Comparison of the Usefulness of CBCT and MRI in TMD Patients According to Clinical Symptoms and Age
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Imaging Analysis
2.2.1. CBCT Evaluation
2.2.2. MRI Evaluation
2.3. Data Grouping and Analysis
- Type I (neither CBCT nor MRI findings): no CBCT or MRI findings.
- Type II (only CBCT findings): at least one CBCT finding, but no MRI findings.
- Type III (only MRI findings): at least one MRI finding, but no CBCT findings.
- Type IV (both CBCT and MRI findings): at least one CBCT finding and at least one MRI finding.
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ingawalé, S.; Goswami, T. Temporomandibular joint: Disorders, treatments, and biomechanics. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 37, 976–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Cheng, J.G.; Li, G.; Shi, X.Q.; Zhang, J.Z.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Ma, X.C. Detection accuracy of condylar bony defects in Promax 3D cone beam CT images scanned with different protocols. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2013, 42, 20120241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shetty, U.S.; Burde, K.N.; Naikmasur, V.G.; Sattur, A.P. Assessment of condylar changes in patients with temporomandibular joint pain using digital volumetric tomography. Radiol. Res. Pract. 2014, 2014, 106059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zain-Alabdeen, E.H.; Alsadhan, R.I. A comparative study of accuracy of detection of surface osseous changes in the temporomandibular joint using multidetector CT and cone beam CT. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2012, 41, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- dos Anjos Pontual, M.L.; Freire, J.S.; Barbosa, J.M.; Frazao, M.A.G.; dos Anjos Pontual, A.; Fonseca da Silveira, M.M. Evaluation of bone changes in the temporomandibular joint using cone beam CT. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2012, 41, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tasaki, M.M.; Westesson, P.L. Temporomandibular joint: Diagnostic accuracy with sagittal and coronal MR imaging. Radiology 1993, 186, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arayasantiparb, R.; Mitrirattanakul, S.; Kunasarapun, P.; Chutimataewin, H.; Netnoparat, P.; Sae-Heng, W. Association of radiographic and clinical findings in patients with temporomandibular joints osseous alteration. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emshoff, R.; Innerhofer, K.; Rudisch, A.; Bertram, S. Clinical versus magnetic resonance imaging findings with internal derangement of the temporomandibular joint: An evaluation of anterior disc displacement without reduction. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2002, 60, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emshoff, R.; Brandlmaier, I.; Bertram, S.; Rudisch, A. Relative odds of temporomandibular joint pain as a function of magnetic resonance imaging findings of internal derangement, osteoarthrosis, effusion, and bone marrow edema. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2003, 95, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emshoff, R.; Brandlmaier, I.; Bertram, S.; Rudisch, A. Risk factors for temporomandibular joint pain in patients with disc displacement without reduction—A magnetic resonance imaging study. J. Oral Rehabil. 2003, 30, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larheim, T.A.; Westesson, P.L.; Sano, T. MR grading of temporomandibular joint fluid: Association with disk displacement categories, condyle marrow abnormalities and pain. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2001, 30, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, R.; Yanagi, Y.; Oki, K.; Hisatomi, M.; Santos, K.C.P.; Bamgbose, B.O.; Fujita, M.; Okada, S.; Minagi, S.; Asaumi, J. Assessment of MRI findings and clinical symptoms in patients with temporomandibular joint disorders. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2018, 47, 20170412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurita, H.; Kojima, Y.; Nakatsuka, A.; Koike, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Kurashina, K. Relationship between temporomandibular joint (TMJ)-related pain and morphological changes of the TMJ condyle in patients with temporomandibular disorders. Dento maxillofac. Radiol. 2004, 33, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, H.S.; Kim, W.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, J.-Y. Relationships between disk displacement, joint effusion, and degenerative changes of the TMJ in TMD patients based on MRI findings. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2012, 40, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arayasantiparb, R.; Tsuchimochi, M.; Mitrirattanakul, S. Transformation of temporomandibular joint disc configuration in internal derangement patients using magnetic resonance imaging. Oral Sci. Int. 2012, 9, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koh, K.J.; Park, H.N.; Kim, K.A. Relationship between anterior disc displacement with/without reduction and effusion in temporomandibular disorder patients using magnetic resonance imaging. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2013, 43, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wanman, A.; Agerberg, G. Mandibular dysfunction in adolescents. I. Prevalence of symptoms. Acta Odontol. Scand. 1986, 44, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Guo, C.; Awad, M. Hyaluronate for temporomandibular joint disorders. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2003, Cd002970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros Vde, M.; Seraidarian, P.I.; Côrtes, M.I. The impact of orofacial pain on the quality of life of patients with temporomandibular disorder. J. Orofac. Pain 2009, 23, 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Tjakkes, G.H.; Reinders, J.J.; Tenvergert, E.M.; Stegenga, B. TMD pain: The effect on health related quality of life and the influence of pain duration. Health Qual Life Outcomes 2010, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solberg, W.K.; Woo, M.W.; Houston, J.B. Prevalence of mandibular dysfunction in young adults. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1979, 98, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkes, C.H. Internal derangements of the temporomandibular joint. Pathologic variations. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1989, 115, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlmann, B.; Rammelsberg, P.; Henschel, V.; Kress, B.; Gabbert, O.; Schmitter, M. Prediction of TMJ arthralgia according to clinical diagnosis and MRI findings. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2006, 19, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wiese, M.; Svensson, P.; Bakke, M.; List, T.; Hintze, H.; Petersson, A.; Knutsson, K.; Wenzel, A. Associations between temporomandibular joint symptoms, signs, and clinical diagnosis using the RDC/TMD and radiographic findings in temporomandibular joint tomograms. J. Orofac. Pain 2008, 22, 239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Emshoff, R.; Bertram, F.; Schnabl, D.; Stigler, R.; Steinmassl, O.; Rudisch, A. Condylar Erosion in Patients With Chronic Temporomandibular Joint Arthralgia: A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 74, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westesson, P.L.; Brooks, S.L. Temporomandibular joint: Relation between MR evidence of effusion and the presence of pain and disk displacement. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1992, 159, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, K.; Chiba, M.; Sai, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Nogami, S.; Yamauchi, K.; Takahashi, T. Relationship between temporomandibular joint pain and magnetic resonance imaging findings in patients with temporomandibular joint disorders. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 49, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosgor, H. The relationship between temporomandibular joint effusion and pain in patients with internal derangement. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2019, 47, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Type I | Type II | Type III | Type IV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sound (n = 353) | 7.9 (28) | 2.8 (10) | 47.9 (169) | 41.4 (146) |
| Pain (n = 368) | 7.1 (26) | 2.4 (9) | 41.0 (151) | 49.5 (182) |
| Limited mouth opening (n = 159) | 3.1 (5) | 5.0 (8) | 37.8 (60) | 54.1 (86) |
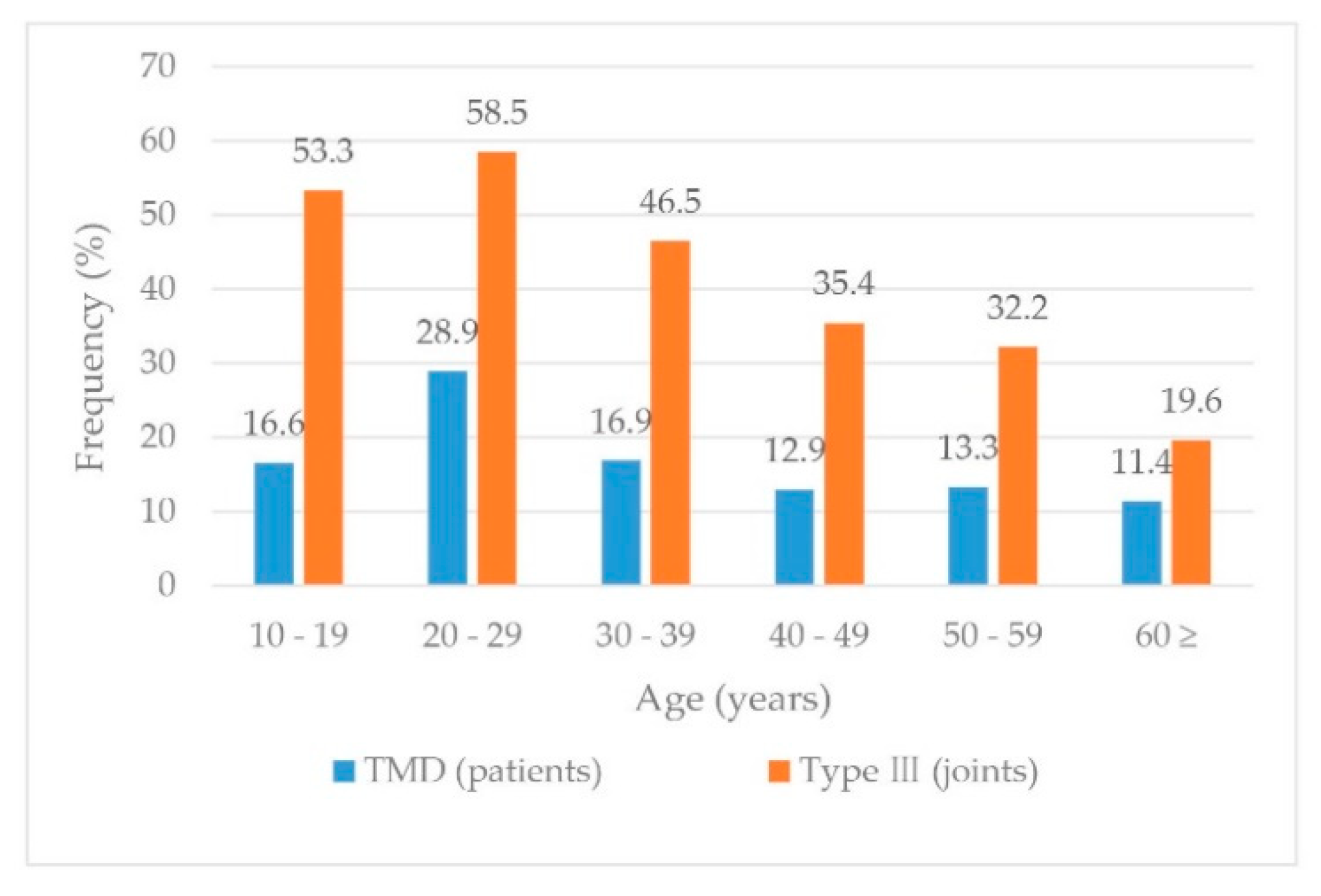
| Age (years) | Type I | Type II | Type III | Type IV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10–19 (n = 75) | 14.7 (11) | 1.3 (1) | 53.3 (40) | 30.7 (23) |
| 20–29 (n = 142) | 4.9 (7) | 5.6 (8) | 58.5 (83) | 31.0 (44) |
| 30–39 (n = 86) | 8.1 (7) | 1.2 (1) | 46.5 (40) | 44.2 (38) |
| 40–49 (n = 65) | 7.7 (5) | 1.5 (1) | 35.4 (23) | 55.4 (36) |
| 50–59 (n = 59) | 3.4 (2) | 3.4 (2) | 32.2 (19) | 61.0 (36) |
| 60 ≥ (n = 46) | 8.7 (4) | 6.5 (3) | 19.6 (9) | 65.2 (30) |
| Age (Years) | Type III | Type I, II, IV | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10–29 (n = 217) | 123 (56.7) | 94 (43.3) | < 0.001 * |
| 30 ≥ (n = 256) | 91 (35.5) | 165 (64.5) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, K.J.; Lee, C.; Choi, Y.J.; Han, S.-S. Comparison of the Usefulness of CBCT and MRI in TMD Patients According to Clinical Symptoms and Age. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3599. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103599
Jeon KJ, Lee C, Choi YJ, Han S-S. Comparison of the Usefulness of CBCT and MRI in TMD Patients According to Clinical Symptoms and Age. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(10):3599. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103599
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Kug Jin, Chena Lee, Yoon Joo Choi, and Sang-Sun Han. 2020. "Comparison of the Usefulness of CBCT and MRI in TMD Patients According to Clinical Symptoms and Age" Applied Sciences 10, no. 10: 3599. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103599
APA StyleJeon, K. J., Lee, C., Choi, Y. J., & Han, S.-S. (2020). Comparison of the Usefulness of CBCT and MRI in TMD Patients According to Clinical Symptoms and Age. Applied Sciences, 10(10), 3599. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103599





