Featured Application
This method based on deep learning may be useful in the computer-aided detection of multiple lesions on chest X-ray images.
Abstract
Automated detection of lung lesions on Chest X-ray images shows good performance to reduce lung cancer mortality. However, it is difficult to detect multiple lesions of single image well and truly, and additional efforts are needed to improve diagnostic efficiency and quality. In this paper, a multi-label classification model combining attention-based neural networks and association-specific contexts is proposed for the detection of multiple lesions on chest X-ray images. A convolutional neural network and a long short-term memory network are first aligned by an attention mechanism to take advantage of both image and text information for the detection, called CNN-ATTENTION-LSTM (CAL) network. In addition, a mining method of implicit association strength to obtain an association network of chest lesions (CLA) network is designed to guide the training of CAL network. The CLA network provides possible clinical relationships between lesions to help the CAL network obtain better predictions. Experimental results on ChestX-ray14 dataset show that our method outperforms some state-of-the-art models under the metrics of area under curve (AUC), precision, recall, and F-score and achieves up to 85.4% in the case of atelectasis and infiltration. It indicates that the method may be useful in the computer-aided detection of multiple lesions on chest X-ray images.
1. Introduction
Many chest lesions such as nodules and effusion [1,2] are early manifestations or complications of lung cancer, the leading cause of cancer-related deaths among men. It is also possible for some lung lesions to be related to other severe diseases, such as respiratory diseases and heart diseases [3,4]. Consequently, the early detection of lung lesions is essential for decreasing the number of deaths around the world [5]. The chest X-ray is one of the most commonly accessible radiological examinations for diagnosis of chest lesions because of its non-invasiveness, small radioactivity, and low cost [6]. However, radiologists must examine a large number of images manually, causing high stress from work and low efficiency of diagnosis.
Computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) provides an automatic classification and computerized results as suggestions for reference to improve the accuracy and efficiency of diagnosis. According to the survey of related literature from 2014 to 2019, both traditional machine learning methods and deep learning methods are used for the classification of medical images. Traditional machine learning includes support vector machine (SVM), K-nearest neighbor method (KNN), random forest, and so on. Zhang et al. classified images on breast cancer datasets and retinal imagesets based on the single class of kernel principal component analysis [7]. Zhang et al. performed classification of magnetic resonance brain images (MRI) based on weighted Fractional Fourier Transform and non-parallel support vector machines [8]. Agrawal et al. used artificial bee colony algorithm combining with k-nearest neighbor algorithm and support vector machine to classify 271 computed tomography (CT) images of cervical cancer [9]. The main disadvantage of traditional machine learning methods is the relatively poor robustness because of the limited capacity of processing large amounts of images. Another major disadvantage is that they need manual feature extractions instead of learning valid features automatically. Thus, more researchers choose deep learning methods to process medical images to overcome these shortcomings (e.g., [10,11,12]).
Deep learning is a kind of representation-learning method connecting layers and nonlinear module to obtain multiple levels of representation automatically. As a deep-learning method, deep convolutional neural networks (CNN) are widely used in image analysis because of the local connectivity and shared weights. These two features not only maintain the affine invariance of CNN, but also reduce the number of parameters, ensuring the capacity of complex data processing. The basic architecture of CNN contains convolutional layers, pooling layers, and fully connected layers. Convolutional layers are stacked to extract features from the previous layer; pooling layers behind are designed to reduce computational complexity; and fully connected layers in the end are used to output the classification result. Many robust CNN frameworks have been designed including VGGnet, Resnet, and Densenet [13,14,15,16]. Recurrent neural network (RNN) shows the state-of-the-art performance in many tasks about processing sequence data, such as speech recognition [17]. Taking word generation as an example, it is necessary to use the information of the previous words to predict the next word of a sentence, because words in a sentence are semantically linked. In the recurrent neural network, the current output of a sequence is also related to the previous output [18], where implication relations between words can be learned. As a a specific recurrent neural network architecture, long short-term memory (LSTM) is designed to model temporal sequences and their long-range dependencies, making it more accurate than conventional RNNs in some cases [19]. The duplicate module in conventional RNN is as simple as a tanh layer, while it is much more complex in LSTM.
As the most popular method for image classifications, deep learning has been designed to detect lesions from Chest X-ray images. Ørting et al. used convolutional neural networks (CNN) to classify tuberculosis in chest X-rays with a dataset size of 1007 images [20]. Anavi et al. used age and gender to visualize patients and improve deep learning frameworks for chest X-ray image retrieval [21]. However, some deep neural network models are trained based on relatively very small-scale dataset from scratch, which may cause over-fitting. In December 2017, NIH announced one of the world’s largest public chest X-ray datasets, called ChestX-ray14. ChestX-ray14 contains 14 type of lesions, 30,805 patients, and 112,120 labeled chest X-ray images [6]. Then, Wang X et al. fine-tuned four standard CNN architectures (AlexNet, VGGNet, GoogLeNet, and ResNet) and ResNet achieved the best result [6,13,14,15,22]. Z. Li et al. presented a model for ChestX-ray14 that simultaneously performed disease classification and localization based on Resnet and a recognition network [23]. P. Rajpurkar et al. utilized a 121-layer DenseNet architecture with little modification to detect pneumonia using ChestX-ray14 [16,24]. Despite good results, they mixed multi-lesion images and single-lesion images together when training and testing. However, multi-lesion detection should be focused on specially because it is irresponsible for the health of a patient to detect a single lesion in a multi-lesion image. Detecting multiple lesions on a chest radiograph can be regarded as a multi-label classification problem. Multi-label classification has been investigated by many scholars in recent years (e.g., [25,26,27],. Among them, Shang-Fu et al. performed multi-label classification of images based on CNN and RNN model. The results illustrate the effectiveness of this model in the multi-label classification problem, and our method is designed for chest radiographs based on similar model structure.
In this study, an improved model for the detection of multiple lesions in single chest X-ray image is proposed. The major model contains a convolutional neural network (CNN) for feature extraction, a long short-term memory network (LSTM) for generating lesions words, and an attention mechanism for aligning visual features with the prediction of lesions. In addition, algorithms are designed for the mining of clinical dependencies between lesions to guide the training process of above-mentioned classification model for further improvement. In this paper, the architecture of our model is described and the detection performance as evaluated with chest X-ray images from ChestX-ray14 dataset is also discussed.
2. Methodology
2.1. Overview
The outline of our overall model for the detection of multiple lesions is shown in Figure 1, containing an input layer, a CNN encoder, an attention-based LSTM decoder, a CLA network, and an output layer. In the CAL network, pre-trained CNN extracts visual feature representations and attention-based LSTM models the attention dynamics of focusing on those lesion regions and generating sequentially words (the name of lesions), as shown in ➁ and ➃. In the CLA network, the strength of associations between lesions are detected and the information are used to adjust the label order adaptively, as shown in ➂. It makes the LSTM in the CAL network learn a more accurate prediction pattern by taking the interdependency of lesions into consider. In this section, we illustrate the details of the construction of each network.
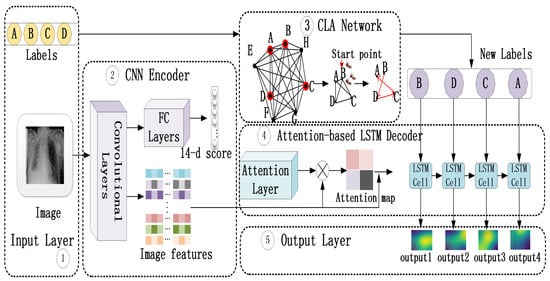
Figure 1.
The outline of our overall model, where CAL network consists of ➁ and ➃, ➂ shows the process of CLA network, and ➄ is the final result.
2.2. CAL Network
2.2.1. CNN Encoder
Convolutional neural networks have been popular in recent years because of their ability to learn representative image feature vectors. As shown in related works, many robust frameworks have been designed including VGGnet, Resnet, Inception-Resnet, and Densenet. They have been trained on ImageNet, a dataset containing 1.3 million natural images, and yield good results. It is a popular way to fine tune these existing deep networks when the scale of the dataset, labeling, and computer hardware are limited. However, more modifications are needed for medical images to guarantee transfer efficiency, as well as overcome over-fitting and some other problems. The first problem is which pre-trained model we should use. Deep CNNs are designed to capture more complicated and advanced features without gradient problems. For chest X-ray images, both the scale of training dataset and the features of a single image are not very complicated, and the structure of the image encoder should not be very deep. Otherwise, it is possible to cause over-fitting problem. VGGnet is therefore chosen as the basic CNN encoder in our model and further modifications are made on it.
The second problem is whether parameters of the encoder should be the same as those pre-trained on ImageNet. There is ample evidence suggesting the transfer learning from natural images to chest X-ray images without training again is not a good choice [6,28]. The difference between medical images and natural images may cause low transfer efficiency and the CNN encoder based on VGGNet or Resnet is therefore trained again using all labeled images with lesions on ChestX-ray14 in our task. The last layer of CNN encoder is changed into 14 output ports, as shown in Figure 1➁. Then, features of multi-label chest X-ray images are extracted from low-level layers, as shown in Figure 1➁.
2.2.2. Attention-Based LSTM Decoder
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) is a kind of neural network that models the dynamic temporal behavior of sequences through connections between the units. LSTM extends RNN by adding three gates to a RNN unit: a forget gate f to control whether to forget some current states, an input gate i to indicate if it should read the input, and an output gate o to control whether to output the state. Figure 1➃ shows the LSTM cells we used and our implementation of LSTM closely follows the one used by Fu et al., as shown in Equation (1) [29]. At time step t, , , , and represent the outputs of the input, forget, and output gates and possible information that can be input into memory cell of the LSTM, respectively. All of them are calculated under the information of previous hidden state , previous generation , and current visual context . T is a properly defined affine transformation, is the logistic sigmoid function, and is the hyperbolic tangent function. Then, the element-wise multiplication between previous memory cell and forget gate is performed to forget some information from previous memory cell and remember the rest. As shown in Equation (2), the result is added to the information selected from the candidate state and the current memory cell is formed. This is an important step for LSTM to keep a long memory. The current hidden state is obtained through the element-wise multiplication between the output of output gate and , as shown in Equation (3). Then, the current word is generated according to the current hidden state and visual context , as shown in Equation (4).
The visual context vector is obtained by attention mechanism and input LSTM cell at time step t. Visual attention was first used in natural image captioning, where the learned alignments correspond very well to human intuition [30]. Similar to natural images, lesion regions in chest X-ray images also need to be focused using attention mechanism, as shown in Figure 1➃.
To use visual contexts, L D-dimensional feature vectors are first extracted from the trained CNN encoder, as shown in Equation (5). Then, the probability of focusing on the ith location is computed by an attention model , as shown in Equation (6). The inputs to the attention model is the extracted features, the hidden state , and the previously generated word . After that, weighted sum is used to update the visual context vector , as shown in Equation (7).
2.3. CLA Network
Studies have suggested that there are either strong or implicit associations between diseases [31,32]. For chest lesions, a chest X-ray image containing cardiomegaly is more likely to contain pulmonary edema because of the left ventricular failure and chronic nasopharyngeal obstruction [33,34]. Studies also show both fibrosis and emphysema are associated with respiratory disease [35,36]. The association information between chest lesions provide possibilities of appearing in the same image and it gives the CAL network a direction to seek for possible lesions.
Algorithms are proposed to build CLA network and adjust the label orders (Algorithms 1 and 2). To estimate the correlation strength between lesions, the number of lesion i in ChestX-ray14 database, the number of lesion j in ChestX-ray14 database and the times when both lesion i and lesion j are in an image are counted. Then, they are used to calculate Jaccard distances between lesions [37]. After building the association graph, a subgraph from graph <L,E >is selected for each image i, where multiple lesions (labels) are vertexes and edges connect the selected vertexes in graph <L,E >. If there are two lesions shown in an image, the orders of these two lesions are adjusted according to the degree of vertexes in each subgraph <, >. If there are more than two lesions shown in an image, ant colony algorithm is used to find the shortest path among these lesions according to the subgraph [38]. The number of ants is set as one fewer than the number of lesions. Pheromone importance factor is set as 1. Heuristic function importance factor is set as 5. Pheromone evaporation rate is set as 0.1. Ants start from random nodes and climb to other nodes iteratively. If there are three lesions shown in an image, the shortest path is calculated without the last sub-path. If there are more than three lesions shown in an image, the shortest path is calculated with the last sub-path. After reaching the terminal condition, the shortest path is obtained where vertexes (lesions) are tightly connected to each other. The lesion with the highest degree is set as the first position of the adjusted labels because the high degree indicates the strong correlation with other lesions. The order of vertexes in the shortest path is the updated label order of an image to train LSTM in CAL network. Table 1 shows some symbols, definitions, and their descriptions.

Table 1.
Symbols, definitions, and their descriptions.
Figure 1➂ shows an example of adjusting the label order for a four-lesion image. A subgraph containing the four lesions is first selected from the built CLA network and then a start lesion and a shortest path are chosen according to our algorithm. The final path is exactly the new order of our training label for a single image.
| Algorithm 1 Building association graph. |
| Input: N,M,C,L,CXNL,CXNLA,E Output: association graph <L,E>
|
| Algorithm 2 Adjusting label orders. |
| Input: graph <L,E >, LABP Output: LABO
|
3. Experiments
3.1. Dataset
ChestX-ray14 dataset is one of the largest accessible chest X-ray image datasets in the world. In the ChestX-ray14 dataset, there are 112,120 labeled chest X-ray images, of which 60,361 chest X-ray images are lesion-free and 51,759 chest X-ray images are labeled with lesion information. These 51,759 chest X-ray images involve 14 types of lesions: infiltration, effusion, atelectasis, nodule, mass, pneumothorax, consolidation, pleural thickening (PT), cardiomegaly, emphysema, edema, fibrosis, pneumonia, and hernia. Table 2 shows image numbers labeled by each lesion type in the ChestX-ray14 dataset. The image number of infiltration, effusion, atelectasis, nodule, mass, pneumothorax, consolidation, PT, cardiomegaly, emphysema, edema, fibrosis, pneumonia, and hernia is 19,894, 13,317, 11,559, 6331, 5782, 5302, 4667, 3385, 2776, 2516, 2303, 1686, 1431, and 227, respectively. In total, 20,795 chest X-ray images are labeled by two or more lesions, called multi-lesion images. Among them, the image number labeled by infiltration, effusion, atelectasis, nodule, mass, pneumothorax, consolidation, PT, cardiomegaly, emphysema, edema, fibrosis, pneumonia, and hernia is 10,345, 9360, 7243, 3626, 3643, 3108, 3344, 2259, 1582, 1624, 1672, 959, 1109, and 117, respectively, as shown in the third row of Table 2. These 20,795 multi-lesion images involved 820 types of lesion combinations. The image number of each type varies, ranging from a few thousand to a few. For example, there are 3865 images labeled by both infiltration and effusion; 2528 images labeled by both effusion and atelectasis; 1667 images labeled by both infiltration and atelectasis; 737 images labeled by atelectasis, effusion, and infiltration; and 81 images labeled by atelectasis, consolidation, effusion and infiltration. The sole goal of this study was to detect all lesions from single chest radiograph by classifying 14 lesion types. Therefore, 20,795 multi-lesion chest X-ray images were mainly used for model training and testing. Single-lesion chest radiographs were only used to pre-train image feature extractor, which is a part of our model.

Table 2.
Image numbers labeled by lesion type in the ChestX-ray14 dataset.
3.2. Pre-Processing and Training
Image data and label data need to be pre-processed before training. For image data, all chest X-ray images were first scaled from a size of 1024 × 1024 to 224 × 224 and converted into RGB channels. To reduce the risk of overfitting, chest X-ray images were then rotated at 45 and 90 degree angles for data augmentation. Fourteen lesion types were converted into 14 integers ranging from 0 to 13 when the image extractors were trained and tested. For the detection task of multiple lesions on single images, lesion types were converted into 14 integers, ranging from 3 to 16, while ‘0’ represents the null character ‘<NULL>’, ‘1’ represents the start indicator ‘<START>’, and ‘2’ represents the end indicator ‘<END>’. For example, infiltration, effusion, and atelectasis qwew represented by 3, 4, and 5, respectively. After preprocessing, the label of a multi-lesion chest X-ray image containing infiltration, effusion, and atelectasis is [1 3 4 5 2]. The image data and the label data were saved in two .pkl files and connected by the corresponding image ID during training.
There are three steps to train our whole model. The CNN part of CAL network was first trained as a simple 14-class classification task using images with lesions on ChestX-ray14, as shown in Figure 1➁. The purpose of this step is to increase the transfer efficiency between medical images and natural images, acquiring more discriminative features. Then, image features extracted from low-level layer of CNN encoder were input into the attention-based LSTM decoder and trained iteratively, as shown in Figure 1➁➃. After that, reordered labels obtained from CLA network were utilized to train a new attention-based LSTM decoder using original image features and updated ground truth, as shown in Figure 1➁–➃.
When training the image feature extractor in the first step, both single-lesion images and multi-lesion images were used. Wang et al. [6] first built the ChestX-ray14 dataset and classified ChestX-ray14 dataset into different lesion types. Similar to Wang et al. [6], the images were divided into a training set, validation set, and test set at a ratio of 7:1:2 in our experiments. Further, cross-validation was used to get a credible evaluation of the model.
Multi-lesion images were used in the second and third steps because the final outputs of our method were multiple lesion types. The 20,795 multi-lesion images were divided into a training set, validation set, and test set at a ratio of 8:1:1 and a ten-fold cross validation procedure was also applied. The images were first shuffled and then divided into 10 folds. In each type of lesion combination, images should be shuffled by patient ID rather than image ID to reduce the overlap of both patient ID and lesion combination type between three subsets. We only adopted this "shuffle" strategy for lesion combinations with large scale samples in the experiment because there are hundreds of types of lesion combinations and most of them only hold a few samples. Each time, eight folds were used as the training set, one fold was used as the validation set, and one fold was used as the test set. The above process was repeated 10 times and each image was only used once for the validation or test.
The experimental environment was an ubuntu linux server with 2 GeForce GTX 1080 Ti GPUs and the models were developed with Python and Tensorflow 1.2 (GPU and ubuntu version), a deep learning framework. The neural network was trained by stochastic gradient descent (SGD), with a batch size of 32 and a learning rate of 0.001. According to the distribution of label length, the length of LSTM C was set as 2, 3, and 4 (except for the start indicator and end indicator), respectively.
3.3. Results
Extracting discriminative features from images is a crucial step in this study. Therefore, we first verified the performance of our approach without considering the dependency between lesions. Table 3 compares our CNN encoders based on VGGNet (ours-vgg) and Resnet (ours-res) with the methods proposed in the last three years by Wang et al. [6], Aviles-Rivero et al. [39] and Yao et al. [40] under AUC value for multi-classification problem of ChestX-ray14 dataset, where bold numbers indicate the best AUC value in each row. Among them, Yao et al. [40] claimed that their dataset is assigned in the same way as Wang et al. [6]. Table 3 shows that our best average AUC value is 0.791. In addition, our method achieves better results in detecting lesions such as atelectasis, effusion, infiltration, etc.

Table 3.
Result evaluation and comparison by AUC.
As the research objective of this work, the whole model’s ability of detecting lesion sequences was the focus of our validation. Table 4 compares the recall, precision, and F-score value of the proposed approaches to other methods, where bold numbers indicate the best AUC value in each column. CXNet-m2-b [41] is a model for image-based detection of multiple chest lesions proposed in this year. Vinyals, O. et al. [42] proposed a classical CNN-RNN model which we call SAT here and trained again using our dataset. Vggc4-CAL, Vggc5-CAL, Resb3-CAL, and Resb4-CAL mean the visual features are trained from conv4 layer of Vggnet, conv5 layer of Vggnet, block3 layer, and block4 layer of Resnet, respectively. ‘Improvements-1’ shows the improvements of our best model from CXNet-m2-b. ‘Improvements-2’ shows the improvements of our best model from SAT. CLA means the CLA network is used to take advantage of the interdependencies between lesions.

Table 4.
Evaluation and comparison of models on precision, recall, and F-score value.
Figure 2, generated using gephi software, shows the CLA network built by Algorithm 1 and correlation intension between two lesions are labeled as edge weights. The thickness of the edges rather than the length also reflects the strength of the association between the two lesions. The thicker is the edge, the stronger is the association. According to different combination of lesions in ChestX-ray14 dataset, different subgraphs are detected, as shown in Figure 2. Algorithm 2 was used to process these subgraphs and output updated label orders.
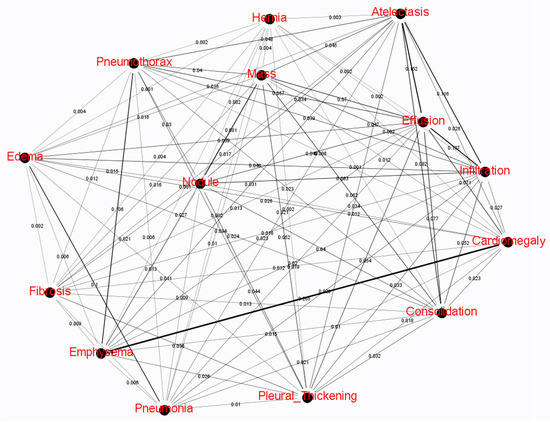
Figure 2.
The CLA network built by Algorithm 1. The thickness of an edge implies the correlation intension between two lesions.
Table 5 shows the label sequence of some lesion combinations before and after the updates, whose lengths are and . “Original order” refers to the order of lesion labels for single chest X-ray image in ChestX-ray14 dataset. “Updated order” refers to the order of lesion labels for single chest X-ray image after updates. “Update order” is the output of Algorithm 2, which was obtained by mining the subgraphs detected from the association graph Figure 2. A, CA, CO, ED, E, EM, I, M, P, and PX mean atelectasis, cardiomegaly, consolidation, edema, effusion, empysema, infiltration, mass, pneumonia, and pneumothorax, respectively.

Table 5.
Some examples of the original label order and updated label order detected as shown in Figure 2 by Algorithm 2.
Figure 3 shows that the ant colony algorithm in Algorithm 2 gradually converges to the shortest path as the number of iterations increases. It can be seen that the shortest path in each subgraph can be found after around 10 iterations. According to the number of nodes in the subgraph, the number of iterations in our experiments were set as 8, 14, and 20, respectively.
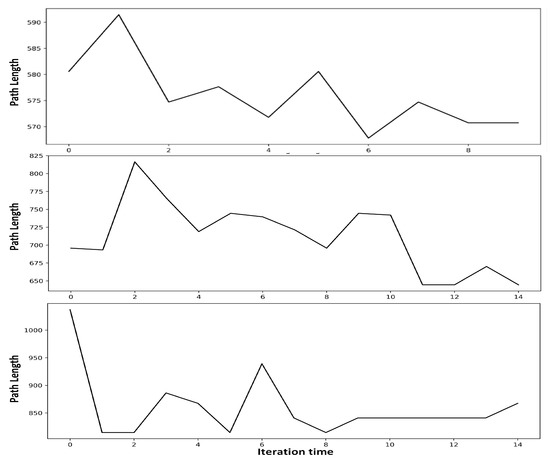
Figure 3.
Convergence process of ant colony algorithm in Algorithm 2.
Figure 4 shows visualization results of eight examples by highlighting the class-specific discriminative regions. In each example, the first image is a chest X-ray image, the text on the top of rest images represents the corresponding predictions of the model. The number below the text represents the confidence level of the model prediction. Most predictions have high confidence, but some predictions have low confidence. For example, although all lesions on the chest radiograph in ➆ group are correctly identified, the confidence level for “effusion” is only 0.21. Except for the first image, images are superpositions of the gray-scale image and the corresponding chest X-ray image (the first image). The brighter is the gray-scale image, the greater is the contribution of the corresponding area of the chest X-ray image to the prediction result. However, the corresponding active area cannot be clearly seen because the gray-scale images obscure the chest X-ray image under it. Therefore, colored boxes are used to indicate the active location of the predicted lesion. For example, the red box of the second image in ➀ group outlines the brightest part of the gray-scale image, which corresponds to the area surrounded by the red box of the first image in ➀ group. This area of the chest X-ray image contributes the most to the “cardiomegaly” prediction. The pink box of the third image in ➀ group outlines the brightest part of the gray-scale image, which corresponds to the area surrounded by the pink box of the first image in ➀ group. This area of the chest X-ray image contributes the most to the “emphysema” prediction.
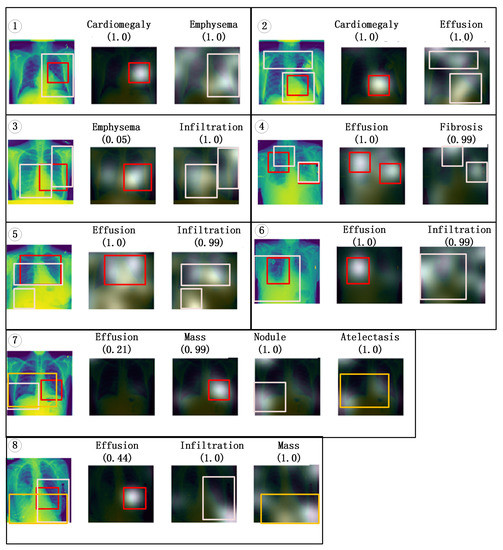
Figure 4.
Visualization results of Vggc5-CAL-CLA model.
It can be seen in Table 4 that Vggc5-CAL-CLA obtains the best precision, recall, and F-score value among these algorithms, peaking at 74.1% when C = 4, while SAT obtains the worst results when C = 2, 3, and 4. The improvements of Vggc5-CAL-CLA on precision, recall, and F-score from SAT are up to 10.9%, 10.5%, and 10.7%, respectively. Vggc5-CAL obtains the second highest values and peaks at both 73.9% when C =2. Vggc5-CAL shows higher values than Vggc4-CAL, Resb3-CAL, and Resb4-CAL. It is also clear that most methods show a downward trend of precision, recall, and F-score from C = 2 to 4 except for Vggc5-CAL-CLA.
In Table 6, precision, recall, and F-score value of some categories are shown, where A, CO, E, and I mean atelectasis, consolidation, effusion, and infiltration, respectively. It can be seen that the images with effusion and infiltration, atelectasis and infiltration, and atelectasis and effusion can be recognized correctly with more than 75% precision, recall, and F-score value, with atelectasis and infiltration achieving up to 85.4%.

Table 6.
Evaluation of Vggc5-CAL-CLA on precision, recall, and F-score value for the detection of some lesion combinations.
4. Discussion
Most of the current studies have proposed advanced classification methods for single-lesion chest radiographs and achieved good results. However, many diseases have complications that can be shown on one chest radiograph. This paper commits to diagnosing all possible lesions from a single image.
The performance of our image feature extractor in Table 3 was first verified by ChestX-ray14 dataset. AUC was used as the metric for two reasons. Firstly, AUC is recommended as a single number measure to over accuracy when there is a skewed sample distribution, and ChestX-ray14 is extremely imbalanced [41,43]. Secondly, it is widely used as the only measure in many studies which proposed multi-class methods for ChestX-ray14. Our methods were compared with three methods proposed in the last three years for multi-classification problem of ChestX-ray14 dataset. The purpose of Table 3 is to verify whether the image feature extractor we trained is useful rather than showing higher AUC values. If the AUC values are very low, the training of our image feature extractor fails. If AUC values of our image feature extractor are similar to AUC values in most other research work, the image feature extractor we trained is available. It was found that the 30 AUC scores of our image feature extractors are not low and some are even higher than those of other methods listed in Table 3, which is satisfactory. Note that slightly higher AUC values do not mean that the corresponding image feature extractor contributes more to our research goal. For example, the average AUC value of “ours-res” is higher than “ours-vgg”. However, the model extracting image features from “ours-vgg” obtains the best results, as shown in Table 4 and Table 6.
As the goal of our work is to solve a multi-lesion classification problem; the whole model’s performance of detecting multiple lesions simultaneously was then verified under precision, recall, and F-score. The whole multi-label classification model is similar to a language model where outputs of each image are continuous lesion names, as with the simplest sentence. Therefore, precision, recall, and F-score, measurement indicators in both natural language processing and classification problems, were used. As shown in Table 4, 24 experiments were conducted to determine which feature extractor is better and weather CLA network is useful. Results on precision, recall, and F-score were also compared with two other methods. It was found that all of our methods are better than SAT. However, only when CLA network is added or image features are extracted from an appropriate layer is our method better than cxnet-m2-b. It illustrates that the quality of image features has a great influence on the results and the dependency between lesions provided by CLA network improves the model’s performance. The results in Table 5 also show that the original order of the lesions is not optimal for most lesion combinations. Of the 14 lesion combinations in Table 5, only one kind of lesion combination remains the same before and after the update. CLA network method makes the relationship between the lesions in each lesion combination closer by considering association information. From the results in Table 4, it is clear that conv5 layer of Vggnet extracts more discriminative features than conv4 layer of Vggnet, and block4 layer and block3 layer of Resnet. The performances of Vggc5-CAL-CLA and Resb3-CAL-CLA are better than Vggc5-CAL and Resb4-CAL, respectively. It implies that CLA network helps CAL network get better predictions by providing possible clinical dependencies between lesions.
As shown in Table 6, as the best model in our work, the performance of Vggc5-CAL-CLA was verified by categories of effusion and infiltration; atelectasis and infiltration; atelectasis and effusion; atelectasis, effusion, and infiltration; and atelectasis, consolidation, effusion, and infiltration. Data in Table 4 were obtained based on all types of lesion combinations in ChestX-ray14, while Table 6 shows lesion combinations whose sample scales are relatively large. The values of Vggc5-CAL-CLA in Table 6 are much higher than those in Table 4. The difference implies that the performance of our model is better for some categories with large scale. For some multi-lesion images with few training samples, the detection result cannot be good. For example, it is difficult to recognize images with both mass and pneumonia (only 11 images in total) because of the difficulty of learning a solid pattern from such a small training set. The poor results of these images make the values in Table 4 much lower than the values in Table 6. In the future, models should be improved to take measures against imbalance.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, an improved classification model is proposed using CNN, LSTM, attention mechanism, and association mining. Evaluation results using AUC, precision, recall, and F-score values show that our methods are better than some state-of-the-art methods and CLA network improves the performance of CAL networks. Our model achieves up to 85.4% on precision, recall, and F-score value in the case of atelectasis and infiltration, where image features are extracted from conv-5 layer of Vggnet and CLA network are made used. It can be seen from the experimental results that our method has better classification performance and detection effect for disease types with larger sample sizes. In future work, we will take measures against imbalance problem to make further improvements. More reasonable data collection strategies should be adopted to reduce the gap in the number of samples for each lesion type. The loss function specifically for the imbalance problem should also be designed to make the model pay more attention to lesion types with fewer samples during the learning process.
Author Contributions
Methodology, S.X.; software, S.X.; validation, S.X., J.G., and G.Z.; investigation, G.Z.; resources, G.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, S.X.; visualization, S.X.; supervision, J.G. and R.B.; and funding acquisition, R.B. and J.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was sponsored by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61571049, 61601033 and 61977006).
Conflicts of Interest
No conflict of interest exits in the publication of this manuscript.
References
- Harwood, T.R.; Gracey, D.R.; Yokoo, H. Pseudomesotheliomatous carcinoma of the lung: a variant of peripheral lung cancer. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1976, 65, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangani, N.K.; Naliath, S.M. Pseudomesotheliomatous Type of Sarcomatoid Squamous Cell Lung Cancer Presenting With Hemothorax. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2018, 106, e201–e203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triplette, M.; Attia, E.; Akgün, K.; Campo, M.; Rodriguez-Barradas, M.; Pipavath, S.; Shahrir, S.; Wongtrakool, C.; Goetz, M.B.; Kim, J.; et al. The differential impact of emphysema on respiratory symptoms and six-minute walk distance in HIV infection. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. (1999) 2017, 74, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sforza, A.; Carlino, M.V.; Guarino, M.; Russo, S.; Albano, G.; Paladino, F.; Mancusi, C. A case of pulmonary edema: The critical role of lung-heart integrated ultrasound examination. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2018, 88, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teramoto, A.; Fujita, H.; Yamamuro, O.; Tamaki, T. Automated detection of pulmonary nodules in PET/CT images: Ensemble false-positive reduction using a convolutional neural network technique. Med. Phys. 2016, 43 Pt 1, 2821–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Peng, Y.; Lu, L.; Lu, Z.; Bagheri, M.; Summers, R.M. ChestX-ray8: Hospital-scale chest X-ray database and benchmarks on weakly-supervised classification and localization of common thorax diseases. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2097–2106. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Coenen, F.; Xiao, J.; Lu, W. One-class kernel subspace ensemble for medical image classification. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2014, 2014, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.D.; Chen, S.; Wang, S.H.; Yang, J.F.; Phillips, P. Magnetic resonance brain image classification based on weighted-type fractional Fourier transform and nonparallel support vector machine. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2015, 25, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, V.; Chandra, S. Feature selection using Artificial Bee Colony algorithm for medical image classification. In Proceedings of the 2015 Eighth International Conference on Contemporary Computing (IC3), Noida, India, 20–22 August 2015; pp. 171–176. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Kim, J.; Lyndon, D.; Fulham, M.; Feng, D. An ensemble of fine-tuned convolutional neural networks for medical image classification. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2016, 21, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frid-Adar, M.; Diamant, I.; Klang, E.; Amitai, M.; Goldberger, J.; Greenspan, H. GAN-based synthetic medical image augmentation for increased CNN performance in liver lesion classification. Neurocomputing 2018, 321, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaludin, A.; Kadir, T.; Zisserman, A. SpineNet: Automated classification and evidence visualization in spinal MRIs. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 41, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, A.B. System and Method for Speech Recognition Using Deep Recurrent Neural Networks. U.S. Patent 9,263,036, 16 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, M.; Paliwal, K.K. Bidirectional recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, T.; Zahid, U. Long short-term memory recurrent neural network architectures for Urdu acoustic modeling. Int. J. Speech Technol. 2019, 22, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyboe Ørting, S.; Petersen, J.; Cheplygina, V.; Thomsen, L.H.; Wille, M.M.; de Bruijne, M. Feature learning based on visual similarity triplets in medical image analysis: A case study of emphysema in chest CT scans. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.07131. [Google Scholar]
- Anavi, Y.; Kogan, I.; Gelbart, E.; Geva, O.; Greenspan, H. Visualizing and enhancing a deep learning framework using patients age and gender for chest X-ray image retrieval. In Proceedings of the SPIE Medical Imaging, San Diego, CA, USA, 7 July 2016; Volume 9785, p. 978510. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems Conference, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3 December 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Han, M.; Xue, Y.; Wei, W.; Li, L.J.; Li, F.-F. Thoracic disease identification and localization with limited supervision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8290–8299. [Google Scholar]
- Rajpurkar, P.; Irvin, J.; Zhu, K.; Yang, B.; Mehta, H.; Duan, T.; Ding, D.; Bagul, A.; Langlotz, C.; Shpanskaya, K.; et al. Chexnet: Radiologist-level pneumonia detection on chest X-rays with deep learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.05225. [Google Scholar]
- Vluymans, S.; Cornelis, C.; Herrera, F.; Saeys, Y. Multi-label classification using a fuzzy rough neighborhood consensus. Inf. Sci. 2018, 433, 96–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.B.; Plastino, A.; Zadrozny, B.; Merschmann, L.H. Categorizing feature selection methods for multi-label classification. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2018, 49, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Chen, Y.C.; Yeh, C.K.; Wang, Y.C. Order-free RNN with visual attention for multi-label classification. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Wu, H.; Bie, R. CXNet-m1: Anomaly detection on chest X-rays with image-based deep learning. IEEE Access 2018, 7, 4466–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Jin, J.; Cui, R.; Sha, F.; Zhang, C. Aligning where to see and what to tell: Image captioning with region-based attention and scene-specific contexts. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 2321–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Ba, J.; Kiros, R.; Cho, K.; Courville, A.; Salakhudinov, R.; Zemel, R.; Bengio, Y. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2015, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 2048–2057. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Song, Y.; Caballero, B.; Cheskin, L.J. Association between obesity and kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffee, B.W.; Weston, S.J. Association between chronic periodontal disease and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Periodontol. 2010, 81, 1708–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luke, M.J.; Mehrizi, A.; Folger, G.M.; Rowe, R.D. Chronic nasopharyngeal obstruction as a cause of cardiomegaly, cor pulmonale, and pulmonary edema. Pediatrics 1966, 37, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dodek, A.; Kassebaum, D.G.; Bristow, J.D. Pulmonary edema in coronary-artery disease without cardiomegaly: paradox of the stiff heart. N. Engl. J. Med. 1972, 286, 1347–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobbs, B.D.; De Jong, K.; Lamontagne, M.; Bossé, Y.; Shrine, N.; Artigas, M.S.; Wain, L.V.; Hall, I.P.; Jackson, V.E.; Wyss, A.B.; et al. Genetic loci associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease overlap with loci for lung function and pulmonary fibrosis. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oelsner, E.C.; Carr, J.J.; Enright, P.L.; Hoffman, E.A.; Folsom, A.R.; Kawut, S.M.; Kronmal, R.A.; Lederer, D.J.; Lima, J.A.; Lovasi, G.S.; et al. Per cent emphysema is associated with respiratory and lung cancer mortality in the general population: A cohort study. Thorax 2016, 71, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Chao, M.; Lo, Y.C. Automatic skin lesion segmentation using deep fully convolutional networks with jaccard distance. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 1876–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, M.; Gambardella, L.M. Ant colony system: A cooperative learning approach to the traveling salesman problem. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 1997, 1, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviles-Rivero, A.I.; Papadakis, N.; Li, R.; Sellars, P. GraphX-NET Chest X-ray Classification Under Extreme Minimal Supervision. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 504–512. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; Prosky, J.; Poblenz, E.; Covington, B.; Lyman, K. Weakly supervised medical diagnosis and localization from multiple resolutions. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.07703. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, G.; Bie, R.; Kos, A. CXNet-m2: A Deep Model with Visual and Clinical Contexts for Image-Based Detection of Multiple Lesions. In International Conference on Wireless Algorithms, Systems, and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 407–418. [Google Scholar]
- Vinyals, O.; Toshev, A.; Bengio, S.; Erhan, D. Show and tell: A neural image caption generator. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3156–3164. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, C.X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, H. AUC: A statistically consistent and more discriminating measure than accuracy. Ijcai 2003, 3, 519–524. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).