Extended SSH Model in Non-Hermitian Waveguides with Alternating Real and Imaginary Couplings
Abstract
1. Introduction
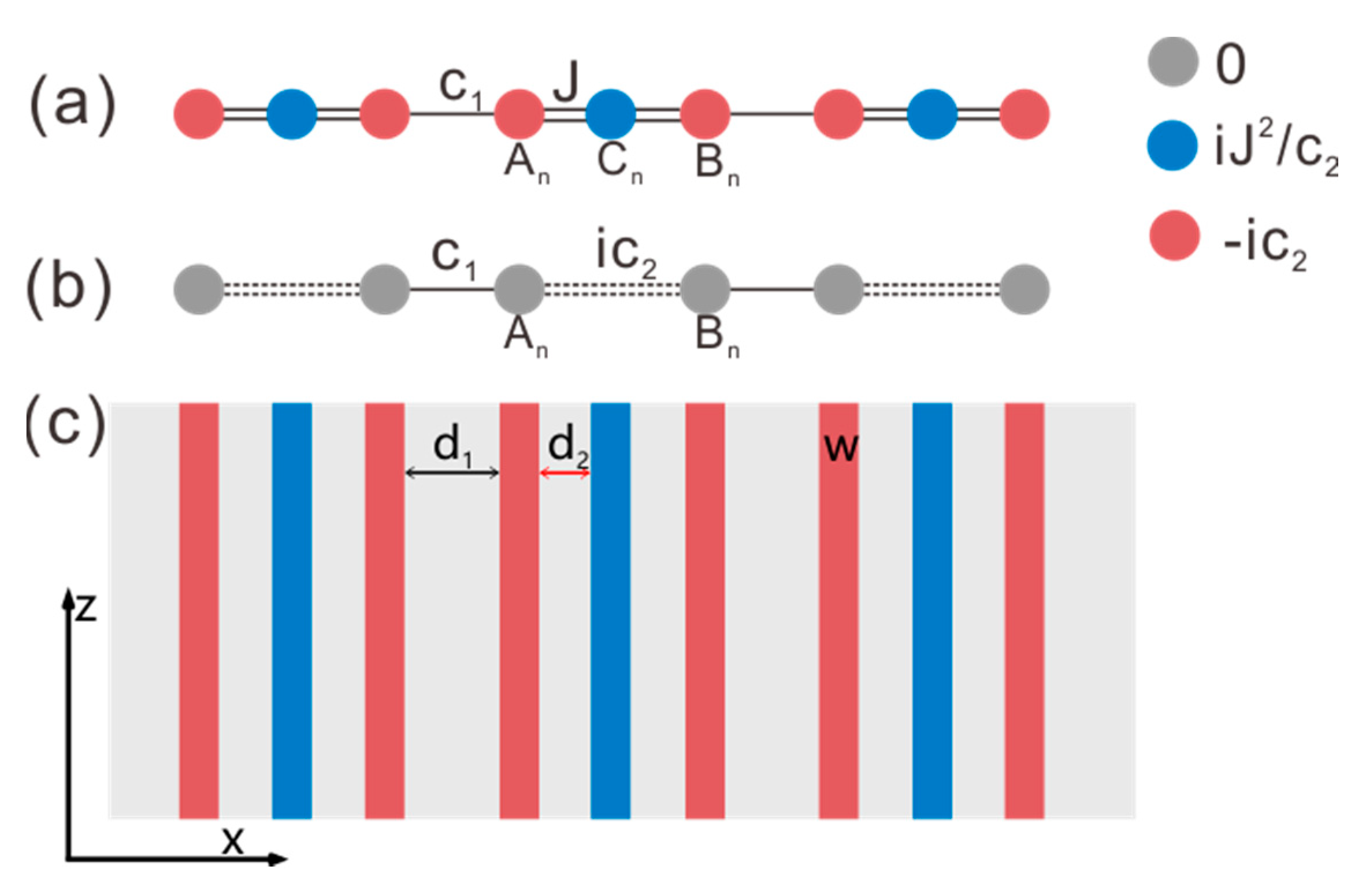
2. Geometry and Theoretical Model
3. Bloch Mode
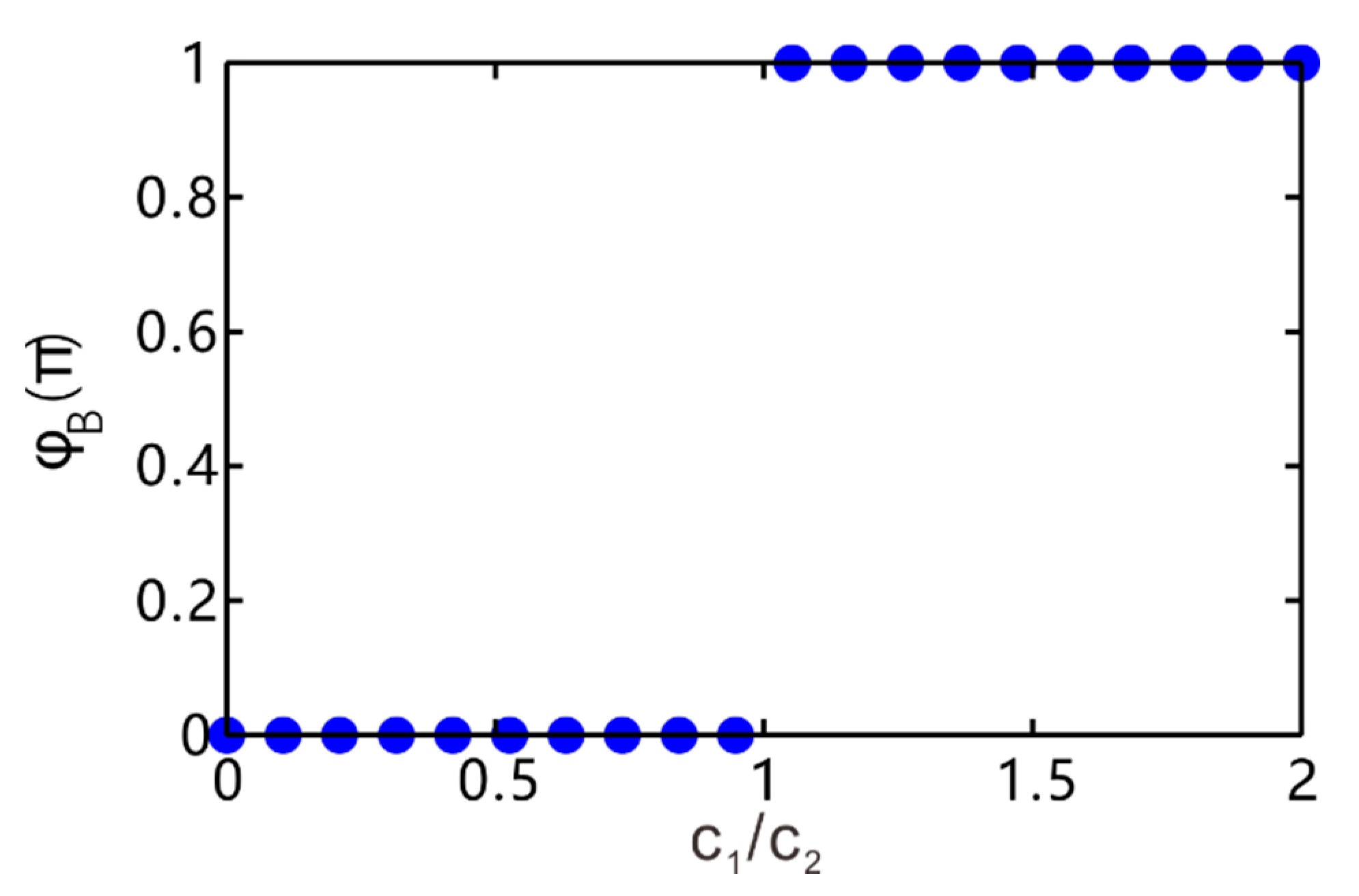
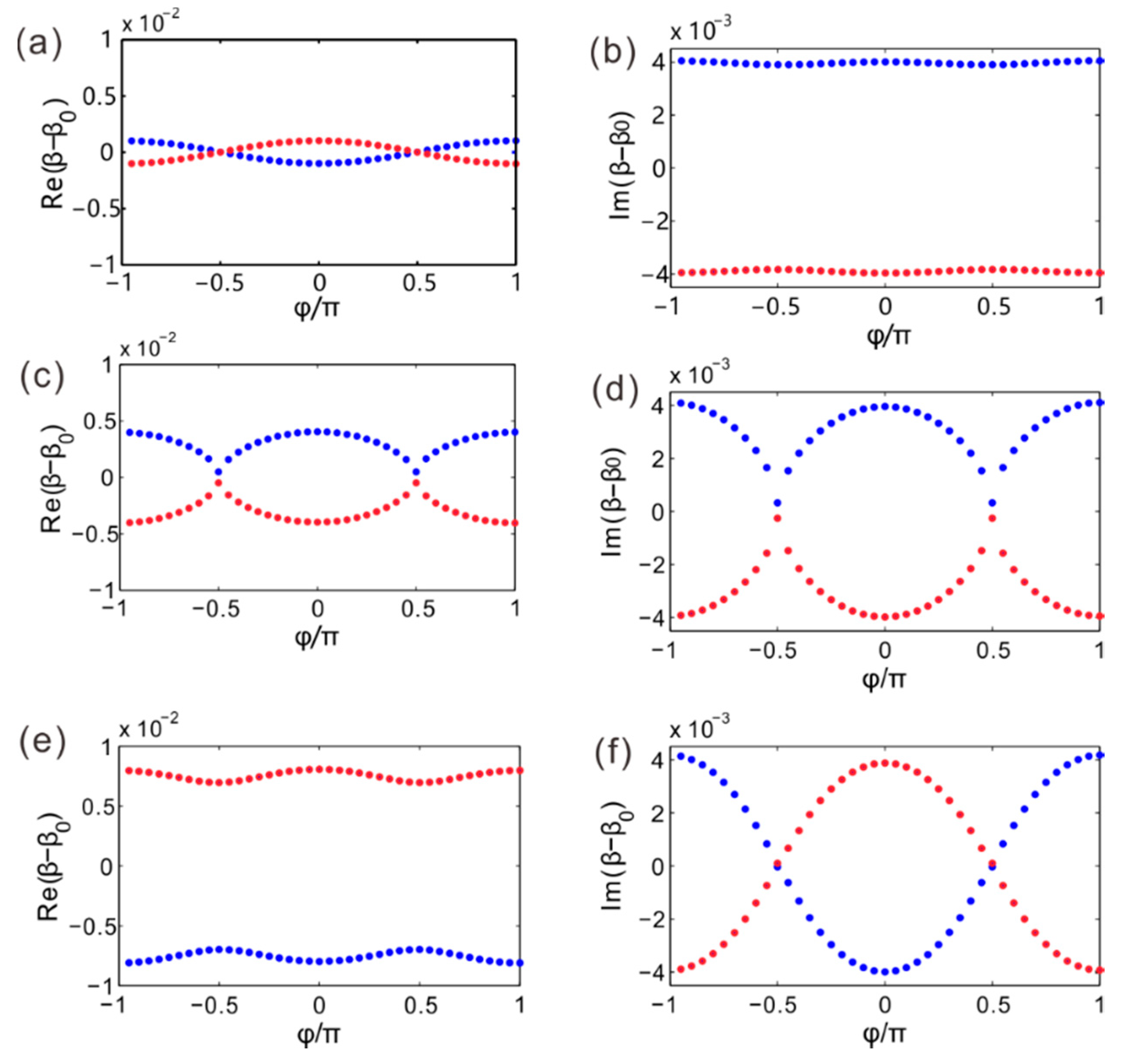
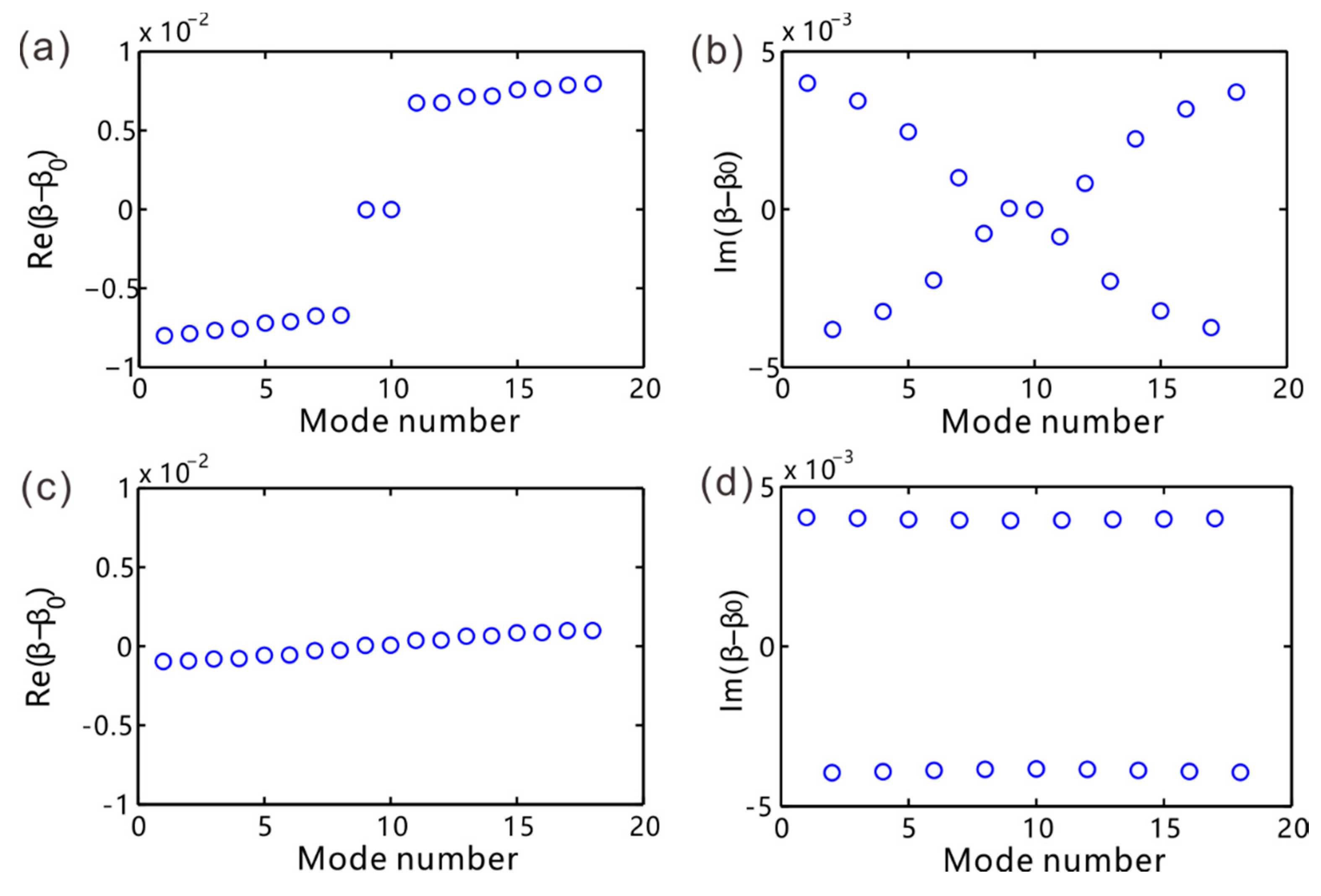
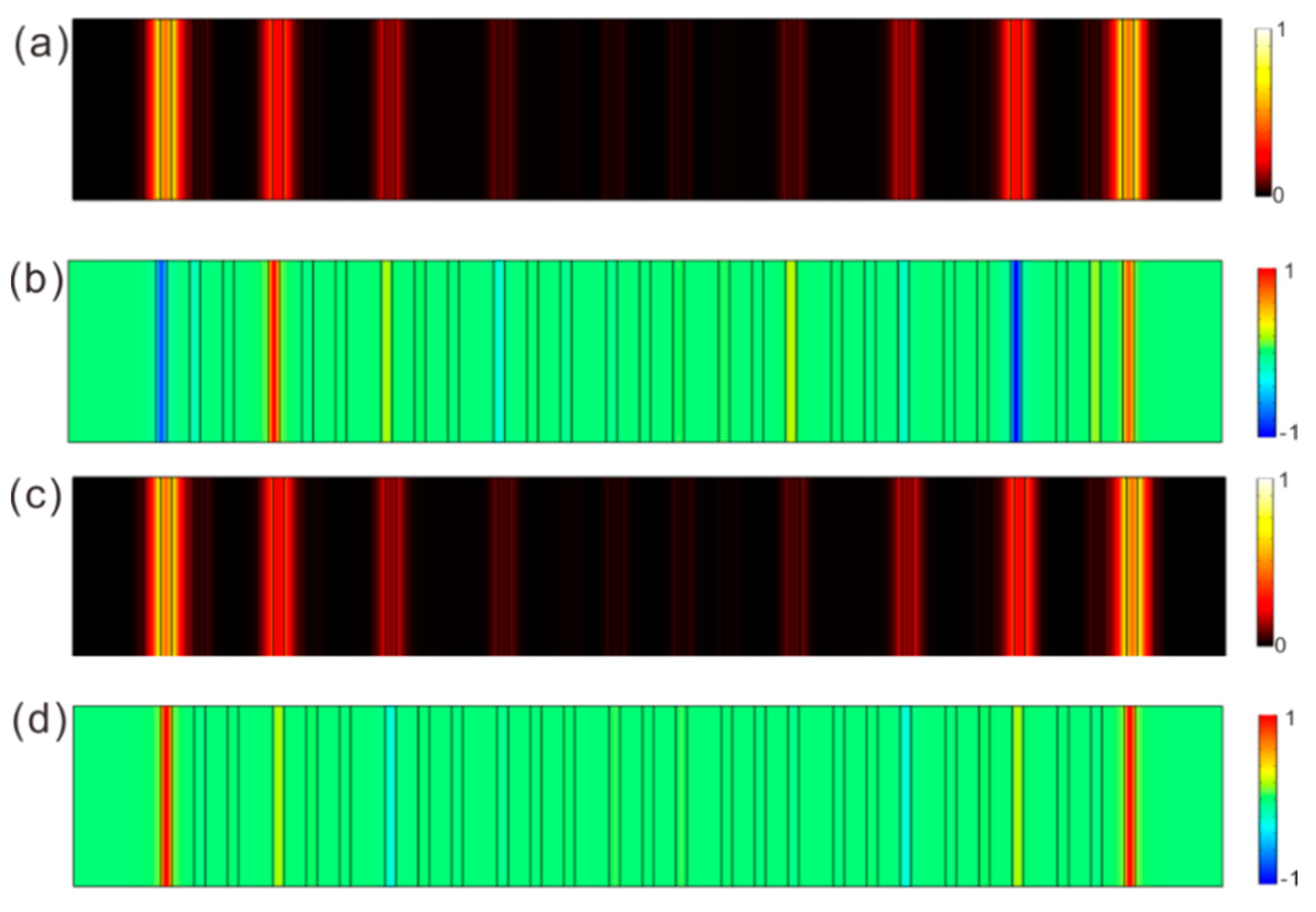
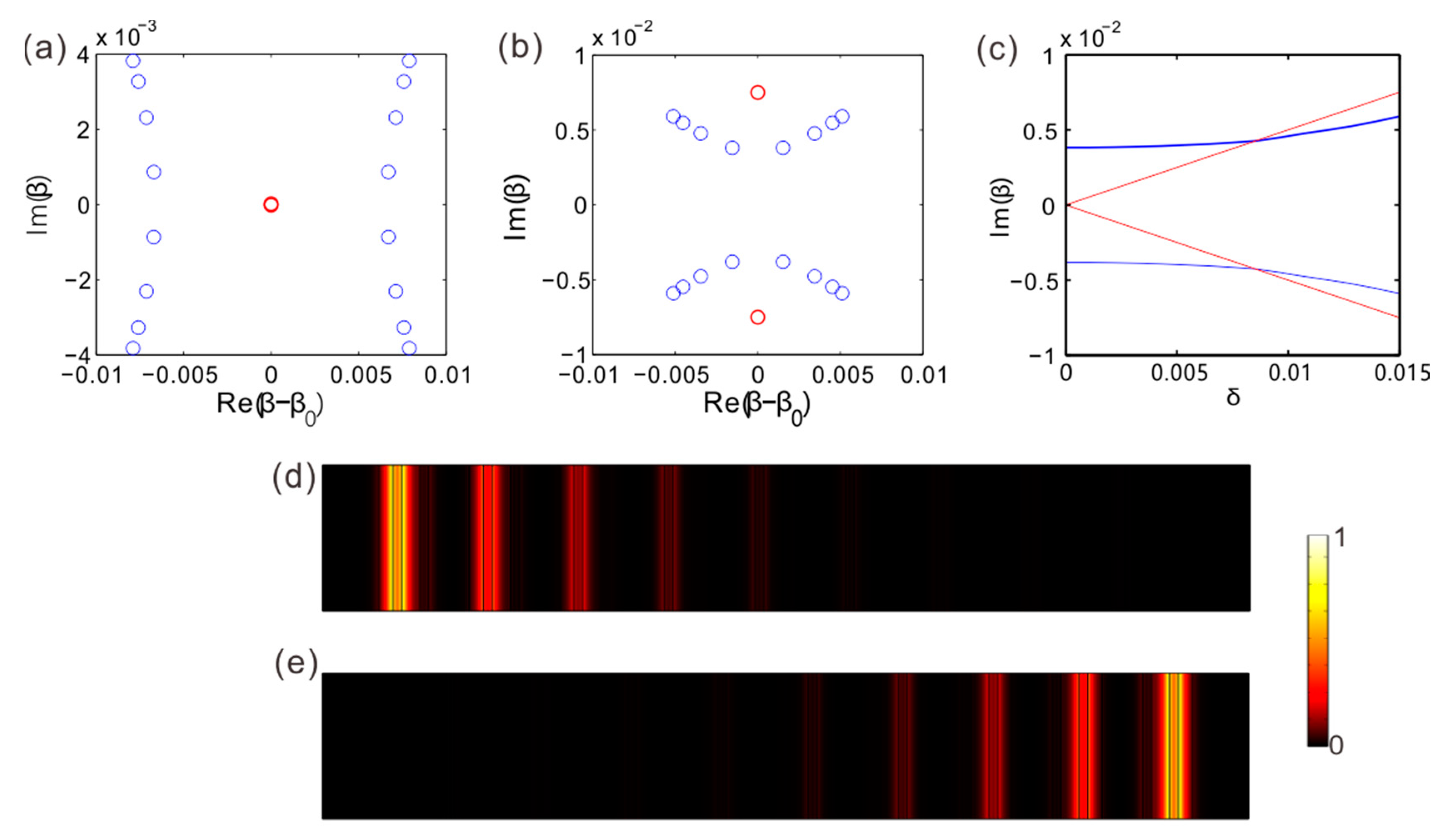
4. Topological Edge Modes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, W.P.; Schrieffer, J.R.; Heeger, A.J. Solitons in Polyacetylene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1978, 42, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbóth, J.K.; Oroszlány, L.; Pályi, A. The Su-Schrieffer-Heeger (SSH) Model. In A Short Course on Topological Insulators. Lecture Notes in Physics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; p. 919. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco-Redondo, A.; Andrea, I.; Collins, M.; Harari, G.; Lumer, Y.; Rechtsman, M.; Eggleton, B.; Segev, M. Topological optical waveguiding in silicon and the transition between topological and trivial defect states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 163901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, T.; Zhu, S. Topologically protected interface mode in plasmonic waveguide arrays. Laser Photon. Rev. 2015, 9, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Wang, L.; Xiao, M.; Wen, W.; Chan, C.; Han, D. Topological edge modes in multilayer graphene systems. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 21585–21595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, S.; Wang, B.; Long, H.; Wang, K.; Lu, P. Topological edge modes in non-Hermitian plasmonic waveguide arrays. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 11132–11143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.X.; Zhao, C.Y. Wideband tunable infrared topological plasmon polaritons in dimerized chains of doped-silicon nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 127, 073106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.G.; Qin, C.; Zhao, D.; Shen, Y.; Xu, X.; Bao, M.; Jia, H.; Zhu, X. Experimental demonstration of anomalous Floquet topological insulator for sound. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, D.; Belic, M.; Zhao, Y. Spatiotemporal solitons in cold Rydberg atomic gases with Bessel optical lattices. Appl. Math. Lett. 2020, 106, 106230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Joannopoulos, D.; Soljačić, M. Topological photonics. Nat. Photon. 2014, 8, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Chen, X.; Panoiu, N.; Ye, F. Topological surface plasmons in superlattices with changing sign of the average permittivity. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 4281–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, D.; Guo, H.; Huang, M.; Ke, S. Plasmonic Jackiw-Rebbi Modes in Graphene Waveguide Arrays. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Gou, W.; Xiao, T.; Gadway, B.; Yan, B. Topological characterizations of an extended Su–Schrieffer–Heeger model. npj Quantum Inf. 2019, 5, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, N.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liao, Q.; Zhao, D.; Ke, S. Topological bound modes in optical waveguide arrays with alternating positive and negative couplings. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2020, 52, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, P.; Zhao, D.; Zhong, D.; Liu, W. Topological plasmonic modes in graphene-coated nanowire arrays. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2019, 51, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ke, S.; Qin, C.; Wang, B.; Long, H.; Wang, K.; Lu, P. Topological interface modes in graphene multilayer arrays. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 103, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.Q.; Pan, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, D.; Yu, A.; Gover, H.; Zhang, T.; Li, L.Z.; Zhu, S. Observation of Anomalous π Modes in Photonic Floquet Engineering. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 173901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wakabayashi, K. Novel Topological Phase with a Zero Berry Curvature. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 118, 076803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Deng, W.; Shi, F.; Zhao, F.; Chen, M.; Dong, J. Direct observation of corner states in second-order topological photonic crystal slabs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 233902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Wang, Z. Edge States and Topological Invariants of Non-Hermitian Systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 086803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveirinha, M.G. Topological theory of non-Hermitian photonic systems. Phys. Rev. B 2019, 99, 125155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuce, C. Topological phase in a non-Hermitian PT symmetric system. Phys. Lett. A 2015, 379, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuce, C.; Ramezani, H. Topological states in a non-Hermitian two-dimensional Su-SchriefferHeeger model. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 100, 032102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, M.; Alù, A. Exceptional points in optics and photonics. Science 2019, 363, 6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Q.; Wu, S.; Wang, B.; Lu, P. Optical imaginary directional couplers. J. Lightwave Technol. 2018, 36, 2510–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Xu, B.; Guo, H.; Xu, W.; Zhong, D.; Ke, S. Low Threshold Optical Bistability in Aperiodic PT-Symmetric Lattices Composited with Fibonacci Sequence Dielectrics and Graphene. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Ke, S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, B.; Lu, P. Optical bistability of graphene embedded in parity-time-symmetric photonic lattices. JOSA B 2019, 36, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhao, D.; Cao, H.; Xu, B.; Xu, W.; Ke, S. Exceptional Points in Non-Hermitian Photonic Crystals Incorporated with a Defect. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhong, D.; Hu, Y.; Ke, S.; Liu, W. Imaginary modulation inducing giant spatial Goos–Hänchen shifts in one-dimensional defective photonic lattices. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2019, 51, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, T.; Chan, C.T. Dynamically encircling an exceptional point in anti-parity time symmetric systems: Asymmetric mode switching for symmetry-broken modes. Light Sci. Appl. 2019, 8, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.; Wang, B.; Qin, C.; Long, H.; Wang, K.; Lu, P. Exceptional points and asymmetric mode switching in plasmonic waveguides. J. Lightwave Technol. 2016, 34, 5258–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.; Wang, B.; Long, H.; Wang, K.; Lu, P. Topological mode switching in a graphene doublet with exceptional points. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2017, 49, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Q.; Liu, W. Adiabatic transfer of surface plasmons in non-Hermitian graphene waveguides. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2018, 50, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, D.; Liu, W. Strong absorption near exceptional points in plasmonic waveguide arrays. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2018, 50, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parto, M.; Wittek, S.; Hodaei, H.; Harari, G.; Miguel, A.B.; Ren, J.; Mikael, C.R.; Segev, M.; Demetrios, N.C.; Khajavikhan, M. Edge-Mode Lasing in 1D Topological Active Arrays. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 113901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuce, C. Non-Hermitian anomalous skin effect. Phys. Lett. A 2020, 384, 126094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.; Zhao, D.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q.; Liao, Q.; Wang, B.; Lu, P. Topological bound modes in anti-PT symmetric optical waveguide arrays. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 13858–13870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keil, R.; Poli, C.; Heinrich, M.; Arkinstall, J.; Weihs, G.; Schomerus, H.; Szameit, A. Universal Sign Control of Coupling in Tight-Binding Lattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 213901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wen, J.; Huang, Y. Anti-parity-time Symmetry in Passive Nanophotonics. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.11151. [Google Scholar]
- Kremer, M.; Petrides, I.; Meyer, E.; Heinrich, M.; Zilberberg, O.; Szameit, A. A square-root topological insulator with non-quantized indices realized with photonic Aharonov-Bohm cages. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Liu, Y.; You, L. Anti-PT symmetry in dissipatively coupled optical systems. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 96, 053845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieu, S. Topological phases in the non-Hermitian Su-Schrieffer-Heeger model. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 9, 045106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüter, C.; Makris, K.; El-Ganainy, R.; Christodoulides, D.; Segev, M.; Kip, D. Observation of parity–time symmetry in optics. Nat. Phys. 2010, 6, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Z.; Fu, N.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, D.; Ke, S. Extended SSH Model in Non-Hermitian Waveguides with Alternating Real and Imaginary Couplings. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103425
Fu Z, Fu N, Zhang H, Wang Z, Zhao D, Ke S. Extended SSH Model in Non-Hermitian Waveguides with Alternating Real and Imaginary Couplings. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(10):3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103425
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Ziwei, Nianzu Fu, Huaiyuan Zhang, Zhe Wang, Dong Zhao, and Shaolin Ke. 2020. "Extended SSH Model in Non-Hermitian Waveguides with Alternating Real and Imaginary Couplings" Applied Sciences 10, no. 10: 3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103425
APA StyleFu, Z., Fu, N., Zhang, H., Wang, Z., Zhao, D., & Ke, S. (2020). Extended SSH Model in Non-Hermitian Waveguides with Alternating Real and Imaginary Couplings. Applied Sciences, 10(10), 3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103425




