Abstract
This paper focuses on the domain-specific senses of words and proposes a method for detecting predominant sense depending on each domain. Our Domain-Specific Senses (DSS) model is an unsupervised manner and detects predominant senses in each domain. We apply a simple Markov Random Walk (MRW) model to ranking senses for each domain. It decides the importance of a sense within a graph by using the similarity of senses. The similarity of senses is obtained by using distributional representations of words from gloss texts in the thesaurus. It can capture large semantic context and thus does not require manual annotation of sense-tagged data. We used the Reuters corpus and the WordNet in the experiments. We applied the results of domain-specific senses to text classification and examined how DSS affects the overall performance of the text classification task. We compared our DSS model with one of the word sense disambiguation techniques (WSD), Context2vec, and the results demonstrate our domain-specific sense approach gains 0.053 F1 improvement on average over the WSD approach.
1. Introduction
The most frequent words generally have many senses than less frequent words [1], so determining a proper sense of the word in a context is a challenging task in Natural Language Processing (NLP). The benefits from disambiguating a sense of a word can utilize in many applications, that is, Machine Translation, Question Answering, and Text Classification. Various techniques are applied to identify the actual sense of a word. The simplified version is to apply the First Sense Heuristic (FSH) that chooses the first or predominant sense of a word. It is often used as a baseline for supervised word sense disambiguation (WSD) systems [2,3] because it is powerful, especially for words with highly skewed sense distributions [2,4]. However, the disadvantage of the FSH obtained from the WordNet is a small amount of SemCor corpus which causes data sparseness problems, that is, we cannot apply the FSH to the senses that do not appear in SemCor corpus. Furthermore, the FSH is not based on the domain but instead on the simple frequency counts of SemCor corpus. Consider the noun word, “party”. There are five noun senses of “party” in the WordNet [5]. The first sense of “party” is “an organization to gain political power”, and the usage of it would frequently be found in the domain of “politics” more than the “law” domain. On the other hand, the fifth sense of “party”, that is, “a person involved in legal proceedings” tends to be used in the “law” domain. A technique, predominant sense detection or domain-specific sense identification is an approach for detecting a sense of a word which is a most frequent use in a specific domain.
In this paper, we focus on domain-specific senses of nouns and verbs and propose a method for detecting predominant sense in each domain/category. Our model employs distributed representations of words learned by using Word2Vec and thus does not require manual annotation of sense-tagged data. We apply a simple Markov Random Walk (MRW) model to rank senses for each domain. The sense similarity scores which is used to decide the importance of senses is obtained by using distributed representations of, WordNet. To examine the effectiveness of our detection method, we apply the results to text classification on the dataset collected from the Reuters corpus. The result obtained by the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) shows that our model gains great improvement over the result without assigning the Domain-Specific Senses (DSS). Moreover, we compared our DSS model with one of the word sense disambiguation techniques, Context2vec [6] in the text classification task. The results demonstrate the DSS approach gains a great improvement over the WSD approach.
The main contributions of our work can be summarized—(1) we propose a method for identifying domain-specific noun senses which leverage distributed representations of words and thus do not require manual annotation of sense-tagged data, while some of the existing work required a considerable amount of hand-labeling data. (2) From the perspective of robustness, the method is automated and required only documents from the given domains/categories such as the Reuters corpus, and thesaurus with gloss texts such as WordNet. The method is easily applicable to a new domain or sense inventory, given sufficient documents. (3) We empirically evaluate our model and show that the result of domain-specific senses is effective than WSD in the text classification task.
2. Related Work
Semantic-oriented applications such as Question Answering and Machine Translation systems need not only fine-grained and large-scale semantic knowledge but also tune the sense of the word heuristic depending on the domain in which the word is used. Magnini et al. presented a lexical resource where WordNet 2.0 synsets were annotated with Subject Field Codes (SFC) [7,8]. They annotated 96% of WordNet synsets of the noun hierarchy, while mapping domain labels for word senses were semi-automated and required hand-labeling.
Several authors have attempted to use different techniques to solve with the WSD technique [9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. Some of them addressed the problem and have attempted to use specific domain knowledge and showed that it improves WSD performance compared with generic supervised WSD [16,17,18]. Abualhaija et al. [19] proposed the D-bee method which assumed hive as target word is chosen at random and the number of bees was determined from the number of word sense of the target word. Each bee carried one sense and then move to find the random senses of the next word to calculate the similarity value, the bee with the maximum similarity value is used for identifying the proper senses in a context. Lopez-Arevalo et al. [20] proposed an unsupervised WSD approach for lexical sample task with two corpora containing test corpus which had ambiguous words and their instances were assigned by hand-labeling. The second was auxiliary corpus which was generated from web pages to obtain more contexts and their instances are unlabeled. They reported that the results by using two domain-specific corpora(finance, sports) had better performance compared with general-domain corpus (British National Corpus [BNC]), and even better than FS heuristics.
McCarthy et al. proposed an automated method for assigning predominant noun senses [21]. They found words with a similar distribution to the target word from parsed data. The motivation for their work is similar to ours, that is, to capture predominant senses in different domains by ranking senses among documents. They tested 38 words containing two domains of Sports and Finance from the Reuters corpus [22], while we tested 14 domains with 4488 senses in all. Fukumoto et al. [23] also proposed an approach to acquired Identifying Domain-Specific Senses (IDSS) and applied to text classification. However, they only focused on nouns. Moreover, their method is based on the traditional Support Vector Machines (SVMs), that is, the selection of the associated senses and text classification are conducted by using SVMs.
In the context of similarity metric, there have been many attempts which project documents into implicit semantic space, for example, Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) [24] and Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) [25]. Mikolov et al. presented Word2Vec model that is a well known shallow model for training text and generates word embedding [26]. Le and Mikolov developed Doc2Vec [27] by adding the paragraph vector that is a numeric representation of a document based on Word2Vec. They proposed two different models including the Distributed Model of Paragraph Vectors(PV-DM) and the Distributed Bag of Words version of Paragraph Vector (PV-DBOW) which are similar to Continuous Bag of Words (CBOW) and Skip-gram, respectively. Kiros et al. proposed unsupervised learning named Skip-thoughts model for learning vector representations of sentences with the ordering of sentences for training model [28]. Skip-thoughts model has three components consisting encoder network, previous decoder network, next decoder network. Pagliardini et al. proposed Sent2Vec which builds document embeddings by averaging the word embeddings [29]. Another attempt is Earth Mover’s Distance (EMD) proposed by Rubner [30] that is one of the solvers for a transportation problem to find out the shortest distance from one distribution to another distribution. The result showed similarity of image retrieval effectively. Wan [31] adopted EMD to measure document similarity because EMD-based measure allowed many-to-many matching between subtopics whereas the existing Optimal Matching (OM) based measure allowed only one-to-one matching. Therefore, evaluating the document similarity with EMD-base measure is more suitable. Kusner et al. presented WMD to compute the similarity between two sentences [32].
In the context of graph-based model, a well-known technique is to utilize the analysis the strength of relationship between nodes(vertices) through edges(links) and the direction of relationship (undirected graphs, directed graphs) that can lead to detect the latent information in the graph. Each vertex initially votes other vertices and then applied the ranking algorithm to measure the importance of vertex in the graph. Many authors adopted graph-base model to their works that is, text semantic similarity [33], document summarization [34] WSD [35]. Reddy attempted to use the Personalized PageRank algorithm [36] over a graph representing WordNet to disambiguate ambiguous words [37]. They combined sense distribution scores and keyword ranking scores into the graph to personalize the graph for the given domain. The results showed that exploiting domain-specific information within the graph-based methods generated better results than using them was an individual. However, sense distribution scores were based on the frequency of neighbors of the target word from the thesaurus which was difficult to capture the distance between individual words. Recently, Dongsuk [38] proposed a word similarity method based on the semantic structure of BabelNet from a knowledge-based graph. They evaluated on the SemEval-2013 and SemEval-2015 dataset and the results indicated their method performed better than the state-of-art method in the SemEval-2013 dataset. Kutuzov [39] presented Path2vec which encoded synset paths between graph nodes into dense vectors. Their results were better than graph embedding baselines. Perozzi et al. presented DeepWalk to learn latent representations of vertices in a network [40]. They used local information obtained from truncated random walks to learn latent representations by treating walks as the equivalent of sentences. They applied DeepWalk to several multi-label network classification tasks including Flickr and Youtube and showed that it outperforms baseline methods.
In the context of text classification, many authors have attempted to apply deep learning techniques including LSTM technique [41,42,43,44], CNN [45], the attention based CNN [46], bag-of-words based CNN [47], Simple Graph Convolution (SGC) [48], the combination of CNN, Gated Recurrent Units (GRU) and attention mechanism [49], and the combination of CNN and recurrent neural network [50] to text classification. In the real world, Luz de Araujo et al. [51] built a dataset from Brazilian legal documents and tested document classification with different techniques to reduce sorting cases by humans. The F1 score results demonstrate the CNN and the Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM) outperform than other techniques. A celebrated technique was proposed by Kim [52] that applied CNN technique which was commonly used in computer vision into sentence classification. He reported simple CNN which was tuned with little hyperparameters that could obtain impressive results on multiple benchmarks. Zhang and Wallace [53] reported tuning for the number of feature maps and filter region size are the important factors. Furthermore, They proposed grouped weight sharing for external resource such as Brown clusters, WordNet, and so forth, into text classification. They used the two-channel model as input. The first channel was word embedding from external resources and the second channel was weight-sharing embedding among resources. The result showed two-channel perform better than single-channel. Most of them demonstrated that neural network models were powerful for learning features from texts, while they focused on single-label or a few labels problem. Several efforts had been made to multi-labels [54]. Liu et al. explored a family of new CNN models which were tailored for extreme multi-label classification [55]. They used a dynamic max pooling scheme, a binary cross-entropy loss, and a hidden bottleneck layer to improve the overall performance. The results by using six benchmark datasets where the label-set sizes were up to 670 K showed that their method attained at the best or second best in comparison with seven state-of-the-art methods including FastText [56] based CNN. However, all of these attempts aimed at utilizing a large volume of data. Nooralahzadeh et al. proposed Domain-specific Word embeddings using oil and gas corpus and evaluate them with the CNN model and obtained effective results [57]. Wang et al. [58] proposed an approach for short text classification that merged explicit representation and implicit representation together. They mapped a short text into semantic concepts and then constructed word-concept embedding after that was supplied into a CNN to learning explicit knowledge. Furthermore, they concatenated output from a separate CNN with character embedding [59] as the input in fully-connected layer of main network, so with this technique they could obtain morphemes level. Wang et al. attempt was similar to our work, while their method used fine-grained and large-scale semantic knowledge that needed to tune the word sense heuristic depending on the domain in which the word is used.
3. Acquisition of Domain-Specific Senses
The first sense heuristic is very powerful and often uses as a baseline of sense disambiguation systems. However, the major problems to use it as a sense disambiguation heuristic [1] contain the predominant sense of a word varies according to the source of the document belonging to the domain and the other problem is obtaining predominant senses, they need manual annotation of the corpus which causes a relatively small amount of resources such as SemCor. A methodology to find domain-specific senses without requiring manual annotation of data is needed.
Walker, and Amsler [60] proposed a method that determined domain from context using LDOCE (the Longman Dictionary Of Contemporary English) with counting a frequency of subject code of each word in a context which subject code had the highest count is assigned to the domain of context. Gale et al. [61] proposed one sense in the context and they reported shared sense in the same context is 98%. Magnini et al. [7] proposed WordNet Domains that was a lexical resource and they labeled 96% coverage of noun hierarchy, however, the domain annotation on word sense is still manually.
The goal of our model is to identify predominant sense distributions of a word depending on the domain. Figure 1 illustrates our Framework. Our approach has three stages: pre-processing, measuring senses similarity and ranking senses. Pre-processing stage is to create senses list for each category. We first collect the documents of each category in the Reuters corpus in XML document format, often used as input for text processing. Each document is clearly structured including a category as stated in the automated processing of documents [62]. We extract the word that has frequency more than five and then apply with Part-Of-Speech (POS) tagger to obtain nouns and verbs list. We then use them as query to retrieve their senses with gloss texts in the WordNet. For Measuring senses similarity stage, we create senses embedding from gloss texts and calculate sense similarity with WMD. The last stage is ranking senses. We applied a simple graph centrality algorithm, Markov Random Walk (MRW) to the extracted noun words from the documents assigned to a specific domain/category and identify domain-specific senses for the domain. The idea of the MRW model is that of voting. When one vertex links to another one, it is casting a vote for that other vertex. The ranking is conducted by two metrics. One is a metric that the larger the number of votes that are cast for a vertex, the higher the importance of the vertex. Another is a metric that how important the vote itself is. We applied the algorithm to detect the domain-specific-sense of words.
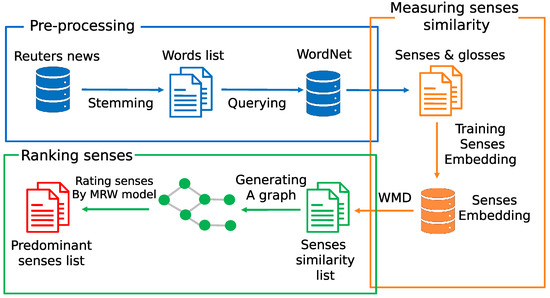
Figure 1.
Framework of Domain-Specific Senses (DSS).
A graph denotes = (V, E). It demonstrates the relationships between senses in a domain and it includes V is the set of vertices, and each vertex in V is the gloss text from WordNet. E is a set of edges, which is a subset of V×V. Each edge in E is associated with an affinity weight between senses and (i ≠ j). The standard cosine measure is used for calculating for the weight between senses. Two vertices are connected if their affinity weight is larger than 0 ans we let = 0 to avoid self transition. The transition probability from to is then defined by
We used the row-normalized matrix = to describe G with each entry corresponding to the transition probability, where = . To make U a stochastic matrix, the rows with all zero elements are replaced by a smoothing vector with all elements set to . The matrix form of the saliency score can be formulated in a recursive form as in the MRW model.
where = in Equation (2) is the vector of saliency scores for the senses. is a column vector with all elements equal to 1. is the damping factor. We set to 0.85, as in the PageRank [63]. The final transition matrix is given by
Each score of the sense in a specific domain is obtained by the principal eigenvector of the matrix. We applied the algorithm for each domain. The input of the MRW model is a graph consisting of vertices, that is, each possible noun sense appeared in a specific domain and edges with similarity value between vertices. We represent each noun sense as its gloss text extracted from the thesaurus, WordNet. We calculated sense similarity by using the WMD that measures the dissimilarity between two sentences as the minimum amount of distance that the embedded words of one sentence need to travel to reach the embedded words of another sentence. The word embedding is learned by using Word2Vec [26] with Skip-grams.
Let ∈ be a Word2Vec embedding matrix for vocabulary size of n words. The column, ∈ indicates the embedding of the word in d-dimensional space. We represent gloss text of each sense as normalized Bag-Of-Words (nBOW) vector, g∈. The objective of the model is to minimize cumulative cost C of moving the gloss text g to :
in Equation (4) shows that outgoing flow from word i equals . Similarly, indicates that incoming flow to word j matches . Each score of the sense in a specific domain is obtained by the principal eigenvector of the matrix. We applied the algorithm for each domain. We note that the matrix M is a high-dimensional space. Therefore, we used a ScaLAPACK, a library of high-performance linear algebra routines for distributed memory MIMD parallel computing [64], which includes routines for solving systems of linear equations, least squares, eigenvalue problems.
We selected all word senses according to rank score for each domain and make a sense-domain list. For each word w in a document, find the sense s that has the highest score within the list. If a domain with the highest score of the sense s and a domain in a document appeared in the word w match, s is regarded as a domain-specific sense of the word w.
4. Application to Text Classification
Our hypothesis about text classification is that the document assigned to a specific category includes predominant word sense related to the category. We combined the knowledge of domain-specific senses with the embedding of documents. Our model is shown in Figure 2. It is the combination between documents and sense embeddings that is, each word in the document is disambiguated and is replaced to its DSS sense key obtained from the WordNet. We used it as the input of the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). With this model, we can learn rich features from both the word level and the sense level, simultaneously.
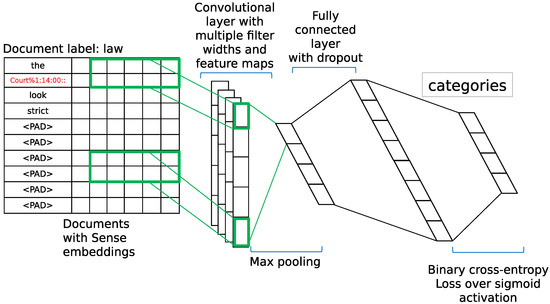
Figure 2.
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model for text classification.
Similar to other CNN models [47,55], our model, which is shown in Figure 2, is based on [52]. Let ∈ be the k-dimensional word vector with the i-th word in the input of CNN obtained by applying Skip-gram model provided in Word2Vec. The input with length n is represented as = ∈. A convolution filter ∈ is applied to a window size of h words to produce a new feature, = where b∈ indicates a bias term and f refers to a non-linear activation function. We applied this convolution filter to each possible window size in the input and obtained a feature map, m∈. As shown in Figure 2, we then apply a max-pooling operation over the feature map and obtain the maximum value as a feature of this filter. We obtained multiple filters by varying window sizes and multiple features. These features form a pooling layer and are passed to a fully connected layer. In the fully connected layer, we applied dropout [65]. The dropout randomly sets values in the layer to 0. Finally, we obtained the probability distribution over categories. The network is trained with the objective that minimizes the binary cross-entropy (BCE) of the predicted distributions and the actual distributions by performing stochastic gradient descent.
5. Experiments
We evaluate our method using the 1996 Reuters corpus and WordNet 3.0 thesaurus. Moreover, we applied the results of DSS to the text classification task to examine how well the automatically acquired senses contribute to classification accuracy by comparing one of the WSD techniques, Context2vec.
5.1. Acquisition of Domain-Specific Senses
The Reuters corpus consists of 806,791 documents organized into 126 categories. There are no existing sense-tagged data for domains that we can utilize for evaluation. Therefore, we used the Subject Field Codes (SFC) resource which semi-automatically annotates WordNet 2.0 synsets with domain labels [7]. The SFC consists of 115,424 words assigning 168 domain labels which include some of the Reuter’s categories. We manually assigned Reuter’s categories to SFC labels which are shown in Table 1. “# doc” in Table 1 refers to the number of documents in each category. “# min” and “# max” indicate the minimum and the maximum number of word frequencies that appear in each category respectively.

Table 1.
The Reuters and Subject Field Codes (SFC) category correspondences.
In a pre-processing step, a POS tagger and lemmatizer from Stanford CoreNLP [66] were applied to the Reuters corpus and then we divided it into three for the experiments including training dataset for 3 months, test dataset for 6 months, and validation dataset for 3 months.
The test dataset was fed in DSS. The initial step was to choose the first 20,000 words with the highest frequency from each category. Every word was converted to lowercase, removed punctuation, and stopwords, and applied lemmatization. Next, we selected only nouns and verbs then used them as a query into Wordnet to find out the word senses and their glosses for built the Word2vec model with their glosses. The 14 different models were created according to category.
The Word2vec parameters consisted of the number of dimensions to 100, the window size to 5, Skip-gram as the training algorithm, and Hierarchical softmax as the model training. We used the word embedding from the Word2vec model to measure sense similarity score for WMD which was a method for comparing dissimilarity score between sentences and then we rated the score with MRW which was used to determine the importance of senses. Eventually, the predominant senses per each category is obtained. The training data was used to estimate K% words (senses) according to rank score, and test data was used to test the method using the estimated value K. We manually evaluated a sense-domain list. As a result, we set K to 10%.
Table 2 shows the results obtained by the topmost 10% senses according to rank score. “Sense” indicates the total number of senses which should be assigned to each category. “DSS” and “SFC” refer to the number of senses obtained by our method and appeared in the SFC resource, respectively. “Correct” shows the number of senses tagged with the best domain ranking appearing in both of our method and SFC. “F-sccore” indicates F-measure of one domain tagging. “IRS” refers to Inverse Rank Score and the higher the IRS value, the better the system performance. “IRS” refer to IRS of one domain tagging. “P_IRS” indicates the perfect correct value of IRS. We can see from Table 2 that the overall performance depends on the categories. The best performance of one domain is “Finance”. In contrast, the results of “Politics” and “Administrator(Admin.)” are 0.462∼0.533.

Table 2.
The results of sense assignments.
Table 3 illustrates some examples obtained by our method but that does not appear in the SFC. Table 3 gives an example for each domain. For example, military sense of the word “Redoubt” and the act of meting out the justice of “Administration” which are correctly obtained by our method but does not occur in the SFC resource. This clearly supports the usefulness of our automated method.

Table 3.
Sense example identified by our method.
5.2. Qualitative Analysis of Errors
We perform this stage to reflect the error of our results obtained from Table 2 and use it to improve the further method. We found three main types of error.
- 1.
- The Semantic similarity measure with WMD
Figure 3 presents the F-score against the percent of the topmost ranking of predominant senses. This graph shows that WMD performs well approximately topmost 10%∼20% of senses. However, when topmost senses increases more than 30%, the F-score declines below 0.5. From the observation, we need to investigate semantic similarity measure for improving further performance.
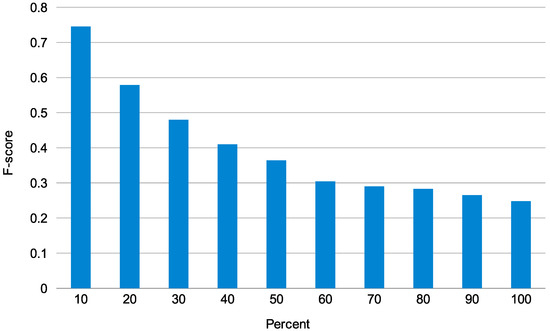
Figure 3.
F-score against the percent of topmost of senses.
- 2.
- The number of domains per word
The larger the number of domains per word, the harder it is to identify the correct domain. Consider, the word “Apprehend” and “Arrest” both words have the same sense, that is, “(take into custody), the police nabbed the suspected criminals”. The word “Apprehend” is found only two domains while the word “Arrest” is used more often for 14 domains. From this example, Identifying a correct domain to the word “Arrest” is difficult than “Apprehend”. To solve this problem, we need to extend our model to assign more than one domain which is similar to the multi-label text classification task.
- 3.
- The closeness sense of the domains
The worst results are “Politics” and “Administration” because they are semantically close with each other, that is, the word “section”, we found 14 domains in all and it is tagged as “Politics” with the best-ranking order, 136, while the second-ranking as “Administration” was 143 and it was correctly assigned. As a result, the evaluation of the word “section” is incorrect, even though both the order of ranking are closer with each other compared to other domains. From this observation, we should identify a sense of both domains correctly for further improvement.
5.3. Text Classification
For comparison of the performance between WSD and our DSS models, we choose the Context2vec model as a WSD method. The 3-month Reuters Training dataset is fed to Context2vec model and it creates context embeddings and target word embeddings. Both embeddings are used as input to Supervised WSD tasks along with Senseval-3 English lexical samples for training and use a 6-month Reuters dataset for testing to acquire the Context2vec’s predicted senses in each context.
The DSS’s predicted senses are applied for text classification to examine how the results obtained by our method affect classification performance. For each category, we divide a 6-month Reuters dataset into two folds—80% for training and 20% for test data. We further divided the training data into two folds—80% for training data and 20% for validation data. Our model setting for CNN is shown in Table 4. The validation data is used for tuning these settings with the Optuna framework [67] Dropout rate1 in Table 4 shows dropout immediately after the embedding layer, and Dropout rate2 denotes dropout in a fully connected layer. We chose MSF (Multiplicative Scoring Function) with a threshold value of 0.5 to distinguish multi-label classification [68].

Table 4.
CNN model settings.
The categorization using CNN is as follows—for the target category, we replace each word in the test document with its sense key. If the category assign to the test document by CNN model and the target category match, the test document is judged to classify into the target category. The procedure is applied to each test document and the target category. The results are summarized in Table 5.

Table 5.
Classification performance (Topmost 10%).
Table 5 shows categories, categorization performance (F-score) with and without domain-specific senses. “CNN” refers to the result without domain-specific senses and “DSS” shows the results obtained by our method. “SFC” shows the results from gold-standard SFC codes. “WSD” refers to the results by Context2vec. DSS shows that the results obtained by DSS are statistically significant compared to those obtained by CNN. Similarly, SFC indicates that the results by SFC are statistically significant compared to those by CNN. We used a t-test, p-value < 0.05. In WSD result, we only used 18 words with 22 senses in all, each of which appears in SFC. In contrast, in our DSS, we used the topmost 10% of the target words that have 442 senses in all.
Overall, the results show that domain-specific senses improved text classification performance. The best improvement is “Religion” (+0.216), and the worst is “Art” (+0.012). In contrast, SFC is the best improvement (+0.147) for “Fashion” and the worst “Religion” (−0.051). One reason is that “Religion” is frequently associated with “Politics” and “Military” and its document size is smaller than the other two categories according to Table 1, however, it betters than WSD significantly at 0.165.
The text classification used here is very simple, that is, CNN with single channel. There are lots of text categorization techniques applicable to the small number of training documents [58,69], and it will be worthwhile examining these with our model.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we present an unsupervised method for detecting the DSS for the problem that how to choose an appropriate sense of a context, based on word embedding learning which leverages distributed representations of words and thus does not require manual annotation of sense-tagged data. The text classification task has empirically proven that DSS is able to achieve a better performance than WSD method. The DSS results attained at F-score 0.745 for 442 senses, furthermore when applying them to text classification, we obtained the classification accuracy as the Macro F-score is 0.832 that exceed the WSD method 0.053. There are several directions for future work. We are going to apply our DSS method on other datasets or different languages other than English and examine the performance to demonstrate the robustness of our method. We focused on the gloss texts of WordNet in this work. We utilize another thesaurus, for example, Roget’s by using corpus statistics. This is a rich space for further exploration. We should extend the method by using other part-of-speech other than nouns and verbs. We also need to compare the method to the state-of-the-art text classification techniques [55,58]. Our framework utilizes WMD and PageRank. The computational cost of WMD is , where p denotes the number of distinct words in the documents [70] and that of PageRank is where N indicates the matrix dimension and k refers to the number of repetition. We need to investigate a method to improve run-time efficiencies. Finally, we are going to utilize our method to the other NLP applications such as machine translation and question answering.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.W. and F.F.; methodology, A.W. and F.F.; software, A.W. and K.S.; validation, A.W. and F.F.; investigation, A.W. and F.F.; writing—original draft preparation, A.W.; writing—review and editing, F.F.; supervision, F.F.; funding acquisition, A.W. and F.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Grant-in-aid for JSPS, Grant Number 17K00299, and Support Center for Advanced Telecommunications Technology Research, Foundation, scholarship for Prince of Songkla University, and research assistant grant for University of Yamanashi.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- McCarthy, D.; Koeling, R.; Weeds, J.; Carroll, J. Unsupervised Acquisition of Predominant Word Senses. Comput. Linguist. 2007, 33, 553–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeling, R.; McCarthy, D.; Carroll, J. Domain-Specific Sense Distributions and Predominant Sense Acquisition. In Proceedings of the Human Language Technology Conference and Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–8 October 2015; pp. 419–426. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, B.; Palmer, M. The English All-Words Task. In Proceedings of the SENSEVAL-3, 3rd International Workshop on the Evaluation of Systems for the Semantic Analysis of Text, Barcelona, Spain, 25–26 July 2004; pp. 41–43. [Google Scholar]
- Yarowsky, D.; Florian, R. Evaluating Sense Disambiguation Performance Across Diverse Parameter Spaces. Nat. Lang. Eng. 2002, 8, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.A. WordNet: A Lexical Database for English. Commun. ACM 1995, 38, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melamud, O.; Goldberger, J.; Dagan, I. context2vec: Learning Generic Context Embedding with Bidirectional LSTM. In Proceedings of the 20th SIGNLL Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning, Berlin, Germany, 11–12 August 2016; pp. 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Magnini, B.; Cavaglia, G. Integrating Subject Field Codes into WordNet. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Language and Evaluation (LREC’00), Athens, Greece, 30 May 2000; pp. 1413–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Magnini, B.; Strapparava, C.; Pezzulo, G.; Gliozzo, A. The Role of Domain Information in Word Sense Disambiguation. Nat. Lang. Eng. 2002, 8, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Pedersen, T. An adapted Lesk algorithm for word sense disambiguation using WordNet. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computational Linguistics and Intelligent Text Processing, Mexico City, Mexico, 17–23 February 2002; pp. 136–145. [Google Scholar]
- Chaplot, D.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Paranjape, A. Unsupervised word sense disambiguation using Markov Random Field and dependency parser. In Proceedings of the 29th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Austin, TX, USA, 25–30 January 2015; pp. 2217–2223. [Google Scholar]
- Lesk, M. Automatic sense disambiguation using machine readable dictionary: How to tell a pine cone from an ice cream cone. In Proceedings of the 5th annual international conference on Systems documentation, Toronto, ON, Canada, 8–11 June 1986; pp. 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Mihalcea, R. Co-training and self-training for Word Sense Disambiguation. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning (CoNLL-2004) at HLT-NAACL 2004, Boston, MA, USA, 6–7 May 2004; pp. 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, C.; Wei, L.; Rohini, R.K.; Huifeng, L.; Laurie, C. Context clustering for word sense disambiguation based on modeling pairwise context similarities. In Proceedings of the SENSEVAL-3, 3rd International Workshop on the Evaluation of Systems for the Semantic Analysis of Text, Barcelona, Spain, 25–26 July 2004; pp. 187–190. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, T. A Decision Tree of Bigrams is and Accurate Predictor of Word Sense. arXiv 2001, arXiv:cs/0103026. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Rao, J.; Hu, Q. Supervised word sense disambiguation using semantic diffusion kernel. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2014, 27, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agirre, E.; Lacalle, O.L.D.; Soroa, A. Knowledge-based WSD on Specific Domains: Performing better than Generic Supervised WSD. In Proceedings of the 21st International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI-09, Pasadena, CA, USA, 11–17 July 2009; pp. 1501–1506. [Google Scholar]
- Faralli, S.; Navigli, R. A New Minimally-Supervised Framework for Domain Word Sense Disambiguation. In Proceedings of the 2012 Joint Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and Computational Natural Language Learning, Jeju Island, Korea, 12–14 July 2012; pp. 1411–1422. [Google Scholar]
- Taghipour, K.; Ng, H.T. Semi-Supervised Word Sense Disambiguation Using Word Embeddings in General and Specific Domains. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference of the North America Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Denver, CO, USA, 31 May–5 June 2015; pp. 314–323. [Google Scholar]
- Abualhaija, S.; Tahmasebi, N.; Forin, D.; Zimmermann, K. Parameter Transfer across Domains for Word Sense Disambiguation. In Proceedings of the International Conference Recent Advances in Natural Language Processing, RANLP 2017, Varna, Bulgaria, 4–6 September 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Arevalo, I.; Sosa-Sosa, V.J.; Rojas-Lopez, F.; Tello-Leal, E. Improving Selection of Synsets from WordNet for Domain-specific Word Sense Disambiguation. Comput. Speech Lang. 2017, 41, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, D.; Koeling, R.; Weeds, J.; Carroll, J. Finding Predominant Word Senses in Untagged Text. In Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL-04), Barcelona, Spain, 21–26 July 2004; pp. 279–286. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, T.; Stevenson, M.; Whitehead, M. The Reuters Corpus Volume 1 - from Yesterday’s News to Tomorrow’s Language Resources. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’02), Las Palmas, Spain, 29–31 May 2002; pp. 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto, F.; Suzuki, Y. Identifying Domain-specific Senses and Its Application to Text Classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development, Valencia, Spain, 25–26 October 2010; pp. 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Deerwester, S.; Dumais, S.T.; Furnas, G.W.; Landauer, T.K.; Harshman, R. Indexing by Latent Semantic Analysis. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 1990, 41, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M.; Ng, A.Y.; Jordan, M.I. Latent Dirichlet Allocation. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 993–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1301.3781. [Google Scholar]
- Le, Q.; Mikolov, T. Distributed Representations of Sentences and Documents. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1405.4053. [Google Scholar]
- Kiros, R.; Zhu, Y.; Salakhutdinov, R.; Zemel, R.S.; Torralba, A.; Urtasun, R.; Fidler, S. Skip-thought vectors. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.06726. [Google Scholar]
- Pagliardini, M.; Gupta, P.; Jaggi, M. Unsupervised Learning of Sentence Embeddings Using Compositional n-Gram Features. In Proceedings of the NAACL-HLT, New Orleans, LA, USA, 1–6 June 2018; pp. 528–540. [Google Scholar]
- Rubner, Y.; Tomasi, C.; Guibas, L.J. The Earth Mover’s Distance As a Metric for Image Retrieval. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2000, 2, 99–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X. A Novel Document Similarity Measure Based on Earth Mover’s Distance. Inf. Sci. 2007, 177, 3718–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusner, M.J.; Sun, Y.; Kolkin, N.L.; Weinberger, K.Q. From Word Embeddings to Document Distances. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; Volume 37, pp. 957–966. [Google Scholar]
- Ramage, D.; Rafferty, A.N. Random Walks for Text Semantic Similarity. In Proceedings of the 2009 Workshop on Graph-based Methods for Natural Language Processing (TextGraphs-4), Suntec, Singapore, 7 August 2009; pp. 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Mihalcea, R. Language Independent Extractive Summarization. In Proceedings of the ACL Interactive Poster and Demonstration Sessions, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 25–30 June 2005; pp. 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, R.; Mihalcea, R. Unsupervised Graph based Word Sense Disambiguation using Measures of Word Semantic Similarity. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Semantic Computing, Irvine, CA, USA, 17–19 September 2007; pp. 363–369. [Google Scholar]
- Agirre, E.; Soroa, A. Personalizing Pagerank for Word Sense Disambiguation. In Proceeding of the 12th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, EACL’09; Association for Computational Linguistics: Athens, Greece, 2009; pp. 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, S.; Inumella, A.; McCarthy, D.; Stevenson, M. IIITH: Domain Specific Word Sense Disambiguation. In Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, Uppsala, Sweden, 15–16 July 2010; pp. 387–391. [Google Scholar]
- Dongsuk, O.; Sunjae, K.; Kyungsun, K.; Youngjoong, K. Word Sense Disambiguation Based on Word Similarity Calculation Using Word Vector Representation from a Knowledge-based Graph. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Santa Fe, NM, USA, 20–26 August 2018; pp. 2704–2714. [Google Scholar]
- Kutuzov, A.; Panchenko, A.; Kohail, S.; Dorgham, M.; Oliynyk, O.; Biemann, C. Learning Graph Embeddings from WordNet-based Similarity Measures. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.05611. [Google Scholar]
- Perozzi, B.; AI-Rfou, R.; Skiena, S. DeepWalk: Online Learning of Social Representations. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1403.6652. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, S.; Vinyals, O.; Strope, B.; Roy, S.; Dean, T.; Heck, L.P. Contextual LSTM(CLSTM) models for large scale NLP tasks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.06291. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, W.; Yu, K. Bidirectional LSTM-CRF models for sequence tagging. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1508.01991. [Google Scholar]
- Kågebäck, M.; Salomonsson, H. Word Sense Disambiguation using a Bidirectional LSTM. In Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Cognitive Aspects of the Lexicon (CogALex-V), Osaka, Japan, 12 December 2016; pp. 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Huang, Z. Bi-directional LSTM recurrent neural network for Chinese word segmentation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.04874. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zhao, L.; Bian, J.; Qin, T.; Liu, G.; Liu, T.-Y. Dual Transfer Learning for Neural Machine Translation with Marginal Distribution Regularization. In Proceedings of the 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, D.; Dyer, C.; He, X.; Smola, A.; Hovy, E. Hierarchical Attention Networks for Document Classification. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–17 June 2016; pp. 1480–1489.
- Johnson, R.; Zhang, T. Semi-Supervised Convolutional Neural Networks for Text Categorization via Region Embedding. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1504.01255. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, T.; Souza, A., Jr.; Fifty, C.; Yu, T.; Weinberger, Q. Simplifying Graph Convolutional Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.07153. [Google Scholar]
- Abreu, J.; Fred, L.; Macêdo, D.; Zanchettin, C. Hierarchical Attentional Hybrid Neural Networks for Document Classification. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.06610. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Lee, H.; Radev, D.R. Dependency Sensitive Convolutional Neural Networks for Modeling Sentences and Documents. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–17 June 2016; pp. 1512–1521. [Google Scholar]
- Luz de Araujo, P.H.; Campos, T.E.; Braz, F.A.; Silva, N.C. VICTOR: A dataset for Brazilian legal documents classification. In Proceedings of the 12th Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, Marseille, France, 11–16 May 2020; pp. 1449–1458. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y. Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; pp. 1746–1751. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wallace, B.C. A Sensitivity Analysis of (and Practitioners’ Guide to) Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1510.03820. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R.; Zhang, T. Effective Use of Word Order for Text Categorization with Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.1058. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Chang, W.-C.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y. Deep Learning for Extreme Multi-Label Text Classification. In Proceedings of the 40th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Tokyo, Japan, 7–11 August 2017; pp. 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Joulin, A.; Grave, E.; Bojanowski, P.; Mikolov, T. Bag of Tricks for Efficient Text Classification. In Proceedings of the 15th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics; Association for Computational Linguistics: Valencia, Spain, 2017; pp. 427–431. [Google Scholar]
- Nooralahzadeh, F.; Øvrelid, L.; Lønning, J.T. Evaluation of Domain-specific Word Embeddings using Knowledge Resources. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC2018), Miyazaki, Japan, 7–12 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Yan, J. Combining Knowledge with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Short Text Classification. In Proceedings of the 26th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Melbourne, Australia, 19–25 August 2017; pp. 2915–2921. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Jernite, Y.; Sontag, D.; Rush, A.M. Character-aware neural language models. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1508.06615. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, D.E.; Amsler, R.A. The use of machine-readable dictionaries in sublanguage analysis. Analyzing Language in Restricted Domains. In Analyzing Language in Restricted Domains; Grishman, R., Kittredge, R., Eds.; Lawrence Erlbaum: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Gale, W.A.; Church, K.W.; Yarowsky, D. One Sense Per Discourse. In Proceedings of the workshop on Speech and Natural Language, New York, NY, USA, 23–26 February 1992; pp. 233–237. [Google Scholar]
- Cristani, M.; Bertolaso, A.; Scannapieco, S.; Tomazzoli, C. Future paradigms of automated processing of business documents. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Sci. 2018, 40, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brin, S.; Page, L. The Anatomy of a Large-scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine. Comput. Netw. ISDN Syst. 1998, 30, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netlib, Netlib Repository at UTK and ORNL. 2007. Available online: http://www.netlib.org/scalapack (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Hinton, G.E.; Srivastava, N.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R.R. Improving Neural Networks by Preventing Co-Adaptation of Feature Detectors. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1207.0580. [Google Scholar]
- Manning, C.; Surdeanu, M.; Bauer, J.; Finkel, J.; Bethard, S.; McClosky, D. The Stanford CoreNLP Natural Language Processing Toolkit. In Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: System Demonstrations, Baltimore, MD, USA, 23–24 June 2014; pp. 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Akiba, T.; Sano, S.; Yanase, T.; Ohta, T.; Koyama, M. Optuna: A Next-generation Hyperparameter Optimization Framework. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.10902. [Google Scholar]
- Shimura, K.; Li, J.; Fukumoto, F. HFT-CNN: Learning Hierarchical Category Structure for Multi-label Short Text Categorization. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018; pp. 811–816. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Zhu, K.Q. A Probabilistic Taxonomy for Text Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2012 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 20–24 May 2012; pp. 481–492. [Google Scholar]
- Pele, O.; Werman, M. Fast and Robust Earth Mover’s Distances. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 29 September–2 October 2009; pp. 460–467. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).