The Rise of FinTech and the Journey Toward a Cashless Society: Investigating the Use of Mobile Payments by SMEs in Oman in the Context of Vision 2040
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Background
2.1. Economic Context
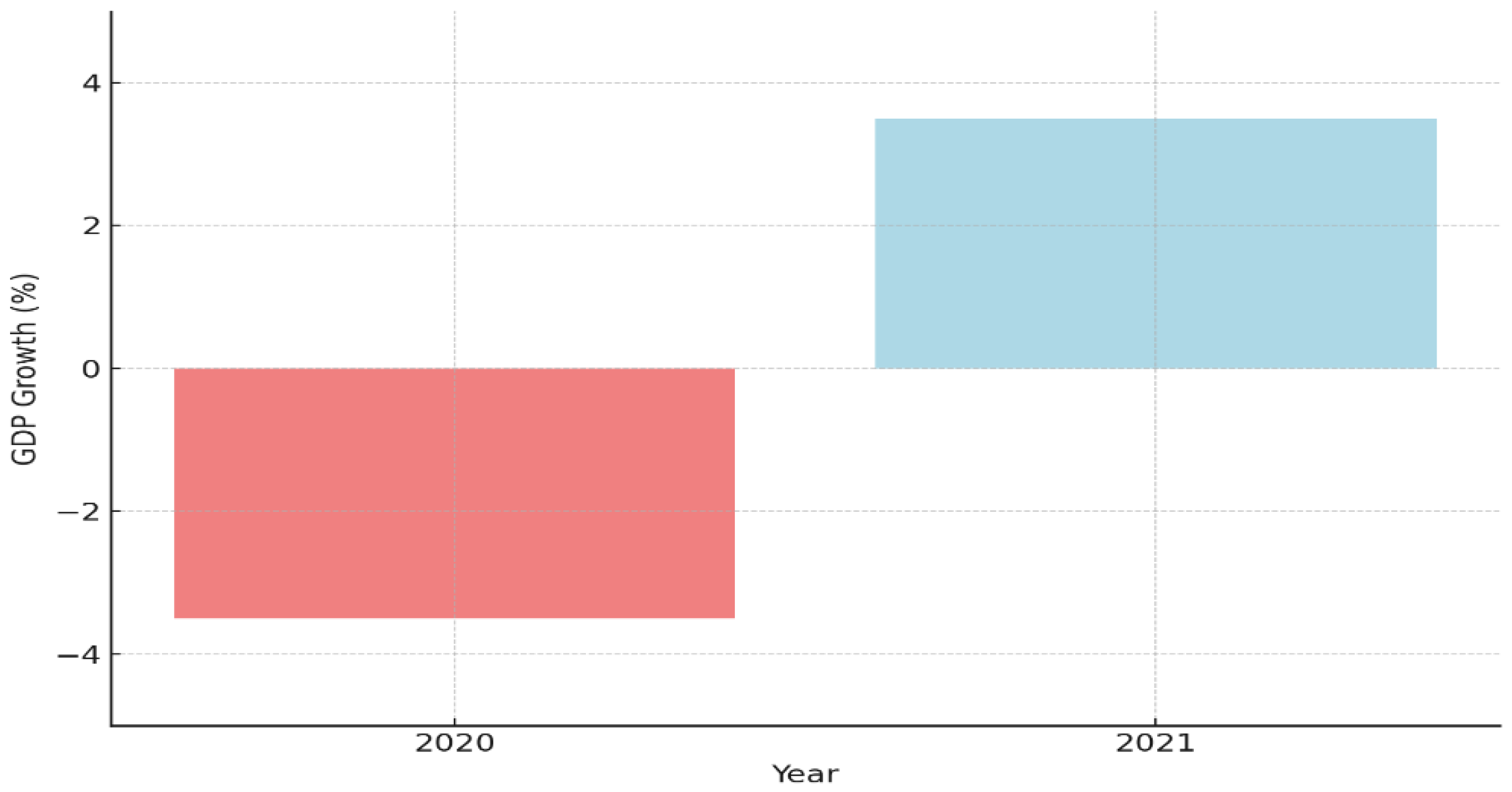
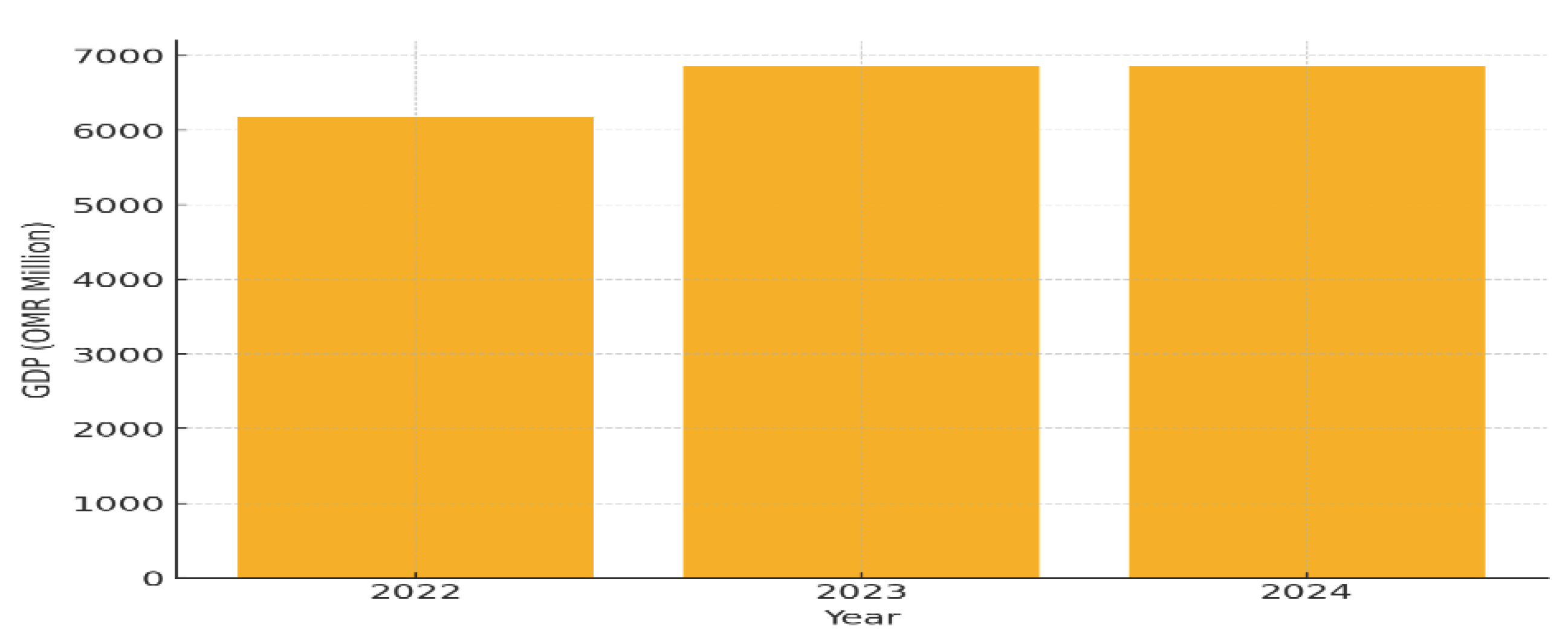
2.1.1. Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
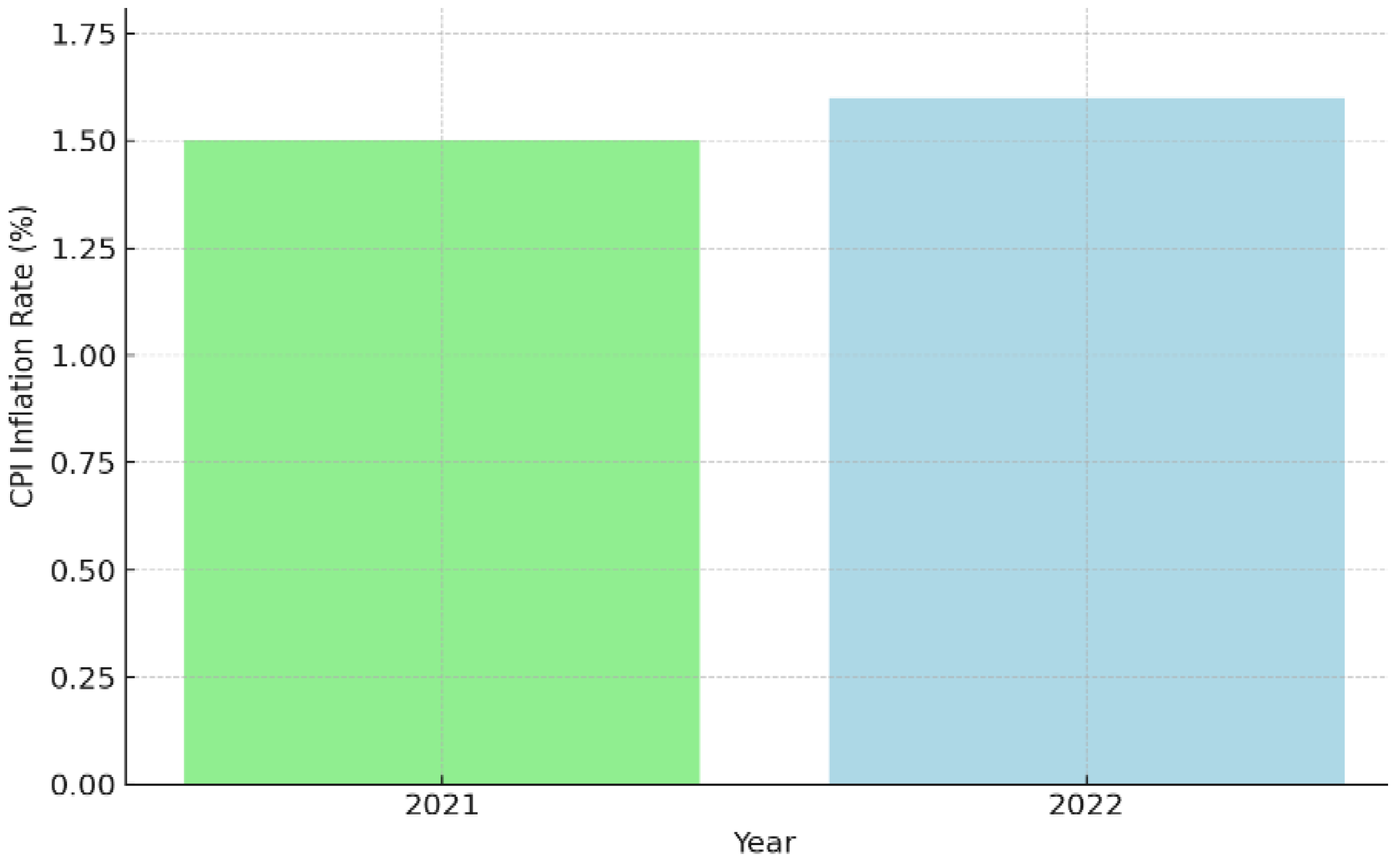
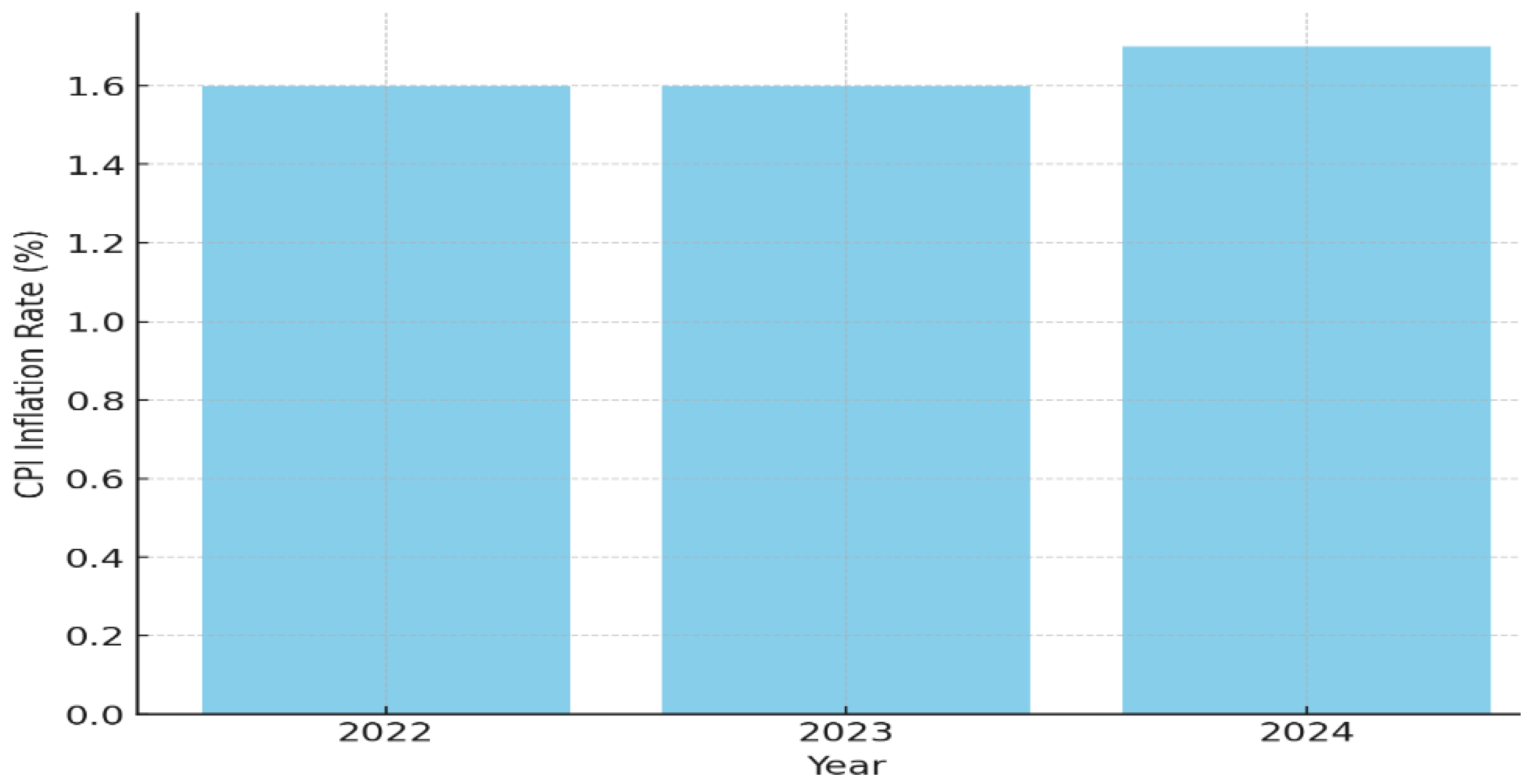
2.1.2. Consumer Price Index (CPI)
2.2. Government Finance Statistics
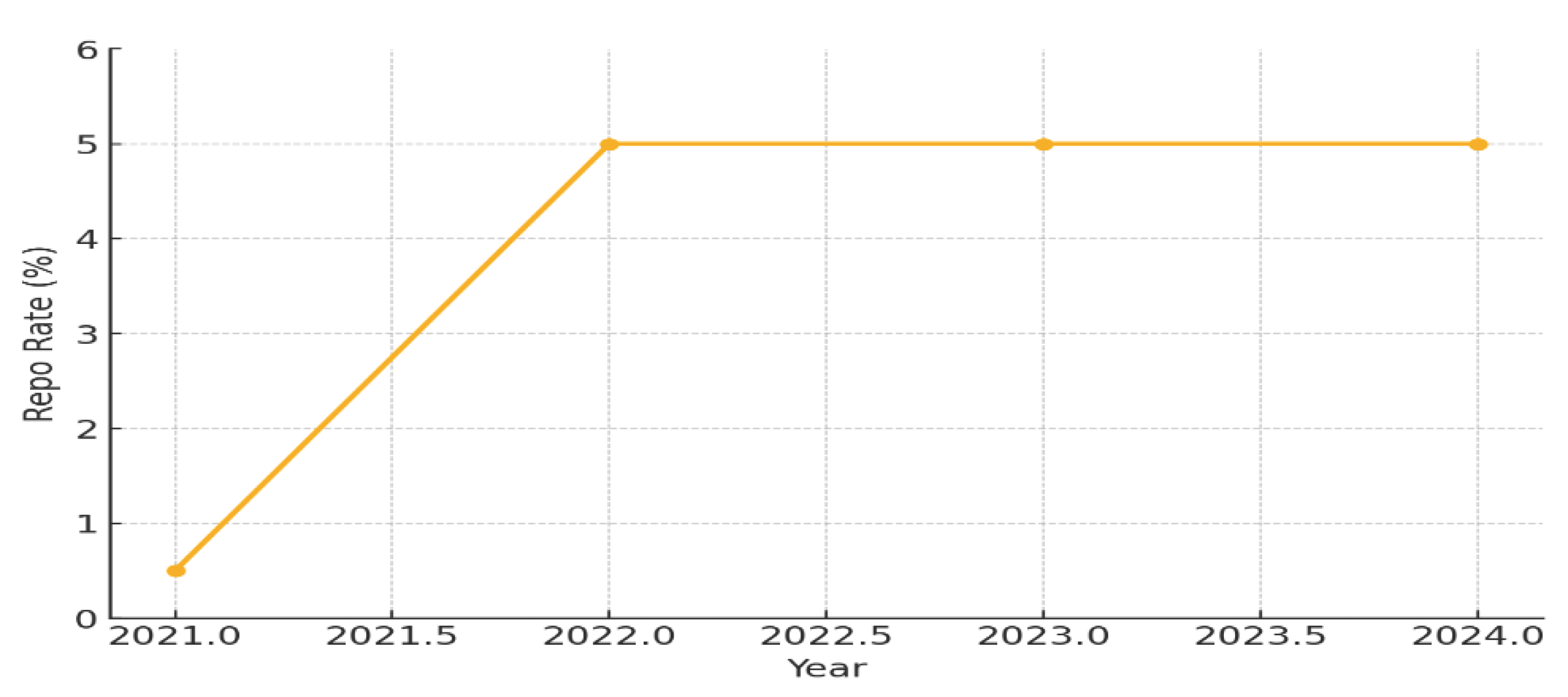
Interest Rates and Financial Access
3. Literature Review and Hypothesis Development
3.1. Global Growth of Mobile Payment Platforms
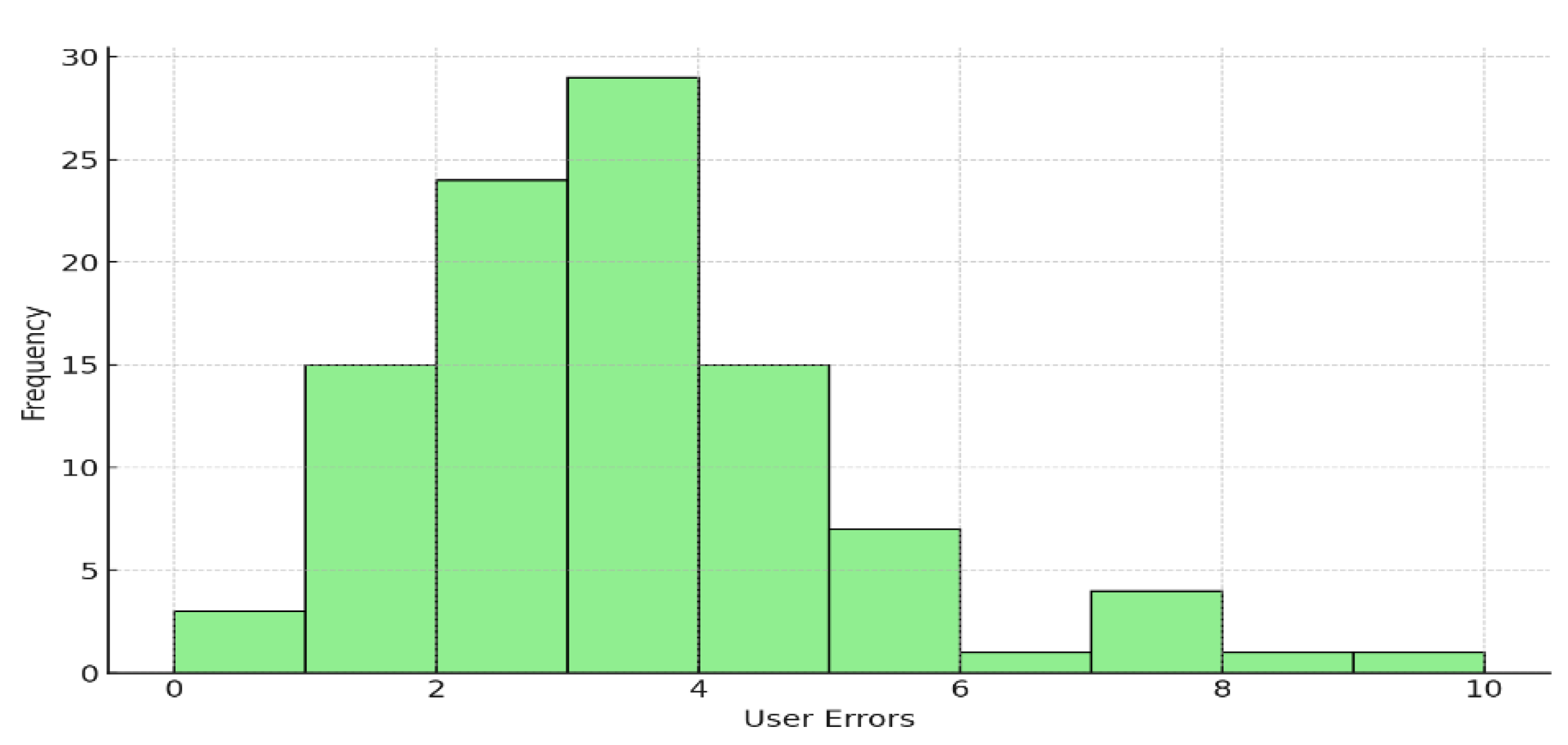
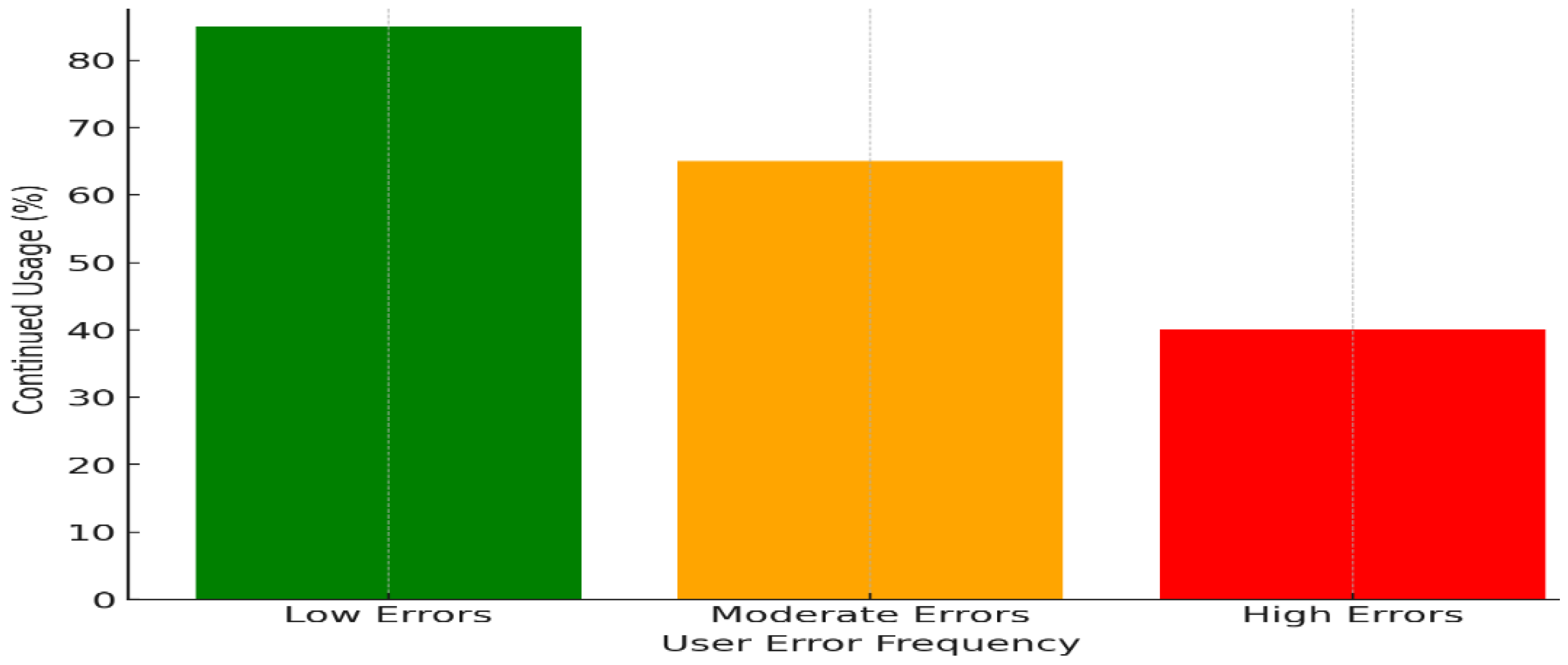
3.2. Insights on User Behavior and Errors
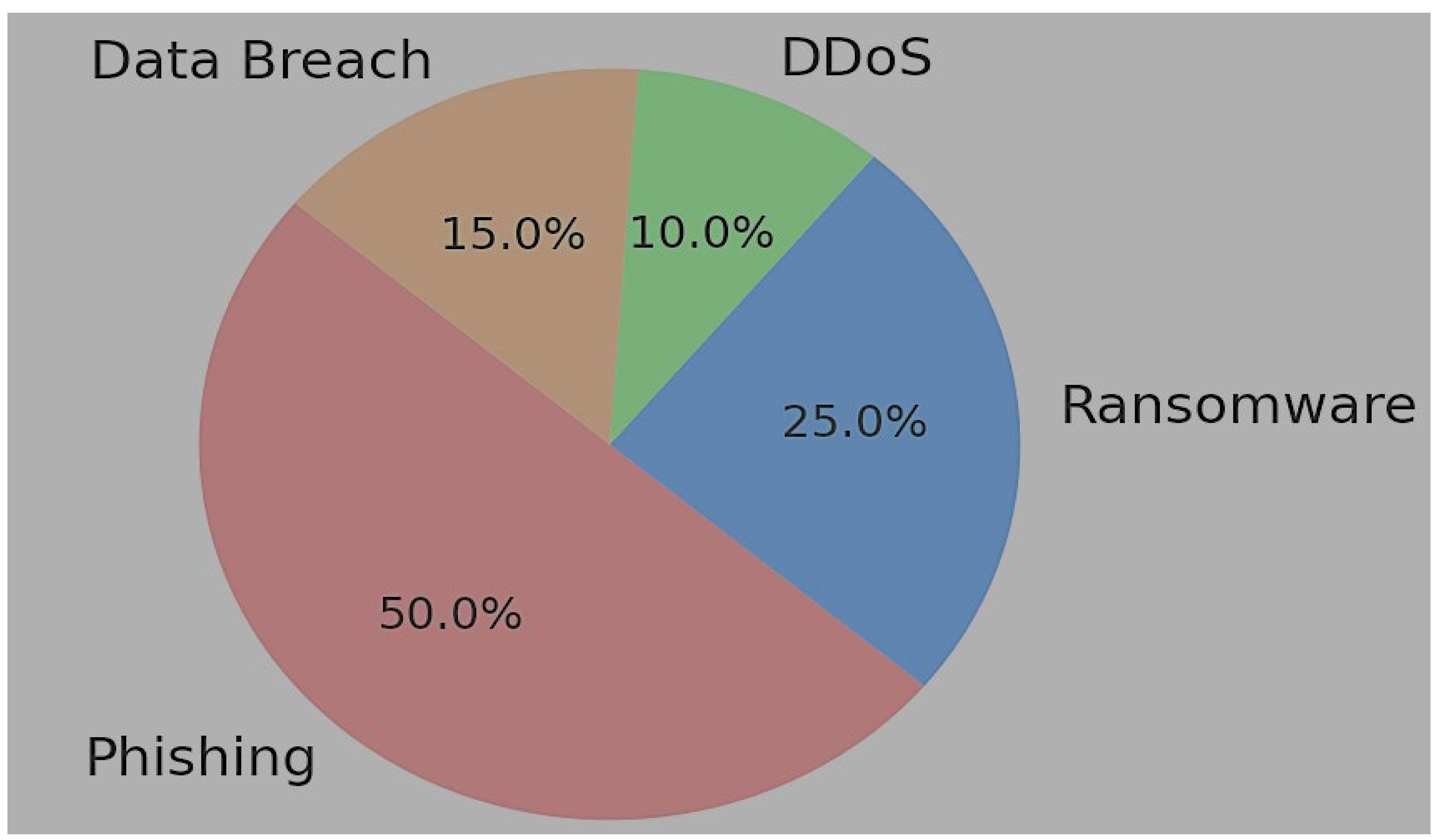
3.3. Security and Cybersecurity Challenges in Mobile Payment Adoption
3.4. Challenges Facing Small Businesses’ Adoption
3.5. Regional Context and Policy Relevance
3.6. Technology Acceptance and Transaction Cost Perspectives
3.7. Extension of TAM and TCT Frameworks
4. Methodology
4.1. Research Design
4.2. Data Collection
4.3. Key Variables Analyzed
4.4. Rigorous Analytical Framework
4.5. Statistical Methods
4.6. Data Analysis Methodology
5. Results
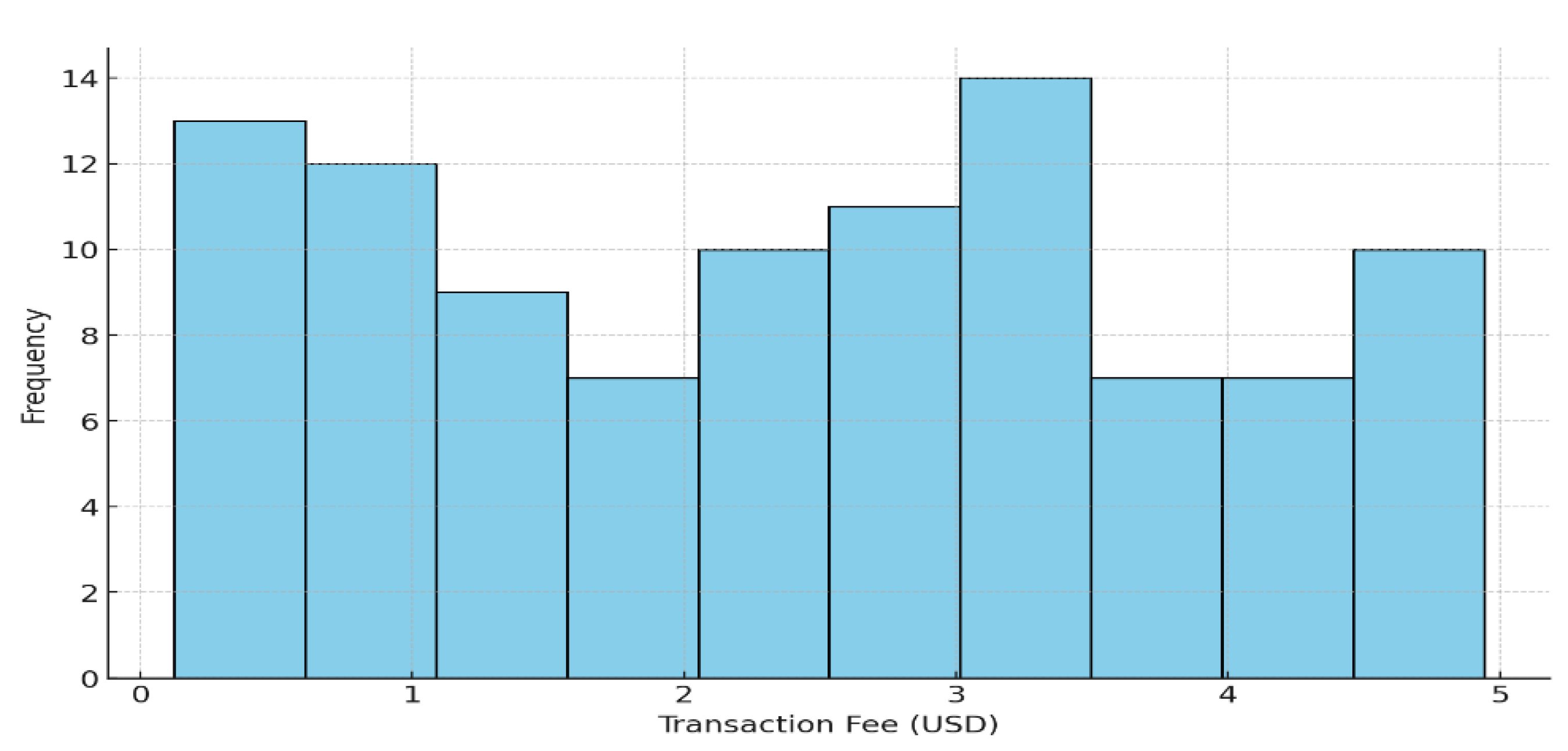
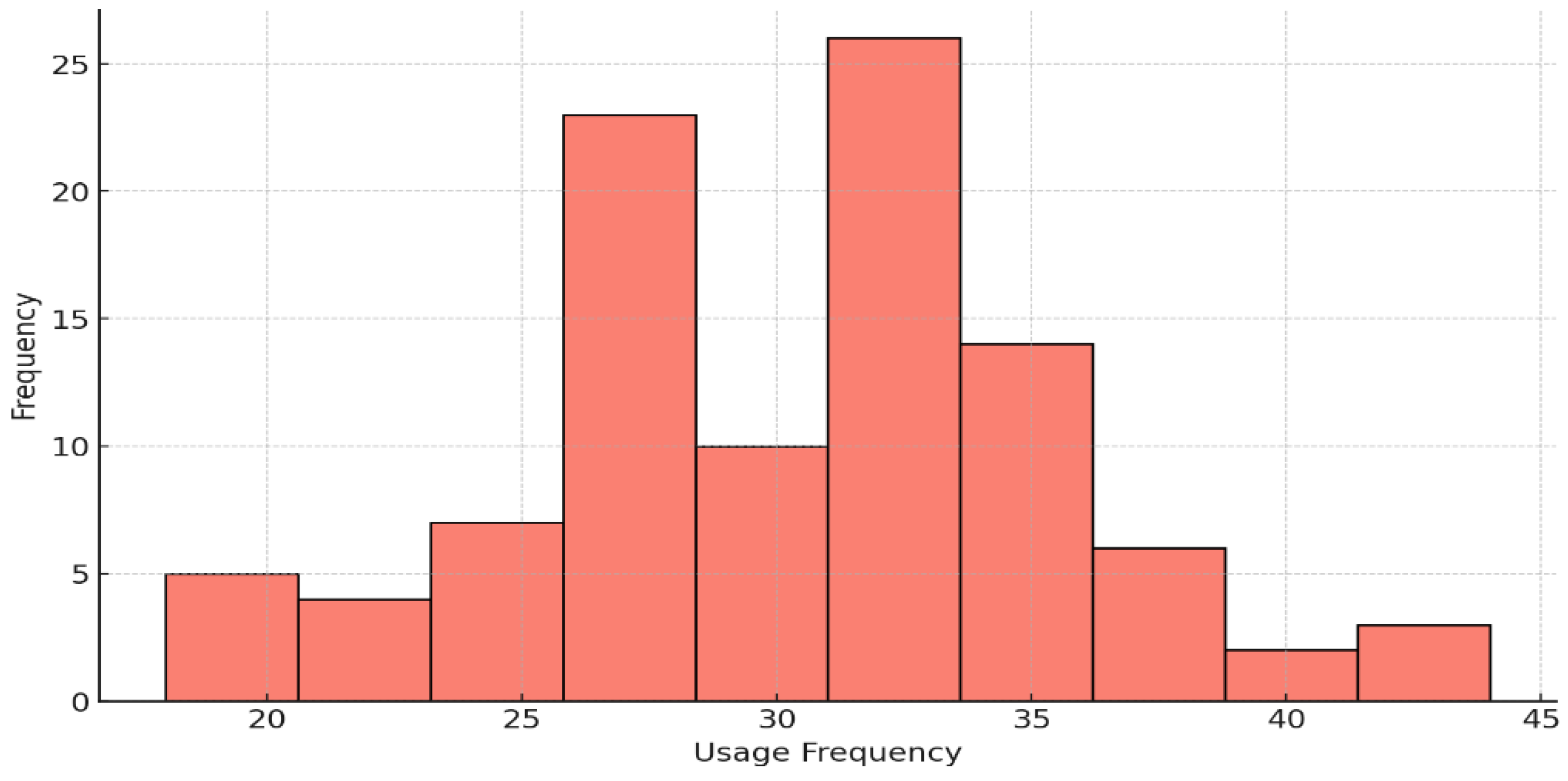
5.1. Descriptive Statistics
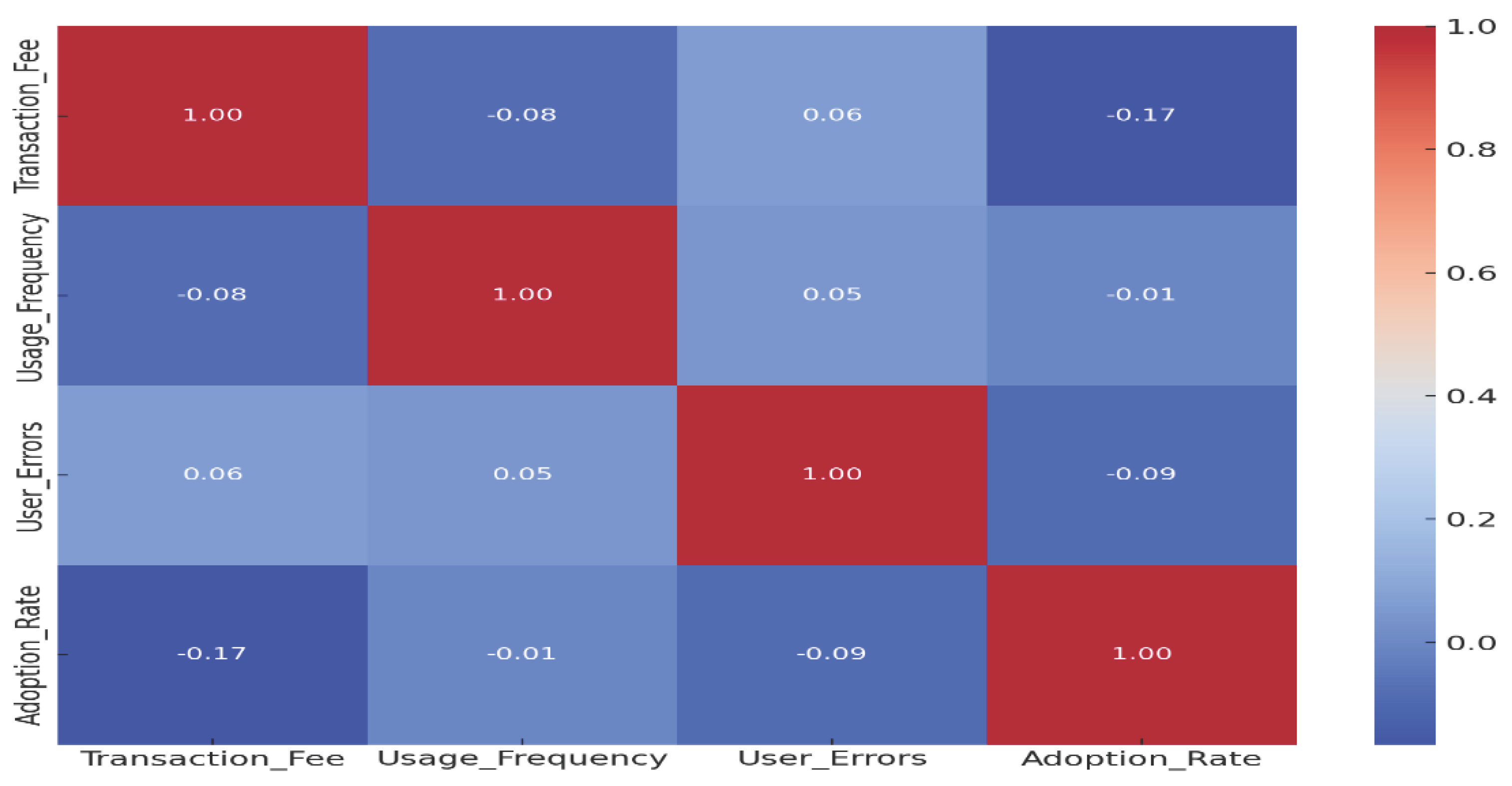
5.2. Inferential Statistics
5.3. Hypothesis Testing Results
5.3.1. Forecasting Mobile Payment Growth (2024–2026)
5.3.2. Key Drivers for Growth
5.3.3. Forecasting Approach
6. Discussion
6.1. Financial Obstacles
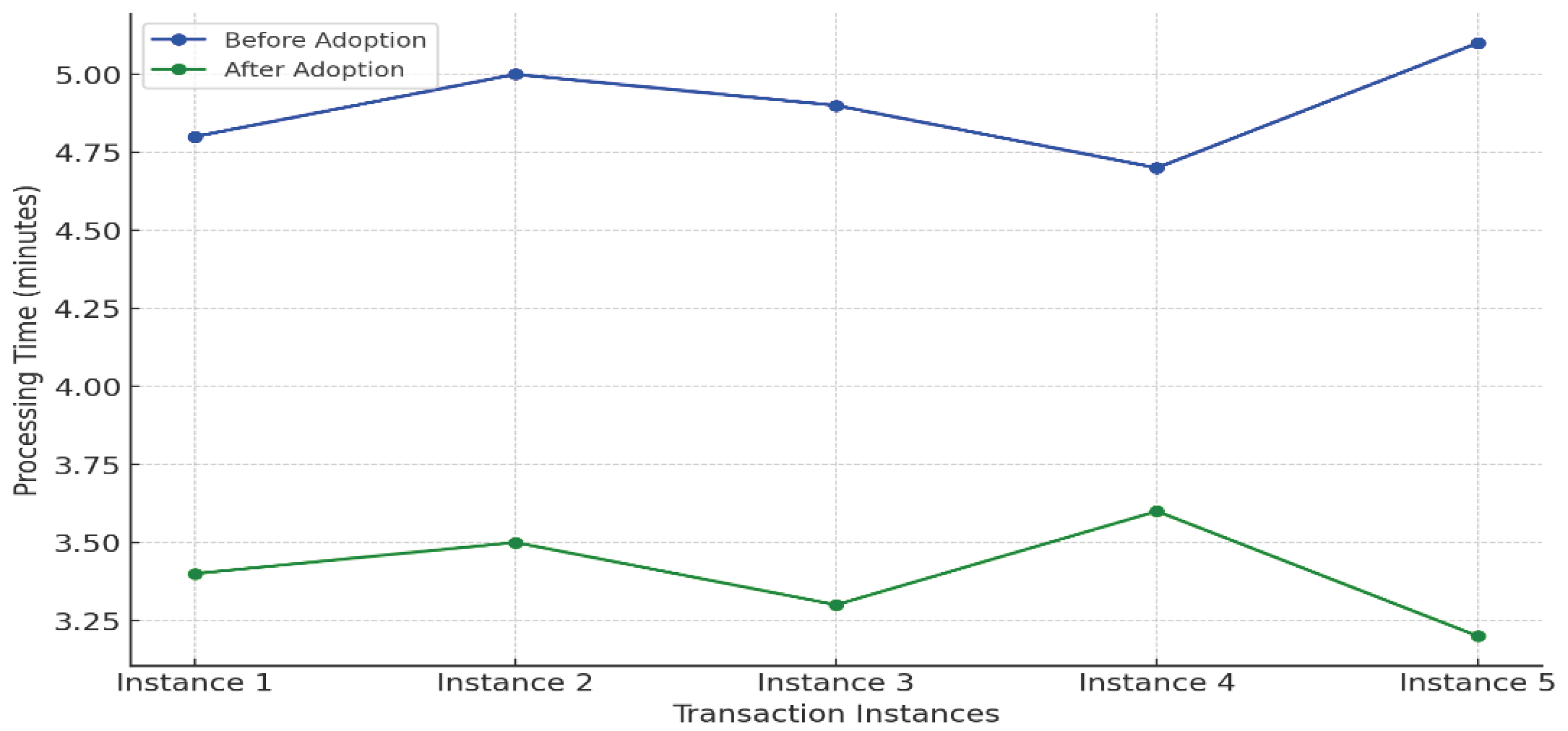
6.2. Operational Efficiency
6.3. Policy Recommendations
6.4. Practical Recommendations
7. Conclusions
The Limitations and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- 6Wresearch. (2023). Oman mobile wallet market (2024–2030)—Trends, outlook & forecast. 6Wresearch. Available online: https://www.6wresearch.com/industry-report/oman-mobile-wallet-market-outlook (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- Ahamed, F., & Shukla, V. K. (2023, March 9–10). The rise of the Omani digital payment sector: Trends, adoption, and future. 2023 International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Knowledge Economy (ICCIKE), Dubai, United Arab Emirates. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ghunaimi, H. (2023). SME hotel. Zenodo. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Lawati, M. (2022). Establishment of new financial service authority. DLA Piper. Available online: https://www.dlapiper.com/en-MA/insights/publications/2024/04/establishment-of-new-financial-service-authority (accessed on 9 October 2024).
- Al-Muharrami, S., & Al-Zaidi, A. (2019). Large projects in light of Oman’s diversification strategy: The case of the special economic zone in Duqm. Social and Economic Analyses, 11(2), 178–186. Available online: https://journals.uni-vt.bg/sia/eng/vol11/iss2/art8 (accessed on 8 October 2024). [CrossRef]
- Bureau of Economic Analysis. (n.d.). Gross domestic product (GDP). U.S. Department of Commerce. Available online: https://www.bea.gov/help/glossary/gross-domestic-product-gdp (accessed on 9 October 2024).
- Central Bank of Oman (CBO). (2023). Financial stability report. Central Bank of Oman. [Google Scholar]
- Central Bank of Oman (CBO). (2024). Regulatory framework for digital financial transactions. Central Bank of Oman. [Google Scholar]
- Church, J. D. (2016). Comparing the Consumer Price Index with the gross domestic product price index and gross domestic product implicit price deflator. Monthly Labor Review. Available online: https://www.bls.gov/opub/mlr/2016/article/comparing-the-cpi-with-the-gdp-price-index-and-gdp-implicit-price-deflator.htm (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Quarterly, 13(3), 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, S., & Chen, L. (2005). Mobile payments in developing countries: The role of infrastructure and regulations. Information Systems Research, 16(2), 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Efron, B., & Tibshirani, R. J. (1993). An introduction to the bootstrap. Chapman & Hall. [Google Scholar]
- Field, A. (2018). Discovering statistics using IBM SPSS statistics (5th ed.). Sage Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, G., & Miller, J. (2022). The challenges of digital payment integration for small businesses. Journal of Finance and Business Economics, 41(2), 201–215. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L., & Waechter, K. A. (2017). Examining the role of initial trust in user adoption of mobile payment services: An empirical investigation. Information Systems Frontiers, 19(3), 525–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GlobalData. (2023). Oman cards and payments—Opportunities and risks to 2026. GlobalData. Available online: https://www.globaldata.com/store/report/oman-cards-and-payments-market-analysis/ (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- Hagemann, R. P. (1982). The variability of inflation rates across household types. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking, 14(4), 494–510. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/1991657 (accessed on 8 October 2024). [CrossRef]
- Hox, J. J., Moerbeek, M., & Van de Schoot, R. (2017). Multilevel analysis: Techniques and applications (3rd ed.). Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- International Monetary Fund. (2020). Consumer price index manual: Concepts and methods. International Monetary Fund. Available online: https://www.elibrary.imf.org/view/book/9781484354841/9781484354841.xml (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- Khan, A. (2021). Mobile payments and digital financial inclusion: A systematic review. Journal of Financial Technology and Innovation, 7(1), 45–60. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C., Mirusmonov, M., & Lee, I. (2010). An empirical examination of factors influencing the intention to use mobile payment. Computers in Human Behavior, 26(3), 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, R. B. (2015). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling (4th ed.). Guilford Press. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J., Kang, H., & Zhang, J. (2020). Exploring user errors in biometric authentication and their impact on continued use. Journal of Information Technology Management, 11(2), 102–115. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J., Wang, Y., & Zhao, H. (2023). Mobile payment adoption and usage in emerging markets. International Journal of Financial Studies, 11(2), 120–135. [Google Scholar]
- Mallat, N. (2007). Exploring consumer adoption of mobile payments: A qualitative study. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 16(4), 413–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msomi, T. S., & Kandolo, K. M. (2023). Sustaining small and medium-sized enterprises through financial awareness and access to digital finance in South Africa. Investment Management and Financial Innovations, 20(1), 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscat Daily. (2024, July 16). GDP grows 1.7% to RO9.537bn in Q1 2024. Muscat Daily. Available online: https://www.muscatdaily.com/2024/07/16/gdp-grows-1-7-to-ro9-537bn-in-q1-2024/ (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- Muthuraman, P., Venkatesh, V., & Srivastava, S. (2022). Mobile payment systems in emerging markets: Challenges and opportunities. Journal of Global Information Technology Management, 25(1), 41–65. [Google Scholar]
- Mylonas, P., Schich, S., & Bloch, D. (2000). Monetary policy and economic stability. OECD Economic Outlook, 2000(2), 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Centre for Statistics and Information (NCSI). (2022). Consumer price index: Monthly inflation report. Available online: https://apps1.ncsi.gov.om/nsdp/ (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Oman Observer. (2023a). Apple Pay to boost cashless, cardless transactions. Available online: https://www.omanobserver.om/article/1159577/business/banking/apple-pay-to-boost-cashless-cardless-transactions (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Oman Observer. (2023b). ATMs battle mobile payments in Oman. Available online: https://www.omanobserver.om/article/1163372/oman/atms-battle-mobile-payments-in-oman (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Oman Observer. (2023c). Mobile payments need further encouragement. Available online: https://www.omanobserver.om/article/1134553/oman/mobile-payments-need-further-encouragement (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Patel, R., & Singh, M. (2021). Security challenges and user experience in mobile payment platforms. Journal of Information Technology and Business, 13(1), 45–59. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, E. M. (2003). Diffusion of innovations (5th ed.). Free Press. [Google Scholar]
- Rybina, A., & Shalyhina, N. (2022). The role of interest rates in economic stability. Journal of Financial Policy, 24(3), 115–133. [Google Scholar]
- Sallem, R., Ghunaimi, H., & Al Balushi, J. (2024). Toward a teaching model of the entrepreneurship course in Oman using the design thinking approach: The inspiring COVID-19 experience for better online teaching. In A. Mishrif (Ed.), Perspectives on human capital development. Palgrave Macmillan. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista. (2023). Digital payments worldwide report. Available online: https://www.statista.com/outlook/dmo/fintech/digital-payments/worldwide (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- TAS News Service. (2024, January 9). 11.7% increase in Oman’s postpaid mobile phone subscriptions. The Arabian Stories. Available online: https://www.thearabianstories.com/2024/01/09/11-7-increase-in-omans-postpaid-mobile-phone-subscriptions/ (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Times of Oman. (2024). Repo rate for local banks decreases by 25 basis points. Times of Oman. Available online: https://timesofoman.com/article/151875-repo-rate-for-local-banks-decreases-by-25-basis-points (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- Trend Micro. (2022). Annual cybersecurity report: Cyber threats and trends. Available online: https://www.trendmicro.com (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. (n.d.). Consumer price index: Frequently asked questions. Available online: https://www.bls.gov/cpi/questions-and-answers.htm (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- Wagner, A. K., Soumerai, S. B., Zhang, F., & Ross-Degnan, D. (2002). Segmented regression analysis of interrupted time series studies in medication use research. Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics, 27(4), 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, O. E. (1986). The economic institutions of capitalism: Firms, markets, relational contracting. Free Press. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, C. W. T., & Tsui, T. C. (2019). Automated payment over the counter—A study of Alipay, WeChat wallet and octopus currently used in Mainland China and Hong Kong. In The future of the commercial contract in scholarship and law reform fourth annual conference (Oct 2019). Institute of Advanced Legal Studies. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y., Ghose, A., & Xiao, B. (2023). Mobile payment adoption: An empirical investigation of alipay. Information Systems Research, 35(2), 807–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZAWYA. (2024, July 16). Oman GDP grows 1.7% at constant prices during Q1 2024. ZAWYA. Available online: https://www.zawya.com/en/economy/gcc/oman-gdp-grows-17-at-constant-prices-during-q1-2024-pmoau6vr (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- Zhao, Y., Wang, J., & Chen, Z. (2021). Reducing transaction processing time in mobile payments through biometric technology. International Journal of Digital Finance, 8(2), 89–102. [Google Scholar]




| Year | Number of Transactions (In Millions) | Transaction Value (In Billion OMR) |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 199.2 | 24.1 |
| 2022 | 274.4 | 27.3 |
| Year | Cyberattacks (In Millions) | Financial Loss (OMR) | Average Recovery Time (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 6.0 | 10M | 3 |
| 2020 | 8.5 | 15M | 5 |
| 2021 | 10.5 | 25M | 7 |
| 2022 | 12.0 | 35M | 9 |
| Variables | Definition |
|---|---|
| Adoption Rates | The percentage of consumers and businesses utilizing mobile payment platforms in Oman, reflecting the overall uptake of digital payments. |
| Transaction Volume | The total number of transactions processed through mobile payment systems, including Apple Pay and Google Pay, indicating platform usage frequency. |
| Transaction Value | The cumulative monetary value of transactions conducted via mobile platforms, offering insights into the financial scale of mobile payment adoption. |
| User Errors | Common issues impacting user experience and trust, such as authentication failures and security-related challenges that may hinder adoption rates. |
| Scenario | 2024 Projections | 2025 Projections | 2026 Projections |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best Case | 13.95 | 16.45 | 19.27 |
| Moderate Case | 13.68 | 15.60 | 17.78 |
| Worst Case | 13.44 | 15.05 | 16.85 |
| Year | Projected Transaction Volumes (Index, 2023 = 100) | Projected Transaction Values (Index, 2023 = 100) |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 175.0 | 160.0 |
| 2025 | 306.3 | 256.0 |
| 2026 | 535.9 | 409.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Ghunaimi, H.; Almaqtari, F.A.; Wesonga, R.; Elmashtawy, A. The Rise of FinTech and the Journey Toward a Cashless Society: Investigating the Use of Mobile Payments by SMEs in Oman in the Context of Vision 2040. Adm. Sci. 2025, 15, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci15050178
Al Ghunaimi H, Almaqtari FA, Wesonga R, Elmashtawy A. The Rise of FinTech and the Journey Toward a Cashless Society: Investigating the Use of Mobile Payments by SMEs in Oman in the Context of Vision 2040. Administrative Sciences. 2025; 15(5):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci15050178
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Ghunaimi, Hisham, Faozi A. Almaqtari, Ronald Wesonga, and Ahmed Elmashtawy. 2025. "The Rise of FinTech and the Journey Toward a Cashless Society: Investigating the Use of Mobile Payments by SMEs in Oman in the Context of Vision 2040" Administrative Sciences 15, no. 5: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci15050178
APA StyleAl Ghunaimi, H., Almaqtari, F. A., Wesonga, R., & Elmashtawy, A. (2025). The Rise of FinTech and the Journey Toward a Cashless Society: Investigating the Use of Mobile Payments by SMEs in Oman in the Context of Vision 2040. Administrative Sciences, 15(5), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci15050178






