Abstract
The purpose of this paper is to analyse the link between the adoption of sustainability practices and new product development (NPD) in manufacturing companies. From a triple bottom line (TBL) perspective and considering different theoretical approaches, this study hypothesises on the effect of both internal and external sustainability practices, distinguishing between collaborative and controlling initiatives, on the success of new products. Using a unique database of 281 companies across three industries taken from the fourth round of the High-Performance Manufacturing project, the findings shows that both monitoring and collaborative actions with suppliers demonstrate positive impacts on NPD success. Internal sustainability practices do not have a direct effect on NPD success but are determinant in supporting external sustainability practices.
1. Introduction
Sustainability has been considered as being significant in creation of competitive advantage and as a driver of innovation for manufacturing firms (Claudy et al. 2016; Nidumolu et al. 2009). Companies are becoming more aware of the importance of sustainability and are increasingly incorporating the features of sustainable businesses into their corporate and operation strategies (Paulraj et al. 2017). Driven from popular notion of triple bottom line perspective (people, planet and profit) of Elkington (1998), sustainability is considered as taking simultaneously responsible approaches towards society, environment, and economy (Adams et al. 2016).
Literature in the field have identified that innovation practices among the supply chain helps companies to achieve sustainability (Lintukangas et al. 2019). Firms with a higher level of sustainability orientation are more likely to implement sustainability-oriented innovation (Adams et al. 2016; Claudy et al. 2016). In this context, new product development (NPD) is a determinant for a company’s success and integrating their supplier-related sustainability practices into the early stages of NPD is key to improving both sustainability and operational performance of new products (Gmelin and Seuring 2014; Jabbour et al. 2015).
Nevertheless, prior evidence bridging between innovation and NPD with sustainability in operations management, has analysed the association of sustainably-oriented innovations and innovation outcomes, considering the role of mediating factors such as organisational leadership, culture, market knowledge competences, and customer focus regarding this association (Claudy et al. 2016; Jin et al. 2019; Obal et al. 2020). In this context, many other studies sought to develop a systematic approach to sustainable new products (Ahmad et al. 2018; Tuli and Shankar 2015), suggesting tools and mechanism to link sustainability with NPD, such as environmental or eco-design, eco-innovation, recyclability, and lean thinking (Nepal et al. 2011; Oliveira et al. 2018; Rossi et al. 2016). However, to our knowledge, very few empirical studies have attempted to explore any links between the adoption of sustainability practices from a broad perspective, considering both internal and external and the association between them, to explain NPD success. This confirms that sustainability orientation and NPD is still one of the least understood areas in sustainability management (Cheng 2020; Claudy et al. 2016), with very limited empirical evidences (Adams et al. 2016; Neutzling et al. 2018). Sustainability and NPD are in the core of success for manufacturing companies nowadays and therefore, advancing in the knowledge on how both things interact is on great importance (Hallstedt et al. 2013; Lintukangas et al. 2019).
This study aims to shed new light on the abovementioned issue by analysing how and to what extent a firm’s sustainability practices affect the success of its NPD. For this purpose, sustainability practices are grouped into internal sustainability practices and external sustainability practices. Internal practices are those sustainability practices that are applied to the firm’s internal operations, while external practices are those that are implemented beyond the boundaries of the firm, particularly with suppliers (Laari et al. 2016; Sancha et al. 2019). These practices typically require a certain level of cooperation with, and monitoring of, close supply chain actors (Danese et al. 2019). In addition, NPD success is classified to external and internal measures. Internal measure refers to the development process including time, quality, and other technical aspects of the product while the external success measure refers mostly to the non-technical dimensions including customer satisfaction and financial issues (García et al. 2008). As such, the expected effects of adopting these practices on NPD success are neither immediate nor intuitive.
The objective is to advance the understanding on the topic considering the existence of trade-offs between different strategies (e.g., monitoring vs. collaboration) and the difficulties that NPD managers face in balancing sustainability targets with the demands of supply chain actors and external pressures (Claudy et al. 2016). Hence, the theoretical part of the paper develops three sets of hypotheses that take advantage of statements of natural resource-based view (NRBV) theory, social capital theory, and transaction cost theory which help to understand the link between sustainability and NPD. The SmartPLS approach is used to test the hypothesised relationships. The data used comes from the fourth round of the High-Performance Manufacturing project and includes a total of 281 interviews across three industries in 16 countries.
This study contributes to the literature in several ways. First, it contributes to the debate on how manufacturing firms can improve the success of their new products. Our study advances these research streams by proposing how a buying firm could enhance NPD success through investing on sustainability issues in their operational process under NRBV theoretical perspective as well as extending the requirements to their supply chain through sustainability-related practices with suppliers under social capital and transactional cost theoretical frameworks. We seek to facilitate the exchange between these three perspectives by highlighting how they complement and support each other.
Second, unlike the previous studies on suppliers’ integration in NPD considering only the importance of green suppliers’ collaboration for NPD success (Kähkönen et al. 2017; Neutzling et al. 2018; Wang et al. 2021), this study contributes to the field by differentiating various sustainability practices and distinguishing between different measures of NPD success.
Third, developing two separated constructs for external sustainability practices of focal firms (i.e., supplier monitoring and supplier collaboration practices) provides some additional insights on the trade-offs between these two ways to manage sustainability with suppliers and their effects on NPD success. Therefore, this study throws light on the unique impact of different sustainability practices on different measures of NPD success. The results highlight the benefits of adopting both controlling and collaborative frameworks of sustainability for the success of new products. Furthermore, the results of this study provide useful insights for both managers seeking to adopt sustainable practices and policymakers seeking to further promote a sustainable supply chain.
Fourth, while many other studies are limited to the sample data from a specific industry or only one country, this study gathers the empirical evidence using a unique database that integrated 281 manufacturing firms from across 3 industries and 16 countries located in Asia, Europe, and America. Using such a multi-country, multi-industry sample contributes significantly to the empirical investigations related to the impact of sustainability on the success of NPD.
The rest of this paper is organised as follows: Section 2 presents a literature review. In Section 3, development of hypotheses is explained. The empirical methodology, the statistic treatment, and empirical results are presented in Section 4. Section 5 closes the paper with conclusions, implications, and future research opportunities.
2. Theoretical Framework
Previous research on sustainability as well as in NPD has demonstrated that a focal firm’s actions towards the environment and innovation are not only limited to its own performance but also to the actions of close supply chain members (Chen and Chen 2019). Firms, therefore, have no option other than integrating sustainability features into their operation and extending it to their key partners, but also should simultaneously take up some activities for behavioural/relational issues related to interaction with them. It requires to explain this phenomenon through different theoretical lenses while considering their potential trade-offs. In this context, the natural resource-based view (NRBV) theory provides a framework that emphasises the importance of environmental factors in terms of a firm’s green competences (Hart 1995). A sustainability strategy includes the adoption of intra–inter organisational environmental practices that may permit the building of causally ambiguous resources through continuous learning and repeated practices, for example, from pollution prevention strategies as well as the creation of complex resources through environmental collaboration in product stewardship or sustainable development projects (Shi et al. 2012).
By incorporating environmental requirements in NPD, a focal firm is able to improve environmental performance of new products in terms of energy efficiency and environmental footprint (Gerstlberger et al. 2014; Wang et al. 2021), resulting in enhanced performance of new products in terms of time to market, quality, and cost of R&D (Wang et al. 2021). Collaborative teams integrated by sustainability-oriented firms are more likely to find environmentally-friendly innovations in new products and processes, achieving more efficiently the use of resources and producing less waste and environmental burdens, which ultimately drive enhanced performance and NPD success (Claudy et al. 2016).
Close to this view, social relationships within supply chains can be formulated through different forms of inter-organisational activities (Putnam 1995), which are particularly relevant for NPD and for sustainability (Woo et al. 2016). For instance, through supplier involvement in NPD, the level of information processing and information transfer from one party to another is improved (Wlazlak et al. 2018), facilitating the voluntary sharing of innovative ideas, access to technology, knowledge, R&D services, and resources required for NPD (Du et al. 2016; Mazzola et al. 2015). Further, the firm´s social capital obtained from buyer-supplier interaction enhances the innovation search span of the firm causing reduction in the search cost (Du et al. 2016). To convert such relational social capital to the rent for superior performance of NPD, a specific capability is needed (Zhang and Wu 2013). NRBV provides such capability in the sustainability-oriented buyer-supplier relationship to integrate such joint efforts in the form of NPD practices with sustainability environmental objectives. Therefore, the communication, information sharing, knowledge exchange, and the trust under the long-term buyer-supplier collaborative relationship promotes the joint innovative efforts and facilitates joint solution development to sustainability issues during NPD (Lee 2015).
However, based on the transaction cost theory, different governing mechanisms, including supplier assessment and collaboration, have been proposed to focal firms in order to manage the relationship with their suppliers which can affect both sustainability and NPD (Gimenez and Sierra 2013). Only sustainability-committed suppliers can design and develop new sustainable products and invest in new sustainability processes (Chen and Chen 2019; Jansson et al. 2017). Further, the selection of a supplier with a high level of sustainability orientation, either as a source of sustainability-related knowledge or as a source of technological and R&D services, strengthens the NPD outcome (Cheng 2020). Accordingly, monitoring-oriented strategies are usually conducted by focal firms to select, control, evaluate, and verify suppliers with respect to their compliance with sustainability requirements (Gualandris et al. 2015).
3. Hypothesis Development
3.1. External Sustainability Practices (Collaboration) and NPD Success
Suppliers can positively influence both environmental and operational performance of supply chains (e.g., Croom et al. 2018; Geng et al. 2017). It has been stated that firms integrate sustainability concepts into their supply chains to achieve sustainability development through different strategies (Neutzling et al. 2018). Collaborative practices in sustainability that include the involvement of suppliers in joint projects on product co-development is suggested to improve sustainability performance (Danese et al. 2019), innovation performance (Kähkönen et al. 2017), as well as the environmental performance of R&D projects (De Stefano and Montes-Sancho 2018) of manufacturing companies.
Under collaborative relationships, the focal firm provides suppliers with the required communication, training, and technological knowledge to improve supplier capabilities and the performance of new products in accordance with sustainability requirements (Busse et al. 2016; Lawson et al. 2015). In addition to enhancement of knowledge, these interactions lead to increased satisfaction among the partners’ employees and encourages them to participate proactively in NPD (Gmelin and Seuring 2018a). Building relational collaboration also decreases conflict, information asymmetry, and likely opportunistic behaviour among supply chain actors, and also permits firms to practice sustainability strategies across their organisations (Neutzling et al. 2018). Finally, through boosting information processing capacity, a collaborative framework on NPD can diminish “strategic uncertainties” in the buyer and supplier relationship (Wong et al. 2020).
Moreover, focal firms with higher sustainability orientation are better able to boost organisational learning by involving their supply chain members, particularly the NPD team of their suppliers to think innovatively about how to integrate those sustainability requirements into the NPD processes (Cheng 2020; Claudy et al. 2016). This type of sustainability-oriented buyer-supplier relational collaboration fulfils joint learning processes, skills and resource sharing, and innovation capability developments necessary for the implementation of sustainability strategies that may benefit the development of new products (Chiarini 2012; Neutzling et al. 2018). Consequently, while interfirm problem solving is facilitated, firms involved in such interorganisational relationships reap the benefits of interfirm knowledge exchanges through a learning process and idea generation for environmentally-friendly design solutions that boost new product innovations (Lawson et al. 2015). This enhances a firm’s environmental competences and knowledge, and contributes to the building of reputation and brand image (Ageron et al. 2012) and cost reduction (Neutzling et al. 2018; Wong et al. 2020; Woo et al. 2016).
Additionally, prior research confirms the positive link between sustainability-related buyer-suppliers’ collaboration in NPD with innovation (NPD) performance (Cheng 2020; Kähkönen et al. 2017). Wang et al. (2021) based on a dataset of 212 American manufacturers found that sustainability-oriented collaborative practices with suppliers enhance NPD performance, not only through significant reduction in environmental burdens of the new product, but also by fostering economic sustainability of NPD in terms of lower cost of R&D, higher flexibility of R&D, and reduced energy-resources consumption. Further, by providing additional resources and capabilities under such collaborative approaches contributes to environmental and social solutions during NPD without transferring the extra costs of high-priced external experts and extra investment of resources to buyers (Cousins and Lawson 2007; Gmelin and Seuring 2018b). In the background, enhanced knowledge of sustainability in NPD may facilitate joint decision-making on NPD-related issues, improving outcomes of new products (Petersen et al. 2003), and enhancing a firm’s corporate reputation and image with regard to society and the environment (Neutzling et al. 2018).
In accordance with these arguments, the following hypothesis is proposed:
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
The adoption of external collaborative practices in sustainability has a positive effect on both internal and external NPD success.
3.2. External Sustainability Practices (Monitoring) and NPD Success
External sustainability practices can also be developed through monitoring. End customers increasingly demand sustainability-oriented products (Gmelin and Seuring 2014) which lead manufacturing companies that are looking for environmental benefits to impose sustainability requirements on their suppliers, for example, by minimising the consumption rate of resources or by providing health, safety, and work welfare to society (Marshall et al. 2015; Pagell and Wu 2009). A monitoring approach in a sustainability-oriented buyer-supplier relationship seeking to ensure compliance performance of suppliers through different practices includes supplier selection practices, company visits for an audit, the assessment of suppliers through their conduct, a request to suppliers to sign a code of environmental conduct, an audit through certification of suppliers’ environmental management systems, or a request to suppliers to pay a minimum ‘living’ wage (Danese et al. 2019).
Involving suppliers in the NPD process while requesting them to follow sustainability principals has some risks for buyer companies, particularly due to the risk of supplier incompetence in project execution (Goldberg and Schiele 2018). Further, suppliers might follow unethical behaviour in performing sustainability practices if the uncertainty relevant to the adoption of those sustainability initiatives is high or the adoption of those activities require considerable investment in their specific assets (Wang and Dai 2018). In addition, there is a potentiality of opportunistic behaviour and sustainability-related information asymmetric in the relationship (Carey et al. 2011; Lee 2015). As a result, to reduce the risk of incompliance to sustainability requirements or the risk of transactional- related cost, companies undertake monitoring practices resulting in higher costs, more time, and greater efforts (Gimenez and Tachizawa 2012; Gualandris et al. 2015)
However, sustainability requirements in NPD dictated that by buying firms implies suppliers to strictly follow eco-efficiency production so as to be more responsible towards their environment, society, and economics (Gimenez and Tachizawa 2012). Prior research has identified a strong correlation between environmental compliance and green performance of NPD, since proactive sustainability-oriented buying firms prefer to selectively work for NPD with only key suppliers with a higher level of sustainability orientation (Lee and Kim 2011). Through conducting suppliers’ monitoring practices, the adverse environmental attributes of NPD can be eliminated (Pujari 2006). Further, the implementation of environmental management system by suppliers has a positive impact on the association of supplier involvement in sustainable design practices and performance through more possibilities of offering environmental ideas and enhancement of environmental benefits (Wang et al. 2021). Among other things, monitoring practices look to ensure that teams working in NPD are sufficiently knowledgeable and aware of the sustainability requirements, have sufficient knowledge about environmentally-friendly techniques in manufacturing (Fish 2015), and avoid potential opportunistic behaviour and information asymmetry (Chen and Chen 2019; Gualandris et al. 2015). Thus, we can hypothesise that:
Hypothesis 1 (H2a).
The adoption of external monitoring practices in sustainability has a positive effect on internal NPD success.
On the other hand, adopting monitoring practices for sustainability may have positive effects on sustainability performance of new products through enhanced corporate social responsibility and reputation (Gimenez and Sierra 2013) since buying firms only interact with sustainability-committed suppliers (Wang and Dai 2018). Monitoring enables companies to control for abusive working conditions and child labour, ensuring employee wellbeing and satisfaction (Gualandris et al. 2015). Moreover, there is evidence that relating sustainability issues to NPD can enhance the environmental performance of new products by applying product life cycle technologies and improving market performance through better alignment with customer expectations (Jabbour et al. 2015). Further, suppliers’ adoption and implementation of environmental sustainability programs (e.g., acquiring ISO 14000 certificates) can improve the environmental and economic performance of NPD (Wang et al. 2021). In summary, ensuring that the supply network works in accordance with both social and sustainability responsibilities may improve the image, reputation, and market performance of new products.
Hypothesis 1 (H2b).
The adoption of external monitoring practices in sustainability has a positive effect on external NPD success.
3.3. Internal Sustainability Practices and NPD Success
Firms increasingly encounter pressures for sustainability from various internal and external stakeholders (Paulraj et al. 2017). Research has affirmed that the values behind sustainability issues drive a firm’s sustainability culture and orientation to move beyond mere economic concerns to align its corporate philosophy, strategies and culture with TBL perspectives, and extend it to their supply chain (Pagell and Wu 2009). Firms with a higher sustainability orientation are more likely to adopt sustainability practices and compliance strategies, including environmental management systems such as ISO 14001 that impose pressure on their supply chains to also adopt an environmental management system (Cheng 2020; Claudy et al. 2016; Marshall et al. 2015). Furthermore, firms with high levels of sustainability orientation are probably better workplaces for sustainability-minded employees (Du et al. 2016) whose moral motives and commitment to sustainability brings to bear internal pressure on firms to adopt sustainability principles and practices along the supply chain (Chen and Chen 2019).
In line with NRBV, focal firms that tackle environmental problems by implementing various reactive and proactive environmental strategies within their operations create value by addressing stakeholder expectations and by conforming to environmental regulations (Buysse and Verbeke 2003). Greater involvement in proactive environmental strategies (i.e., a greater sustainability culture) is more likely to lead to the probable adoption of green supply chain practices, especially supplier monitoring and assessment by focal firms (Marshall et al. 2015; Wu et al. 2012). Additionally, supply chain management is considered as a cross-organisational activity. In the context of social capital theory, the establishment of social relationships between focal firms and suppliers based on trust, values, and communication can result in the development of the same goals and visions among the partners, particularly regarding sustainability (Wu et al. 2012). Accordingly, focal firms with high levels of sustainability orientation due to the practise of various environmentally- and socially-oriented strategies are more likely to work with only sustainability-oriented suppliers (Wang and Dai 2018), therefore, they may regularly apply monitoring practices to ensure their suppliers´ compliance to sustainability and standards (Laari et al. 2016). Furthermore, those sustainability-oriented focal firms are more probably sharing their knowledge and collaborating with their suppliers on sustainability issues (Claudy et al. 2016; Wu et al. 2012). Thus, we propose the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 1 (H3a).
The adoption of internal sustainability practices is positively associated with the adoption of external sustainability practices.
Internal sustainability practices embrace various environmental- and social-related activities adopted and implemented by a focal firm in its in-house processes such as applying internal environmental management system, developing environmental policies, and adopting internal social, responsible management practices (Laari et al. 2016; Wang and Dai 2018). In the context of manufacturing, a focal firm´s internal sustainability practices link the environmental- and social-related activities with manufacturing practices in order to enhance the benefits and returns, for instance, value, quality of product, efficiency in the use of resources, working conditions, health system, and safety, as well as to reduce the environmental burdens such as air and soil pollution, cost, waste, and resources consumption (Moldavska and Welo 2017). Accordingly, a sustainability-oriented focal firm during NPD may incorporate TBL considerations in NPD looking for identifying and taking advantage of the opportunities for innovation (Du et al. 2016).
In the NRBV context, addressing sustainability issues during NPD processes, such as through pollution prevention, eco-design practices, or product life cycle analysis method, enables firms to tackle environmental issues and increase their eco-efficiency, for example, through design focused on reduction of waste generation or design for reusability and recyclability (González-Benito and González-Benito 2006; Shi et al. 2012). Moreover, adopting internal sustainability practices by sustainability-oriented firms helps to improve their operational efficiency in terms of quality and cost, and effectively use their resources because of the NPD team being more encouraged to find innovative solutions to environmental and social issues (Claudy et al. 2016). The conventional competence established by these sustainability-oriented innovation activities boosts the sustainable competitive advantage through cost-saving and better sustainability performance (Brulhart et al. 2017; Buysse and Verbeke 2003). Jabbour et al. (2015), in their empirical study, confirmed the direct influence of green product development not only on market performance as indicated by company reputation and image and the meeting of customer expectations, but also on operational performance in terms of flexibility, process improvements, quality conformity, and short lead times. In sum, we posit the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 1 (H3b).
The adoption of internal sustainability practices is positively associated with NPD success.
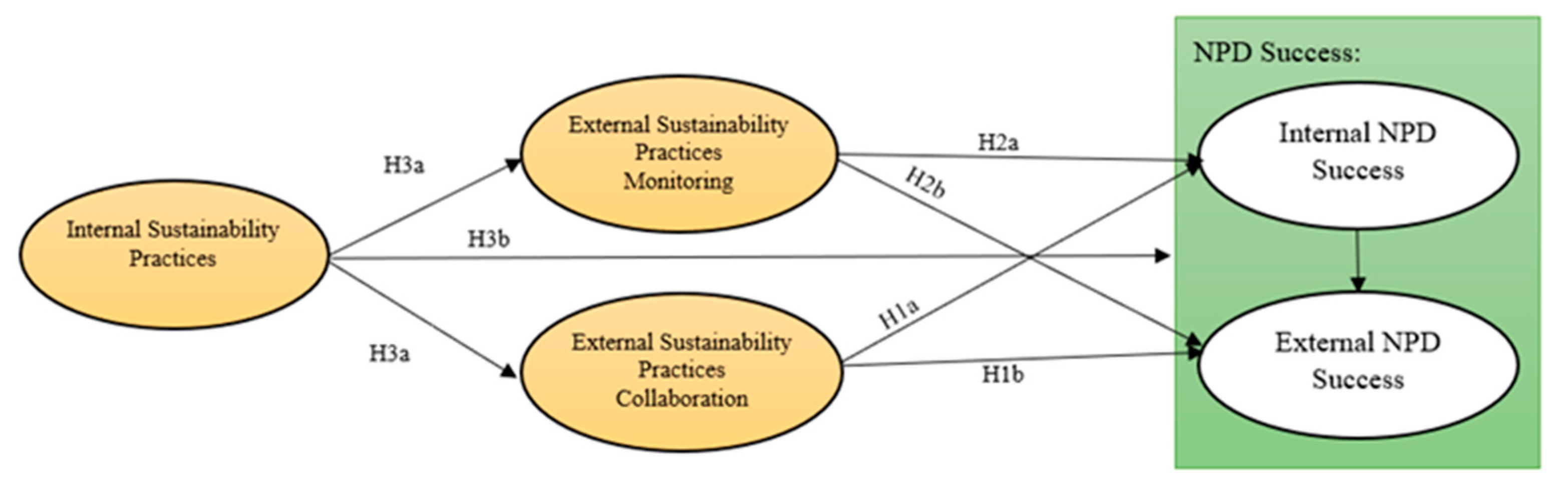
According to the previous hypotheses, the conceptual model was developed as shown in Figure 1.
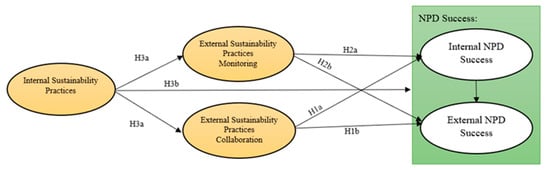
Figure 1.
Structural model proposed: Hypothesis statements.
4. Methodology
4.1. Sample and Data Collection
The data used for empirical analysis was composed of 281 manufacturing plants from three major industries (mechanical, electronics, and transportation equipment) that participated in the fourth round of the High-Performance Manufacturing (HPM) project. More than 25 research groups from 16 countries across Europe, America, and Asia are involved in the project. The local research team in each country was responsible to contact the sample plant and conduct the research. The sample was selected randomly from the master list of plants in each country (Danese et al. 2019). Table 1 reports the data distribution according to the sector and country.

Table 1.
Industry to country distribution.
The survey method was used to collect data. The unit of analysis was the plant and not the company since different practices and performance are observed in different locations. A set of 12 questionnaires specific to different operational management areas was administered through interviews with a number of plant managers. One of these sets of questionnaires was specific to sustainability issues and the other to NPD processes. Scales and items integrating all of the questionnaires had previously been used and validated by related literature. The questionnaires in each functional area were completed by two informants who were knowledgeable about that area (e.g., the section related to environmental affairs was filled by two environmental affairs managers). As a result, each plant submitted 23 questionnaires from different informants. The response rate was approximately 65% in each country.
In addition to some countermeasure practices, such as using a mix of item types (i.e., perceptual scales and objective data) in each section of the questionnaire, or mixing items for the same scale from different parts of the questionnaire sections, the research teams asked more than one respondent in each plant to fill in a questionnaire with the goal of triangulation of information and to avoid common method bias problems (Danese et al. 2019). The adequacy of the sample was tested through the Keiser–Meyer–Olkin (KMO) test. Further, Harman’s single factor test indicates that the total variance explained by a single factor was 0.3687, indicating that there is no clear evidence for common method bias (Podsakoff et al. 2003).
4.2. Measures
For this study, only those questionnaire sections that included questions related to sustainability affairs and the success of NPD were considered. Regarding sustainability practices, respondents were requested to “indicate the degree to which their plant is engaged in the initiative/practices” by listing several examples (see Appendix A). As for NPD success, the respondents were asked to consider the success of the products recently launched by the firm in terms of reaching firm operational and market NPD goals. Accordingly, the multiple item constructs were developed as follows:
- In line with the concept behind NRBV, the Internal Sustainability Practices (ISP) of this study refers to a firm´s evaluation of the efficiency of its own processes, not only through prevention and controlling practices but also environmental improvement through the reduction of environmental accidents and disposal of excess materials or equipment (Montabon et al. 2007).
- External Collaborative Sustainability Practices (ESPc) include interorganisational collaborative practices between focal firms and their suppliers (Danese et al. 2019).
- External Monitoring Sustainability Practices (ESPm) refer to sustainability-related supplier assessment practices imposed by focal firms (Danese et al. 2019).
- The external success of the NPD (ENPD) construct refers to the external (or market) dimension of NPD success (García et al. 2008) that includes customer satisfaction and overall commercial success items.
- The internal success of the NPD (INPD) construct refers to the internal (or operational) dimension of NPD success (García et al. 2008) that includes time to market, ease of manufacturing, and unit manufacturing cost items.
The description and the items integrating composites can be viewed in Appendix A.
Finally, regarding control variables, previous research has sought to examine the moderating impact of firm size, sector, and country region on innovation outcome, particularly for NPD (Claudy et al. 2016; Kähkönen et al. 2017). Further, scholars in this field recommend taking into account the information of R&D spending as control variables since they may be related to NPD outcomes (Karaman Kabadurmus 2020; Zhang and Wu 2013). The following five firm-specific factors were included in the mode as control variables:
- The industry to which the sample plant belongs labelled as Industry. The industry control variables were created by coding dummy variables for each sector. Due to dispersion of sectors amongst firms, the mechanical sector with the highest homogeneous industry group (110 firms, 40% of the sample) was chosen to use as reference for control of the analysis (Kähkönen et al. 2017).
- The level of development of the country in which the sample manufacturing firm is located is labelled as Developed.
- Due to the distribution of the number of employees as indicator of firm size being right skewed, the logarithm transformation was used to improve the normal distribution of the size.
- The percentage of plant sales from products introduced in the last five years is labelled as R&D_Intensity.
- The number of employees working in R&D for new product design/redesign development practices is labelled as R&D_Size.
Among these control variables, R&D Intensity, R&D_Size, as well as firm size can be considered as a firm´s resources to allocate for NPD. The descriptive analysis and the correlation matrix are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Descriptive statistics and correlations matrix.
4.3. Data Analysis and Results
To test the hypothesised relationship between the constructs, this study took advantage of the partial least square (PLS) method as a variance-based approach to structural equation modelling. Three reasons are behind the use of the PLS method for analysis of the data in this study (Peng and Lai 2012). First, PLS is considered as an appropriate tool to analyse a study with exploratory characteristics. In particular, this study analyses a relationship that has been minimally studied in the literature (i.e., the adoption of sustainability practices in buyer-supplier relationships and its effect on the success of NPD). Second, PLS allows researchers to estimate highly complex models in which exogenous variables are correlated and the magnitude of the moderating effect is important. Several trades-offs emerged from the analysis of the effect of adopting different sustainability practices and NPD success. In particular, the market outcome of NPD was correlated with the operational dimension. Third, PLS makes it possible to estimate both reflective and formative constructs within the same research model. This study tests the relationship of reflective independent variables (ISP, ESPm, and ESPc) with formative dependent variables (INPD and ENPD).
As for sample size, PLS follows the rule of 10 times the most complex relationship within the research model determined by (1) the construct with the largest number of formative indicators and (2) the largest number of independent variables influencing a dependent variable (Peng and Lai 2012). In this study, the largest number of formative indicators is three and the largest number of independent variables that influence dependent variables is three. Accordingly, the sample size of 281 is more than the minimum sample size requirement as per the rule of 10 times PLS.
The PLS model of this study also embraces two stages: the assessment of the measurement model and the evaluation of the path model (Hair et al. 2016). The former involves the valuation of reflective constructs in terms of indicator reliability, internal consistency, discriminant and convergent validity, and formative constructs in terms of collinearity among indicators as well as convergent validity. The latter evaluates the hypothesised relationship between constructs in terms of sign, magnitude, and significance.
4.4. Measurement Assessment
To estimate the research model, SmartPLS 3.0 was used. At the first, the five main theoretical constructs (i.e., ISP, ESPc, ESPm, INPD, and ENPD) were grouped into three reflective constructs related to the sustainability practices (independent variables) and two formative constructs related to success of NPD (dependent variables). The reason to consider the dependent variables as formative constructs is because, conceptually, the success of NPD is defined by its indicator measures, such as cost, quality, or customer satisfaction, in which each indicator can have its own independent effect on the success and any change in one of these indicators, for example, manufacturing quality, is not necessarily associated with, nor can it be replaced by, a change to other indicators such as manufacturing cost.
Since assessment criteria are different depending on the nature of constructs, two separate assessments are reported in this study for reflective and formative constructs. Table 3 presents the various criteria for reflective constructs, including the criteria for convergent validity of both indicators and constructs as well as the consistency reliability of the constructs. Regarding convergent validity, only two items had item loadings less than the threshold of 0.7 but higher than 0.4 (i.e., item loadings of S_Int01 = 0.683 and S_Int05 = 0.663). As their removal would not have contributed any significant improvement to the composite reliability and average variance extracted (AVE) values, they were kept in the model (Hair et al. 2016). In addition, the other item loadings were above 0.7 and all were significant at 0.000, demonstrating that convergent validity exists at the level of indicators (Peng and Lai 2012). The AVE results show that all values are above the minimum value of 0.5 (see Table 3). In addition, the internal consistency reliability for evaluation of reflective measures was appraised through composite reliability and Cronbach’s alpha (Hair et al. 2016). In this model, both values were higher than the criterion of 0.700, indicating high reliability for all three constructs (see Table 3).

Table 3.
Measurement properties of constructs.
Regarding formative constructs, scholars have suggested that formative item weights (including weight, sign, and magnitude) and multicollinearity among items should be evaluated with an item level test, while discriminant validity and nomological validity of the formative constructs should be examined with a composite level test (Peng and Lai 2012). The criteria for item weight should be higher than 0.10 (Andreev et al. 2009), while the collinearity statistics variance inflation factor (VIF) value should be less than 3.3 (Shmueli et al. 2019) to ensure the nonexistence of multicollinearity.
The results in Table 3 show that the criteria for both item weights and multicollinearity among items are fulfilled in this study. The nomological validity of formative constructs shows that for both NPD success constructs, there is a significant and positive relationship with some of their antecedents (Peng and Lai 2012).
Discriminant validity for reflective indicators was assessed through the Fornell–Larcker criterion (Henseler et al. 2014) by comparing the square root value of the AVE of each composite with its correlation with any other construct in the model. As presented in Table 2, all square roots of AVE were greater than interconstruct correlations confirming the existence of discriminant validity amongst the constructs (Hair et al. 2016).
For formative indicators, the procedure proposed by Peng and Lai (2012) for discriminant validity was followed and the average of intraconstruct item correlations for each construct and its correlations with other constructs in the model were computed. The result of this study shows that the average of intraconstruct item correlations for these two constructs (ENPD = 0.533 and INPD = 0.423) is greater than the average of their interconstruct correlations (ENPD = 0.312 and INPD = 0.355). In summary, the measurement model shows that all constructs are consistent, reliable, and valid.
4.5. Structural Model Evaluation
The structural model with PLS-PM, as a non-parametric technique, is assessed through standard model estimation and relies on the bootstrapping procedure to test the path model relationships in terms of the statistical significance of the model parameters. Routine bootstrapping is recommended for the consideration of 5000 resamples (Hair et al. 2016). However, the results of this study maintain consistency in terms of significance and magnitude after a resampling of 1000, 2000, and 5000. The quality of the structural model was examined by evaluating multicollinearity issues through examining VIF values of all sets of predictor composites. All observed values including outer and inner VIF values were below the threshold of 3.3 (Shmueli et al. 2019), demonstrating that multicollinearity is not critical in our model.
The results of path model evaluation are presented in Table 4. A preliminary analysis reveals that different sustainability practices have different effects on two dimensions of NPD success. It can be observed that while collaborative practices have strong, direct, and positive effects on internal NPD success (ESPc -> INPD = 0.197), their effect on external success of new product seems to be positive and indirect (ESPc -> ENPD = 0.041). Accordingly, hypothesis H1 is supported partially since the adoption of collaborative external sustainability practices positively affects NPD success. Likewise, monitoring practices show a positive, strong, and significant effect on internal success of new products (ESPm -> INPD = 0.160) while it reports a positive and indirect effect on external (market) success of NPD (ESPm -> ENPD = 0.071). Accordingly, the estimation results could provide partial support for the hypotheses related to monitoring practices, thus H2a and H2b were not fulfilled completely. Regarding the adoption of internal sustainability practices, estimation results show that while this kind of practice does not have a direct effect on NPD success (therefore, H3b cannot be supported), it has an indirect effect through the positive effect of the adoption of external sustainability practices (thus, H3a is supported).

Table 4.
Significance testing results of the structural model path coefficients and total effects.
On the other hand, the path coefficient between two measures of NPD success (internal and external), as well as between internal sustainability practices and both groups of external sustainability practices (collaboration and monitoring), is amongst the highest (0.638, 0.645, and 0.626, respectively). In accordance with the percentile method, the confidence interval does not need to include the value of 0 to ensure significance. In this sense, the path coefficients 1, 5, 6, and 7 have a statistically different effect from 0. Finally, as far as the size of the effects of the variables is concerned, the f2 value (Cohen 1988) shows that the effect of both collaborative and monitoring approaches on internal measures of success are small compared to the size of the effect between two measures of success (INPD and ENPD) and the size of the effect between internal sustainability practices, and both monitoring and collaboration practices (see Table 4).
As for controlling variables, the results of the present study reveal that only the R&D_Size which controls the number of employees working on new product design/redesign development has a significant relationship with NPD success. Further, the chosen sector (mechanical) reports a positive and significant association with NPD success.
Finally, the coefficient of determination (R2) of endogenous dependent constructs demonstrates the proportion of the variance for each dependent construct explained by its indicators. In this study, the R2 values for endogenous constructs of ESPc, ESPm, ENPD, and INPD are 0.416, 0.392, 0.428, and 0.098, respectively. The summary of result for hypothesis testing is presented in Table 5.

Table 5.
Summary of hypothesis testing.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
The aim of this study was to analyse how and to what extent the adoption of sustainability practices can affect the success of new products. To address this issue, this study argues that each set of sustainability practices (internal, external collaborative, and external monitoring) implemented by the firm has a different effect on NPD success. Under theoretical frameworks of NRBV, social capital and transaction cost, and using a PLS-SEM approach, empirical findings confirm that various sustainability practices adopted by a focal firm have different effects for both operational dimensions (internal) and for market dimensions (external) of new products’ success. More specifically, estimations demonstrate that the adoption of external sustainability practices directly improves the success of new products in terms of operational (internal) outcomes and indirectly reinforces the markets’ (external) measure of the success of new products. This result is aligned with the knowledge, experience, resources, and technology sharing benefits obtained by establishing social capital in buyer-supplier relationships.
Despite the primary expectation for a negative link between monitoring approaches and internal NPD success in virtue of transactional cost associated with these types of practices, the evidence confirms our hypothesis and reveals that the adoption of assessment-based attitude towards regulation and standard, can assure suppliers’ compliance and their implementation of proactive strategies which, in result, foster the technical attributes of NPD. Our result is consistent with the previous notion that the compliance performance of suppliers is related to green product innovation development (Lee and Kim 2011).
On the other hand, the results report that adopting practices aimed to reduce input consumption and emissions have an indirect effect on the success of new products through the positive effect on the adoption of external sustainability practices. One possible reason for the negative insignificant result for direct effect of internal practices with internal (operational aspect) NPD success might be that in contrary with reactive environmental strategies such as pollution control or improving the workforce environment through indoor air quality, the proactive environmental practices targeted in improvement of energy efficiency or pollution prevention do not yield immediate benefits for a firm. Further, the negative insignificant result for the association of these practices with external (market dimension) NPD success also can be explained through the requirements of initial investment in technology, training, and re-defining organizational processes which may offset the overall commercial success of the NPD at the beginning stage (Laari et al. 2016). However, these findings indicate that a focal firm´s sustainability orientation (internally and externally) enable NPD success.
To be concluded, the distinction between internal and external dimensions contributes to significant improvement in the understanding of how NPD success works in relation with sustainability in manufacturing. While the adoption of sustainability practices explains the success of new products related to cost, quality, and ease of manufacturing by only 9.80%1, the explanation power is 42.80% when also considering market dimension of success in line with García et al. (2008). Moreover, the adoption of external sustainability practices is reinforced by the adoption of internal sustainability practices. The results highlight that in the context of NPD and sustainability initiatives, the participation of internal functions and external supply chain agents is required (Hemonnet-Goujot et al. 2019) and, therefore, actions including collaborative and monitoring sustainability practices with suppliers can positively influence the performance of products. Hence, trust and close relationships built on a basis of collaboration in sustainability among the supply chain is a determinant for NPD success. As a result, this paper sheds new light on the alignment of sustainable supply chain management and innovation performance (NPD), thus contributing to a better picture regarding the relation between sustainability in the supply chain and NPD. Moreover, these results have also several implications for theory and practice.
For practitioners, this study highlights that adopting sustainability practices has a positive external effect on firm performance. In particular, evidence shows that the use of both inter-firm monitoring and collaboration with suppliers have positive effects on new products, not only improving aspects related to the production process but also in terms of commercial success in the long term. These results are an invitation for managers to invest in sustainability, adopting a proactive approach using sustainability in a broader way. Moreover, when firms evaluate their suppliers to make their supply chains more environmentally and socially responsible, they enable their suppliers to develop new products with environmental appeal, and reap the advantages that stem from better organizational (environmental, social, and operational) performance. Firms willing to enhance their new products´ operational features may enjoy benefits investing in the adoption of sustainable approaches in their relational social networks while intending to improve their image, reputation, and overall commercial success can find benefits from complimentary internal and external sustainability strategies. Contrary to the previous studies which only consider the significance of green suppliers’ collaboration for NPD success (Kähkönen et al. 2017; Neutzling et al. 2018; Wang et al. 2021), in this study, we observed that both monitoring and collaborative sustainability practices independently strengthen NPD success. Furthermore, this paper debates the nature of the sustainability-oriented relationship by illuminating the unique impact of different collaborative and monitoring practices on different measures of NPD success, and thus could bring forth useful insights for managers. For example, as for focal firms´ managers, technically and financially, it might be important to know which type of sustainability practices influence the success of NPD (and how), and which aspects of success will be affected. Having a better image of the association of sustainability and NPD helps these managers to develop their corporate strategies more appropriately.
The challenge is, therefore, twofold. First, to carry out the necessary internal investments in sustainability aligned with the environment, people, and performance (TBL), which do not always allow firms to observe short-term benefits. By doing so, the objectives of the organisation would be aligned not only with obtaining benefits but also with reinforcing the commitment to the environment and to people (Neutzling et al. 2018). The positive significant effect of R&D_size control variables indicate that if managers develop and cheer up the spirit of commitment to sustainability in their employees then sustainable-oriented employees working in R&D can act as a motivation for sustainability-related knowledge sharing with external partners (suppliers) during a new product development process. In addition, this paper demonstrates the positive effects of adopting a more advanced approaches to sustainability, because as observed, investing in internal sustainability practices enhance the development of supply chain relationships, which are a determinant for the success of new products.
Second, managers face the challenge of managing the trade-offs between their inhouse sustainability related operations and collaboration and control with suppliers. This result supports the idea of complementarity of different sustainability practices adopted and implemented by focal firms. Within the preview of NRBV and social capital theories, such sustainability-focused relational interactions facilitate knowledge exchange, technological and resources sharing under respect and trust which are ambient for joint practices (NPD). The strong significant effect on the market dimension (external) of new product success is attained when the internal practices and collaborative approaches with suppliers are implemented (ISP->ESPc->INPD->ENPD with coefficient of 0.164 and p = 0.011). In other words, manufacturing firms in joint efforts with their suppliers by integrating environmental consideration in development of new products can improve the operational features of new products which, in turn, enhances the value for customers and strengthens the market attributes of the success.
For academia, this study shows the existence of positive externalities through adopting sustainability practices regarding the success of a new product. Understanding these effects requires an investigation of the intersection of different but related frameworks. For instance, linking social capital with NRBV perspectives, the development of new products through sustainability-oriented collaborative relationships between a focal firm and its suppliers develops a required capability to convert such interaction to more value for customers through fostering trust, mutual respect, and knowledge and capabilities sharing possibilities between parties which eventually promotes NPD success. However, while a sustainability-oriented relationship requires a certain level of commitment and behaviour towards sustainability by suppliers, the transaction cost theory prevents the existence of a cost-related monitoring mechanism implemented by a focal firm to monitor compliance performance of suppliers. This highlights that understanding the effects of sustainability on performance needs to consider a broad perspective which looks at the interlinking of different theoretical approaches which may complement each other and help to improve the understanding of a complex phenomenon. Accordingly, this paper suggests the interconnection of the NRBV, social capital, and transaction cost theories as useful theoretical lenses for differentiating the impact of sustainability-oriented supply chain management on NPD success.
Moreover, the empirical evidence also suggests new lines for future research on the sustainability–NPD link. However, a first limitation of the paper is that effective involvement of supply chain members (internal and external) is supposed to be affected by sustainability practices but is not directly measured. Involvement of supply chain members has been indicated as a determinant of NPD success, however, the link between involvement and sustainability orientation was not. Future research should consider the mediating/moderating effect of sustainability on supply involvement to explain NPD success. Another limitation is that the sustainability orientation was considered as the driver of the link between sustainability practices and NPD success, however, the effect of this factor was not examined. Future research may take into account the mediating effect of sustainability orientation in this association. Further, while this research has advanced our understanding about the relationship between sustainability and NPD success, the study is conditioned by the cross-sectional nature of the data; future research should look for conclusive results using longitudinal analysis. Finally, the link between sustainability and NPD success could be affected by contextual factors. Hence, further research in future studies should consider small versus large firms, developed versus developing countries, or manufacturing versus service companies.
Author Contributions
We would like to declare that all authors have the same contribution listed as follows: Z.A.-G. and A.B.-P.: Conceptualization; methodology; software; validation; formal analysis; investigation; resources; data curation; writing—original draft preparation; writing—review and editing; visualization; supervision; project administration; funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded and conducted within the frameworks of the following projects: PID2020-115018RB-C31 (AEI/FEDER, UE) research project financed by the Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities and the European Regional Development Funds; PID2019-105001GB-I00 (Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación-Spain), ECO 2017–86305-C4-4-R (Ministerio de Economía, Industria y Competitividad).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
1. This research obtained the reward of the best paper in the PhD workshop in Business and Management which was held by Universitat Internacional de Catalunya (UIC) on 15–16 June 2021; 2. The authors would like to draw the readers’ attention to the fact that a primary version of the study was presented in some conferences before this article was published; 3. The authors would like to acknowledge the comments and suggestions done by two anonymous reviewers during the review process in Journal of MDPI Administrative Sciences.
Conflicts of Interest
We would like to declare that the authors declare no conflict of interest. Further, the funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A
| Variables | Items | Description | Mean | Std. Dev. | Mean Ave. |
| ISP | 3.924 | ||||
| S-Int01 | Water efficiency | 3.651 | 0.901 | ||
| S-Int02 | Reducing waste in internal processes (e.g., improving yield or efficiency) | 3.990 | 0.730 | ||
| S-Int03 | Improving the workforce environment (e.g., indoor air quality) | 4.033 | 0.733 | ||
| S-Int04 | Pollution prevention (eliminating emissions or waste) | 4.044 | 0.773 | ||
| S-Int05 | Pollution control (scrubbing, waste treatment) | 4.113 | 0.917 | ||
| S-Int06 | Decreasing the likelihood or impact of an environmental accident | 3.904 | 0.811 | ||
| S-Int07 | Complying with an industry-wide code of conduct | 3.901 | 0.890 | ||
| S-Int08 | Environmental improvements in the disposition of your organization’s scrap or excess material (re-use, recycling, etc.) | 4.025 | 0.757 | ||
| S-Int09 | Environmental improvements in the disposition of your organization’s equipment | 3.657 | 0.863 | ||
| ESPc | 3.102 | ||||
| S-ExtC01 | Encouraging suppliers to improve the environmental performance of their processes | 3.179 | 1.035 | ||
| S-ExtC02 | Providing design specification to suppliers in line with environmental requirements (e.g., green purchasing, blacklist of raw materials) | 3.273 | 1.117 | ||
| S-ExtC03 | Co-development with suppliers to reduce the environmental impact of the product (e.g., eco-design, green packaging, recyclability) | 3.064 | 0.982 | ||
| S-ExtC04 | Involvement of suppliers in the re-design of internal processes (e.g., remanufacturing, reduction of by-products) | 2.893 | 1.000 | ||
| ESPm | 3.144 | ||||
| S-ExtM01 | Requesting that your suppliers sign a code of environmental conduct | 2.984 | 1.258 | ||
| S-ExtM02 | Visiting suppliers’ plants or ensuring that they are not using sweatshop labour | 3.016 | 1.122 | ||
| S-ExtM03 | Ensuring that suppliers comply with child labour laws | 3.256 | 1.352 | ||
| S-ExtM04 | Incorporating environmental considerations in evaluating and selecting suppliers | 3.321 | 0.989 | ||
| ENPD | 3.715 | ||||
| NPDS_Ext01 | Customer satisfaction | 3.780 | 0.699 | ||
| NPDS_Ext02 | Overall commercial success | 3.650 | 0.723 | ||
| INPD | 3.262 | ||||
| NPDS_Int01 | Time to market | 3.224 | 0.850 | ||
| NPDS_Int02 | Ease of manufacturing | 3.388 | 0.755 | ||
| NPDS_Int03 | Unit manufacturing cost | 3.175 | 0.803 |
Note
| 1 | The association only considers the individual effect of sustainability practices on NPD success. There are many other factors affecting NPD success, the effects of which have not been included in the model. These include lean practices (e.g., Oliveira et al. 2018); employee involvement (e.g., Rangus and Slavec 2017); employees´ collective motivation (e.g., Zhao and Chadwick 2014), and early supplier integration (e.g., Goldberg and Schiele 2018). |
References
- Adams, Richard, Sally Jeanrenaud, John Bessant, David Denyer, and Patrick Overy. 2016. Sustainability-oriented Innovation: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Management Reviews 18: 180–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ageron, Blandine, Angappa Gunasekaran, and Alain Spalanzani. 2012. Sustainable supply management: An empirical study. International Journal of Production Economics 140: 168–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Shamraiz, Kuan Yew Wong, Ming Lang Tseng, and Wai Peng Wong. 2018. Sustainable product design and development: A review of tools, applications and research prospects. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 132: 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreev, Pavel, Hanan Maoz, Tsipi Heart, and Nava Pliskin. 2009. Validating formative partial least squares (PLS) models: Methodological review and empirical illustration. Paper presented at the ICIS 2009 Proceedings—Thirtieth International Conference on Information Systems, Phoenix, AZ, USA, December 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Brulhart, Franck, Sandrine Gherra, and Magalie Marais. 2017. Are environmental strategies profitable for companies? The key role of natural competences from a resource-based view. Management Decision 55: 2126–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, Christian, Martin C. Schleper, Menglei Niu, and Stephan M. Wagner. 2016. Supplier development for sustainability: Contextual barriers in global supply chains. International Journal of Physical Distribution and Logistics Management 46: 442–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buysse, Kristel, and Alain Verbeke. 2003. Proactive environmental strategies: A stakeholder management perspective. Strategic Management Journal 24: 453–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, Sinéad, Benn Lawson, and Daniel R. Krause. 2011. Social capital configuration, legal bonds and performance in buyer-supplier relationships. Journal of Operations Management 29: 277–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Yinfei, and Injazz J. Chen. 2019. Mixed sustainability motives, mixed results: The role of compliance and commitment in sustainable supply chain practices. Supply Chain Management 24: 622–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Colin C. J. 2020. Sustainability Orientation, Green Supplier Involvement, and Green Innovation Performance: Evidence from Diversifying Green Entrants. Journal of Business Ethics 161: 393–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarini, Andrea. 2012. Lean Organization: From the Tools of the Toyota Production System to Lean Office. Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer Science & Business Media, vol. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Claudy, Marius C., Mark Peterson, and Mark Pagell. 2016. The Roles of Sustainability Orientation and Market Knowledge Competence in New Product Development Success. Journal of Product Innovation Management 33: 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Jacob. 1988. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. Abingdon, UK: Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Cousins, Paul D., and Benn Lawson. 2007. The effect of socialization mechanisms and performance measurement on supplier integration in new product development. British Journal of Management 18: 311–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croom, Simon, Vidal Natalia, Spetic Wellington, Marshall Donna, and McCarthy Lucy. 2018. Impact of social sustainability orientation and supply chain practices on operational performance. International Journal of Operations and Production Management 38: 2344–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danese, Pamela, Andrea Lion, and Andrea Vinelli. 2019. Drivers and enablers of supplier sustainability practices: A survey-based analysis. International Journal of Production Research 57: 2034–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, M. Cristina, and María J. Montes-Sancho. 2018. Supply chain environmental R&D cooperation and product performance: Exploring the network dynamics of positional embeddedness. Journal of Purchasing and Supply Management 24: 288–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Shuili, Goksel Yalcinkaya, and Ludwig Bstieler. 2016. Sustainability, Social Media Driven Open Innovation, and New Product Development Performance*. Journal of Product Innovation Management 33: 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkington, John. 1998. Partnerships from cannibals with forks: The triple bottom line of 21st-century business. Environmental Quality Management 8: 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, Lynn A. 2015. Managerial Best Practices to Promote Sustainable Supply Chain Management & New Product Development. Vienna: InTech. [Google Scholar]
- García, Nuria, M. José Sanzo, and Juan A. Trespalacios. 2008. New product internal performance and market performance: Evidence from Spanish firms regarding the role of trust, interfunctional integration, and innovation type. Technovation 28: 713–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Ruoqi, S. Afshin Mansouri, and Emel Aktas. 2017. The relationship between green supply chain management and performance: A meta-analysis of empirical evidences in Asian emerging economies. International Journal of Production Economics 183: 245–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerstlberger, Wolfgang, Mette Præst Knudsen, and Ian Stampe. 2014. Sustainable development strategies for product innovation and energy efficiency. Business Strategy and the Environment 23: 131–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez, Cristina, and Elcio M. Tachizawa. 2012. Extending sustainability to suppliers: A systematic literature review. Supply Chain Management 17: 531–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez, Cristina, and Vicenta Sierra. 2013. Sustainable Supply Chains: Governance Mechanisms to Greening Suppliers. Journal of Business Ethics 116: 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmelin, Harald, and Stefan Seuring. 2014. Determinants of a sustainable new product development. Journal of Cleaner Production 69: 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmelin, Harald, and Stefan Seuring. 2018a. Social and Environmental Dimensions of Organizations and Supply Chains. Cham: Springer International Publishing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmelin, Harald, and Stefan Seuring. 2018b. Sustainability and New Product Development: Five Exploratory Case Studies in the Automotive Industry. In Social and Environmental Dimensions of Organizations and Supply Chains. Cham: Springer, pp. 211–32. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, Janina, and Holger Schiele. 2018. Early Supplier Integration: Assessing Supplier Innovation Ideas. IEEE Engineering Management Review 46: 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Benito, Javier, and Óscar González-Benito. 2006. A review of determinant factors of environmental proactivity. Business Strategy and the Environment 15: 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualandris, Jury, Robert D. Klassen, Stephan Vachon, and Matteo Kalchschmidt. 2015. Sustainable evaluation and verification in supply chains: Aligning and leveraging accountability to stakeholders. Journal of Operations Management 38: 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hair, Joseph F., Jr., G. Tomas M. Hult, Christian Ringle, and Marko Sarstedt. 2016. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM). Thousand Oaks: Sage publications. [Google Scholar]
- Hallstedt, Sophie I., Anthony W. Thompson, and Pia Lindahl. 2013. Key elements for implementing a strategic sustainability perspective in the product innovation process. Journal of Cleaner Production 51: 277–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, Stuart L. 1995. A natural-resource-based view of the firm. Academy of Management Review 20: 986–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemonnet-Goujot, Aurélie, Delphine Manceau, and Céline Abecassis-Moedas. 2019. Drivers and Pathways of NPD Success in the Marketing–External Design Relationship. Journal of Product Innovation Management 36: 196–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, Jörg, Christian M. Ringle, and Marko Sarstedt. 2014. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 43: 115–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jabbour, Charbel Jose Chiappetta, Daniel Jugend, Ana Beatriz Lopes De Sousa Jabbour, Angappa Gunasekaran, and Hengky Latan. 2015. Green product development and performance of Brazilian firms: Measuring the role of human and technical aspects. Journal of Cleaner Production 87: 442–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, Johan, Jonas Nilsson, Frida Modig, and Gabriella Hed Vall. 2017. Commitment to Sustainability in Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises: The Influence of Strategic Orientations and Management Values. Business Strategy and the Environment 26: 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Zhongqi, Jyoti Navare, and Richard Lynch. 2019. The relationship between innovation culture and innovation outcomes: Exploring the effects of sustainability orientation and firm size. R and D Management 49: 607–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kähkönen, Anni Kaisa, Katrina Lintukangas, Paavo Ritala, and Jukka Hallikas. 2017. Supplier collaboration practices: Implications for focal firm innovation performance. European Business Review 29: 402–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman Kabadurmus, Fatma Nur. 2020. Antecedents to supply chain innovation. International Journal of Logistics Management 31: 145–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laari, Sini, Juuso Töyli, Tomi Solakivi, and Lauri Ojala. 2016. Firm performance and customer-driven green supply chain management. Journal of Cleaner Production 112: 1960–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, Benn, Daniel Krause, and Antony Potter. 2015. Improving Supplier New Product Development Performance: The Role of Supplier Development. Journal of Product Innovation Management 32: 777–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Ki Hoon, and Ji Whan Kim. 2011. Integrating suppliers into green product innovation development: An empirical case study in the semiconductor industry. Business Strategy and the Environment 20: 527–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Su-Yol. 2015. The effects of green supply chain management on the supplier’s performance through social capital accumulation. Supply Chain Management 20: 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintukangas, Katrina, Anni Kaisa Kähkönen, and Jukka Hallikas. 2019. The role of supply management innovativeness and supplier orientation in firms’ sustainability performance. Journal of Purchasing and Supply Management 25: 100558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, Donna, Lucy McCarthy, Ciarán Heavey, and Paul McGrath. 2015. Environmental and social supply chain management sustainability practices: Construct development and measurement. Production Planning and Control 26: 673–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzola, Erica, Manfredi Bruccoleri, and Giovanni Perrone. 2015. Supply chain of innovation and new product development. Journal of Purchasing and Supply Management 21: 273–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moldavska, Anastasiia, and Torgeir Welo. 2017. The concept of sustainable manufacturing and its definitions: A content-analysis based literature review. Journal of Cleaner Production 166: 744–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montabon, Frank, Robert Sroufe, and Ram Narasimhan. 2007. An examination of corporate reporting, environmental management practices and firm performance. Journal of Operations Management 25: 998–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, Bimal P., Om Prakash Yadav, and Rajesh Solanki. 2011. Improving the npd process by applying lean principles: A case study. EMJ-Engineering Management Journal 23: 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neutzling, Daiane Mülling, Anna Land, Stefan Seuring, and Luis Felipe Machado do Nascimento. 2018. Linking sustainability-oriented innovation to supply chain relationship integration. Journal of Cleaner Production 172: 3448–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidumolu, Ram, Coimbatore K. Prahalad, and Madhavan R. Rangaswami. 2009. Why sustainability is now the key driver of innovation. Harvard Business Review 87: 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Obal, Michael, Todd Morgan, and George Joseph. 2020. Integrating sustainability into new product development: The role of organizational leadership and culture. Journal of Small Business Strategy 30: 43–57. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, Gilson Adamczuk, Kim Hua Tan, and Bruno Turmina Guedes. 2018. Lean and green approach: An evaluation tool for new product development focused on small and medium enterprises. International Journal of Production Economics 205: 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagell, Mark, and Zhaohui Wu. 2009. Building a more complete theory of sustainable supply chain management using case studies of 10 exemplars. Journal of Supply Chain Management 45: 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulraj, Antony, Injazz J. Chen, and Constantin Blome. 2017. Motives and Performance Outcomes of Sustainable Supply Chain Management Practices: A Multi-theoretical Perspective. Journal of Business Ethics 145: 239–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, David Xiaosong, and Fujun Lai. 2012. Using partial least squares in operations management research: A practical guideline and summary of past research. Journal of Operations Management 30: 467–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, Kenneth J., Robert B. Handfield, and Gary L. Ragatz. 2003. A model of supplier integration into new product development. Journal of Product Innovation Management 20: 284–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, Philip M., Scott B. MacKenzie, Jeong-Yeon Lee, and Nathan P. Podsakoff. 2003. Common Method Biases in Behavioral Research: A Critical Review of the Literature and Recommended Remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology 88: 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujari, Devashish. 2006. Eco-innovation and new product development: Understanding the influences on market performance. Technovation 26: 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnam, Robert D. 1995. Tuning in, tuning out: The strange disappearance of social capital in America. PS: Political Science & Politics 28: 664–83. [Google Scholar]
- Rangus, Kaja, and Alenka Slavec. 2017. The interplay of decentralization, employee involvement and absorptive capacity on firms’ innovation and business performance. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 120: 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, Marta, Michele Germani, and Alessandra Zamagni. 2016. Review of ecodesign methods and tools. Barriers and strategies for an effective implementation in industrial companies. Journal of Cleaner Production 129: 361–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancha, Cristina, Christina W. Y. Wong, and Cristina Gimenez. 2019. Do dependent suppliers benefit from buying firms’ sustainability practices? Journal of Purchasing and Supply Management 25: 100542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Victor Guang, S. C. Lenny Koh, James Baldwin, and Federica Cucchiella. 2012. Natural resource based green supply chain management. Supply Chain Management 17: 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmueli, Galit, Marko Sarstedt, Joseph F. Hair, Jun-Hwa Cheah, Hiram Ting, Santha Vaithilingam, and Christian M. Ringle. 2019. Predictive model assessment in PLS-SEM: Guidelines for using PLSpredict. European Journal of Marketing 53: 2322–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuli, Prashant, and Ravi Shankar. 2015. Collaborative and lean new product development approach: A case study in the automotive product design. International Journal of Production Research 53: 2457–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Jing, and Jun Dai. 2018. Sustainable supply chain management practices and performance. Industrial Management and Data Systems 118: 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Yuan, Sachin B. Modi, and Tobias Schoenherr. 2021. Leveraging sustainable design practices through supplier involvement in new product development: The role of the suppliers’ environmental management capability. International Journal of Production Economics 232: 107919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wlazlak, Paraskeva, Kristina Säfsten, Per Hilletofth, and Glenn Johansson. 2018. Integration of Suppliers’ Workflows in the OEMs’ New Product Development Process. Procedia Manufacturing 25: 479–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Chee Yew, Christina W. Y. Wong, and Sakun Boon-itt. 2020. Effects of green supply chain integration and green innovation on environmental and cost performance. International Journal of Production Research 58: 4589–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, Chungwon, Moon Gyu Kim, Yanghon Chung, and Jae Jeung Rho. 2016. Suppliers’ communication capability and external green integration for green and financial performance in Korean construction industry. Journal of Cleaner Production 112: 483–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Guo-Ciang, Jyh-Hong Ding, and Ping-Shun Chen. 2012. The effects of GSCM drivers and institutional pressures on GSCM practices in Taiwan’s textile and apparel industry. International Journal of Production Economics 135: 618–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Junfeng, and Wei-ping Wu. 2013. Social capital and new product development outcomes: The mediating role of sensing capability in Chinese high-tech firms. Journal of World Business 48: 539–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Zheng Jane, and Clint Chadwick. 2014. What we will do versus what we can do: The relative effects of unit-level NPD motivation and capability. Strategic Management Journal 35: 1867–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).