An Enhanced Adaptive Perturb and Observe Technique for Efficient Maximum Power Point Tracking Under Partial Shading Conditions
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
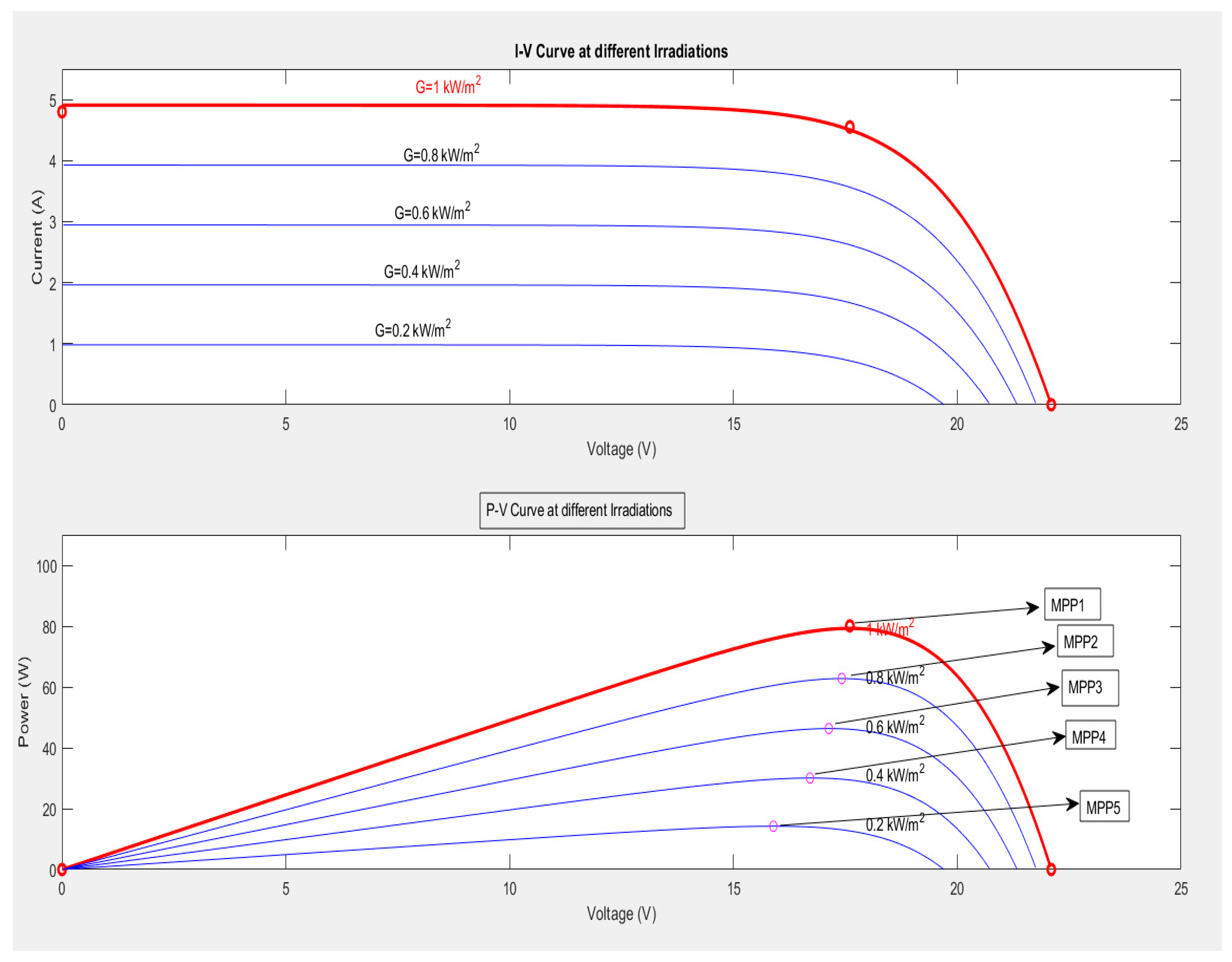
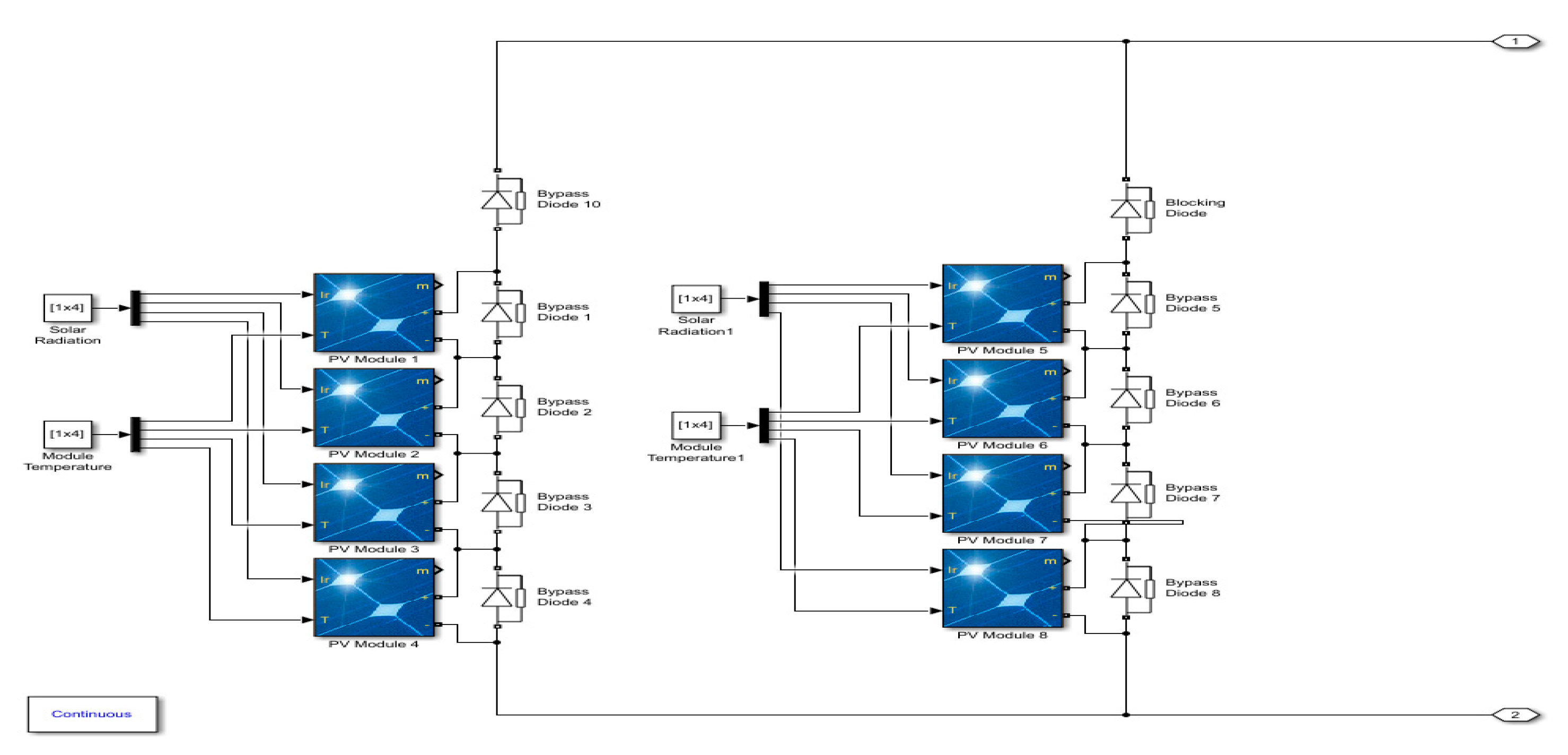
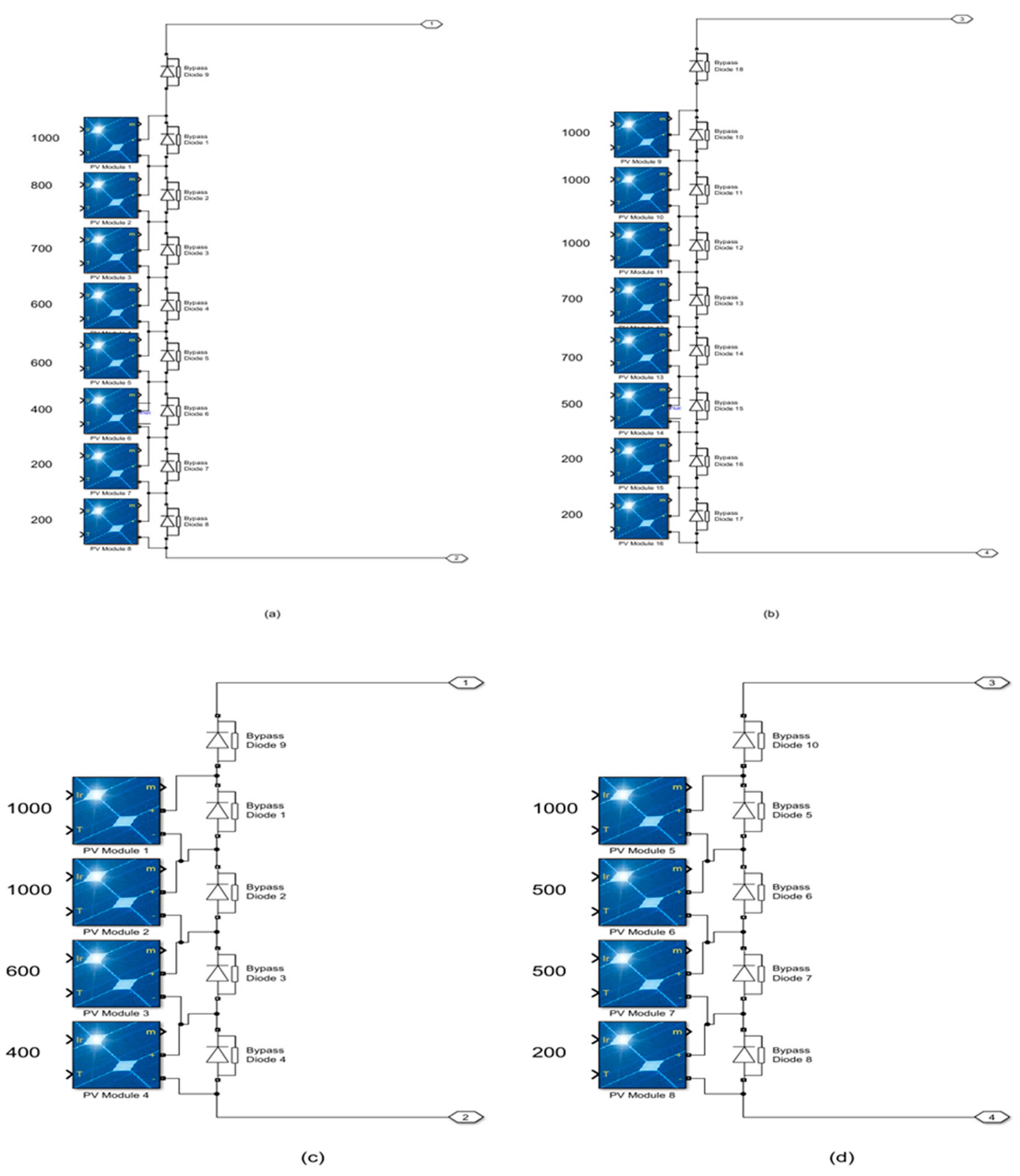
2. Partial Shading Effect Implementation
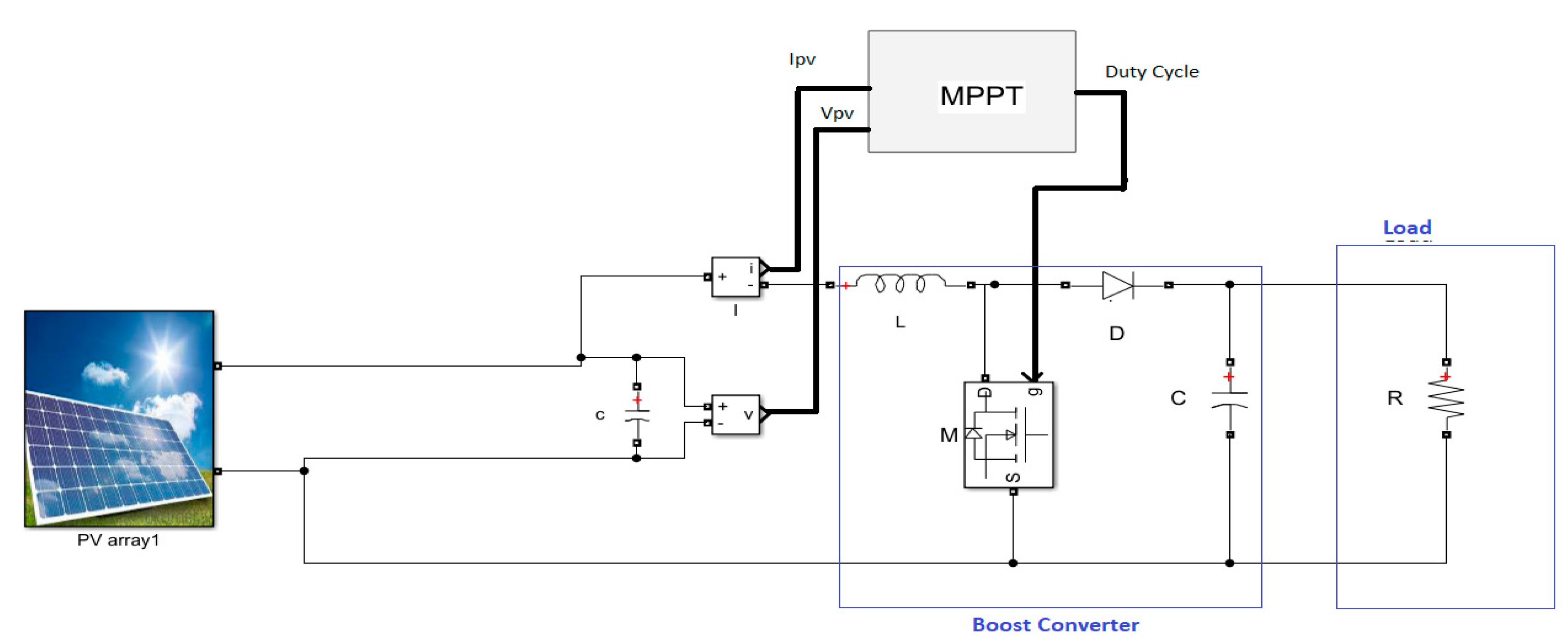
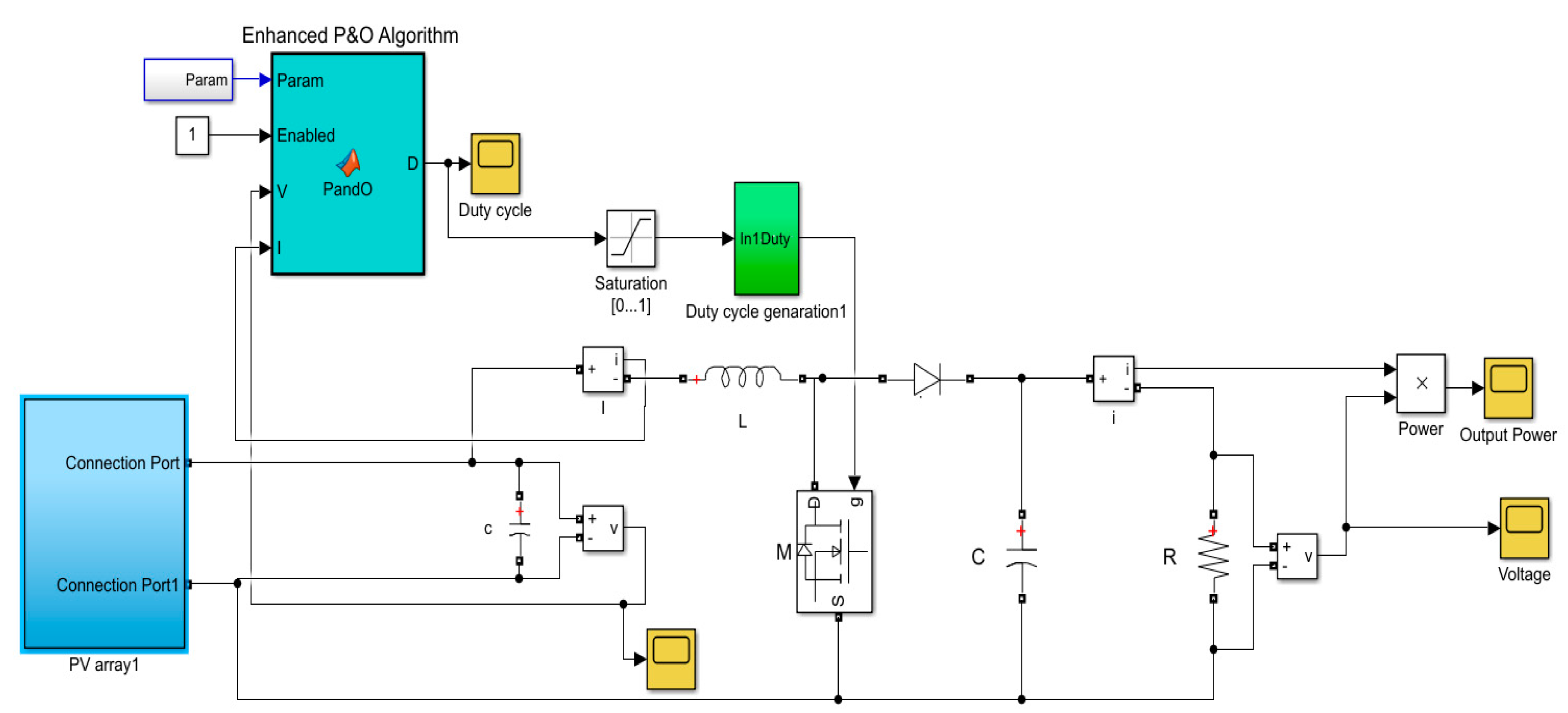
3. DC/DC Boost Converter Design
4. Enhanced P&O Algorithm
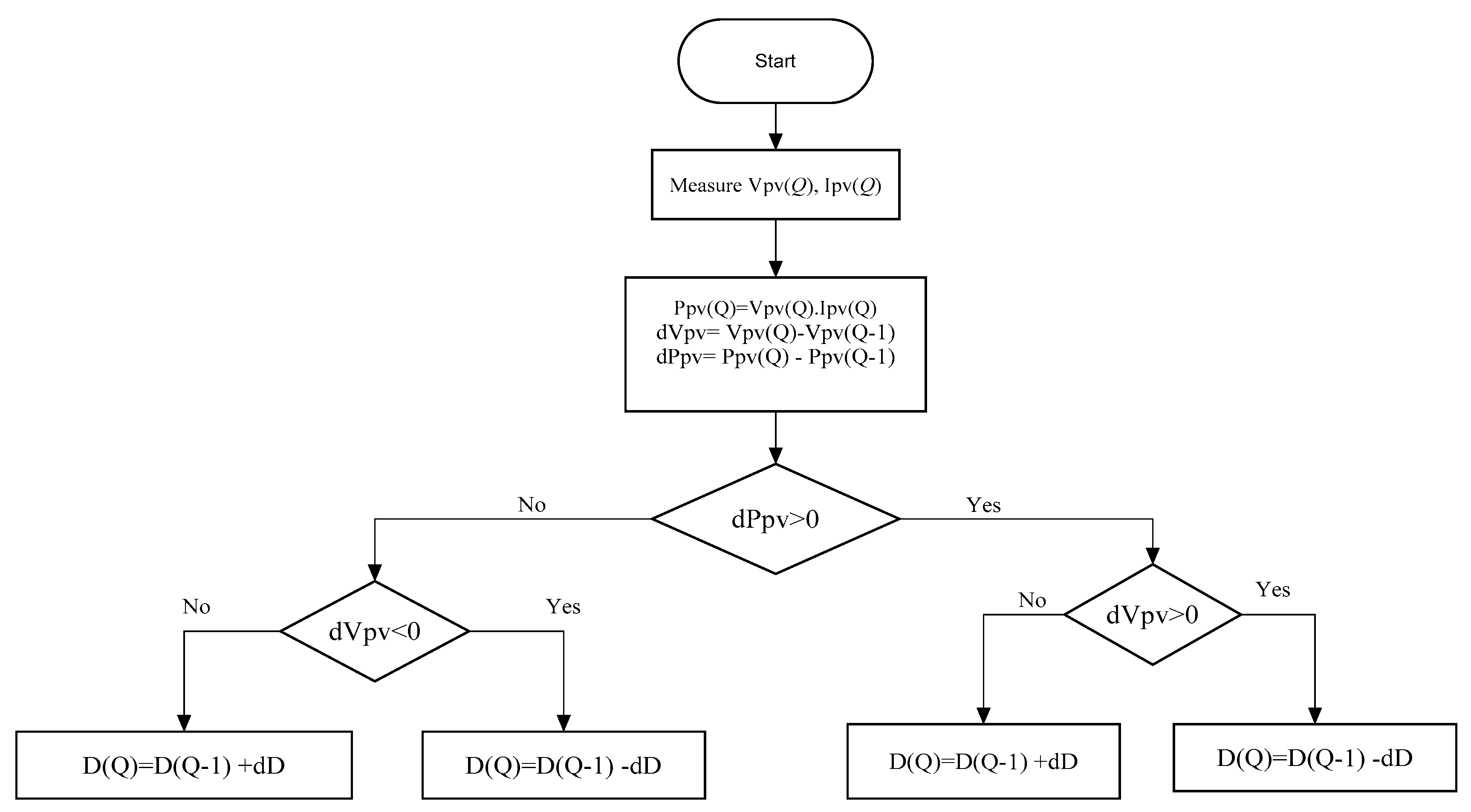
4.1. The Conventional P&O Technique
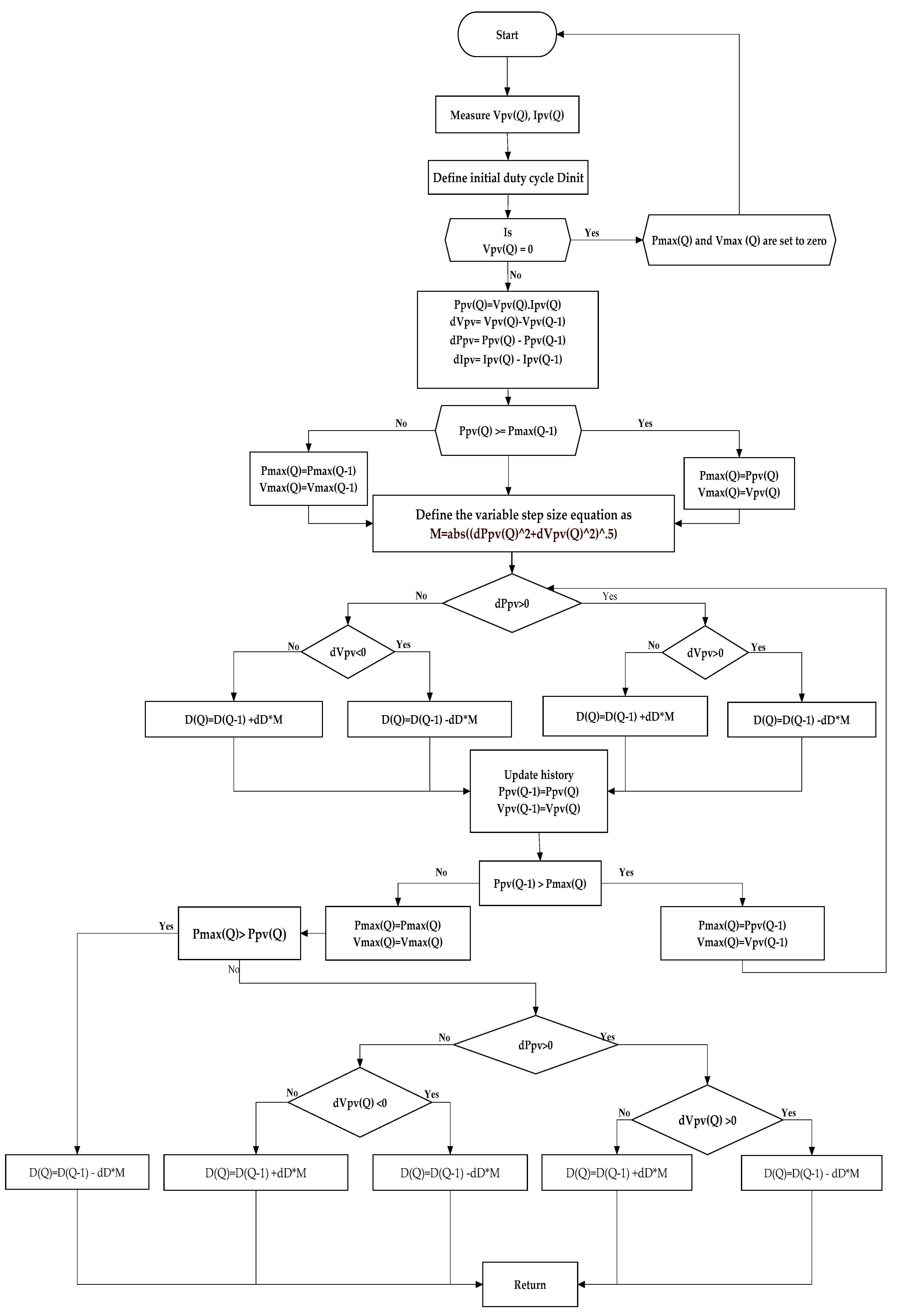
4.2. Enhanced P&O MPPT
5. Simulation Results
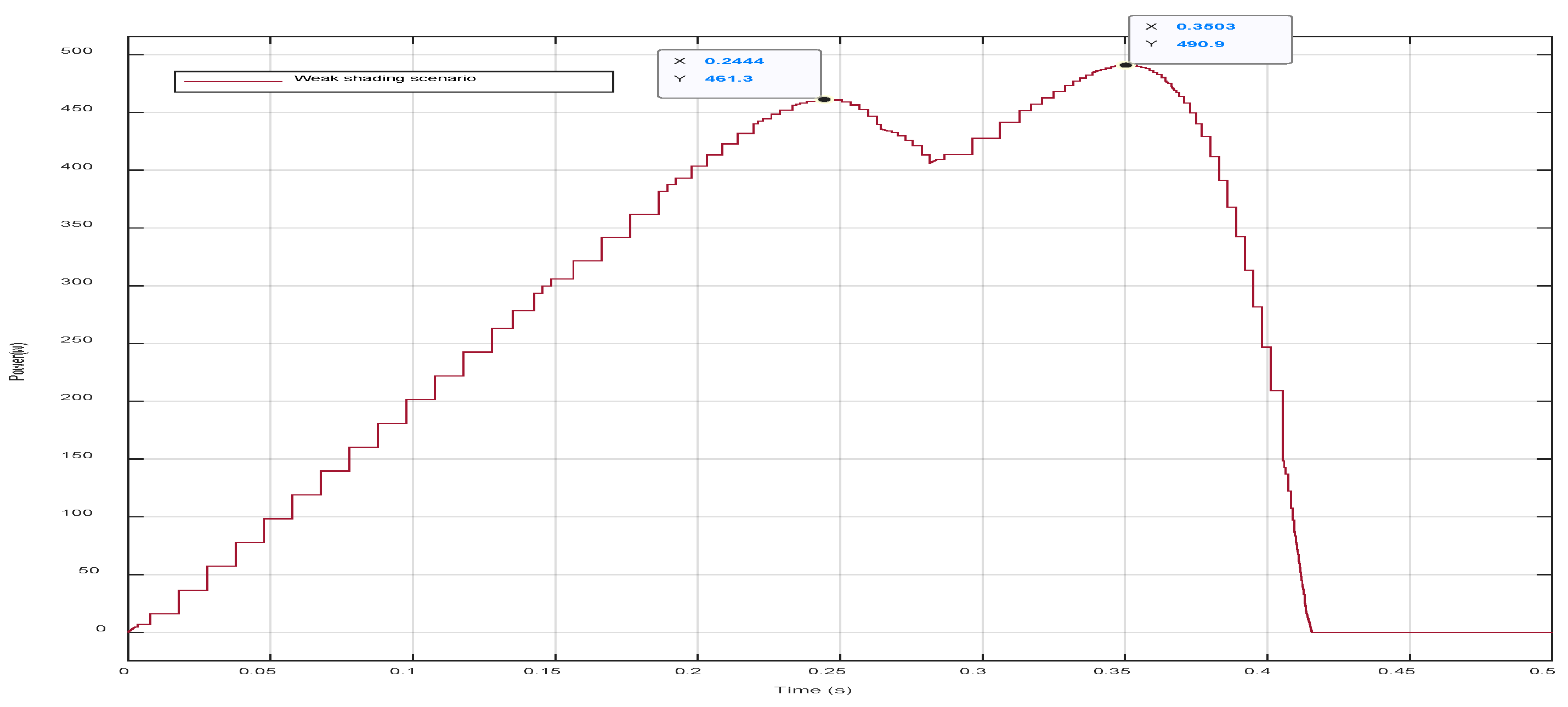
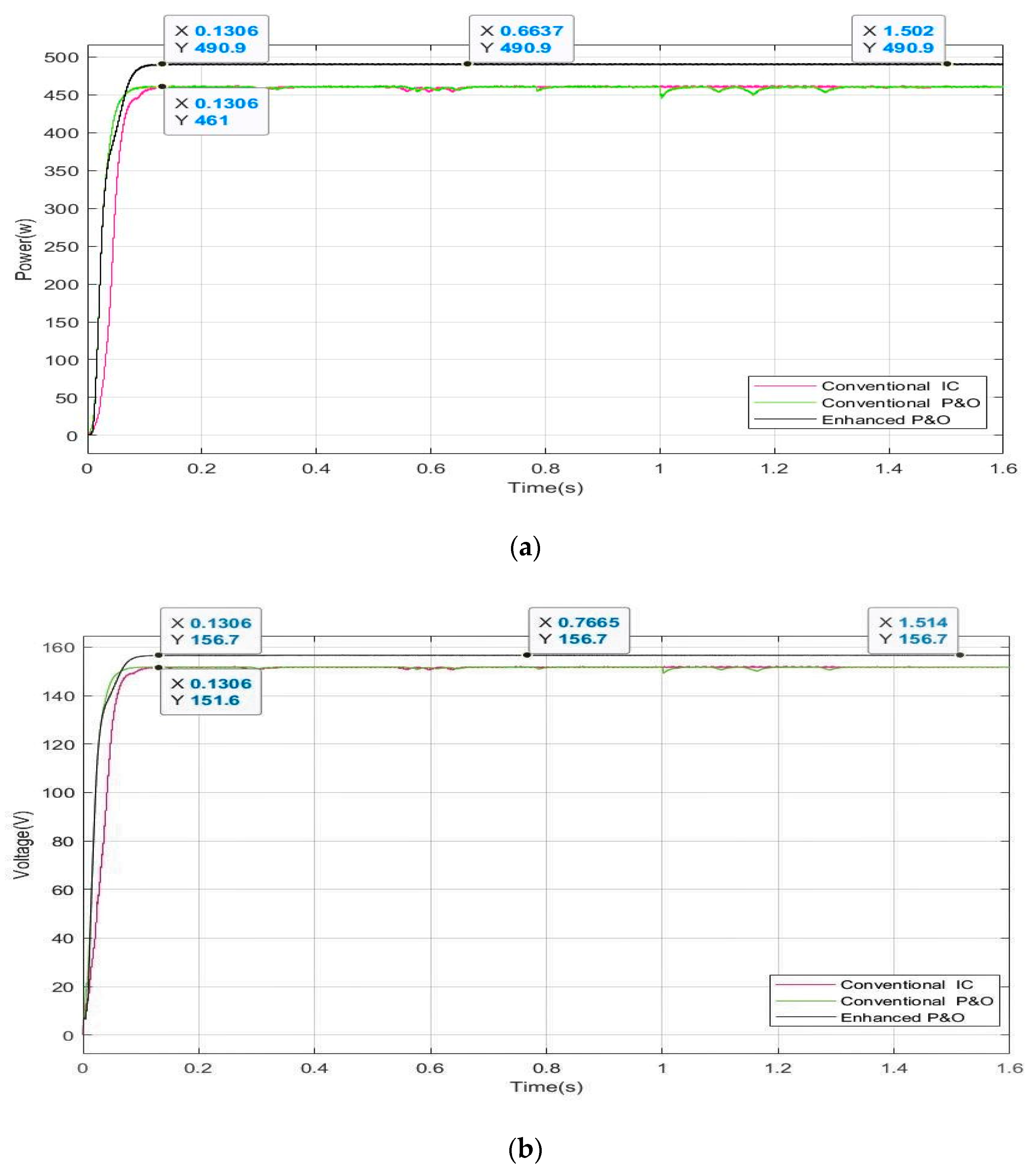
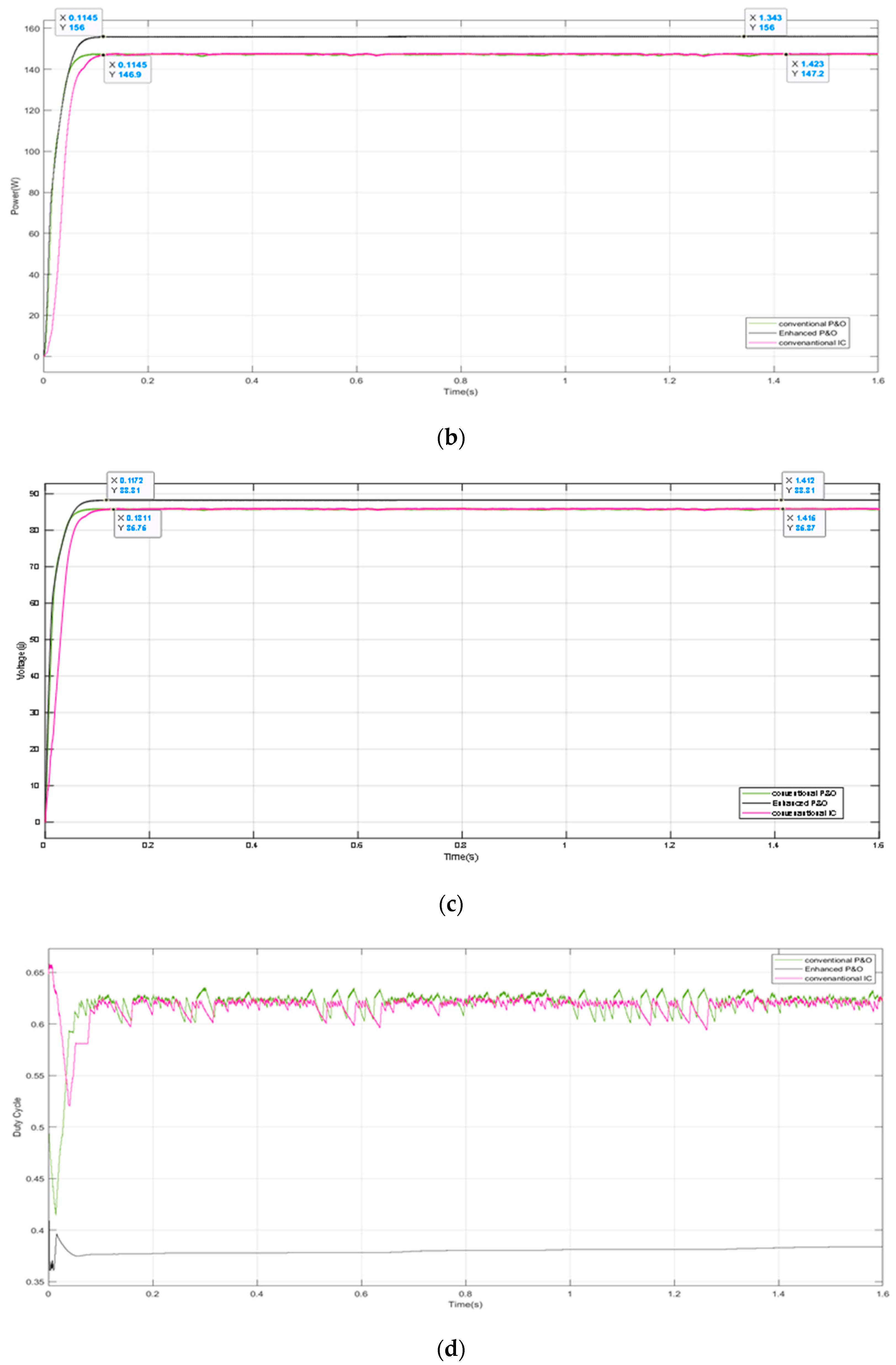
5.1. Case One: Weak Shading Pattern
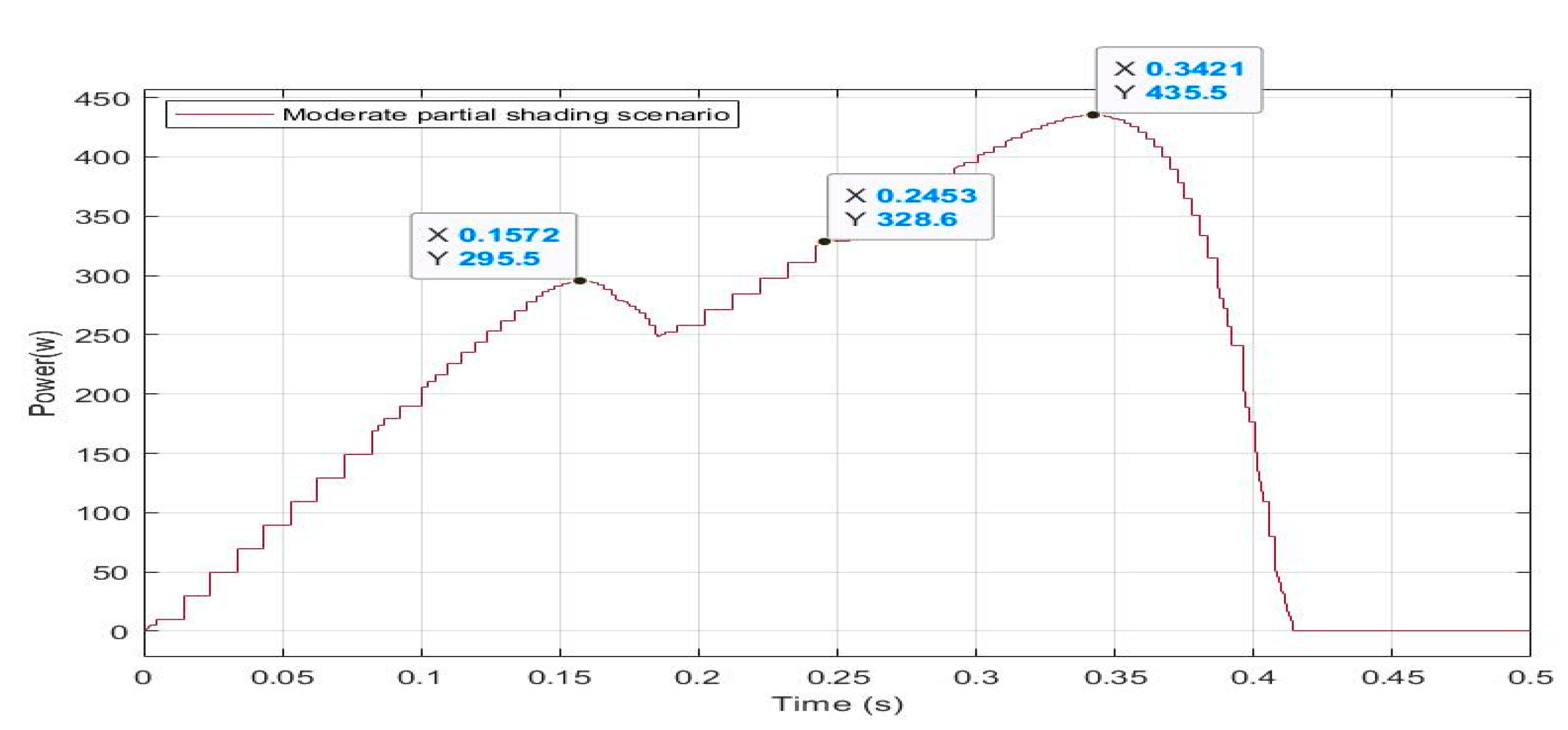
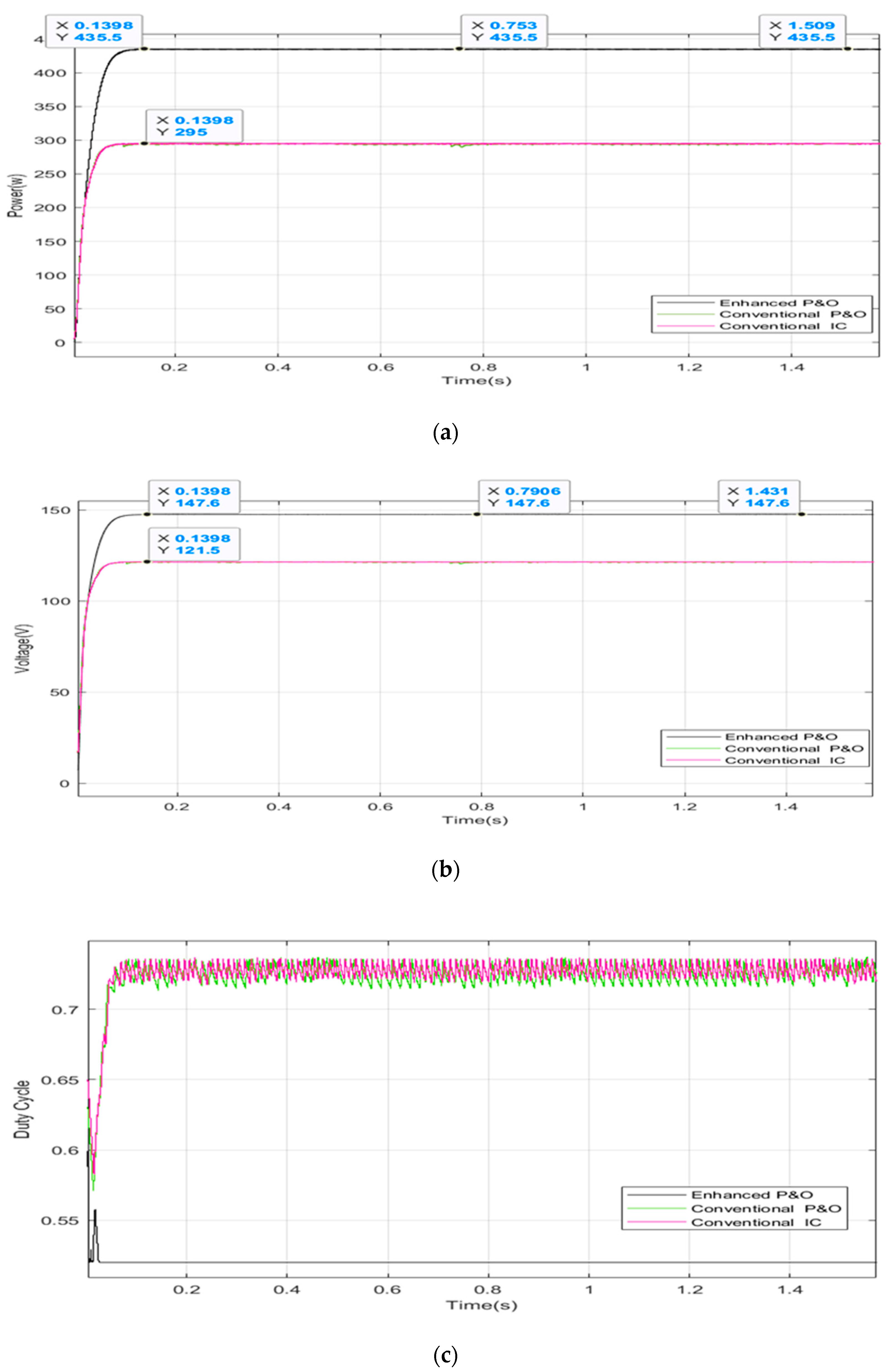
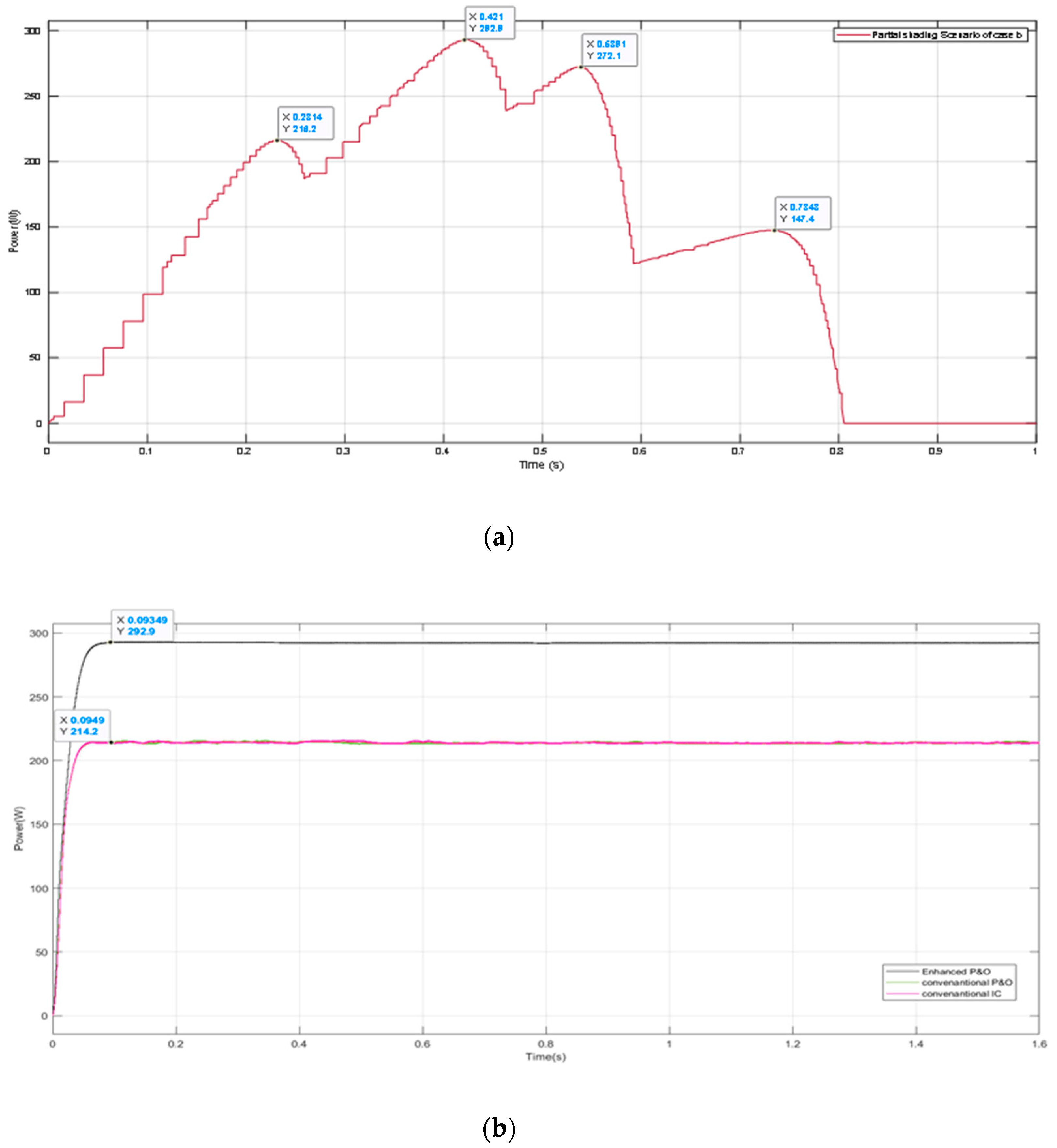
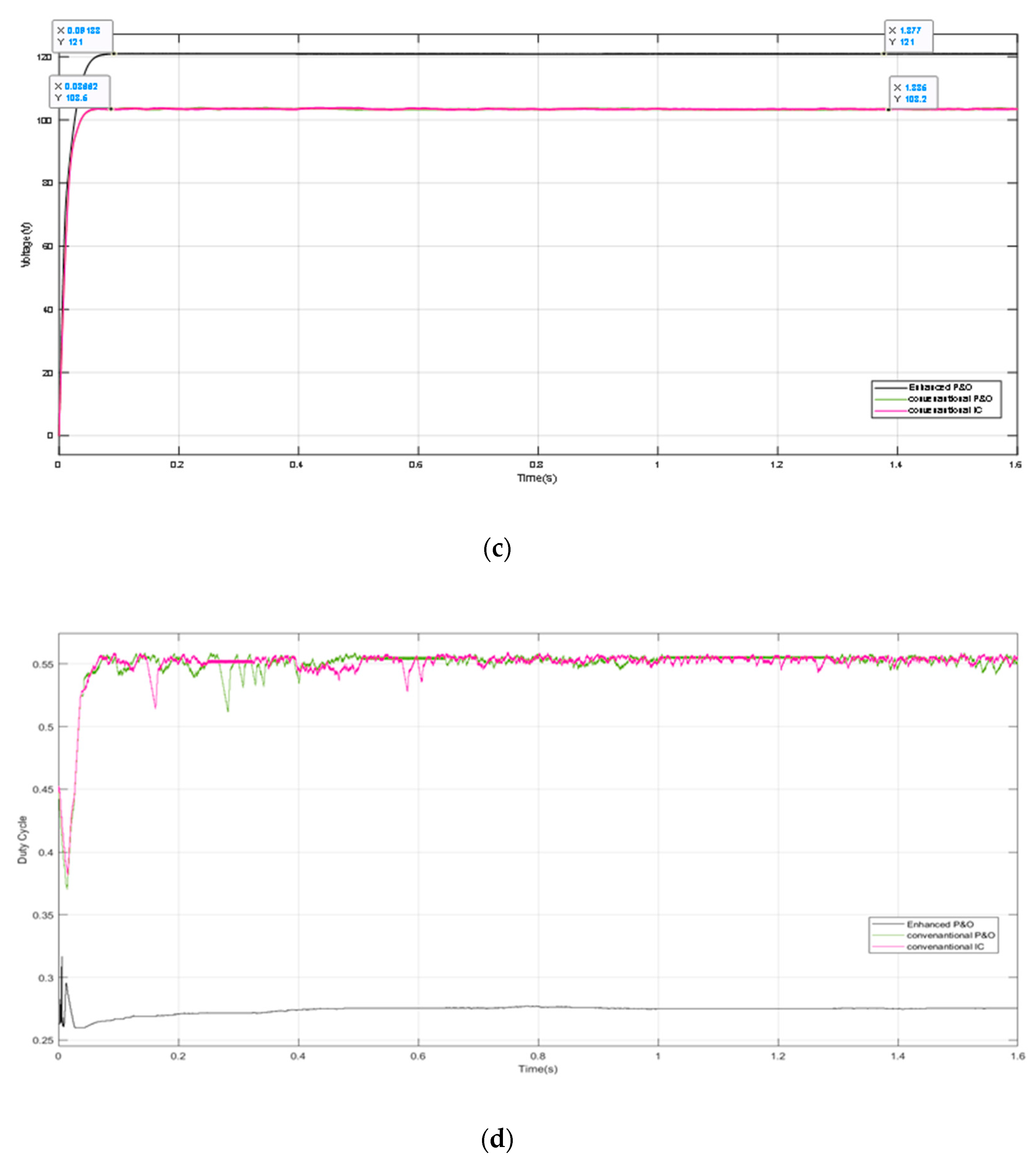
5.2. Case Two: Moderate Partial Shading Pattern
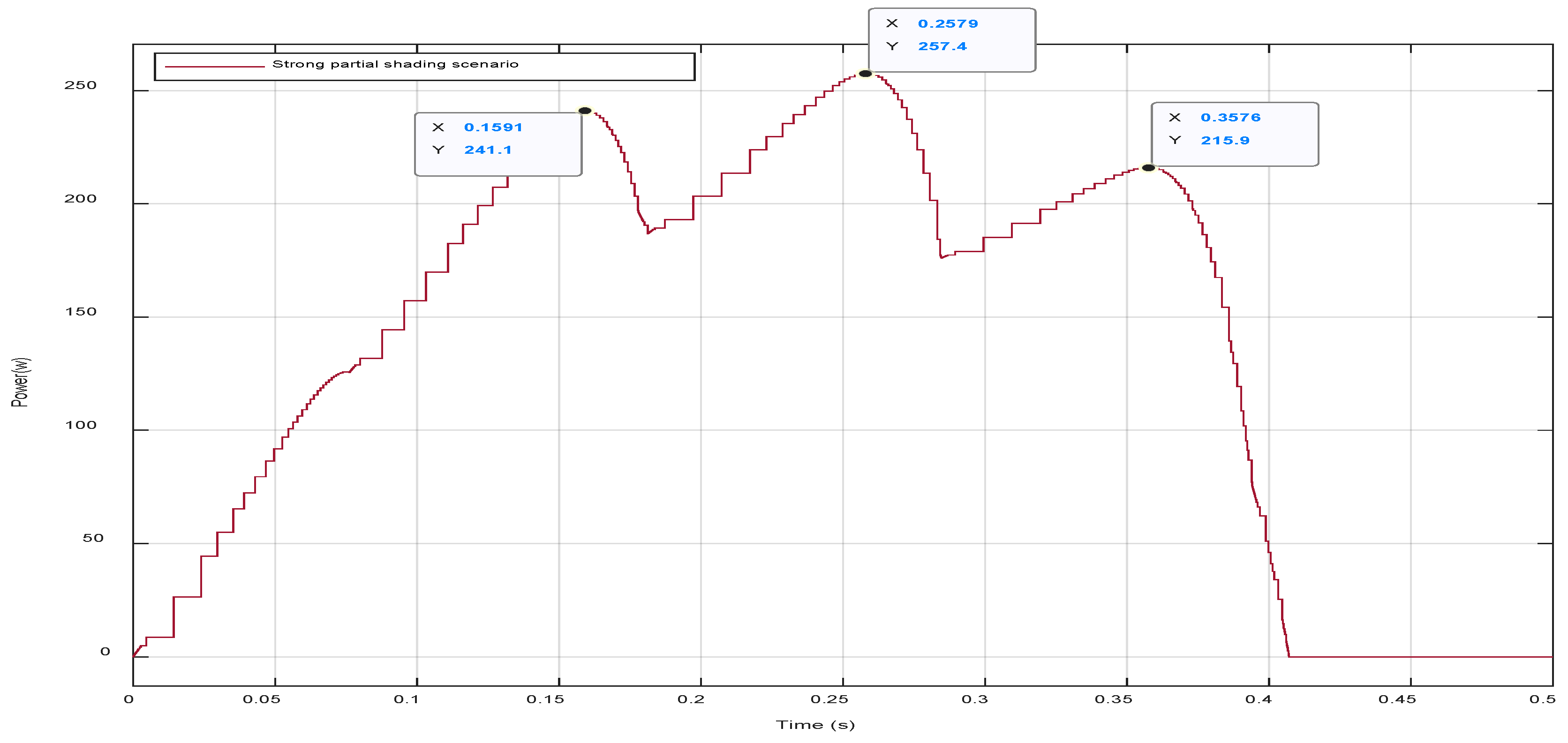
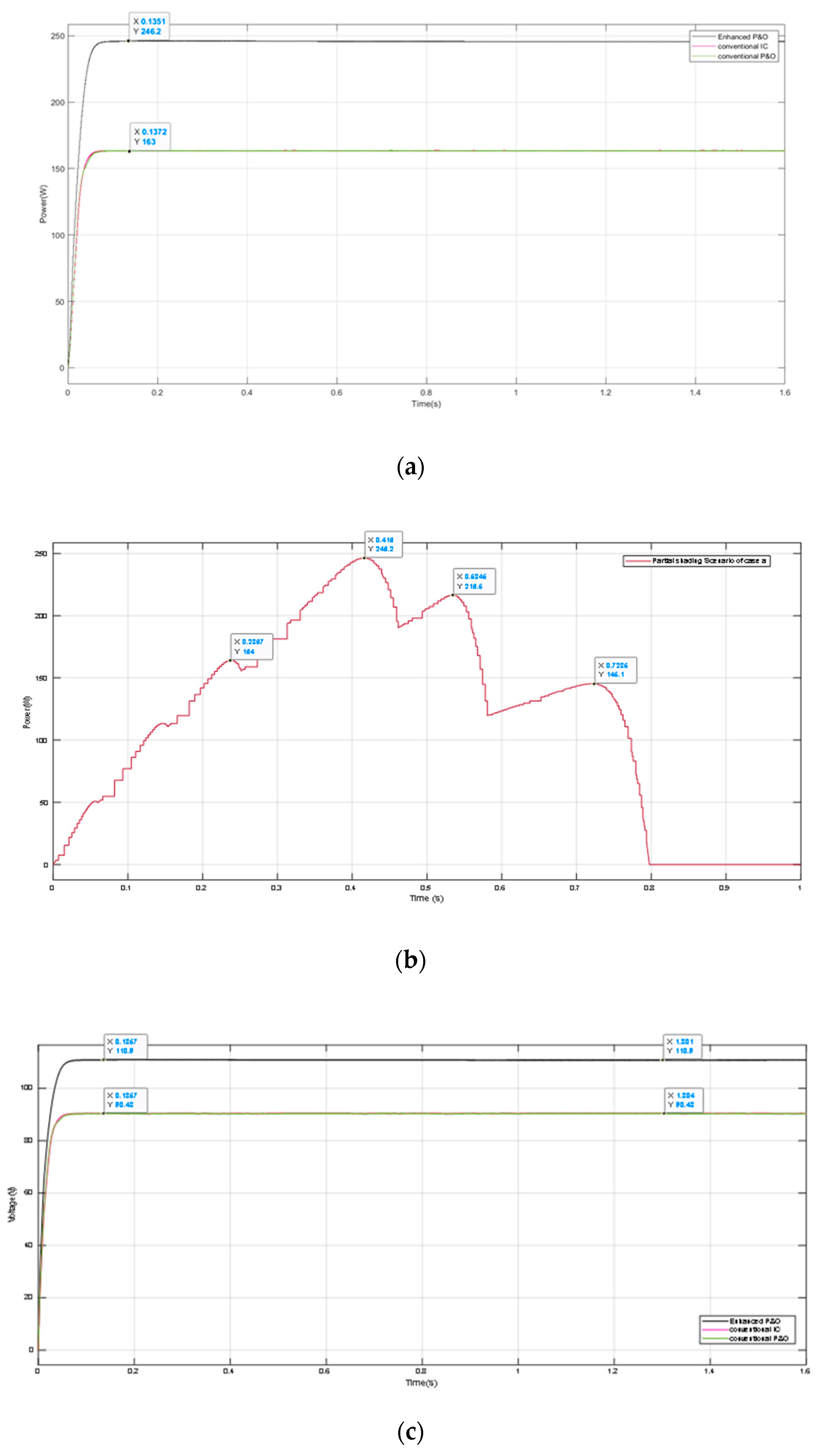
5.3. Case Three: Strong Partial Shading Pattern
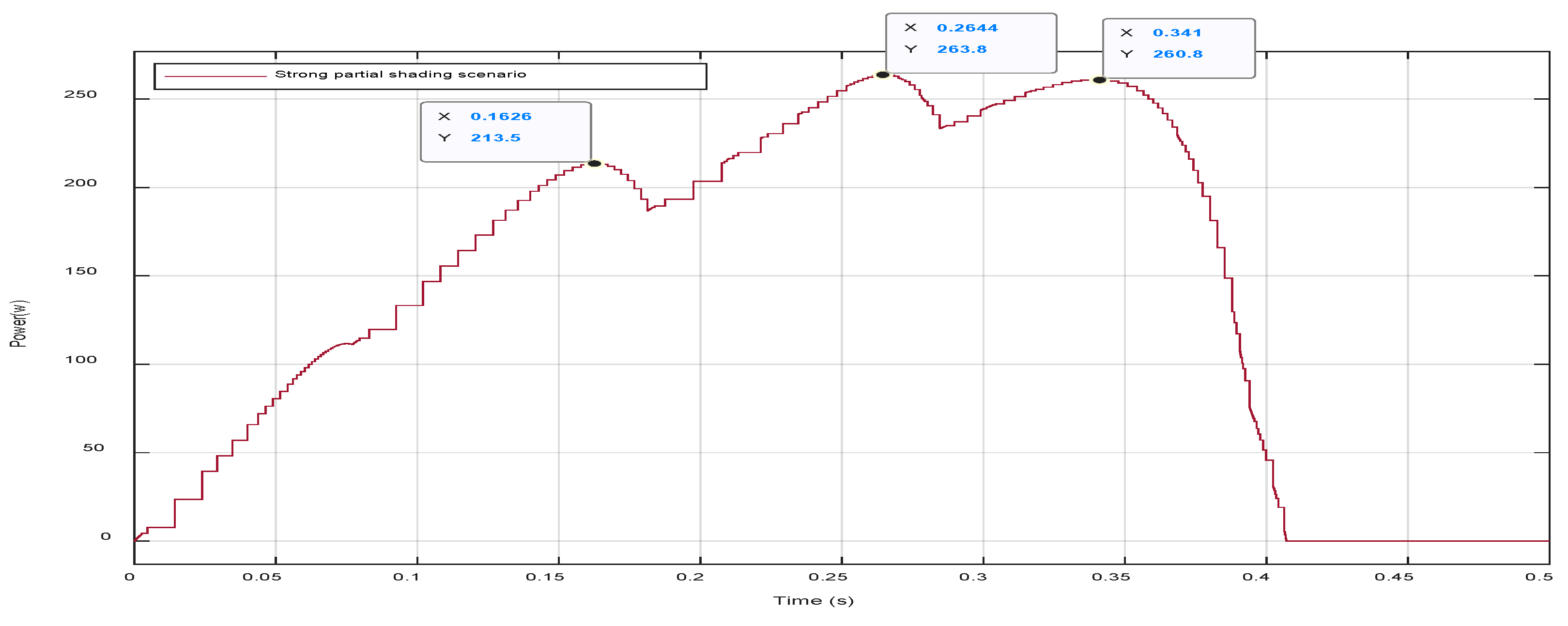
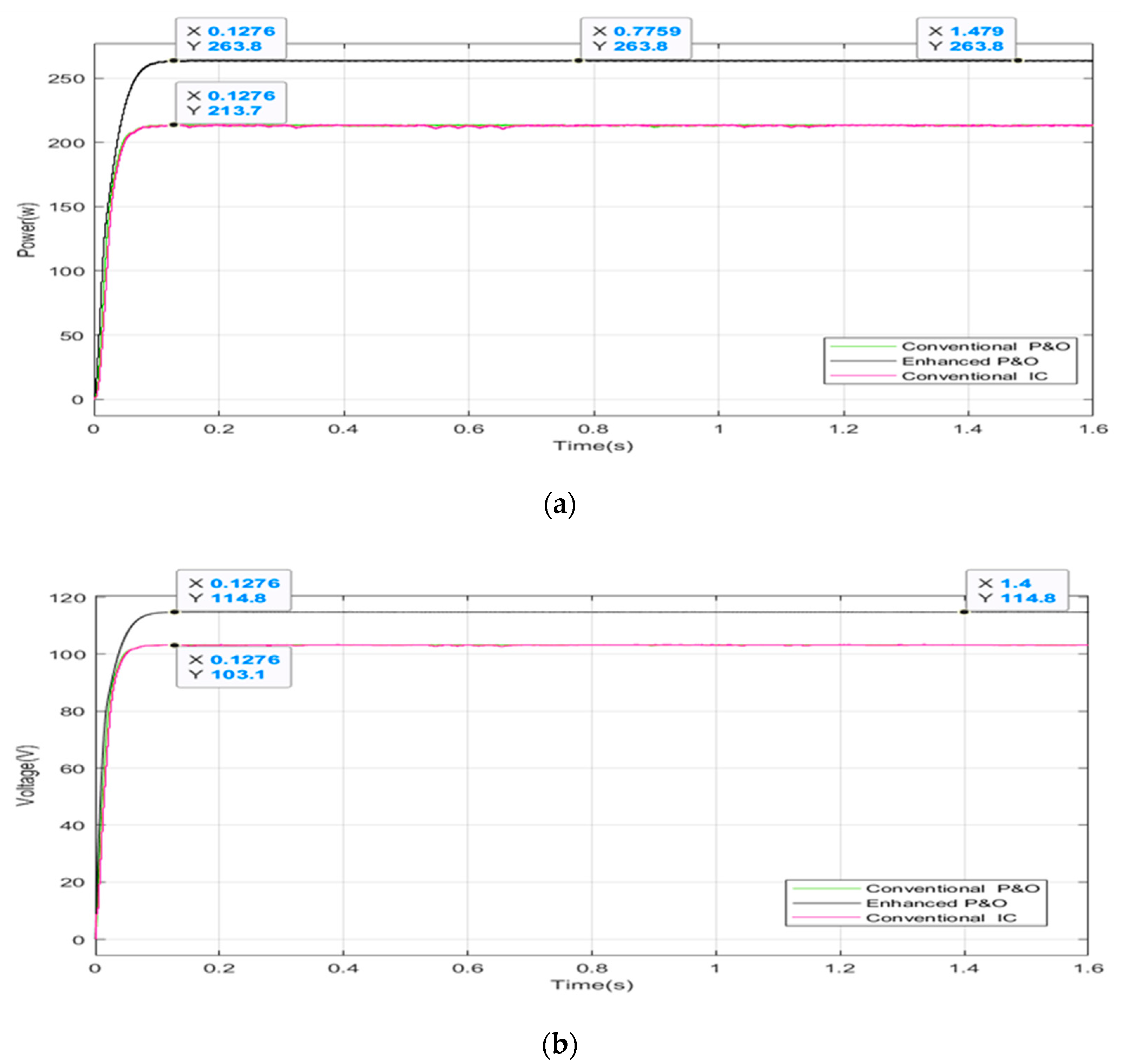
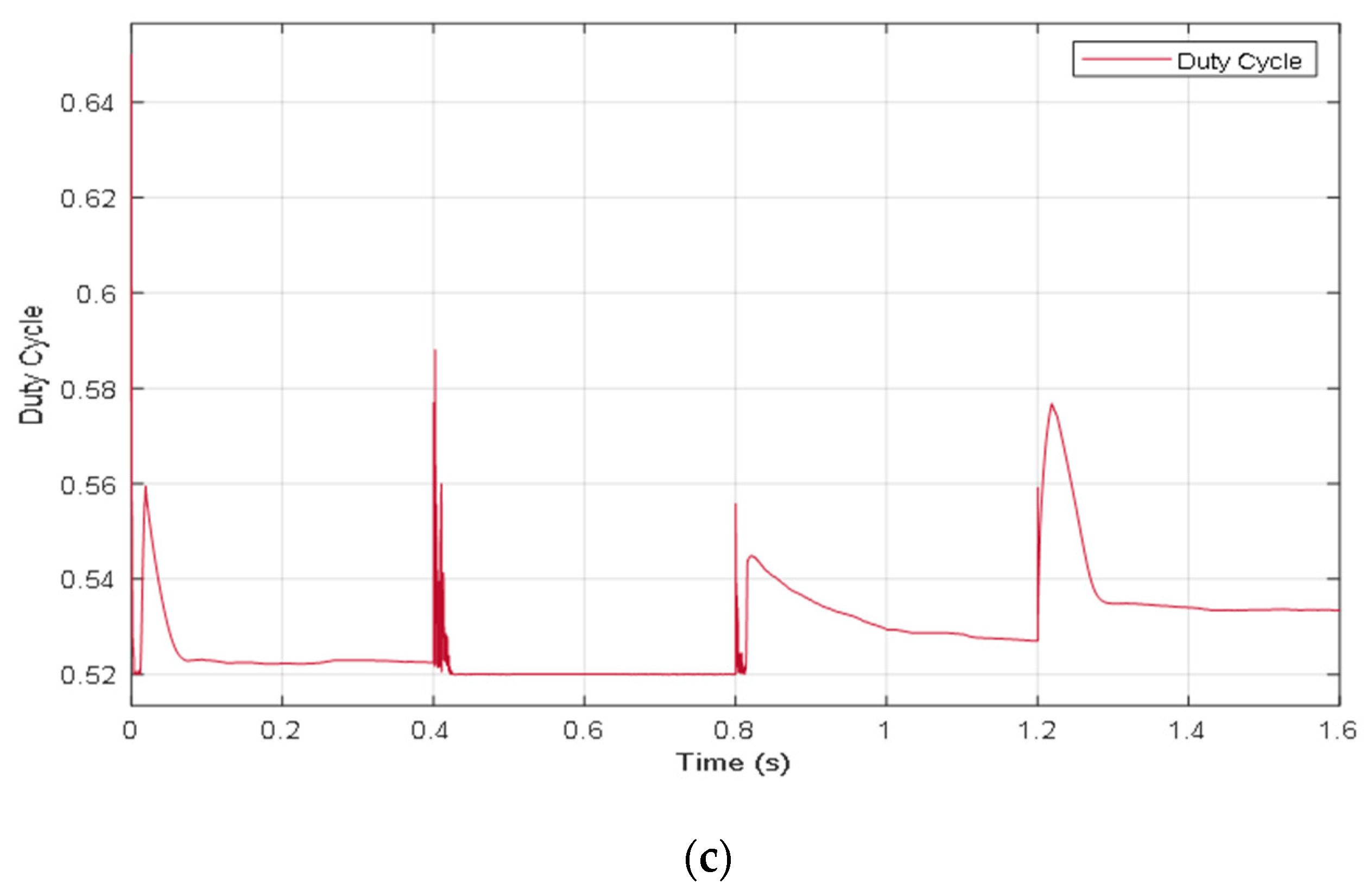
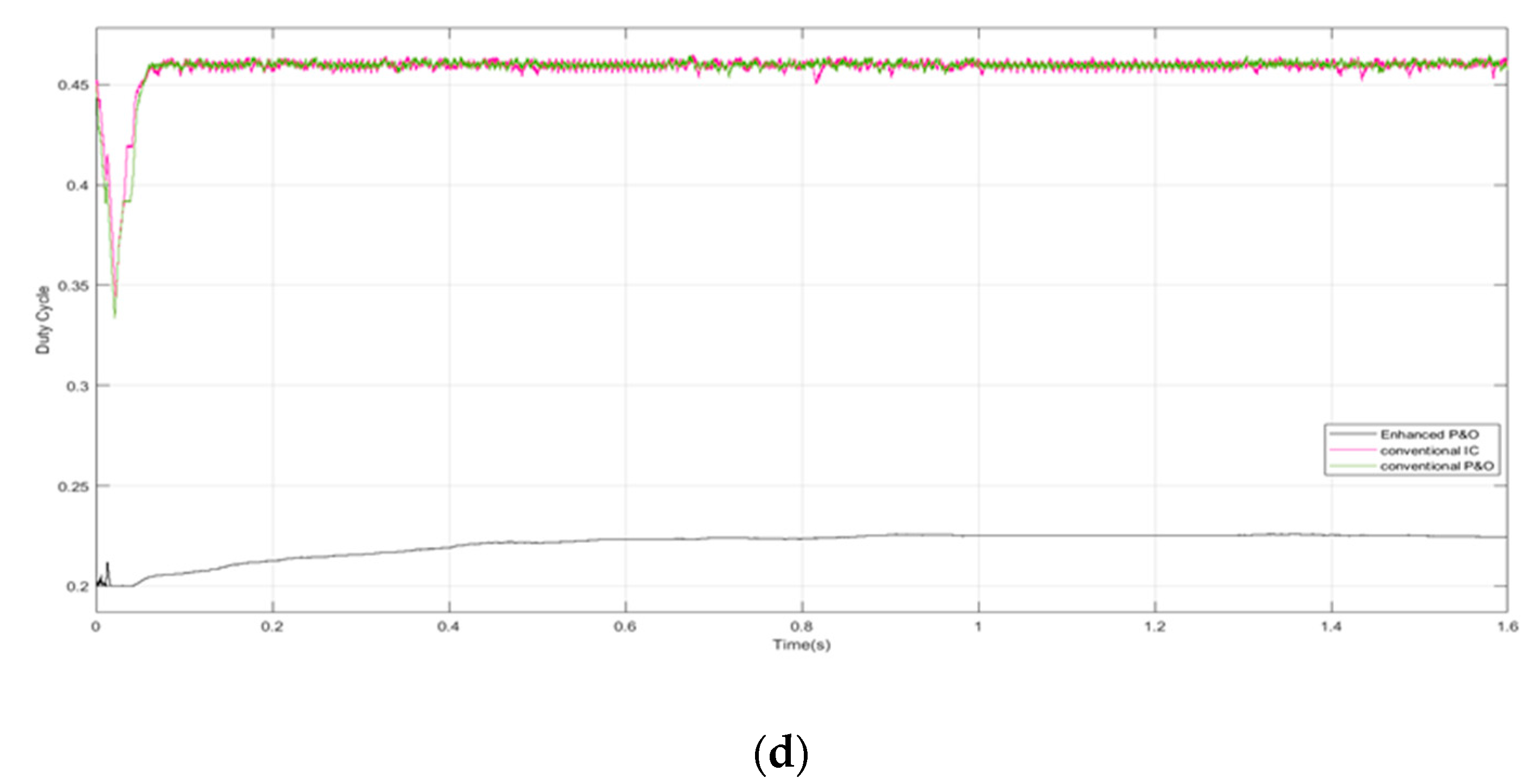
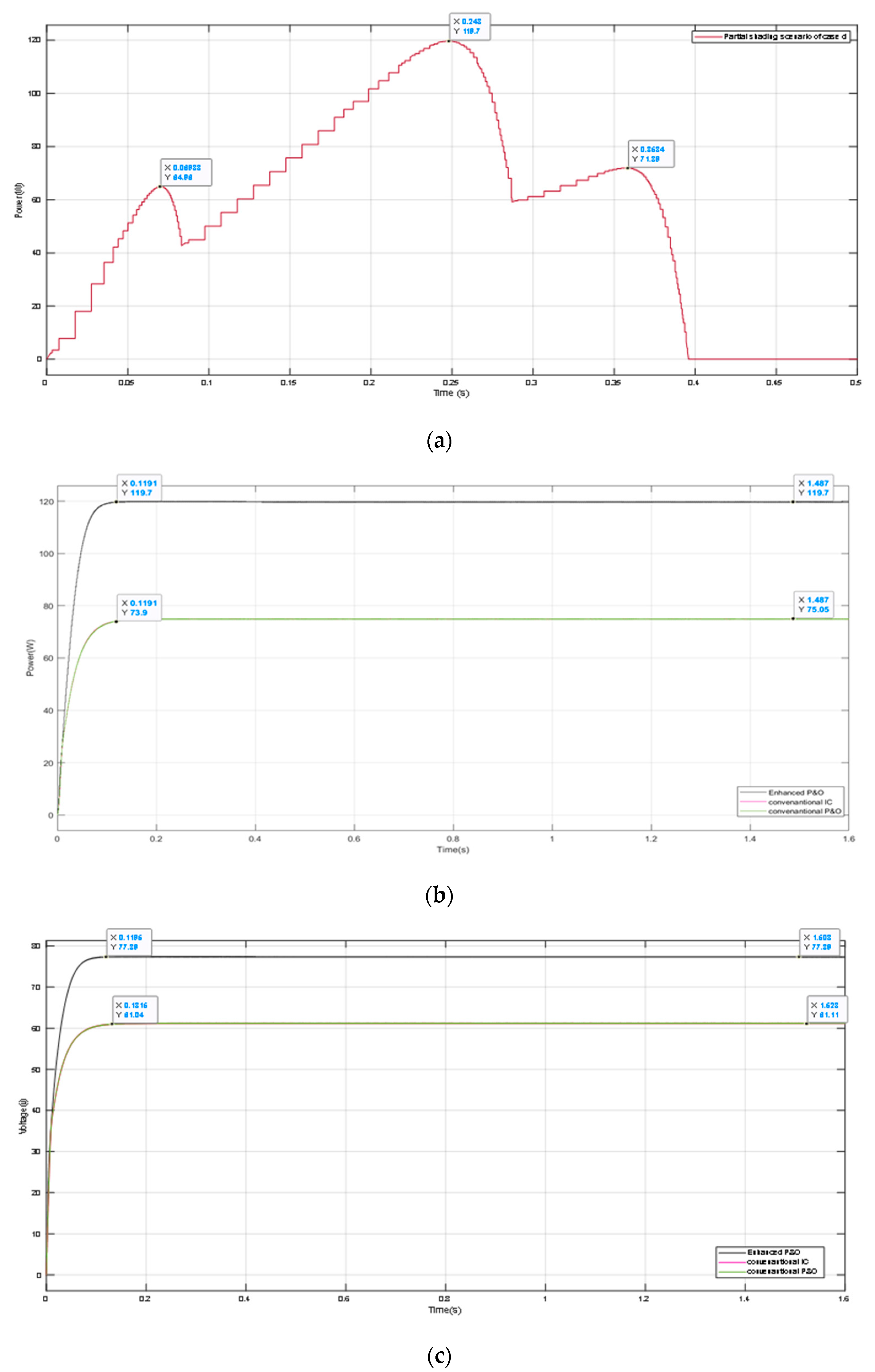
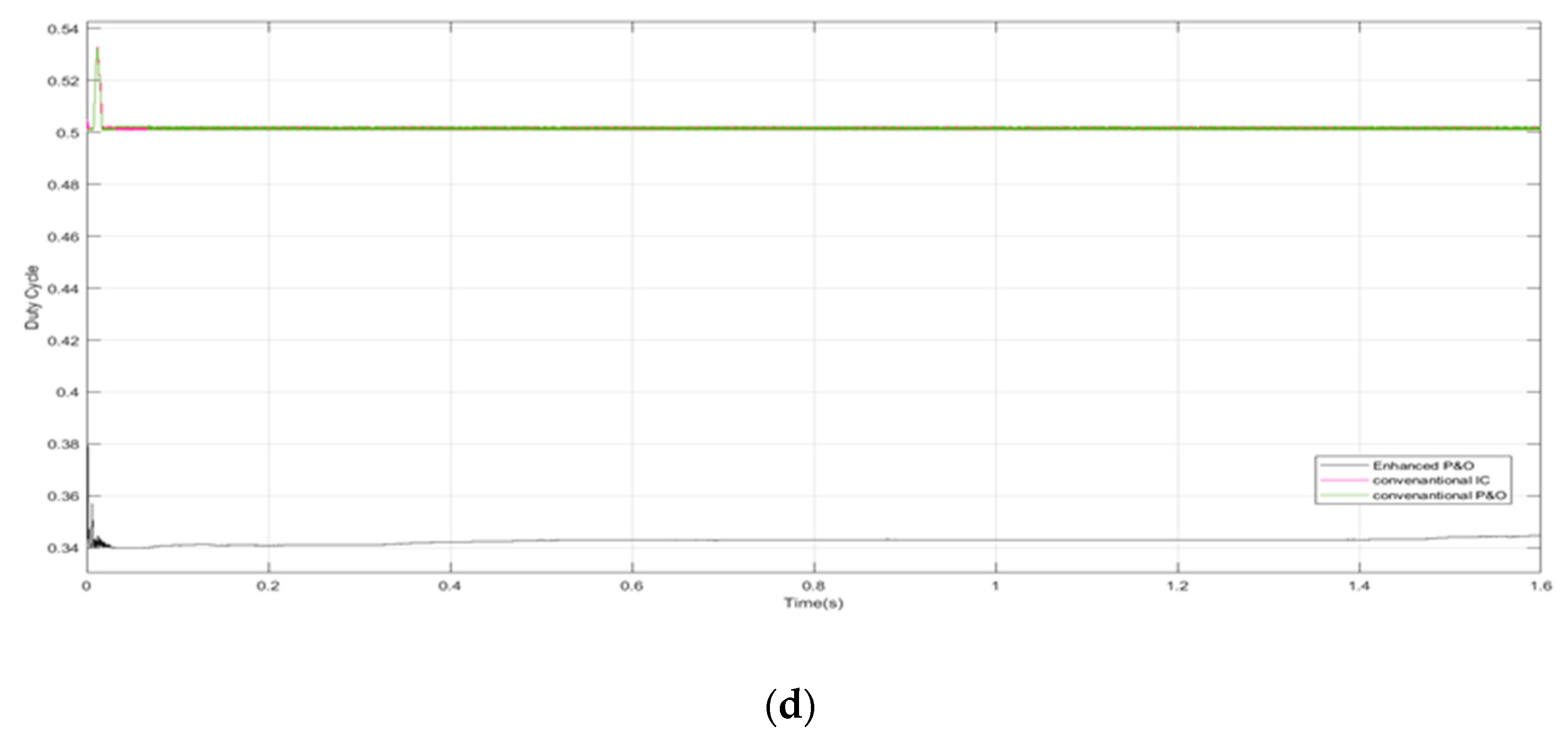
5.4. Case Four: Strong Partial Shading Pattern
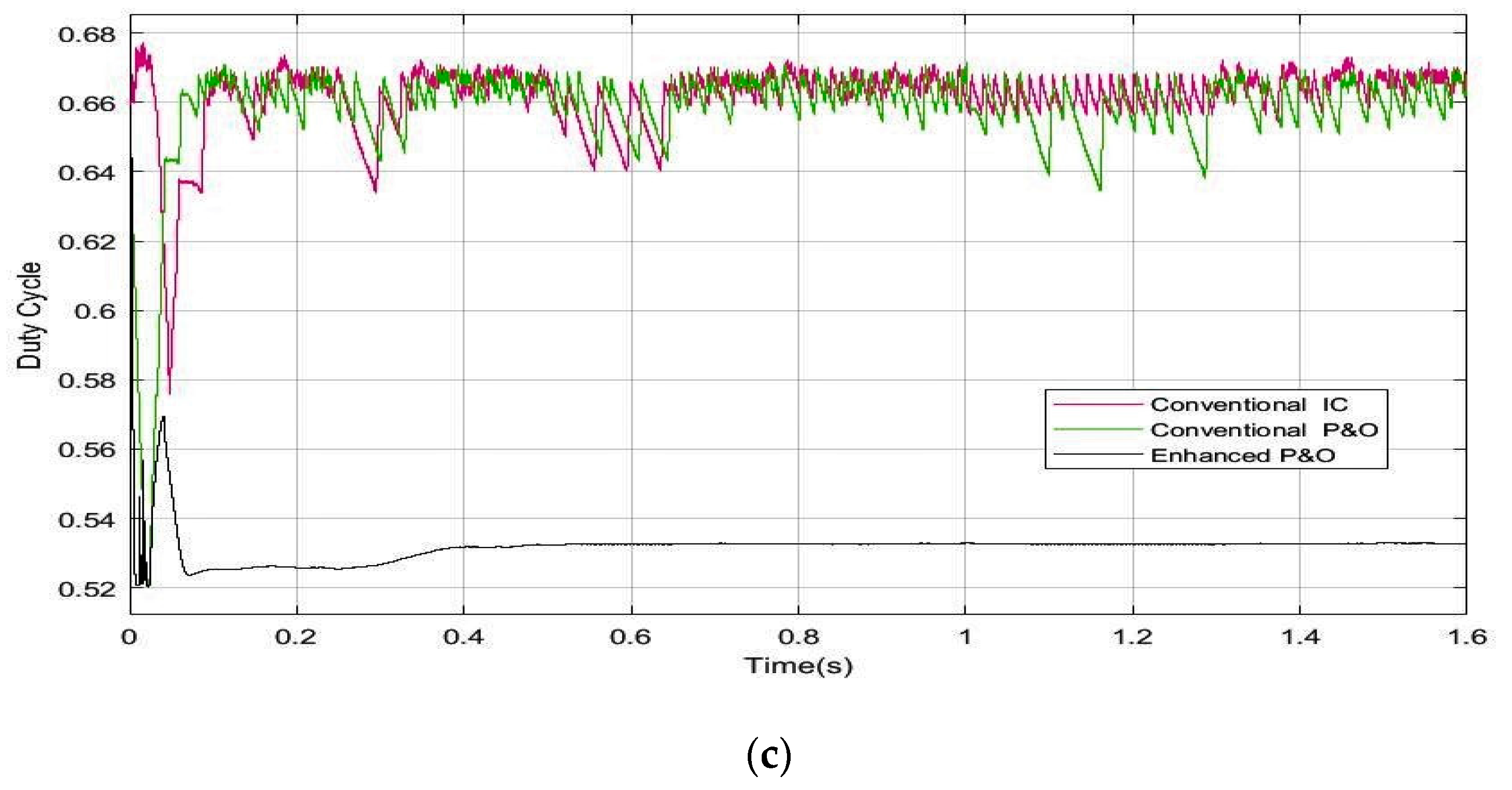
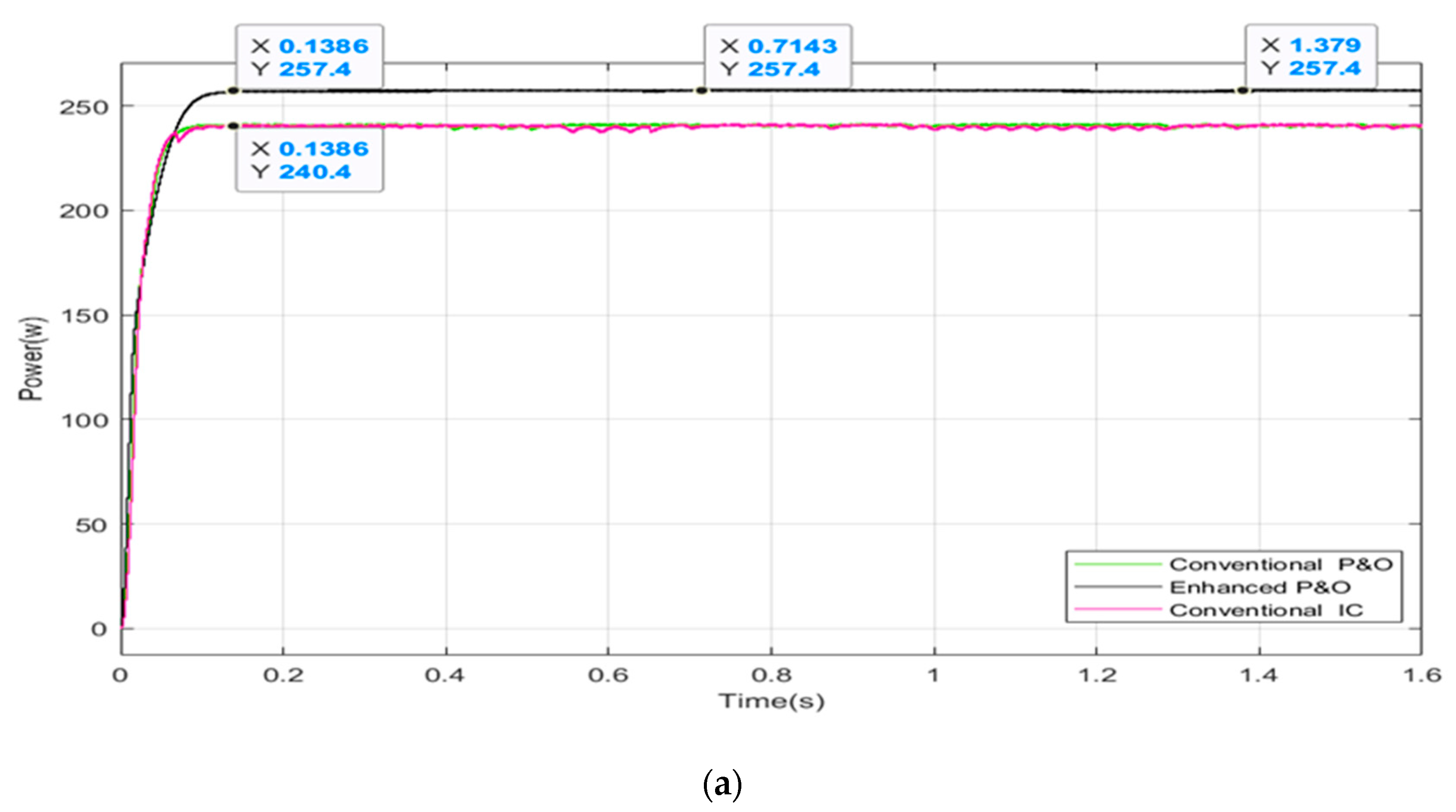
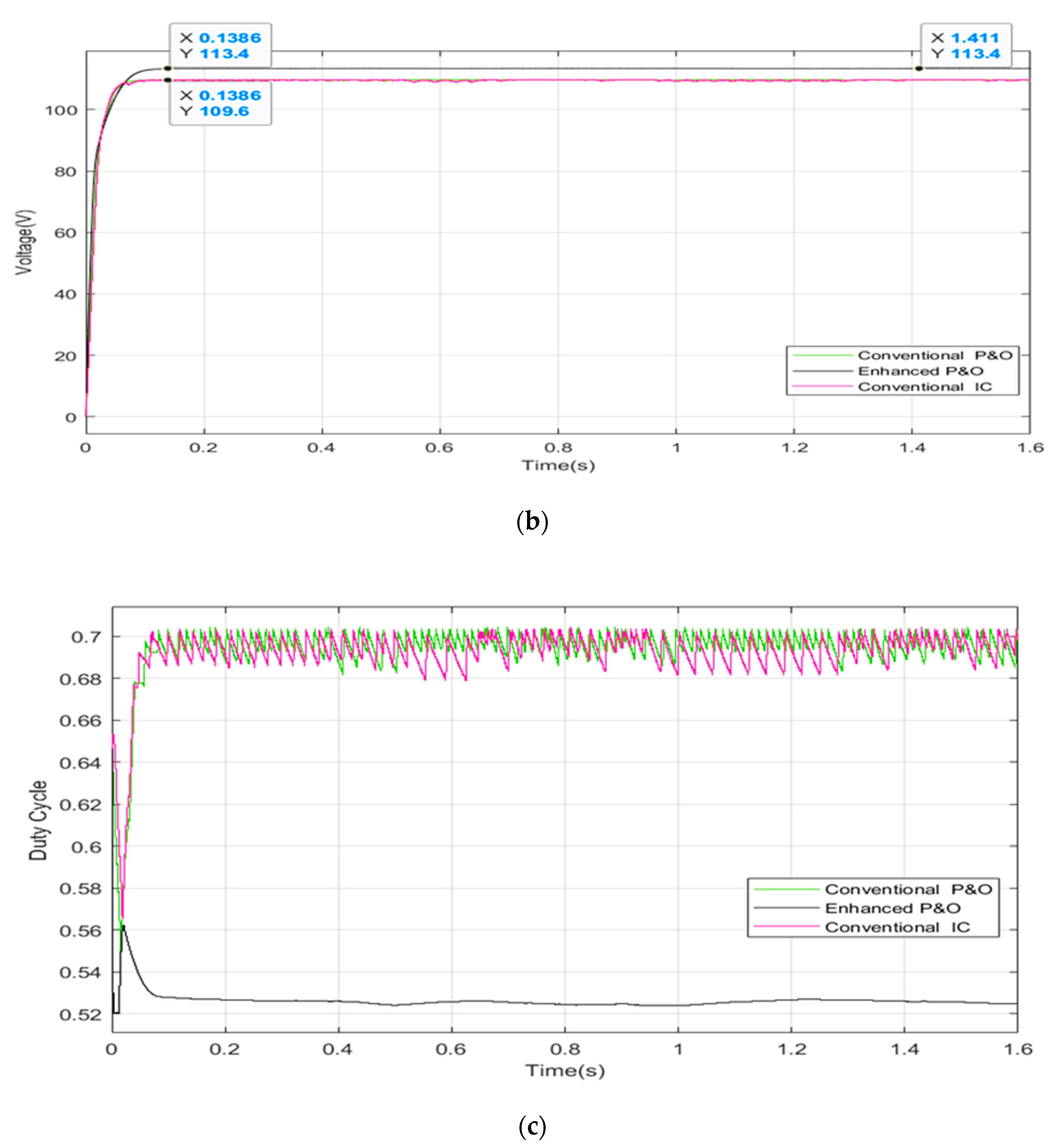
5.5. Discussion of the Simulation Results
6. Analysis of the Proposed Enhanced P&O for Partial Shading
7. Additional Configuration Testing
8. Future Work
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Fazal, M.R.; Kamran, M.; ul Haq, I.; Abbas, Z.; Ayyaz, M.N.; Mudassar, M. Modified Perturb and Observe MPPT algorithm for partial shading conditions. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. 2019, 9, 721–731. [Google Scholar]
- Suhadolnik, L.; Pohar, A.; Novak, U.; Likozar, B.; Mihelic, A.; Ceh, M. Continuous photocatalytic, electrocatalytic and photo-electrocatalytic degradation of a reactive textile dye for wastewater-treatment processes: Batch, microreactor and scaled-up operation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 72, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanam, J.J.; Simon, Y.F. Modeling of a Photovoltaic Array in MATLAB Simulink and Maximum Power Point Tracking Using Neural Network. J. Electr. Electron. Syst. 2018, 2, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Bjelajac, A.; Kopač, D.; Fecant, A.; Tavernier, E.; Petrović, R.; Likozar, B.; Janaćković, D. Micro-kinetic modelling of photocatalytic CO2 reduction over undoped and N-doped TiO2. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitenc, M.; Horvat, B.; Likozar, B.; Drazi, G.; Orel, Z.C. The impact of ZnO load, stability and morphology on the kinetics of the photocatalytic degradation of caffeine and resazurin. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 136–137, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukriz, A.; Messalti, S.; Harrag, A. Design, simulation, and hardware implementation of novel optimum operating point tracker of PV system using adaptive step size. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 101, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounden, N.A.; Ann Peter, S.; Nallandula, H.; Krithiga, S. Fuzzy logic controller with MPPT using line-commutated inverter for three-phase grid-connected photovoltaic systems. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subudhi, B.; Pradhan, R. A comparative study on maximum power point tracking techniques for photovoltaic power systems. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2013, 4, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, T.H.; Wu, X. Maximum power point tracking using a variable antecedent fuzzy logic controller. Sol. Energy 2016, 137, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouselham, L.; Hajji, M.; Hajji, B.; Bouali, H. A New MPPT-based ANN for Photovoltaic System under Partial Shading Conditions. Energy Procedia 2017, 111, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaque, K.; Salam, Z.; Amjad, M.; Mekhilef, S. An Improved Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)-Based MPPT for PV with Reduced Steady-State Oscillation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 3627–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal Awan, M.; Mahmood, T. A Novel Ten Check Maximum Power Point Tracking Algorithm for a Standalone Solar Photovoltaic System. Electronics 2018, 7, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, J.P.; Babu, T.S.; Rajasekar, N. A comprehensive review on solar PV maximum power point tracking techniques. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 826–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukasik, S.; Kowalski, P.A. Study of Flower Pollination Algorithm for Continuous Optimization. In Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, Proceedings of the 7th IEEE International Conference Intelligent Systems IS’2014, Warsaw, Poland, 24–26 September 2014; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, R.; Murtaza, A.F.; Sher, H.A. Power tracking techniques for efficient operation of photovoltaic array in solar applications—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 101, 82–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaque, K.; Salam, Z.; Lauss, G. The performance of Perturb and Observe and incremental conductance maximum power point tracking method under dynamic weather conditions. Appl. Energy 2014, 119, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qichang, D.; Jiajun, L.; Pan, D.; Bei, H.; Mingxuan, M. An Improved Variable Step PO and Global Scanning MPPT Method for PV Systems under Partial Shading Condition. In Proceedings of the 2015 7th International Conference on Intelligent Human-Machine Systems and Cybernetics, Hangzhou, China, 26–27 August 2015; Volume 1, pp. 382–386. [Google Scholar]
- Aashoor, F.A.O.; Robinson, F.V.P. A variable step size Perturb and Observe algorithm for photovoltaic maximum power point tracking. In Proceedings of the 2012 47th International Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC), London, UK, 4–7 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Killi, M.; Samanta, S. Modified Perturb and Observe MPPT Algorithm for Drift Avoidance in Photovoltaic Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 5549–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkaid, A.; Colak, I.; Kayisli, K. Implementation of a modified P&O-MPPT algorithm adapted for varying solar radiation conditions. Electr. Eng. 2017, 99, 839–846. [Google Scholar]
- Bizon, N. Global Maximum Power Point Tracking (GMPPT) of Photovoltaic array using the Extremum Seeking Control (ESC): A review and a new GMPPT ESC scheme. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 524–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almi, M.F.; Belmili, H.; Arrouf, M.; Bendib, B. A novel adaptive variable step size p&o mppt algorithm. Acad. J. Sci. 2016, 6, 533–540. [Google Scholar]
- Spertino, F.; Ahmad, J.; Di Leo, P.; Ciocia, A. A method for obtaining the I-V curve of photovoltaic arrays from module voltages and its applications for MPP tracking. Sol. Energy 2016, 139, 489–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.; Rajagopalan, C. Experimental evaluation of a partially shaded photovoltaic system with a fuzzy logic-based peak power tracking control strategy. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2016, 10, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S.; Rout, P.K. Comparative study of M-FIS FLC and modified P&O MPPT techniques under partial shading and variable load conditions. In Proceedings of the 2015 Annual IEEE India Conference (INDICON), New Delhi, India, 17–20 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Aouchiche, N.; Aitcheikh, M.S.; Becherif, M.; Ebrahim, M.A. AI-based global MPPT for partial shaded grid connected PV plant via MFO approach. Sol. Energy 2018, 171, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataineh, K.; Eid, N. A hybrid maximum power point tracking method for photovoltaic systems for dynamic weather conditions. Resources 2018, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundareswaran, K.; Peddapati, S.; Palani, S. MPPT of PV Systems Under Partial Shaded Conditions Through a Colony of Flashing Fireflies. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2014, 29, 463–472. [Google Scholar]
- Kolsi, S.; Samet, H.; Amar, M.B. Design Analysis of DC-DC Converters Connected to a Photovoltaic Generator and Controlled by MPPT for Optimal Energy Transfer throughout a Clear Day. J. Power Energy Eng. 2014, 2, 42166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, R.W.; Maksimovic, D. Fundamentals of Power Electronics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hayat, A.; Faisal, A.; Javed, M.Y.; Hasseb, M.; Rana, R.A. Effects of input capacitor (cin) of boost converter for photovoltaic system. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Computing, Electronic and Electrical Engineering (ICE Cube), Quetta, Pakistan, 11–12 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, B.; Mohapatra, A.; Mohanty, K.B. Selection criteria of dc-dc converter and control variable for MPPT of PV system utilized in heating and cooking applications. Cogent Eng. 2017, 4, 1363357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, N.; Johari, D.; Ismail, N.F.N.; Salam, Z. DC-DC boost converter design for fast and accurate MPPT algorithms in stand-alone photovoltaic system. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 2018, 9, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, D.W. Power Electronics; Tata McGraw-Hill: New Delhi, India, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ishaque, K.; Salam, Z. A comprehensive MATLAB Simulink PV system simulator with partial shading capability based on two-diode model. Sol. Energy 2011, 85, 2217–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollimalla, S.K.; Mishra, M.K. A Novel Adaptive P&O MPPT Algorithm Considering Sudden Changes in the Irradiance. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2014, 29, 602–610. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, T.; Zilouchian, A.; Messenger, R. A proposed maximum power point tracking algorithm based on a new testing standard. Sol. Energy 2013, 89, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



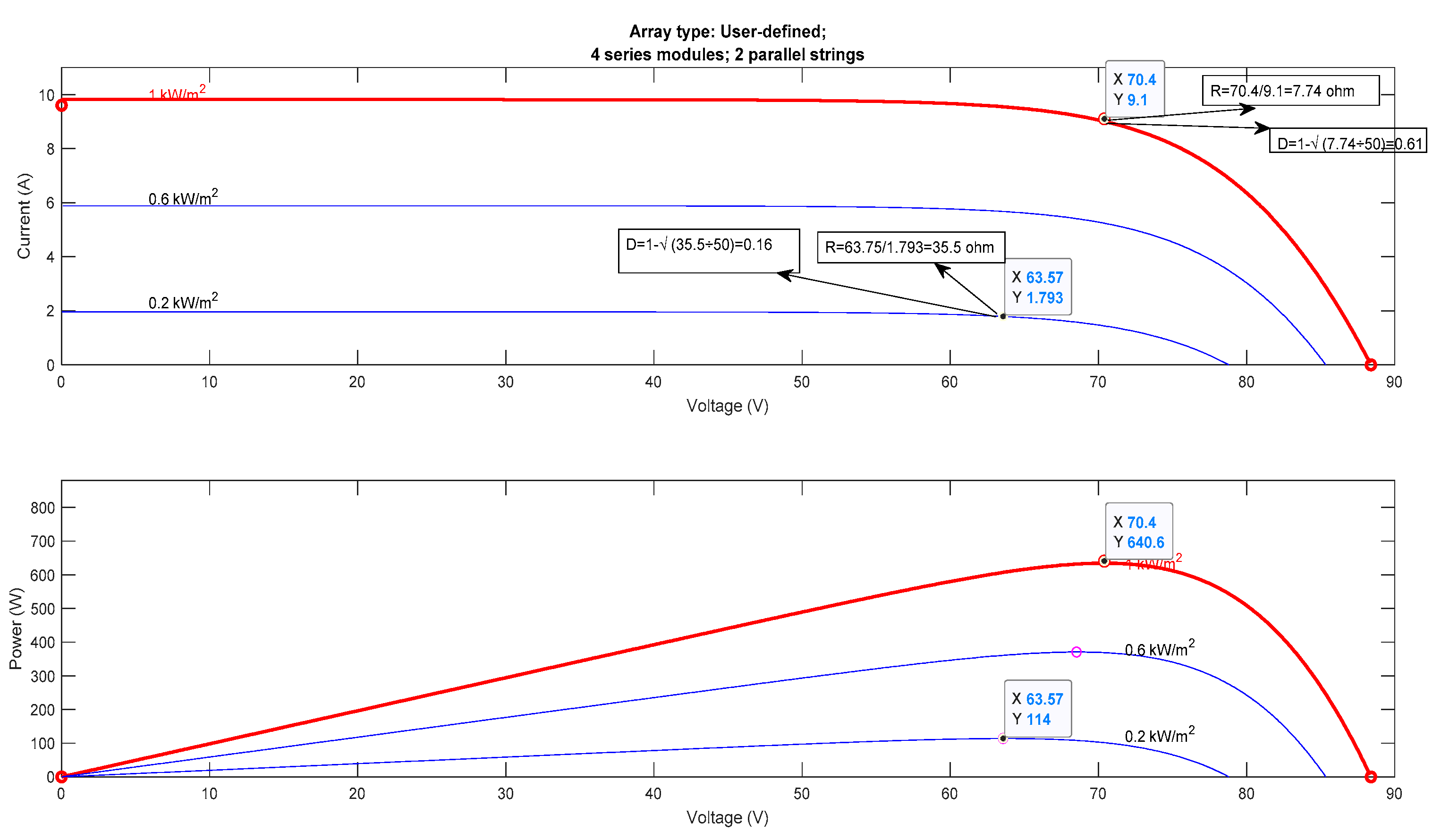
| Irradiance (W/m2) | Vmpp (V) | Impp (A) | Pmpp (W) | Rmpp (Ω) | Dmpp | Vout (V) | Iout (A) | RL (Ω) | L (mH) | C (µF) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 (Higher) | 70.4 | 9.1 | 640.6 | 7.74 | 0.61 | 179 | 3.6 | 50 | 1.6 | 500 |
| 200 (Lower) | 63.57 | 1.793 | 114 | 35.5 | 0.16 | 75.7 | 1.5 |
| Case | Irradiation of the First Four Series Modules | Irradiation of the Second Four Series Modules | Power at GMPP |
|---|---|---|---|
| One (Weak shading) | [1000,1000,1000,800] | [1000,1000,1000,600] | 490.9 W |
| Two (Moderate shading) | [1000,1000,800,800] | [1000,1000,500,500] | 435.5 W |
| Three (Strong shading) | [1000,1000,600,400] | [800,600,400,200] | 257.4 W |
| Four (Strong shading) | [1000,1000,600,400] | [600,400,400,400] | 263.8 W |
| Case | Irradiation of the Parallel First and Second Series Modules | Ideal Power at GMMP (A) | Tracked Power at GMMP (B) | Tracking Speed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| One (Weak shading) | [1000,1000,1000,800] [1000,1000,1000,600] | 490.9 W | 490.9 W | 100% | 0.13 s |
| Two (Moderate shading) | [1000,1000,800,800] [1000,1000,500,500] | 435.5 W | 435.5 W | 100% | 0.139 s |
| Three (Strong shading) | [1000,1000,600,400] [800,600,400,200] | 257.4 W | 257.4 W | 100% | 0.137 s |
| Four (Strong shading) | [1000,1000,600,400] [600,400,400,400] | 263.8 W | 263.8 W | 100% | 0.127 s |
| Case Three (Strong Shading 0–0.4 s) | 257.4 W | 257.4 W | 100% |
| Case Two (Moderate shading 0.4–0.8 s) | 435.5 W | 435.5 W | 100% |
| Case Four (Strong shading 0.8–1.2 s) | 260.3 W | 263.8 W | 98.67% |
| Case One (Weak shading 1.2–1.6 s) | 490.9 W | 490.9 W | 100% |
| Ref. | Year | Converter Type | Steady State Oscillations | Speed of Tracking | Tracking Efficiency | Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed algorithm | 2020 | Boost Converter | Nil | Highest | Highest | Very Low |
| [1] | 2019 | DC/DC Buck converter | Low | High | High | Reasonable |
| [27] | 2018 | Boost Converter | Low | High | High | High |
| [17] | 2015 | Boost Converter | Low | High | Average | Reasonable |
| [16] | 2015 | SEPIC converter | Low | High | Low | Medium |
| [18] | 2012 | Buck converter | High | High | Medium | High |
| [28] | 2018 | Boost converter | High | High | Medium | High |
| [10] | 2017 | Boost converter | Medium | High | Medium | High |
| [9] | 2016 | SEPIC converter | Low | High | High | High |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahmod Mohammad, A.N.; Mohd Radzi, M.A.; Azis, N.; Shafie, S.; Atiqi Mohd Zainuri, M.A. An Enhanced Adaptive Perturb and Observe Technique for Efficient Maximum Power Point Tracking Under Partial Shading Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3912. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113912
Mahmod Mohammad AN, Mohd Radzi MA, Azis N, Shafie S, Atiqi Mohd Zainuri MA. An Enhanced Adaptive Perturb and Observe Technique for Efficient Maximum Power Point Tracking Under Partial Shading Conditions. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(11):3912. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113912
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahmod Mohammad, Altwallbah Neda, Mohd Amran Mohd Radzi, Norhafiz Azis, Suhaidi Shafie, and Muhammad Ammirrul Atiqi Mohd Zainuri. 2020. "An Enhanced Adaptive Perturb and Observe Technique for Efficient Maximum Power Point Tracking Under Partial Shading Conditions" Applied Sciences 10, no. 11: 3912. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113912
APA StyleMahmod Mohammad, A. N., Mohd Radzi, M. A., Azis, N., Shafie, S., & Atiqi Mohd Zainuri, M. A. (2020). An Enhanced Adaptive Perturb and Observe Technique for Efficient Maximum Power Point Tracking Under Partial Shading Conditions. Applied Sciences, 10(11), 3912. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113912






