Fabrication and Characterization of Porous Core–Shell Graphene/SiO2 Nanocomposites for the Removal of Cationic Neutral Red Dye
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the SiO2/rGO Nanocomposites
2.3. Characterizations
2.4. Experimental Method
3. Results and Discussion
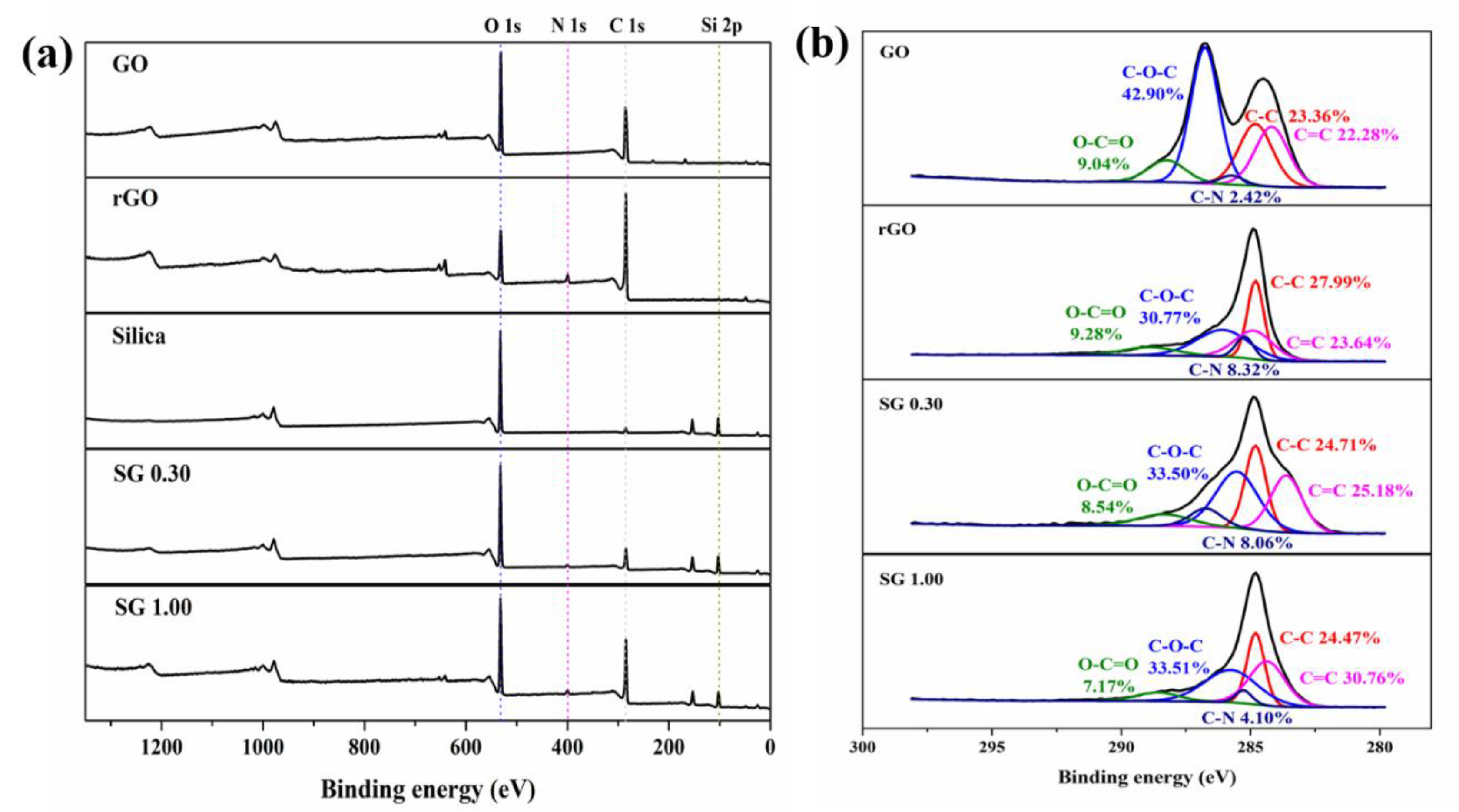
3.1. Characterizations of the Samples
3.2. Adsorption Equilibrium and Kinetics of SiO2 and the rGO/SiO2 Composites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Yang, Z. Industrial water pollution, water environment treatment, and health risks in China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Currell, M.J.; Cao, G. Deep challenges for China’s war on water pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Tu, L.-Y.; Liang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.-H.; Li, W. Coconut-based activated carbon fibers for efficient adsorption of various organic dyes. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 42280–42291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hameed, B.; Din, A.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption of methylene blue onto bamboo-based activated carbon: Kinetics and equilibrium studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alver, E.; Metin, A.Ü. Anionic dye removal from aqueous solutions using modified zeolite: Adsorption kinetics and isotherm studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 200-202, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesraoui-Ouki, S.; Cheeseman, C.R.; Perry, R. Natural zeolite utilisation in pollution control: A review of applications to metals’ effluents. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1994, 59, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ma, W.; Chen, C.; Zhao, J.; Shuai, Z. Efficient Degradation of Toxic Organic Pollutants with Ni2O3/TiO2-xBxunder Visible Irradiation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 4782–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, X.-L.; Xu, W.-H.; Huang, X.-J.; Liu, J.-H.; Xu, A.-W. Stable Organic–Inorganic Hybrid of Polyaniline/α-Zirconium Phosphate for Efficient Removal of Organic Pollutants in Water Environment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2686–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczęśniak, B.; Choma, J.; Jaroniec, M. Gas adsorption properties of graphene-based materials. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 243, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Du, Q.; Sun, J.; Jiao, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, K.; et al. Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution by graphene. Colloids Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2012, 90, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Li, J.; Ren, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, X. Few-Layered Graphene Oxide Nanosheets As Superior Sorbents for Heavy Metal Ion Pollution Management. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 10454–10462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Tao, Y. Removal of Formaldehyde from the Indoor Environment Using Porous Carbons and Silicas. Recent Innov. Chem. Eng. (Former. Recent Pat. Chem. Eng.) 2020, 13, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutter, P.W.; Flege, J.-I.; Sutter, E.A. Epitaxial graphene on ruthenium. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Bai, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, E.; Dai, H. Highly conducting graphene sheets and Langmuir–Blodgett films. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Annamalai, K.; Liu, L.; Tao, Y. Highly exposed nickel cobalt sulfide–rGO nanoporous structures: An advanced energy-storage electrode material. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 9991–9997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, K.; Liu, L.; Tao, Y. Highly Nanoporous Nickel Cobaltite Hexagonal Nanostructure-Graphene Composites for the Next Generation Energy Storage/Conversion Devices. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1700219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geim, A.K. Graphene: Status and Prospects. Science 2009, 324, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.H.; Jun, Y.-S.; Gerbec, J.A.; See, K.A.; Stucky, G.D.; Jung, H.-T. Sulfur infiltrated mesoporous graphene–silica composite as a polysulfide retaining cathode material for lithium–sulfur batteries. Carbon 2014, 69, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Wang, W.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, L.-J.; Wang, Y.-X.; Tang, J.; Wang, J.; Shen, W.; et al. Classification, Synthesis, and Application of Luminescent Silica Nanoparticles: A Review. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supit, S.W.M.; Shaikh, F.U.A. Durability properties of high volume fly ash concrete containing nano-silica. Mater. Struct. 2015, 48, 2431–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.L.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Tuning mesoporous silica dissolution in physiological environments: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 8761–8771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watcharotone, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Stankovich, S.; Piner, R.; Jung, I.; Dommett, G.H.B.; Evmenenko, G.; Wu, S.-E.; Chen, S.-F.; Liu, C.-P.; et al. Graphene−Silica Composite Thin Films as Transparent Conductors. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1888–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadipelli, S.; Guo, Z.X. Graphene-based materials: Synthesis and gas sorption, storage and separation. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 69, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, W.-L.; Guan, X.-T.; Fan, L.; Zhao, Y.-B.; Cao, W.-Q.; Wang, C.-Y.; Cao, M. Strong and thermostable polymeric graphene/silica textile for lightweight practical microwave absorption composites. Carbon 2016, 100, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varghese, S.S.; Lonkar, S.P.; Singh, K.; Swaminathan, S.; Abdala, A.A. Recent advances in graphene based gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2015, 218, 160–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Chen, B.; He, M.; Hu, B. Graphene oxide–silica composite coating hollow fiber solid phase microextraction online coupled with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry for the determination of trace heavy metals in environmental water samples. Talanta 2014, 123, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, M.; Wang, H.; Pei, Y.; Rao, H.; Du, X. Three-dimensional graphene aerogels–mesoporous silica frameworks for superior adsorption capability of phenols. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 153, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Liang, M.; Han, D.; Wang, Z. Multifunctional sandwich-like mesoporous silica–Fe3O4–graphene oxide nanocomposites for removal of methylene blue from water. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 39964–39972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Lu, W. Preparation of Silica/Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanosheet Composites for Removal of Organic Contaminants from Water. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 5734–5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcano, D.C.; Kosynkin, D.V.; Berlin, J.M.; Sinitskii, A.; Sun, Z.; Slesarev, A.; Alemany, L.B.; Lu, W.; Tour, J.M. Improved Synthesis of Graphene Oxide. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4806–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzati, R. Derivation of Pseudo-First-Order, Pseudo-Second-Order and Modified Pseudo-First-Order Rate Equations from Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms for adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 392, 123705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process. Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tan, S.J.; Horikawa, T.; Do, D.D.; Nicholson, D.; Liu, J. Water adsorption on carbon—A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 250, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersan, G.; Apul, O.G.; Perreault, F.; Karanfil, T. Adsorption of organic contaminants by graphene nanosheets: A review. Water Res. 2017, 126, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, C.; Yao, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J. Rapid adsorption of neutral red from aqueous solutions by Zn3[Co(CN)6]2.nH2O nanospheres. J. Mol. Liq. 2013, 184, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J. Study on the adsorption of Neutral Red from aqueous solution onto halloysite nanotubes. Water Res. 2010, 44, 1489–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iram, M.; Guo, C.; Guan, Y.; Ishfaq, A.; Liu, H. Adsorption and magnetic removal of neutral red dye from aqueous solution using Fe3O4 hollow nanospheres. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, N.; El-Khouly, S.; Ahmed, S.; El-Nabarawy, T.; Tao, Y. Superior adsorption of cationic dye on novel bentonite/carbon composites. Asia Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Ma, D.; Mao, G.Y.; Zhang, M.M.; Han, R.P. Adsorption of Neutral Red from Solution by Bio-Chars Produced from Pyrolysis of Wheat Straw. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 322, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Han, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; He, X.; Han, R. Equilibrium, kinetic and mechanism study for the adsorption of neutral red onto rice husk. Desalin. Water Treat. 2009, 12, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çoruh, S.; Geyikçi, F.; Elevli, S. Adsorption of Neutral Red Dye from an Aqueous Solution onto Natural Sepiolite Using Full Factorial Design. Clays Clay Miner. 2011, 59, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Fu, H.; Lu, Y.; Yin, H.; Yu, L.; Ma, L.; Han, J. Adsorption Optimization and Mechanism of Neutral Red Onto Magnetic Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4/SiO2 Nanocomposites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 8252–8262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Han, P.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, M. Kinetics and isotherms of Neutral Red adsorption on peanut husk. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelenin, R.M.; Kheder, S.; Farag, H.K.; El Nabarawy, T. Removal of Cationic Neutral Red Dye from Aqueous Solutions using Natural and Modified Rice Straw. Egypt. J. Chem. 2017, 60, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| 10 mg/L NR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 (g mg−1 min−1) | Qe(theo) (mg g−1) | Qe(exp) (mg g−1) | R2 | |
| SiO2 | 0.00183 | 3.08774 | 6.853 | 0.88963 |
| SG 0.05 | 0.06663 | 0.54623 | 2.564 | 0.88130 |
| SG 0.10 | 0.01538 | 0.94818 | 6.233 | 0.92896 |
| SG 0.20 | 0.04993 | 5.59599 | 11.415 | 0.96972 |
| SG 0.30 | 0.25666 | 23.32906 | 12.853 | 0.96010 |
| SG 0.50 | 0.04295 | 17.44791 | 12.754 | 0.99298 |
| SG 1.00 | 0.05905 | 11.42164 | 12.555 | 0.84625 |
| 25 mg/L NR | ||||
| SiO2 | 0.00093 | 6.74796 | 9.505 | 0.98911 |
| SG 0.30 | 0.03375 | 29.60994 | 36.030 | 0.98066 |
| 50 mg/L NR | ||||
| SiO2 | 0.00256 | 27.66644 | 49.263 | 0.84640 |
| SG 0.30 | 0.00761 | 49.14524 | 66.635 | 0.97839 |
| 10 mg/L NR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K2 (g mg−1 min−1) | Qe(theo) (mg g−1) | Qe(exp) (mg g−1) | R2 | |
| SiO2 | 0.00217 | 7.024 | 6.853 | 0.98982 |
| SG 0.05 | 0.37591 | 2.573 | 2.564 | 0.99989 |
| SG 0.10 | 0.10984 | 6.286 | 6.233 | 0.99993 |
| SG 0.20 | 0.01827 | 11.834 | 11.415 | 0.99985 |
| SG 0.30 | 0.03387 | 13.441 | 12.853 | 0.99829 |
| SG 0.50 | 0.00333 | 14.401 | 12.754 | 0.99255 |
| SG 1.00 | 0.00629 | 14.489 | 12.555 | 0.99234 |
| 25 mg/L NR | ||||
| SiO2 | 0.00015 | 11.051 | 9.505 | 0.92476 |
| SG 0.30 | 0.00151 | 39.541 | 36.030 | 0.99604 |
| 50 mg/L NR | ||||
| SiO2 | 0.00026 | 50.839 | 49.263 | 0.99934 |
| SG 0.30 | 0.00026 | 72.993 | 66.635 | 0.99945 |
| Adsorbent | Maximum Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Initial Concentration of NR (mg/L) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| rGO/SiO2 nanocomposites | 66.635 | 50 | This study |
| Zn3[Co(CN)6]2.nH2O nanospheres | 24.06 | 50 | [35] |
| Halloysite nanotubes | 24.96 | 50 | [36] |
| Fe3O4 hollow nanospheres | 29.5 | 50 | [37] |
| Bentonite/carbon composites | 46 | 50 | [38] |
| Biochar | 14.5 | 80 | [39] |
| Rice husk | 26.5 | 100 | [40] |
| Natural sepiolite | 36.32 | 100 | [41] |
| Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4/SiO2 Nanocomposites | 39.95 | 100 | [42] |
| Peanut husk | 35.1 | 150 | [43] |
| Urea-treated colloidal carbon | 52 | 200 | [44] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Chen, T.; Xu, B.; Chen, Y. Fabrication and Characterization of Porous Core–Shell Graphene/SiO2 Nanocomposites for the Removal of Cationic Neutral Red Dye. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8529. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238529
Wang J, Chen T, Xu B, Chen Y. Fabrication and Characterization of Porous Core–Shell Graphene/SiO2 Nanocomposites for the Removal of Cationic Neutral Red Dye. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(23):8529. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238529
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Junyi, Tianlu Chen, Biao Xu, and Yueqiu Chen. 2020. "Fabrication and Characterization of Porous Core–Shell Graphene/SiO2 Nanocomposites for the Removal of Cationic Neutral Red Dye" Applied Sciences 10, no. 23: 8529. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238529
APA StyleWang, J., Chen, T., Xu, B., & Chen, Y. (2020). Fabrication and Characterization of Porous Core–Shell Graphene/SiO2 Nanocomposites for the Removal of Cationic Neutral Red Dye. Applied Sciences, 10(23), 8529. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238529





