Improved U-Net: Fully Convolutional Network Model for Skin-Lesion Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
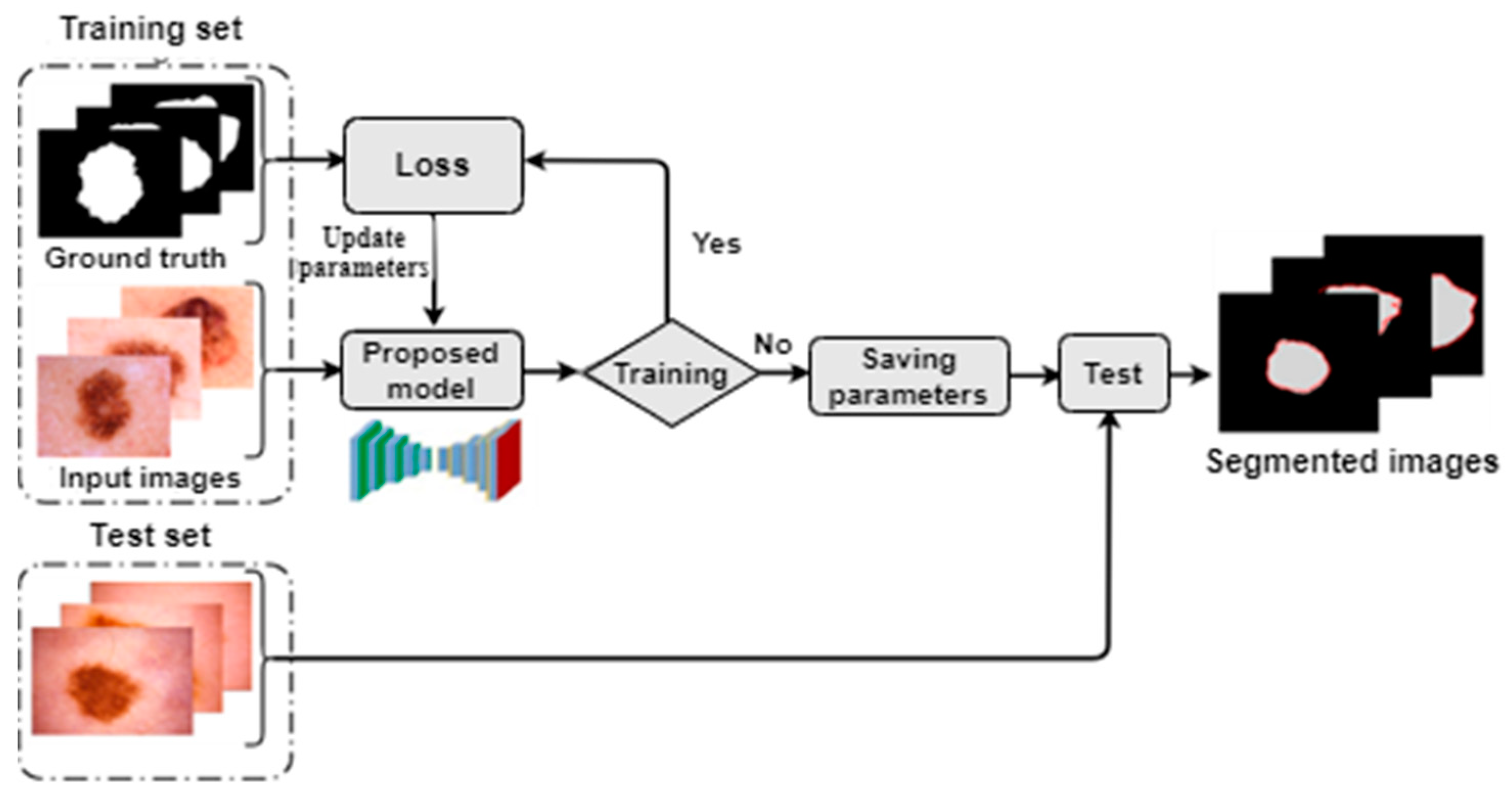
2.1. Overview
2.2. Dataset
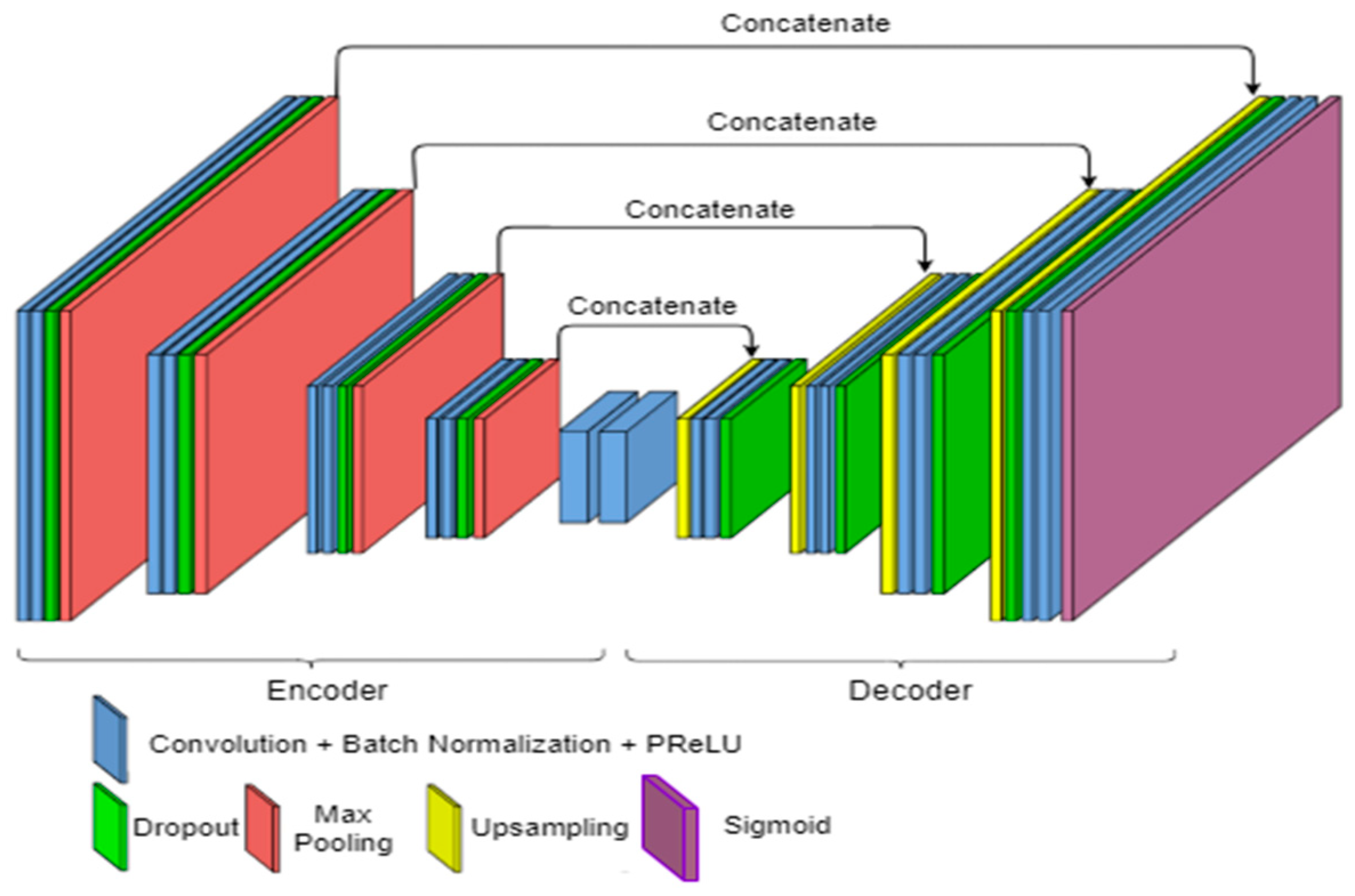
2.3. Proposed Method Architecture
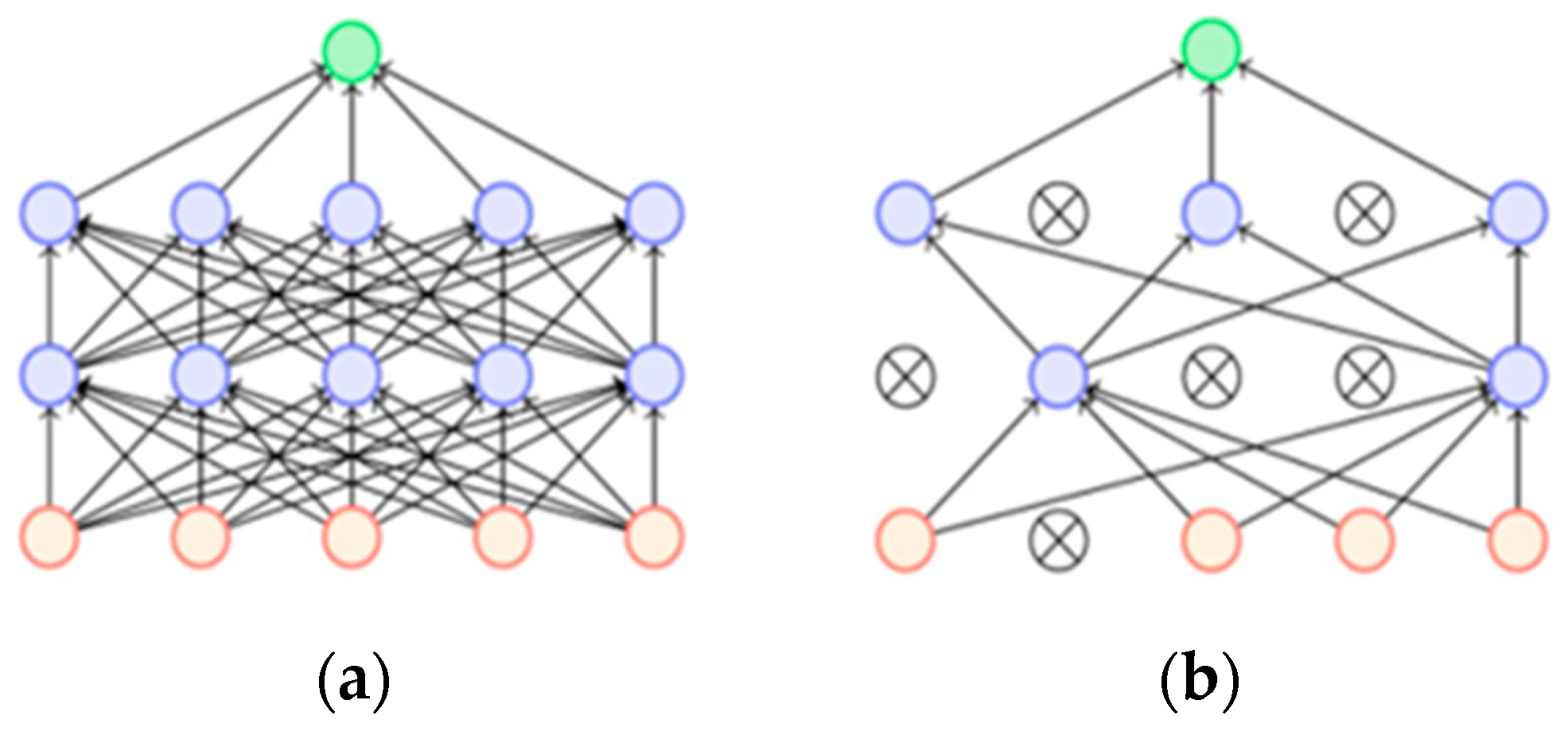
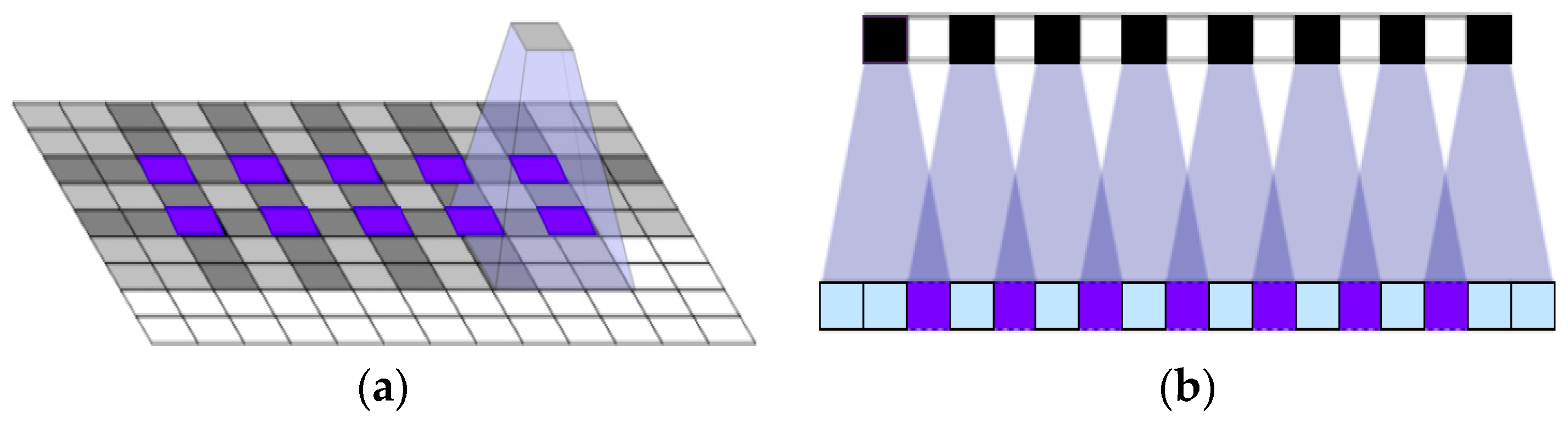
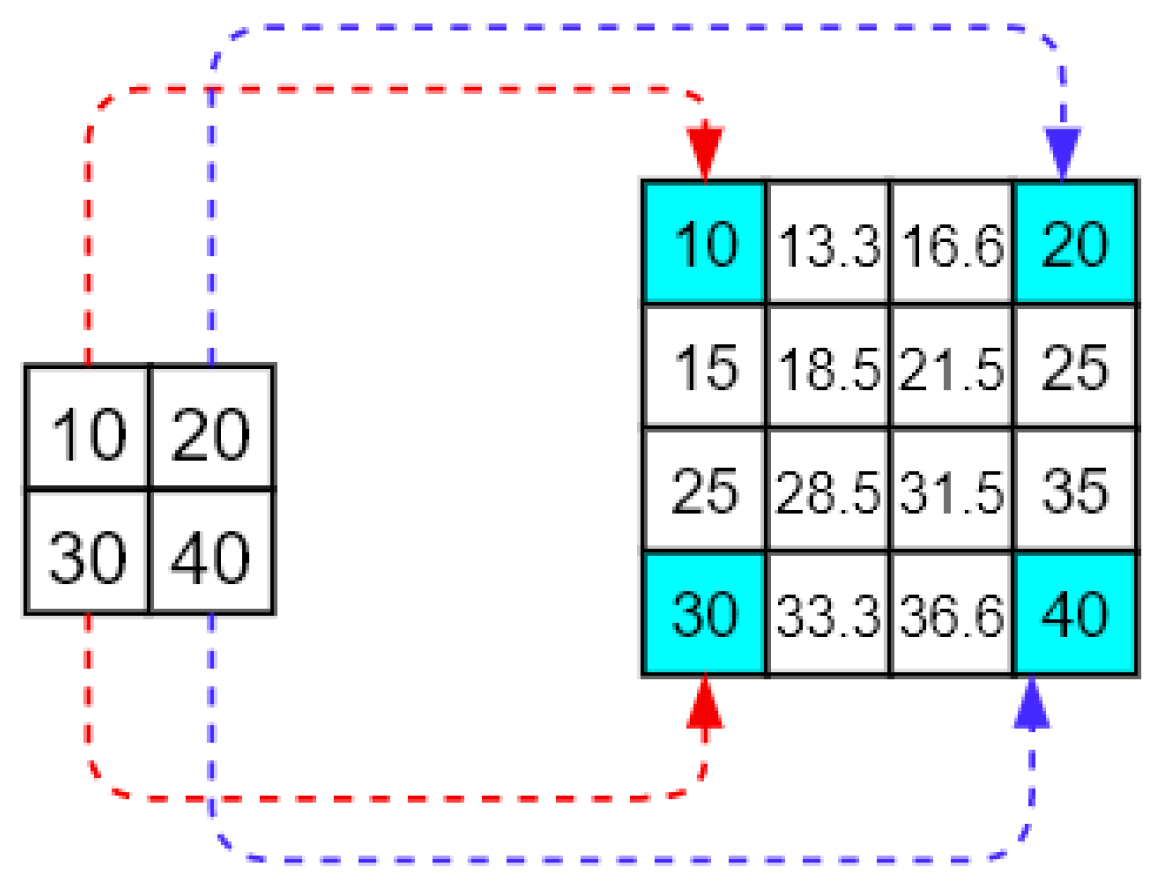
2.4. Upsampling Method
2.5. Activation Functions
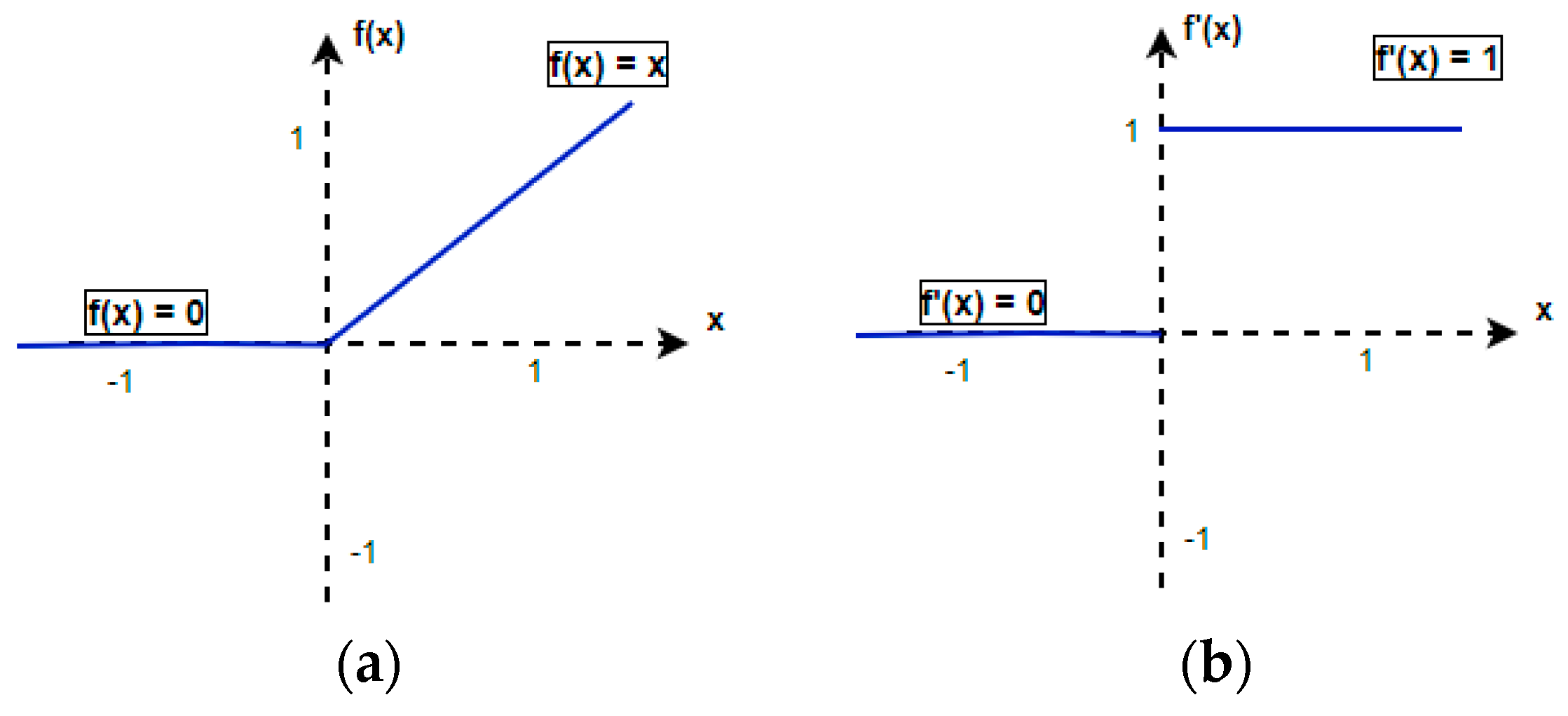
2.5.1. ReLU
- The learning rate is too high.
- There is a large negative bias.
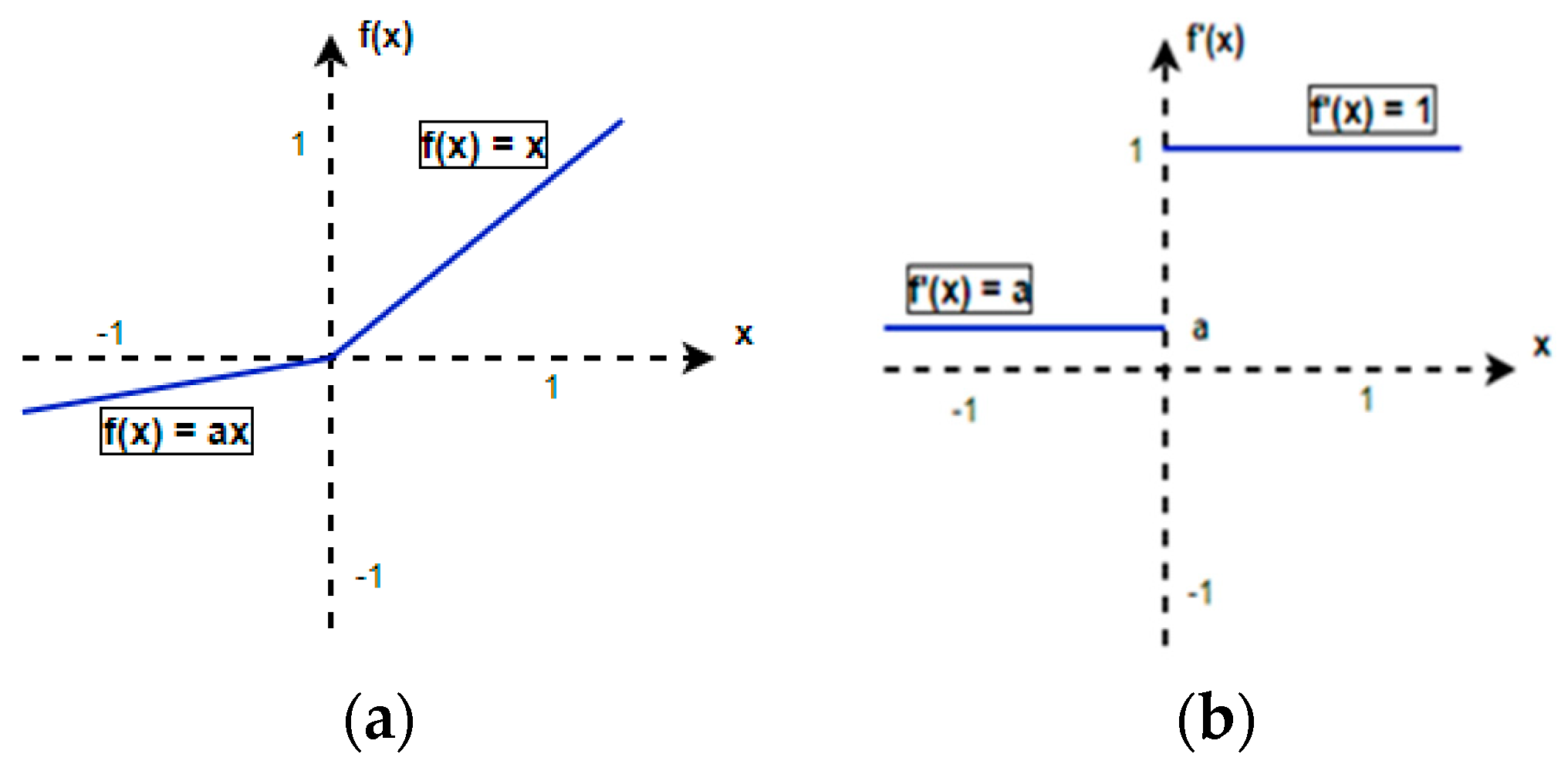
2.5.2. PReLU
3. Experimental Settings
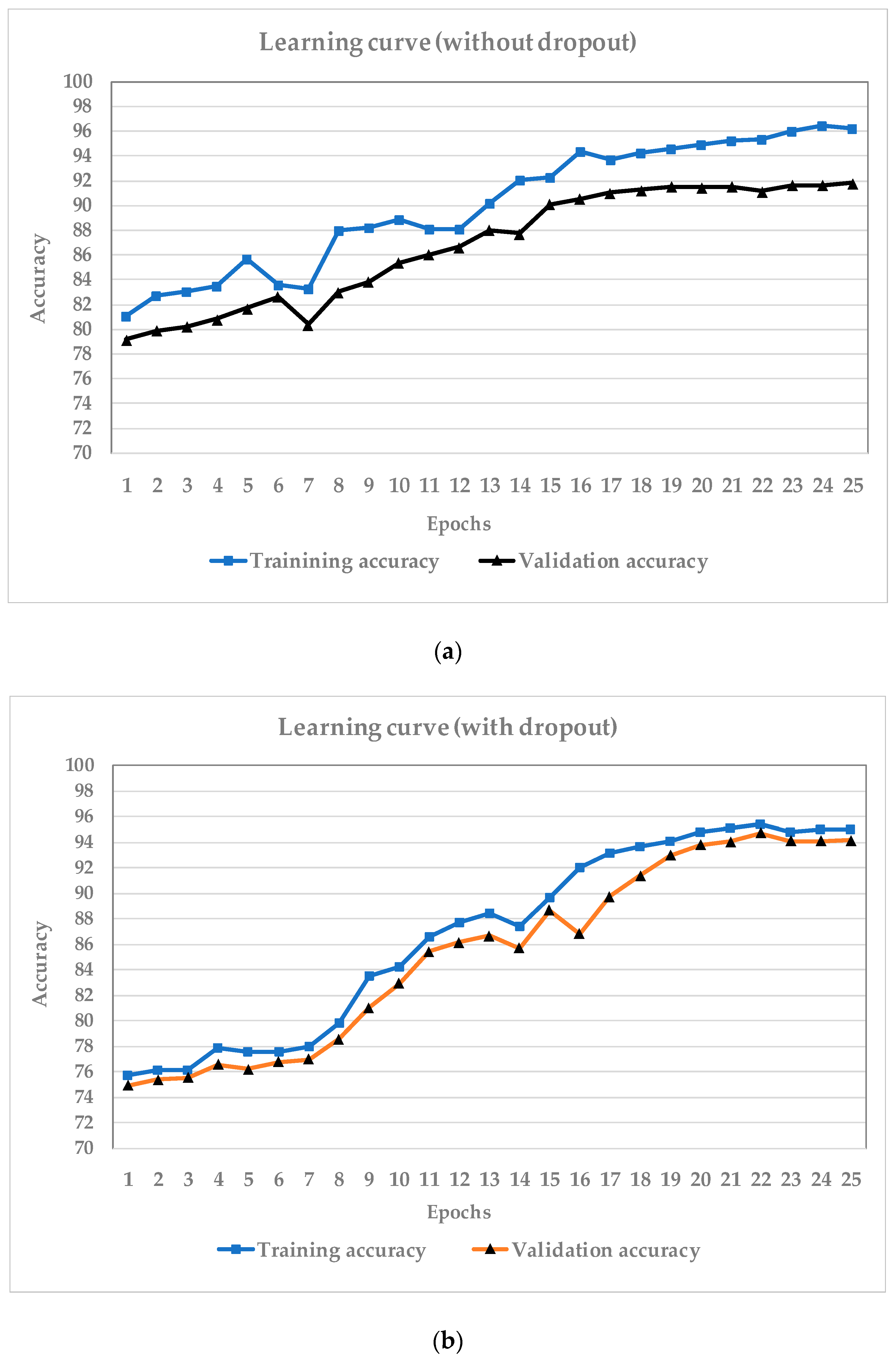
3.1. Training Network
3.2. Data Augmentation
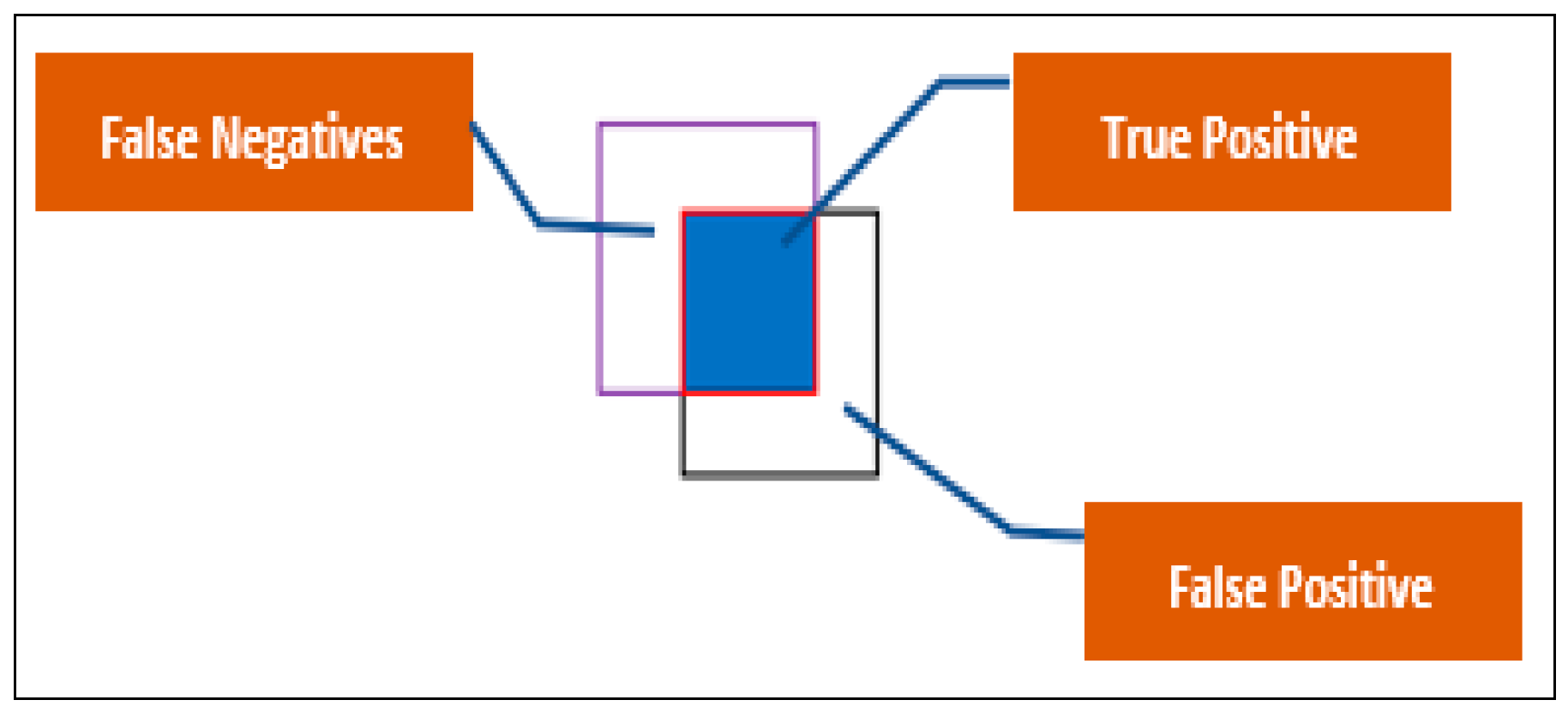
3.3. Evaluation Metrics
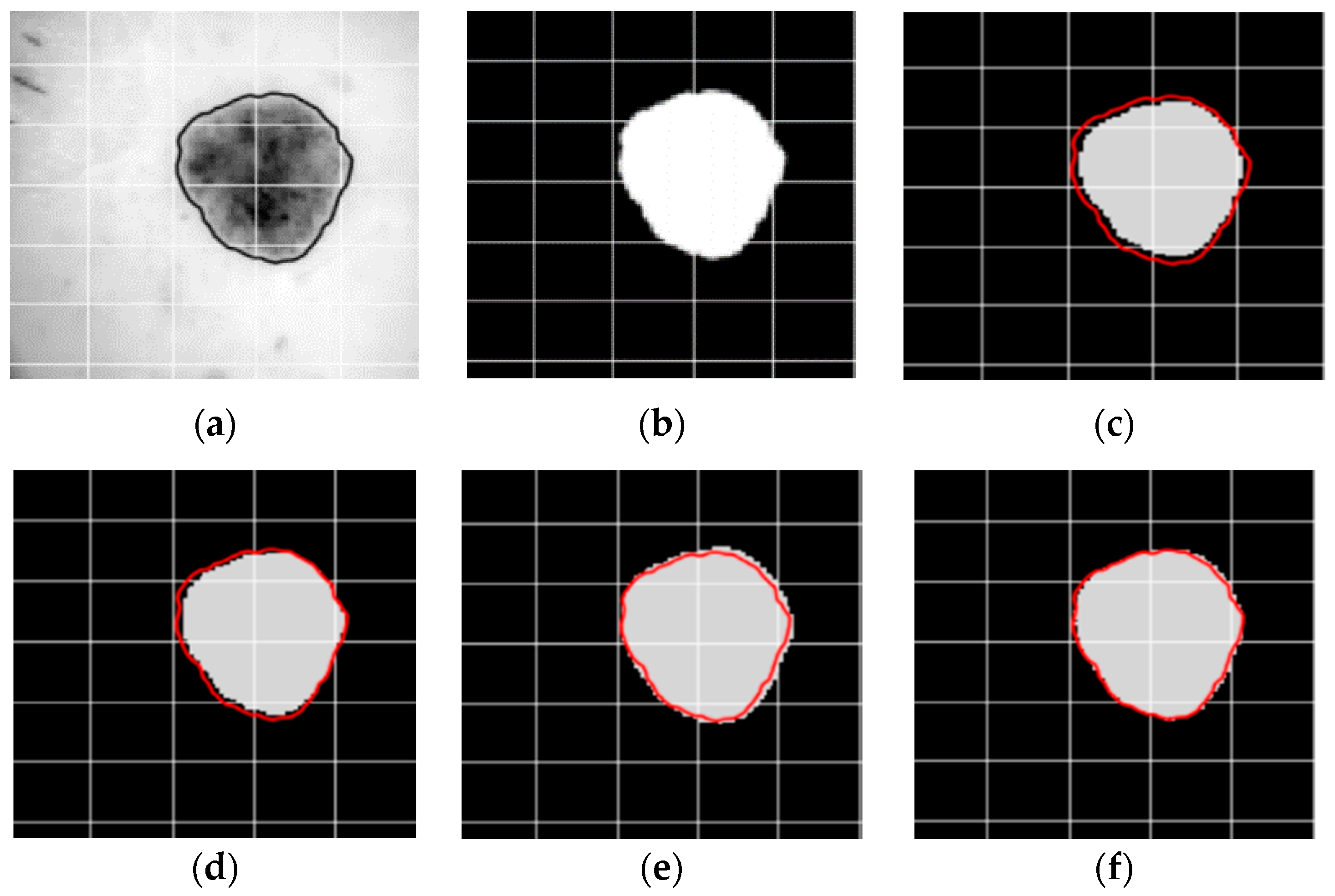
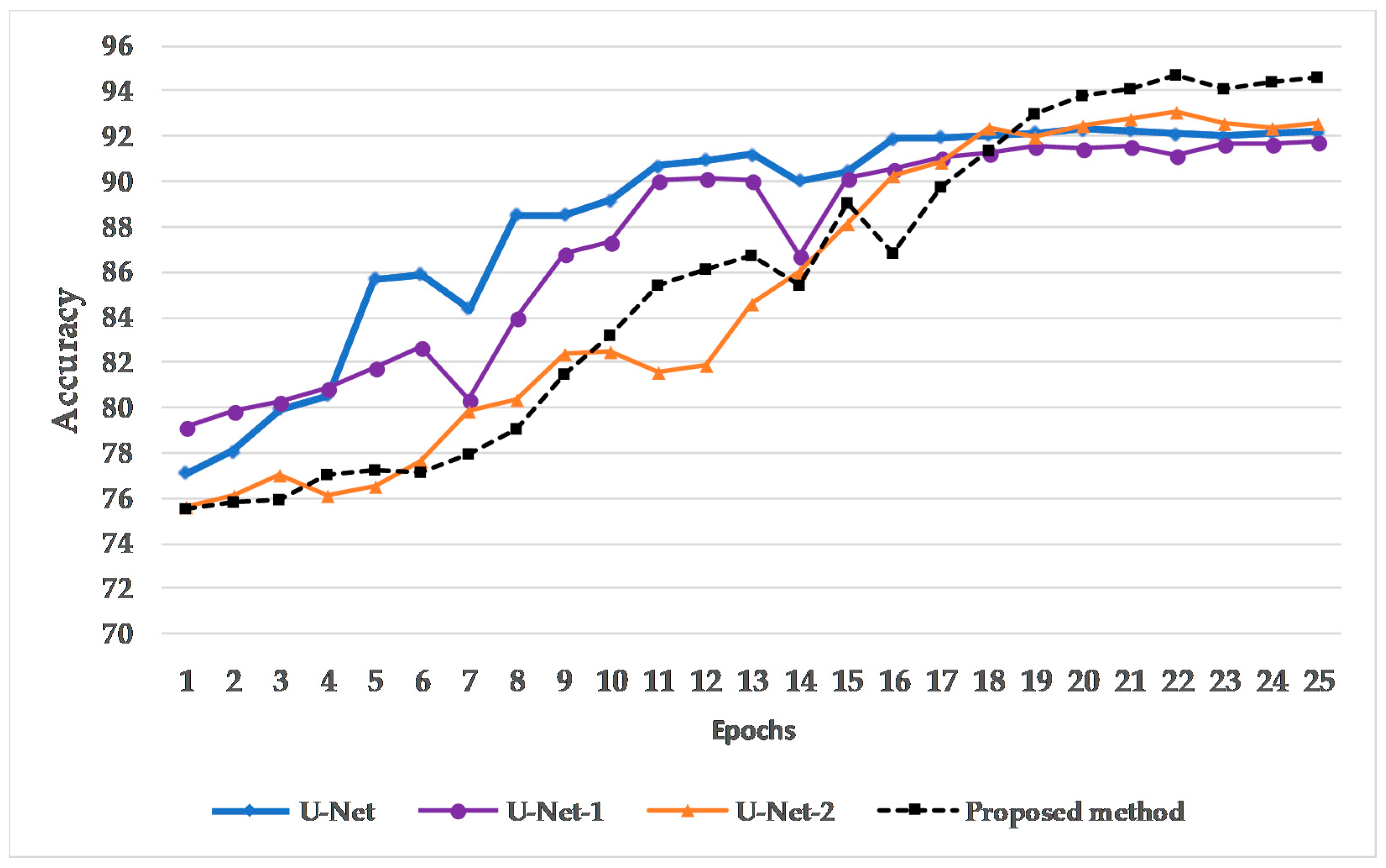
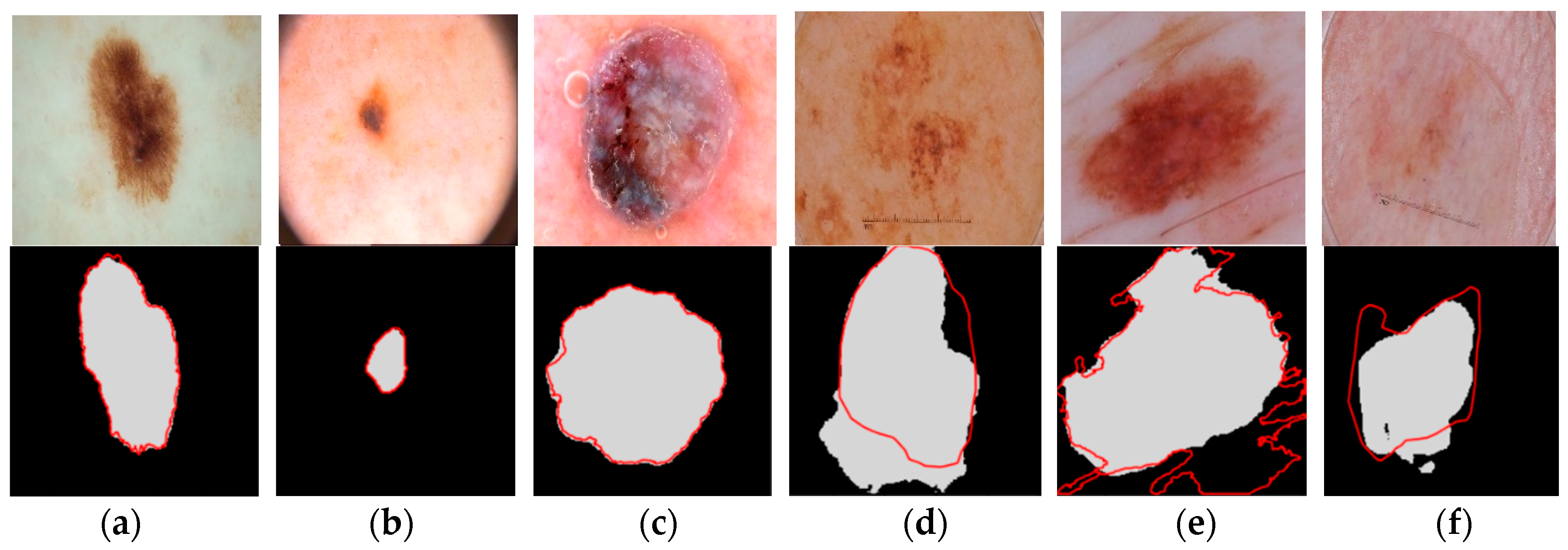
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutman, D.; Codella, N.C.F.; Celebi, E.; Helba, B.; Marchetti, M.; Mishra, N.; Halpern, A. Skin Lesion Analysis toward Melanoma Detection: A Challenge at the International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2016, hosted by the International Skin Imaging Collaboration (ISIC). arXiv 2016, arXiv:1605.01397. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, M.O.; Hyunsoon, C.; Young, J.W. International agency for research on cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2003, 4, 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Brady, M.S.; Oliveria, S.A.; Christos, P.J.; Berwick, M.; Coit, D.G.; Katz, J.; Halpern, A.C. Patterns of detection patients with cutaneous melanoma: Implications for secondary prevention. Cancer 2000, 89, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittler, H.; Pehamberger, H.; Wolff, K.; Binder, M. Diagnstic accuracy of dermoscopy. Lancet Oncol. 2002, 3, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelhamer, E.; Long, J.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, G.; He, Y.; Yu, Z.; Yang, X.; Yang, R.; Zhang, L. Preparation of novel high copper ions removal membranes by embedding organosilane-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotube. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 2322–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J.; Berkeley, U.C.; Malik, J. Rich Feature Hierarchies for accurate Object Detection and Segmentation. Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 2014, 1, 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial Pyramid Pooling in Deep Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sermanet, P.; Eigen, D.; Zhang, X.; Mathieu, M.; Fergus, R.; LeCun, Y. OverFeat: Integrated Recognition, Localization and Detection using Convolutional Networks. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6229. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Zhang, N.; Darrell, T. Do convnets learn correspondence? Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 2, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Donahue, J.; Girshick, R.; Darrell, T. Part-based R-CNNs for fine-grained category detection. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2014, 8689 LNCS, 834–849. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, P.; Dosovitskiy, A.; Brox, T. Descriptor Matching with Convolutional Neural Networks: A Comparison to SIFT. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1405.5769. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, N.; Ahmed, I.; Kiran, M.; Rehman, H.; Din, S.; Paul, A.; Reddy, A.G. Automatic segmentation of liver & lesion detection using H-minima transform and connecting component labeling. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, W.; Ma, C.; Shen, J.; Shao, L.; Porikli, F. See More Know More Unsupervised Video Object Segmentation with Co-Attention CVPR 2019 paper. Cvpr 2019, 1, 3623–3632. [Google Scholar]
- Falk, T.; Mai, D.; Bensch, R.; Çiçek, Ö.; Abdulkadir, A.; Marrakchi, Y.; Böhm, A.; Deubner, J.; Jäckel, Z.; Seiwald, K.; et al. U-Net: Deep learning for cell counting, detection, and morphometry. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Girshick, R.; Arbeláez, P.; Malik, J. Learning rich features from RGB-D images for object detection and segmentation. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2014, 8695 LNCS, 345–360. [Google Scholar]
- Firdaus-Nawi, M.; Noraini, O.; Sabri, M.Y.; Siti-Zahrah, A.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Latifah, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. Pertanika J. Trop. Agric. Sci. 2011, 34, 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan, B.; Arbeláez, P.; Girshick, R.; Malik, J. Simultaneous Detection and Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2014, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 297–312. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Bae, W.C.; Masuda, K.; Chung, C.B.; Hwang, D. Fine-grain segmentation of the intervertebral discs from MR spine images using deep convolutional neural networks: BSU-Net. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Fu, Y.; Wei, X.; Wang, H. An improved image semantic segmentation method based on superpixels and conditional random fields. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, M.; Luo, Y. A coarse-to-fine fully convolutional neural network for fundus vessel segmentation. Symmetry 2018, 10, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Lew, S.M. On the Exploration of Convolutional Fusion Networks for Visual Recognition. In Proceedings of the MultiMedia Modeling; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 177–189. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Shen, L. Skin lesion analysis towards melanoma detection using deep learning network. Sensors 2018, 18, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WALLACH, B. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. A World Made Money 2017, 241–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, K.; Sun, J. R-fcn: Object detection via region-based fully convolutional networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2016, 379–387. [Google Scholar]
- Eigen, D.; Fergus, R. Predicting depth, surface normals and semantic labels with a common multi-scale convolutional architecture. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 13–16 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Yao, T.; Liu, D.; Mei, T. Fully Convolutional Adaptation Networks for Semantic Segmentation. Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 6810–6818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2015, 9351, 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Shin, Y.; Su, Y.; Karniadakis, G.E. Dying ReLU and Initialization: Theory and Numerical Examples. NIPS 2019, 107, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. NIPS 2012, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, S.C.; Yu, J. Why RELU Units Sometimes Die: Analysis of Single-Unit Error Backpropagation in Neural Networks. Conf. Rec. Asilomar Conf. Signals Syst. Comput. 2019, 2018, 864–868. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Alex, K.; Sutskever, I.; Ruslan, S. Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 299, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://challenge.kitware.com/#phase/5841916ccad3a51cc66c8db0 (accessed on 24 October 2019).
- Kamrul Hasan, S.M.; Linte, C.A. A Modified U-Net Convolutional Network Featuring a Nearest-neighbor Re-sampling-based Elastic-Transformation for Brain Tissue Characterization and Segmentation. 2018 IEEE West. New York Image Signal Process. Work. WNYISPW 2018 2018, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glorot, X.; Bordes, A.; Bengio, Y. Deep sparse rectifier neural networks. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 15, 315–323. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, A.L.; Hannun, A.Y.; Ng, A.Y. Rectifier Nonlinearities Improve Neural Network Acoustic Models. Pdfs.Semanticscholar.Org. 2007, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Ranzato, M.; Monga, R.; Mao, M.; Yang, K.; Le, Q.V.; Nguyen, P.; Senior, A.; Vanhoucke, V.; Dean, J.; et al. On rectified linear units for speech processing. ICASSP IEEE Int. Conf. Acoust. Speech Signal. Process. Proc. 2013, 3517–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vis. 2015, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Wang, N.; Chen, T.; Li, M. Empirical Evaluation of Rectified Activations in Convolutional Network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.00853. [Google Scholar]
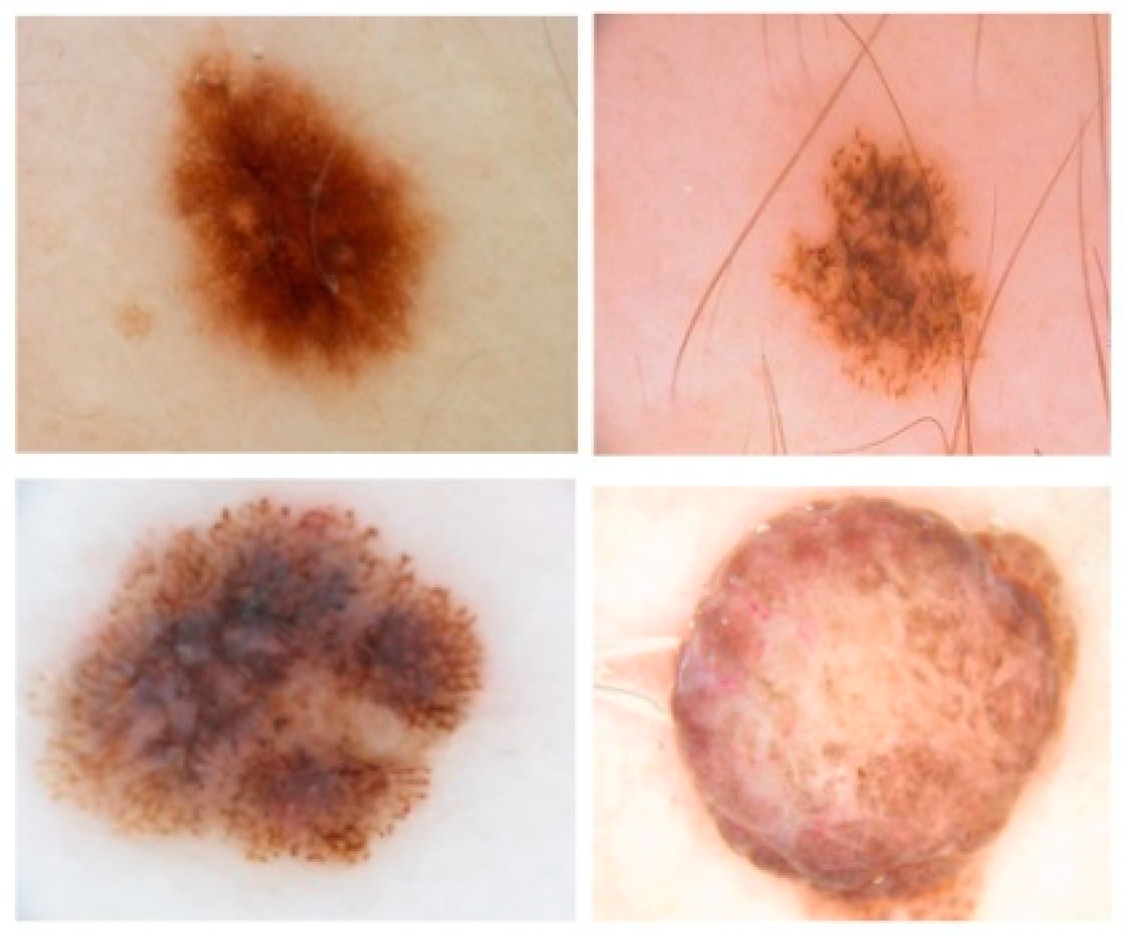
| Model | Pixel Accuracy | Dice | IoU |
|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | 91.12% | 78.23% | 39.26% |
| FCN-1 | 90.47% | 81.85% | 40.51% |
| FCN-2 | 91.34% | 83.26% | 41.84% |
| Proposed method | 94.36% | 88.33% | 44.05% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanjar, K.; Bekhzod, O.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Paul, A.; Kim, J. Improved U-Net: Fully Convolutional Network Model for Skin-Lesion Segmentation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3658. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103658
Sanjar K, Bekhzod O, Kim J, Kim J, Paul A, Kim J. Improved U-Net: Fully Convolutional Network Model for Skin-Lesion Segmentation. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(10):3658. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103658
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanjar, Karshiev, Olimov Bekhzod, Jaeil Kim, Jaesoo Kim, Anand Paul, and Jeonghong Kim. 2020. "Improved U-Net: Fully Convolutional Network Model for Skin-Lesion Segmentation" Applied Sciences 10, no. 10: 3658. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103658
APA StyleSanjar, K., Bekhzod, O., Kim, J., Kim, J., Paul, A., & Kim, J. (2020). Improved U-Net: Fully Convolutional Network Model for Skin-Lesion Segmentation. Applied Sciences, 10(10), 3658. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103658





