Directly Printed Hollow Connectors for Microfluidic Interconnection with UV-Assisted Coaxial 3D Printing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
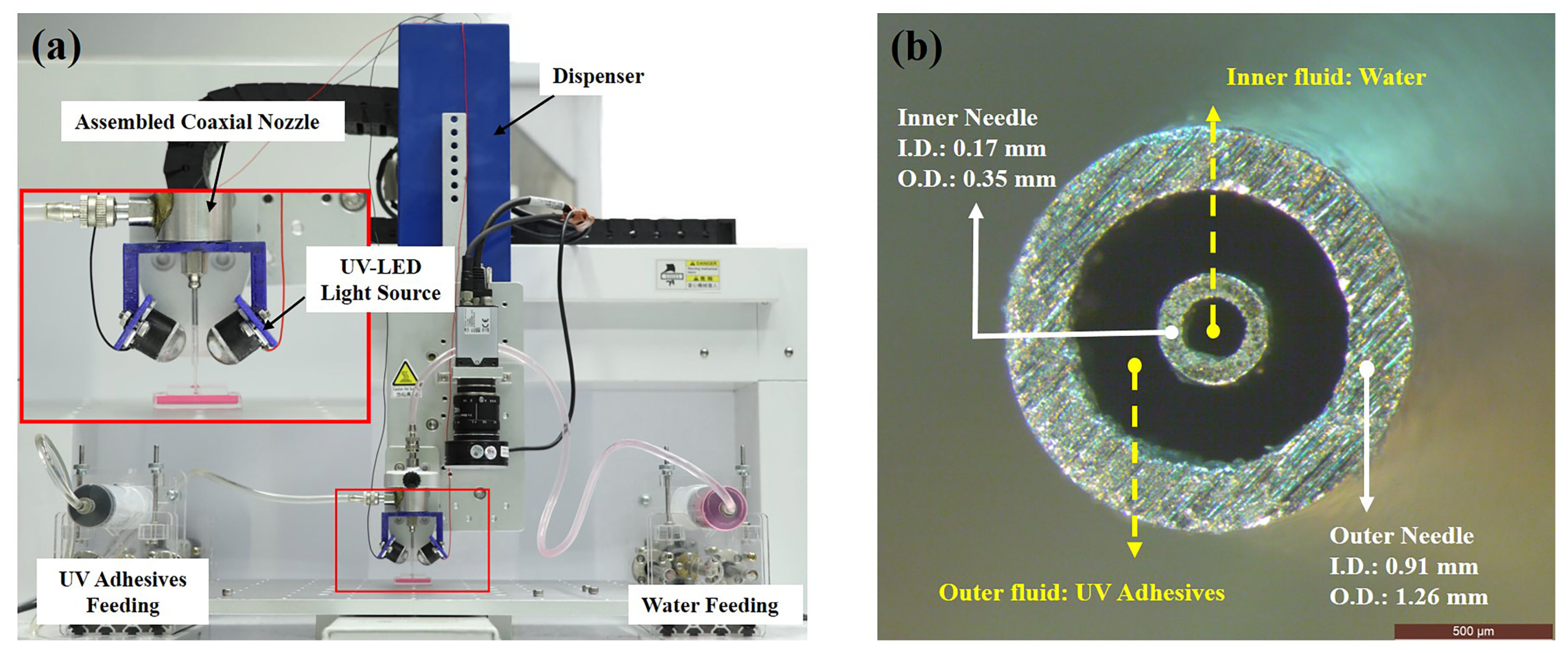
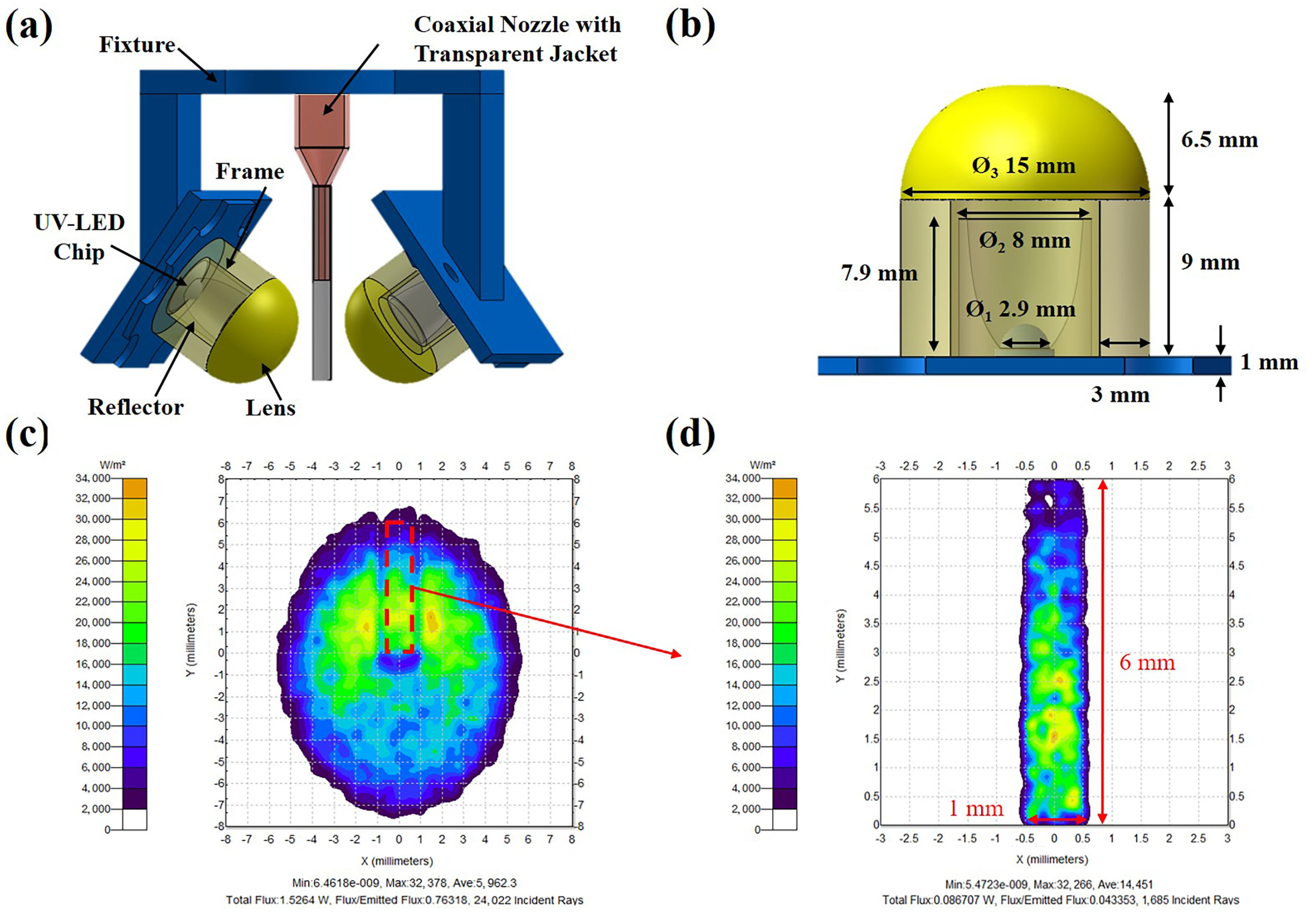
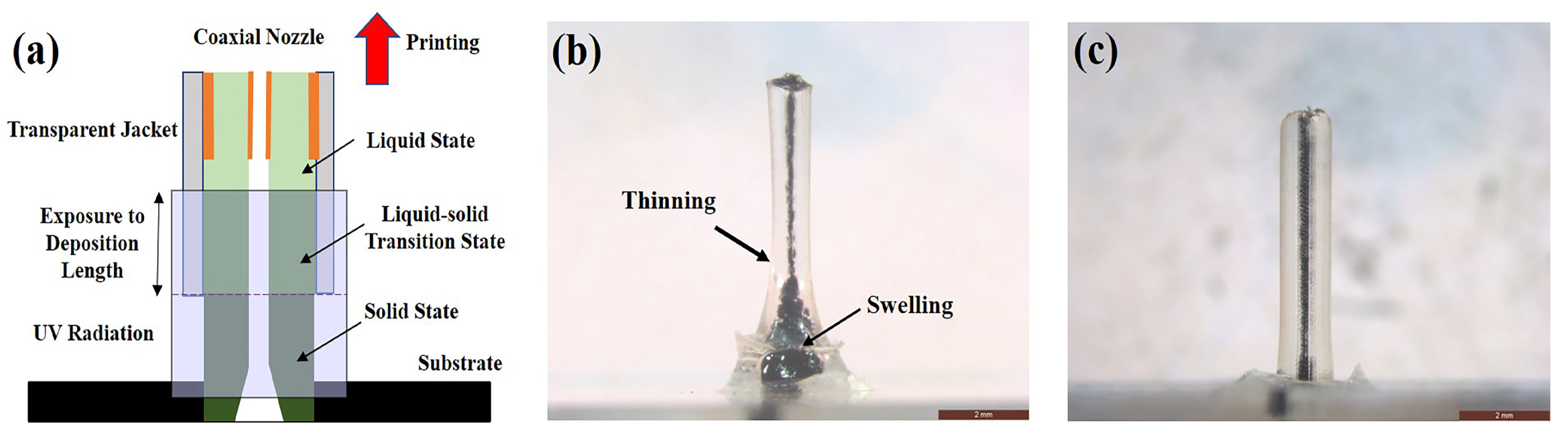
2.2. UV-Assisted Coaxial 3D Printing System
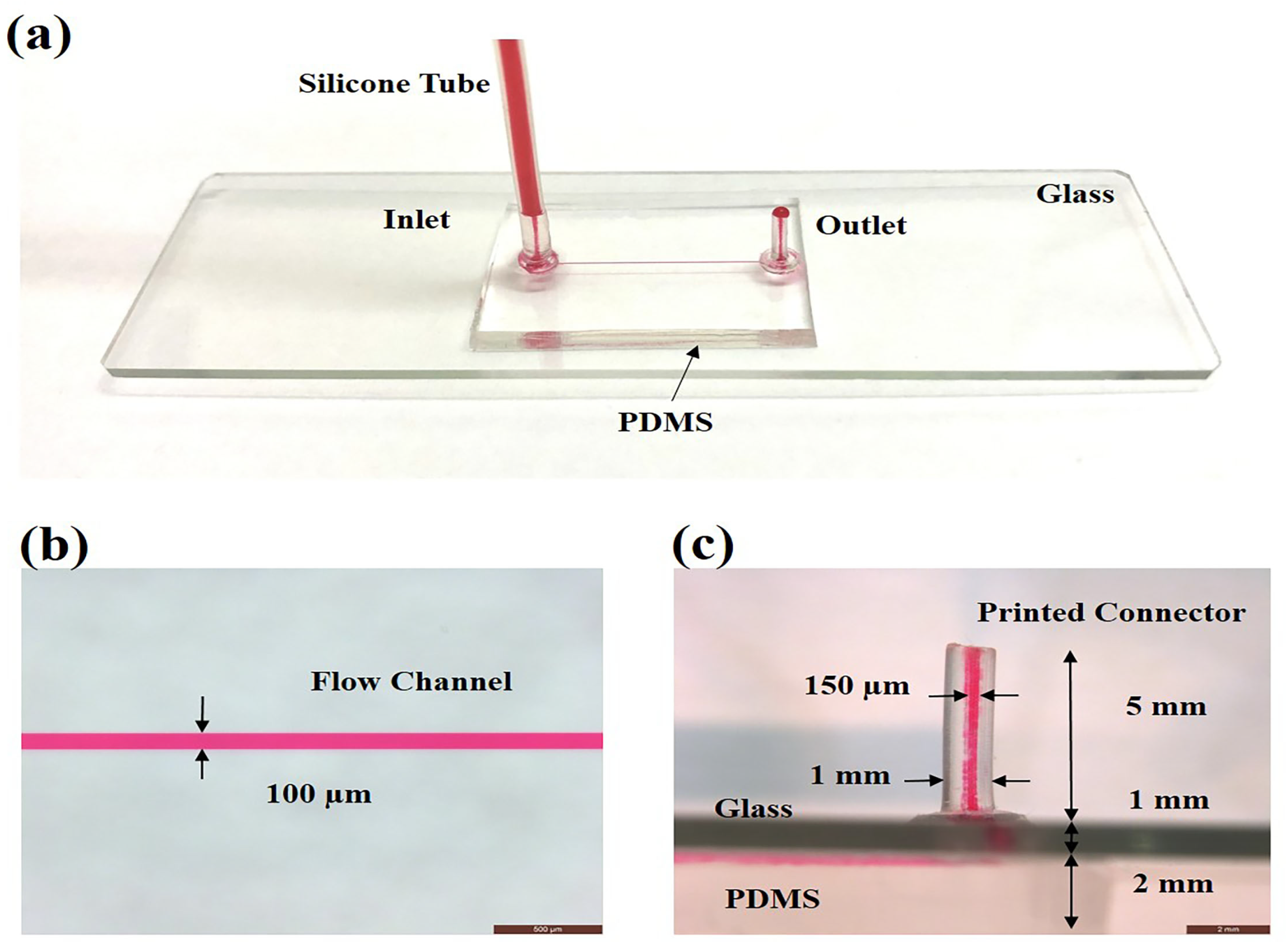
2.3. Fabrication of PDMS–Glass Microfluidic Device
3. Results and Discussion
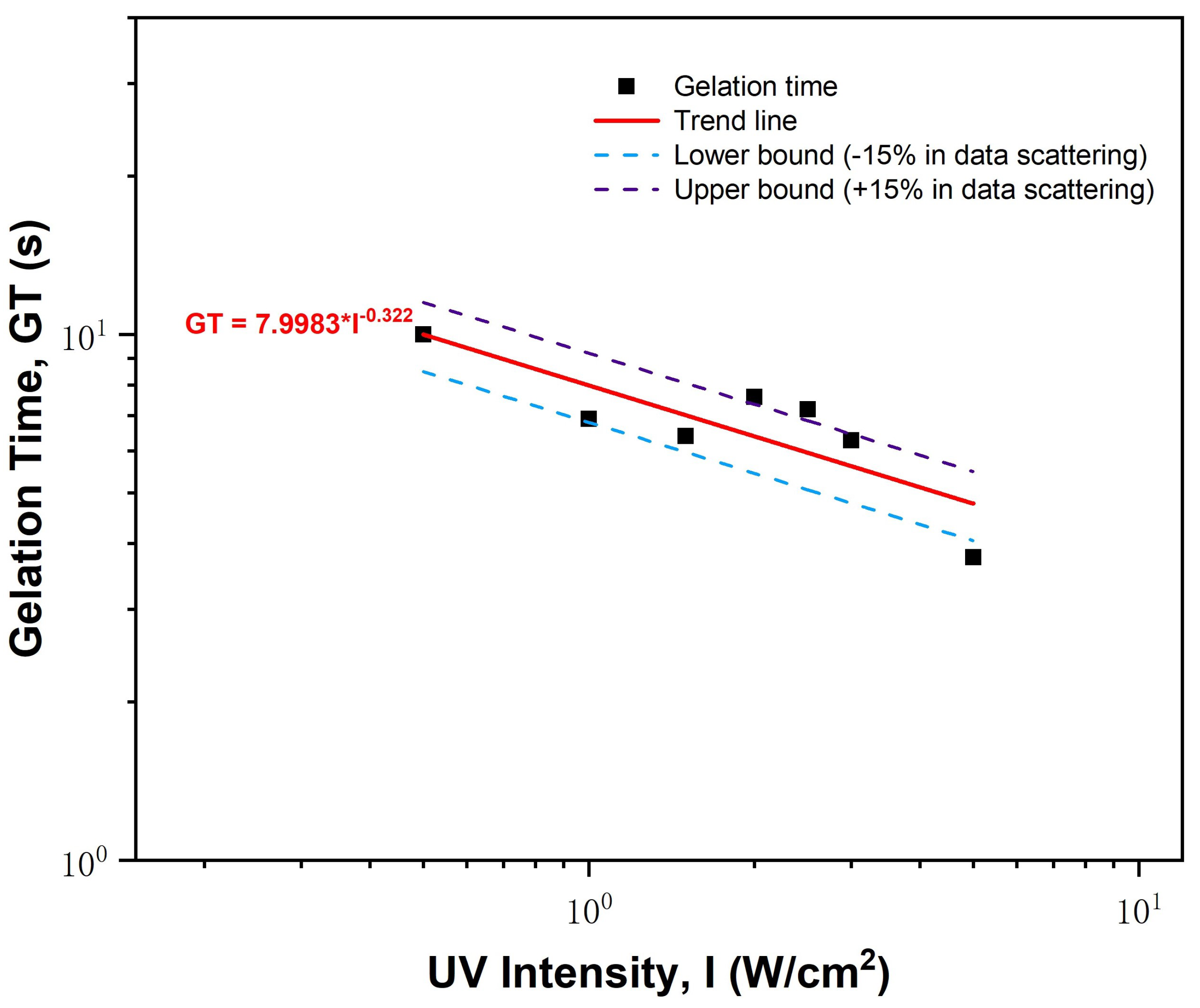
3.1. UV Rheological Characterization
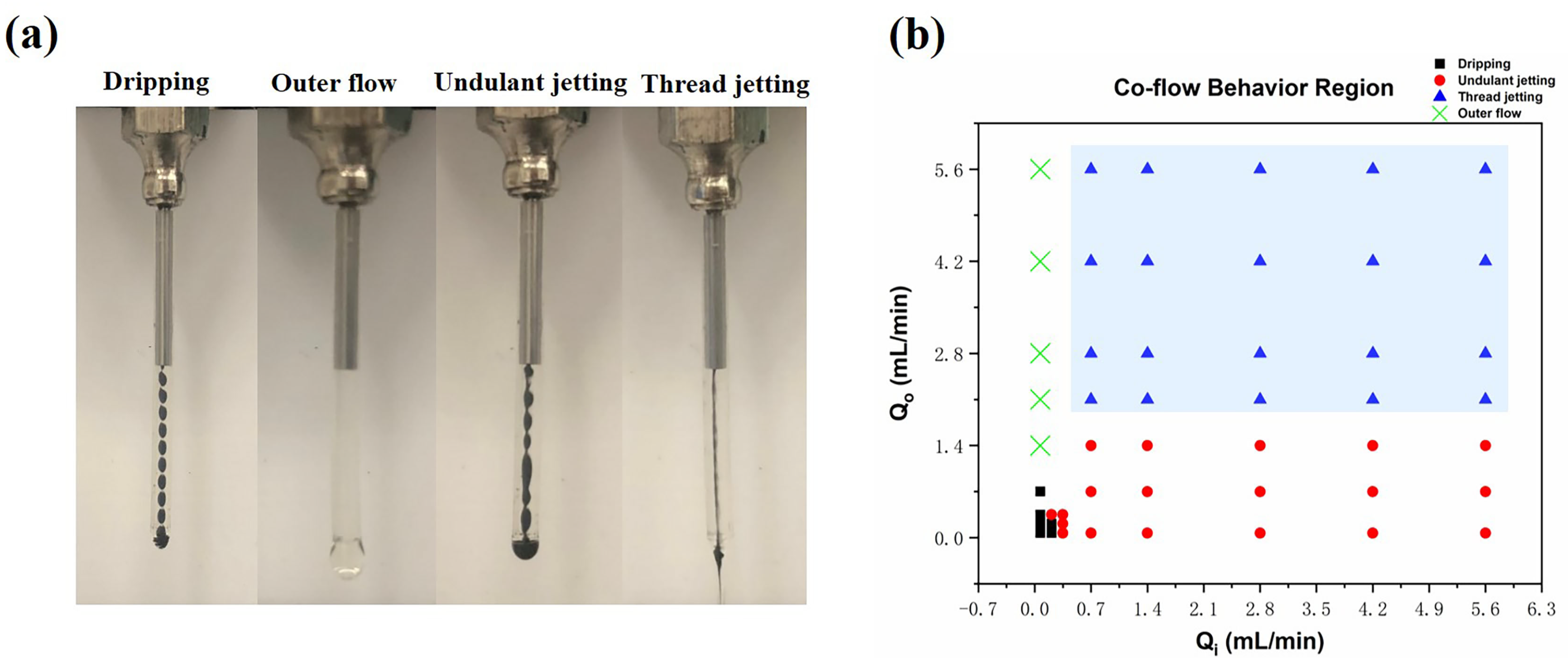
3.2. Co-Flow Criterion for Printing Process
3.3. Pre-Curing Criterion for Printing Process
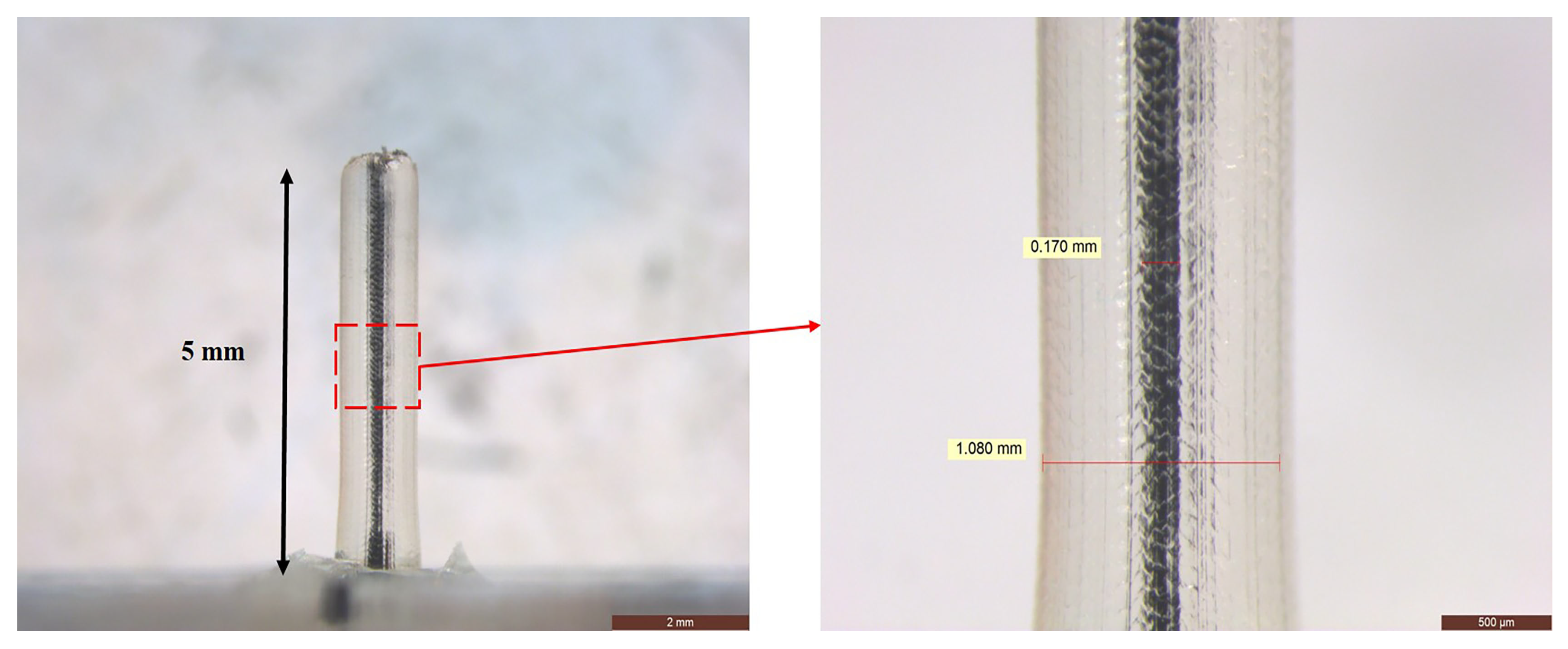
3.4. Demonstration of Printed Connectors for Microfluidic Interconnections
3.5. Discussion on Substrate Materials
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary File 1Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atencia, J.; Beebe, D.J. Controlled microfluidic interfaces. Nature 2005, 437, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitesides, G.M. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 2006, 442, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Convery, N.; Gadegaard, N. 30 years of microfluidics. Micro Nano Eng. 2019, 2, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.H.; Park, T. Connector-Free World-to-Chip Interconnection for Microfluidic Devices. Micromachines 2019, 10, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temiz, Y.; Lovchik, R.D.; Kaigala, G.V.; Delamarche, E. Lab-on-a-chip devices: How to close and plug the lab? Microelectron. Eng. 2015, 132, 156–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravesen, P.; Branebjerg, J.; Jensen, O.S. Microfluidics-a review. J. Micromech. Microeng. 1993, 3, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, B.; Collins, S.; Smith, R. Interlocking mechanical and fluidic interconnections for microfluidic circuit boards. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2004, 112, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, B.; Jaeggi, D.; Mourlas, N.; Van Drieenhuizen, B.; Williams, K.; Maluf, N.; Kovacs, G. Novel interconnection technologies for integrated microfluidic systems. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1999, 77, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkandjiev, K.; Riegger, L.; Kosse, D.; Welsche, M.; Gutzweiler, L.; Zengerle, R.; Koltay, P. Microfluidics in silicon/polymer technology as a cost-efficient alternative to silicon/glass. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2011, 21, 025008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, J.C.; Duffy, D.C.; Anderson, J.R.; Chiu, D.T.; Wu, H.; Schueller, O.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Fabrication of microfluidic systems in poly (dimethylsiloxane). ELECTROPHORESIS 2000, 21, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, A.M.; Chang-Yen, D.A.; Gale, B.K. Characterization of interconnects used in PDMS microfluidic systems. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2005, 15, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, H.J.; Yeh, S.L.; Peng, C.C.; Liao, W.H.; Tung, Y.C. Polydimethylsiloxane-polycarbonate microfluidic devices for cell migration studies under perpendicular chemical and oxygen gradients. JoVE 2017, 120, e55292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabourin, D.; Snakenborg, D.; Dufva, M. Interconnection blocks: A method for providing reusable, rapid, multiple, aligned and planar microfluidic interconnections. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19, 035021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, H.; Locascio, L.E. Polymer microfluidic devices. Talanta 2002, 56, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Zhou, J.; Wu, H. Materials for microfluidic chip fabrication. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2396–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkbeiner, T.; Soergel, H.L.; Koschitzky, M.P.; Ahrens, R.; Guber, A.E. Ultrasonic welding for the rapid integration of fluidic connectors into microfluidic chips. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2019, 29, 065011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.; Wang, Z.; De Rooij, N. Microfluidic connectors by ultrasonic welding. Microelectron. Eng. 2009, 86, 1354–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wägli, P.; Guélat, B.; Homsy, A.; De Rooij, N. Microfluidic devices made of UV-curable glue (NOA81) for fluorescence detection based applications. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference onMiniaturized Systems for Chemistry and Life Sciences, Groningen, The Netherlands, 3–7 October 2010; pp. 1937–1939. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, J.H.; Lin, L. Micro-to-macro fluidic interconnectors with an integrated polymer sealant. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2001, 11, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Pan, T. Fit-to-Flow (F2F) interconnects: Universal reversible adhesive-free microfluidic adaptors for lab-on-a-chip systems. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Pan, T. Universal adhesive-free fit-to-flow microfluidic connections. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE 24th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Cancun, Mexico, 23–27 January 2011; pp. 372–375. [Google Scholar]
- Bhagat, A.A.S.; Jothimuthu, P.; Pais, A.; Papautsky, I. Re-usable quick-release interconnect for characterization of microfluidic systems. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 17, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Maeda, R. Socket with built-in valves for the interconnection of microfluidic chips to macro constituents. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1013, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooksey, G.A.; Plant, A.L.; Atencia, J. A vacuum manifold for rapid world-to-chip connectivity of complex PDMS microdevices. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1298–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkachenko, E.; Gutierrez, E.; Ginsberg, M.H.; Groisman, A. An easy to assemble microfluidic perfusion device with a magnetic clamp. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atencia, J.; Cooksey, G.A.; Jahn, A.; Zook, J.M.; Vreeland, W.N.; Locascio, L.E. Magnetic connectors for microfluidic applications. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waheed, S.; Cabot, J.M.; Macdonald, N.P.; Lewis, T.; Guijt, R.M.; Paull, B.; Breadmore, M.C. 3D printed microfluidic devices: Enablers and barriers. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1993–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.; Paydar, O.H.; Candler, R.N. 3D printed molds for non-planar PDMS microfluidic channels. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 226, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonyár, A.; Sántha, H.; Ring, B.; Varga, M.; Kovács, J.G.; Harsányi, G. 3D Rapid Prototyping Technology (RPT) as a powerful tool in microfluidic development. Procedia Eng. 2010, 5, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckwith, A.L.; Borenstein, J.T.; Velásquez-García, L.F. Monolithic, 3D-printed microfluidic platform for recapitulation of dynamic tumor microenvironments. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2018, 27, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Velásquez-García, L.F. Monolithic FFF-printed, biocompatible, biodegradable, dielectric-conductive microsystems. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2017, 26, 1356–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Whitesides, G.M. Soft lithography. Ann. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1998, 28, 153–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Xia, Y.; Whitesides, G.M. Soft lithography for micro-and nanoscale patterning. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higham, A.K.; Bonino, C.A.; Raghavan, S.R.; Khan, S.A. Photo-activated ionic gelation of alginate hydrogel: Real-time rheological monitoring of the two-step crosslinking mechanism. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 4990–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonino, C.A.; Samorezov, J.E.; Jeon, O.; Alsberg, E.; Khan, S.A. Real-time in situ rheology of alginate hydrogel photocrosslinking. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 11510–11517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeimirad, M.; Zadhoush, A. Melt-spun liquid core fibers: A CFD analysis on biphasic flow in coaxial spinneret die. Fibers Polym. 2018, 19, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, C.; Fischer, P.; Windhab, E.J. Drop formation in a co-flowing ambient fluid. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2004, 59, 3045–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.C.; Davoodi, P.; Tong, Y.W.; Wang, C.H. Computational study of core-shell droplet formation in coaxial electrohydrodynamic atomization process. AIChE J. 2016, 62, 4259–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Solutions | Mechanical Property | Interconnect Density | Clogging Issue | Target Material | Fabrication Efficiency | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRIE interlock structures [7,8] | Poor | High | No | Silicon | Low | High |
| Tubings or needles through punched holes [11,12] | Fair | High | No | PDMS | High | Low |
| Ultrasonic welding [16,17] | Good | Moderate | Yes | Thermopalstic | High | Moderate |
| Adhesive gluing [18,19] | Good | High | Yes | All | High | Low |
| Fixing accessories [20,21,22,23,24,25,26] | Good | Moderate /Low | No | All | Moderate /Low | Moderate |
| Monolithic 3D printed connectors [30,31] | Fair | Moderate | No | Photosensitive resin /thermoplastic | High | Moderate |
| This work | Good | Moderate | No | All | High | Moderate |
| Material | Refractive Index at 365 nm | Absorption Coefficient at 365 nm () |
|---|---|---|
| Glass | 1.54 | 0.001 |
| Aluminum | 0.40 | |
| Silicone | 1.54 | 0.12 |
| UV Intensity (W/) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 5.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gelation Time (s) | 10.0 | 6.9 | 6.4 | 7.6 | 7.2 | 6.3 | 3.8 |
| Pre-Cure Time (s) | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5.5 | 6 | 6.5 | 7.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Success rate | 0% | 0% | 0% | 20% | 50% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Q.; Lo, J.C.C.; Lee, S.-W.R. Directly Printed Hollow Connectors for Microfluidic Interconnection with UV-Assisted Coaxial 3D Printing. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103384
Xu Q, Lo JCC, Lee S-WR. Directly Printed Hollow Connectors for Microfluidic Interconnection with UV-Assisted Coaxial 3D Printing. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(10):3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103384
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Qianwen, Jeffery Chi Chuen Lo, and Shi-Wei Ricky Lee. 2020. "Directly Printed Hollow Connectors for Microfluidic Interconnection with UV-Assisted Coaxial 3D Printing" Applied Sciences 10, no. 10: 3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103384
APA StyleXu, Q., Lo, J. C. C., & Lee, S.-W. R. (2020). Directly Printed Hollow Connectors for Microfluidic Interconnection with UV-Assisted Coaxial 3D Printing. Applied Sciences, 10(10), 3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103384





