Quasi-Equilibrium and Unsteady Mass Transfer of Low-Grade Bloedite in the Process of Static Water Dissolution
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
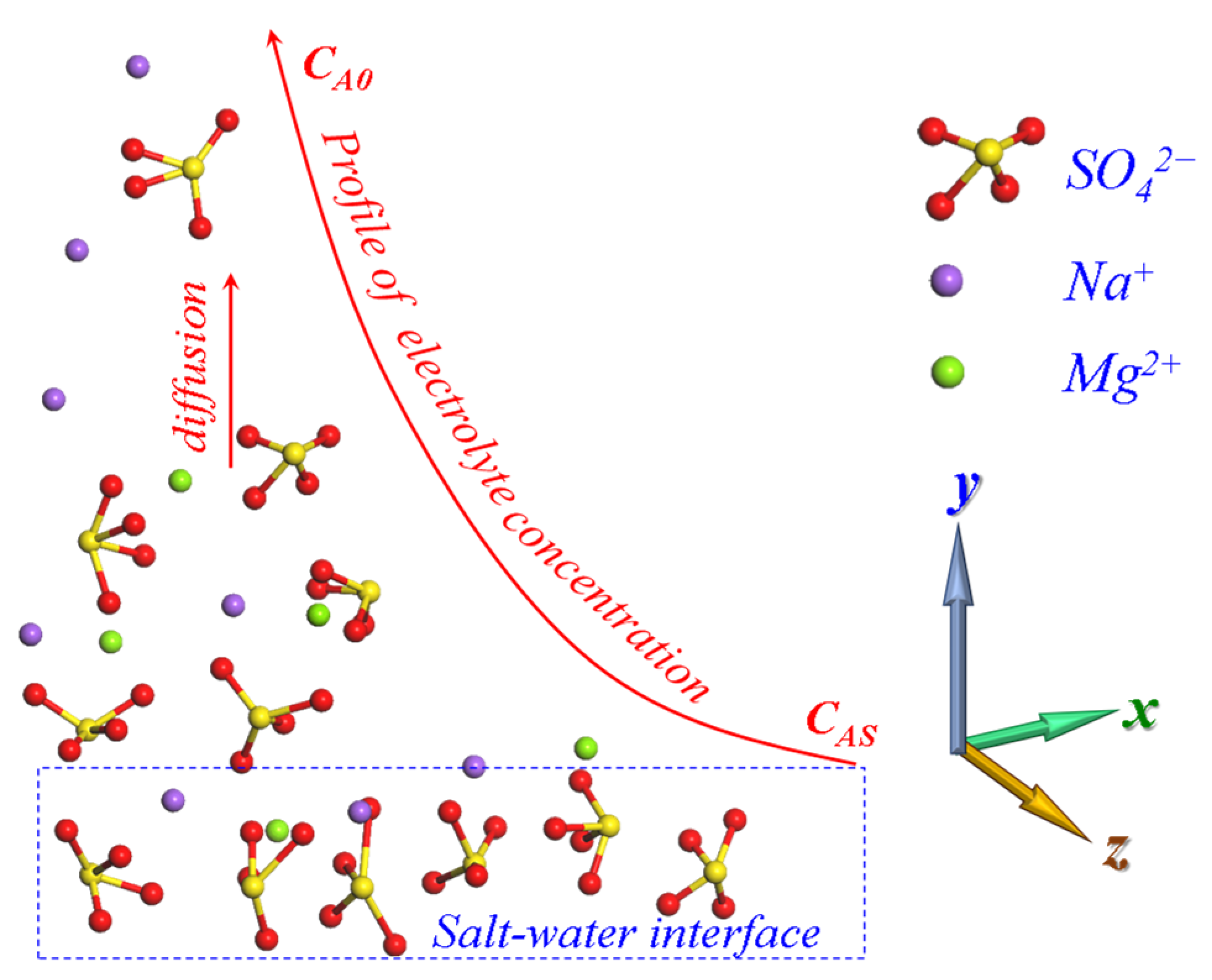
3. Dynamics Model of Unsteady Mass Transfer
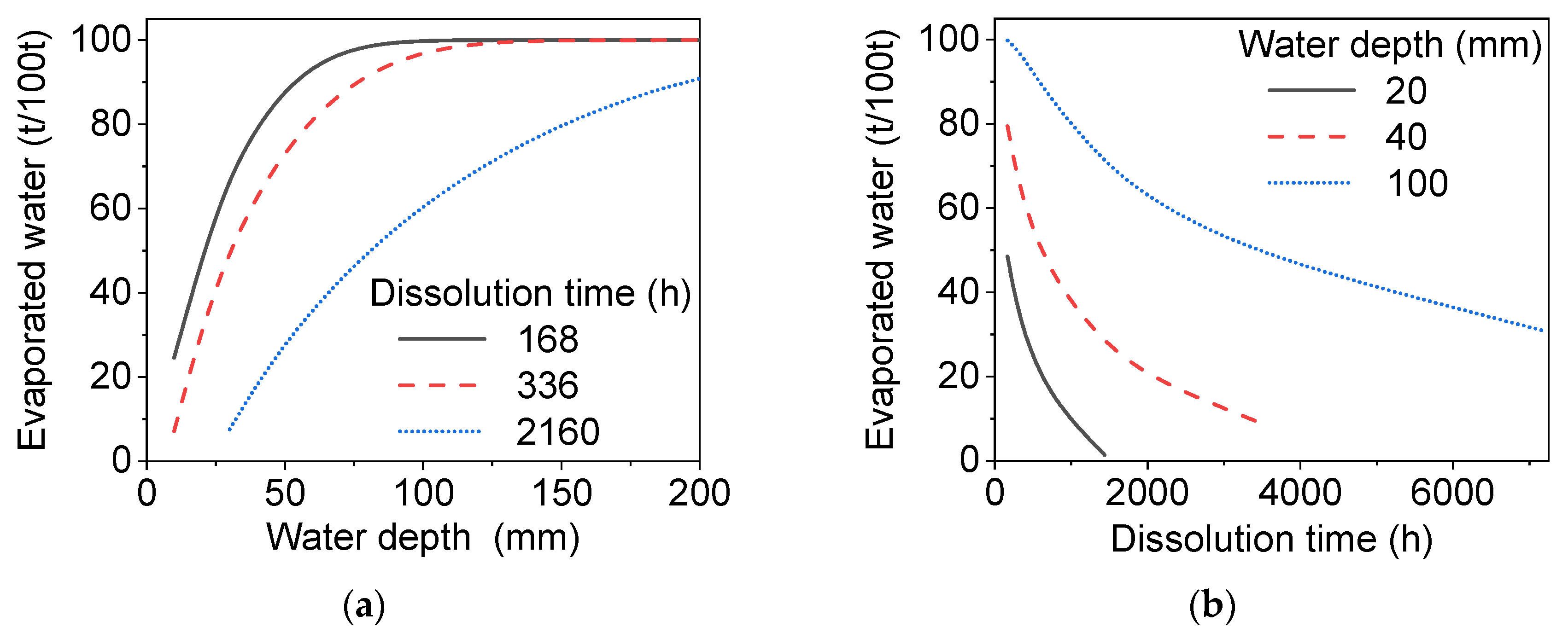
4. Results and Discussion
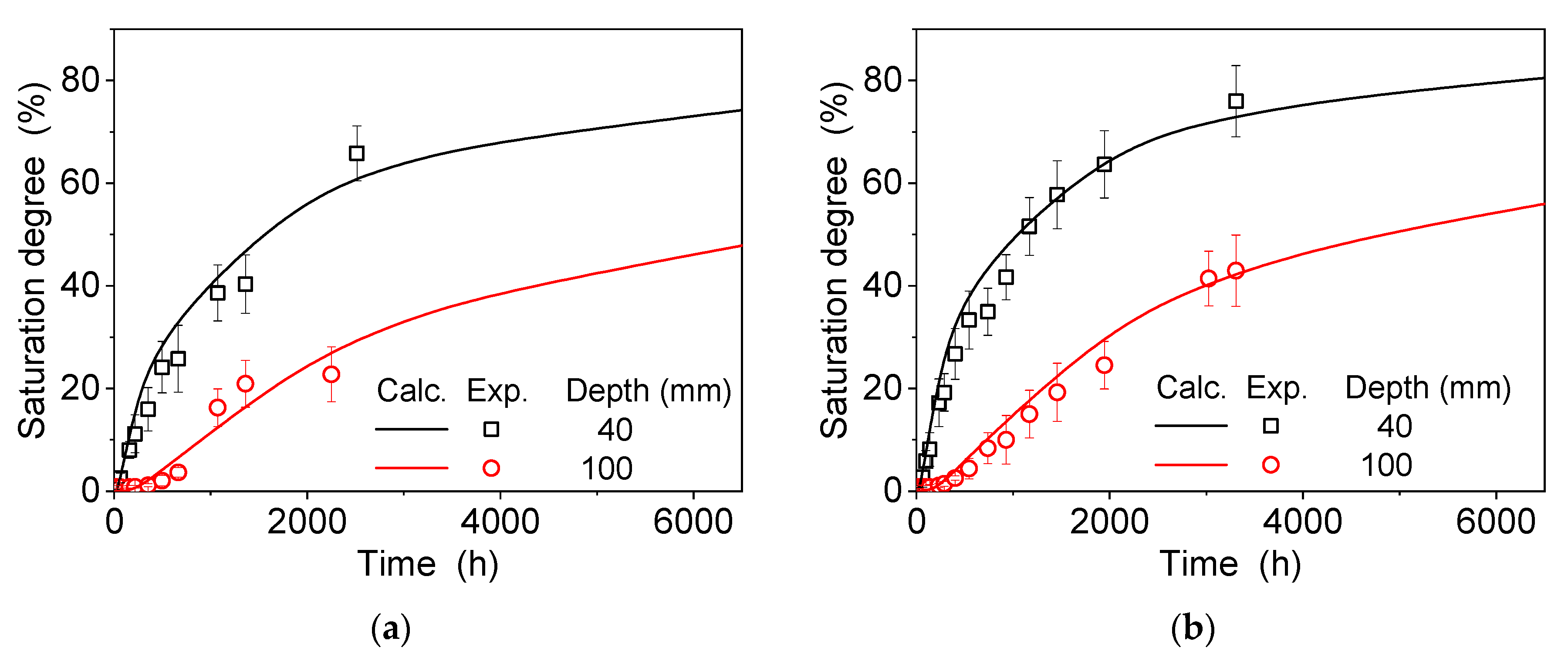
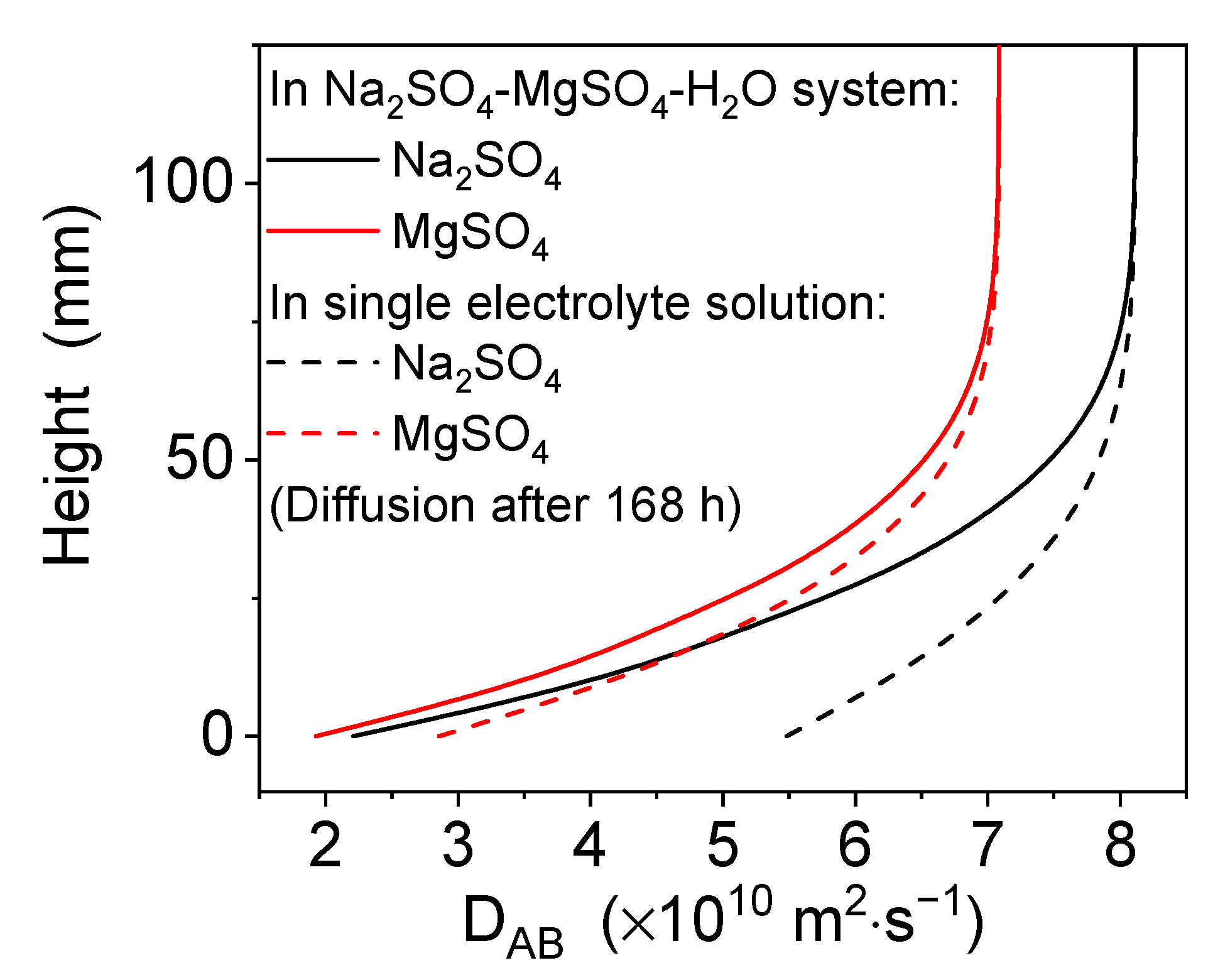
4.1. Dissolution and Diffusion Processes of a Single Electrolyte
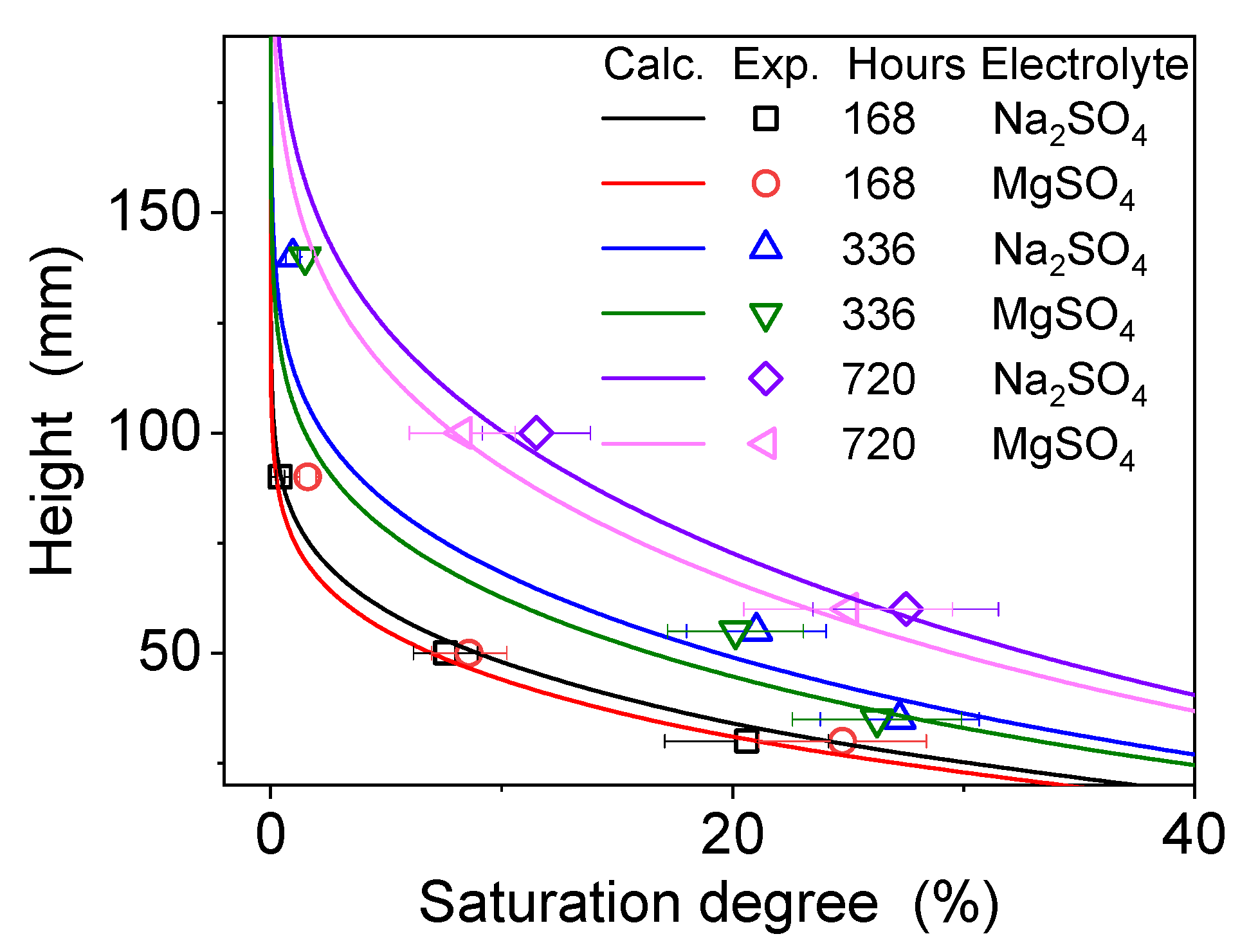
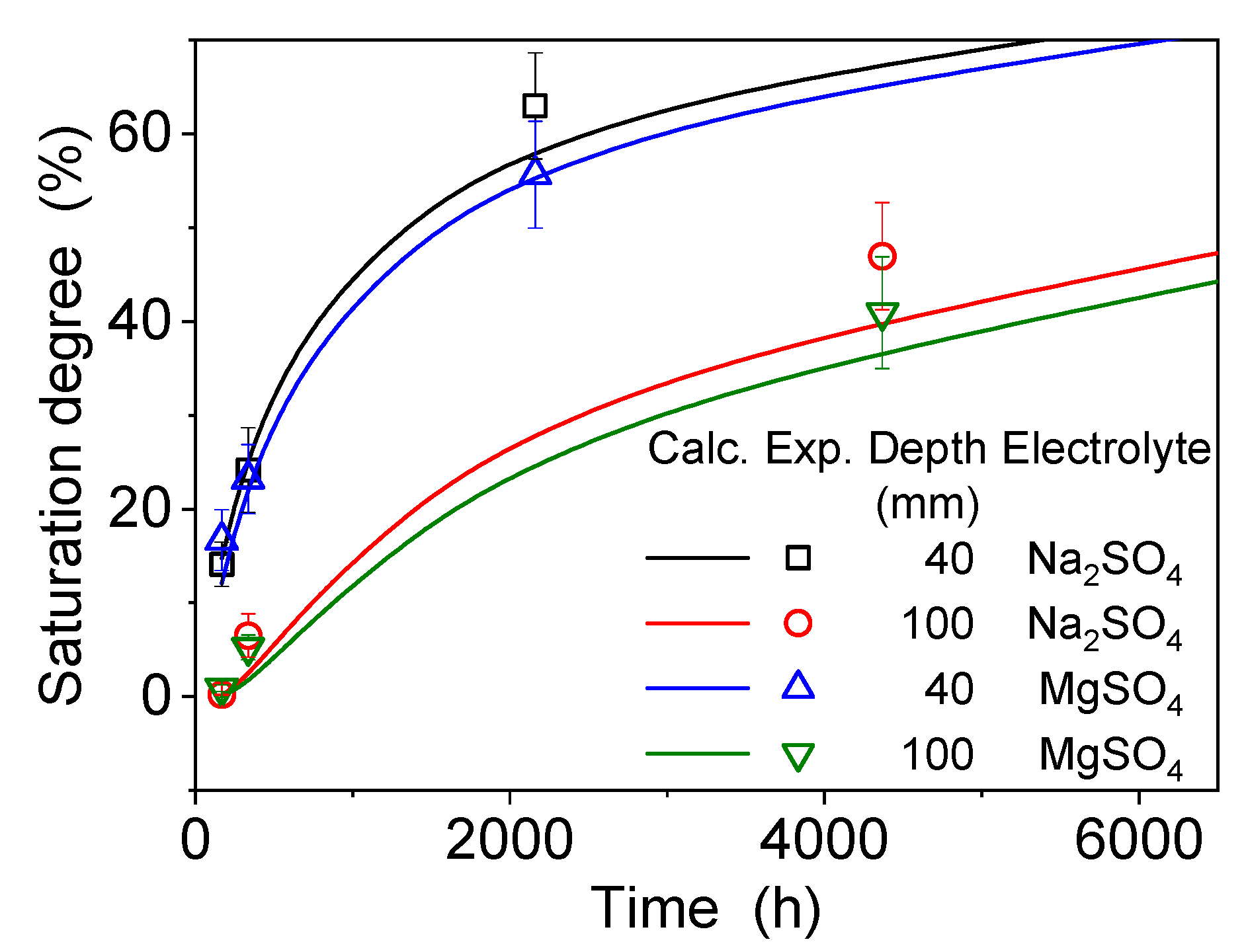
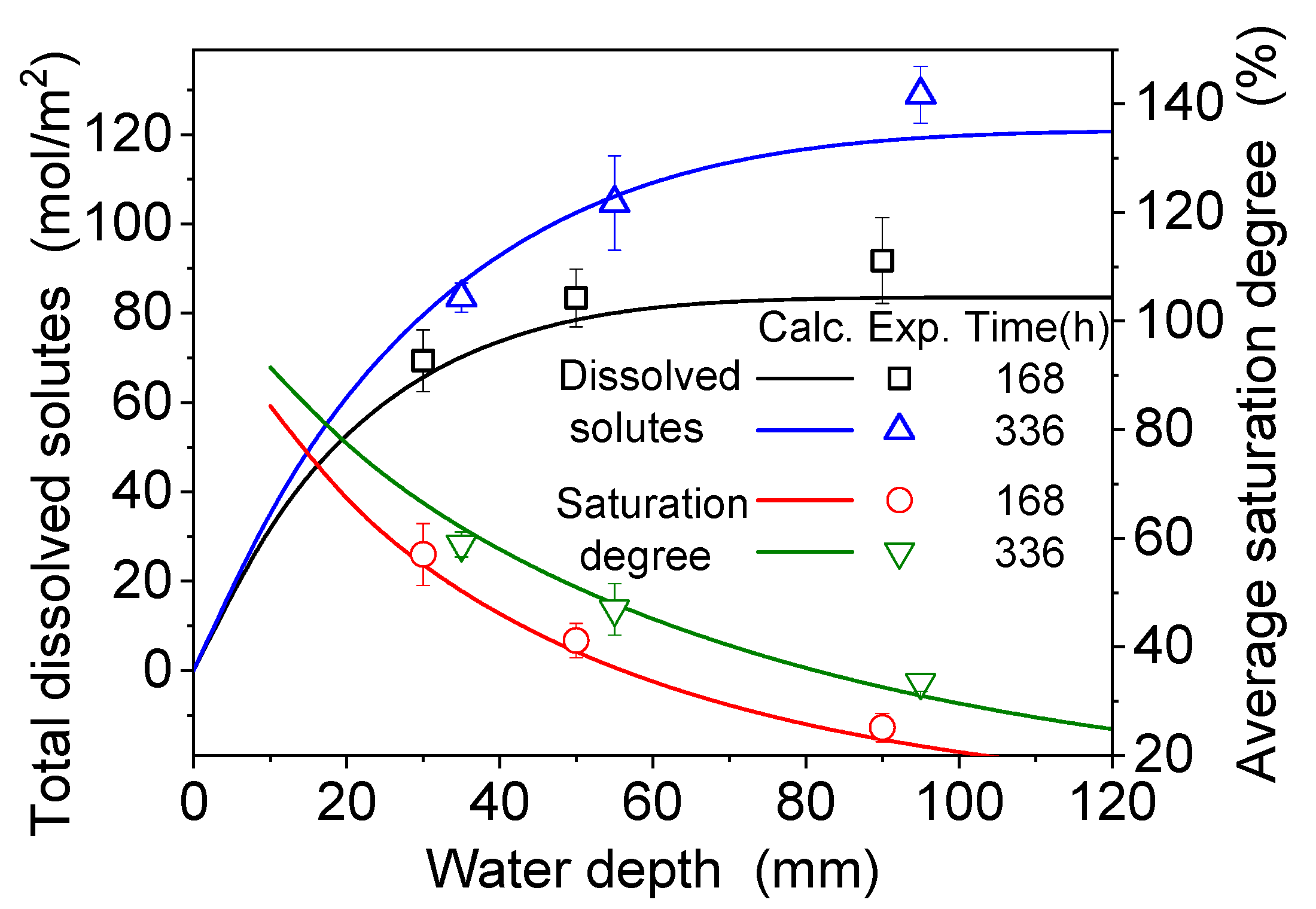
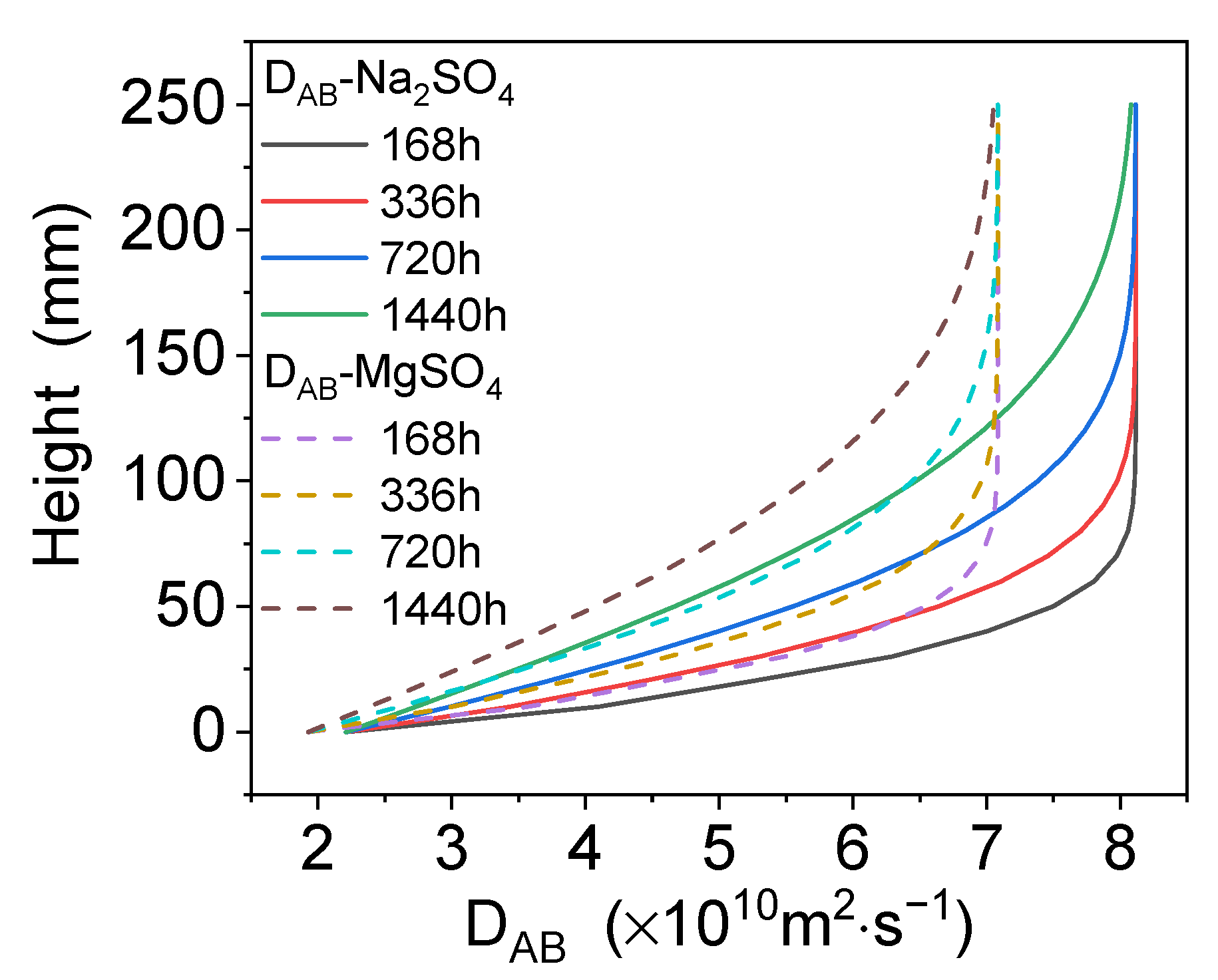
4.2. Dissolution and Diffusion Processes of Bloedite
4.3. Distribution of Local Mass Transfer Coefficients in a Mixed Electrolyte System
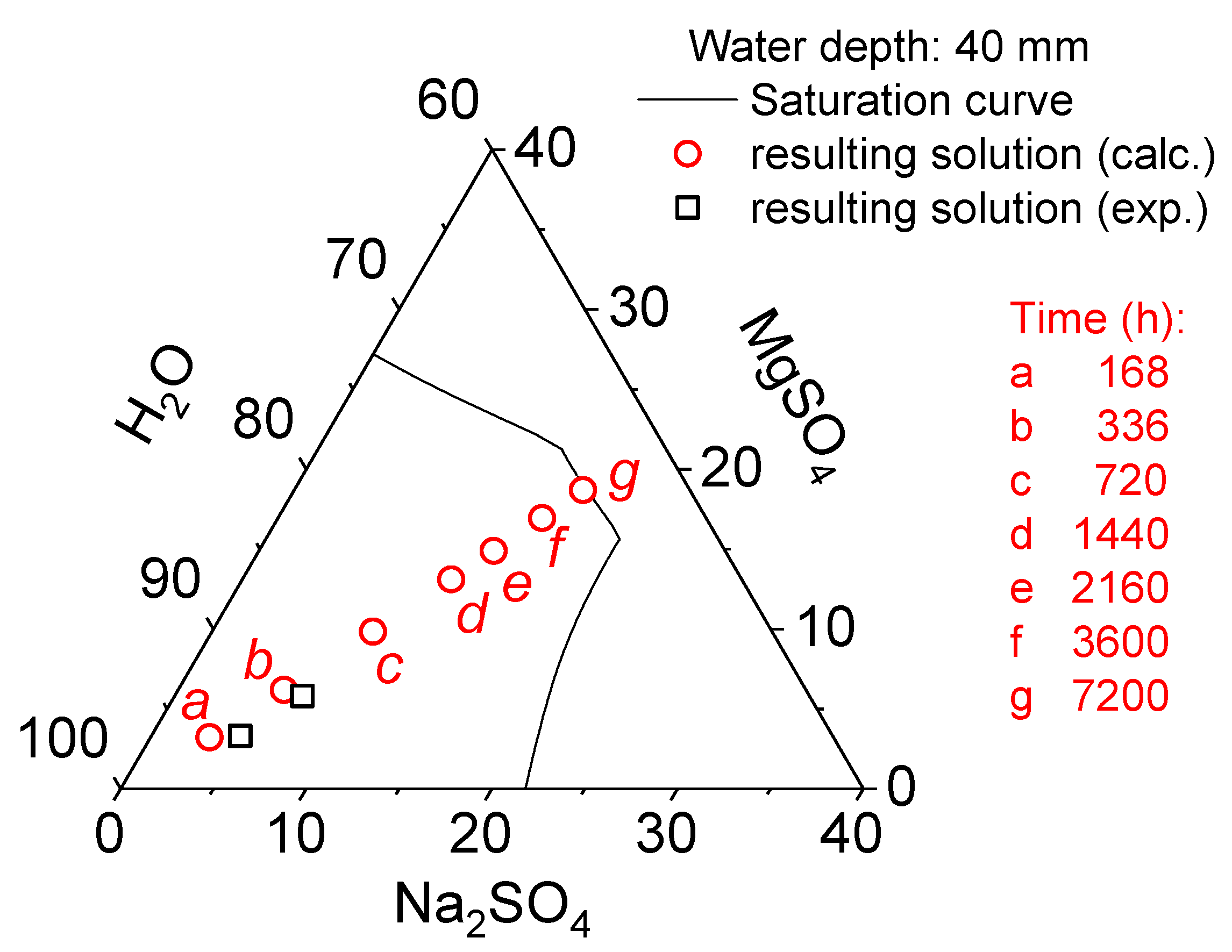
4.4. Phase Diagram Analysis and Process Optimization Strategy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sonmez, I.; Celik, M. Recent bloedite from Ishakli Lake, Cankiri-Corum Basin, Turkey: A mineralogical and hydrogeochemical investigation. Carbonates Evaporites 2017, 32, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Létolle, R.; Aladin, N.; Filipov, I.; Boroffka, N.G.O. The Future Chemical Evolution of the Aral Sea from 2000 to the Years 2050. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2005, 10, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.H.; Fang, X.M.; Galy, A.; Wang, H.L.; Song, X.S.; Wang, X.X. Hydrated sulfate minerals (bloedite and polyhalite): Formation and paleoenvironmental implications. Carbonates Evaporites 2020, 35, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comodi, P.; Nazzareni, S.; Balić-Žunić, T.; Zucchini, A.; Hanfland, M. The high-pressure behavior of bloedite: A synchrotron single-crystal X-ray diffraction study. Am. Mineral. 2014, 99, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynaud, M.; Rousse, G.; Abakumov, A.M.; Sougrati, M.T.; Van Tendeloo, G.; Chotard, J.N.; Tarascon, J.M. Design of new electrode materials for Li-ion and Na-ion batteries from the bloedite mineral Na2Mg(SO4)2·4H2O. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 2671–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.F.; Liu, J.R. One-step hydrothermal preparation of magnesium hydroxide sulphate hydrate whiskers using raw ore of mirabilite associated with bloedite. Mater. Res. Innov. 2015, 19 (Suppl. 2), 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dima, R.; Zamfirescu, F.; Gjiu, C.L.; Dima, V. The modelling of the dissolution process of salt ore from Ocnele Mari deposit. Rev. Chim. Buchar. 2004, 55, 609–613. [Google Scholar]
- Chairawiwut, W.; McMartin, D.W.; Azam, S. Salts Removal from Synthetic Solution-Potash Brine by Non-Planted Constructed Wetlands. Water 2016, 8, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Wu, L.; Cheng, F. Kinetics of static immersed leaching of low-grade sea-type evaporites based on theoretical and experimental investigation of unsteady-state mass transfer. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo’allim, A.A.; Kamal, M.R.; Muhammed, H.H.; Soom, M.A.M.; Zawawi, M.A.M.; Wayayok, A.; Man, H.C. Assessment of Nutrient Leaching in Flooded Paddy Rice Field Experiment Using Hydrus-1D. Water 2018, 10, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriamihaja, S.; Padmanabhan, E.; Ben-Awuah, J.; Sokkalingam, R. Static dissolution-induced 3D pore network modification and its impact on critical pore attributes of carbonate rocks. Petrol. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xu, L.; Xian, X. Fractal-like kinetic characteristics of rock salt dissolution in water. Colloid. Surface A 2002, 201, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, G.; Guo, Z.C. Water leaching kinetics and recovery of potassium salt from sintering dust. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. 2013, 23, 3770–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tošić, M.B.; Nikolić, J.D.; Grujić, S.R.; Živanović, V.D.; Zildžović, S.N.; Matijašević, S.D.; Ždrale, S.V. Dissolution behavior of a polyphosphate glass into an aqueous solution under static leaching conditions. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2013, 362, 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Soliev, L. Phase equilibria in the Na,K,Mg,Ca‖SO4,Cl-H2O system at 50 °C in the astrakhanite crystallization region. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 58, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.F.; Cao, J.L.; Wang, J.J.; Dou, S.Y.; Wang, R. Phase diagrams of Na2SO4-MgSO4-(NH4)2SO4-H2O system at 25 °C and their application. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2014, 367, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.Y.; Cao, J.L.; Jin, H.Y.; Liu, X.W. Phase diagrams of Na2SO4–MgSO4–CO(NH2)2–H2O system at 25 °C and their application. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2012, 57, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogorodova, L.P.; Melchakova, L.V.; Gritsenko, Y.D.; Vigasina, M.F.; Kosova, D.A.; Ksenofontov, D.A. Thermal and Thermochemical Study of Blodite (Astrakhanite). Geochem. Int. 2020, 58, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Z.; Hu, Y.D.; Wu, L.Y.; Chen, X. A new model in correlating and calculating the solid-liquid equilibrium of salt-water systems. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 24, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.D.; Kang, Q.Y.; Zhang, J.B.; Zhang, H.L.; Yuan, J.J.; Sha, Z.L. Non-equilibrium State Salt-forming Phase Diagram: Utilization of Bittern Resource in High Efficiency. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 18, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Gang, H.; Ma, Y.; Yang, S.; Mu, B. Migration Behavior of Lithium during Brine Evaporation and KCl Production Plants in Qarhan Salt Lake. Minerals 2017, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, S.; Lin, T.H.; Hsu, J.P. Unsteady dissolution of particle of various shapes in a stagnant liquid. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 123, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rard, J.A.; Albright, J.G.; Miller, D.G. Diffusion Onsager Coefficients Lij for the NaCl + Na2SO4 + H2O System at 298.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2009, 54, 636–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufreche, J.F.; Duvail, M.; Siboulet, B.; Jardat, M.; Bernard, O. Modelling of mutual diffusion for associated electrolytes solution: ZnSO4 and MgSO4 aqueous solutions. Mol. Phys. 2014, 112, 1405–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, K.; John, M.; Heuss-Aßbichler, S.; Schaller, V. Influence of Salinity and Pb on the Precipitation of Zn in a Model System. Minerals 2018, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Dou, Z.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J. Leaching kinetics of rare earth elements and fluoride from mixed rare earth concentrate after roasting with calcium hydroxide and sodium hydroxide. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 173, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Ling, Z.; Han, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, Q. Distribution, Source Identification, and Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in the Sediment Core from the Estuarine Region of the Golmud River to the Qarhan Salt Lake, Qinghai, China. Minerals 2019, 9, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, W. Effect of Fly Ash as Cement Replacement on Chloride Diffusion, Chloride Binding Capacity, and Micro-Properties of Concrete in a Water Soaking Environment. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elakneswaran, Y.; Owaki, E.; Nawa, T. Modelling Long-Term Durability Performance of Cementitious Materials under Sodium Sulphate Interaction. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Cao, Q.; Guan, Y.; Cheng, H.; Wang, X.; Miller, J.D. FTIR analysis of water structure and its influence on the flotation of arcanite (K2SO4) and epsomite (MgSO4·7H2O). Int. J. Miner. Process. 2013, 122, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, A.; Rahbar-Kelishami, A. MD simulation and evaluation of the self-diffusion coefficients in aqueous NaCl solutions at different temperatures and concentrations. J. Mol. Liq. 2013, 187, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, H.; Wei, L.; Cheng, F. Quasi-Equilibrium and Unsteady Mass Transfer of Low-Grade Bloedite in the Process of Static Water Dissolution. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8813. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10248813
Cheng H, Wei L, Cheng F. Quasi-Equilibrium and Unsteady Mass Transfer of Low-Grade Bloedite in the Process of Static Water Dissolution. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(24):8813. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10248813
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Huaigang, Lina Wei, and Fangqin Cheng. 2020. "Quasi-Equilibrium and Unsteady Mass Transfer of Low-Grade Bloedite in the Process of Static Water Dissolution" Applied Sciences 10, no. 24: 8813. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10248813
APA StyleCheng, H., Wei, L., & Cheng, F. (2020). Quasi-Equilibrium and Unsteady Mass Transfer of Low-Grade Bloedite in the Process of Static Water Dissolution. Applied Sciences, 10(24), 8813. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10248813




