Abstract
In this work, the structural, magnetic and mechanical properties of Nd16Fe76−xCoxB8 alloys with a varying Co content of x = 0, 10, 20 and 25 were experimentally investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Mössbauer spectrometry (MS) and vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM) at room temperature (RT), and microhardness tests were performed. The system presented hard Nd2Fe14B and the Nd1.1Fe4B4 phases for samples with x = 0; when the concentration increased to x = 20 and 25, the CoO phase appeared. All MS data showed ferromagnetic behavior (eight sextets: sites 16k1, 16k2, 8j1, 8j2, 4c, 4e, sb) associated with the hard and soft magnetic phases, and one paramagnetic component (doublet: site d) associated with the minority Nd1.1Fe4B4 phase, which was not identified by XRD. All samples were magnetically hard and presented hard magnetic behavior. The increase of Co content in these samples did not improve the hard magnetic properties but increased the critical temperature of the system and decreased the crystallite size of the hard phase. There was a general tendency towards increased microhardness with cobalt content that was attributable to cobalt doping, which reduces the lattice parameters and porosities within the sample, improving its hardness.
1. Introduction
NdFeB permanent magnets have been investigated since 1983 [1,2,3] and continue to be investigated [4,5] due to their high energy density (~450 kJm−3) [6], which makes them useful for a number of different applications including acoustic transducers, air conditioning, electric bikes, wind turbines, hybrid and electric cars and hard disk drives, among others [7]. For these reasons, efforts are being devoted to obtaining an improvement in their magnetic and physical properties. Nanocomposite permanent magnets are composed of soft (α-Fe or Fe3B) and hard (Nd2Fe14B) nanocrystalline magnetic phases and attract a great deal of interest because they exhibit unusual properties, such as a remanence relation (Mr/Ms) larger than 0.5 (the Stoner–Wohlfarth limitation) due to the exchange coupling between these two phases [8]. Among earlier works into nanocomposite magnet, a study was carried out by Coehoorn, R et al. [9] that investigated Fe3B/Nd2Fe14B with magnetic properties of 0.3 T and 93 kJm−3 for coercive and magnetic energy, respectively. After these works, different theoretical models [10,11,12] were proposed in order to improve the general understanding of exchange-coupled nanocomposite magnets. A number of studies were reported for thin films; for example, Cui, W et al. [13] investigated Nd2Fe14B/FeCo anisotropic nanocomposite films and obtained values of the maximum energy product between 400 and 500 kJm−3 through an exchange-coupling mechanism. On the other hand, Yang. F et al. [4] recently investigated bonded magnets of NdFeB with SrFe12O19 ferrite by additive manufacturing (3D printing); for a sample with 20 wt% of ferrite, they obtained a relatively low surface roughness of ~6 μm and a tensile strength of 12 MPa. However, they obtained a decrease in the magnetic properties of saturation magnetization (Ms), remanent magnetization (Mr), coercive field (Hc) and maximum energy product (BH)max upon increasing the content wt% of ferrite. Other recent work on the NdFeB system using the same principle was reported in [5], where the phase and hyperfine structure of melt-spun nanocrystalline (Ce1-xNdx)16Fe78B6 alloys were studied. These results suggest that alloys are composed specifically of the (NdCe)2Fe14B phase; however, phases such as (CeNd)Fe2 and (CeNd)Fe4B4 have also been identified. The Mössbauer fit was carried out using six sextets and two doublet components; the average magnetic hyperfine field using Mössbauer and the magnetic properties Ms, Hc and (BH)max increased for compositions from x = 0 to x = 0,7.These properties are sensible to the type of elements of the hard [14,15,16,17,18,19] and soft phases [14,20], to the grain size of the hard phase [15,16,21,22,23,24] and to the different techniques used to prepare them [25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36]. In addition to studies of magnetic properties, it is also important to consider the mechanical properties of permanent magnets. Many efforts have been made to find ways to improve these mechanical properties [2,37]; previous efforts have mainly focused on modifying the compositions by the addition of doping elements such as Al, Ti, Nb, Ga, Cu, Cr, Zr, etc. [38,39].
Considering the tetragonal crystalline stature of Co with uniaxial anisotropy and an atomic ratio of 1.25 Å, comparable to that of Fe (1.26 Å), we studied the effect of the addition of Co on the structural, magnetic and mechanical properties of Nd16Fe76−xCoxB8 alloys (x = 0, 10, 20, and 25) obtained through an arc-furnace and characterized them by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Mössbauer spectrometry (MS), vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM) and microhardness studies.
2. Materials and Methods
Alloys of the Nd16Fe76−xCoxB8 (x = 0, 10, 20, and 25) system were prepared by mixing and compacting high-purity fine powders (purity higher than 99.9%) of Fe, Nd, B and Co. These samples were prepared by the arc-melting method under an Ar atmosphere. The resulting ingots were compacted into pellets and encapsulated and evacuated under vacuum, in a quartz ampule, and finally heat treated at 1073 K for 30 min, followed by water quenching. Afterwards, the ingots were partially hand ground (particle size below 100 μm). All prepared samples were characterized by MS, XRD, VSM and microhardness tests. Mössbauer measurements were performed in a constant acceleration spectrometer at room temperature with transmission geometry using a 57Co(Rh) source of 25 mCi. All spectra were fitted with the MOSFIT program [40], and the isomeric deviation values were in reference to α-Fe. The XRD measurements were performed at room temperature using Cu-Kα radiation in transmission geometry in the 2θ range between 20° and 90°. The patterns were refined by using the GSAS program [41], which is based on the Rietvelt method combined with Fourier analysis, to describe the broadening of the lines. This refinement yielded the average values of the lattice parameters and of the crystallite sizes and quantified the obtained structural phases. A physical property measurement system (PPMS) equipped with a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) was used for magnetic measurements up to 3T. The demagnetization factor of the randomly shaped particles was not taken into consideration. The measurements were made at the Excellence Centre for New Materials (CENM) of Universidad del Valle, Colombia. Vickers hardness tests were performed on heat-treated samples, which were polished to a mirror finish with alumina with a 0.05 µm particle size. Microhardness maps were created with an automated Leco AMH43 microhardness device, on different areas of the samples, applying a load of 200 g and a holding time of 15 s.
3. Results
3.1. XRD
Figure 1 shows the XRD patterns obtained for samples with different Co concentrations. These patterns reveal that all samples presented a tetragonal Nd2Fe14B hard phase (space group P42/mmm) and an Nd1.1Fe4B4 phase (tetragonal structure and orthorhombic space group Pccn) [42,43,44,45]. Additionally, a CoO phase (Wurzita structure and space group P63mc) was detected for high concentrations of Co (x = 20 and 25). It can be noted that the intensity of the peaks corresponding to the Nd2Fe14B phase was slightly reduced and those of Nd1.1Fe4B4 increased when the Co content increased.
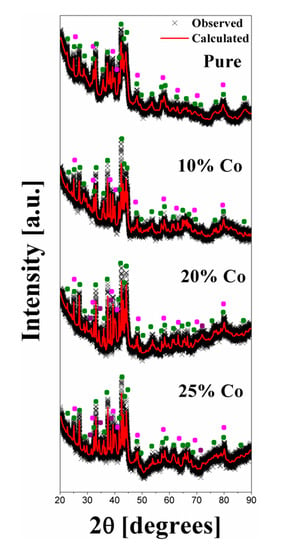
Figure 1.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the Nd16Fe76−xCoxB8 samples with x = 0, 10, 20, and 25 at room temperature, when ● Nd2Fe14B, ● Nd1.1Fe4B4 and ● CoO.
Rietveld refinement allowed us to determine the type of structures with these alloys. The parameter values for samples with a stoichiometry of Nd16Fe76−xCoxB8 with x = 0, 10, 20 and 25 are reported in Table 1. These data indicate that the crystallite size for Nd1.1Fe4B4 and Nd2Fe14B phases was in the nanometer range, from 5 to 90 nm. The crystallite size parallel to the Nd1.1Fe4B4 and Nd2Fe14B phases increases with increased concentrations of cobalt. It can be noted that the two phases of parallel crystallite sizes are greater than the perpendicular ones, indicating that the crystallite shape is not spherical but elongated in that direction. The refinement of the mean crystallite size of the hard phase is required in order to obtain higher remanence values [46,47] and to increase the ferromagnetic exchange coupling between the soft and hard grains [10]. The obtained values of the crystallite size indicate that these melted alloys are nanostructured.

Table 1.
Structural parameters of the Nd16Fe76−xCoxB8 samples with x = 0, 10, 20, and 25.
Table 1 shows the quantitative evolution with the Co content of the weight fraction of the different obtained phases. It can be noted that the Co also decreases the stability of the hard phase, and the decomposition of this phase is conducive to the increase of the Nd1.1Fe4B4 phase.
Figure 2a,b shows the behavior of the lattice parameters with respect to the cobalt concentration of the Nd2Fe14B and Nd1.1Fe4B4 phases for all samples. It is observed that, for x = 0, 10, 20 and 25, the lattice parameters a and c of Nd2Fe14B and Nd1.1Fe4B4 phases decrease considerably with the variation of the concentration of cobalt. This behavior is a consequence of the substitution of Fe by Co atoms, which has an atomic radius (1.25 Å) lower than the atomic radius of Fe (1.26 Å), causing the lattice to reduce. These parameters are consistent with those reported in the literature [48,49].
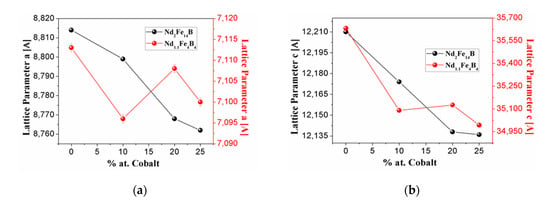
Figure 2.
(a) Lattice parameter a as a function of the Co content of the Nd2Fe14B and Nd1.1Fe4B4 phases. (b) Lattice parameter c as a function of the Co content of the Nd2Fe14B and Nd1.1Fe4B4 phases.
3.2. Mossbauer Results
The Mössbauer spectra of Nd16Fe76−xCoxB8 (x = 0, 10, 20 and 25) samples, collected at RT, are shown in Figure 3. To fit these spectra, several subspectra were required, which were associated with the Nd2Fe14B, α-Fe and Nd1.1Fe4B4 phases. The last phase was not identified by XRD. Seven sextets were used to fit the magnetic part of the spectra, with six of them corresponding to those reported for the hard phase (16k1, 16k2, 8j1, 8j2, 4c and 4e) and the other corresponding to the α-Fe phase (sb) reported by Hernandez et al. [50,51,52]. As can be observed, the Mössbauer spectrum of the sample with x = 0 is typical of the Nd2Fe14B phase [8]. It was necessary to add a small doublet (site d) in order to obtain the best fit, and this was attributed to the paramagnetic Nd1.1Fe4B4 phase [50]. The Mössbauer parameters, such as the hyperfine magnetic field (Hhf), isomer shift (IS), quadrupole splitting (QS) and area of each subspectra, are listed in Table 2. The value of line width (Γ) takes values of 0.33 mm/s for all sextets and 0.40 mm/s for doublets, which is attributable to the degree of disorder of the samples.
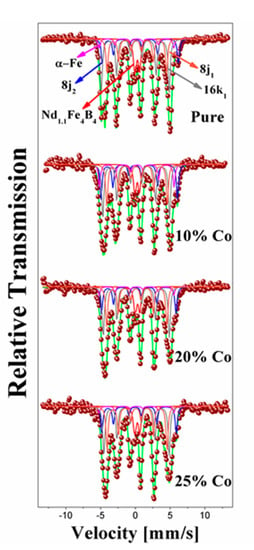
Figure 3.
Mössbauer spectra of the Nd16Fe76-xCoxB8 samples with x = 0, 10, 20 and 25 at room temperature.

Table 2.
Hyperfine parameters: hyperfine field Hhf, relative area and sites of the Mössbauer spectra of the Nd16Fe76−xCoxB8 samples with x = 0, 10, 20 and 25.
Figure 4a shows the variation of the hyperfine field, Hhf, of the different inequivalent Fe sites in the Nd2Fe14B hard magnetic phase as a function of Co content. It can be noted that the hyperfine field of the different sites has a tendency to decrease. This decrease is mainly due to the cobalt having a magnetic moment (1.71 μB/atom) lower than the magnetic moment of iron (2.22 μB/atom), and this result suggests that cobalt atoms enter within the lattice of Nd2Fe14B. However, for site 4c and 16k2 a higher rate of decrease of the hyperfine field with the cobalt concentration occurs; only for the 10% increase of cobalt does this result indicate that the cobalt atoms have a preference for substituting iron atoms at those sites. However, for 10% of cobalt, a higher rate of increase of the hyperfine field can occur because, in these sites, there is a higher presence of Fe neighbors than in the other sites for the different concentrations of doping with cobalt. These results agree with those of Liao et al. [52].
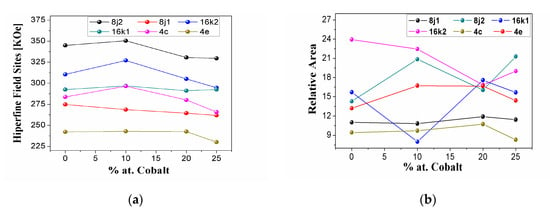
Figure 4.
(a) Hyperfine field of Fe sites (16k1, 16k2, 8j1, 8j2, 4c and 4e) of the hard magnetic phase Nd2Fe14B as a function of Co content. (b) Relative area of Fe sites (16k1, 16k2, 8j1, 8j2, 4c and 4e) of the hard magnetic phase Nd2Fe14B as a function of Co content.
In Figure 4b, the results are also consistent, which shows a high decrease in the relative area of 4c, confirming the preference of cobalt atoms by replacing iron atoms at these sites, comparing sites 8j1, 8j2, 16k1, 16k2 and 4e, which have a tendency to increase their relative area; thus, the cobalt does not replace iron atoms in these sites, and the ferromagnetism of these sites increases.
It can be observed in Figure 5a that there is a general tendency of the mean hyperfine field (MHF) to decrease as the cobalt content increases. Here, Figure 5a shows a peak at around 10% of doping with cobalt, which corresponds to Figure 4a, where an increase in the sites of hyperfine fields is evidenced due to the high presence of Fe atoms as first neighbors. Figure 5b shows the behavior of the relative area of site d (Nd1.1Fe4B4) and site sb (α-Fe) relative to Co content. The diminishing relative area of ^site d (Nd1.1Fe4B4) suggests that substituting iron atoms by cobalt atoms destabilizes the Nd1.1Fe4B4 phase. Besides, this Figure 5b shows that the relative area of the α-Fe phase decreases with the cobalt content. Only about 10% of cobalt increases the α-Fe phase, which is consistent with the previous results shown in Figure 4a and Figure 5a. These results indicate that cobalt atoms diffuse into the structure of Nd2Fe14B, substituting and expelling iron atoms and producing segregated Fe.
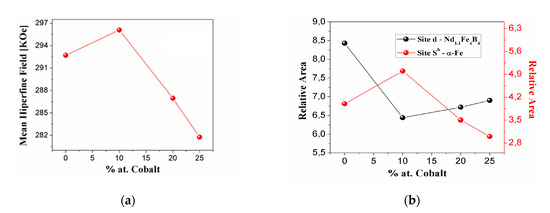
Figure 5.
(a) Mean hyperfine field of the Nd16Fe76−xCoxB8 samples with x = 0, 10, 20 and 25 at room temperature. (b) Variation of relative spectral area of the α-Fe (Sb) and Nd1.1Fe4B4 (d) sites as a function of Co content.
3.3. Magnetic Properties
Figure 6 shows the hysteresis loops for the alloys with x = 0, 10, 20 and 25. All samples show a predominant Nd2Fe14B hard magnetic phase. However, the addition of cobalt reduces the size and width of the hysteresis loop, especially for x = 25. These samples reach the saturation magnetization when the fields are higher than 2.5 T. On the other hand, the values of the coercive field Hc decrease with the increase of Co content, as shown in Figure 7a. Despite this decrease in coercivity, all samples still display a hard magnetic character.
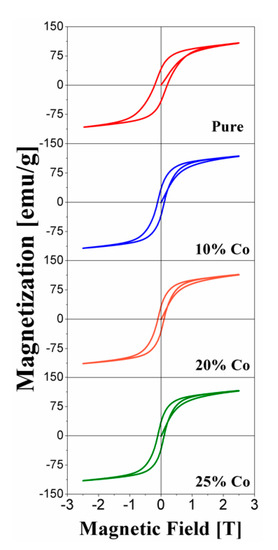
Figure 6.
Hysteresis loop of the Nd16Fe76−xCoxB8 samples with x = 0, 10, 20 and 25 at room temperature.
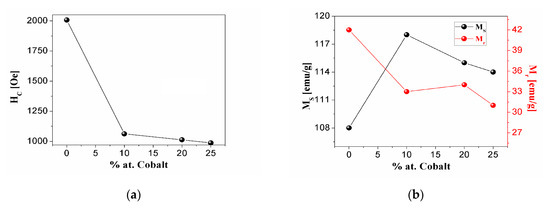
Figure 7.
(a) Variation of coercive field Hc as a function of Co content. (b) Variation of saturation magnetization Ms and remanent magnetization Mr as a function of Co content.
Figure 7b shows the behavior of the saturation magnetization Ms and of the remanent magnetization Mr with the concentration of cobalt. It can be concluded that increasing the concentration of cobalt increases the saturation magnetization and decreases the remanent magnetization. This behavior can be explained by the faxt that cobalt has a lower magnetic moment than iron and also stimulates the creation of only one CoO phase, and this does not limit the creation of the Nd2Fe14B hard magnetic phase. These results agree with those reported by Lin et al. [53]. Further domain structure analysis is needed to shed light on the magnetization process of these exchange-coupled systems upon Co doping.
3.4. Microhardness
The mechanical properties of the studied samples depend mainly on the microstructure, which is determined by the composition, the fabrication process and sintering temperature [17]. We carried out a hardness evolution of the system Nd16Fe76−xCoxB8 with x = 0, 10, 20 and 25 as a function of the atomic percentage of cobalt. The microhardness values of the samples with respect to the cobalt content are displayed in Figure 8a. A general tendency of microhardness increasing with cobalt content is observed. The heat treatment promotes the diffusion of the cobalt atoms within the NdFeB matrix, increasing the grain size, which in turns reduces the lattice parameter and the porosity in the sample, resulting finally in the improvement of its hardness, as can be seen in the microhardness images presented in Figure 8b.
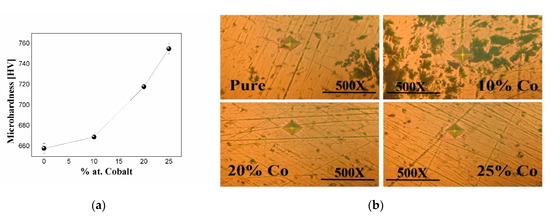
Figure 8.
(a) Variation of the microhardness as a function of Co content. (b) Images of the trace made for obtaining the microhardness at 500× as a function of Co content.
4. Conclusions
From the results of the present work, it can be concluded that the substitution of Fe by Co atoms in the Nd16Fe76−xCoxB8 nanocomposite alloy decreases the hard magnetic character of the system. The increase of the Co content decreases the stability of the hard phase. The hard phase decreases due the decrease of the 4c site when Co content increases. The magnetic softening of the samples is principally due to the low ferromagnetic coupling between the soft and hard phases. There is a general trend of increasing microhardness with cobalt content, which is attributable to the role of cobalt doping in reducing the lattice parameters and porosities in the sample. In summary, the coupling between NdFeB and Co generates nanostructured systems that favor the formation of hard and soft magnetic phases and improves the ductility conditions, improving the magnetic and mechanical properties of exchange-coupling magnets.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.S.T.H., G.A.P.A., D.O.L.; methodology, J.S.T.H., H.B.R.; software, J.S.T.H., H.M.S.; validation, J.S.T.H., G.A.P.A., D.O.L.; formal analysis, J.S.T.H., A.T.; investigation, J.S.T.H.; writing—original draft preparation, J.S.T.H.; writing—review and editing, A.T.; supervision, D.O.L., J.T.; project administration, D.O.L., G.A.P.A.; funding acquisition, D.O.L., G.A.P.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by COLCIENCIAS, grant number FP 44842-104-2016 and The Estancia Posdoctoral Colciencias was funded by Convocatoria 811-2018.
Acknowledgments
The authors express special thanks to the Research Office of the Universidad del Tolima and COLCIENCIAS, under Contract FP 80740-415-2019, for the financing of this work. Part of the research was also sponsored by the Army Research Laboratory and was accomplished under Cooperative Agreement Number W911NF-19-2-0030. The views and conclusions contained in this document are those of the authors and should not be interpreted as representing the official policies, either expressed or implied, of the Army Research Laboratory or the U.S. Government. The U.S. Government is authorized to reproduce and distribute reprints for Government purposes notwithstanding any copyright notation herein. The authors would like to thank Anit Giri, from the U.S. Army Research Laboratory for the critical discussion of the results.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Croat, J.J.; Herbst, J.F.; Lee, R.W.; Pinkerton, F.E. High-energy product Nd-Fe-B permanent magnets. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1984, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagawa, M.; Fujimura, S.; Togawa, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Matsuura, Y. New material for permanent magnets on a base of Nd and Fe (invited). J. Appl. Phys. 1984, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjipanayis, G.C. Nanophase hard magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Z.; Ye, S.; Sui, Y.; Volinsky, A.A. 3D printing of NdFeB bonded magnets with SrFe12O19 addition. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.Z.; Yu, H.Y.; Guo, W.T.; Zhang, J.S.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Hussain, M.; Liu, Z.W.; Greneche, J.M. Phase and Hyperfine Structures of Melt-spun Nanocrystalline (Ce1-xNdx)16Fe78B6 Alloys. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madugundo, R.; Rama Rao, N.V.; Schönhöbel, A.M.; Salazar, D.; El-Gendy, A.A. Recent Developments in Nanostructured Permanent Magnet Materials and Their Processing Methods. In Magnetic Nanostructured Materials: From Lab to Fab; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fischbacher, J.; Kovacs, A.; Gusenbauer, M.; Oezelt, H.; Exl, L.; Bance, S.; Schrefl, T. Micromagnetics of rare-earth efficient permanent magnets. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, R.W.; Kadin, A.M.; Clemente, G.B.; Keem, J.E. High performance isotropic permanent magnet based on Nd-Fe-B. J. Appl. Phys. 1987, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coehoorn, R.; de Mooij, D.B.; Duchateau, J.P.W.B.; Buschow, K.H.J. Novel Permanent Magnetic Materials Made by Rapid Quenching. J. Phys. Colloq. 1988, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneller, E.F.; Hawig, R. The exchange-spring magnet: A new material principle for permanent magnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1991, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullerton, E.E.; Jiang, J.S.; Bader, S.D. Hard/soft magnetic heterostructures: Model exchange-spring magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ortega, A.; Estrader, M.; Salazar-Alvarez, G.; Roca, A.G.; Nogués, J. Applications of exchange coupled bi-magnetic hard/soft and soft/hard magnetic core/shell nanoparticles. Phys. Rep. 2015, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.B.; Takahashi, Y.K.; Hono, K. Nd2Fe14B/FeCo anisotropic nanocomposite films with a large maximum energy product. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.C.; Chiou, D.Y.; Wu, S.H.; Ma, B.M.; Bounds, C.O. High performance α-Fe/Nd2Fe14B-type nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.C.; Dahlgren, M.; Grössinger, R.; Wiesinger, G. Spin-reorientation transition in nano-, micro- and single-crystalline Nd2Fe14B. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villas-Boas, V.; Romero, S.A.; Missell, F.P. Flash annealing and magnetic interactions in Pr4Fe78B. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.P.; Liu, W.Q.; Huang, Y.L.; Ma, S.C.; Zhong, Z.C. Effects of sintering temperature on the mechanical properties of sintered NdFeB permanent magnets prepared by spark plasma sintering. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.Z.; Kong, F.Q.; Xiong, W.; Li, B.Q.; Li, J.; Wang, L. New La-Fe-B ternary system hydrogen storage alloys. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.Y.; Xu, Z.; Peng, S.; Rong, C.; Liu, J.P.; Sun, S. A facile synthesis of SmCo5 magnets from core/shell Co/Sm 2O3 nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt, I.; Davies, H.A. Exchange coupled nanocomposite hard magnetic alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyola Lozano, D.; Zamora, L.E.; Pérez Alcázar, G.A.; Rojas, Y.A.; Bustos, H.; Greneche, J.M. Magnetic and structural properties of the Nd2(Fe 100-xNbx)14B system prepared by arc melting. Hyperfine Interact. 2006, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.Y.; Takahashi, Y.K.; Hono, K. Fabrication and characterization of highly textured Nd-Fe-B thin film with a nanosized columnar grain structure. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 043901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.Z.; Sun, X.K.; Xiong, L.Y.; Cao, S.T.; Zhang, X.X.; Liu, W.; Geng, D.Y.; Zhang, Z.D. Relation between structure and magnetic properties of Nd2(Fe, Co, Mo)14B/α-Fe nanocomposite magnets. J. Alloy. Compd. 2002, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcanover, J.A.; Paduani, C.; Ardisson, J.D.; Pérez, C.A.S.; Yoshida, M.I. Mössbauer effect and magnetization studies of Nd16Fe 76 - XRuxB8 alloys. Acta Mater. 2005, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukagawa, T.; Ohkubo, T.; Hirosawa, S.; Hono, K. Nano-sized disorders in hard magnetic grains and their influence on magnetization reversal at artificial Nd/Nd2Fe14B interfaces. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.B.; Takahashi, Y.K.; Hono, K. Microstructure optimization to achieve high coercivity in anisotropic Nd-Fe-B thin films. Acta Mater. 2011, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T. Electrical resistivity and magnetic properties of Nd-Fe-B alloys produced by melt-spinning technique. J. Alloy. Compd. 2010, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.M.; Herchenroeder, J.W.; Smith, B.; Suda, M.; Brown, D.; Chen, Z. Recent development in bonded NdFeB magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keavney, D.J.; Fullerton, E.E.; Pearson, J.E.; Bader, S.D. High-coercivity, c-axis oriented Nd2Fe14B films grown by molecular beam epitaxy. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, T.; Koyama, S.; Kasai, Y.; Panchanathan, V. Low rare-earth Nd–Fe–B bonded magnets with improved irreversible flux loss. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corfield, M.R.; Williams, A.J.; Harris, I.R. Effects of long term annealing at 1000 °C for 24 h on the microstructure and magnetic properties of Pr-Fe-B/Nd-Fe-B magnets based on Nd16Fe76B8 and Pr16Fe76B. J. Alloy Compd. 2000, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.; Tian, M.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhang, D.T.; Niu, P.L.; Yang, F. Microstructure and magnetic properties of anisotropic Nd-Fe-B magnets produced by spark plasma sintering technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2006, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian, S.; Chandrasekaran, V.; Markandeyulu, G.; Iyer, K.J.L.; Rama Rao, K.V.S. Effect of Al, Cu, Ga, Nb additions on the magnetic properties and microstructural features of sintered NdFeB. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, M.; Qiao, Y. High-performance α-Fe/Pr2Fe14B-type nanocomposite magnets produced by hot compaction under high pressure. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, V.; Gutoiu, S.; Dorolti, E.; Isnard, O.; Chicina, I. The influence of short time heat treatment on the structural and magnetic behaviour of Nd 2 Fe 14 B/α-Fe nanocomposite obtained by mechanical milling. J. Alloy. Compd. 2011, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu, V.; Schultz, L. Two-phase high-performance Nd-Fe-B powders prepared by mechanical milling. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, J.A.; Herchenroeder, J.W.; Wright, J.L.; Easton, D.S. Fracture toughness of Nd2Fei4B magnets. Mater. Trans. Jim 1996, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.H.; Zhu, M.G.; Li, W.; Lian, F.Z. Effects of Nb on the coercivity and impact toughness of sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymura, S.; Wyslocki, J.J.; Rabinovich, Y.M.; Bala, H. Domain structure, magnetic and mechanical properties of Nd Fe B magnets with different grain size. Phys. Status Solidi (a) 1994, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varret, F.; Teillet, J. Unpublished MOSFIT program. Maine University: Le Mans, France.
- Larson, A.C.; von Dreele, R.B. General Structure Analysis System (GSAS); Los Alamos National Laboratory Report LAUR: Laur, Philippines, 2004.
- Gao, J.; Volkmann, T.; Roth, S.; Löser, W.; Herlach, D.M. Phase formation in undercooled NdFeB alloy droplets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2001, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.C.; Li, Y. A new structure of Nd1+εFe4B4 phase in NdFeB magnet. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gang, S.; Lianxi, H.; Erde, W. Preparation, microstructure, and magnetic properties of a nanocrystalline Nd12Fe82B6 alloy by HDDR combined with mechanical milling. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Zeng, X.; Fu, D.; Deng, F. Differences in microstructure and magnetic properties between directly-quenched and optimally-annealed Nd-Fe-B nanocomposite materials. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2010, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Gong, W. Magnetic hysteresis in melt-spun Nd-Fe-Al-B-Si alloys with high remanence. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaf, A.; Buckley, R.A.; Davies, H.A. New nanocrystalline high-remanence Nd-Fe-B alloys by rapid solidification. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1993, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzoni, F.; Gavigan, J.P.; Givord, D.; Li, H.S.; Moze, O.; Pareti, L. 3d magnetism in R2Fe14B compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1987, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagawa, M.; Hirosawa, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Fujimura, S.; Matsuura, Y. Nd-Fe-B Permanent Magnet Materials. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1987, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.S.T.; Tabares, J.A.; Alcázar, G.A.P. Structural, magnetic, and mechanical hardness characterization of the alloy Nd16(Fe76−xNix)B8 with x = 0, 10, 20, and 25. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Morrish, A.H.; Zhou, X.Z.; Hu, B.P.; Zhang, S.G. Mössbauer study of the permanent-magnet material Nd 2(Fe1-xNix)14B. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.X.; Altounian, Z.; Ryan, D.H. Cobalt site preferences in iron rare-earth-based compounds. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Liu, Z.X.; Sun, Y.X.; Bai, C.X.; Zhao, T.S. Effect of exchange interaction on spin reorientation in the Nd2Fe14B system. Phys. Rev. B 1989, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).