Abstract
DNA-protein conjugates are useful molecules for construction of biosensors. Herein, we report the development of an enzymatically-conjugated DNA aptamer–protein hybrid molecule for use as a bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET)-based biosensor. DNA aptamers were enzymatically conjugated to a fusion protein via the catalytic domain of porcine circovirus type 2 replication initiation protein (PCV2 Rep) comprising residues 14–109 (tpRep), which was truncated from the full catalytic domain of PCV2 Rep comprising residues 1–116 by removing the flexible regions at the N- and C-terminals. For development of a BRET-based biosensor, we constructed a fusion protein in which tpRep was positioned between NanoLuc luciferase and a fluorescent protein and conjugated to single-stranded DNA aptamers that specifically bind to either thrombin or lysozyme. We demonstrated that the BRET ratios depended on the concentration of the target molecules.
1. Introduction
DNA-protein conjugates are useful materials for biosensing applications [1]. Use of DNA in these conjugate molecules allows for both signal amplification as well as molecular recognition (e.g., using DNA aptamers) [2,3,4,5]. DNA aptamers bind to specific molecules with high affinity and specificity. Therefore, DNA aptamer-based biosensing systems have been constructed as conjugates of DNA aptamers and reporter molecules [6,7,8]. Single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) containing aptamer sequences are modified at the 5′ and/or 3′ ends with a fluorophore for use in construction of DNA aptamer-based biosensors [9,10,11,12]. In addition to modification of ssDNA with a fluorophore, a reporter protein can also be conjugated to ssDNA [3,4,5]. However, conventional methods for conjugation of ssDNA to a reporter protein require cumbersome procedures. To overcome these limitations, we developed a method for conjugation of ssDNA to a protein of interest fused with a replication initiation protein (Rep) [5,13]. In this method, a protein fused with Rep can be covalently linked to ssDNA via enzymatic reaction, without the need for any chemical modification of the ssDNA. Recently, the catalytic domain of porcine circovirus type 2 Rep comprising residues 1-116 (pRep) was employed to construct DNA-NanoLuc luciferase (NanoLuc) conjugates [5]. DNA-NanoLuc conjugates were applied for use in a DNA aptamer-sandwich assay system. Moreover, pRep retains its DNA binding activity regardless of whether the protein of interest is fused to the N-terminus or C-terminus.
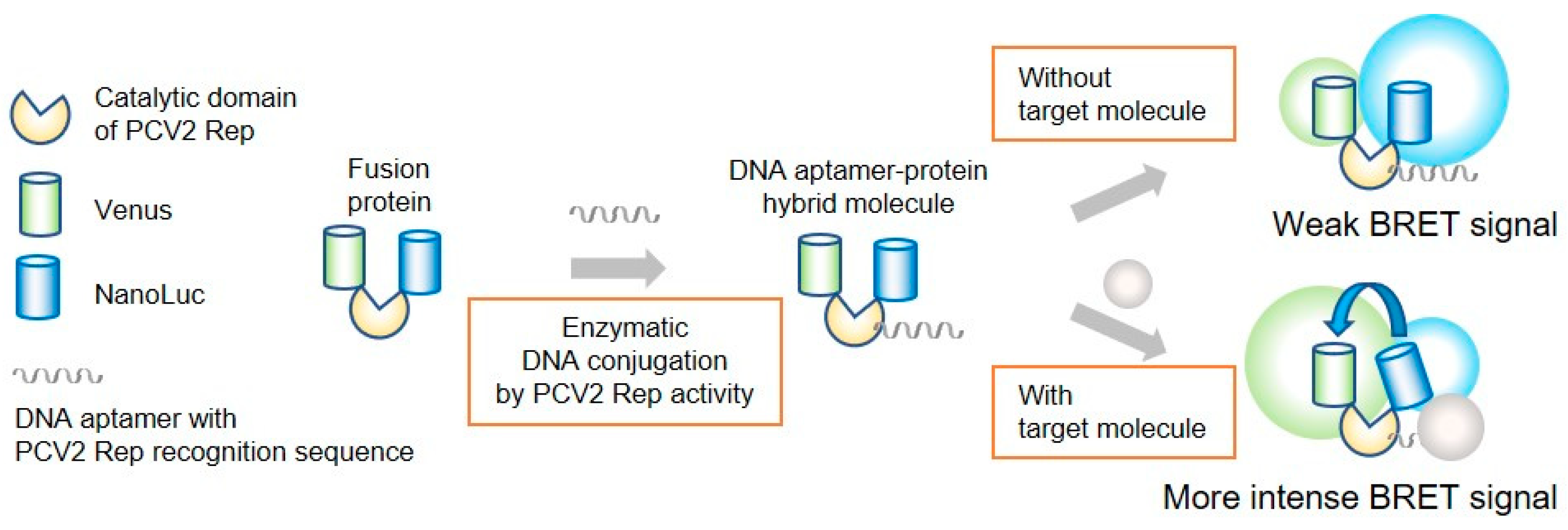
Bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET)-based biosensors are frequently used in biosensing methods [14,15,16]. For the design of intramolecular BRET sensors, sensory domains that lead to conformational changes are located between donor and acceptor molecules, such as luciferase and a fluorescent protein. Therefore, we decided to design a fusion protein for application as a BRET biosensor, in which pRep was positioned between luciferase and a fluorescent protein, and then a DNA aptamer was conjugated via pRep. It was anticipated that our designed fusion protein conjugates containing DNA aptamers might undergo conformational changes upon binding of a target molecule to the DNA aptamer (Figure 1). BRET efficiency is dependent on not only the distance between the donor and acceptor molecules, but also their relative orientations. In our design, it was speculated that larger change in the distance between donor and acceptor molecules would not be occurred even when a target molecule binds to the DNA aptamer. However, the BRET efficiency was expected to change through alteration of their orientation upon binding of a target molecule to the DNA aptamer.
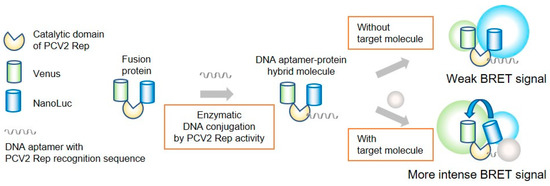
Figure 1.
BRET-based biosensor with DNA-protein conjugates. The catalytic domain PCV2 Rep was fused with Venus and NanoLuc. A DNA aptamer with the PCV2 Rep recognition sequence was enzymatically conjugated to the fusion protein via Rep.
Herein, we tested this idea by constructing a fusion protein in which pRep was positioned between Venus as an acceptor fluorophore and NanoLuc as an energy donor. Overlap of the bioluminescent emission spectrum with the excitation spectrum of the acceptor fluorophore is important for selection of a BRET molecule pair. The combination of Venus and NanoLuc has been previously applied in several BRET-based sensors [15,16]. Energy transfer occurs when the donor and acceptor molecules are within 10 nm of each other in proximity [14,17]. Based on the known structure of pRep, we expected that BRET between NanoLuc and Venus would occur in the designed fusion protein. As noted above, the BRET efficiency depends not only on the distance between the donor and acceptor molecules, but also their relative orientations. To overcome limitations associated with molecular orientation, linkers are generally inserted between the sensory domain and the BRET molecules to allow for a certain degree of movement of the BRET molecules [14]. pRep exhibits flexible regions at the N- and C-terminals [18]. In the present study, we expected the orientation change upon binding of target molecules to sensor. To allow movement of the BRET molecules only when the target molecules bind to the DNA aptamer conjugated to the fusion protein, we constructed a truncated pRep variant from the catalytic domain of PCV2 Rep comprising residues 14–109 (tpRep). By using tpRep, the BRET efficiency is expected to change through alteration of the orientation upon binding of the target molecule to the DNA aptamer. Herein, truncated pReps were expressed in Escherichia coli and subsequently purified, and the DNA binding abilities were evaluated. Finally, tpRep was used to construct DNA-protein conjugates with thrombin- and lysozyme-binding DNA aptamers, and the resultant DNA-protein conjugates were evaluated for use as a BRET-based biosensor.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Construction of Plasmids
For expression of Rep mutants, the plasmids pET-His-pRep1-109, pET-His-pRep14-116 and pET-His-tpRep, were constructed as follows. pReps with the flexible N- and/or C-terminus regions truncated were constructed by site-directed mutagenesis. First, truncated pRep without the flexible 7-amino acid C-terminus, namely pRep1-109, was constructed by site-directed mutagenesis using the primer set 5′-TGGAGCTGTCGACTAAGGTACCCTC-3′ and 5′-TAGTCGACAGCTCCACACTCCATTA-3′. pET-His-pRep, which was previously constructed in our laboratory, was used as a template [5]. The resultant plasmid was named pET-His-pRep1-109. Truncated pRep without the flexible 13-amino acid N-terminus, namely pRep14-116, and tpRep were constructed by the same procedure using the primer set 5′-CGAATTCCACAAACGTTGGGTCTTC-3′ and 5′-ACGTTTGTGGAATTCGCCCATGGCATG-3′. pET-His-pRep and pET-His-pRep1-109 were used as templates, respectively. The resultant plasmids were named pET-His-pRep14-116 and pET-His-tpRep, respectively.
The pET28-VenusΔ10-pRep-NanoLuc-His plasmid for expression of the fusion protein VenusΔ10-pRep-NanoLuc-His (VpRNH), in which the pRep protein was fused to the N-terminus of NanoLuc and the C-terminus of VenusΔ10, was constructed as follows. The VenusΔ10 fragment was amplified by PCR using the primer set 5′-tacgaattcagtaaaggagaagaacttttc-3′ and 5′-ggcgaattcggtacccccagcagctgttac-3′, and Nano-lantern(cAMP-1.6)/pRSETB (Addgene #53591) was used as a template. The amplified fragment was cloned into pUC18 and its sequence was confirmed. The resultant plasmid, pUC18-VenusΔ10, was digested with EcoR I. The obtained fragment was inserted into the pET28-pRep-NanoLuc-His plasmid, which was previously constructed in our laboratory, and digested with the same restriction enzyme.
The pET28-VenusΔ10-tpRep-NanoLuc-His plasmid for expression of the fusion protein VenusΔ10-tpRep-NanoLuc-His (VtpRNH), in which the tpRep protein was fused to the N-terminus of NanoLuc and the C-terminus of VenusΔ10, was constructed as follows. To destroy an EcoR I restriction site located at the beginning of the VenusΔ10 sequence, a single nucleotide base of pET28-VenusΔ10-pRep-NanoLuc-His was changed by site-directed mutagenesis using the primer set 5′-GGCGATTTATGAGTAAAGGAGAAGAA-3′ and 5′-ACTCATAAATTCGCCCATGGTATATCT-3′. The resultant plasmid, pET28-delEcoRI-VenusΔ10-pRep-NanoLuc-His, was digested with EcoR I and Sal I to remove the fragment encoding pRep and the inserted tpRep fragment derived from pET-His-tpRep was digested with the same restriction enzymes. The resultant plasmid was named pET28-VenusΔ10-tpRep-NanoLuc-His.
2.2. Protein Expression and Purification
For protein expression, the respective plasmids were introduced into E. coli BL21(DE3)-competent cells. Transformed cells were inoculated in LB medium with 50 μg/mL ampicillin for expression of Rep mutants and with 20 μg/mL kanamycin for expression of the fusion proteins VpRNH and VtpRNH. Cells were then cultured at 37 °C until the OD660 reached 0.6~0.8, followed by addition of 1 mM isopropyl-β-D(-)-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) for induction of protein expression. Cells were cultured overnight at 16 °C for expression of fusion proteins and for 6 h at 25 °C for expression of Rep mutants. Cells were then harvested by centrifugation. The collected cells were suspended in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS: 150 mM NaCl, 16 mM Na2HPO4, 4 mM NaH2PO4, pH 7.4) and disrupted by sonication, followed by centrifugation to obtain the soluble fraction. The supernatant was added to ProfinityTM IMAC Ni-Charged Resin (Bio-Rad) equilibrated with PBS followed by rotation at 4 °C for 30 min. After rotation, the samples were washed with Ni-NTA buffer (0.5 M NaCl, 20 mM phosphate buffer, pH 8.0) 5 times, and then washed twice with Ni-NTA buffer containing 10 mM imidazole. Proteins were eluted with Ni-NTA buffer containing 10, 100, 150 mM imidazole. The eluted samples were dialyzed against PBS 3 times using dialysis tubing. The concentrations of purified proteins were evaluated using a BCA assay kit (Pierce).
2.3. Evaluation of DNA Binding Ability of pRep
The ssDNA oligonucleotide Rep sub31 (5′-AAGTATTACAAAAACCAGCGCAGTTGGGCAG-3′) was used for evaluation of the DNA binding ability of pRep. The underlined sequence denotes the PCV2 Rep recognition sequence. Purified proteins (5 μM) were mixed with Rep sub31 (5 μM) in 10 μL of reaction buffer, PBS with 2.5 mM MgCl2. After incubation for 30 min at 37 °C, the samples were run on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), and the gels were stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB).
2.4. Evaluation of Emission Spectra
BRET of purified fusion proteins were evaluated using the Nano-Glo Luciferase Assay System (Promega). Fusion proteins (1 μM) in 50 μL of PBS were mixed with the same volume of Nano-Glo Luciferase Assay Reagent. Emission spectra (350–650 nm) was acquired 10 s after reagent addition using a FP6500 spectrofluorophotometer (JASCO, Tokyo, Japan). Emission spectra were normalized to the peak emission of NanoLuc at 450 nm, which was set to an intensity of 1.00.
2.5. Homogeneous Assay with DNA Aptamer
The single-stranded DNA aptamers for lysozyme, namely Lysoapt 42 (5′-AAGTATTACATCTACGAATTCATCAGGGCTAAAGAGTGCAGAGTTACTTAG-3′), and for thrombin, namely TBA 29 (5′-AAGTATTACAGTCCGTGGTAGGGCAGGTTGGGGTGACT-3′), containing the Rep recognition sequence, were used in the homogeneous assay [19,20]. Human α-thrombin was purchased from Haematologic Technologies. Equal amounts (1 μM each) of VtpRNH and DNA aptamer were mixed in 50 μL of PBS containing 0.5 mM of MgCl2 followed by incubation at 37 °C. After incubation for 30 min, 10 μL of solutions containing varying concentrations of target molecules was added to the mixture of VtpRNH and DNA aptamer followed by incubation at room temperature for 1 h. For the thrombin-binding DNA aptamer-VtpRNH conjugate, samples containing bovine serum albumin (BSA) (instead of thrombin) were evaluated as a negative control. Samples were mixed with the same volume of Nano-Glo Luciferase Assay Reagent. Emission spectra (350-650 nm) were acquired 10 sec after addition of the reagent using a FP6500 spectrofluorophotometer. Emission spectra were normalized to the peak emission of NanoLuc at 450 nm, which was set to an intensity of 1.00. The change in BRET ratio (ΔBRET) was calculated as follows:
ΔBRET = {(emission at 528 nm)/(emission at 450 nm)} − BRET basal ratio
The BRET basal ratio is defined as (emission at 528 nm)/(emission at 450 nm) at 0 μM of the target molecule.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Truncation of the Catalytic Domain of PCV2 Rep
We previously developed a method for site-specific conjugation of ssDNA to a protein of interest via the fused replication initiator protein (Rep), such as conjugation of Gene A* from bacteriophage phiX 174 and the catalytic domain of porcine circovirus type 2 Rep comprising residues 1-116 (pRep) [5,13]. Recently, Gordon’s group reported a similar strategy for construction of DNA-protein conjugates using several Reps, including pRep, as HUH-tags [21]. pRep is much smaller than Gene A* and well-expressed in E. coli. The structure of pRep (Protein Data Bank (PDB) ID:2HW0) exhibits flexible regions at the N- and C-terminals [18]. In our designed fusion protein, Rep was positioned between Venus and NanoLuc. For construction of BRET-based biosensors, flexible linkers are generally inserted between the sensory domain and the BRET molecule to allow for a certain degree of movement of the BRET molecule [14]. In the present study, to allow for movement of BRET molecules only when the target molecule binds to the DNA aptamer conjugated to the fusion protein, use of truncated variants of pRep was required. Truncated variants of pReps were constructed and their DNA binding abilities were evaluated.
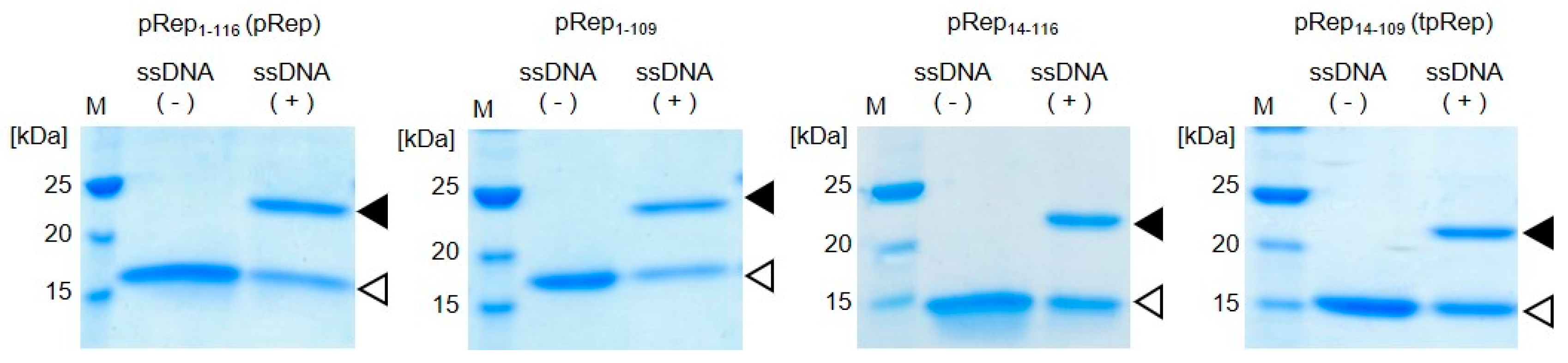
Truncated variants of pRep, namely pRep1-109 lacking the last 7 amino acids in the sequence, pRep14-116 lacking the first 13 amino acids in the sequence, and tpRep (pRep14-109) lacking the flexible regions at both the N- and C-terminals of pRep, were expressed in E. coli and subsequently purified. Truncated pReps were purified from the soluble fraction, similar to pRep. Proteins were mixed with ssDNA containing a Rep recognition sequence for evaluation of the DNA binding abilities of the truncated pReps. After incubation, samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (Figure 2). In addition to the bands appearing at the expected sizes of the protein, all samples also showed other bands at higher molecular weights than pReps without conjugation. Those bands appearing at higher molecular weights were attributed to pReps conjugated with ssDNA. Upon cleavage of specific sequence of ssDNA, PCV2 Rep is conjugate to DNA covalently. In addition of this reaction, PCV2 Rep also catalyze the reaction in the opposite direction [18]. PCV2 Rep has an ability to catalyze joining two ssDNA fragments, a free 3′-OH and the 5′-phosphate covalently linked to Rep, for regeneration of PCV2 Rep recognition sequence. Therefore, there is a possibility to exist unreacted protein. However, this joining activity is not efficient compared to cleavage activity followed by conjugation of DNA with Rep. In this experiment, the ratio of protein and ssDNA is 1:1. By increasing ssDNA concentration, the conjugation efficiencies should increase. These results demonstrate that tpRep retains the ability to covalently bind to ssDNA even after truncation of the flexible regions located at N- and C-terminals of pRep. Therefore, tpRep was used for construction of a BRET-based biosensor with a DNA-protein conjugate.
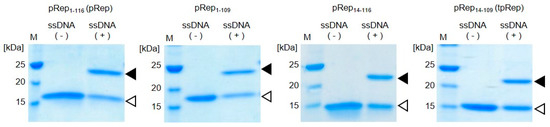
Figure 2.
DNA binding abilities of truncated pRep proteins. The flexible region of the catalytic domain of PCV2 Rep comprising amino acids 1-116 was truncated from the full protein (pRep1-116, abbreviated pRep; MW 15,100); pRep1-109: pRep lacking the last 7 amino acids in the sequence (MW 14,300); pRep14-116: pRep lacking the first 13 amino acids in the sequence (MW 13,700); and pRep14-109, abbreviated tpRep: pRep lacking the flexible regions at both the N- and C-terminals of pRep (MW 12,900); white triangles indicate pRep without DNA and black triangles indicate pRep conjugated with DNA.
3.2. Construction of DNA-Protein Conjugates with NanoLuc and Venus for BRET-Based Biosensor
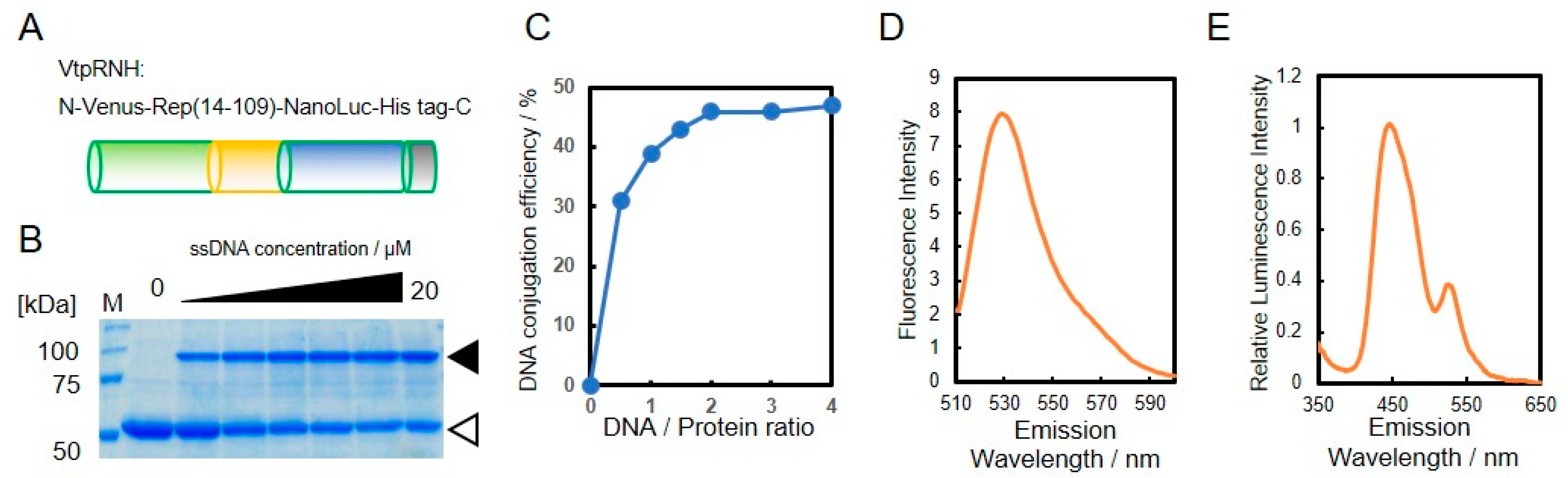
As shown in Figure 1, we designed a BRET-based sensor with DNA-protein conjugates. For construction of the DNA-protein conjugates, the catalytic domain of PCV2 Rep comprising residues 14–109 (tpRep) was fused to the N-terminus of NanoLuc and the C-terminus of VenusΔ10 with a His-tag (Figure 3A). The resultant fusion protein, VtpRNH, was expressed in E. coli and subsequently purified from the soluble fraction with a His-tag located at the C-terminus. After purification, the activities of each domain of VtpRNH were evaluated. First, the DNA binding ability of tpRep in the fusion protein was evaluated (Figure 3B). Even after fusion with NanoLuc and VenusΔ10, tpRep retained its DNA binding ability. The conjugation efficiencies were found increase with increasing DNA concentration. The maximum efficiency was around 50% (Figure 3C). We also evaluated the functions of both Venus and NanoLuc. Venus was shown to fluorescence in the fusion protein (Figure 3D). The emission peak was ~530 nm at an excitation wavelength of 500 nm [22].
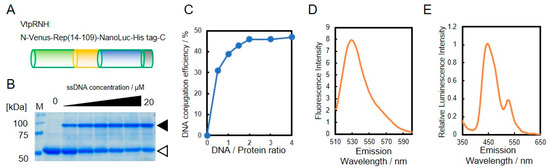
Figure 3.
Evaluation of DNA binding ability of the fusion protein. Design of the constructed fusion protein, VtpRNH (MW 57,900) (A). DNA binding of tpRep in the fusion protein; the concentration of VtpRNH was 5 μM; white triangle indicates pRep without DNA conjugation and black triangle indicates pRep with DNA conjugation (B). DNA-conjugation efficiency of protein was evaluated by ImageJ (C). Emission spectrum of Venus at an excitation wavelength of 500 nm; the concentration of VtpRNH was 3 μM (D). NanoLuc activities of fusion proteins. The emission spectrum was normalized to the peak emission of NanoLuc at 450 nm; final concentration of VtpRNH was 0.5 μM (E).
Bioluminescence of NanoLuc in the fusion protein was also evaluated. The emission spectrum of the fusion protein exhibited a peak at ~450 nm without external excitation, which corresponds to the emission of NanoLuc [23]. These results suggest that VtpRNH retained its NanoLuc activity. Moreover, in addition to the emission peak around 450 nm, there was a small emission peak at ~530 nm. To identify the origin of this peak, the emission spectra were normalized to the peak emission of NanoLuc at 450 nm, which was set to an intensity of 1.00. As shown in Figure 3E, the emission peak of normalized intensity was observed at ~530 nm. The emission peak of Venus occurs at ~530 nm. These results suggest that BRET occurred between NanoLuc and Venus. We measured the emission spectrum after ssDNA binding via Rep to the fusion protein. Even after ssDNA binding to the fusion proteins via Rep, the emission peak at ~530 nm was observed (data not shown).
3.3. Construction and Evaluation of BRET-Based Biosensor with DNA-Protein Conjugates
DNA aptamers are well known molecular binders with specificity to a specific molecule. In the present study, thrombin- and lysozyme-binding DNA aptamers were applied for the construction of a BRET-based biosensor with DNA-protein conjugates. For conjugation of DNA aptamer to the fusion protein via Rep, ssDNA comprised of the DNA aptamer and a Rep recognition sequence were reacted with the fusion protein.
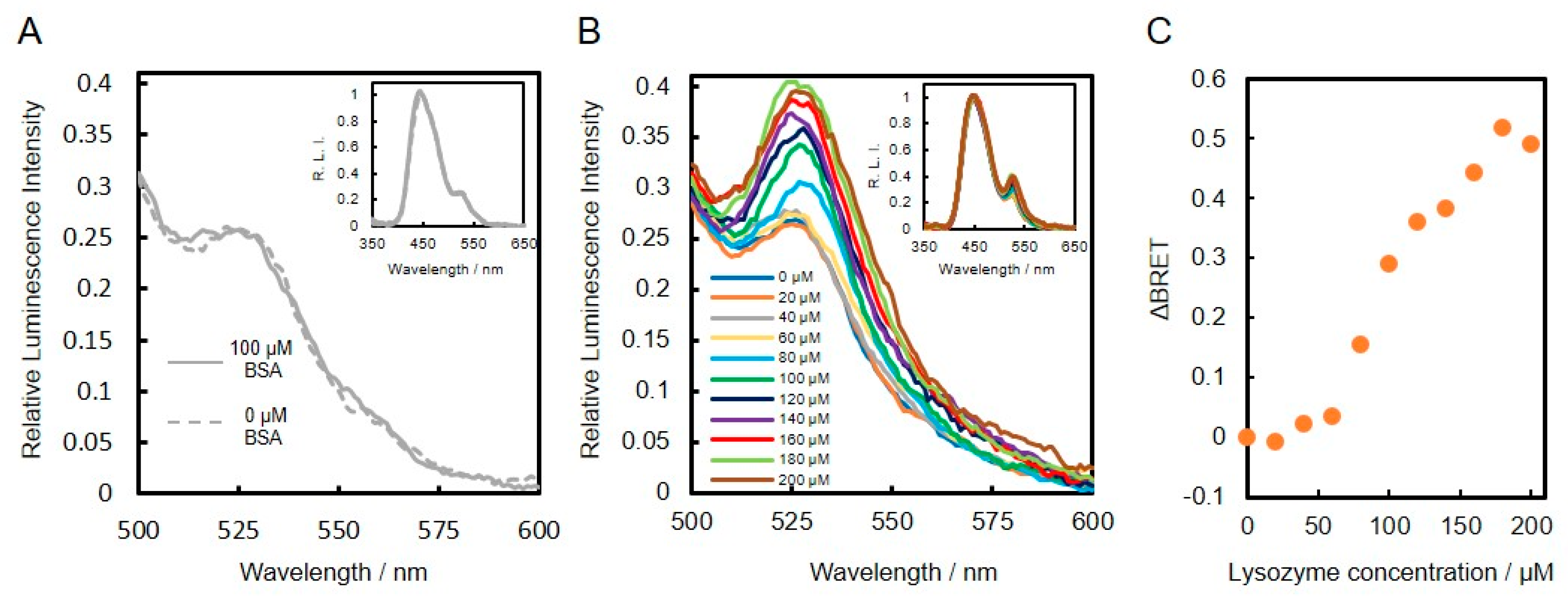
Lysozyme-binding DNA aptamer was first conjugated to VtpRNH. After conjugation, the emission spectra of lysozyme binding DNA aptamer–protein conjugates with or without lysozyme were evaluated. As shown in insets of Figure 4A,B, the emission spectra were normalized to the peak emission of NanoLuc at 450 nm, which was set to an intensity of 1.00. In the presence of BSA (100 μM), the normalized emission spectra of both DNA-protein conjugates with or without BSA were similar (Figure 4A). On the other hand, presence of lysozyme, the normalized emission peaks at 528 nm were found to increase compared to the control without lysozyme (Figure 4B). These results suggest that BRET efficiencies change upon binding of lysozyme to the DNA aptamers. To confirm this speculation, we evaluated the emission spectra in the presence of different concentrations of lysozyme. As shown in Figure 4C, the changes in BRET ratio (ΔBRET) increased with increasing lysozyme concentration. These results confirm that the lysozyme-binding DNA aptamer-VtpRNH conjugate can be used as a BRET-based sensor. The Kd of the lysozyme-binding DNA aptamer is reported to be 30 nM [19]. Compared to this value, the sensitivity of our BRET-based biosensor with the lysozyme-binding DNA aptamer-VtpRNH conjugate is very low. As shown in Figure 3B, there were unreacted DNA. The sensitivity of sensor should be reduced by those unreacted DNA because unreacted DNA bind to target molecule competitively. However, in this case, it is not main reason for the low sensitivity. It was supposed that lysozyme formed aggregate in the presence of unreacted DNA caused by their net charge. Though monomeric lysozyme could not induce conformational change of fusion protein, BRET ratios would be changed by the aggregated lysozyme. The lysozyme binding DNA aptamer-VpRNH conjugate also showed similar results (Figure S1). We expected ΔBRET to be larger for the lysozyme-binding DNA aptamer-VtpRNH conjugate compared with the DNA-VpRNH conjugate because tpRep was truncated to remove the flexible amino acid sequences from the N- and C-terminals. In contrast, the change in BRET ratio for the DNA-VtpRNH conjugate was smaller than that for the DNA-VpRNH conjugate. In case of DNA-VpRNH with high concentration of lysozyme, it was speculated that BRET ratio was changed not only by changes of the orientation but also the distance.
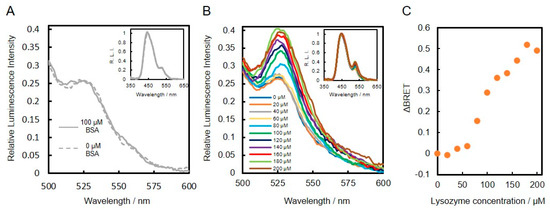
Figure 4.
Evaluation of lysozyme-binding DNA aptamer–protein conjugates with and without target molecules. Normalized emission spectra of lysozyme-binding DNA aptamer-VtpRNH conjugate in the presence of BSA (A) and lysozyme (B). Change in BRET ratio (ΔBRET) as a function of lysozyme concentration (C).
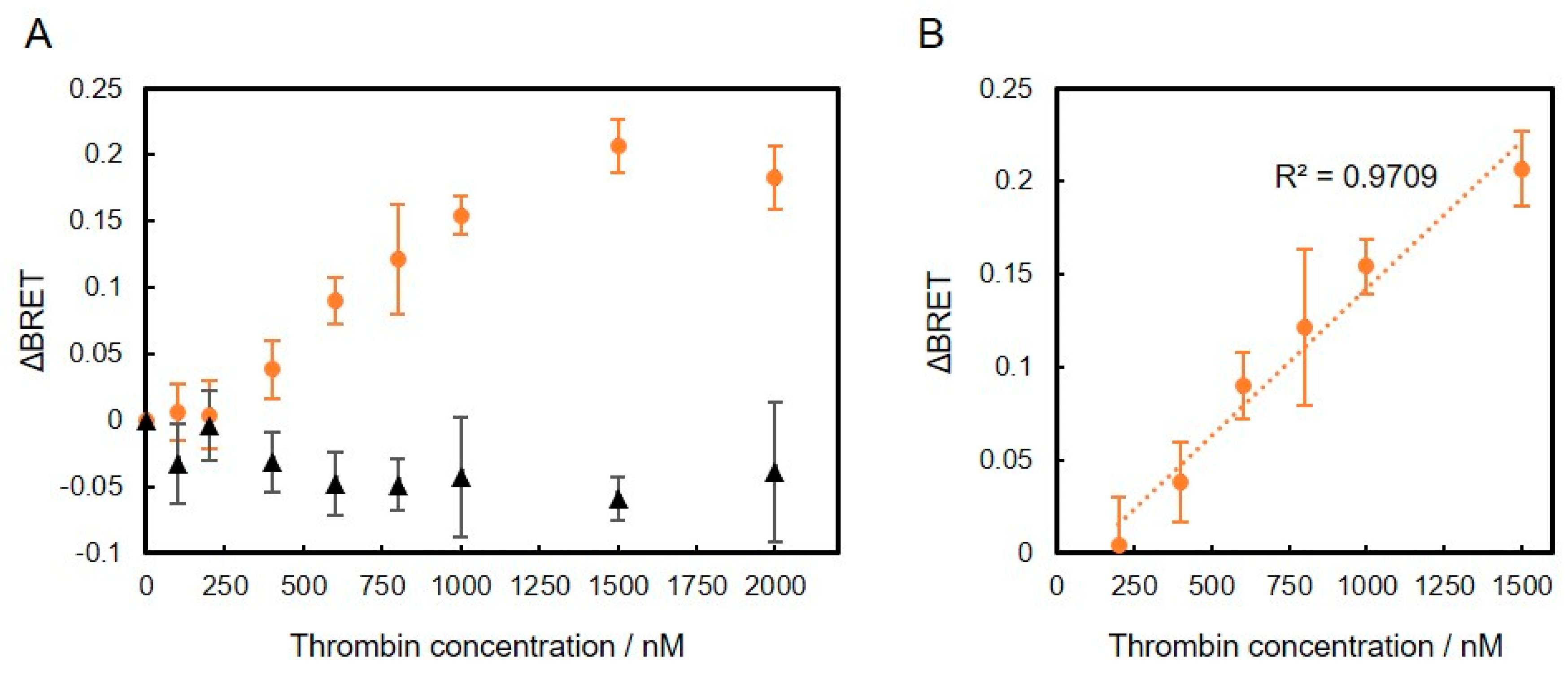
We also evaluated the thrombin-biding DNA aptamer conjugated to VtpRNH for use as a BRET-based biosensor. As shown in insets of Figure 5A,B, the normalized emission spectra of thrombin-binding DNA aptamer- and lysozyme-binding DNA aptamer-VtpRNH conjugates were evaluated in the presence of different thrombin concentrations. As shown in Figure 5A, the emission spectra of the lysozyme-binding DNA aptamer-VtpRNH conjugate were unchanged in the presence of different thrombin concentrations. On the other hand, the emission spectra of thrombin-binding DNA aptamer-VtpRNH conjugate increased with increasing thrombin concentration (Figure 5B). These results were also confirmed by calculation of ΔBRET for each of the conjugates (Figure 5C). These results suggest that the BRET ratio changes only occurred with the appropriate combination of DNA aptamer and target molecules.
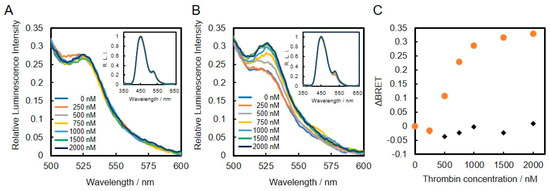
Figure 5.
Evaluation of DNA aptamer-VtpRNH conjugate in the presence of different concentrations of thrombin. Conjugation with lysozyme-binding DNA aptamer (A) or thrombin-binding DNA aptamer (B). Change in BRET ratio (ΔBRET) as a function of thrombin concentration (C). Conjugation with lysozyme-binding DNA aptamer (black diamonds) or thrombin-binding DNA aptamer (orange circles).
Finally, to demonstrate specificity of the conjugates, we evaluated the BRET ratio of the thrombin-binding DNA aptamer-VtpRNH conjugate in the presence of more different concentrations of thrombin or BSA. As shown in Figure 6, ΔBRET of the thrombin-binding DNA aptamer-VtpRNH conjugate increased with increasing thrombin concentration. On the other hand, ΔBRET did not increase in the presence of different BSA concentrations. It is suggested that the ΔBRET depends on the specific binding between DNA aptamers and target molecules. These results further suggest that the thrombin-binding DNA aptamer-VtpRNH conjugate can be used as a BRET-based thrombin biosensor. The Kd of the thrombin-binding DNA aptamer is reported to be ~0.5 nM, which is different from the value obtained from our BRET-based biosensor with the thrombin-binding DNA aptamer-VtpRNH conjugate [20]. One of the reasons of that is existence of unconjugated DNA. In this experiment, same amount of DNA aptamer and VtpRNH were mixed. From the result of Figure 3C, around half of DNA aptamer would remain as unreacted DNA. It should decrease the sensitivity of this sensor. To evaluate the property of BRET sensors, separations of DNA aptamer-VtpRNH conjugates are required. In addition, steric effects would reduce the sensitivity of the sensor. Steric effects are required to induce conformational changes. However, steric effects may also reduce the binding ability of the DNA aptamer. Therefore, the Kd of DNA aptamers should increase in our BRET-based biosensor. The square of the correlation coefficient (R2) of the linear fit equation between concentrations of 200 and 1500 nM is close to 1 (R2 = 0.97). The square of the correlation coefficient was much closer to 1 compared to the results for the thrombin-binding DNA aptamer-VpRNH conjugate (R2 = 0.78) (Figure S2). These differences may be caused by the existence of flexible regions with the pRep protein, which could allow for movement of the BRET molecules even after binding of the target molecule to the DNA aptamer. These results suggest that DNA aptamer-VtpRNH conjugates exhibit the potential for use as BRET-based biosensors. While the sensitivity of these biosensors was too low compared with other DNA aptamer sensors, the sensitivity might be improved by changing the design of the fusion protein and DNA aptamers.
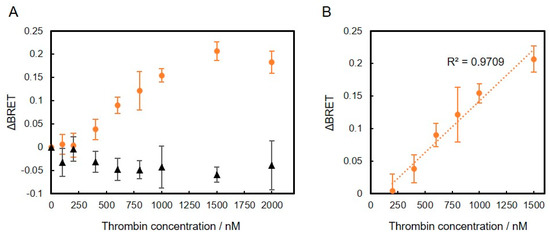
Figure 6.
Change in BRET ratio (ΔBRET) of thrombin-binding DNA aptamer-VtpRNH conjugate as a function of thrombin concentration in the presence of thrombin (orange circles) and BSA (black triangles) (A). Correlation of ΔBRET and thrombin concentration between 200 and 1500 nM (B); each value represents the mean of 4 replicates (n = 4).
4. Conclusions
We constructed DNA aptamer–protein hybrid molecules for use as BRET-based biosensors. Fusion proteins were enzymatically conjugated to DNA aptamers via the catalytic domain of porcine circovirus type 2 replication initiation protein, which was positioned between NanoLuc luciferase and Venus. The catalytic domain of PCV2 Rep was shown to retain its DNA binding activity, even after elimination of the flexible regions at the N- and C-terminals. The resultant DNA aptamer–protein hybrid molecule exhibited a weak BRET signal, even in the absence of the target molecule of the DNA aptamer. However, the BRET signal was found to depend on the concentration of the target molecule. These results demonstrate the potential for use of the designed fusion protein as a DNA aptamer-based platform for construction of BRET-based biosensors.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/10/21/7646/s1, Figure S1. Evaluation of lysozyme-binding DNA aptamer-VpRNH conjugates with and without target molecules. Normalized emission spectra of lysozyme-binding DNA aptamer-VpRNH conjugate in the presence of BSA (A) and lysozyme (B). Change in BRET ratio (ΔBRET) as a function of lysozyme concentration (C), Figure S2. ΔBRET of thrombin of thrombin-binding DNA aptamer-VpRNH conjugate as a function of thrombin concentration (A). Correlation of ΔBRET and thrombin concentration between 200 and 1500 nM (B); each value represents the mean of 4 replicates (n = 4).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.; methodology, M.M., R.H. and Y.M.; investigation, R.H.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M.; writing—review and editing, Y.M. and E.K.; supervision, M.M. and E.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers 16K01388 (M.M.) and 26289310 (E.K.).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhao, D.; Kong, Y.; Zhao, S.; Xing, H. Engineering Functional DNA–Protein Conjugates for Biosensing, Biomedical, and Nanoassembly Applications. Top. Curr. Chem. 2020, 378, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, T.; Smith, C.; Cantor, C. Immuno-PCR: Very sensitive antigen detection by means of specific antibody-DNA conjugates. Science 1992, 258, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, J.; Maruyama, T.; Kitaoka, M.; Kamiya, N.; Goto, M. DNA–enzyme conjugate with a weak inhibitor that can specifically detect thrombin in a homogeneous medium. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 414, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahara, M.; Wakabayashi, R.; Minamihata, K.; Goto, M.; Kamiya, N. Primary Amine-Clustered DNA Aptamer for DNA–Protein Conjugation Catalyzed by Microbial Transglutaminase. Bioconjug. Chem. 2017, 28, 2954–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mie, M.; Niimi, T.; Mashimo, Y.; Kobatake, E. Construction of DNA-NanoLuc luciferase conjugates for DNA aptamer-based sandwich assay using Rep protein. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 41, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Choo, J. Nanomaterial-assisted aptamers for optical sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1859–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassolas, A.; Blum, L.J.; Leca-Bouvier, B.D. Homogeneous assays using aptamers. Analyst 2011, 136, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citartan, M.; Gopinath, S.C.B.; Tominaga, J.; Tan, S.-C.; Tang, T.-H. Assays for aptamer-based platforms. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 34, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokulrangan, G.; Unruh, J.R.; Holub, D.F.; Ingram, B.; Johnson, C.K.; Wilson, G.S. DNA Aptamer-Based Bioanalysis of IgE by Fluorescence Anisotropy. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 1963–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupcich, N.; Chiuman, W.; Nutiu, R.; Mei, S.; Flora, K.K.; Li, Y.; Brennan, J.D. Quenching of Fluorophore-Labeled DNA Oligonucleotides by Divalent Metal Ions: Implications for Selection, Design, and Applications of Signaling Aptamers and Signaling Deoxyribozymes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urata, H.; Nomura, K.; Wada, S.; Akagi, M. Fluorescent-labeled single-strand ATP aptamer DNA: Chemo- and enantio-selectivity in sensing adenosine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 360, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Zhao, Q. A fluorescein labeled aptamer switch for thrombin with fluorescence decrease response. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 3888–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashimo, Y.; Maeda, H.; Mie, M.; Kobatake, E. Construction of Semisynthetic DNA-Protein Conjugates with Phi X174 Gene-A* Protein. Bioconjug. Chem. 2012, 23, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, N.E.; Blumer, J.B.; Hepler, J.R. Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer to Detect Protein-Protein Interactions in Live Cells. In Protein-Protein Interactions; Meyerkord, C.L., Fu, H., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1278, pp. 457–465. ISBN 978-1-4939-2424-0. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Cumberbatch, D.; Centanni, S.; Shi, S.; Winder, D.; Webb, D.; Johnson, C.H. Coupling optogenetic stimulation with NanoLuc-based luminescence (BRET) Ca++ sensing. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, S.; Tsutsui, H.; Suzuki, K.; Agetsuma, M.; Arai, Y.; Jinno, Y.; Bai, G.; Daniels, M.J.; Okamura, Y.; Matsuda, T.; et al. Genetically encoded bioluminescent voltage indicator for multi-purpose use in wide range of bioimaging. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, N.C.; Johnstone, E.K.M.; White, C.W.; Pfleger, K.D.G. NanoBRET: The Bright Future of Proximity-Based Assays. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Rocha, S.; Byeon, I.-J.L.; Gronenborn, B.; Gronenborn, A.M.; Campos-Olivas, R. Solution Structure, Divalent Metal and DNA Binding of the Endonuclease Domain from the Replication Initiation Protein from Porcine Circovirus 2. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 367, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirby, R.; Cho, E.J.; Gehrke, B.; Bayer, T.; Park, Y.S.; Neikirk, D.P.; McDevitt, J.T.; Ellington, A.D. Aptamer-Based Sensor Arrays for the Detection and Quantitation of Proteins. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 4066–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasset, D.M.; Kubik, M.F.; Steiner, W. Oligonucleotide inhibitors of human thrombin that bind distinct epitopes. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 272, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovendahl, K.N.; Hayward, A.N.; Gordon, W.R. Sequence-Directed Covalent Protein–DNA Linkages in a Single Step Using HUH-Tags. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 7030–7035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, T.; Ibata, K.; Park, E.S.; Kubota, M.; Mikoshiba, K.; Miyawaki, A. A variant of yellow fluorescent protein with fast and efficient maturation for cell-biological applications. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, M.P.; Unch, J.; Binkowski, B.F.; Valley, M.P.; Butler, B.L.; Wood, M.G.; Otto, P.; Zimmerman, K.; Vidugiris, G.; Machleidt, T.; et al. Engineered Luciferase Reporter from a Deep Sea Shrimp Utilizing a Novel Imidazopyrazinone Substrate. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).