A Robotic Calibration Method Using a Model-Based Identification Technique and an Invasive Weed Optimization Neural Network Compensator
Abstract
:1. Introduction
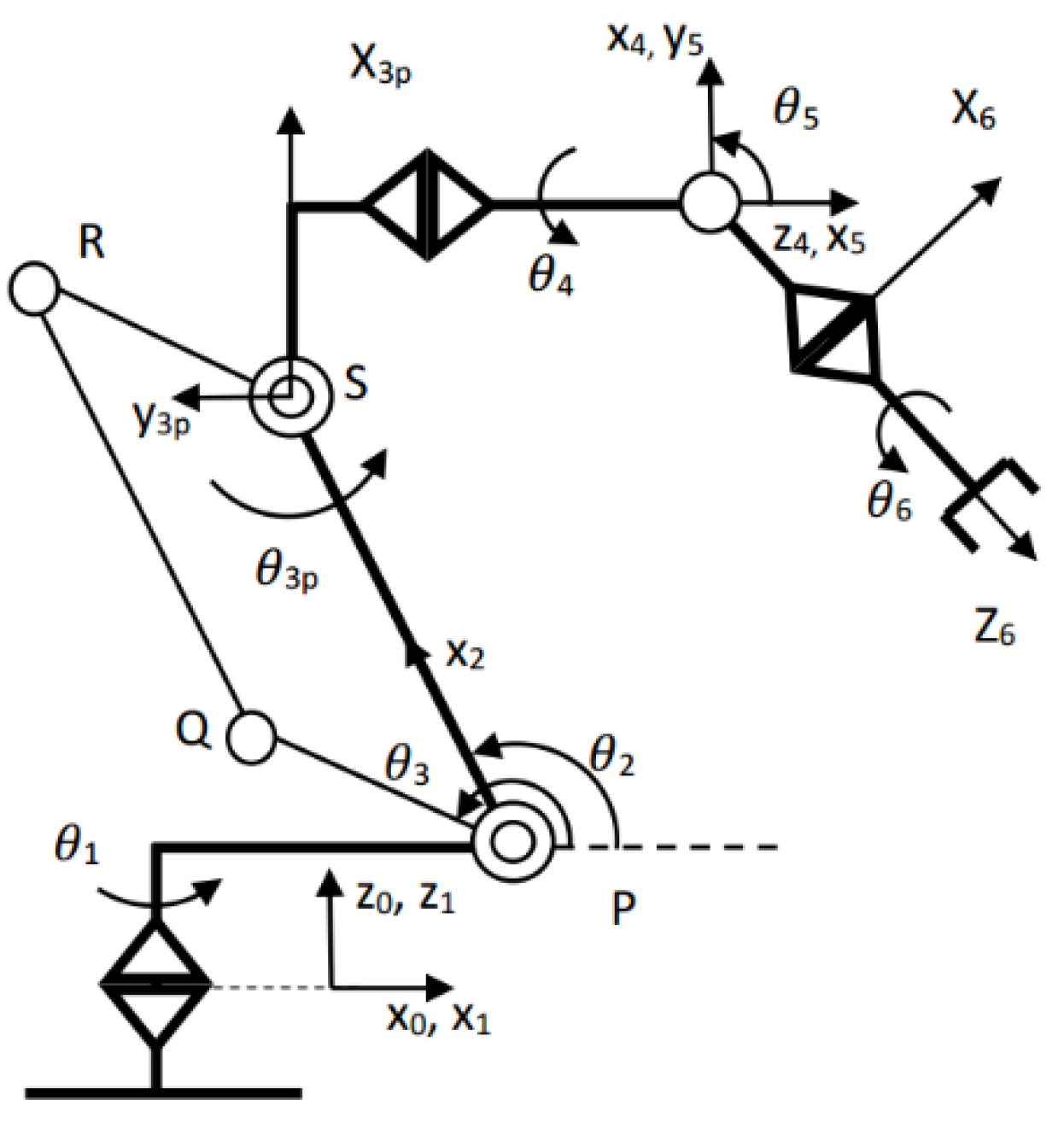
2. Kinematic Model of the HH800 Robot
3. Simultaneous Joint Stiffness and Kinematic Parameters
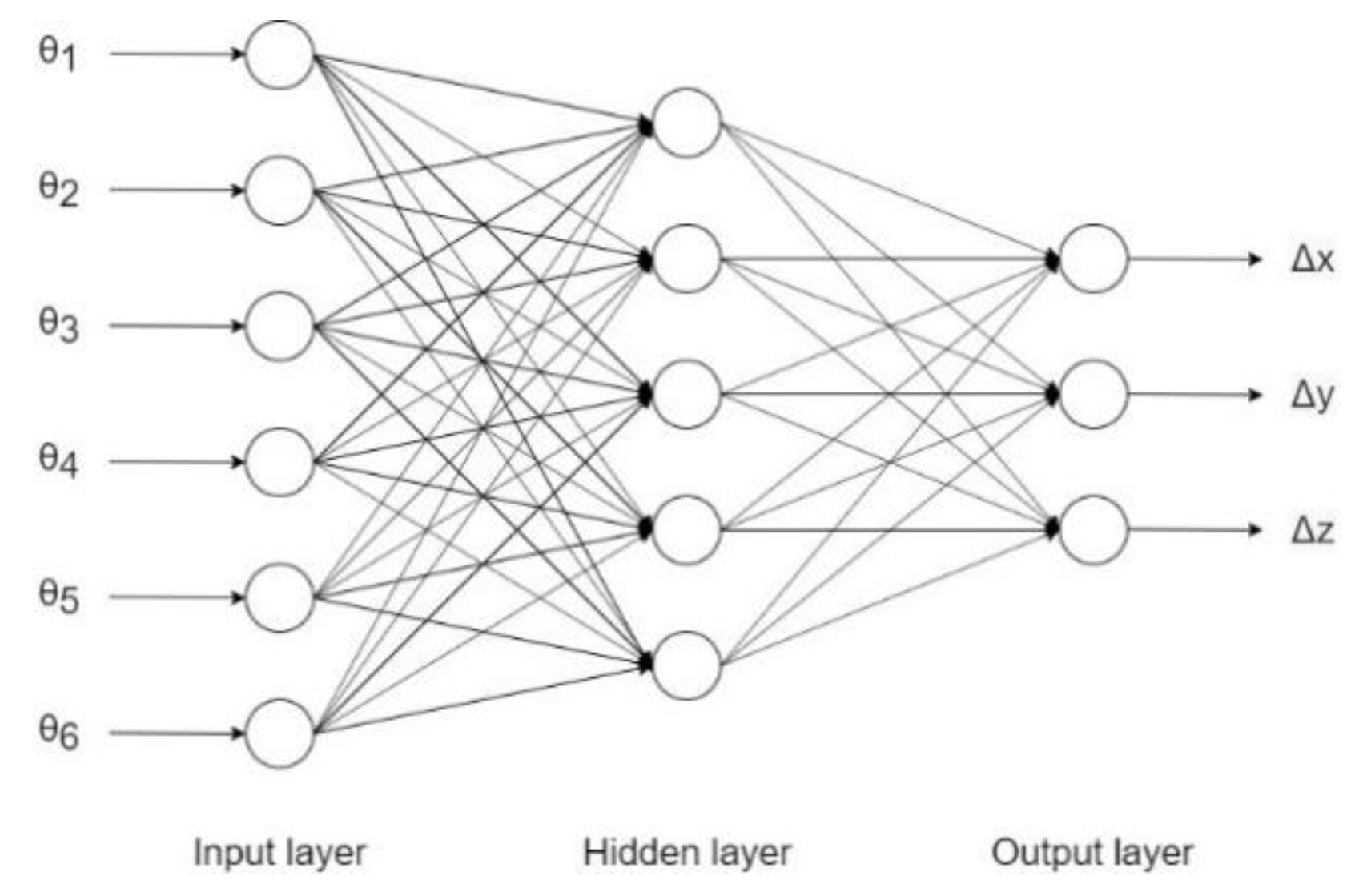
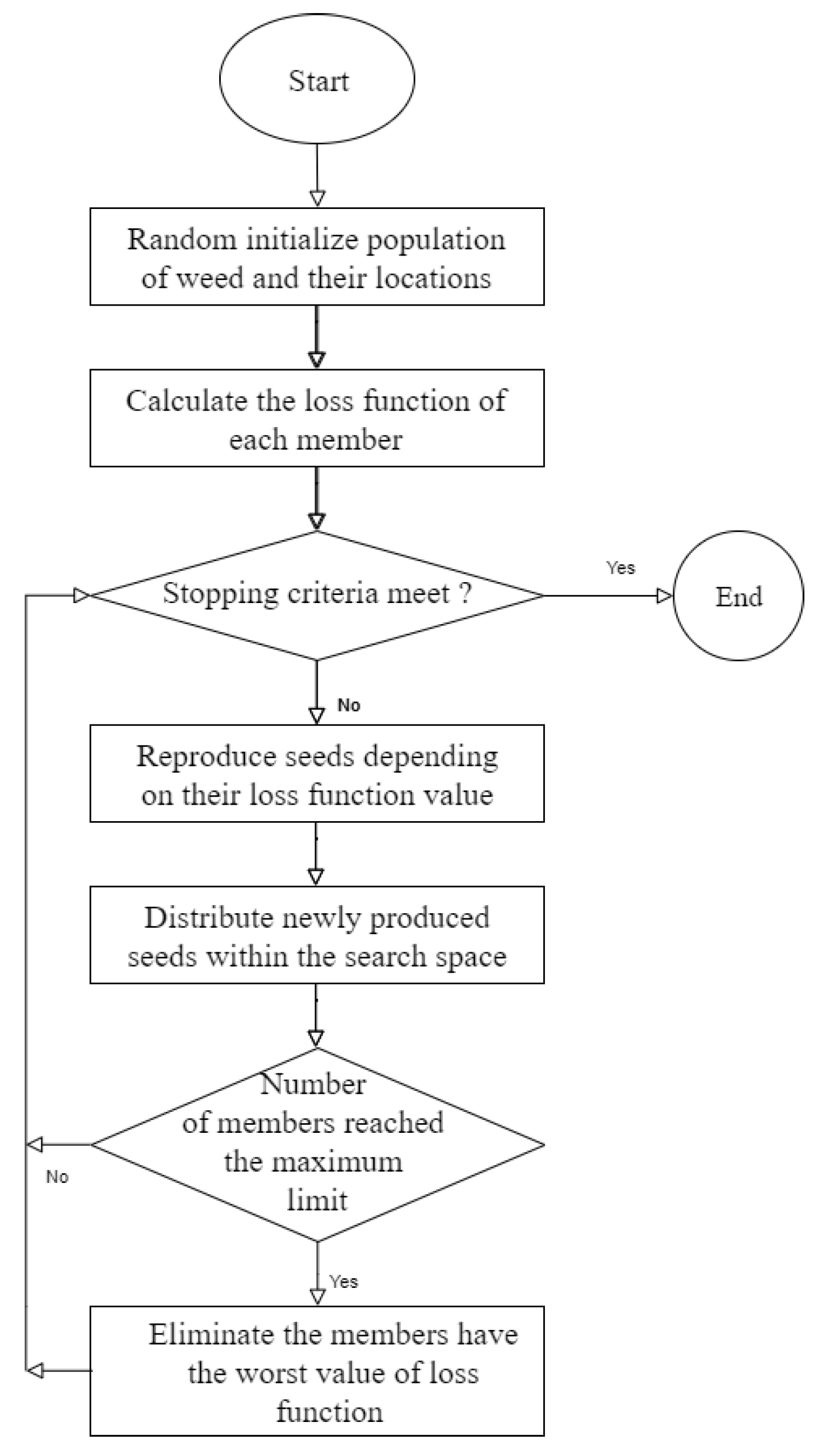
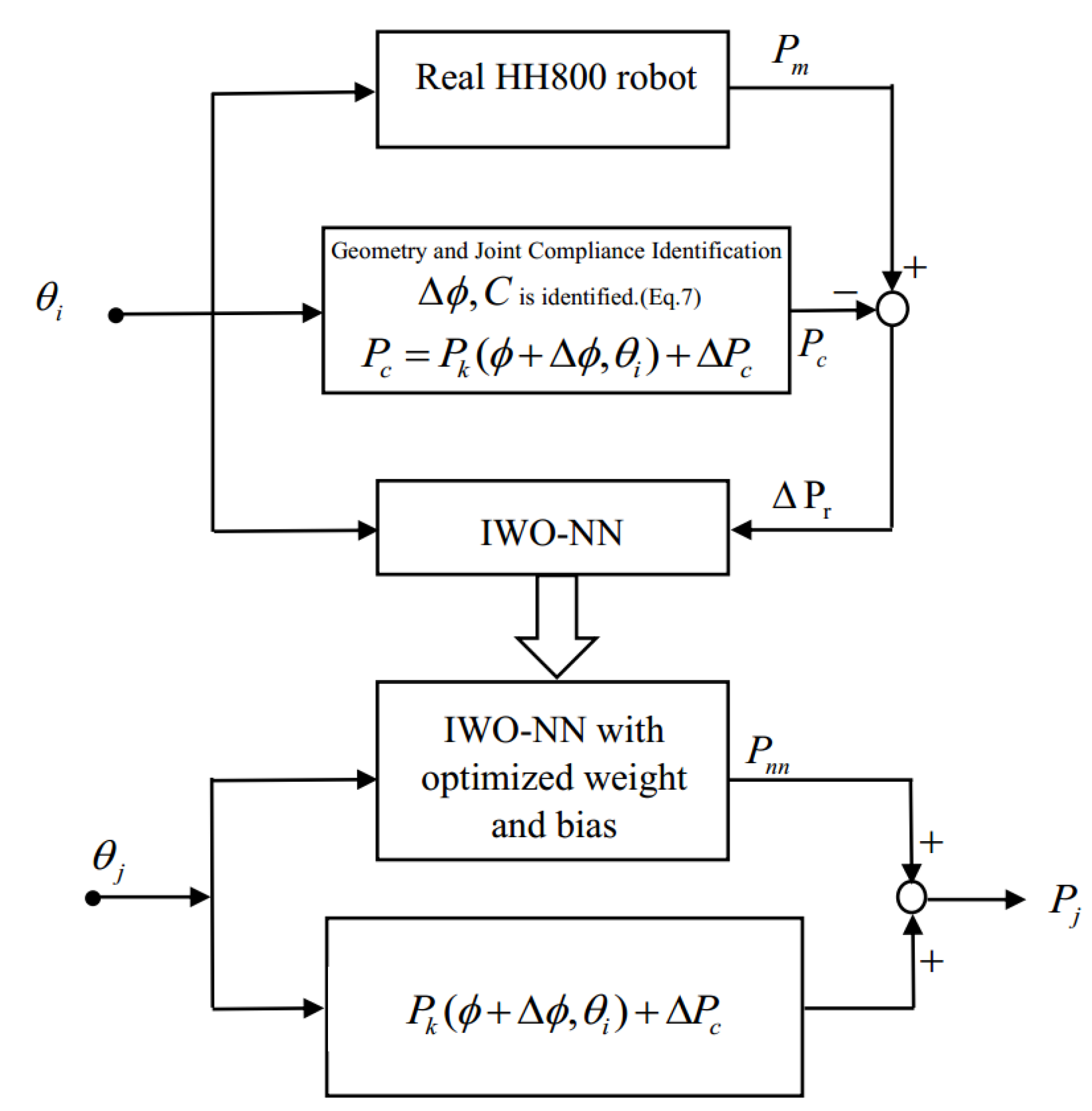
4. IWO-NN Errors Compensator Technique
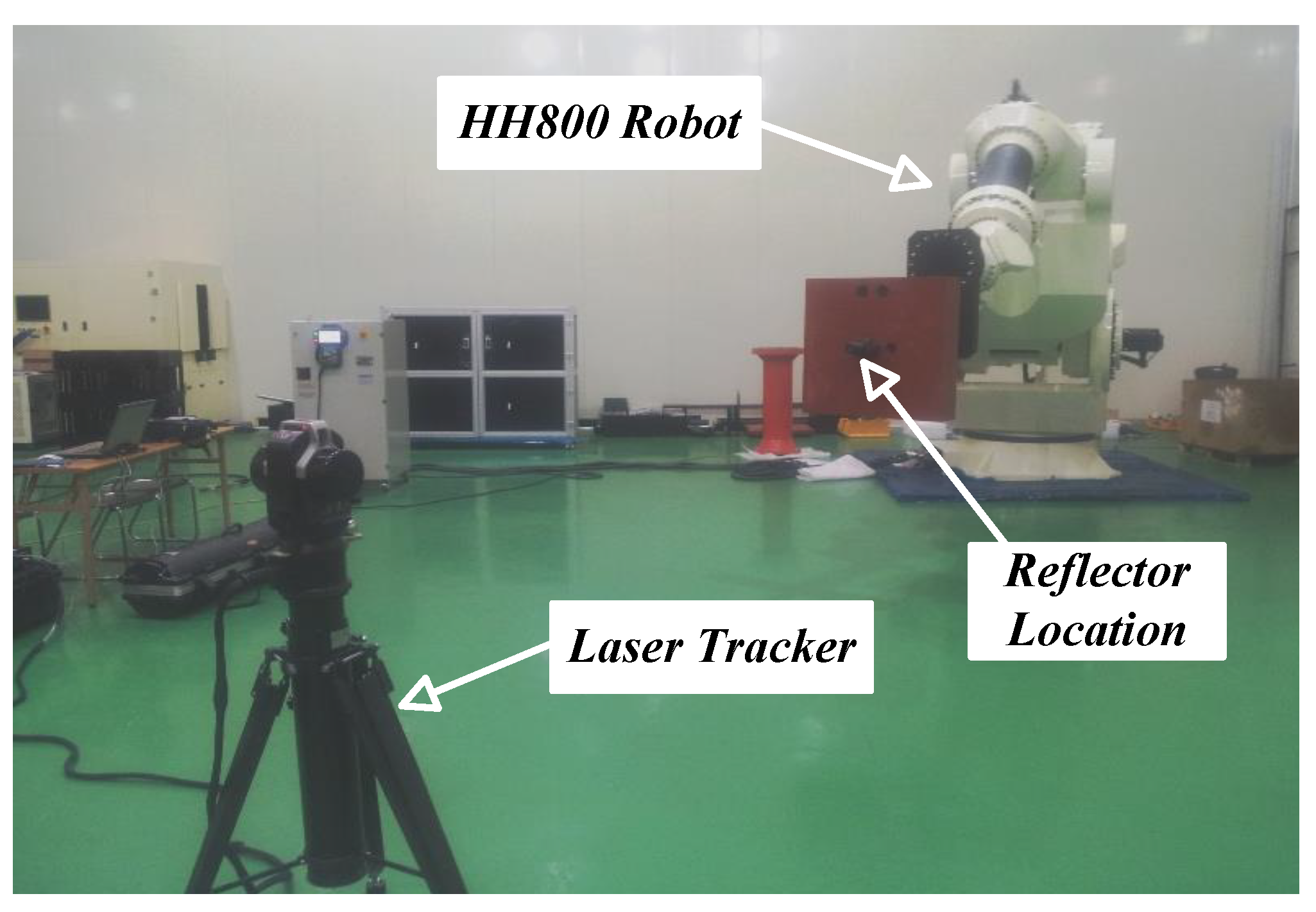
5. Experiment and Validation Results
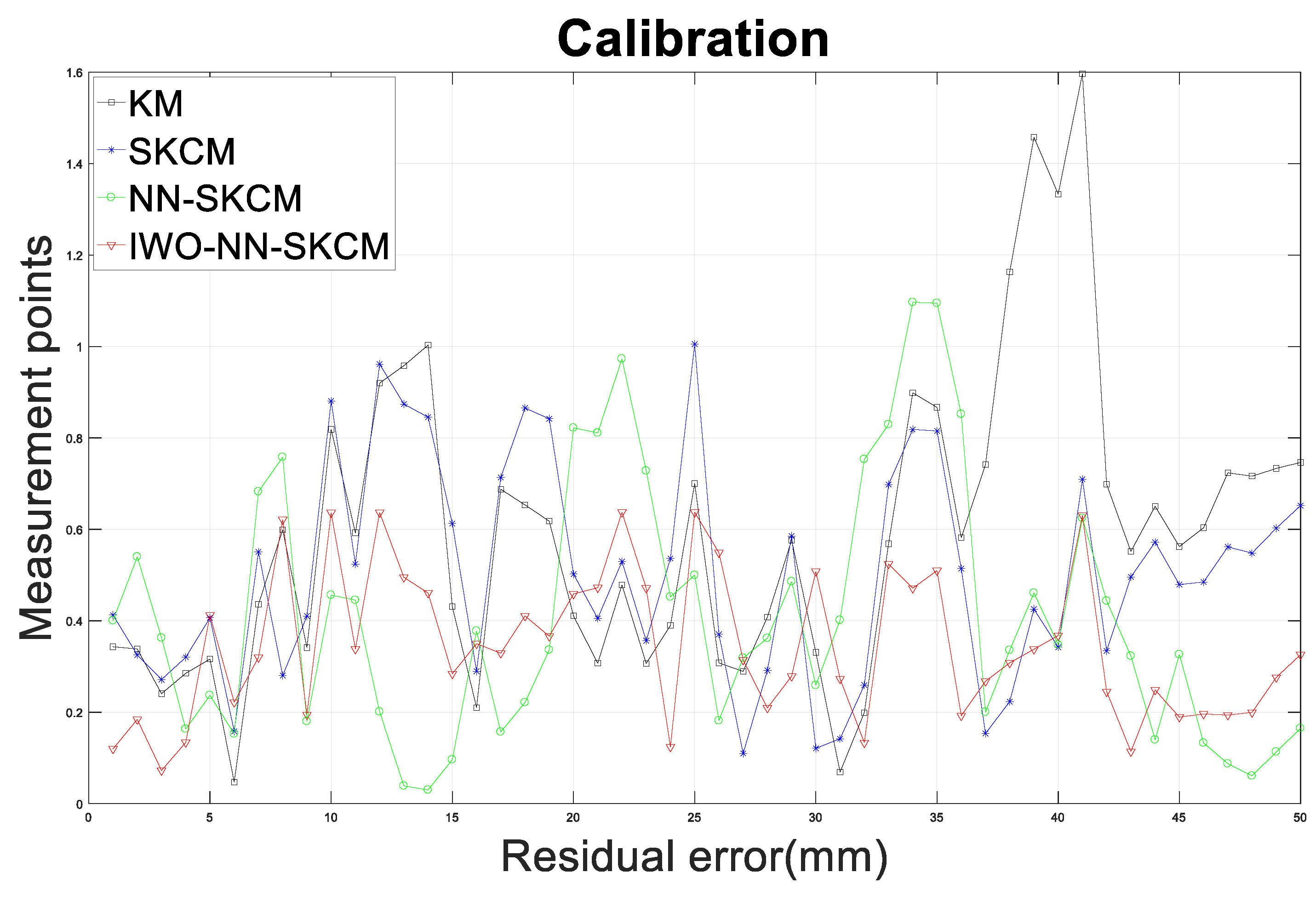
5.1. Experimental Calibration Results
5.2. Experimental Validation Results
5.3. Advantages of the IWO-NN Compensator
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mooring, B.W.; Roth, Z.S.; Driels, M.R. Fundamentals of Manipulator Calibration; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Brisan, C.; Hiller, M. Aspects of calibration and control of PARTNER robots. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Automation, Quality and Testing, Robotics, Cluj-Napora, Romania, 25–28 May 2006; Volume 2, pp. 272–277. [Google Scholar]
- Manne, R. Analysis of two partial-least-squares algorithms for multivariate calibration. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1987, 2, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, H.; Lin, Z. Determination of the identifiable parameters in robot calibration based on the POE formula. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2014, 30, 1066–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Nguyen, H.-N.; Kang, H.-J. Simultaneous identification of joint compliance and kinematic parameters of industrial robots. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2014, 15, 2257–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J.C. Others Introduction to Robotics: Mechanics and Control; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hayati, S.; Mirmirani, M. Improving the absolute positioning accuracy of robot manipulators. J. Robot. Syst. 1985, 2, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayati, S.; Tso, K.; Roston, G. Robot geometry calibration. In Proceedings of the 1988 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 24–29 April 1988; pp. 947–951. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, K.C. Kinematic analysis of manipulators using the zero reference position description. Int. J. Rob. Res. 1986, 5, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Roth, Z.S.; Hamano, F. A complete and parametrically continuous kinematic model for robot manipulators. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 13–18 May 1990; pp. 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, H.; Wang, L.K.; Roth, Z.S. Error-model-based robot calibration using a modified CPC model. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 1993, 10, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, K.; Park, F.C. Kinematic calibration using the product of exponentials formula. Robotica 1996, 14, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Kong, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Lin, Z. Complete, minimal and continuous error models for the kinematic calibration of parallel manipulators based on POE formula. Mech. Mach. Theory 2018, 121, 844–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.-P.; Kazerounian, K. Study and enumeration of singular configurations for the kinematic model of human arm. In Proceedings of the IEEE 26th Annual Northeast Bioengineering Conference (Cat. No. 00CH37114), Storrs, CT, USA, 8–9 April 2000; pp. 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Mooring, B.W. An improved method for identifying the kinematic parameters in a six axis robots. Comput. Eng. Proc. Int. Comput. Eng. Conf. Exhib. 1984 1984, 1, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.N.; Zhou, J.; Kang, H.J. A calibration method for enhancing robot accuracy through integration of an extended Kalman filter algorithm and an artificial neural network. Neurocomputing 2015, 151, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhou, W.; Li, H.; Mo, Y.; Ni, W.; Huang, Q. A New Kind of Accurate Calibration Method for Robotic Kinematic Parameters Based on the Extended Kalman and Particle Filter Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 3337–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Peng, Z.; Liu, Y. The identification of joint parameters for modular robots using fuzzy theory and a genetic algorithm. Robotica 2002, 20, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, D.E.; Lozinski, C.A.; Rourke, J.M. Industrial robot forward calibration method and results. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 1986, 108, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, R.P.; Knasinski, A.B. A Technique to Calibrate Industrial Robots with Experimental Verification. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1990, 6, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renders, J.-M.; Rossignol, E.; Becquet, M.; Hanus, R. Kinematic calibration and geometrical parameter identification for robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1991, 7, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becquet, M. Analysis of flexibility sources in robot structure. In Proceedings of the IMACS/IFAC. Symp. Modeling and Simulation of Distributed Parameters, Hiroshima, Japan, 6–9 October 1987; pp. 419–424. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, C.; Yuan, J.; Ni, J. Nongeometric error identification and compensation for robotic system by inverse calibration. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2000, 40, 2119–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, C.; Caro, S.; Garnier, S.; Furet, B. Joint stiffness identification of six-revolute industrial serial robots. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2011, 27, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lightcap, C.; Hamner, S.; Schmitz, T.; Banks, S. Improved positioning accuracy of the PA10-6CE robot with geometric and flexibility calibration. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2008, 24, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, A.; Tomatis, N.; Tapus, A.; Siegwart, R. Simultaneous localization and odometry calibration for mobile robot. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2003)(Cat. No. 03CH37453), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–31 October 2003; Volume 2, pp. 1499–1504. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lian, B.; Sun, T. Kinematic calibration of a 5-DoF parallel kinematic machine. Precis. Eng. 2016, 45, 242–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swevers, J.; Ganseman, C.; Tukel, D.B.; De Schutter, J.; Van Brussel, H. Optimal robot excitation and identification. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1997, 13, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Kang, H.-J. A hybrid least-squares genetic algorithm--based algorithm for simultaneous identification of geometric and compliance errors in industrial robots. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2015, 7, 1687814015590289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, A.; Wu, D.; Ma, Z. Robot calibration based on multi-thread particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the 2008 6th IEEE International Conference on Industrial Informatics, Daejeon, Korea, 13–16 July 2008; pp. 454–457. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, G. Manipulator calibration based on PSO-RBF neural network error model. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2073, 20026. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kwak, Y.K. Calibration of geometric and non-geometric errors of an industrial robot. Robotica 2001, 19, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, P.Y.; Yang, G. Calibration of industrial robots with product-of-exponential (poe) model and adaptive neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2015; pp. 1448–1454. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning Internal Representations by Error Propagation. In Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in Macrostructure of Cognition; Badford: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986; Volume I. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, M.R.; Patil, R.B. Universal approximation theorem for interval neural networks. Reliab. Comput. 1998, 4, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.-N.; Le, P.-N.; Kang, H.-J. A new calibration method for enhancing robot position accuracy by combining a robot model--based identification approach and an artificial neural network--based error compensation technique. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 1687814018822935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, G.; Liu, F.; San, H.; Wu, X.; Wang, W. Hybrid optimal kinematic parameter identification for an industrial robot based on BPNN-PSO. Complexity 2018, 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Mao, C.; Hang, Q. A robot calibration method based on joint angle division and an artificial neural network. Math. Probl. Eng. 2019, 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takanashi, N. 6 DOF manipulators absolute positioning accuracy improvement using a neural-network. In Proceedings of the EEE International Workshop on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Towards a New Frontier of Applications, Ibaraki, Japan, 3–6 July 1990; pp. 635–640. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Tang, Z.; Tamura, H.; Ishii, M.; Sun, W.D. An improved backpropagation algorithm to avoid the local minima problem. Neurocomputing 2004, 56, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-S.; Xu, X.-H. Genetic neural network and application in welding robot error compensation. In Proceedings of the 2005 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, Guangzhou, China, 18–21 August 2005; Volume 7, pp. 4070–4075. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.; Luo, M.; Bai, K.; Chen, S. A precise positioning method for a puncture robot based on a PSO-optimized BP neural network algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Chen, Y. Hybrid teaching--learning-based optimization and neural network algorithm for engineering design optimization problems. Knowl. Based Syst. 2020, 187, 104836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, J.; Naik, B.; Pelusi, D.; Krishna, A.V. A Comprehensive Review and Performance Analysis of Firefly Algorithm for Artificial Neural Networks. In Nature-Inspired Computation in Data Mining and Machine Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 137–159. [Google Scholar]
- Giri, R.; Chowdhury, A.; Ghosh, A.; Das, S.; Abraham, A.; Snasel, V. A modified invasive weed optimization algorithm for training of feed-forward neural networks. In Proceedings of the Conference Proceedings—IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Istanbul, Turkey, 10–13 October 2010; pp. 3166–3173. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrabian, A.R.; Lucas, C. A novel numerical optimization algorithm inspired from weed colonization. Ecol. Inform. 2006, 1, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, P.-N.; Kang, H.-J. Robot Manipulator Calibration Using a Model Based Identification Technique and a Neural Network With the Teaching Learning-Based Optimization. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 105447–105454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| D-H Parameters of the Main Open Chain | ||||||
| i | αi−1 (deg) | ai−1 (m) | βi−1 (deg) | bi−1 (m) | di (deg) | θi (deg) |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | θ1 |
| 2 | 90 | 0.515 | - | - | 0 | θ2 |
| 3 | 0 | 1.6 | 0 | - | 0 | θ3 |
| 4 | 90 | 0.35 | - | - | 1.9 | θ4 |
| 5 | −90 | 0 | - | - | 0 | θ5 |
| 6 | 90 | 0 | - | - | 0.445 | θ6 |
| T | - | −0.45 | - | 0.11 | 0.930 | - |
| D-H Parameters of the Main Open Chain | ||||||
| L5 (m) | 0.8 | L4 (m) | 1.6 | L3 (m) | 0.8 | |
| K2 | K3 | K4 | K5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stiffness | 6.159 × 107 | 4.388 × 106 | 3.151 × 106 | 2.220 × 106 |
| D-H Parameters of the Main Open Chain | ||||||
| i | αi−1 (deg) | ai−1 (m) | βi−1 (deg) | bi−1 (m) | di (deg) | θI (deg) |
| 1 | 0.8752 | 0.0003 | 0.006 | 0.0001 | 0.0976 | 0.3468 |
| 2 | 89.9412 | 0.5157 | - | - | 0 (X) | −0.8836 |
| 3 | 0.0133 | 1.5998 | 0.001 | - | −0.0014 | −1.2385 |
| 4 | 90.1172 | 0.3545 | - | - | 1.8862 | 3.3033 |
| 5 | −90.038 | 0.0002 | - | - | 4.087 × 10−5 | 2.5786 |
| 6 | 90.0371 | 0.0003 | - | - | 0.445 (X) | 0 (X) |
| T | - | −0.4511 | - | 0.0111 | 0.9279 | - |
| D-H Parameters of the Main Open Chain | ||||||
| L5 (m) | 0.7996 | L4 (m) | 1.601 | L3 (m) | 0.8 (X) | |
| Mean (mm) | Max. (mm) | Std. (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before calibration | 4.5969 | 6.6664 | 0.8408 |
| KC | 0.5961 | 1.5967 | 0.3299 |
| SKC | 0.5038 | 1.005 | 0.2346 |
| NN-SKC | 0.4103 | 1.0967 | 0.2814 |
| IWO-NN-SKCM | 0.3450 | 0.6374 | 0.1624 |
| Mean (mm) | Max. (mm) | Std. (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before calibration | 4.4266 | 6.2749 | 0.6772 |
| KC | 0.5981 | 1.4293 | 0.285 |
| SKC | 0.5458 | 1.0078 | 0.2142 |
| NN-SKC | 0.5187 | 1.0532 | 0.2642 |
| IWO-NN-SKCM | 0.4662 | 0.6538 | 0.1333 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le, P.-N.; Kang, H.-J. A Robotic Calibration Method Using a Model-Based Identification Technique and an Invasive Weed Optimization Neural Network Compensator. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7320. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207320
Le P-N, Kang H-J. A Robotic Calibration Method Using a Model-Based Identification Technique and an Invasive Weed Optimization Neural Network Compensator. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(20):7320. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207320
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe, Phu-Nguyen, and Hee-Jun Kang. 2020. "A Robotic Calibration Method Using a Model-Based Identification Technique and an Invasive Weed Optimization Neural Network Compensator" Applied Sciences 10, no. 20: 7320. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207320
APA StyleLe, P.-N., & Kang, H.-J. (2020). A Robotic Calibration Method Using a Model-Based Identification Technique and an Invasive Weed Optimization Neural Network Compensator. Applied Sciences, 10(20), 7320. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207320





