki, K.; Ota, Y.; Lee, K.; Nishioka, K.; Yamaguchi, M. Is It CPV? Yes, But It Is a Partial CPV. In Proceedings of the 13th Conference on Concentrator Photovoltaic Systems, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1–3 May 2017; Volume 1881, p. 080001. [Google Scholar]
- Kreske, K. Optical design of a solar flux homogenizer for concentrator photovoltaics. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 2053–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontani, D.; Sansoni, P.; Francini, F.; DeLucia, M.; Pierucci, G.; Jafrancesco, D. Optical tests on a curve Fresnel Lens as secondary optics for solar troughs. Int. J. Photoenergy 2017, 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez, P.; Miñano, J.C.; Zamora, P.; Mohedano, R.; Cvetkovic, A.; Buljan, M.; Chaves, J.; Hernández, M. High performance Fresnel-based photovoltaic concentrator. Opt. Express 2010, 18, A25–A40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotal, H.; Fetzer, C.; Boisvert, J.; Kinsey, G.; King, R.; Hebert, P.; Yoon, H.; Karam, N. III–V multijunction solar cells for concentrating photovoltaics. Energy Environ. Sci. 2009, 2, 174–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Niu, P.; Li, Y.; Song, M.; Zhang, J.; Ning, P.; Chen, P. Investigation on high-efficiency Ga0.51In0.49P/In0.01Ga0.99As/Ge triple-junction solar cells for space applications. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 125217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, N.; Inoue, D.; Matsumoto, M.; Matsushita, A.; Higuchi, H.; Aya, Y.; Nakagawa, T. High-efficiency thin and compact concentrator photovoltaics with micro-solar cells directly attached to a lens array. Opt. Express 2015, 23, A594–A603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


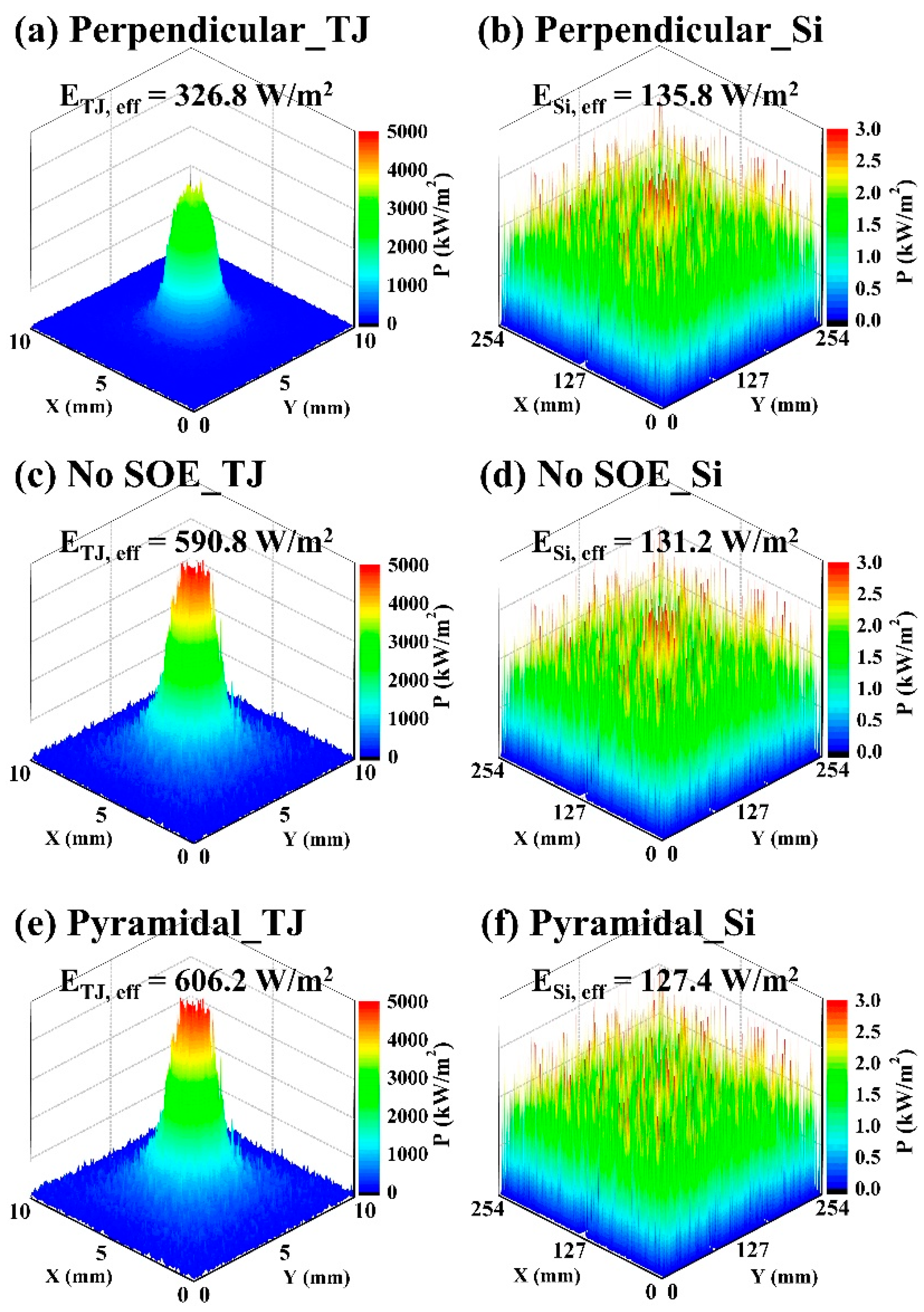
| SOE Angle | ETJ,eff (W/m2) | ETJ,loss (W/m2) | ETJ,loss/ETJ,eff ratio (%) | ESi,eff (W/m2) | ESi,loss (W/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0° (Perpendicular) | 326.8 | 7.2 | 2.2 | 135.8 | 7.3 |
| 10° | 495.6 | 15.1 | 3.1 | 130.6 | 7.1 |
| 20° | 588.6 | 24.1 | 4.1 | 129.8 | 13.5 |
| 30° | 606.2 | 34.5 | 5.7 | 127.4 | 9.9 |
| 40° | 604.7 | 41.7 | 6.9 | 125.8 | 10.2 |
| 50° | 603.4 | 26.1 | 4.3 | 125.1 | 5.2 |
| SOE Height (mm) | ETJ,eff (W/m2) | ETJ,loss (W/m2) | ETJ, loss/ETJ,eff Ratio (%) | ESi,eff (W/m2) | ESi,loss (W/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (No SOE) | 590.8 | 20.4 | 3.5 | 131.2 | 7.1 |
| 5 | 601.8 | 26.1 | 4.3 | 131.5 | 9.8 |
| 10 | 605.2 | 30.9 | 5.1 | 130.3 | 10.4 |
| 15 | 606.2 | 34.5 | 5.7 | 127.4 | 9.9 |
| 20 | 608.3 | 37.9 | 6.2 | 124.8 | 9.3 |
| 100 | 609.7 | 47.4 | 7.8 | 85.4 | 1.6 |
| SOE Configuration | Cell | PMAX (W/m2) | VOC (V) | ISC (A) | Fill factor | Area (cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perpendicular (θ = 0°, h = 15 mm) | Triple-junction | 149.0 | 3.04 | 3.78 | 83.61 | 645.2 |
| silicon | 5.67 (sum of #1–12) | - | - | - | 645.2 | |
| No SOE | Triple-junction | 181.5 | 3.03 | 4.73 | 81.8 | 645.2 |
| silicon | 5.99 (sum of #1–12) | - | - | - | 645.2 | |
| Pyramidal (θ = 30°, h = 15 mm) | Triple-junction | 212.8 | 3.04 | 5.57 | 81.16 | 645.2 |
| silicon | 5.14 (sum of #1–12) | - | - | - | 645.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, W.-L.; Kim, K.-P.; Min, J.-H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Mun, S.-H.; Park, J.-H.; Han, J.-H.; Park, W.-K.; Yoon, S.; Lee, D.-S. Optimization of the Secondary Optical Element of a Hybrid Concentrator Photovoltaic Module Considering the Effective Absorption Wavelength Range. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10062051
Jeong W-L, Kim K-P, Min J-H, Lee J-Y, Mun S-H, Park J-H, Han J-H, Park W-K, Yoon S, Lee D-S. Optimization of the Secondary Optical Element of a Hybrid Concentrator Photovoltaic Module Considering the Effective Absorption Wavelength Range. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(6):2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10062051
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Woo-Lim, Kyung-Pil Kim, Jung-Hong Min, Jun-Yeob Lee, Seung-Hyun Mun, Jeong-Hwan Park, Jang-Hwan Han, Won-Kyu Park, Sewang Yoon, and Dong-Seon Lee. 2020. "Optimization of the Secondary Optical Element of a Hybrid Concentrator Photovoltaic Module Considering the Effective Absorption Wavelength Range" Applied Sciences 10, no. 6: 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10062051
APA StyleJeong, W.-L., Kim, K.-P., Min, J.-H., Lee, J.-Y., Mun, S.-H., Park, J.-H., Han, J.-H., Park, W.-K., Yoon, S., & Lee, D.-S. (2020). Optimization of the Secondary Optical Element of a Hybrid Concentrator Photovoltaic Module Considering the Effective Absorption Wavelength Range. Applied Sciences, 10(6), 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10062051





