Abstract
In practical operating conditions, the Solar-Photo Voltaic (SPV) system experiences multifarious irradiation and temperature levels, which generate power with multiple peaks. This is considered as the nonuniform operating condition (NUOC). This requires accurate tracking of global power peaks to achieve maximum power from SPV, which is a challenging task. Hence, this paper presents an incremental Conductance based Particle Swarm Optimization (ICPSO) algorithm for accurate tracking of maximum global power from active power multiple peaks generated by the SPV. The proposed algorithm continuously adjusts the individual particle’s weight component, which depends on its distance from the global best position during the tracking process. The proposed algorithm has the merit of continuous adjustment of weight components which reduces active power oscillations at the optimal global position area. Proposed ICPSO algorithm has been successfully designed and implemented for Solar-photo voltaic (PV) under nonuniform operating condition. It is established that the proposed algorithm enhances the output power of the Solar-PV up to 7% with the maximum power tracking of 0.1 s compared to other maximum power point tracking algorithms.
1. Introduction
The requirement of maximum power generation from Renewable Energy (RE) sources with excellent quality have increased significantly to minimize the emission of greenhouse gases. Solar-PV power generation system, Wind power generation system, and Fuel-cells based power generation systems are the major RE sources which are integrated to low voltage distribution system. These sources are clean in nature and less polluting compared to conventional sources of energy [1,2]. The output of these sources depends on the machine side converter and grid side converter [3,4]. However, the performance of these converters depends on the implemented control algorithms [5]. These algorithms are helpful for reactive power management, smooth grid synchronization [6] and power quality mitigation at the point of common coupling (PCC) [7]. Among all these RE resources, Solar Photo-Voltaic (SPV) has been found most prominent RE source less clean power generation with high efficiency and low maintenance [8]. It has been recognized that by the end of 2050, the SPV would fulfil 25% of total electrical power needs worldwide, and it will be the second-largest renewable power generation source behind wind energy. This will lead the way for the transformation of the world renewable power generation zones [9]. Also, the conversion efficiency of Solar PV cells is limited, and the output power entirely depends on the irradiation and temperature of nonuniform operating conditions (NUOCs) [10]. Therefore, accurate tracking of global power peaks to achieve maximum power point tracking is a significant challenge for efficient utilization of the SPV array under grid-connected mode or isolated mode of operation [11]. Hence, it is of foremost importance that, SPV array and hybrid wind-PV sources should have maximum efficiency to generate maximum power [12].
An accurate tracking is essential for maximum power point tracking (MPPT), specially in variable atmosphere conditions [13]. In literature, various MPPT algorithms are proposed, such as perturbation and observation (P&O) algorithm is utilized because of its attracting features like simplicity and easy implementation [14]. However, in this algorithm, large fluctuations are generated during the process of tracking maximum power (MPP) tracking under NUOCs. An incremental conductance (I&C) algorithm has been proposed to overcome these problems [15]. This method uses constant measurement steps, which make it possible to track the MPP by measuring the ratio between instantaneous conductance and INC values of the SPV output power. Also, to increase the tracking accuracy of the MPP, a modified version of this algorithm or hybrid method based on gravitational search algorithm–PSO is proposed in [16]. A modified version of I&C algorithm using the initial value incremental conductance strategy for global MPPT is presented in [17]. Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system–PSO based hybrid algorithm for accurate and fast-tracking of MPP with zero oscillation tracking [18], Marginal power-based MPP [19], capacitor selection method [20], combined PSO and perturb and observe method [21], modified genetic algorithm [22] for tracking the global MPPT in Solar-PV system are also reported in literature.
It has been perceived that under nonuniform operating conditions of solar-PV conventional PSO may take high time to reach the steady-state conditions due to arising of large step size, selection of parameters and process involved in the algorithm. Voltage variations also persist during the process of MPP tracking. The computed value of velocity can be responsible for significant overshoot due to multiple global peaks in the Solar-PV power and voltage characteristics, leading to uncertain MPPT [23]. New overall distribution (OD) based MPPT algorithm for tracking of maximum global power has been presented in [11]. However, PSO is integrated into the OD based MPPT algorithm to enhance the accuracy of MPPT. Accuracy is not only criteria for designing of hybrid MPPT algorithm. Hence, Load-current adaptive step-size and perturbation frequency (LCASF) based MPPT algorithm has been presented in [24] for enhancing speed, accuracy, and efficiency of the Solar-PV system. These attractive features have been addressed by designing the high-performance MPPT algorithm in [25] for efficient utilization of maximum power of Solar-PV under continuously changing environmental conditions. Likewise, modified firefly algorithm (MFA) has been proposed for minimizing the drawbacks of local peaks and oscillations of conventional MPPT algorithm under rapid-changing atmospheric conditions [26]. A modified flower pollination algorithm has been designed for enhancing the conversion efficiency of the Solar-PV system under nonuniform operating conditions [27]. Moreover, in [28], authors proposed a fuzzy logic controller (FLC) optimized by a combination of particle swarm optimization (PSO) and genetic algorithm (GA) for MPP tracking under above mentioned operating conditions. PSO and GA are two practical meta heuristic optimization approaches [29,30] with approved efficiency, practical applications and extended variants like predictive data analysis [31], log-scaled variant [32], anaomaly detection [33], Mendelian extension [34], multi criteria decision making [35], etc. In this paper, PSO-GA is optimized by FLC and achieves remarkable output by considering various irradiation and temperature levels. A comparative study of this algorithm with the conventional and hybrid MPP algorithms is also presented. The output performance of this controller is 2–8% better than the other MPP algorithms [28].
In this work, the Incremental Conductance Particle Swarm Optimization (ICPSO) algorithm is designed and implemented for efficient tracking of the global MPP under NUOC. The significant contributions of research work included in this paper are highlighted below:
- Design and application of ICPSO algorithm for extraction of efficient tracking the global maximum power point under NUOC.
- Proposed algorithm is effective to reduce the steady-state oscillations by continuous tracking of weight component.
- Proposed algorithm updates velocity and position of particles using the concept of I&C MPPT algorithm.
- Proposed ICPSO is useful for fast-tracking of the speed with negligible oscillations at the global maximum point compared to other conventional and hybrid MPP algorithms.
- Easy calculation for accurate tracking of global maximum during sudden fluctuations in temperature and irradiance level.
- MATLAB code has been successfully executed for various temperatures and Irradiation condition of Solar-PV array in a practical scenario.
Seven sections are used to arrange contents in the manuscript. Significant introduction to carry out research on the selected topic and main contributions are included in Section 1. Section 2 provides the concept behind the tracking of MPPT. Section 3 describes the system under consideration. Proposed Design and implementation of the proposed MPPT algorithm is presented in Section 4. Concept validation of proposed ICPSO algorithm is detailed in Section 5 using simulation results. Performance comparison of the proposed MPP algorithm with other existed MPP algorithms are described in Section 6, followed by conclusion in Section 7.
2. Concept Behind the Proposed ICPSO Algorithm
The literature is clearly evident that maximum power tracking of Solar-PV is a major issue under NUOC and conventional algorithms are not able to track accurate maximum power during continuous variations in solar irradiance and temperature levels, as they are inefficient to track the global maximum. Hence, there is a strong need to track fast and accurate MPP with the help of the hybrid algorithm. The proposed hybrid MPP algorithm is designed in such a way that, it is effective to accommodate all the changes associated with the PV system and track global MPP accordingly [36]. This is achieved by updating the velocity and position of the preceding particle using incremental and conductance algorithm [37]. As NUOCs changed the direction of the particles, therefore the proposed algorithm includes minimum-maximum acceleration coefficient to improve the searchability of particle swarm optimization. Also, continuous updating of weights and re-initialization of particles, according to changes associated with Solar-PV irradiance and temperature, helps the algorithm to reduce steady-state oscillations and accurate tracking of global MPP. This PowerPoint of solar-PV panels is a function of SPV irradiance and temperature and, with the help of research work presented in [36], characteristics of Solar-PV under different irradiance and temperature levels is as illustrated in Figure 1. Proposed ICPSO is effective to demonstrate better performance due to its attractive features like fast convergence rate and accurate MPP tracking.
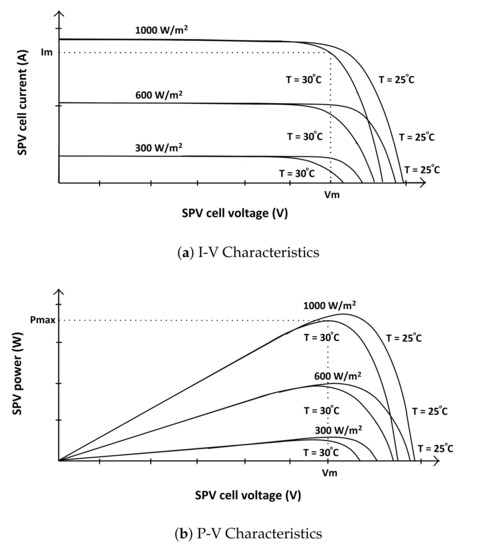
Figure 1.
Characteristics of Solar-PV under different irradiance and temperature levels.
3. System under Consideration
Block diagram of the system under consideration for performance evaluation of the proposed incremental conductance-based particle swarm optimization (ICPSO) algorithm is detailed in Figure 2. An ideal photo-voltaic cell is comprised of a single diode connected in parallel with a light current source, which is connected to the single-phase converter and controlled by the proposed ICPSO based global maximum MPPT algorithm. An electrical equivalent circuit of a solar cell can be represented by a single or double diode model [38]. Single diode equivalent model is found simple with accurate efficiency [39]. The single diode equivalent circuit is as illustrated in Figure 3. In this circuit, the relation between output voltage (V) and current (I) of the solar cell can be expressed by the following relation where the symbols are defined as : current of the solar cell, : saturation current, A: curve fitting factor, : shunt resistance, : series resistance, q: electronic charge, and k: Boltzmann constant [40]. Data of the solar PV system used for the study are available in Appendix A.
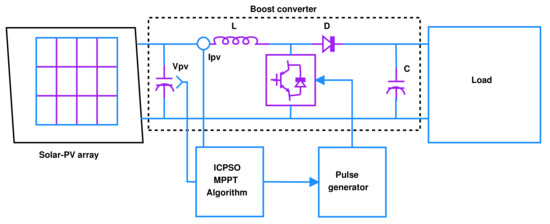
Figure 2.
Block diagram of the system under consideration.
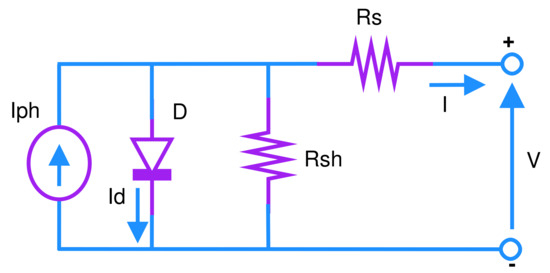
Figure 3.
Single-diode equivalent circuit of Solar-PV system.
4. Design and Implementation of Proposed MPPT Algorithm
The application of conventional Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) algorithm for single power peak values of solar-PV modules is effective. However, nonuniform operating conditions (NUOC) generate multiple peaks, and conventional PSO is not capable of tracking these numerous peak weight components during tracking of maximum power. Hence, conventional PSO needs to be modified for implementation in the NUOC conditions. For this purpose, the concept of I& C has been utilized for updation of particle velocity and position of the PSO algorithm.
4.1. Concept of Incremental Conductance (I & C)
The concept behind the I& C algorithm is to effectively measure the derivative of SPV output power with output voltage [41]. The output power of solar-PV is given as,
where, is output maximum power of SPV, is output voltage of SPV and is output current of SPV. At the point of maximum power, the derivate of power with respect to voltage is computed where slope of the curve is zero.
where, , and represent the changes associated with solar-PV power, voltage and current respectively. However, and are increments in the solar-PV current-voltage sequentially.
The basic equations [42] of are derived using Power-Voltage curve of solar-PV. This algorithm is step by step explained in [43]. Equations of operating point are detailed below:
- →
- Operation point is at maximum power point (MPP)
- →
- Operation point is at left side of MPP
- →
- Operation point is at right side of MPP
4.2. Incremental Conductance Based Particle Swarm Optimization (ICPSO)
The designing of ICPSO algorithm works on the principle of basic PSO where particle velocity and positions are updated using incremental conductance concept in PSO. In this algorithm, the swarm particles are distributed over the global search-space. Feasible solutions are matched with the positions of every particle. The accurate position of each particle is computed using the cost function value, which is then compared with the particle positions as mentioned above. Based on the distance of a particle from these positions, it is assigned a velocity that changes the particle’s position to bring it closer to the global best position [23]. The movement of particles in the global search space for the optimization process of PSO is illustrated in Figure 4 using a phasor concept. The particles are varied according to their position with the help of the equation given below [44].
where, kth iteration is represented by which is presiding position of the ith particle, represents the position of ith particle after the iteration, and represents the computed value of velocity for the same particle for the iteration. The other name of this important computed value is step size (responsible for fast convergence). The particle velocity and position are updated using incremental conductance MPP algorithm, which are described in Equation (3) to Equation (8). The velocity vector is given as,
it can also be rewritten as,
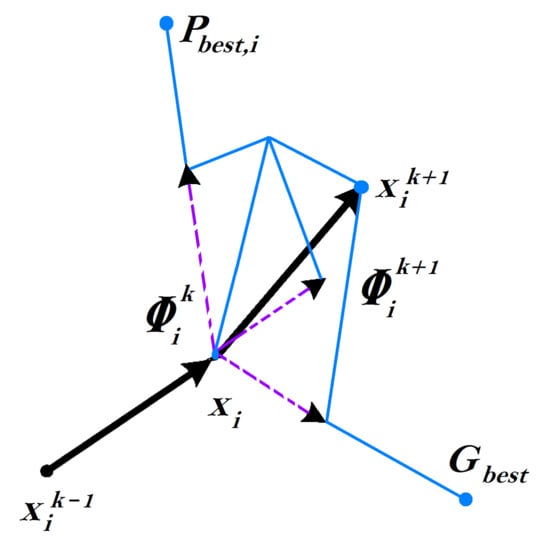
Figure 4.
Movement of particles involved in the optimization process of PSO [44].
Weight (w) component or factor introduces a tendency in the particle to continue to move in same direction with preceding travelling range of [0,1]. The dependency of the velocity of a particle based on its own best position is specified by the cognitive component (). The social component () determines the particle velocity dependence on the global best position observed in the global search-space up to the kth iteration. However, local best position of ith particle can be represents as (). This could be the best suitable solution that same particle has encountered while moving across the global search space. Likewise, global best position () is the best solution perceived among all the particles. In addition, the range of acceleration coefficients () is taken between [0.1–2] and the random number () can be represented as ().
It has been found from the literature that the acceleration coefficients are constant and may affect the searchability of particle swarm optimization due to change in the particle direction. Hence, and conditions are proposed in [37], which is included in ICPSO algorithm to avoid aforementioned conditions (Appendix A). Also, the maximum number of iterations is represented as .
It is well known that the global maximum power point (fitness value) varies most of the time and entirely depends on environmental conditions. Hence, to mitigate the effect of changes associated with environmental condition i.e nonuniform operating conditions due to variation in solar irradiation and temperature, ICPSO continuously updates its weights along with the continuous re-initialization of particles. The re-initialization process with 10% of the change in solar-PV power is as explained in [37].
; new-changed SPV power, ; old-changed SPV power at global MPP of the preceding point of operating. The flow-chart of proposed ICPSO is as depicted in Figure 5.
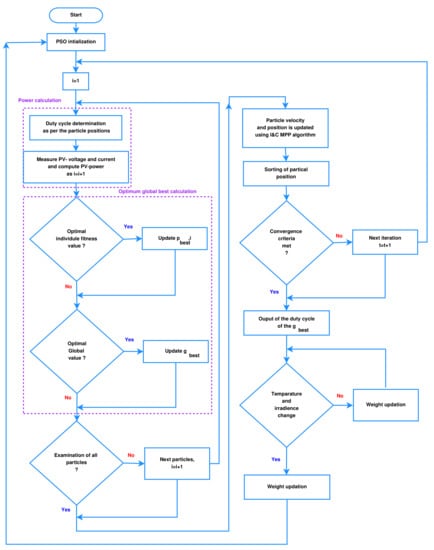
Figure 5.
Proposed ICPSO algorithm.
5. Concept Validation
This section details and discusses simulation results to establish the effectiveness of the proposed ICPSO algorithm. Four practical operating conditions of Solar-PV, which generate power with multiple peaks have been considered to illustrated the multifarious irradiance and temperature levels of NUOC. Proposed algorithm is analysed under Irradiance 1000 W/m, Temperature 25 C, Irradiance 300 W/m, Temperature 25 C, Irradiance 1000 W/m, Temperature 30 C and Irradiance 300 W/m, Temperature 30 C based NUOCs. These are discussed in below mentioned subsections.
5.1. Scenario-1→Irradiance 1000 W/m, Temperature 25 C
Scenario-1, solar-PV input irradiance level of 1000 W/m at a Temperature of 25 C, has been considered for illustrating performance of the proposed ICPSO algorithm for tracking of maximum power. It has been perceived from Figure 6 that, the expected maximum power of SPV is 100 W and obtained power is 97.3 W, which shows the 97.3% efficiency of the proposed algorithm is achieved. The maximum power point has been tracked before 0.1-s without any fluctuations. This fast tracking has been obtained due to the continuous tracking and particle exploration (Global search) process involved in the ICPSO algorithm. The particle exploration process has been visualized at 0.05-s, which shows effectiveness of proposed algorithm.
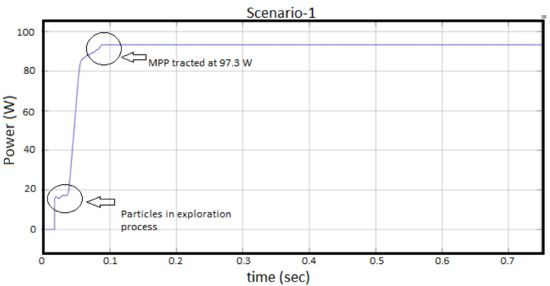
Figure 6.
Performance of ICPSO under Scenario-1.
5.2. Scenario-2→Irradiance 300 W/m, Temperature 25 C
Scenario-2, solar-PV input irradiance level of 300 W/m at a Temperature of 25 C, has been considered for illustrating performance of the proposed ICPSO algorithm for tracking of maximum power under low irradiance. It has been perceived from Figure 7 that, the expected maximum power of SPV is 30 W and obtained power is 27.3 W, which shows that 91% efficiency of the proposed algorithm is achieved. The MPP has been tracked at 0.05-s without any fluctuations. This fast tracking has been obtained due to the continuous tracking and particle exploration process involved in the ICPSO algorithm. The particle exploration process has been visualized at 0.025-s, which shows effectiveness of proposed algorithm.
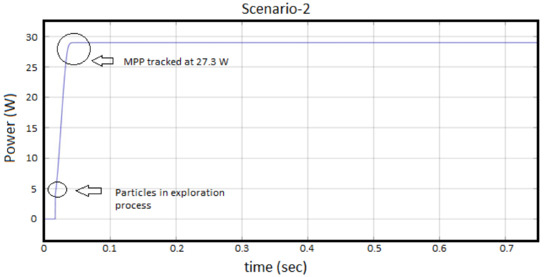
Figure 7.
Performance of ICPSO under Scenario-2.
5.3. Scenario-3→Irradiance 1000 W/m, Temperature 30 C
Scenario-3, solar-PV input irradiance level of 1000 W/m at a Temperature of 30 C, has been considered for illustrating performance of the proposed ICPSO algorithm for tracking of maximum power under high temperature. It has been perceived from Figure 8 that, the expected maximum power of SPV is 87 W and obtained power is 80.4 W, which shows the 92.4% efficiency of the proposed algorithm is achieved. The MPP has been tracked at 0.1-s without any fluctuations. This fast tracking has been obtained due to the continuous tracking and particle exploration process involved in the ICPSO algorithm. The particle exploration process has been visualized at 0.05-s, which shows effectiveness of proposed algorithm.
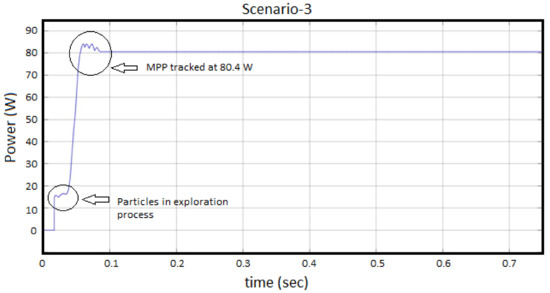
Figure 8.
Performance of ICPSO under Scenario-3.
5.4. Scenario-4→Irradiance 300 W/m, Temperature 30 C
Scenario-4, solar-PV input irradiance level of 300 W/m at a Temperature of 30 C, has been considered for illustrating performance of the proposed ICPSO algorithm for tracking of maximum power under high temperature. It has been perceived from Figure 9 that, the expected maximum power of SPV is 29.5 W and obtained power is 27.8 W, which shows that 94.2% efficiency of the proposed algorithm is achieved. The MPP has been tracked at 0.05-s without any fluctuations. This fast tracking has been obtained due to the continuous tracking and particle exploration (Global search) process involved in the ICPSO algorithm. The particle exploration process has been visualized at 0.025-s, which shows effectiveness of proposed algorithm.
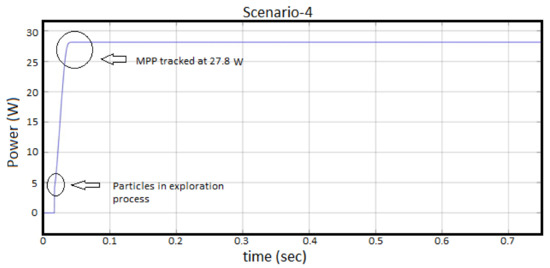
Figure 9.
Performance of ICPSO under Scenario-4.
It has been observed from the results and analysis that, scenario-1 to scenario-4 depicts the nonuniform operating conditions (NUOC). The efficiency of scenario-2 and scenario-4 are found less compared to the effectiveness of scenario-1 and scenario-3, which shows, proposed control algorithm provides excellent results, at a fix temperature level with high irradiance. This research paper aims to present the concept of ICPSO for maximum powerpoint. Therefore only 100 iterations and 50 population size have been selected although efficiency would be increased by increasing population data size and number of iterations. The obtained results reveal that the proposed algorithm is efficiently tracked maximum global power and has stabilized, the oscillation around the MPPT mitigates continuously until another variation in irradiance or temperature takes place. The particles in the exploration process not only updated with fixed irradiance and temperature but it also continuous with variable irradiance and temperature of NUOC. It has been perceived that the absence of oscillation is the attractive feature of the ICPSO algorithm.
5.5. Duty Cycle Updation under Different Irradiance Conditions
In conventional MPP algorithm, there is a lot of fluctuation in the power curve of SPV due to the continuous changing of the duty cycle with each step. However, after completion of every iteration, ICPSO algorithm provides a constant duty cycle which provides minimum fluctuations in the power curve of SPV illustrated in Figure 10, which depicts a clearer insight on the workability of the ICPSO algorithm. It has been perceived from Figure 10 that; the duty cycles are continuously computed with the help of Equations (9) and (10) for the accurate tracking of new MPP during sudden variations or change in irradiation from 1000 W/m to 300 W/m. Likewise, when irradiation changes from 300 W/m to 600 W/m, the updated duty cycles are re-estimated using Equations (9) and (10). The steady-state condition with fewer oscillations has been achieved at 0.1 s.
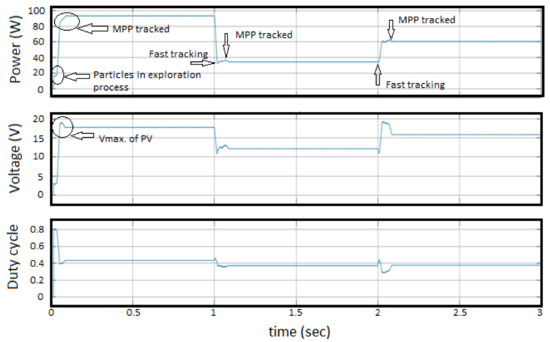
Figure 10.
Duty cycle updation under different irradiance conditions.
6. Comparative Performance Analysis
In conventional MPP algorithm, there is a lot of fluctuation in the power curve of SPV due to continuous change in duty cycle with each step. However, after completion of every iteration, ICPSO algorithm provides a constant duty cycle which provides minimum fluctuations in the power curve of SPV, which is illustrated in Figure 11. In this figure, Proposed ICPSO is compared with the genetic algorithm based PSO (PSO-GA). The concept of implementation of PSO-GA is adopted from [28]. It is found that, if the fuzzy logic controller (FLC) concept is not applied to PSO-GA, MPP is achieved but with fluctuations. It has been perceived from the Figure 11 that, fast, steady-state and tracking of MPP with fewer fluctuations has been achieved by using ICPSO algorithm compared to PSO-GA algorithm. But there is a trade-off of a few watts power loss of maximum power has been observed during comparison of algorithms, which is illustrated one of the limitations of the proposed MPP algorithm.
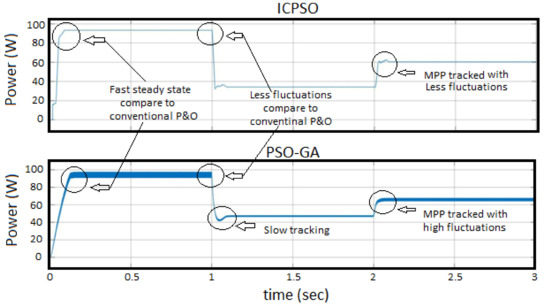
Figure 11.
Comparative analysis of I&C algorithm and proposed ICPSO algorithm.
The significant outcomes are illustrated in Table 1 and Table 2. Table 1 illustrated the comparative performance analysis under variable irradiation and constant temperature level. The tabled data established the effectiveness of the proposed hybrid MPP algorithm. It has been perceived that the performance of the proposed algorithm is not affected during sudden decrements in irradiance level and provide efficient output. Also, Table 2 illustrated the comparative performance analysis under variable temperature and constant irradiation level. The tabled data established the effectiveness of the proposed hybrid MPP algorithm. It has been perceived that the performance of the proposed algorithm is not affected during sudden increments in temperature level and provides efficient output. The PSO-GA based optimized FLC algorithm increases up to 8% of output power, whereas ICPSO increases up to 7% output power. Still, the computational complexity and time for tracking of MPP are less compared to the PSO-GA-FLC algorithm. Table 3 illustrated the comparative performance analysis of various algorithms for maximum power point tracking. It has been noted down that, proposed ICPSO tracked maximum power point at fast compared to other MPP algorithms.

Table 1.
Comparative performance analysis under variable irradiance and constant temperature level.

Table 2.
Comparative performance analysis under variable temperature and constant irradiance level.

Table 3.
Comparative performance analysis of tracking time of MPP.
Regarding comparison, as mentioned above, it can be found that the proposed ICPSO MPP algorithm, when compared with the various MPP algorithms, results in the best trade-off between MPP tracking computational complexity, tracking speed, and ease of implementation. These all are achieved by the utilization of the concept of incremental conductance algorithm in PSO for the continuous updation of particle velocity and position for accurate tracking of MPP under nonuniform operating conditions.
7. Conclusions
In this paper, the Incremental Conductance Particle Swarm Optimization (ICPSO) algorithm for tracking maximum global power is designed and successfully implemented under nonuniform operating conditions (NUOCs). It is depicted that the ICPSO exhibits an adaptive form of the hybrid algorithm. The proposed algorithm used the concept of incremental conductance MPP algorithm for updating particle velocity and position and re-initializes the particles to search for the global MPP, resulting in excellent dynamic response. The proposed algorithm found to enhance the tracking speed with a simple structure and provide efficient performance. It is concluded that the NUOCs of the solar-PV has no apparent influence on the tracking of maximum global power in the presence of ICPSO algorithm. It is found that the proposed algorithm enhances the output power of Solar-PV up to 7% with the maximum power tracking time of 0.1-s compare to other maximum power point tracking algorithms. The motive of the proposed research is to provide the concept of designing of hybrid MPP algorithm using particle swarm optimization under nonuniform operating conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.S.C., O.P.M.; methodology, G.S.C., O.P.M.; software, G.S.C.; validation, G.S.C.; formal analysis, G.S.C.; investigation, G.S.C., O.P.M.; resources, G.S.C., O.P.M.; data curation, G.S.C., O.P.M.; writing–original draft preparation, G.S.C., O.P.M.; writing–review and editing, N.G., M.K., T.S.; visualization, N.G., M.K., T.S.; supervision, N.G., M.K., T.S.,. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
External funding is not received for this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known conflict of interest.
Appendix A
ICO-SPC 100 W Soalr-PV module [37], Soalr-PV maximum power = 100 W, voltage = 17.3 V, current = 5.79 A, maximum number of iterations = 100, population size (swarm size) = 50, damping ratio of inertia coefficient = 0.99, (personal acceleration coefficient) = 2, (social acceleration coefficient) = 2, inertia coefficient = 1.
References
- Kjaer, S.B.; Pedersen, J.K.; Blaabjerg, F. A review of single-phase grid-connected inverters for photovoltaic modules. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2005, 41, 1292–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaabjerg, F.; Teodorescu, R.; Liserre, M.; Timbus, A.V. Overview of control and grid synchronization for distributed power generation systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, A.G.; Mahela, O.P. Power quality assessment and event detection in hybrid power system. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2018, 161, 26–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahela, O.P.; Khan, B.; Alhelou, H.H.; Tanwar, S. Assessment of power quality in the utility grid integrated with wind energy generation. IET Power Electron. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawda, G.S.; Shaik, A.G. Performance Evaluation of Adaline Controlled Dstatcom for Multifarious Load in Weak AC Grid. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE PES GTD Grand International Conference and Exposition Asia (GTD Asia), Bangkok, Thailand, 19–23 March 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 356–361. [Google Scholar]
- Chawda, G.S.; Shaik, A.G. Smooth Grid Synchronization in Weak AC Grid with High Wind Energy Penetration using Distribution Static Compensator. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd International Conference on Smart Grid and Renewable Energy (SGRE), Doha, Qatar, 19–21 November 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chawda, G.S.; Shaik, A.G. Adaptive Reactive Power Control of DSTATCOM in Weak AC Grid with High Wind Energy Penetration. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th India Council International Conference (INDICON), Rajkot, India, 13–15 December 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chawda, G.S.; Shaik, A.G.; Mahela, O.P.; Padmanaban, S.; Holm-Nielsen, J.B. Comprehensive Review of Distributed FACTS Control Algorithms for Power Quality Enhancement in Utility Grid With Renewable Energy Penetration. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 107614–107634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRENA. Global Energy Transformation: A Roadmap to 2050; International Renewable Energy Agency: Abu Dhabi, UAE, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mahela, O.P.; Shaik, A.G. Comprehensive overview of grid interfaced solar photovoltaic systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, D.; Su, W.; Lü, J.; Yu, X. An overall distribution particle swarm optimization MPPT algorithm for photovoltaic system under partial shading. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshi, N.; Padmanaban, S.; Bhaskar, M.S.; Blaabjerg, F.; Holm-Nielsen, J.B. An improved hybrid PV-wind power system with MPPT for water pumping applications. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2020, 30, e12210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhachat, F.; Larbes, C. A review of global maximum power point tracking techniques of photovoltaic system under partial shading conditions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 92, 513–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Singh, B.; Panigrahi, B.K. Integration of solar PV with Low-voltage weak grid system: Using maximize-M Kalman filter and self-tuned P&O algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 9013–9022. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Singh, B.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Chakraborty, C.; Suryawanshi, H.M.; Verma, V. Integration of solar PV with low-voltage weak grid system: Using normalized Laplacian kernel adaptive Kalman filter and learning based InC algorithm. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 10746–10758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshi, N.; Bhaskar, M.S.; Padmanaban, S.; Blaabjerg, F.; Azam, F. New CUK–SEPIC converter based photovoltaic power system with hybrid GSA–PSO algorithm employing MPPT for water pumping applications. IET Power Electron. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhou, X.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y. Analysis of dynamic characteristic for solar arrays in series and global maximum power point tracking based on optimal initial value incremental conductance strategy under partially shaded conditions. Energies 2017, 10, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshi, N.; Padmanaban, S.; Holm-Nielsen, J.B.; Blaabjerg, F.; Bhaskar, M.S. An Experimental Estimation of Hybrid ANFIS–PSO-Based MPPT for PV Grid Integration Under Fluctuating Sun Irradiance. IEEE Syst. J. 2019, 14, 1218–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.A.; Foroushani, H.M.; Blaabjerg, F. Marginal Power-Based Maximum Power Point Tracking Control of Photovoltaic System Under Partially Shaded Condition. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 35, 5860–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santra, S.B.; Chatterjee, D.; Kumar, K.; Bertoluzzo, M.; Sangwongwanich, A.; Blaabjerg, F. Maximum Power Point Trterfaced Converter Suitable for Maximum Power Point Tracking. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundareswaran, K.; Palani, S. Application of a combined particle swarm optimization and perturb and observe method for MPPT in PV systems under partial shading conditions. Renew. Energy 2015, 75, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraban, S.; Petreus, D.; Morel, C. A novel MPPT (maximum power point tracking) algorithm based on a modified genetic algorithm specialized on tracking the global maximum power point in photovoltaic systems affected by partial shading. Energy 2014, 74, 374–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pragallapati, N.; Sen, T.; Agarwal, V. Adaptive velocity PSO for global maximum power control of a PV array under nonuniform irradiation conditions. IEEE J. Photovoltaics 2016, 7, 624–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Qahouq, J.A.A.; Haskew, T.A. Adaptive step size with adaptive-perturbation-frequency digital MPPT controller for a single-sensor photovoltaic solar system. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 28, 3195–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Dasgupta, N.; Mukerjee, A.K. High-performance algorithms for drift avoidance and fast tracking in solar MPPT system. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2008, 23, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.P.; Ye, C.E.; Chen, X. A modified firefly algorithm with rapid response maximum power point tracking for photovoltaic systems under partial shading conditions. Energies 2018, 11, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, T.; Hao, X.; Gu, Q. A novel global maximum power point tracking strategy based on modified flower pollination algorithm for photovoltaic systems under non-uniform irradiation and temperature conditions. Energies 2018, 11, 2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Taghipour, M.; Gharehpetian, G.B.; Abedi, M. Optimized Fuzzy Controller for MPPT of Grid-Connected PV Systems in Rapidly Changing Atmospheric Conditions. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravy, M.; Gupta, N.; Patel, N.; Senjyu, T. Frontier Applications of Nature Inspired Computation; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, N. Advancements in Applied Metaheuristic Computing, 1st ed.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Acharjya, D.; Anitha, A. A comparative study of statistical and rough computing models in predictive data analysis. Int. J. Ambient. Comput. Intell. (IJACI) 2017, 8, 32–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gupta, N.; Patel, N.; Tiwari, B.N.; Khosravy, M. Genetic algorithm based on enhanced selection and log-scaled mutation technique. In Proceedings of the Future Technologies Conference; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 730–748. [Google Scholar]
- Bersch, S.; Azzi, D.; Khusainov, R.; Achumba, I.E. Artificial immune systems for anomaly detection in ambient assisted living applications. Int. J. Ambient. Comput. Intell. (IJACI) 2013, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Khosravy, M.; Patel, N.; Dey, N.; Mahela, O.P. Mendelian Evolutionary Theory Optimization Algorithm. TechRxiv 2020. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.R.; Kumar, C. A multi criteria decision making method for cloud service selection and ranking. Int. J. Ambient. Comput. Intell. (IJACI) 2018, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sera, D.; Kerekes, T.; Teodorescu, R.; Blaabjerg, F. Improved MPPT algorithms for rapidly changing environmental conditions. In Proceedings of the 2006 12th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference, Portoroz, Slovenia, 30 August–1 September 2006; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 1614–1619. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulkadir, M.; Yatim, A.; Yusuf, S. An improved PSO-based MPPT control strategy for photovoltaic systems. Int. J. Photoenergy 2014, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, M.; Hosseinian, S.H.; Fathi, S.H.; Abedi, M.; Gharehpetian, G.B. A new power management scheme for parallel-connected PV systems in microgrids. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2018, 9, 1605–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahela, O.P.; Shaik, A.G. Power quality recognition in distribution system with solar energy penetration using S-transform and Fuzzy C-means clustering. Renew. Energy 2017, 106, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram Ola, S.; Saraswat, A.; Goyal, S.K.; Jhajharia, S.K.; Khan, B.; Mahela, O.P.; Haes Alhelou, H.; Siano, P. A Protection Scheme for a Power System with Solar Energy Penetration. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, Ö.; Teke, A. A Hybrid MPPT method for grid connected photovoltaic systems under rapidly changing atmospheric conditions. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 152, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari-doostabad, H.; Keypour, R.; Khalghani, M.R.; Khooban, M.H. A new approach in MPPT for photovoltaic array based on extremum seeking control under uniform and non-uniform irradiances. Sol. Energy 2013, 94, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J. MPPT control for PV generation system based on an improved inccond algorithm. Procedia Eng. 2012, 29, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaque, K.; Salam, Z.; Amjad, M.; Mekhilef, S. An improved particle swarm optimization (PSO)—Based MPPT for PV with reduced steady-state oscillation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 3627–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).