Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System Predictor with an Incremental Tree Structure Based on a Context-Based Fuzzy Clustering Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
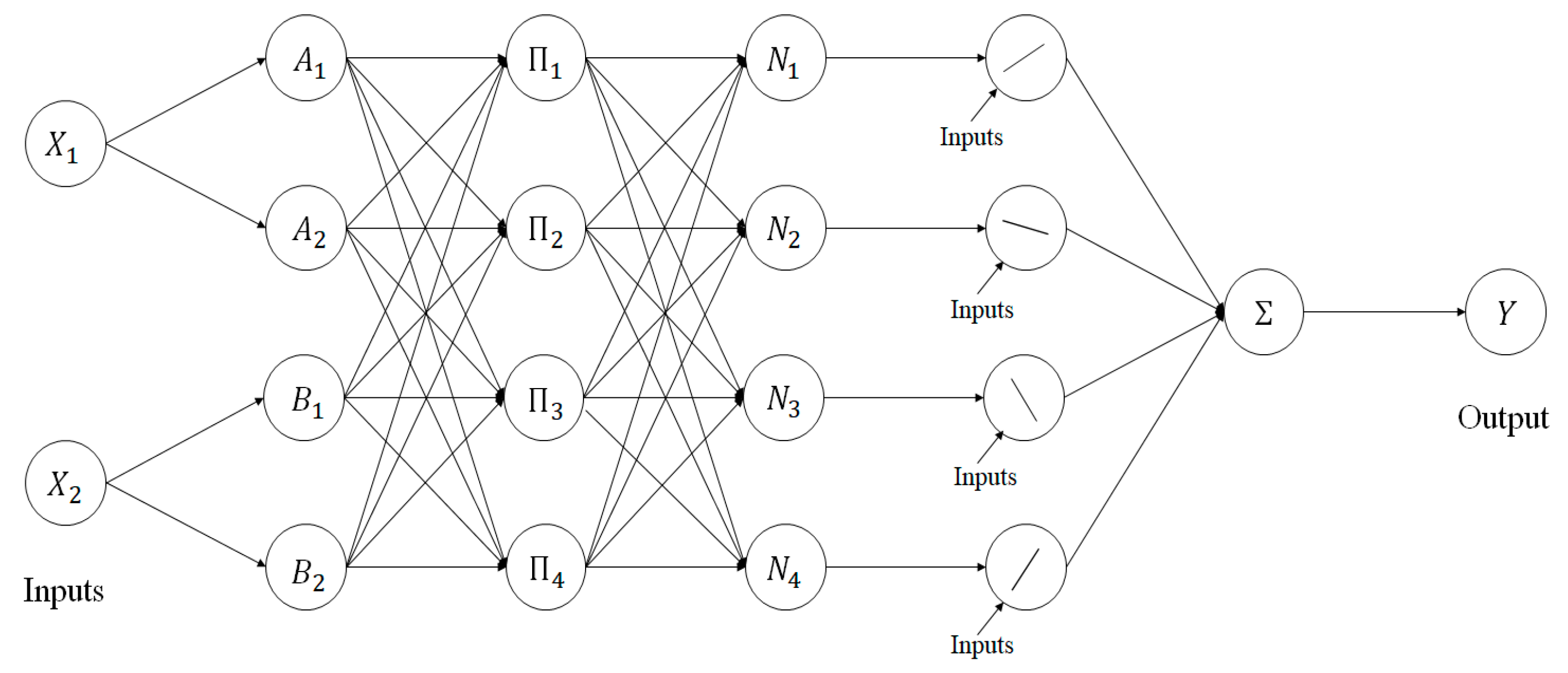
2. ANFIS
2.1. Rule Creation Method
2.2. Structure
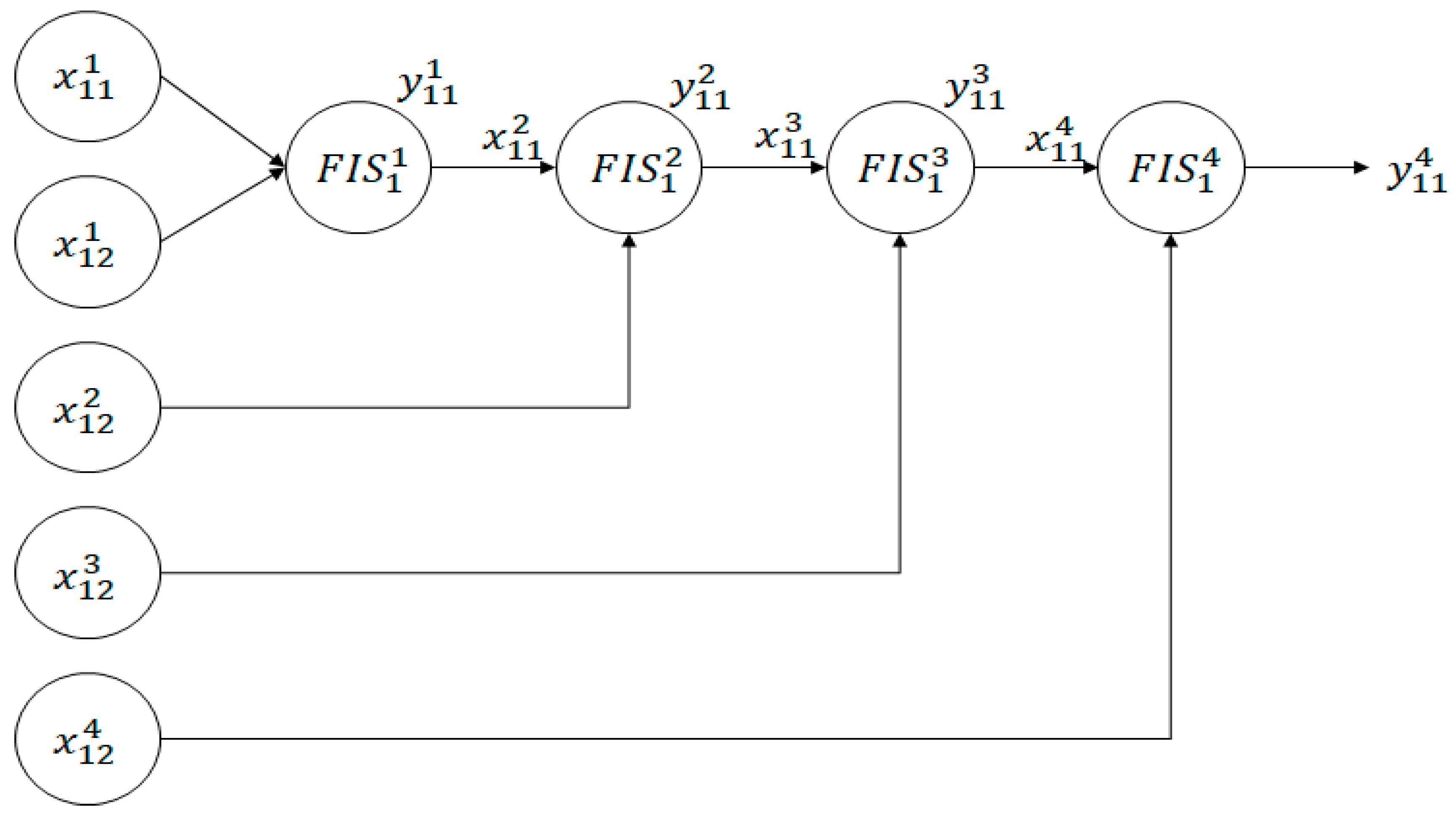
3. ANFIS with an Incremental Tree Structure Based on the CFCM Clustering Method
3.1. CFCM-Clustering-Based Rule Creation Method
3.2. ANFIS with an Incremental Tree Structure
4. Experiment and Analysis
4.1. Building Heating-and-Cooling Dataset
4.2. Experimental Method and Analysis of Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, M.A.; Algarni, F. A healthcare monitoring system for the diagnosis of heart disease in the IoMT cloud environment using MSSO-ANFIS. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 122259–122269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Dong, M.; Wu, C. A new ANFIS for parameter prediction with numeric and categorical inputs. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2010, 7, 645–653. [Google Scholar]
- Son, Y.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.T. A video-quality control scheme using ANFIS architecture in a DASH environment. Korean Soc. Broad Eng. 2018, 23, 104–114. [Google Scholar]
- Kannadasan, K.; Edla, D.R.; Yadav, M.H.; Bablani, A. Intelligent-ANFIS model for predicting measurement of surface roughness and geometric tolerances in three-Axis CNC milling. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 7683–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penghui, L.; Ewees, A.A.; Beyaztas, B.H.; Qi, C.; Salih, S.Q.; Ansari, N.A.; Bhagat, S.K.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Singh, V.P. Metaheuristic optimization algorithms hybridized with artificial intelligence model for soil temperature prediction: Novel model. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 51884–51904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.H.; Bae, Y.C. A prediction of bid price using MLP and ANFIS. J. Korean Inst. Intell. Syst. 2020, 30, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasopoulos, C.T.; Beniakar, M.E.; Kladas, A.G. Multicriteria PM motor design based on ANFIS evaluation of EV driving cycle efficiency. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2018, 4, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnony, I.M.E.; Barakat, S.I.; Mostafa, R.R. Optimized ANFIS model using hybrid metaheuristic algorithms for Parkinson’s disease prediction in IoT environment. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 119252–119270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshedizadeh, M.; Kordestani, M.; Carriveau, R.; Ting, D.S.K.; Saif, M. Power production prediction of wind turbines using a fusion of MLP and ANFIS networks. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2018, 12, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, A.; Nahavandi, S.; Creighon, D. Prediction interval construction and optimization for adaptive neurofuzzy inference systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2011, 19, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz, K.; Shen, S.L.; Sun, W.J.; Yin, Z.Y.; Zhou, A. Prediction model of shield performance during tunneling via incorporating improved particle swarm optimization into ANFIS. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 39659–39671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovzan, D.; Skrjanc, I. Fuzzy space partitioning based on hyperplanes defined by eigenvectors for takagi-sugeno fuzzy model identification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 5144–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiello, C.; Fanelli, A.M.; Lucarelli, M.; Mencar, C. Interpretable fuzzy partitioning of classified data with variable granularity. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 74, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrisdis, A.; Chondrodima, E.; Sarimveis, H. Radial basis function network training using a nonsymmetric partition of the input space and particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2013, 24, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstraete, J. The spatial disaggregation problems: Simulating reasoning using a fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2016, 25, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Teng, C.L. An enhanced hierarchical clustering approach for mobile sensor networks using fuzzy inference systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 4, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.G.; Denoeux, T. BPEC: Belief-peaks evidential clustering. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 27, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Deng, Z.; Cui, C.; Zhang, T.; Choi, K.S.; Gu, S.; Wang, J. Concise fuzzy system modeling integrating soft subspace clustering and sparse learning. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 27, 2176–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sujil, A.; Kumar, R.; Bansal, R.C. FCM clustering-ANFIS-based PV and wind generation forecasting agent for energy management in a smart microgrid. J. Eng. 2019, 2019, 4852–4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neamatollani, P.; Naghibzadeh, M.; Abrishammi, S. Fuzzy-based clustering-task scheduling for lifetime enhancement in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 6831–6844. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Chung, F.L.; Ishibuchi, H.; Wang, S. Imbalanced TSK fuzzy classifier by cross-class bayesian fuzzy clustering and imbalance learning. IEEE Trans. Syst. ManCybern. Syst. 2017, 47, 2005–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, V.K.; Snasel, V.; Abraham, A. Multiobjective programming for type-2 hierarchical fuzzy inference trees. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 26, 915–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.Z. A fractional order general type-2 fuzzy PID controller design algorithm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 52151–52172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.X. A new look at type-2 fuzzy sets and type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2016, 25, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Sundaram, S.; Sundararajan, N. A self-regulated interval type-2 neuro-fuzzy inference system for handling nonstationarities in EEG signals for BCI. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2016, 24, 1565–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Subramanian, K.; Sundaram, S. An evolving interval type-2 neurofuzzy inference system and its metacognitive sequential learning algorithm. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2015, 23, 2080–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ying, H.; Zhang, C. Effects of increasing the footprints of uncertainty on analytical structure of the classes of interval type-2 mamdani and TS fuzzy controllers. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 27, 1881–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyoh, I.; John, R.; Maere, G.; Kayacan, E. Hybrid learning for interval type-2 intuitionistic fuzzy logic systems as applied to identification and prediction problems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 26, 2672–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumati, V.; Patvardhan, S. Interval type-2 mutual subsethod fuzzy neural inference system (IT2MSFuNIS). IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 26, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglarbegian, M.; Melek, W.W.; Mendel, J.M. On the stability of interval type-2 TSK fuzzy logic control systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. ManCybern. Part. B 2010, 40, 798–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia, G.R.; Hagras, H.; Pomares, H.; Ruiz, I.R. Toward a fuzzy logic system based on general forms of interval type-2 fuzzy sets. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 27, 2381–2395. [Google Scholar]
- UUCI Machine Learning Repository. Available online: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets (accessed on 27 November 2020).
- Sugeno, M.; Yasukawa, T. A fuzzy-logic based approach to qualitative modeling. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 1993, 1, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haykin, S. Neural Networks; Macmillan Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, J.S.R. ANFIS: Adaptive-network based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans. Syst. ManCybern. 1993, 23, 665–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.S.R.; Sun, C.T.; Mizutani, E. Neuro-Fuzzy and Soft Computing: A Computational Approach to Learning and Machine Intelligence; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bezdek, J.C. Pattern Recognition with Fuzzy Objective Function Algorithms; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1981; Available online: springer.com/gp/book/9781475704525 (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Bezdek, J.C. Fuzzy Mathematics in Pattern Classification. Ph.D. Thesis, Applied Math Center, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA, 1973. Available online: link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/3-540-27335-2_5 (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Siddique, N.; Adeli, H. Computational Intelligence: Synergies of Fuzzy Logic. Neural Networks and Evolutionary Computing; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pedrycz, W. Conditional fuzzy C-means. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 1996, 17, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: Archive.ics.uci.edi/ml/datasets/Energy+efficiency (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Tsanas, A.; Xifara, A. Accurate quantitative estimation of energy performance of residential buildings using statistical machine learning tools. Energy Build. 2012, 49, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Algorithm | Number of MFs | Number of Rules | Training RMSE | Testing RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid-ANFIS | 2 | 256 | 0.6728 | 2.2471 |
| 3 | - | - | - | |
| 4 | - | - | - | |
| 5 | - | - | - |
| Algorithm | Number of Clusters | Number of Rules | Training RMSE | Testing RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCM-ANFIS | 2 | 2 | 2.5042 | 2.6548 |
| 4 | 4 | 1.7882 | 2.3150 | |
| 6 | 6 | 1.7814 | 2.2088 | |
| 8 | 8 | 1.6466 | 2.1173 | |
| 10 | 10 | 1.6286 | 2.0671 | |
| 12 | 12 | 1.6702 | 2.1142 | |
| 14 | 14 | 1.0611 | 2.2425 | |
| 16 | 16 | 1.3782 | 3.2958 | |
| 18 | 18 | 1.4028 | 3.5073 | |
| 20 | 20 | 1.1791 | 7.1332 |
| Algorithm | Number of Contexts | Number of Clusters | Number of Rules | Training RMSE | Testing RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incremental-CFCM-ANFIS | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2.6915 | 3.1126 |
| 4 | 8 | 2.3334 | 2.7517 | ||
| 6 | 12 | 1.7173 | 2.0464 | ||
| 8 | 16 | 1.5364 | 1.8881 | ||
| 10 | 20 | 1.5260 | 1.8742 | ||
| 12 | 24 | 1.5238 | 1.8738 | ||
| 14 | 28 | 1.5241 | 1.8725 | ||
| 16 | 32 | 1.5343 | 1.9118 | ||
| 18 | 36 | 1.5240 | 1.8725 | ||
| 20 | 40 | 1.5240 | 1.8724 | ||
| 4 | 2 | 8 | 2.5414 | 2.9155 | |
| 4 | 16 | 1.5981 | 1.9542 | ||
| 6 | 24 | 1.5240 | 1.8730 | ||
| 8 | 32 | 1.5241 | 1.8729 | ||
| 10 | 40 | 1.5240 | 1.8726 | ||
| 12 | 48 | 1.5296 | 1.8764 | ||
| 14 | 56 | 1.5248 | 1.8724 | ||
| 16 | 64 | 1.5241 | 1.8719 | ||
| 18 | 72 | 1.5241 | 1.8717 | ||
| 20 | 80 | 1.5241 | 1.8716 | ||
| 6 | 2 | 12 | 1.8964 | 2.2700 | |
| 4 | 24 | 1.5186 | 1.8796 | ||
| 6 | 36 | 1.5232 | 1.8732 | ||
| 8 | 48 | 1.5253 | 1.8729 | ||
| 10 | 60 | 1.5241 | 1.8719 | ||
| 12 | 72 | 1.5241 | 1.8716 | ||
| 14 | 84 | 1.5242 | 1.8713 | ||
| 16 | 96 | 1.5242 | 1.8711 | ||
| 18 | 108 | 1.5242 | 1.8710 | ||
| 20 | 120 | 1.5242 | 1.8705 |
| Algorithm | Hyperparameters | Number of Rules | Training RMSE | Testing RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear regression (LR) | - | - | 3.3453 | 3.0352 |
| Radial basis function network (RBFN) | Learning rate (0.0001) | - | 26.9523 | 25.4493 |
| Grid-ANFIS | 2 MFs | 256 | 0.6728 | 2.2471 |
| FCM-ANFIS | 10 clusters | 10 | 1.6286 | 2.0671 |
| Incremental-CFCM-ANFIS | 6 contexts, 20 clusters | 120 | 1.5242 | 1.8705 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yeom, C.-U.; Kwak, K.-C. Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System Predictor with an Incremental Tree Structure Based on a Context-Based Fuzzy Clustering Approach. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8495. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238495
Yeom C-U, Kwak K-C. Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System Predictor with an Incremental Tree Structure Based on a Context-Based Fuzzy Clustering Approach. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(23):8495. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238495
Chicago/Turabian StyleYeom, Chan-Uk, and Keun-Chang Kwak. 2020. "Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System Predictor with an Incremental Tree Structure Based on a Context-Based Fuzzy Clustering Approach" Applied Sciences 10, no. 23: 8495. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238495
APA StyleYeom, C.-U., & Kwak, K.-C. (2020). Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System Predictor with an Incremental Tree Structure Based on a Context-Based Fuzzy Clustering Approach. Applied Sciences, 10(23), 8495. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10238495






