Abstract
Salinization of coastal aquifer systems constitutes a major threat for groundwater. Especially areas with high population density due to increasing tourist activity may face severe problems. In this study, the GALDIT method was applied in the north side of Rhodes Island, Greece, in order to assess groundwater vulnerability to seawater intrusion. Hydrogeological data were elaborated in geographical information systems (GIS), and appropriate thematic maps were produced. The final vulnerability map was obtained from the combination of the thematic maps using overlying techniques. Based on the application of the GALDIT method, a zone up to 1000 m from the shore is characterized by medium to high vulnerability, while medium vulnerability characterizes the eastern part of the study area. Overexploitation of the aquifer, due to the intense touristic activity in Ialysos area, constitutes the main reason for groundwater salinization due to seawater intrusion in the study area. Consequently, planning of proper groundwater management and systematic monitoring of the groundwater reserves are of the utmost importance in order to solve existing problems and prevent future issues of salinization.
1. Introduction
Groundwater quality degradation is a major problem, as it can affect society, economy, and the environment [1]. An important reason for groundwater quality deterioration is the salinization of coastal groundwater systems due to seawater intrusion. Overexploitation of coastal aquifers for public, agricultural, and tourism use constitutes the main factor for groundwater level drawdown, and hence, groundwater flow is reversed, flowing from the sea toward the mainland [1]. This phenomenon has especially increased the last two decades, and it is very intense in European Mediterranean and Middle Eastern Mediterranean countries, where the climate is semiarid, such as in Portugal and Greece [1,2,3,4,5]. The extent of seawater intrusion is determined by the vulnerability of the aquifer system. Beyond hydrogeological conditions, other factors that affect the vulnerability of an aquifer are water uses as well as hydrological and climate characteristics [1]. Coastal areas with increasing touristic activity, in which the main source for water supply is groundwater, will face severe problems in the future [6].
Over the past years, groundwater vulnerability assessment, mainly in coastal areas, has been studied by several researchers, while various methods have been applied in many countries [7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. The most famous method for seawater intrusion assessment in coastal aquifers is the GALDIT method, which was proposed by Lobo-Ferreira and Cabral [5,6,14]. The acronym GALDIT derived from the acronyms of the following six parameters: Groundwater occurrence (G), aquifer hydraulic conductivity (A), height of groundwater level above sea level (H), distance from the shore (distance inland perpendicular from shoreline) (D), impact of existing status of seawater intrusion in the area (I), and thickness of the aquifer (T) [5,6]. It has been applied in many Mediterranean countries, such as Portugal and Algeria [6,15,16]. It has been also used for the assessment of coastal aquifer vulnerability in Northern Greece, including a coastal plain part of Rhodope [16], a coastal aquifer system at River Nestos Eastern Delta [17] and a coastal area of the River Anthemountas basin [18].
The results of the GALDIT method are shown in thematic maps, which are usually produced using geographical information systems (GIS) [5,14]. GIS facilitates and improves the understanding of groundwater systems, whilst it can contribute to developing groundwater conceptual models [19]. It can produce thematic maps, taking into account both individual parameters and a combination of them, such as topography, geology, hydrology, and land uses [20,21]. Further, it offers different tools and techniques that can be used for automatic data collection, spatial interpolation, and visual representation of results [22]. Especially via the spatial analysis tools, available data and information may be used to process and compose digital terrain models (DTMs), and three dimensional views and slope maps can be created [23,24]. In this study, the GALDIT method, in combination with GIS, has been applied in the north side of Rhodes Island, Greece. Groundwater constitutes the main source of fresh water on Rhodes Island. Hence, the protection of the aquifers is of utmost importance to sustain economic activities, such as tourism, as well as to ensure the water supply safety on the island.
2. Methodology
The parameters of the GALDIT method are the following six [5,6,14]: Groundwater occurrence (G), aquifer hydraulic conductivity (A), height of groundwater level above sea level (L), distance from the shore (distance inland perpendicular from shoreline) (D), impact of existing status of seawater intrusion in the area (I), and thickness of the aquifer (T). A specific weight has been assigned to each parameter (1–4) based on its relative importance to seawater intrusion. Additionally, the parameters value is classified into 4 classes and rated with the values 2.5, 5, 7.5, and 10 (Table 1). A high rating indicates high vulnerability to seawater intrusion. The final index of GALDIT is estimated by the following equation:
where R and W are the rating and the weight, respectively. The final GALDIT-index vulnerability is classified into high (>7.5), moderate (5–7.5), and low (<5). The high GALDIT-index vulnerability illustrates the high vulnerability of the study area.

Table 1.
Rating of GALDIT parameters.
The thematic maps were designed using the tool of spatial analyst of Arc Toolbox of software Αrcmap ArcGIS 10.4. More specifically, the spatial interpolation tool of topo to raster and the reclassify were used for the parameters’ values spatial distribution and rating assignment for each class range and rating, accordingly. The final map was created using the raster calculator tool of Map algebra. Specifically, the rated thematic maps were multiplied with the corresponding weight and overlapped to produce the special distributed values of the vulnerability map. Finally, the values were classified into the vulnerability classes of the GALDIT method. The hydrogeological and hydrological data of the aquifer were derived from previous studies of IGMΕ (Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploitation) [25,26,27,28].
3. Study Area
The study area is located in the North–West part of Rhodes Island, which is located on the southeastern side of the Aegean Sea, Greece, covering an area of 71.56 km2. The main characteristics of Rhodes Island, as a Mediterranean region, are mild rainy winters and dry summers. The highest rates of rainfall are noticed during the months of December and January, while the lowest rates occur during the summer period. A serious concern on Rhodes Island is water resources management, especially in the summer months, where water demands are increased due to high tourist population. It is worth mentioning that the total population of inhabitants is 115,490 (census 2011) and during the summer period the population can overcome 2,000,000 [29,30]. Water demands are mainly covered by groundwater extraction and springs discharge, and some regions are supplied by River Gadouras Dam. During the summer period, wells are over pumped [25].
The GALDIT method was applied in the north coastal side of Rhodes Island, which includes the regions of Kremasti, Ialysos, Pastida, Paradeisi, Damatria, and Maritsa. The geological background of the study area is shown in Figure 1a.
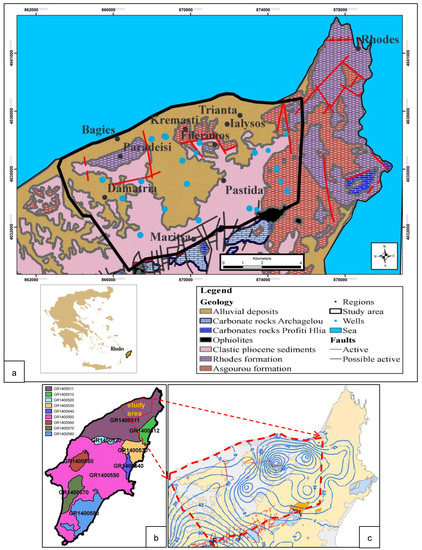
Figure 1.
(a) Geological map of the wider study area. (b) Aquifer systems of Rhodes Island ([31], modified) and study area. (c) Piezometric map (September 2008) of the studied aquifer in North Rhodes Island ([26], modified).
Regarding the hydrological conditions of the wider study area, some relevant rainfall data for the period 2013–2017 are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Mean monthly rainfall values (mm) for the period 2013–2017 [31] and mean annual rainfall value (mm) for the same period.
It is worth mentioning that comparing the mean monthly rainfall values for the periods 1955–2008 (from previous relevant research works) and 2012–2017 regarding the Rhodes meteorological station, it is observed that the rainfall values during the winter months of the period 2012–2017 have decreased, resulting in significant water supply and irrigation problems in many areas of Rhodes City despite the heavy rainfall that occurred in November 2013 (418.4 mm).
4. Hydrogeological Setting
The hydrogeological system of Rhodes Island consists of nine (9) aquifer systems (Figure 1b), which are the following [32]: GR1400511 (North Rhodes Island Α granular aquifer, extent: 355.91 km2), GR1400512 (North Rhodes Island Β granular aquifer, extent: 45.22 km2), GR1400520 (Prophet Elias-Salakos karst aquifer, extent: 23.82 km2), GR1400530 (Seven Springs karst aquifer, extent: 67.12 km2), GR1400540 (Kalathos-Gadouras granular aquifer, extent: 22.25 km2), GR1400550 (Central Rhodes Island granular aquifer, extent: 648.73 km2), GR1400560 (Attavyros karst aquifer, extent: 40.89 km2), GR1400570 (Apolakkia granular aquifer, extent: 67.73 km2), and GR1400580 (Genadi granular aquifer, extent: 132.33 km2).
The North Rhodes Island aquifer system (A and B) consists of alluvial and coastal depositions, of sands, sandstones and conglomerates, as well as marls, marly limestones, and clay. The depth values of the wells in this area range from 20 m to 200 m, while the deepest wells are found in the Ialysos (Trianta) area (within the studied aquifer), with discharge values reaching up to 100 m3/h. The annual groundwater reserves amount to up to 24 × 106 m3, taking into account the lateral outflows from the aquifer system to the sea [25].
The hydrogeological system of the study area is part of the aquifer system GR 1400511 [31] (Figure 1b). The municipal wells which cover the water demands of the city of Rhodes are located in the studied aquifer. Additionally, the irrigation needs are also met with groundwater from the aforementioned aquifer. Obviously, the aquifer is of utmost importance for the water supply sustainability of the island.
The aquifer under investigation is characterized as a granular confined aquifer with values of thickness varying from 10 m to 110 m. The aquifer consists mainly of alluvial and coastal depositions, as well as of sands, sandstones and conglomerates. Transmissivity (T) values vary from 61 to 1400 m2/day, and hydraulic conductivity (K) values range from 1.5 m/day to 35 m/day. Rainfall infiltration percentage has been estimated to 12–15% [25].
In addition, according to relevant hydrochemical research conducted by the Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration (IGME) [28], chloride (Cl−) and bicarbonate (HCO3−) concentration values have been estimated to 44.7–184.0 mg/L and 337–556 mg/L, respectively, for the period of May 2008.
Figure 1c presents a piezometric map of the studied aquifer (September 2008), which contributes to the ascertainment that the overpumping of groundwater combined with the large drilling depth in some wells, far deeper than the sea level, especially in the area of Ialysos (Trianta), has contributed to the salinization of the coastal aquifer system and consequently to the groundwater qualitative and quantitative degradation [25]. In the past 10 years, a significant decline (up to 90 m) of groundwater level below the sea level along the regions of Kremasti–Pastida has been observed [26].
5. Results and Discussion
The GALDIT method was applied in the north side of Rhodes Island. The thematic maps of each parameter are shown in Figure 2.
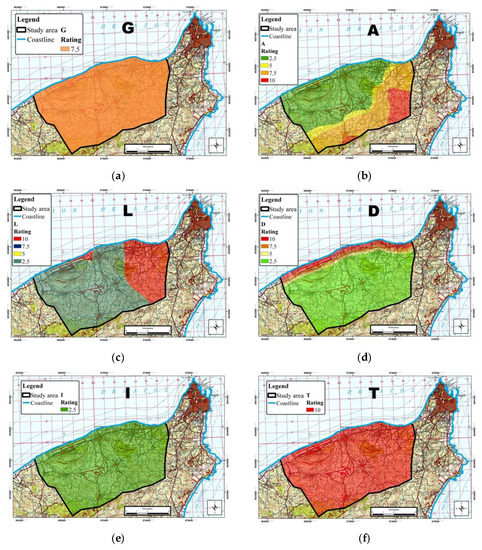
Figure 2.
Thematic maps of GALDIT method parameters: (a) Thematic map of parameter G, (b) thematic map of parameter A, (c) thematic map of parameter L, (d) thematic map of parameter D, (e) thematic map of parameter I, and (f) thematic map of parameter T.
According to the lithological profile, the groundwater aquifer system (G) of the study area is characterized as confined, and thus, the rating of parameter (G) is 10. The aquifer hydraulic conductivity (A) of the study area was estimated by the following equation:
where T is Transmissivity (m2/day), b is thickness (m), and K is hydraulic conductivity. High values of hydraulic conductivity indicate high vulnerability of a coastal aquifer system. Transmissivity values were obtained from pumping tests from previous studies [25]. The thickness was estimated according to the lithological profile of the existing wells [33]. High values of hydraulic conductivity were noticed in the central area of the study area and low values in the coastal area.
T = K × b,
An important parameter for assessing seawater intrusion is groundwater table above sea level. For estimation of the height of groundwater level above sea level (L), the values of the piezometric heads were calculated for the spring period of 2008. Groundwater level in the study area for the wet period of 2008 ranges between 6.93 m to 120.05 m a.s.l. High hydraulic head values exist in the coastal and in the eastern part of the area.
The topographic map of the area and the buffer zone tool of the software ArcMap ArcGIS 10.4 were used in order to determine the distance from the shore (D). The distance from the shoreline has a significant impact on the salinization extent in an area. For instance, areas close to the sea are more affected than the remote ones.
The impact of the existing status of seawater intrusion in the area (I) was determined by the qualitative characteristics of groundwater using the Revelle index, given by Cl−/HCO3−1 + CO32− [6]. The Revelle coefficient values are very low, and so, the parameter I is rated with the value 2.5. This indicates that the specific wells of the study area have not been affected by the seawater intrusion and as a result, due to the spatial interpolation, the total area is rated with low values. The thickness of the aquifer (T) layers, which was estimated according to the existing lithological profiles, is higher than 10 m, and as a result, it is rated with the value 10. The vulnerability of the aquifer is lower where the aquifer thickness is high. The final map of groundwater vulnerability is presented in Figure 3 and Table 3.
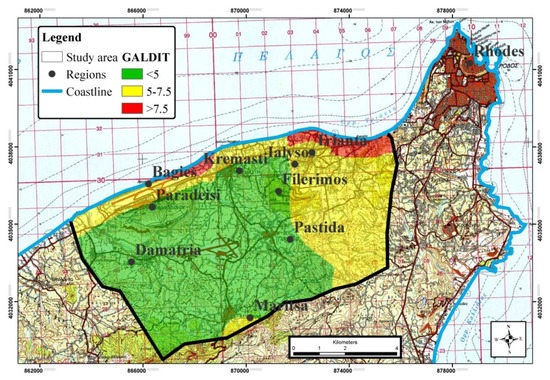
Figure 3.
GALDIT vulnerability map of the aquifer system in the study area.

Table 3.
Distribution of the vulnerability class areas (%) according to GALDIT.
The low zone of vulnerability corresponds to the highest percentage (61.61%), covering an area of 44.09 km2. The medium zone of vulnerability covers a total area of 24.01 km2, including mainly the areas of Kremasti, Ialysos, Bagies, and Filerimos and part of the Pastida and Maritsa areas. Based on IGME studies, decrease of groundwater level in a significant degree (up to 90 m) along the areas of Kremasti–Pastida has been noticed the last 10 years, illustrating the severity of medium zone of vulnerability [26]. The high zone of vulnerability is observed along the coastline of the areas of Bagies (Paradeisi) and Ialysos (Trianta), representing the lowest percentage (4.83%). The high vulnerability of the Ialysos (Trianta) area is confirmed from previous studies [25], in which the salinization of the aquifer was reported. Seawater intrusion in these regions is a consequence of high population density due to the tourist activity. Overexploitation of a groundwater system in areas with high population density, especially in coastal areas, has been mentioned as the main factor of groundwater deterioration and salinization [13,34,35].
However, the low rate of parameter (I) is contradicted by the final results. Revelle coefficient values are very low in all study areas, displaying that the specific wells of the study area have not been affected by the seawater intrusion. This does not mean that the entire aquifer has not been affected. Especially in the Ialysos area (Trianta), according to previous studies, the groundwater system has been affected by seawater intrusion, and as a result, all wells are deactivated [25]. It was not possible to consider the data of these wells in the application of the GALDIT method, and hence, the hydrochemical status of the aquifer was underestimated. The aforementioned constitutes a limitation of the GALDIT application in the study area. A further drawback of the GALDIT method is the demand of a wide variety of qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the aquifer [18]. It is worth mentioning that the assessment procedure of the parameter (I) has been reported as deficient in other studies [18,36].
Hence, the final vulnerability map to seawater intrusion in the study area should be updated in future works supplementing the areas with a lack of measurements. Nevertheless, applying the GALDIT method in this study, the Ialysos area is characterized by medium to high vulnerability due to the characteristics of other parameters and their high contribution to the final index vulnerability. Because of the lack of current data regarding chemical and physical parameters, the current status could be worse. Thus, adapting an integrated water resource management plan in the study area, including allocation of boreholes, pumping trough, deducing pumping rates during the summer period, and banning pumping, could prevent further salinization of the aquifer due to seawater intrusion. It is also necessary to monitor groundwater quality characteristics at least twice per year and to measure systematic groundwater level four (4) times per year in the high-vulnerability zones and two times per year in the medium and low vulnerability zones. Systematic electronic monitoring of selected parameters regarding the quantitative and qualitative status of groundwater is also proposed. Taking into consideration all these restrictions, as well as the results of this study, in further application of the GALDIT method on Rhodes Island, it is recommended to initially record the current status via monitoring of the groundwater system and apply the method afterwards.
6. Conclusions
In this study, groundwater vulnerability in the north coastal side of Rhodes Island was estimated by applying the GALDIT method in a GIS environment. The final map of the GALDIT method illustrated that coastal areas of the north side of Rhodes, especially the Ialysos area, are susceptible to seawater intrusion, as they were characterized by medium to high vulnerability. Using the GALDIT method in future research is expected to increase the GALDIT score, because deactivated brackish wells were not included in the whole process. Hence, the current hydrochemical status of the groundwater might be considered inadequate. The intense tourist activity during the summer period in the study area could lead to further overexploitation of the aquifer system and finally to salinization. Undeniably, drastic measures should be adapted with respect to the provided results of this study in order to prevent further groundwater quality deterioration. Therefore, planning of appropriate groundwater resource management and systematic monitoring of groundwater reserves are significant, especially on islands.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.K. and F.-K.P.; Data curation, Z.M.; Formal analysis, Z.M. and N.K.; Investigation, Z.M.; Methodology, N.K. and F.-K.P.; Software, Z.M. and N.K.; Supervision, N.K. and F.-K.P.; Writing—original draft, Z.M.; Writing—review and editing, N.K. and F.-K.P.
Funding
This research has been funded by the Dodecanese Scholarships Foundation of Greece.
Acknowledgments
This research was conducted in the context of the Master Thesis of Mavriou Zografina (Department of Civil Engineering, Democritus University of Thrace-DUTH), Greece, and has been funded by the Dodecanese Scholarships Foundation of Greece.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Vrba, J. Chapter 5: The Impact of Aquifer Intensive Use on Groundwater Quality; Commission on Groundwater Protection of the International Association of Hydrogeologists (IAH): Prague, Czech Republic, 2002; pp. 113–132. [Google Scholar]
- EUWI. Mediterranean Groundwater Report. Technical report on groundwater management in the Mediterranean and the Water Framework Directive. Available online: https://circabc.europa.eu/sd/a/50c3b2a9-4816-4ab1-9a33-d41c327759e3/Mediterranean%20Groundwater%20Report_final_150207_clear.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2007).
- Petalas, C.; Lambrakis, N. Simulation of intense salinization phenomena in coastal aquifers—The case of the coastal aquifers of Thrace. J. Hydrol. 2006, 324, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaarour, T. Application of GALDIT Index in the Mediterranean Region to Assess Vulnerability to Sea Water Intrusion. Master’s Thesis, Department of Physical Geography and Ecosystem Science Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chachadi, A.G.; Lobo-Ferreira, J.P. Sea water intrusion vulnerability mapping of aquifers using GALDIT method. Coastin—A Coastal Policy Res. Newsl. 2001, 4, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chachadi, A.G.; Lobo-Ferreira, J.P. Assessing aquifer vulnerability to sea water intrusion using GALDIT method: Part 2-GALDIT Indicators Description. In Proceedings of the fourth Inter-Celtic Colloquium on Hydrology and Management of Water Resources, Guimaraes, Portugal, 11–14 July 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Datta, B. Development of multi objective management models for coastal aquifers. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1999, 1252, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.D.; Alcoe, D.W.; Ordens, C.M.; Hutson, J.L.; Ward, J.D.; Simmons, C.T. Current practice and future challenges in coastal aquifer management: Flux-based and trigger-level approaches with application to an Australian case study. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 1831–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhartono, E.; Purwanto, P.; Suripin, S. Seawater Intrusion Modeling on Groundwater Confined Aquifer in Semarang. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 23, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouche, N.; Maanan, M.; Gontara, M.; Rollo, N.; Jmal, I.; Bouri, S. A global risk approach to assessing groundwater vulnerability. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 88, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singaraja, C.; Chidambaram, S.; Anandhan, P.; Prasanna, M.V.; Thivya, C.; Thilagavathi, R. A study on the status of saltwater intrusion in the coastal hard rock aquifer of South India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2015, 17, 443–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motevalli, A.; Moradi, H.R.; Javadi, S. A Comprehensive evaluation of groundwater vulnerability to saltwater up-coning and sea water intrusion in a coastal aquifer (case study: Ghaemshahr-juybar aquifer). J. Hydrol. 2018, 557, 753–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakis, N.; Pavlou, A.; Vargemezis, G.; Voudouris, K.; Soulios, G.; Pliakas, F.; Tsokas, G. Seawater intrusion mapping using electrical resistivity tomography and hydrochemical data. An application in the coastal area of eastern Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 543, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chachadi, A.G.; Raikar, P.S.; Lobo Ferreira, J.P.; Oliveira, M.M. GIS and Mathematical Modelling for the Assessment of Groundwater Vulnerability to Pollution: Application to an Indian Case Study Area in Goa; Laboratório Nacional de Engenharia Civil: Lisbon, Portugal, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bouderbala, A.; Remini, B.; Saaed Hamoudi, A.; Pulido-Bosch, A. Assessment of groundwater vulnerability and quality in coastal aquifers: A case study (Tipaza, North Algeria). Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recinos, N.; Kallioras, A.; Pliakas, F.; Schuth, C. Application of GALDIT index to assess the intrinsic vulnerability to seawater intrusion of coastal granular aquifers. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 1017–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedreira, R.; Kallioras, A.; Pliakas, F.; Gkiougkis, I.; Schuth, C. Groundwater vulnerability assessment of a coastal aquifer system at River Nestos eastern Delta Greece. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 6387–6415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakis, N.; Spiliotis, M.; Voudouris, K.; Pliakas, F.K.; Papadopoulos, B. A fuzzy multicriteria categorization of the GALDIT method to assess seawater intrusion vulnerability of coastal aquifers. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 621, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, V.; Goyal, R. Development of conceptual groundwater flow model for Pali Area, India. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 5, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voudouris, K.; Kazakis, N.; Polemio, M.; Kareklas, K. Assessment of intrinsic vulnerability using the DRASTIC model and GIS in the Kiti aquifer, Cyprus. Eur. Water 2010, 30, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Sener, E.; Sener, S.; Davraz, A. Assessment of aquifer vulnerability based on GIS and DRASTIC methods: A case study of the Senirkent–Uluborlu basin (Isparta, Turkey). Hydrogeol. J. 2009, 17, 2023–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, D.W.; McKinney, D.C.; Maidment, D.R. Use of geographic information systems in ground-water flow modeling. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1996, 122, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancur, T. Una Aproximación al Conocimiento de un Sistema Acuífero Tropical. Caso de Estudio: Bajo Cauca Antioqueño. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Antioquia, Medellín, Colombia, 2008. (In Spanish). [Google Scholar]
- Betancur, T.; Palacio, C.A.; Escobar, J.F. Conceptual Models in Hydrogeology, Methodology and Results. Hydrogeology—A Global Perspective; Gholam, A.K., Ed.; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2012; Volume 5, p. 232. ISBN 978-953-51-0048-5. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration (IGME). Hydrogeological Study—Water District of Aegean Islands. In Project: Recording and Evaluation of Hydrogeological Characteristics of Groundwater and Water Systems in the Country; IGME: Athens, Greece, 2010; Volumes 1 and 2. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration (IGME). Hydrogeological Model of Flow Simulation of a Granular Aquifer System in North Rhodes Island. In Project: Recording and Evaluation of Hydrogeological Characteristics of Groundwater and Water Systems in the Country; IGME: Athens, Greece, 2010. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration (IGME). Field Measurements (Water—Physicochemical Measurements)-Water District of Aegean Islands. In Project: Recording and Evaluation of Hydrogeological Characteristics of Groundwater and Water Systems in the Country; IGME: Athens, Greece, 2010; Volume 1. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration (IGME). Chemical analyses of groundwater (general-specific—trace elements—isotopes)—Water District of Aegean Islands. In Project: Recording and Evaluation of Hydrogeological Characteristics of Groundwater and Water Systems in the Country; IGME: Athens, Greece, 2010; Volume 1. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Hellenic Statistical Authority. Population and Housing Census 2011. Permanent Population. 2011. Available online: http://www.statistics.gr/2011-census-pop-hous (accessed on 1 May 2019).
- Civil Aviation Authority. Air Traffic Statistics, Directorate of Organization and Development, Department of Statistics, 2009–2017. Available online: http://www.ypa.gr/profile/statistics/yearstatistics/ (accessed on 1 May 2019).
- Mavriou, Z. Contribution to the Development of Aquifers Conceptual Models in Rhodes Island. Application of GALDIT Method. Master’s Thesis, Department of Civil Engineering, Democritus University of Thrace, Xanthi, Greece, 2018. (In Greek). [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environment and Energy. 1st Update of River Basin Management Plans of the Aegean Islands Water District; Special Secretariat for Water; Ministry of Environment and Energy: Athens, Greece, 2017. (In Greek)
- Stergiadis, M. Hydrogeological Study in the North Part of Rhodes Island—Simulation of Groundwater Flow Using a Three-Dimensional Model of Groundwater Flow and Princeton Transport Code (PTC) Model. Diploma Thesis, Department of Environmental Engineering, Technical University of Crete, Chania, Greece, 2014. (In Greek). [Google Scholar]
- Werner, A.D.; Bakker, M.; Post, V.E.; Vandenbohede, A.; Lu, C.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T.; Barry, D.A. Seawater intrusion processes, investigation and management: Recent advances and future challenges. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakirevich, A.; Melloul, A.; Shaath, S.; Borisov, V. Simulation of seawater intrusion into the Khan Yunis area of the Gaza strip coastal aquifer. J. Hydrogeol. 1998, 6, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakis, N.; Busico, G.; Colombani, N.; Mastrocicco, M.; Voudouris, K. Limitations of GALDIT to map seawater intrusion vulnerability in a highly touristic coastal area. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 191, 012050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).