Entropic Ranks: A Methodology for Enhanced, Threshold-Free, Information-Rich Data Partition and Interpretation
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. From Rank Products to Entropic Ranks
1.2. Entropy in Biostatistics
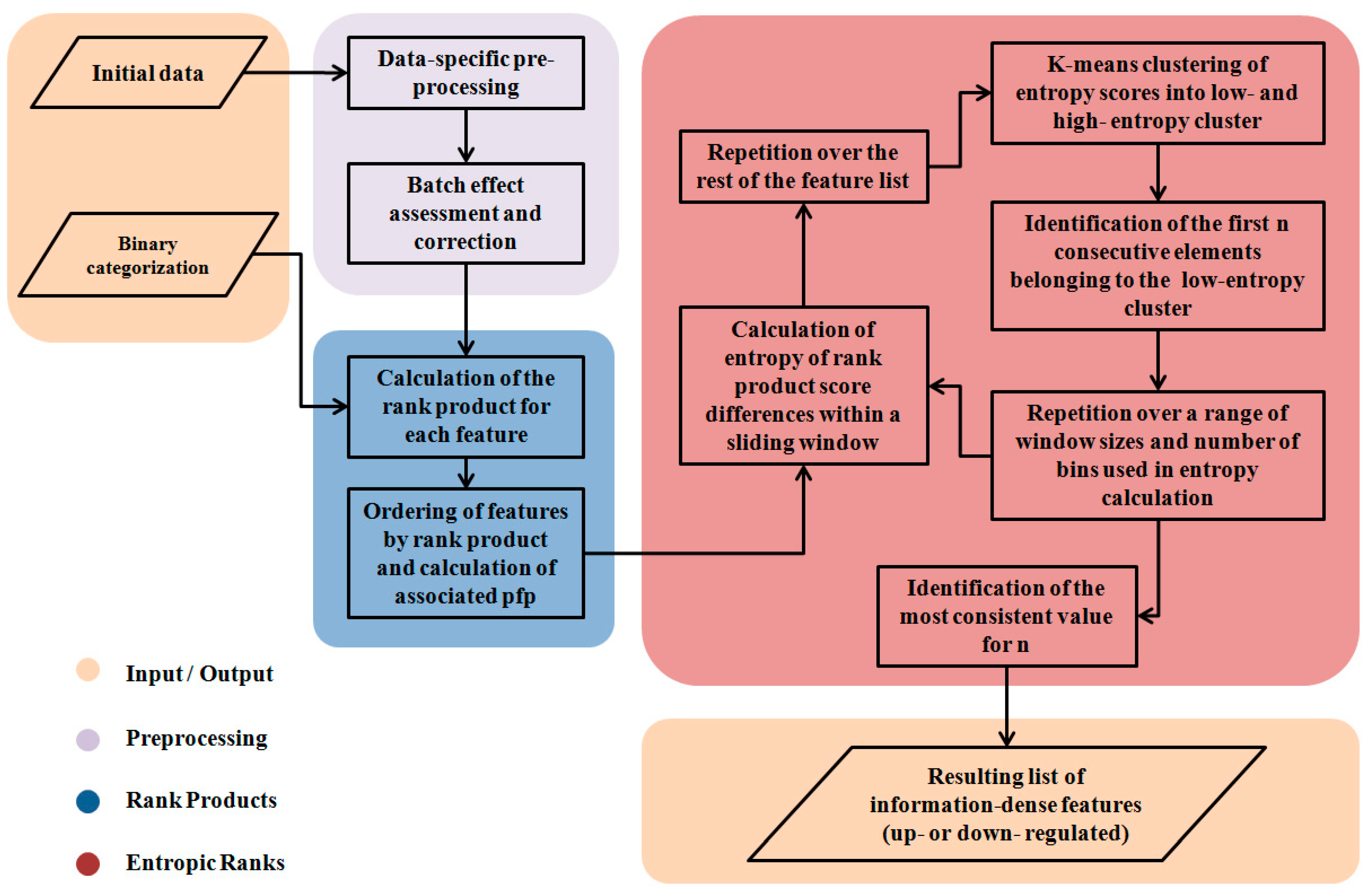
2. Methods
2.1. Rank Product Requirements
- S << N (N: the full set of features);
- Independence of measurements between replicate arrays;
- The intensity of each feature over the range of samples is largely homoscedastic;
- The majority of non-zero fold changes between the sample groups are independent of each other.
2.2. The Segmentation Problem
2.3. Partitioning the RP Distribution
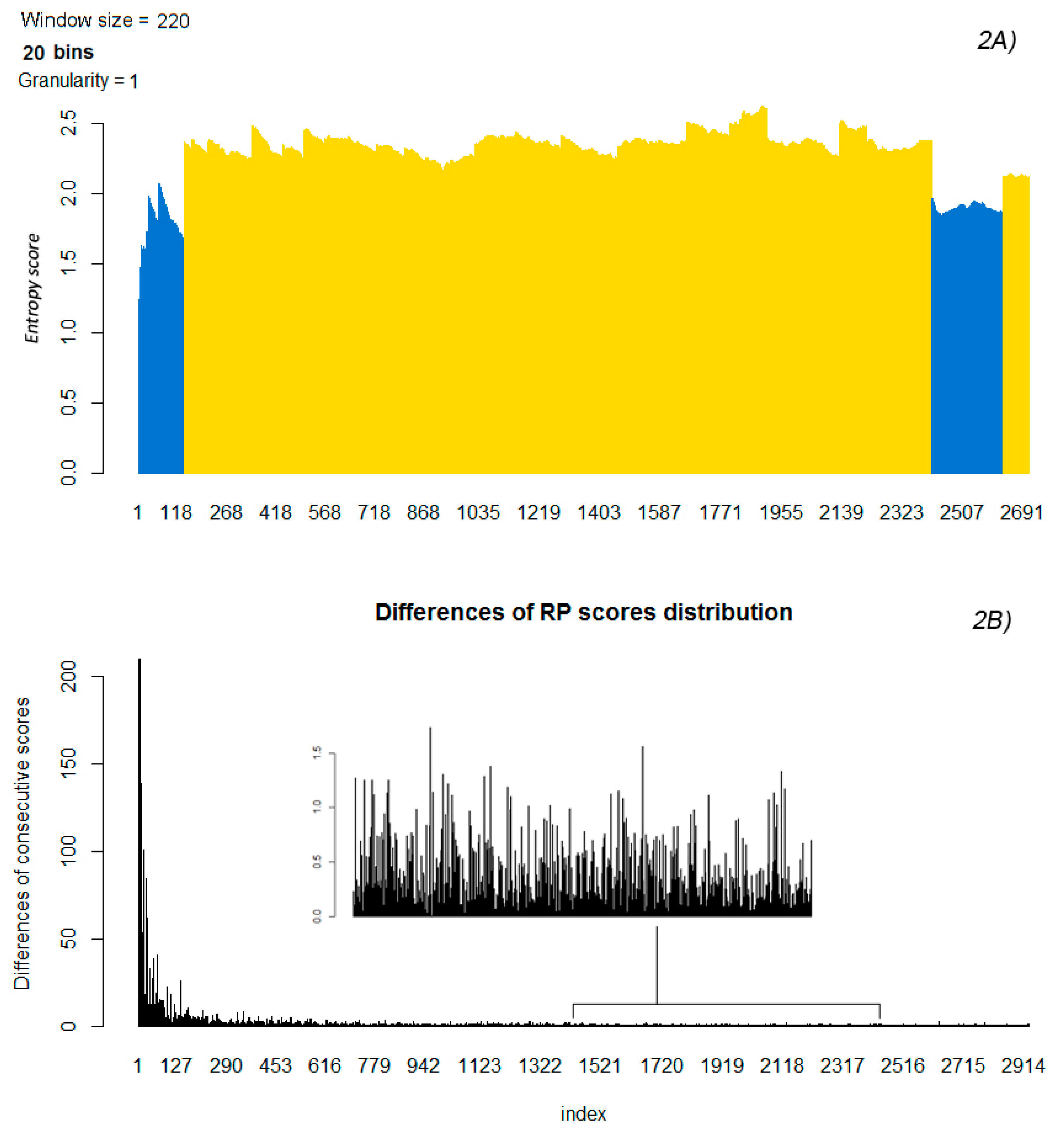
2.4. Differences of Consecutive RP Scores and Entropy
2.5. Partitioning the Entropy Distribution
2.6. K-means Clustering to Calculate n
2.7. Implementation
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation Criteria
3.2. Simulated Data
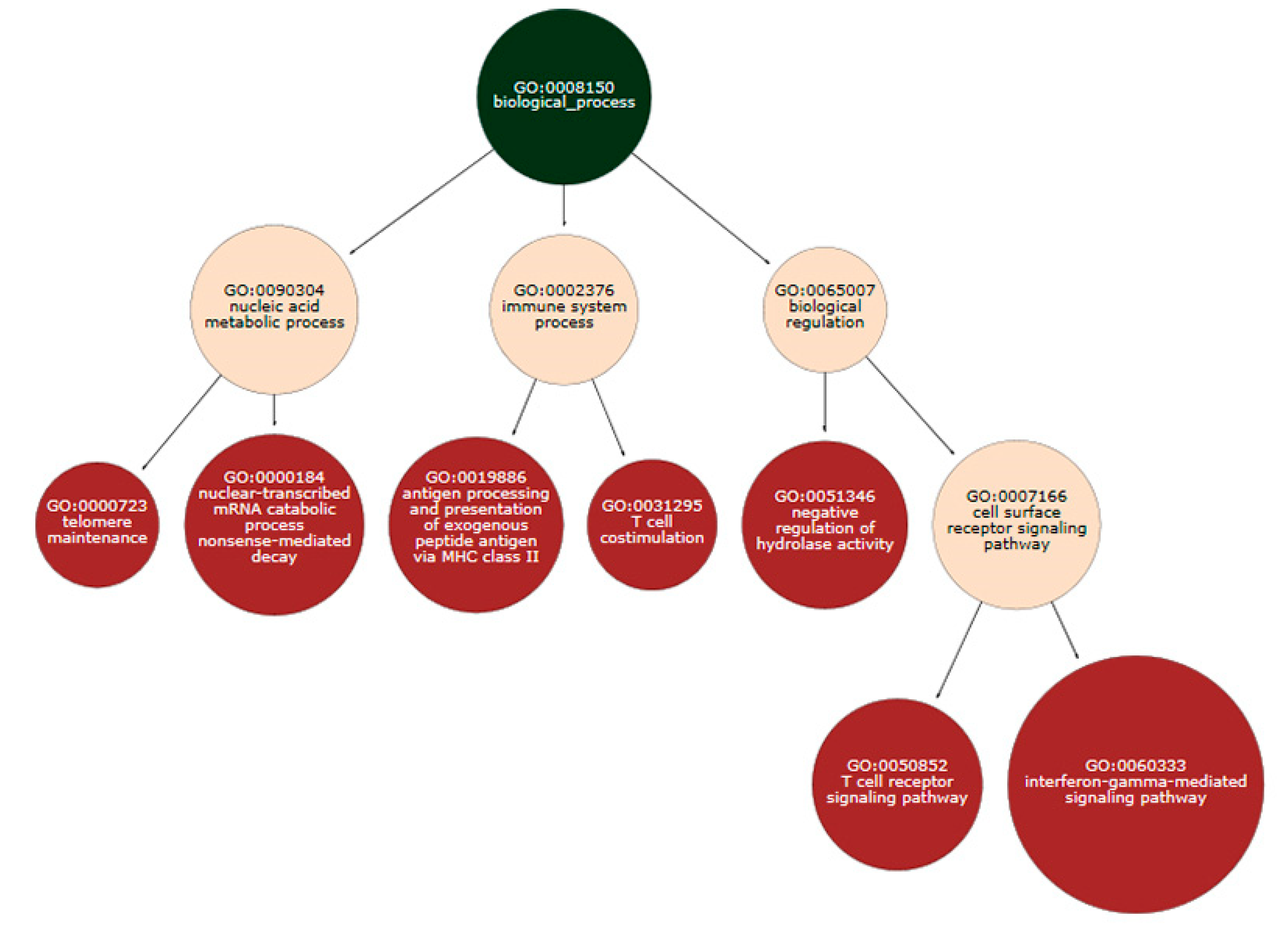
3.3. Series GSE12288
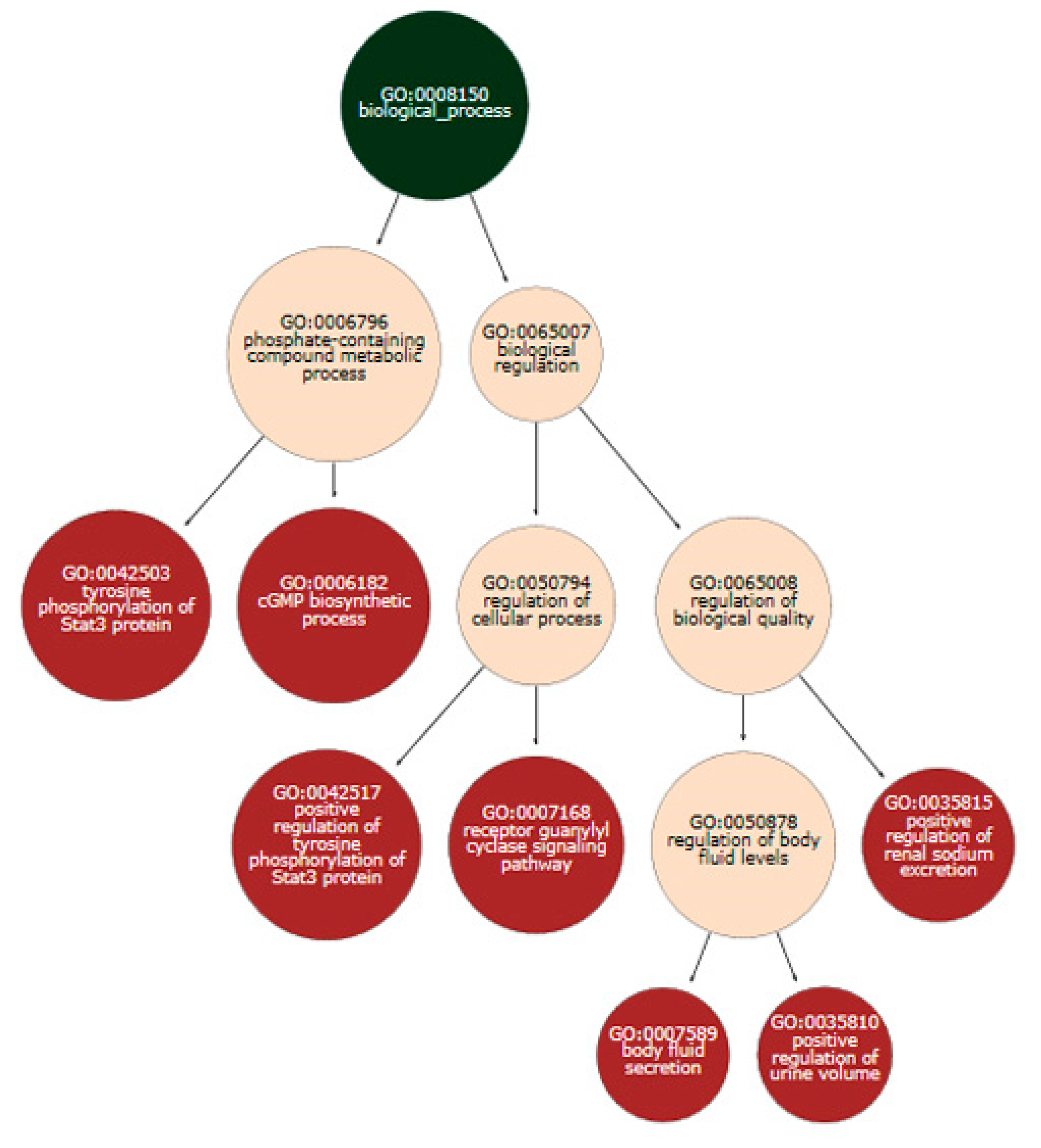
3.4. Series GSE69486
3.5. Series GSE60767
3.6. Series GSE42861
3.7. Series SRP127667
4. Conclusions
Features of Entropic Ranks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsimring, L.S. Noise in Biology. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2014, 77, 026601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leek, J.; McShane, B.B.; Gelman, A.; Colquhoun, D.; Nuijten, M.B.; Goodman, S. Five ways to fix statistics. Nature 2017, 551, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, D.S. ‘One-size-fits-all’ threshold for P values under fire. Nature 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitling, R.; Armengaud, P.; Amtmann, A.; Herzyk, P. Rank products: A simple, yet powerful, new method to detect differentially regulated genes in replicated microarray experiments. FEBS Lett. 2004, 573, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalman, M.R.; Deeter, A.; Nimishakavi, G.; Duan, Z. Fold change and p-value cutoffs significantly alter microarray interpretations. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federico, A.; Serra, A.; Kieu Ha, M.; Kohonen, P.; Choi, J.-S.; Liampa, I.; Nymark, P.; Sanabria, N.; Cattelani, L.; Fratello, M.; et al. Transcriptomics in Toxicogenomics, Part II: Preprocessing and Differential Expression Analysis for High Quality Data. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Carratore, F.; Jankevics, A.; Eisinga, R.; Heskes, T.; Hong, F.; Breitling, R. RankProd 2.0: A refactored bioconductor package for detecting differentially expressed features in molecular profiling datasets. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2774–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.Y. A Simple Rank Product Approach for Analyzing Two Classes. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Krishnan, A.; Mondry, A. An Entropy-based gene selection method for cancer classification using microarray data. BMC Bioinform. 2005, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, H. Entropy based sub-dimensional evaluation and selection method for DNA microarray data classification. Bioinformation 2008, 3, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlanello, C.; Serafini, M.; Merler, S.; Jurman, G. Entropy-based gene ranking without selection bias for the predictive classification of microarray data. BMC Bioinform. 2003, 4, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Xin, Y.; Zhao, Y. Cancer classification using entropy analysis in fractional Fourier domain of gene expression profile. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2018, 32, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, R.; Fang, H.; Cheng, F.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Y. Entropy-based consensus clustering for patient stratification. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2691–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, T.Q.; Ryu, T.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, D. Inferring Gene Regulatory Networks from Microarray Time Series Data Using Transfer Entropy. Twent. IEEE Int. Symp. Comput. Based Med Syst. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, C.; Mcclung, C.; Donald, B. A maximum entropy algorithm for rhythmic analysis of genome-wide expression patterns. Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Bioinform. Conf. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambelli, F.; Mastropasqua, F.; Picardi, E.; D’Erchia, A.M.; Pesole, G.; Pavesi, G. RNentropy: An entropy-based tool for the detection of significant variation of gene expression across multiple RNA-Seq experiments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, M.V.; Ferreira, T.A.; Freitas, A.C.; Balbino, V.Q. An entropy-based approach for the identification of phylogenetically informative genomic regions of Papillomavirus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 2026–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eisinga, R.; Breitling, R.; Heskes, T. The exact probability distribution of the rank product statistics for replicated experiments. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausser, J.; Strimmer, K. Entropy inference and the James-Stein estimator, with application to nonlinear gene association networks. J. Mach. Learn. 2009, 10, 1469–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.Y.; Tan, C.M.; Kou, Y.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Meirelles, G.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: Interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutsandreas, T.; Binenbaum, I.; Pilalis, E.; Valavanis, I.; Papadodima, O.; Chatziioannou, A. Analyzing and visualizing genomic complexity for the derivation of the emergent molecular networks. Int. J. Monit. Surveill. Technol. 2016, 4, 30–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- UZH, Robinson Statistical Bioinformatics Group. Available online: http://imlspenticton.uzh.ch/robinson_lab/benchmark_collection/ (accessed on 1 December 2018).
- Sinnaeve, P.R.; Donahue, M.P.; Grass, P.; Seo, D.; Vonderscher, J.; Chibout, S.-D.; Kraus, W.E.; Sketch, M., Jr.; Nelson, C.; Ginsburg, G.S.; et al. Gene expression patterns in peripheral blood correlate with the extent of coronary artery disease. PLoS ONE 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.P.; Grondin, C.J.; Johnson, R.J.; Sciaky, D.; King, B.L.; Mcmorran, R.; Wiegers, J.; Wiegers, T.C.; Mattingly, C.J. The Comparative Toxicogenomics Database: Update 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillet, M.; Lynch, J.M.; Sanna, B.; York, A.J.; Zheng, Y.; Molkentin, J.D. Cdc42 is an antihypertrophic molecular switch in the mouse heart. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 3079–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, R.; Zheng, D.; Bai, J.; Xie, J.; Dai, Q.; Xu, B. Altered melusin pathways involved in cardiac remodeling following acute myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2012, 21, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, S.; Vasilevsky, N.; Engelstad, M.; Foster, E.; McMurry, J.; Ayme, S.; Baynam, G.; Bello, S.M.; Boerkoel, C.F.; Boycott, K.M.; et al. The Human Phenotype Ontology in 2017. Nucl. Acids Res. 2017, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, J.A.; Eppig, J.T.; Kadin, J.A.; Richardson, J.E.; Smith, C.L.; Bult, C.J. Mouse Genome Database (MGD)-2017: Community knowledge resource for the laboratory mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringwald, M. The Mouse Gene Expression Database (GXD). Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, D.; Mundo, A.F.; Haw, R.; Milacic, M.; Weiser, J.; Wu, G.; Caudy, M.; Garapati, P.; Gillespie, M.; Kamdar, M.R.; et al. The Reactome pathway knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabregat, A.; Jupe, S.; Matthews, L.; Sidiropoulos, K.; Gillespie, M.; Garapati, P.; Robin, H.; Bijay, J.; Florian, K.; Bruce, M.; et al. The Reactome Pathway Knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, N.; Lee, E. Antioxidant effects of selenocysteine on replicative senescence in human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. BMB Rep. 2017, 50, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DbGaP/Database of Genotypes and Phenotypes National Center for Biotechnology Information. National Library of Medicine (NCBI/NLM). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gap (accessed on 21 March 2019).
- Santos, A.; Tsafou, K.; Stolte, C.; Pletscher-Frankild, S.; O’Donoghue, S.I.; Jensen, L.J. Comprehensive comparison of large-scale tissue expression datasets. Peer J. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachmann, A.; Torre, D.; Keenan, A.B.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lee, H.J.; Silverstein, M.C.; Wang, L.; Maayan, A. Massive Mining of Publicly Available RNA-seq Data from Human and Mouse. Nat. Commun 2017, 9, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, A.I.; Wiltshire, T.; Batalov, S.; Lapp, H.; Ching, K.A.; Block, D.; Zhang, J.; Soden, R.; Hayakawa, M.; Kreiman, G.; et al. A gene atlas of the mouse and human protein-encoding transcriptomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6062–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, G.S.; Weir, B.A.; Vazquez, F.; Tamayo, P.; Scott, J.A.; Rusin, S.; East-Seletsky, A.; Ali, L.D.; Gerath, W.F.; Pantel, S.E.; et al. Parallel genome-scale loss of function screens in 216 cancer cell lines for the identification of context-specific genetic dependencies. Sci. Data 2014, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukali, C.I.; Aydin, M.; Ozkok, E.; Bilge, E.; Orhan, N.; Zengin, A.; Kara, I. Do schizophrenia and bipolar disorders share a common disease susceptibility variant at the MMP3 gene? Prog. Neuro Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 33, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurvich, A.; Begemann, M.; Dahm, L.; Sargin, D.; Miskowiak, K.; Ehrenreich, H. A role for prostaglandins in rapid cycling suggested by episode-specific gene expression shifts in peripheral blood mononuclear cells: A preliminary report. Bipolar Disor. 2014, 16, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitz, J.B.; Teague, T.K.; Misaki, M.; Macaluso, M.; Wurfel, B.E.; Meyer, M.; Drevets, D.; Yates, W.; Gleason, O.; Drevets, W.C.; et al. Treatment of bipolar depression with minocycline and/or aspirin: An adaptive, 2x2 double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase IIA clinical trial. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossner, P.; Tulupova, E.; Rossnerova, A.; Libalova, H.; Honkova, K.; Gmuender, H.; Pastorkova, A.; Svecova, V.; Topinka, J.; Sram, R.J. Reduced gene expression levels after chronic exposure to high concentrations of air pollutants. Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2015, 780, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM (TM). McKusick-Nathans Institute of Genetic Medicine, Johns Hopkins University (Baltimore, MD) and National Center for Biotechnology Information, National Library of Medicine (Bethesda, MD). Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/ (accessed on 21 March 2019).
- Rajagopalan, S.; Brook, R.D. Air pollution and type 2 diabetes: Mechanistic insights. Diabetes 2012, 61, 3037–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene Ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Expansion of the Gene Ontology knowledgebase and resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45. [CrossRef]
- Iii, C.A. Lung Cancer, Cardiopulmonary Mortality, and Long-term Exposure to Fine Particulate Air Pollution. JAMA 2002, 287, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huiming, L.; Xin, Q.; Qin’geng, W. Heavy Metals in Atmospheric Particulate Matter: A Comprehensive Understanding Is Needed for Monitoring and Risk Mitigation. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 47, 13210–13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Aryee, M.J.; Padyukov, L.; Fallin, M.D.; Hesselberg, E.; Runarsson, A.; Reinius, L.; Acevedo, N.; Taub, M.; Ronninger, M.; et al. Epigenome-wide association data implicate DNA methylation as an intermediary of genetic risk in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kular, L.; Liu, Y.; Ruhrmann, S.; Zheleznyakova, G.; Marabita, F.; Gomez-Cabrero, D.; James, T.; Ewing, E.; Lindén, M.; Górnikiewicz, B.; et al. DNA methylation as a mediator of HLA-DRB1*15:01 and a protective variant in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slenter, D.N.; Kutmon, M.; Hanspers, K.; Riutta, A.; Windsor, J.; Nunes, N.; Mélius, J.; Cirillo, E.; Coort, S.L.; Digles, D.; et al. WikiPathways: A multifaceted pathway database bridging metabolomics to other omics research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohensinner, P.J.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Telomere dysfunction, autoimmunity and aging. Aging Dis. 2011, 2, 524. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hohensinner, P.J.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Targets of immune regeneration in rheumatoid arthritis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgin-Lavialle, S.; Aouba, A.; Mouthon, L.; Londono-Vallejo, J.A.; Lepelletier, Y.; Gabet, A.S.; Hermine, O. The telomere/telomerase system in autoimmune and systemic immune-mediated diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2010, 9, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehner, M.J.; Coehlo, N.K.; Zhang, Z.; Bianco, F.B.; Wang, J.; Rice, J.A.; Protopapas, P.; Alcock, C.; Axelrod, T.; Byun, Y.-I.; et al. The TAOS Project: Statistical Analysis of Multi-Telescope Time Series Data. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2010, 122, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aasi, J.; Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abernathy, M.R.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; et al. First low frequency all-sky search for continuous gravitational wave signals. Phys. Rev. D. 2016, 93, 042007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitling, R.; Herzyk, P. Rank-Based Methods As A Non-Parametric Alternative Of The T-Statistic For The Analysis Of Biological Microarray Data. J. Bioinform. Comput. Biol. 2005, 3, 1171–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.D.; Campbell, M.J.; Kejariwal, A.; Mi, H.; Karlak, B.; Daverman, R.; Diemer, K.; Muruganujan, A.; Narechania, A. PANTHER: A library of protein families and subfamilies indexed by function. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2129–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, K.C.; Blankesteijn, W.M. Wnt Signaling in Cardiac Disease. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 5, 1183–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| GEO Accession | Type | Original Publication S | Entropic Ranks S | RP Maximum p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE12288 | Differentially expressed | 160 | 18 * | <0.0001 |
| 86 ** | <0.0001 | |||
| GSE69486 | Upregulated | 127 | 135 | 0.0027 |
| Downregulated | 330 | 89 | 0.0083 | |
| GSE60767 [winter 2009] | Upregulated | 0 | 29 | <0.0001 |
| Downregulated | 0 | 53 | <0.0001 | |
| GSE60767 [summer 2009] | Upregulated | 0 | 33 | <0.0001 |
| Downregulated | 0 | 26 | <0.0001 | |
| GSE60767 [winter 2010] | Upregulated | 0 | 34 | <0.0001 |
| Downregulated | 0 | 41 | <0.0001 | |
| GSE42861 | Upregulated | NA | 24 | <0.0001 |
| Downregulated | NA | 98 | <0.0001 | |
| SRP127667 | Upregulated | NA | 32 | <0.0001 |
| Downregulated | NA | 37 | <0.0001 |
| GEO Accession | Organism | Type of Samples | Array | Samples | Cases | Controls |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE12288 | H. sapiens | Total RNA from leukocytes in peripheral blood | Affymetrix Human Genome U133A Array | 222 | 110 | 112 |
| GSE69486 | H. sapiens | Total RNA from fibroblasts from skin biopsies | Illumina HumanHT-12 V4.0 Expression Beadchip | 12 | 10 | 2 |
| GSE60767 | H. sapiens | Total RNA was extracted from leukocytes | Illumina HumanHT-12 V3.0 Expression Beadchip | 466 | 312 | 154 |
| GSE42861 | H. sapiens | DNA from blood leukocytes | Illumina HumanMethylation450 BeadChip | 44 | 20 | 24 |
| SRP127667 | H. sapiens | DNA from sorted cardiac myocyte nuclei | Illumina HiSeq 2500 | 13 | 10 | 3 |
| Disease Name | Disease ID | Disease Categories | Corrected p-Value for Original Analysis | Corrected p-Value for Entropic Ranks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stroke | MESH:D020521 | Cardiovascular disease|nervous system disease | 0.00408 | 0.00504 |
| Infarction, Middle Cerebral Artery | MESH:D020244 | Cardiovascular disease|nervous system disease | 5.88 × 10−6 | 0.00712 |
| Cardiovascular Diseases | MESH:D002318 | Cardiovascular disease | - | 0.01264 |
| Cerebral Arterial Diseases | MESH:D002539 | Cardiovascular disease|nervous system disease | - | 0.01484 |
| Cerebral Infarction | MESH:D002544 | Cardiovascular disease|nervous system disease | - | 0.01484 |
| Intracranial Arterial Diseases | MESH:D020765 | Cardiovascular disease|nervous system disease | - | 0.01829 |
| Vascular Diseases | MESH:D014652 | Cardiovascular disease | 1.23 × 10−4 | 0.01950 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Lastic, H.-X.; Liampa, I.; G. Georgakilas, A.; Zervakis, M.; Chatziioannou, A. Entropic Ranks: A Methodology for Enhanced, Threshold-Free, Information-Rich Data Partition and Interpretation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7077. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207077
de Lastic H-X, Liampa I, G. Georgakilas A, Zervakis M, Chatziioannou A. Entropic Ranks: A Methodology for Enhanced, Threshold-Free, Information-Rich Data Partition and Interpretation. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(20):7077. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207077
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Lastic, Hector-Xavier, Irene Liampa, Alexandros G. Georgakilas, Michalis Zervakis, and Aristotelis Chatziioannou. 2020. "Entropic Ranks: A Methodology for Enhanced, Threshold-Free, Information-Rich Data Partition and Interpretation" Applied Sciences 10, no. 20: 7077. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207077
APA Stylede Lastic, H.-X., Liampa, I., G. Georgakilas, A., Zervakis, M., & Chatziioannou, A. (2020). Entropic Ranks: A Methodology for Enhanced, Threshold-Free, Information-Rich Data Partition and Interpretation. Applied Sciences, 10(20), 7077. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207077







