Development of an NT-ProBNP Assay Reagent Based on High Specific Activity Alkaline Phosphatase CmAP and an Improved Coupling Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. CmAP Cloning, Expression and Purification
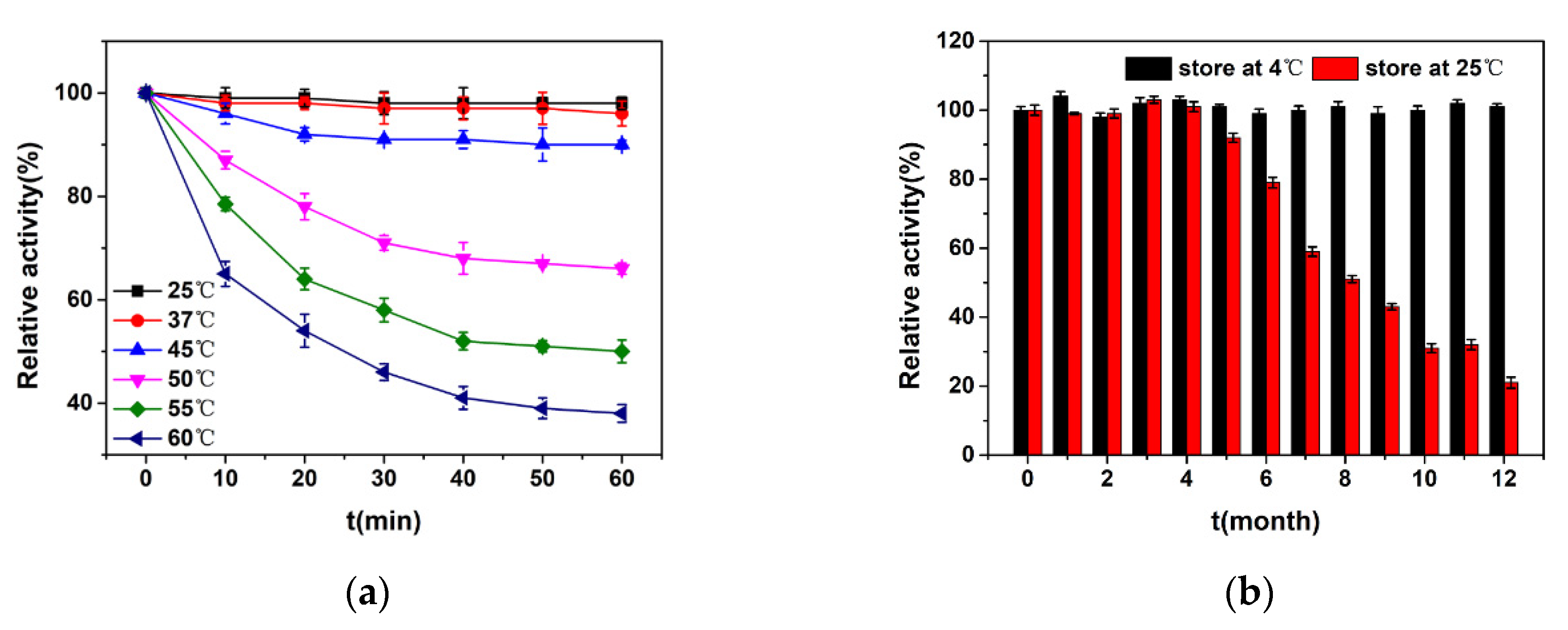
2.4. Enzyme Activity Characterisation
2.5. ALP Labelling of the NT-proBNP Detection Antibody
2.6. Immunomagnetic Particles Labelling of the NT-proBNP Capture Antibody
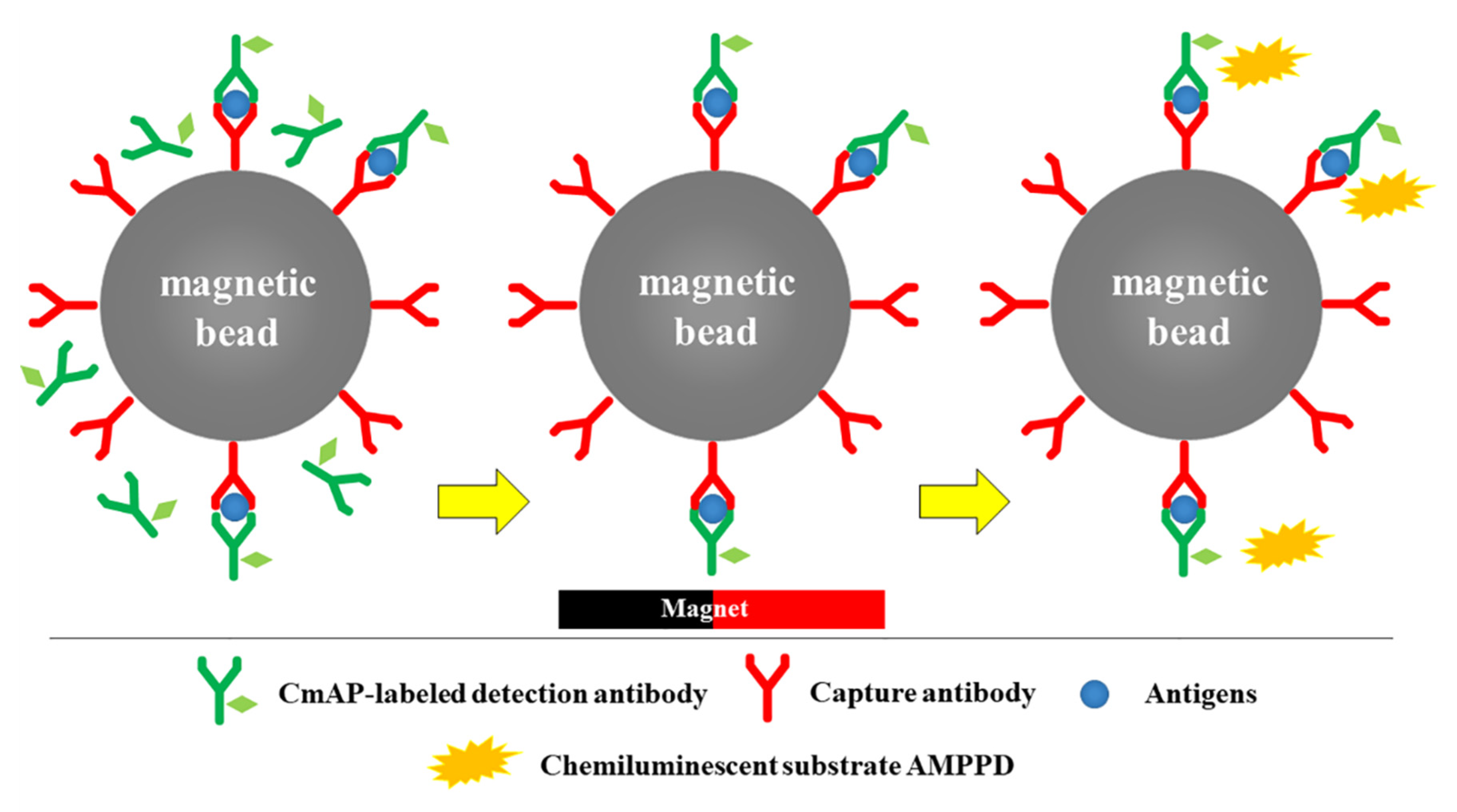
2.7. CLEIA Method
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Purified Recombinant CmAP
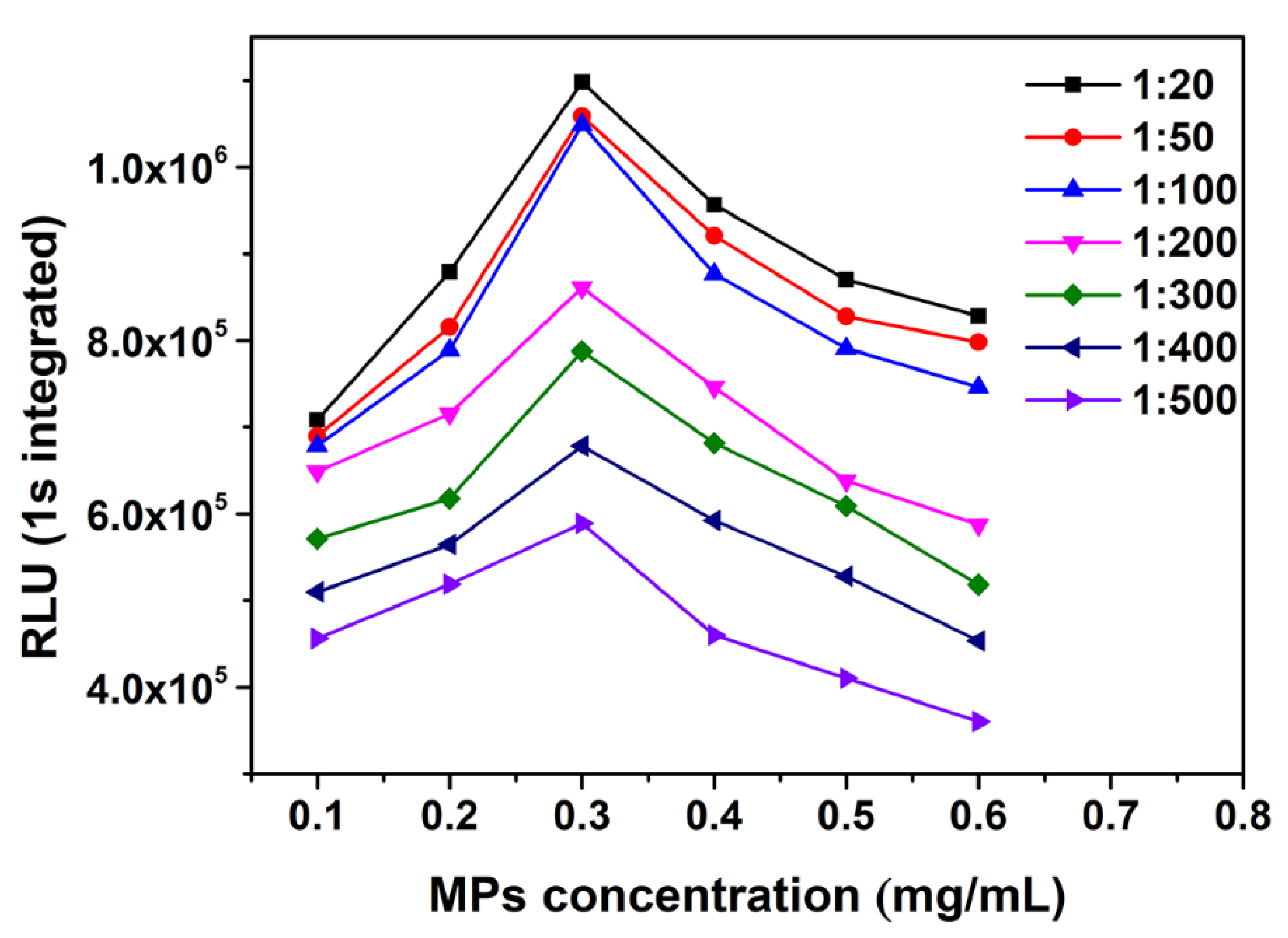
3.2. Influence of Immunoreagents
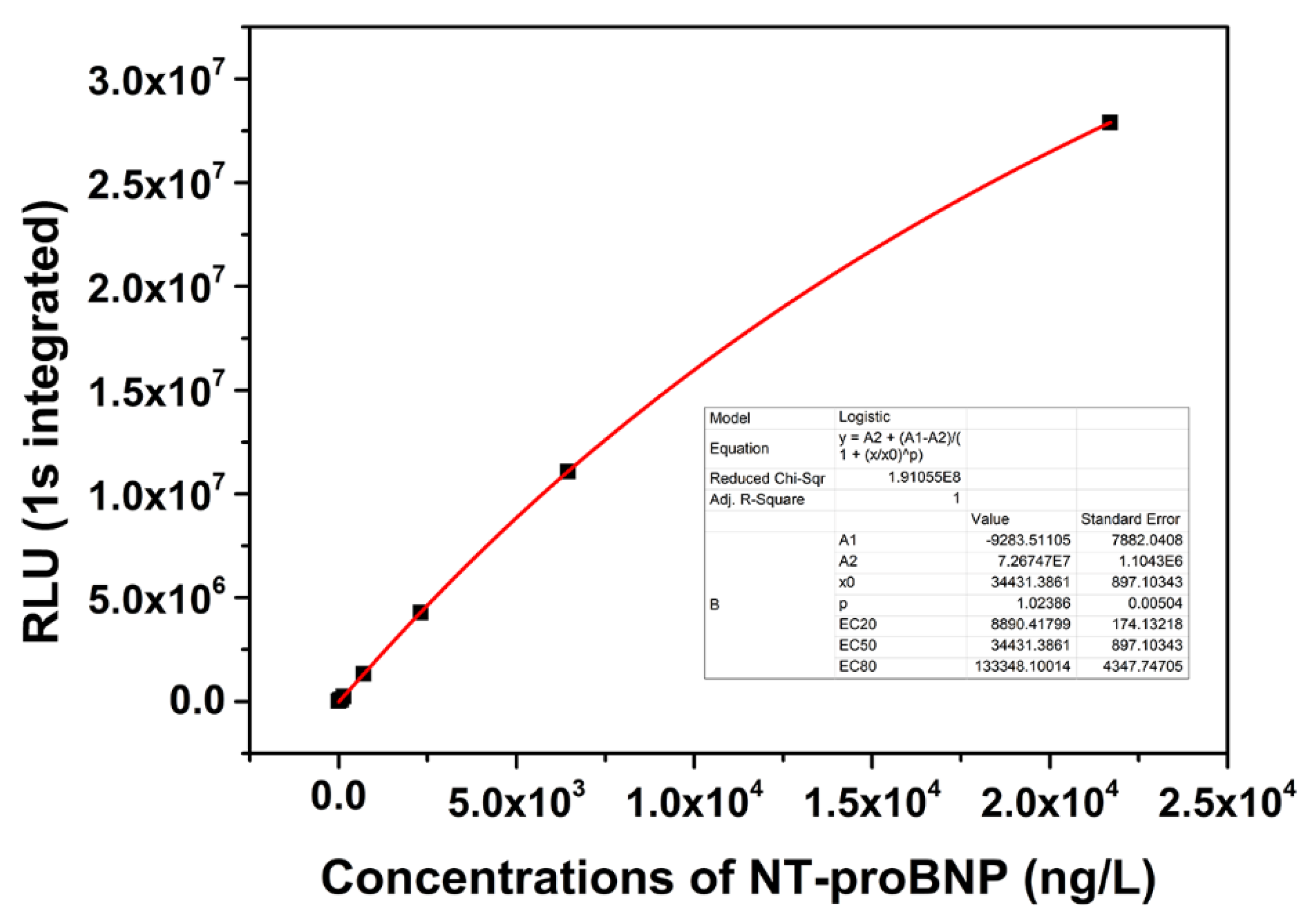
3.3. Standard Curve and Sensitivity
3.4. Recovery and Precision
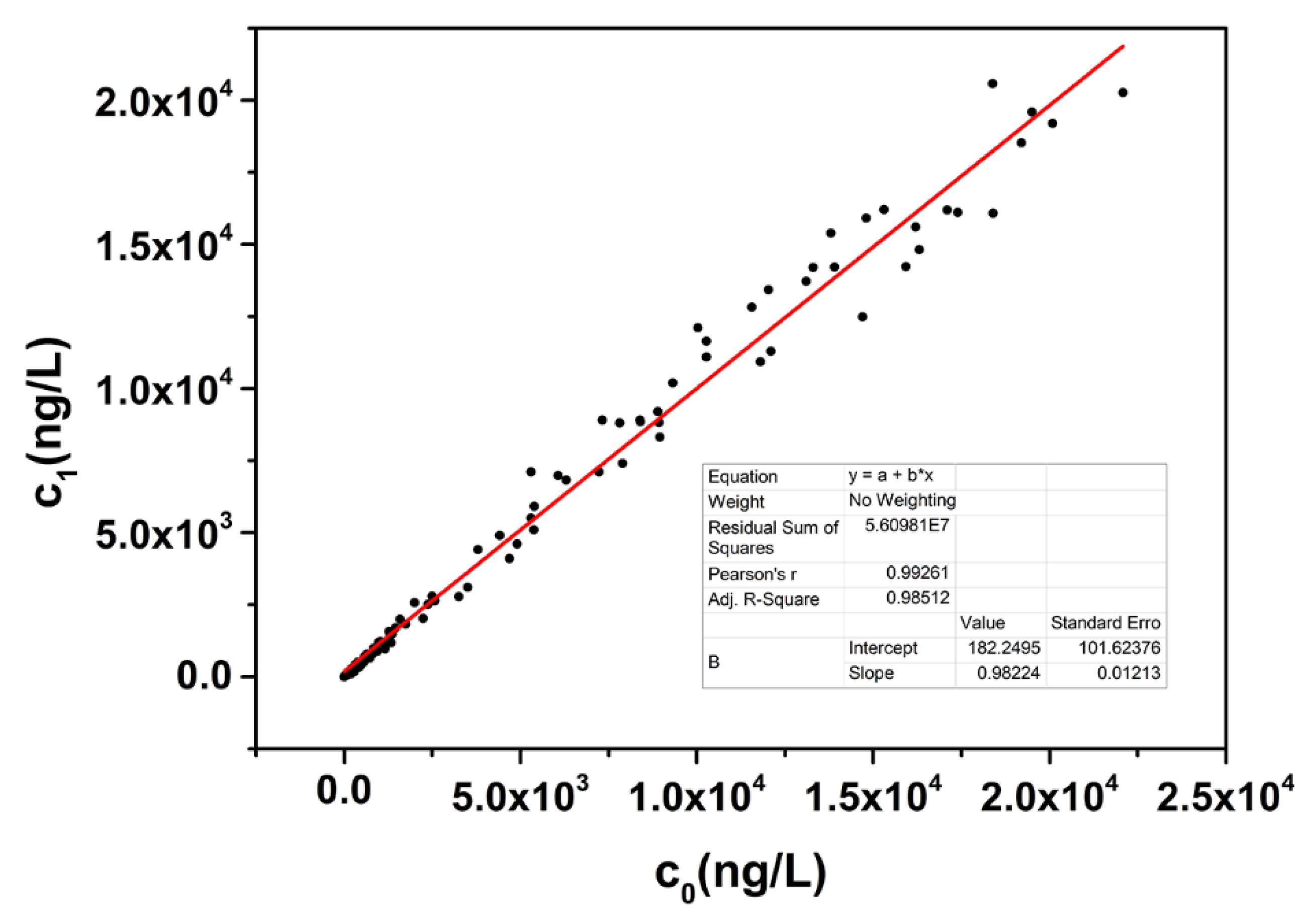
3.5. Linearity-Dilution Effect
3.6. Specificity and Interferences
3.7. Comparison with the Roche NT-proBNP Diagnostic System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, R.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Yue, Z.; Liu, G. Magnetic-particle-based, ultrasensitive chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for free prostate-specific antigen. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 801, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Lin, J.-M.; Wang, X.; Xin, T.-B.; Liang, S.-X.; Li, Z.-J.; Hu, G.-M. Magnetic particle-based chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for free thyroxine in human serum. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 50, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.-L.; Ren, H.-L.; Li, Y.-S.; Hu, P.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.-S.; Yan, D.-M.; Hui, Q.; Liu, D.; Lin, C.; et al. A magnetic particles-based chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for rapid detection of ovalbumin. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 459, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.; Liang, G. Alkaline Phosphatase-Triggered Simultaneous Hydrogelation and Chemiluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1041–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azam, G.; Shibata, T.; Kabashima, T.; El-Mahdy, A.F.M. Alkaline phosphatase-labeled macromolecular probe for sensitive chemiluminescence detection of proteins on a solid-phase membrane. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Wu, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Qu, L.; Harrington, P.D.B. A competitive chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for rapid and sensitive determination of enrofloxacin. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 93, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Yang, M.; Yu, D.; Yu, C. Pyrophosphate as substrate for alkaline phosphatase activity: A convenient flow-injection chemiluminescence assay. Lumin 2017, 32, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plisova, E.Y.; Balabanova, L.A.; Ivanova, E.P.; Kozhemyako, V.B.; Mikhailov, V.V.; Agafonova, E.V.; Rasskazov, V.A. A Highly Active Alkaline Phosphatase from the Marine Bacterium Cobetia. Mar. Biotechnol. 2005, 7, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasu, E.; Ichiyanagi, A.; Gomi, K. Cloning and expression of a highly active recombinant alkaline phosphatase from psychrotrophic Cobetia marina. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 34, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, H.-H.; Yeh, C.-W.; Hsu, C.F.; Hsu, L.; Chi, S. Multiscale Entropy Analysis with Low-Dimensional Exhaustive Search for Detecting Heart Failure. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, S.A.; Booth, R.A.; Santaguida, P.L.; Don-Wauchope, A.; Brown, J.A.; Oremus, M.; Ali, U.; Bustamam, A.; Sohel, N.; Mckelvie, R.; et al. Use of BNP and NT-proBNP for the diagnosis of heart failure in the emergency department: A systematic review of the evidence. Heart Fail. Rev. 2014, 19, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streng, K.W.; Ter Maaten, J.M.; Cleland, J.G.; O’Connor, C.M.; Davison, B.A.; Metra, M.; Givertz, M.M.; Teerlink, J.R.; Ponikowski, P.; Bloomfield, D.M.; et al. Associations of Body Mass Index with Laboratory and Biomarkers in Patients with Acute Heart Failure. Circ. Hear. Fail. 2017, 10, e003350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, T.; Gegenhuber, A.; Poelz, W.; Haltmayer, M. Comparison of the Biomedica NT-proBNP Enzyme Immunoassay and the Roche NT-proBNP Chemiluminescence Immunoassay: Implications for the Prediction of Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Structural Heart Disease. Clin. Chem. 2003, 49, 976–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, T.; Gegenhuber, A.; Poelz, W.; Haltmayer, M. Diagnostic accuracy of B type natriuretic peptide and amino terminal proBNP in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure. Heart 2005, 91, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogia, S.; Ho, J. Biomarkers: Heart Failure. Encycl. Cardiovasc. Res. Med. 2018, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnsworth, C.W.; Bailey, A.L.; Jaffe, A.S.; Scott, M.G. Diagnostic concordance between NT-proBNP and BNP for suspected heart failure. Clin. Biochem. 2018, 59, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, T.I.; Chen, H.H.; Kao, J.T. Comparison of Abbott AxSYM and Roche Elecsys 2010 for measurement of BNP and NT-proBNP. Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 369, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.; Gurbuz, Y.; Niazi, J.H. Biosensors for cardiac biomarkers detection: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 171–172, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Meng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xi, R. Chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay using magnetic nanoparticles for detection of neuron specific enolase in human serum. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 722, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.T.; Wang, H.J.; Xiong, C.Y.; Chai, Y.Q.; Yuan, R. An ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for NT-proBNP based on self-catalyzed luminescence emitter coupled with PdCu@carbon nanohorn hybrid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, M.; Bieniarz, C. Fc Site-Specific Labeling of Immunoglobulins with Calf Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase. Bioconjugate Chem. 1994, 5, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wan, X.; Lu, S.; Zhang, L.; Yu, S.; Lu, X. Evaluation of a magnetic particles-based chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for Golgi protein 73 in human serum. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 445, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lin, J.-M.; Ying, X. Evaluation of carbohydrate antigen 50 in human serum using magnetic particle-based chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 598, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Li, Z.-J.; Ying, X.-T.; Lin, J.-M. Development of high-performance magnetic chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for α-fetoprotein (AFP) in human serum. Clin. Chim. Acta 2008, 393, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Li, H.; Hu, G.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Lin, J.-M. Development of a rapid and sensitive magnetic chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay for detection of luteinizing hormone in human serum. Clin. Biochem. 2009, 42, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhao, G.; Li, X.; Miao, J.; Fang, J.; Wei, Q.; Cao, W. Electrochemiluminescence immunoassay for the N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide based on resonance energy transfer between a self-enhanced luminophore composed of silver nanocubes on gold nanoparticles and a metal-organic framework of type MIL-125. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Method | Total Activity (U) | Total Protein (mg) | Specific Activity (U/mg) | Yield (%) | Purification (fold) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude extract | 61,300 | 472 | 130 | 100 | 1 |
| High Q | 44,180 | 49 | 902 | 72 | 7 |
| Phenyl HP | 33,800 | 5.2 | 6500 | 55 | 50 |
| SephacrylTM S-300 | 31,520 | 2.4 | 13,133 | 51 | 101 |
| Antigens | Tested Concentration (ng/mL) | NT-proBNP Concentration Determined (ng/L) | CR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| cTn complex | 100 | NA | 0 |
| CK-MB | 100 | NA | 0 |
| Myoglobin | 500 | NA | 0 |
| BNP | 100 | 8.8 | 0.0088 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.-C.; He, X.; Qiao, S.-P.; Liu, Z.-N.; Gao, Y.-Z. Development of an NT-ProBNP Assay Reagent Based on High Specific Activity Alkaline Phosphatase CmAP and an Improved Coupling Method. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238682
Li H-C, He X, Qiao S-P, Liu Z-N, Gao Y-Z. Development of an NT-ProBNP Assay Reagent Based on High Specific Activity Alkaline Phosphatase CmAP and an Improved Coupling Method. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(23):8682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238682
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hai-Chao, Xin He, Shan-Peng Qiao, Zhen-Ni Liu, and Yu-Zhou Gao. 2020. "Development of an NT-ProBNP Assay Reagent Based on High Specific Activity Alkaline Phosphatase CmAP and an Improved Coupling Method" Applied Sciences 10, no. 23: 8682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238682
APA StyleLi, H.-C., He, X., Qiao, S.-P., Liu, Z.-N., & Gao, Y.-Z. (2020). Development of an NT-ProBNP Assay Reagent Based on High Specific Activity Alkaline Phosphatase CmAP and an Improved Coupling Method. Applied Sciences, 10(23), 8682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238682




