Study on the Influence of Sapphire Crystal Orientation on Its Chemical Mechanical Polishing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
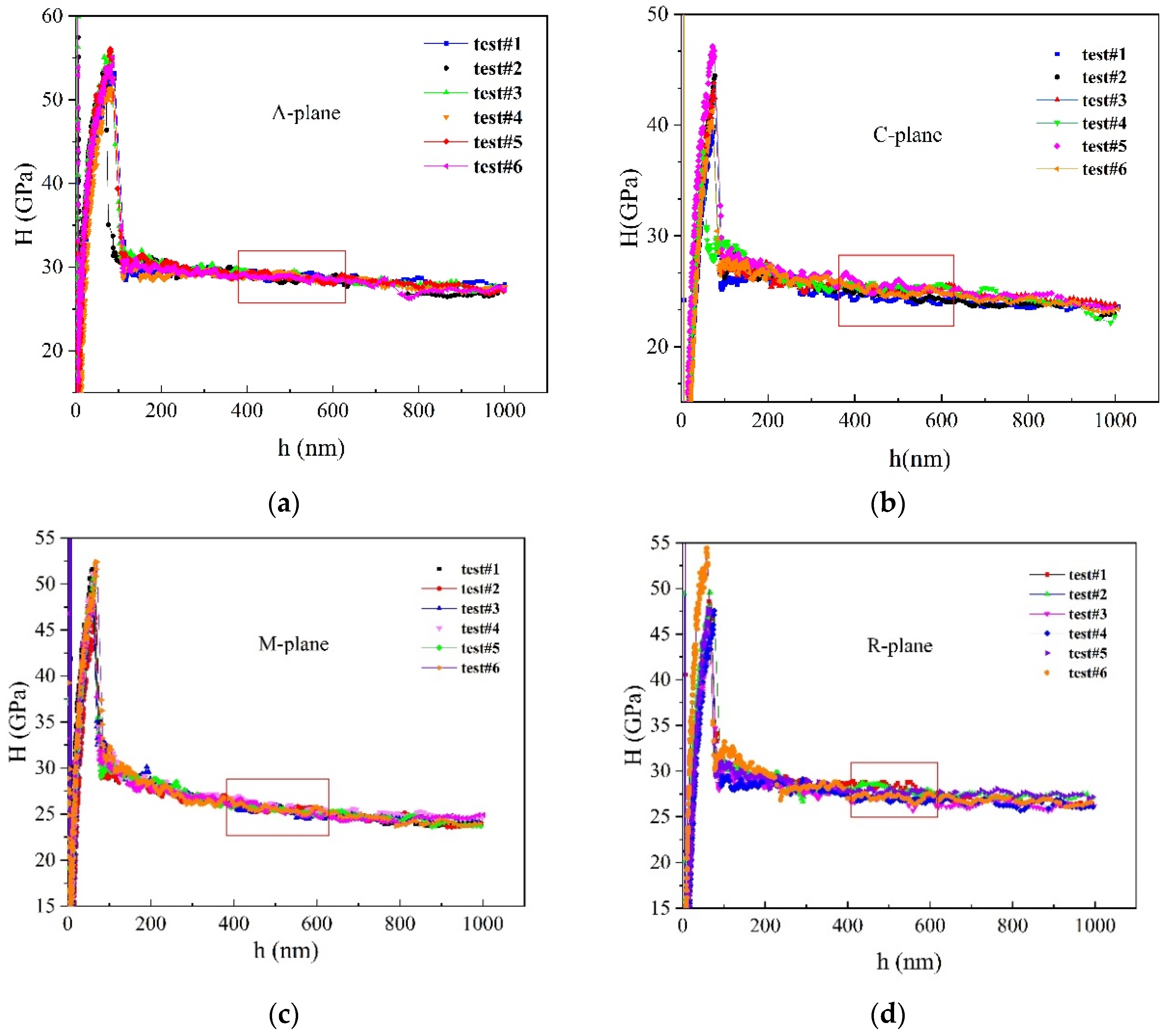
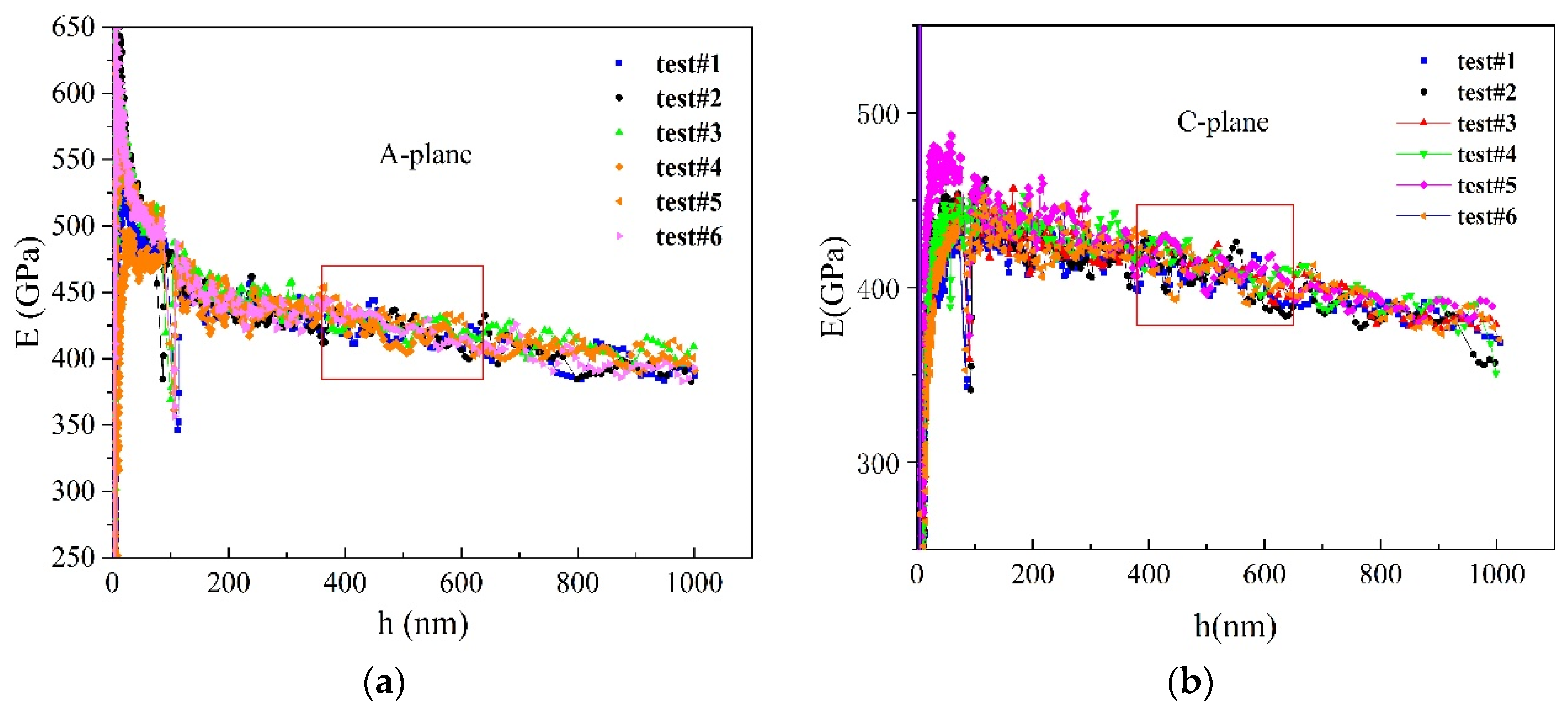
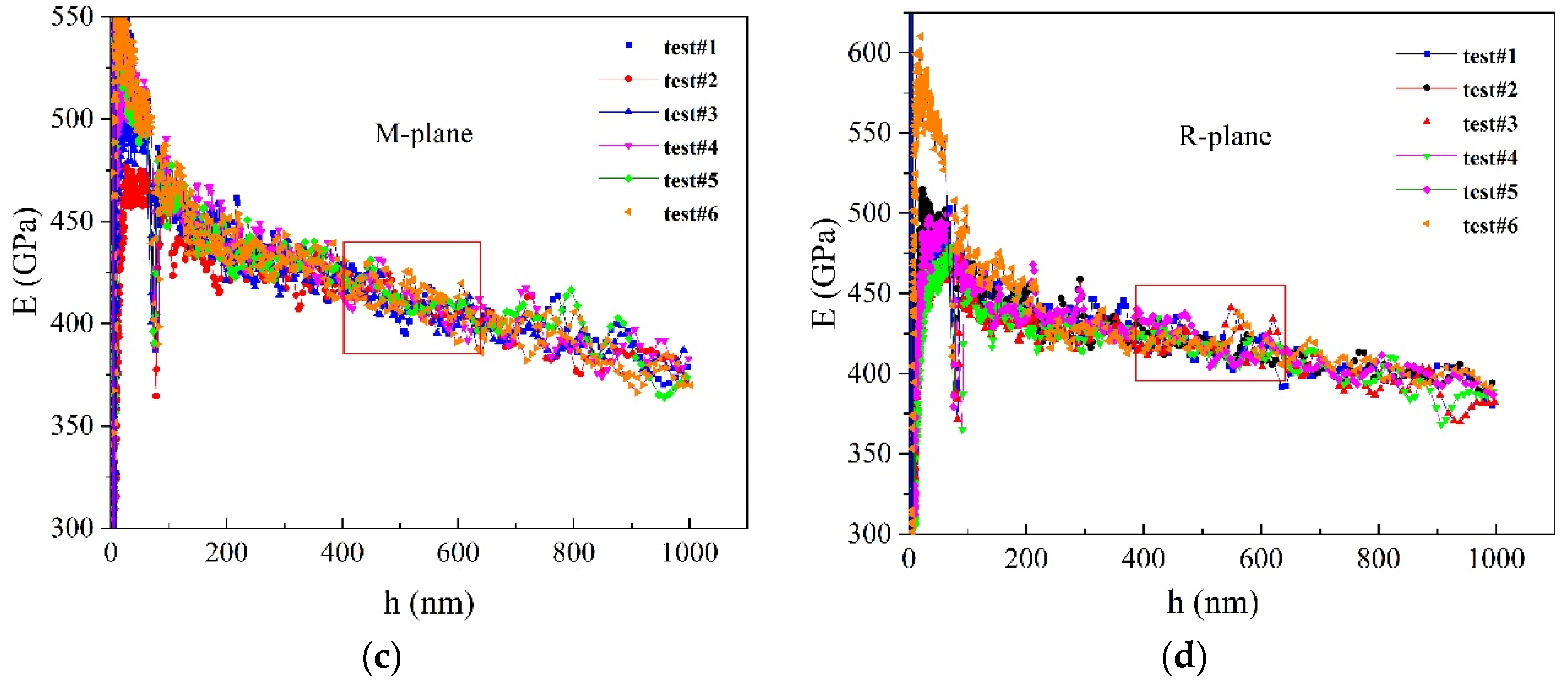
2.1. Nanoindentation Experiment
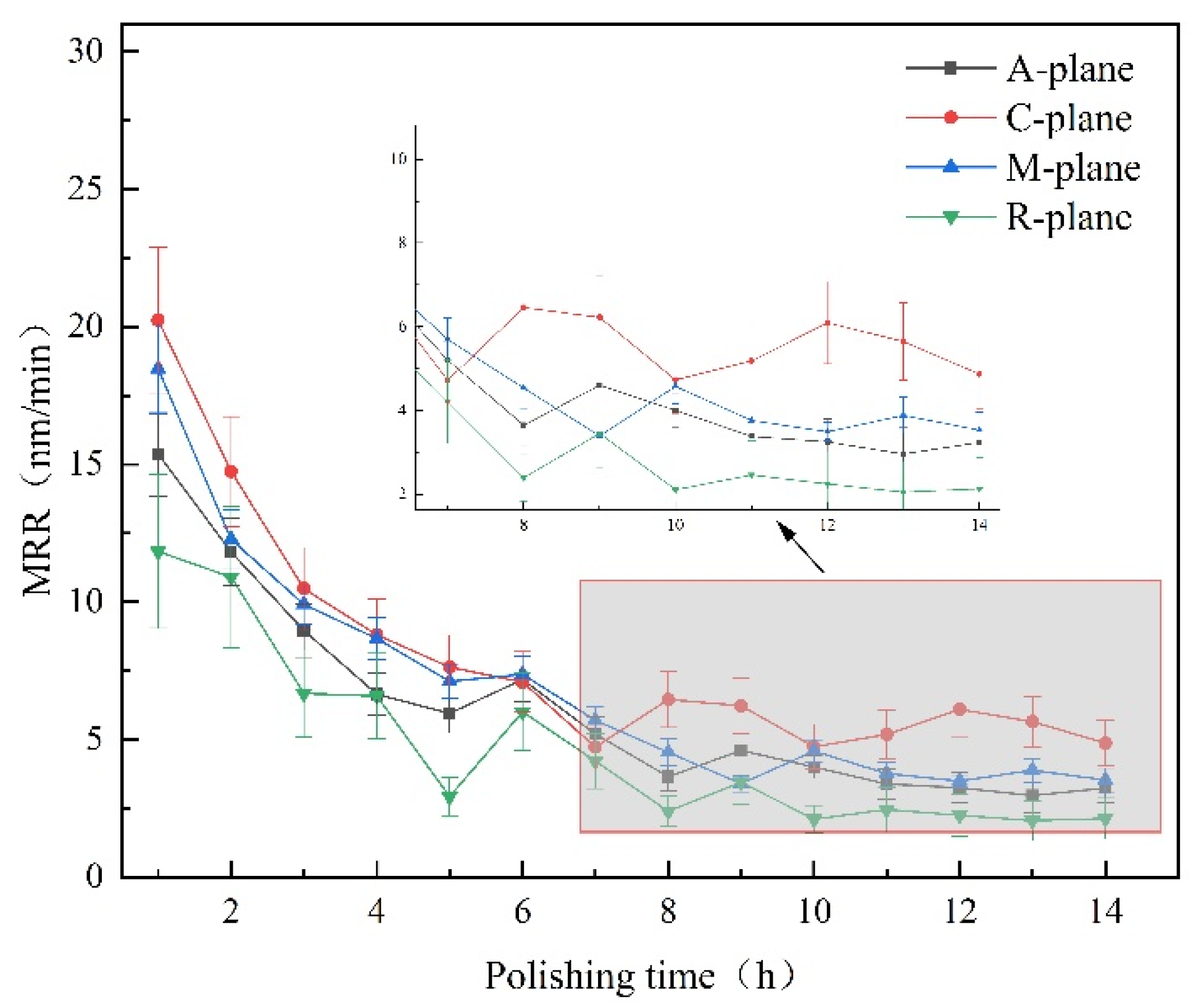
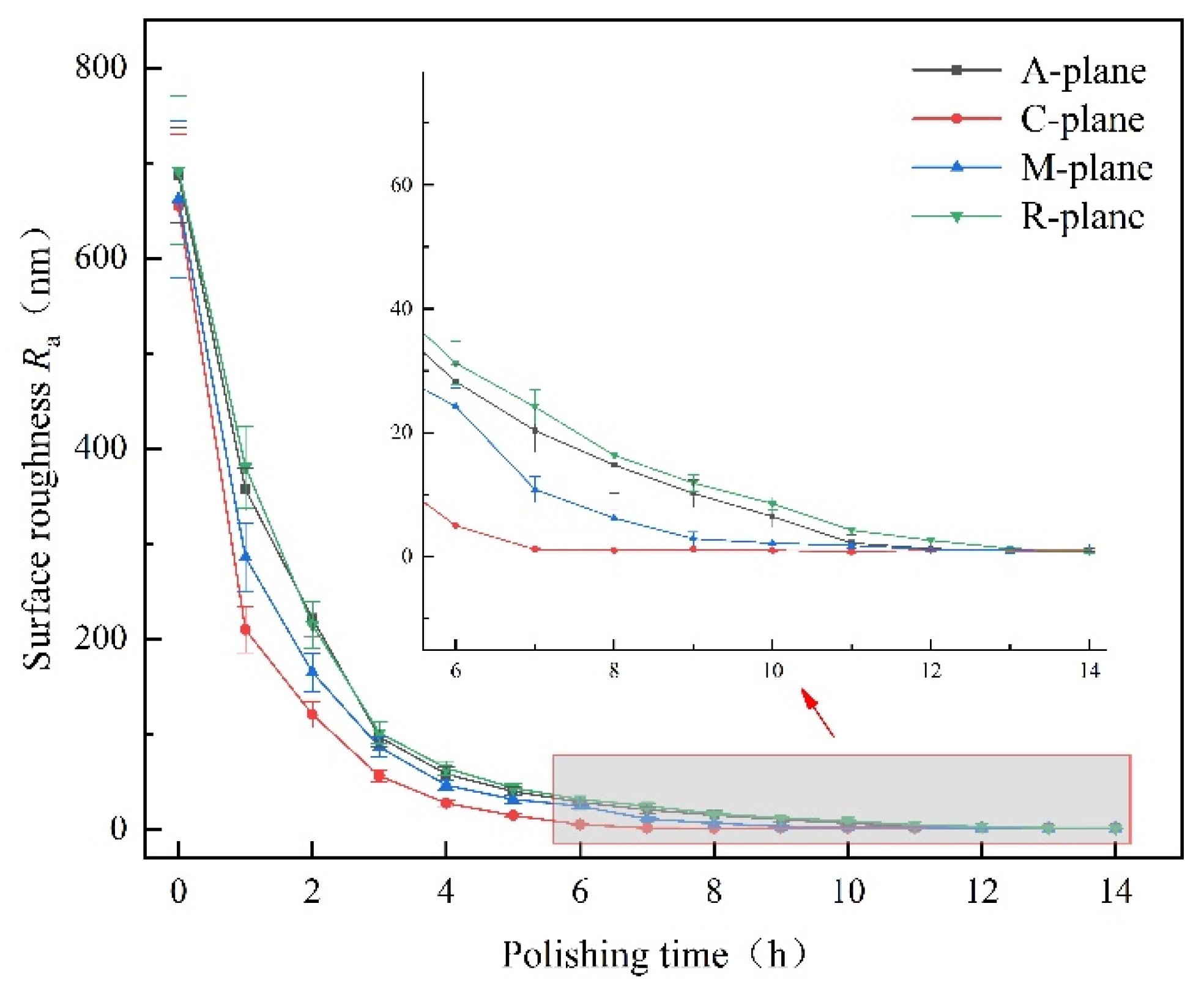
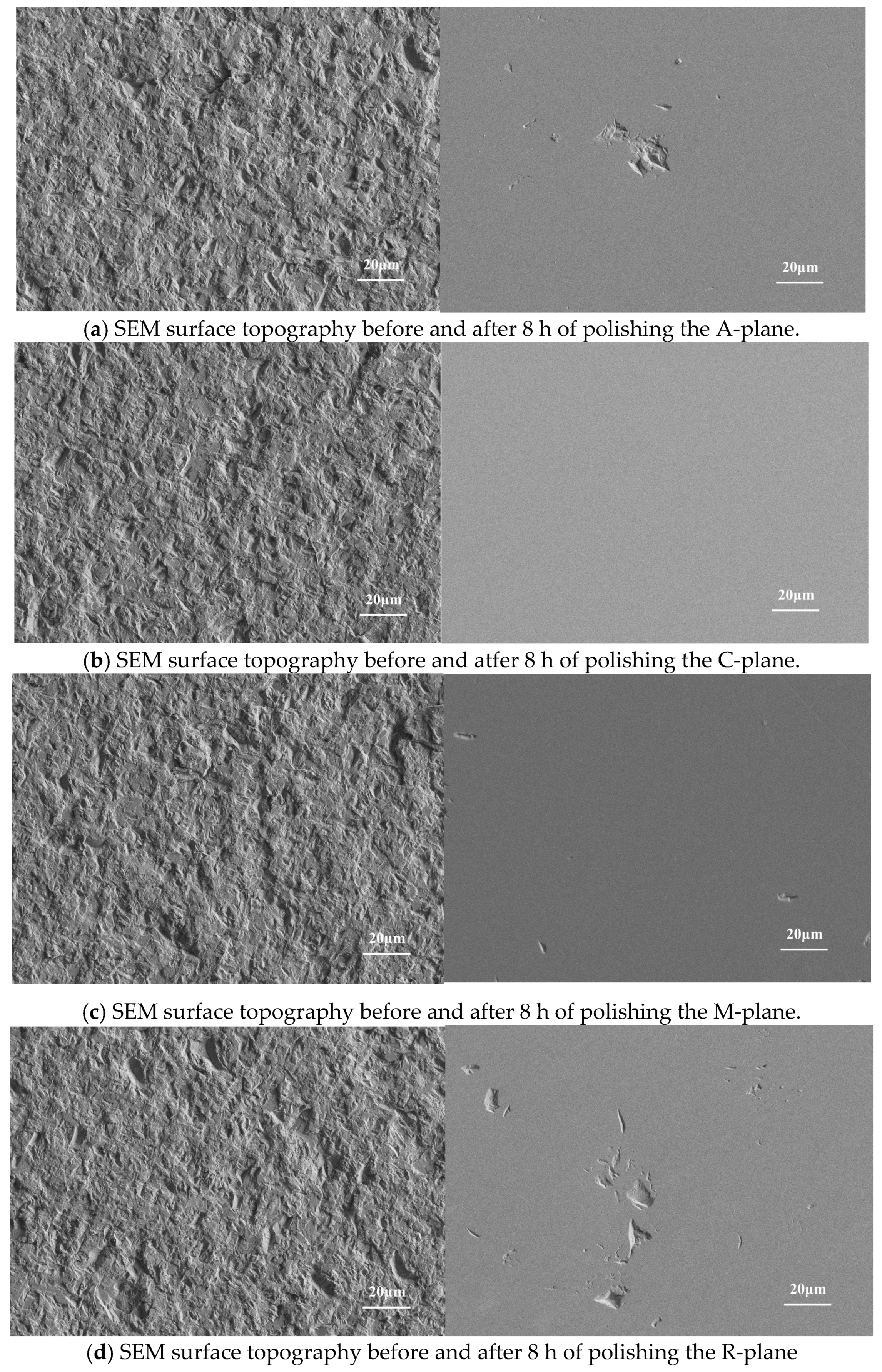
2.2. CMP Processing Experiment
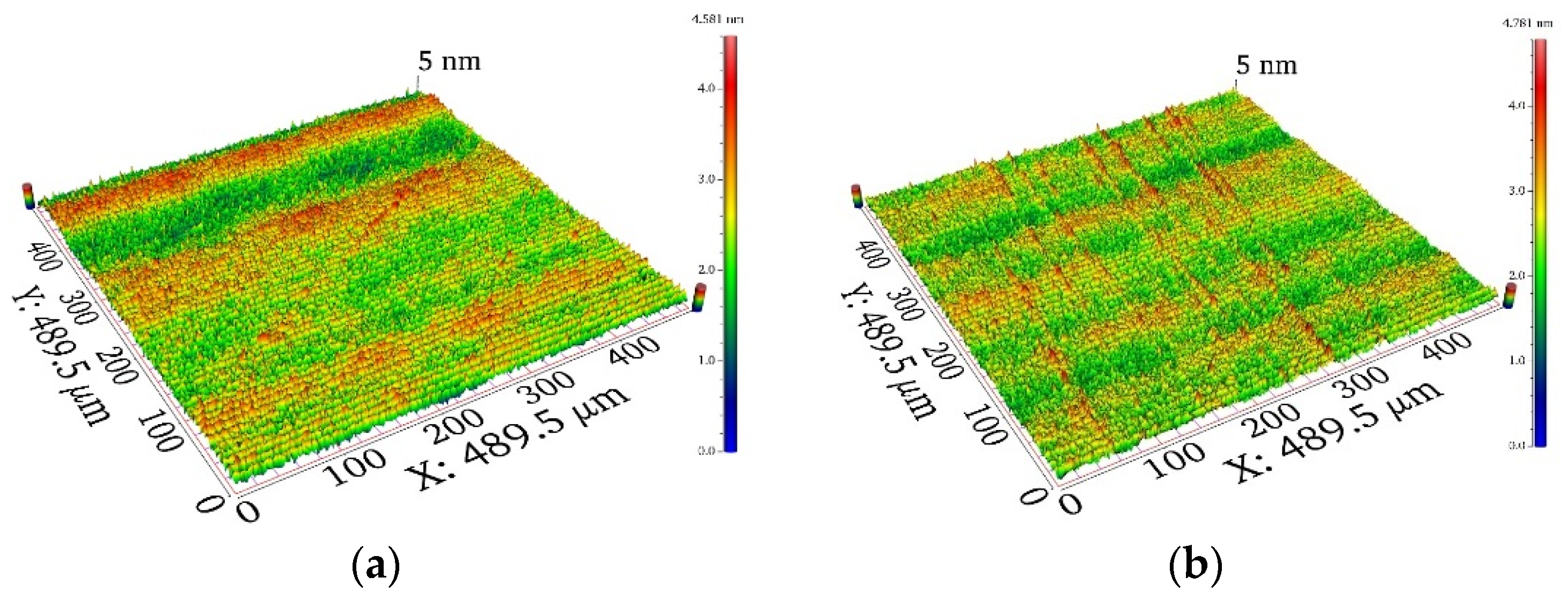
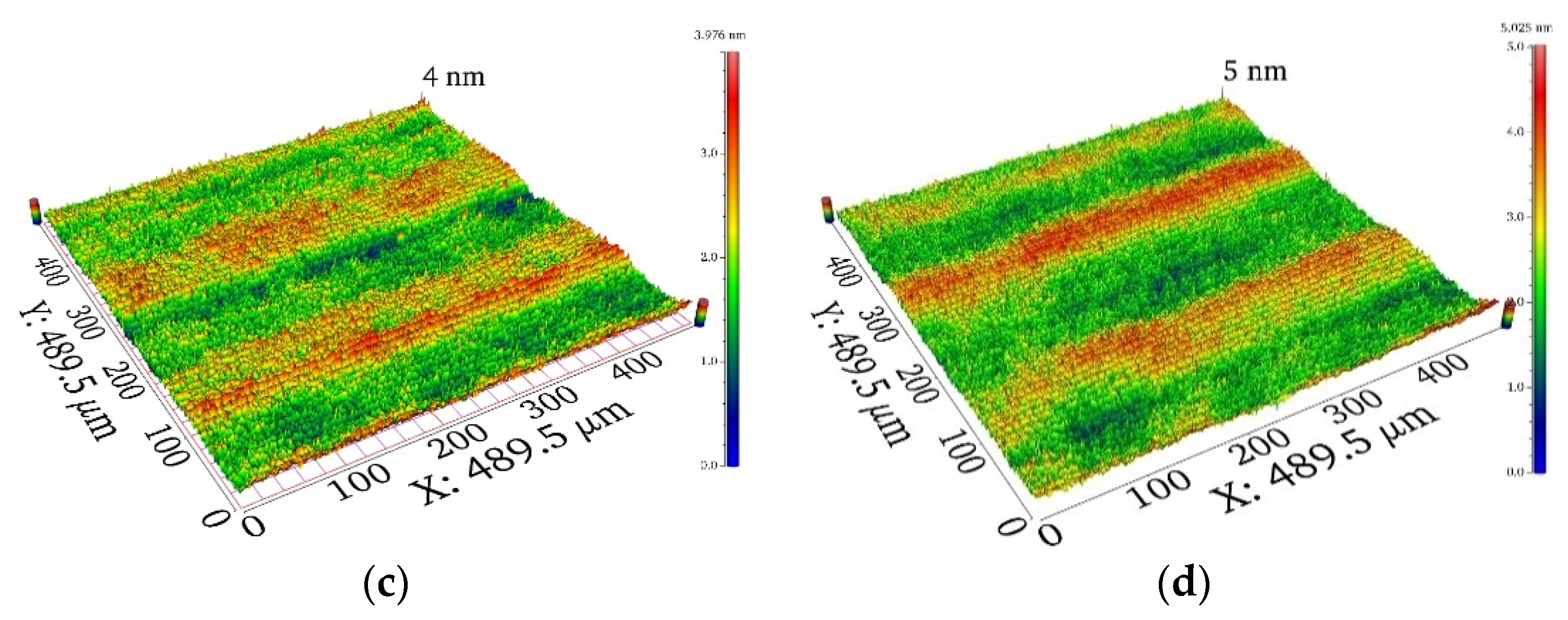
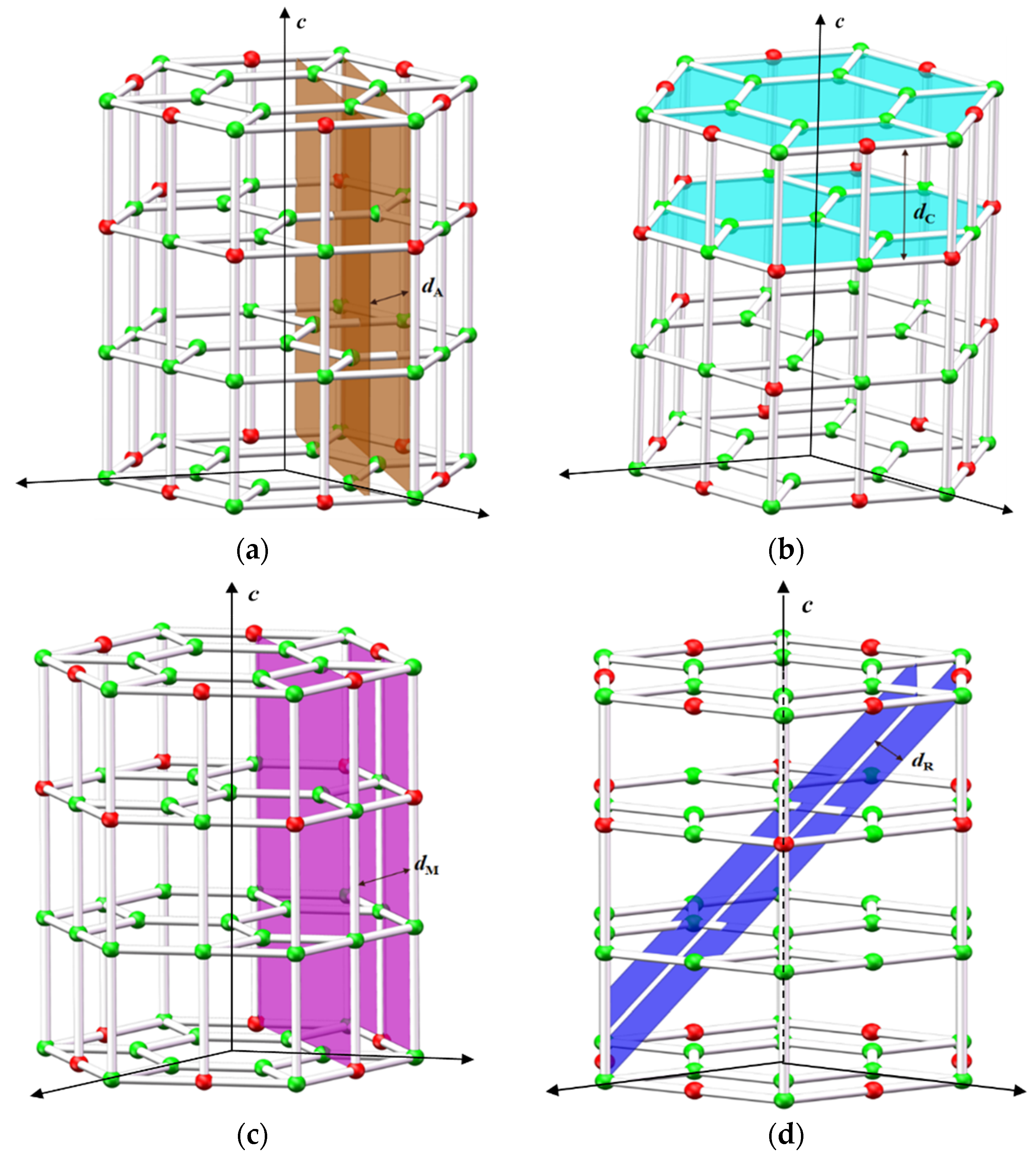
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- Nanoindentation experiments were performed on sapphire with different crystal orientations by nanoindentation technology, and the hardness and elastic modulus increased in sequence according to the C-plane, M-plane, A-plane, R-plane.
- Polishing experiment results on sapphire with different crystal planes showed that the material removal rate of the A-, C-, M- and R-planes were 3.95, 5.93, 4.16, and 2.47 nm/min. The C-plane sapphire could obtain better surface quality in a shorter processing time.
- The calculation of the adjacent atomic structures of different crystal orientations indicated that the C-plane was the easiest crystal plane to achieve material removal, and the R-plane was the most difficult to process which was consistent with the previous polishing experiment results. Moreover, the research results have great guiding significance for the engineering application of sapphire processing with different crystal planes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, T.C.; Yuan, J.L.; Deng, Q.F.; Feng, K.P.; Xu, W. Contrast Experiments in Dielectrophoresis Polishing (DEPP)/Chemical Mechanical Polishing (CMP) of Sapphire Substrate. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Lu, X.; Pan, G.; Lei, Y.; Luo, J. Ultrasonic flexural vibration assisted chemical mechanical polishing for sapphire substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 3936–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zou, C.; Shi, X.; Pan, G.; Luo, G.; Zhou, Y. Fe-Nx/C assisted chemical–mechanical polishing for improving the removal rate of sapphire. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 343, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Pan, G.; Chen, Z.-G.; Gong, H.; Xu, L.; Zou, C. AFM and XPS studies on material removal mechanism of sapphire wafer during chemical mechanical polishing (CMP). J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 9921–9928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, P.; Mizumoto, Y.; Kakinuma, Y.; Min, S. Machinability study of single-crystal sapphire in a ball-end milling process. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2017, 18, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aida, H.; Doi, T.; Takeda, H.; Katakura, H.; Kim, S.-W.; Koyama, K.; Yamazaki, T.; Uneda, M. Ultraprecision CMP for sapphire, GaN, and SiC for advanced optoelectronics materials. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2012, 12, S41–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Zhang, P.; Cheng, G.; Jiang, F.; Lu, X. Crystalline orientation effects on material removal of sapphire by femtosecond laser irradiation. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 23501–23508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, J.J.; Kim, D.; Sokol, J.J.; Zazzera, L.A.; Romero, V.D.; Atkinson, M.R.; Nabulsi, F.; Zhang, H. A case for 2-body material removal in prime LED sapphire substrate lapping and polishing. J. Manuf. Process. 2013, 15, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, H.; Jeong, H.; Choi, S.; Lee, Y.; Jeong, M.; Jeong, H. Macroscopic and microscopic investigation on chemical mechanical polishing of sapphire wafer. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 1256–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.S.; Kim, J.; Park, Y.; Na, H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Yoon, E.; Kim, Y.W. The effects of strained sapphire (0001) substrate on the structural quality of GaN epilayer. Phys. Status Solidi (b) 2004, 241, 2722–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, M.; Gao, J.; Li, G. A comparative study on the properties of c-plane and a-plane GaN epitaxial films grown on sapphire substrates by pulsed laser deposition. Vacuum 2016, 128, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagne, A.; Pathak, S.; Maeder, X.; Michler, J. Plasticity and fracture of sapphire at room temperature: Load-controlled microcompression of four different orientations. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, C.A. Nanoindentation studies of materials. Mater. Today 2006, 9, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Shen, Y.G.; Lu, C. Nanoscale elastic–plastic deformation and stress distributions of the C plane of sapphire single crystal during nanoindentation. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 1865–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Cao, L.; Hang, W.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, J. Crystallographic orientation effect on the incipient plasticity and its stochastic behavior of a sapphire single crystal by spherical nanoindentation. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 15554–15564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabadelo, V.; Pathak, S.; Saeidi, F.; Parlinska-Wojtan, M.; Wasmer, K. Nanoindentation deformation and cracking in sapphire. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 9835–9845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjima, B.; Anoop, K.M. Interaction of nanoscale damages with static and dynamic contact induced damages in alumina: A novel approach using nanoindentation. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 24982–24998. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q.F.; Lu, J.; Xu, X.P.; Jiang, F. Removal mechanism of sapphire wafers (0001, 112¯0 and 101¯0) in mechanical planarization machining. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 16178–16184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Wu, J.; Gong, Y.; Wen, X.; Wen, Q. Grinding forces in micro slot-grinding (MSG) of single crystal sapphire. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2017, 112, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xu, X. Material removal mechanism of sapphire substrates with four crystal orientations by double-sided planetary grinding. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 7813–7822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Jiang, F.; Xu, X.; Duan, N.; Wen, Q.; Lu, X. Research on the machinability of A-plane sapphire under diamond wire sawing in different sawing directions. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 10310–10320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Vehoff, H. Dependence of nanohardness upon indentation size and grain size – A local examination of the interaction between dislocations and grain boundaries. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nix, W.D.; Gao, H. Indentation size effects in crystalline materials: A law for strain gradient plasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1998, 46, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, L.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, J.; Guo, L.; Hong, T.; Hang, W.; Ma, Y. Study on the Influence of Sapphire Crystal Orientation on Its Chemical Mechanical Polishing. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8065. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10228065
Cao L, Zhang X, Yuan J, Guo L, Hong T, Hang W, Ma Y. Study on the Influence of Sapphire Crystal Orientation on Its Chemical Mechanical Polishing. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(22):8065. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10228065
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Linlin, Xiang Zhang, Julong Yuan, Luguang Guo, Teng Hong, Wei Hang, and Yi Ma. 2020. "Study on the Influence of Sapphire Crystal Orientation on Its Chemical Mechanical Polishing" Applied Sciences 10, no. 22: 8065. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10228065
APA StyleCao, L., Zhang, X., Yuan, J., Guo, L., Hong, T., Hang, W., & Ma, Y. (2020). Study on the Influence of Sapphire Crystal Orientation on Its Chemical Mechanical Polishing. Applied Sciences, 10(22), 8065. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10228065




