Use of CaO Loaded Mesoporous Alumina for Defluoridation of Potable Groundwater Containing Elevated Calcium Levels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of COMA
2.2. Characterization of COMA
2.3. Adsorption Studies on Defluoridation
2.3.1. Determination of Optimum COMA Dosage
2.3.2. Determination of the Effect of the Initial Fluoride Level
2.3.3. Determination of the Effect of Contact Time
2.3.4. Determination of Optimum pH
2.3.5. Determination of the Effect of the Initial Calcium Level
2.4. Fluoride Analysis
2.5. Adsorption Isotherm and Kinetic Models
3. Results and Discussion
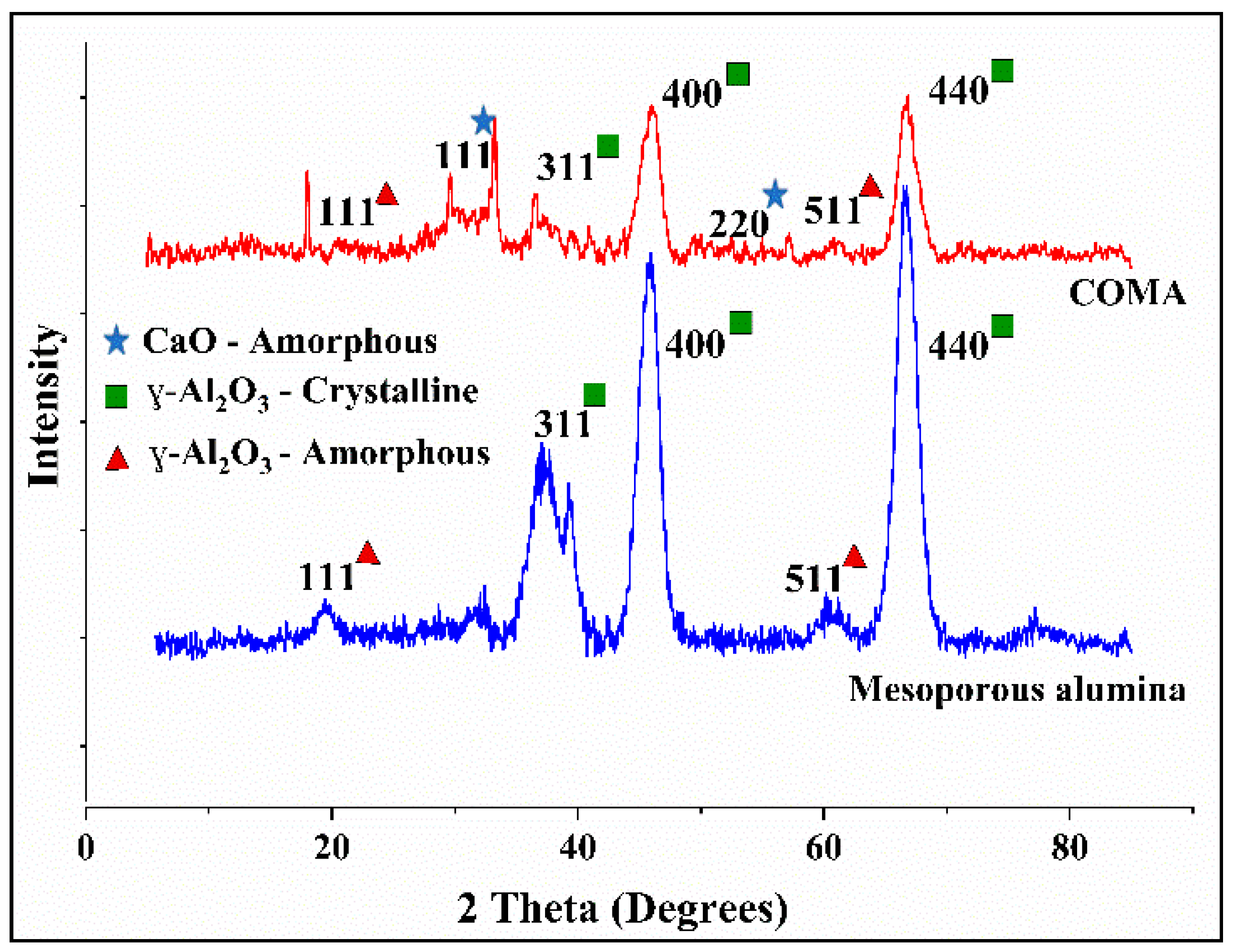
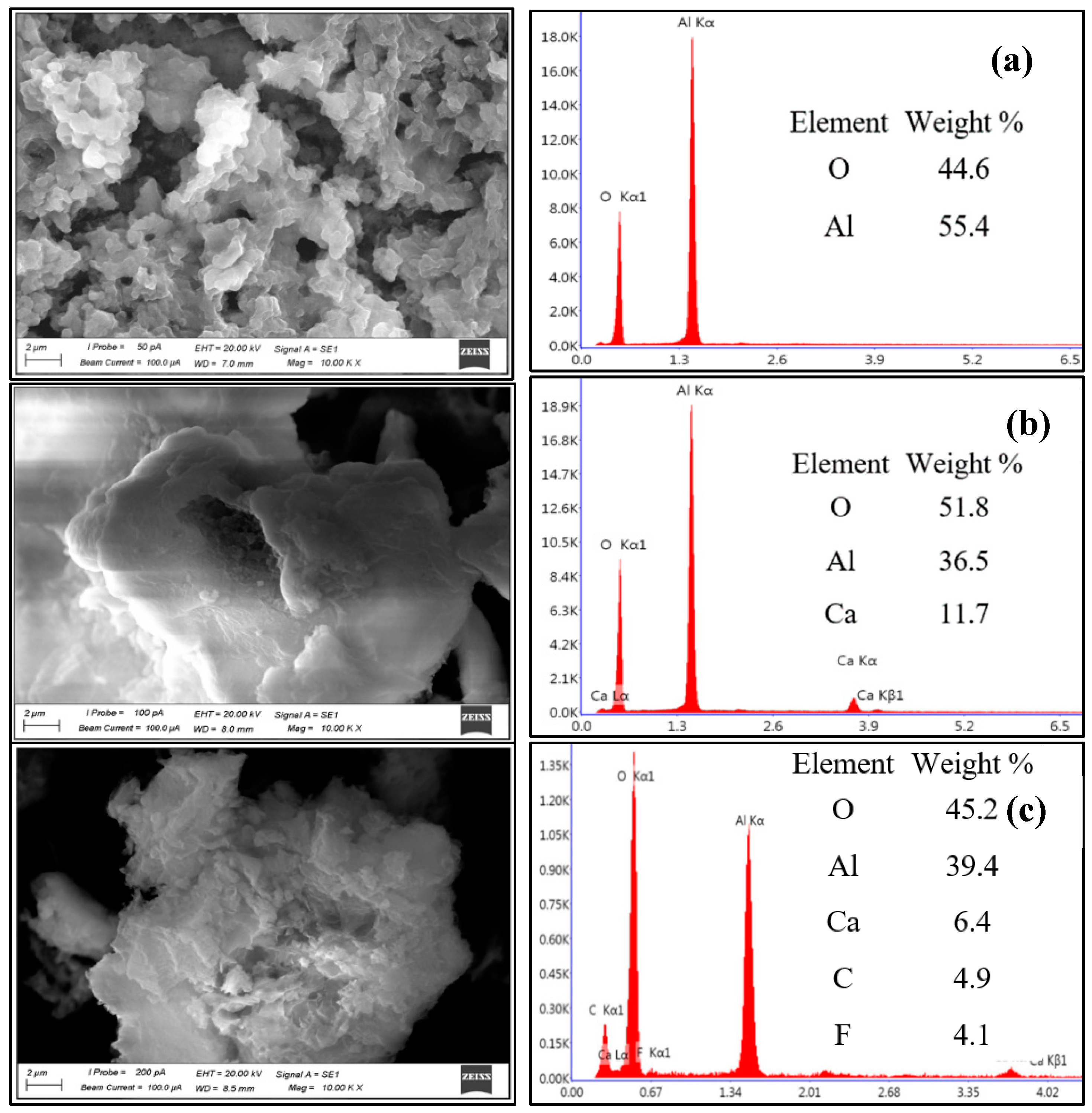
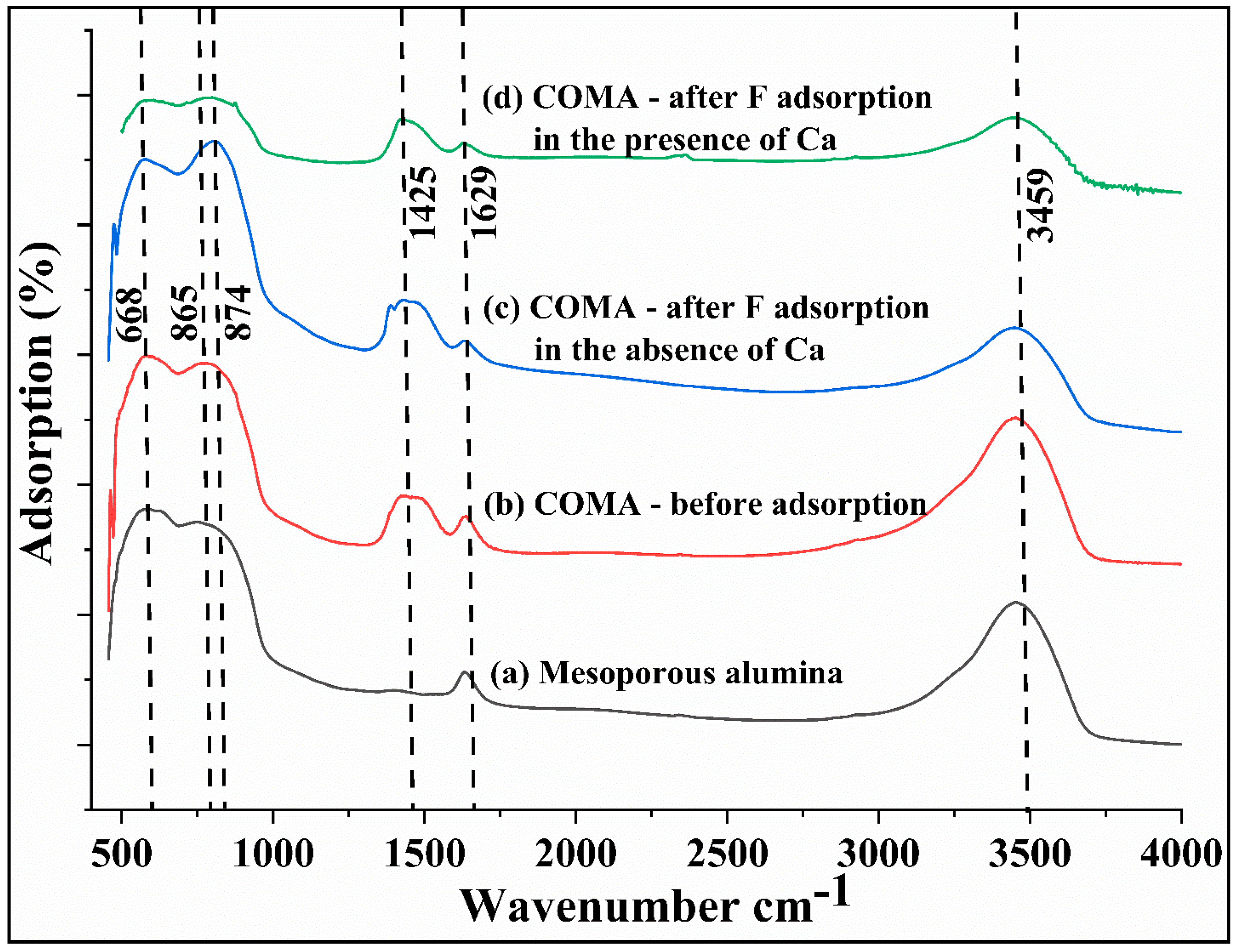
3.1. Characterization of the Adsorbent
3.2. Adsorption Studies for Defluoridation
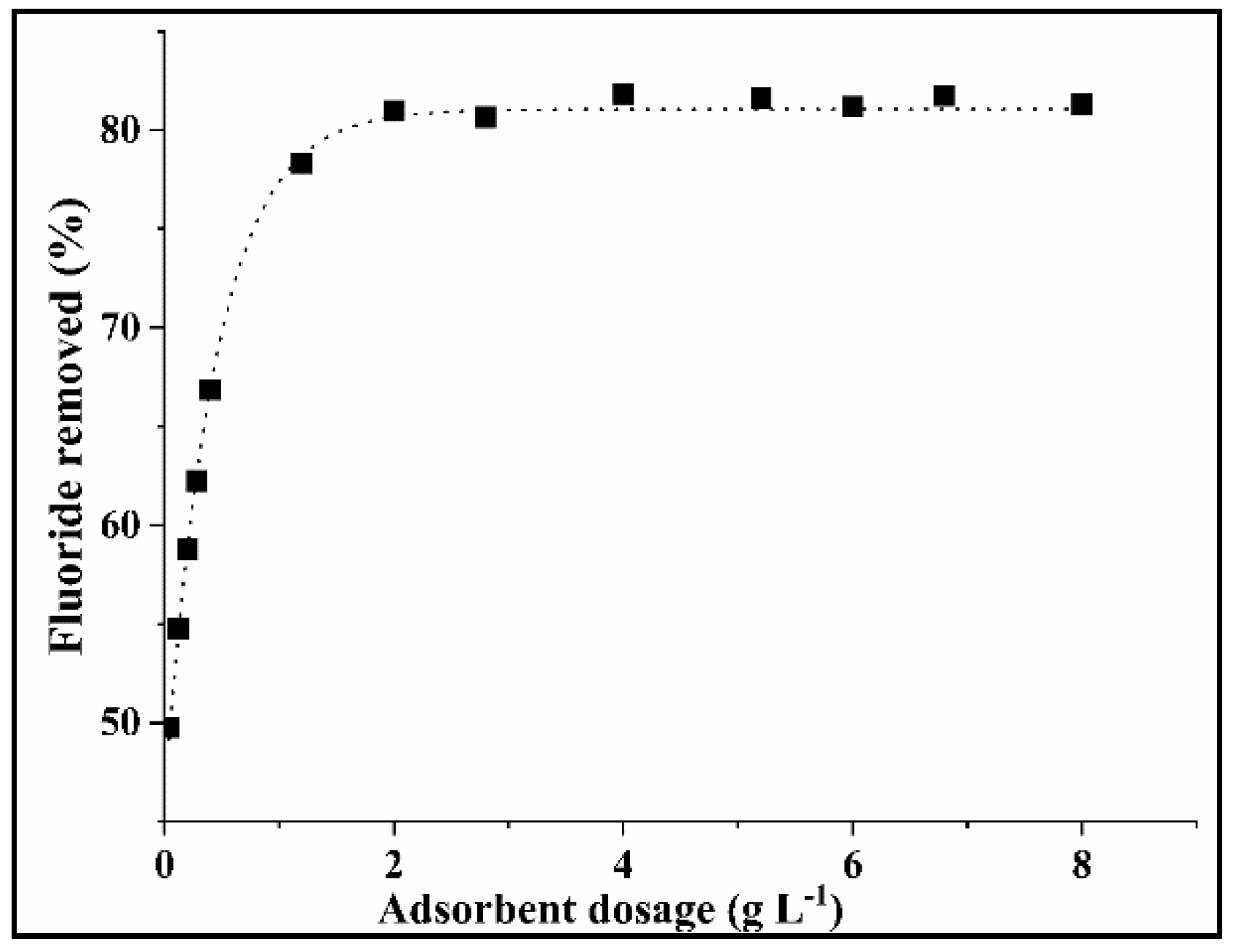
3.2.1. Effect of the COMA Dosage
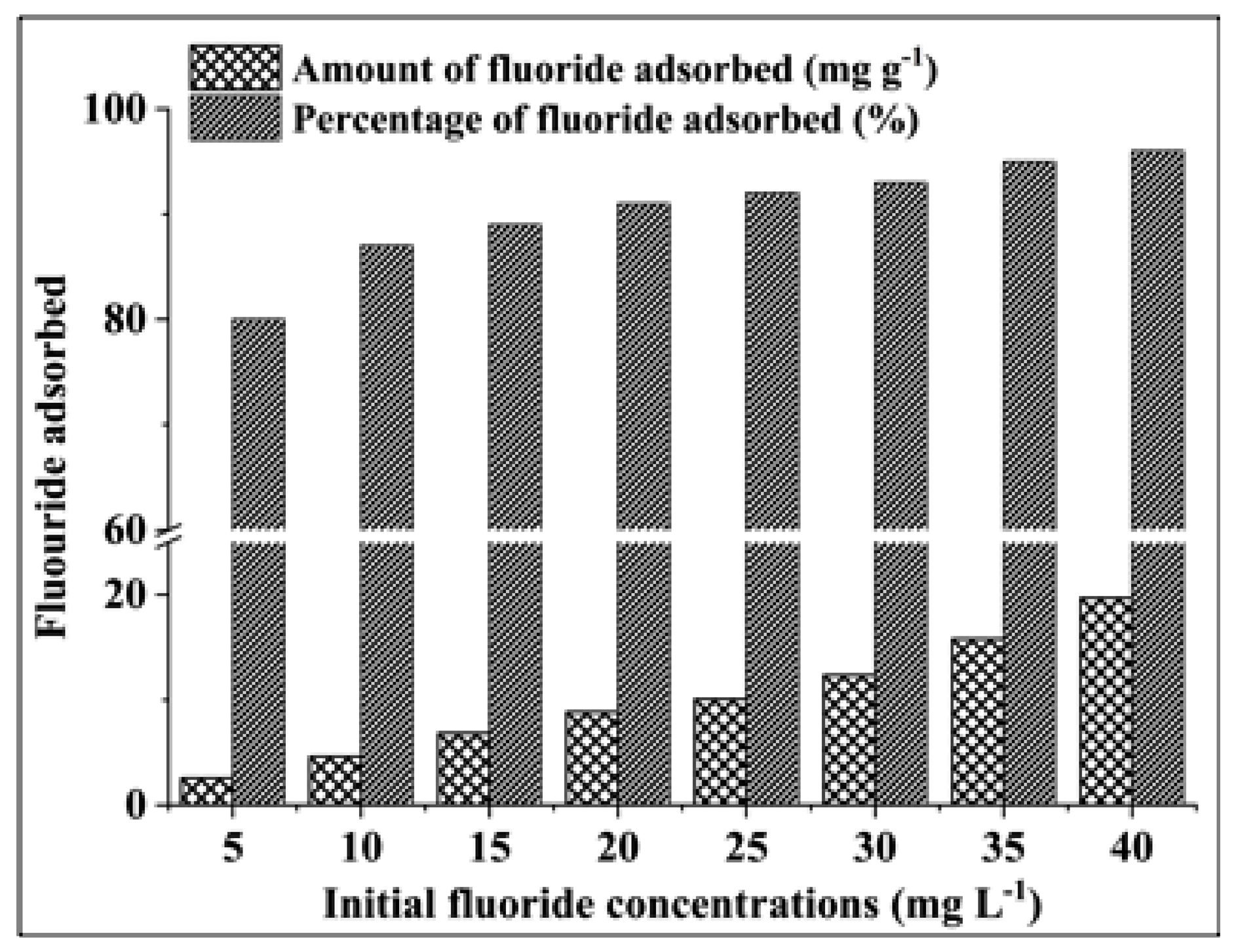
3.2.2. Effect of Initial Fluoride Concentration
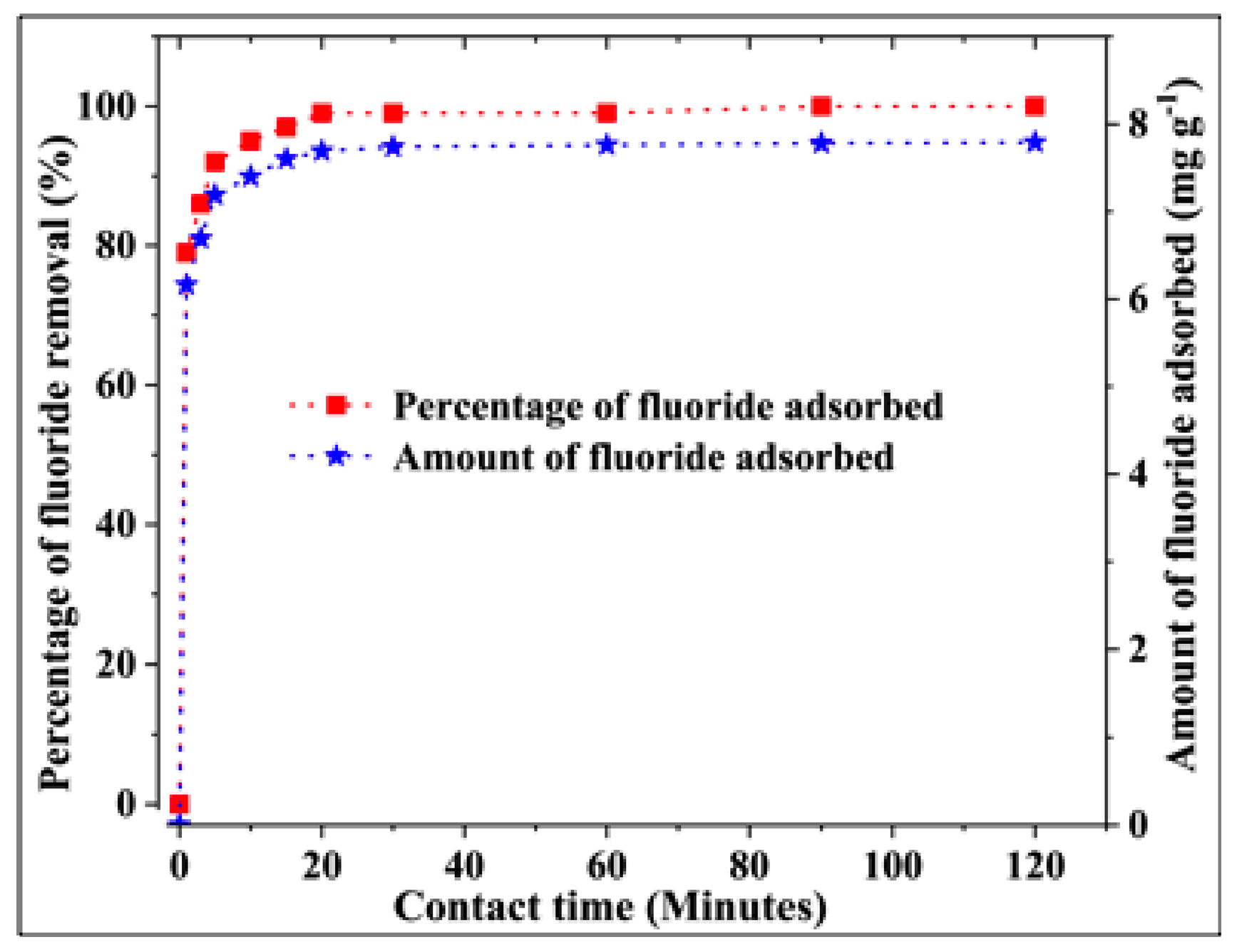
3.2.3. Effect of the Contact Time
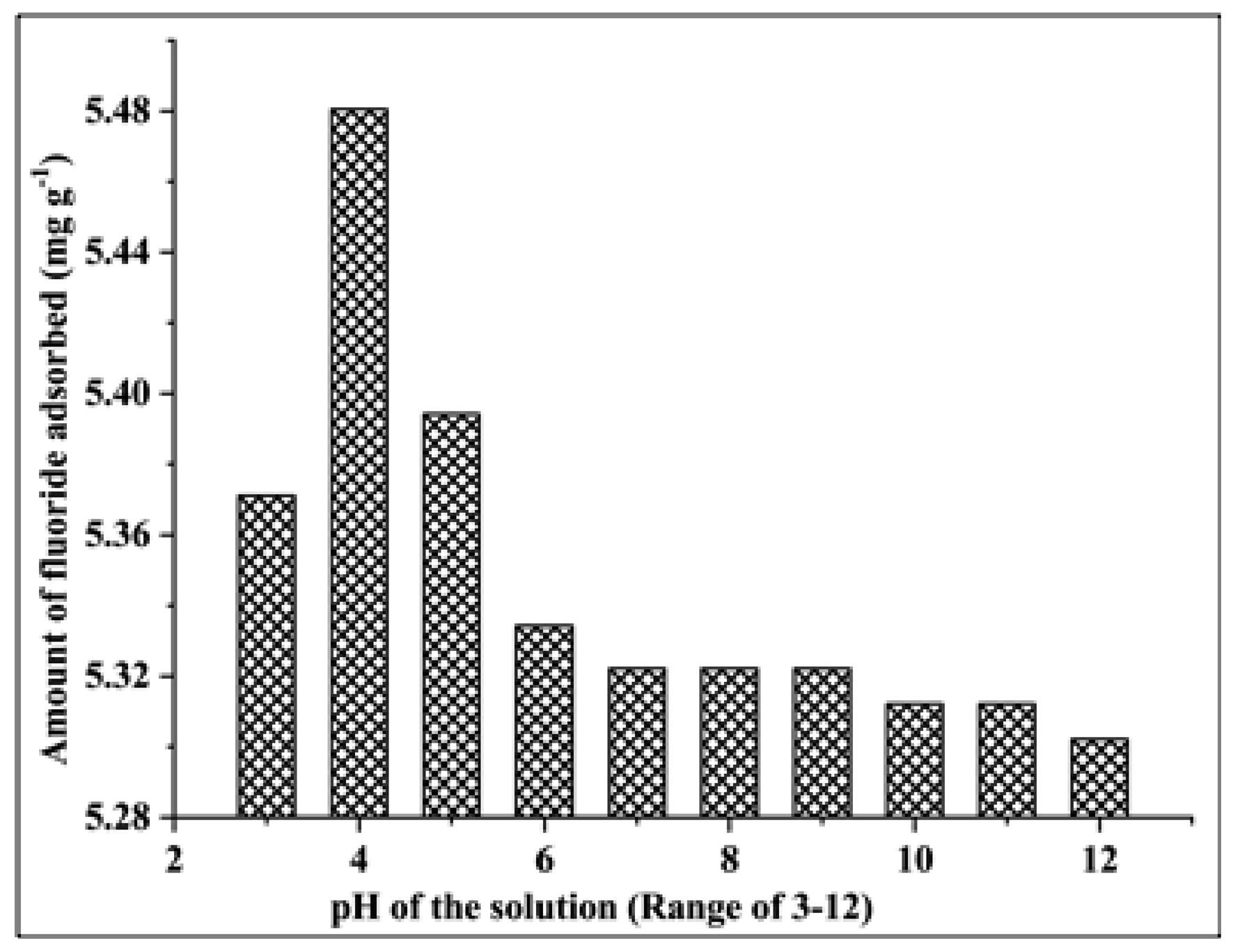
3.2.4. Effect of the pH of the Solution
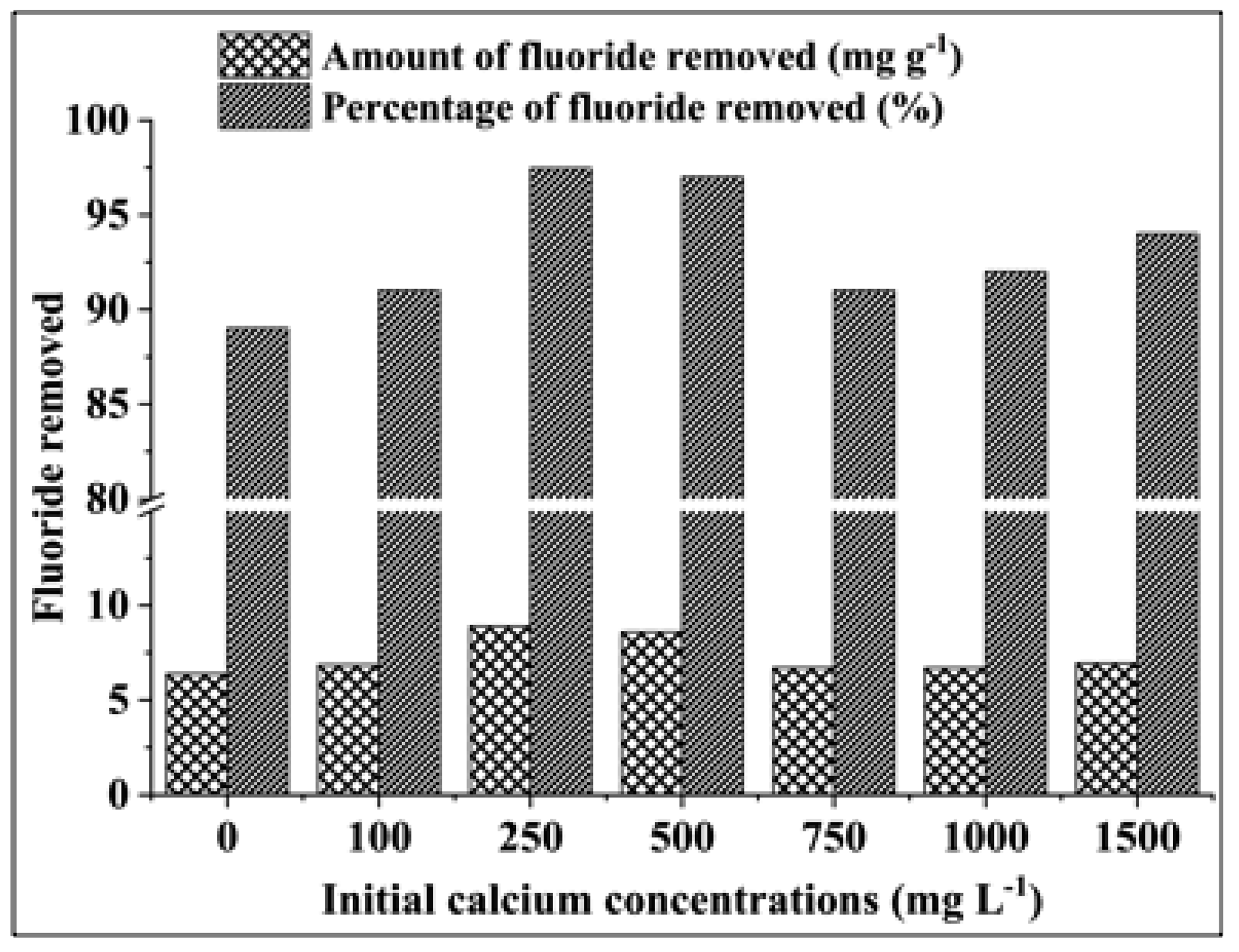
3.2.5. Effect of the Initial Calcium Concentration
3.3. Adsorption Isotherms and Kinetics Models for Fluoride
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saxena, K.L.; Sewak, R. Fluoride consumption in endemic villages of India and Its remedial measures. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Invent. 2015, 4, 58–73. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho, L.M.; Torres, A.; Saha, D.; Deng, S. Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics of fluoride on sol-gel-derived activated alumina adsorbents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 349, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currell, M.; Cartwright, I.; Raveggi, M.; Han, D. Controls on elevated fluoride and arsenic concentrations in groundwater from the Yungchen Basin. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrajith, R.; Padmasiri, J.P.; Dissanayake, C.B.; Prematilaka, K.M. Spatial distribution of fluoride in groundwater of Sri Lanka. J. Natl. Sci. Found. Sri Lanka 2012, 40, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality: 4th Edition Incorporating the 1st Addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 370–373. [Google Scholar]
- Dharma-wardana, M.; Amarasiri, S.L.; Dharmawardene, N.; Panabokke, C. Chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology and ground-water ionicity; study based on Sri Lanka. Environ. Geochem. Health 2015, 37, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, A.; Amerasinghe, P.; Manthrithilake, H.; Arasalingam, S. Review of Literature on Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology (CKDu) in Sri Lanka; Working Paper 158; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Kumar, E.; Sillanpaa, M. Fluoride removal from water by adsorption—A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 811–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijerathna, C.; Weragoda, S.; Kawakami, T. A Review of Chronic Kidney Disease Due to Unknown Etiology and groundwater quality in Dry Zone, Sri Lanka. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Applied Science and Environmental Engineering, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 20–21 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Meenakshi; Maheshwari, R. Fluoride in drinking water and its removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, B137, 456–463. [Google Scholar]
- Habuda-Stanić, M.; Ravančić, M.E.; Flanagan, A. A Review on adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solution. Materials 2014, 7, 6317–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnakoti, P.; Chunduri, A.L.A.; Vankayala, R.K.; Patnaik, S.; Kamisetti, V. Enhanced fluoride adsorption by nanocrystalline c-alumina: Adsorption kinetics, isotherm modelling and thermodynamic studies. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2413–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansiwal, A.; Pillewan, P.; Biniwale, R.B.; Rayalu, S.S. Copper oxide incorporated mesoporous alumina for defluoridation of drinking water. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 129, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Gong, W.; Lan, H.; Yang, T.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Simultaneous removal of arsenate and fluoride by iron and aluminum binary oxide: Competitive adsorption effects. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 92, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, N.; Yang, W.; You, X. Sulfate-doped Fe3O4/Al2O3 nanoparticles as a novel adsorbent for fluoride removal from drinking water. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4040–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Sánchez, J.J.; Solache-Ríos, M.; Martínez-Miranda, V.; Solís-Morelos, C. Removal of fluoride ions from drinking water and fluoride solutions by aluminum modified iron oxides in a column system. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 407, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayananda, D.; Sarva, V.R.; Prasad, S.V.; Arunachalam, J.G. Preparation of CaO loaded mesoporous Al2O3: Efficient adsorbent for fluoride removal from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 248, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayananda, D.; Sarva, V.R.; Prasad, S.V.; Arunachalam, J.; Ghosh, N.N. A Simple Aqueous Solution Based Chemical Methodology for Preparation of Mesoporous Alumina: Efficient Adsorbent for Defluoridation of Water. Part. Sci. Technol. 2015, 33, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Lu, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, Y.; Yang, S. Synthesis of large mesoporous γ-Al2O3 form coal-series kaolin at room temperature. Mater. Lett. 2013, 91, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Zhao, S.; Asuha, S. Novel approach of synthesis of mesoporous γ-AlOOH powder from Coal-bearing Kaolinite and its enhanced adsorption performance for Congo Red and fluoride. Solid State Phenom. 2019, 288, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarneau, A.; Mehlhorn, D.; Guenneau, F.; Coasne, B.; Villemot, F.; Minoux, D.; Aquino, C.C.; Dath, J. Specific surface areas determination for microporous/mesoporous materials: The case of mesoporous FAU-Y zeolites. Langmuir 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–471. [Google Scholar]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multi molecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinin, M.M. The potential theory of adsorption of gases and vapours for adsorbents with energetically non-uniform surfaces. Chem. Rev. 1960, 60, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempkin, M.I.; Pyzhev, V. Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalyst. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 1940, 12, 327–356. [Google Scholar]
- Lagergren, S. About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens Handlingar 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinković, D.M.; Stanković, M.V.; Veličković, A.V.; Avramović, J.M.; Cakić, M.D.; Veljković, V.B. The synthesis of CaO loaded onto Al2O3 from calcium acetate and its application in transesterification of the sunflower oil. Adv. Technol. 2015, 4, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Chang, P.; Lee, Y.; Lee, T.; Lai, Y.; Chen, S. Morphological and structural evolution of mesoporous calcium aluminate nanocomposites by microwave-assisted synthesis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 183, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imtiaz, A.; Farrukh, M.A.F.; Khaleeq-ur-rahman, M.; Adnan, R. Micelle-Assisted synthesis of Al2O3⋅CaO nanocatalyst: Optical properties and their applications in photodegradation of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 641420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesbani, A.; Sitompul, S.O.C.; Mohadi, R.; Hidayati, N. Characterization and utilisation of Calcium Oxide (CaO) thermally decomposed from fish bones as a catalyst in the production of biodiesel from waste cooking oil. Makara J. Technol. 2016, 20, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, A.; El-Wakeelb, S.; Mostafa, B.; El-Shahatc, M.F. Removal of Pb, Cd, Cu and Ni from aqueous solution using nanoscale zero-valent iron particles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2196–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathibha, C.; Sharma, B.; Chunduri, L.A.; Aditha, S.K.; Rattan, T.; Venkataramaniah, K. Nano Calcium-Aluminum Mixed Oxide: A Novel and Effective Material for Defluoridation of Drinking Water. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, E.; Bhatnagar, A.; Kumar, U.; Sillanpa, M. Defluoridation from aqueous solutions by nano-alumina: Characterization and sorption studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehiraa, S.; Kanamori, S.; Nagashima, K.; Saeki, T.; Visbal, H.; Fukui, T.; Hirao, K. Controllable hydrogen release via aluminum powder corrosion in calcium hydroxide solutions. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2013, 1, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, S.; Wang, R.; Yang, L.; He, L.H.; Liu, X. Biosorption of copper, zinc, cadmium and chromium ions from aqueous solution by natural foxtail millet shell. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 165, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ileperuma, O.A.; Dharmagunawardhane, H.A.; Herath, K.P. Dissolution of aluminium from sub-standard utensils under high fluoride stress: A possible risk factor for chronic renal failure in the North-Central Province. J. Natl. Sci. Found. Sri Lanka 2009, 37, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandurangappaa, C.; Lakshminarasappab, B.N.; Nagabhushana, B.M. Synthesis and characterisation of CaF2 nanocrystals. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 489, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Saharan, V.K.; George, S. Studies on performance characteristics of calcium and magnesium amended alumina for defluoridation of drinking water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1364–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Z.Q.; Han, B.; Su, C.L.; Han, Q.; Chen, W.Z. Biosorption of copper ions from aqueous solution using rape straw powders: Optimisation, equilibrium and kinetic studies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 150, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillotson, M.J.; Brett, P.M.; Bennett, R.A.; Grau-Crespo, R. Adsorption of organic molecules at the TiO2(110) surface: The effect of van der Waals interactions. Surf. Sci. 2015, 632, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshadi, M.; Amiri, M.J.; Mousavi, S. Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic investigations of Ni(II), Cd(II), Cu(II) and Co(II) adsorption on barley straw ash. Water Resour. Ind. 2014, 6, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nigussie, W.; Zewge, F.; Chandravanshi, B. Removal of excess fluoride from water using waste residue from alum manufacturing process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Fu, J.; Jin, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, M.; Fu, X. Evaporation-induced self-assembly (EISA) synthesized mesoporous bimetalic oxides (MBOs) enabling enhanced co-uptake of arsenate and fluoride from water. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 94, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Patel, R. Evaluation of removal efficiency of fluoride from aqueous solution using quick lime. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 143, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasana, H.M.S.; Perera, G.D.R.K.; Gunawardena, P.S.; Fernando, P.S.; Bandara, J. WHO water quality standards Vs Synergic effect(s) of fluoride, heavy metals and hardness in drinking water on kidney tissues. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dissanayake, C.B.; Chandrajith, R. Groundwater fluoride as a geochemical marker in the etiology of chronic kidney disease of unknown origin in Sri Lanka. Ceylon J. Sci. 2017, 46, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Jin, S.; Lu, Q.; Ji, J. Adsorption isotherm, kinetic and mechanism of expanded graphite for sulfadiazine antibiotics removal from aqueous solutions. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 2629–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dada, A.O.; Olalekan, A.P.; Olatunya, A.M.; Dada, O. Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin-Radushkevich Isotherms Studies of Equilibrium Sorption of Zn2+ Unto Phosphoric Acid Modified Rice Husk. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 2012, 3, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jayaweera, M.; Sudasinghe, M.; Gunawardana, B.; Peiris, A.; Manatunge, J. Use of CaO Loaded Mesoporous Alumina for Defluoridation of Potable Groundwater Containing Elevated Calcium Levels. Environments 2019, 6, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments6060066
Jayaweera M, Sudasinghe M, Gunawardana B, Peiris A, Manatunge J. Use of CaO Loaded Mesoporous Alumina for Defluoridation of Potable Groundwater Containing Elevated Calcium Levels. Environments. 2019; 6(6):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments6060066
Chicago/Turabian StyleJayaweera, Mahesh, Madhusha Sudasinghe, Buddhika Gunawardana, Achini Peiris, and Jagath Manatunge. 2019. "Use of CaO Loaded Mesoporous Alumina for Defluoridation of Potable Groundwater Containing Elevated Calcium Levels" Environments 6, no. 6: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments6060066
APA StyleJayaweera, M., Sudasinghe, M., Gunawardana, B., Peiris, A., & Manatunge, J. (2019). Use of CaO Loaded Mesoporous Alumina for Defluoridation of Potable Groundwater Containing Elevated Calcium Levels. Environments, 6(6), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments6060066





