A Comparative Study of Indoor Radon Levels between Two Similar Dwellings Using CONTAM Software
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Building
2.2. The CONTAM Software
2.3. Modeling Approach
- G = Generation rate [mass of contaminant/time]
- D = Effective removal rate [mass of air/time]
- C = Current concentration [mass of contaminant/mass of air]
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Realistic Generation Rates for Indoor Radon Sources
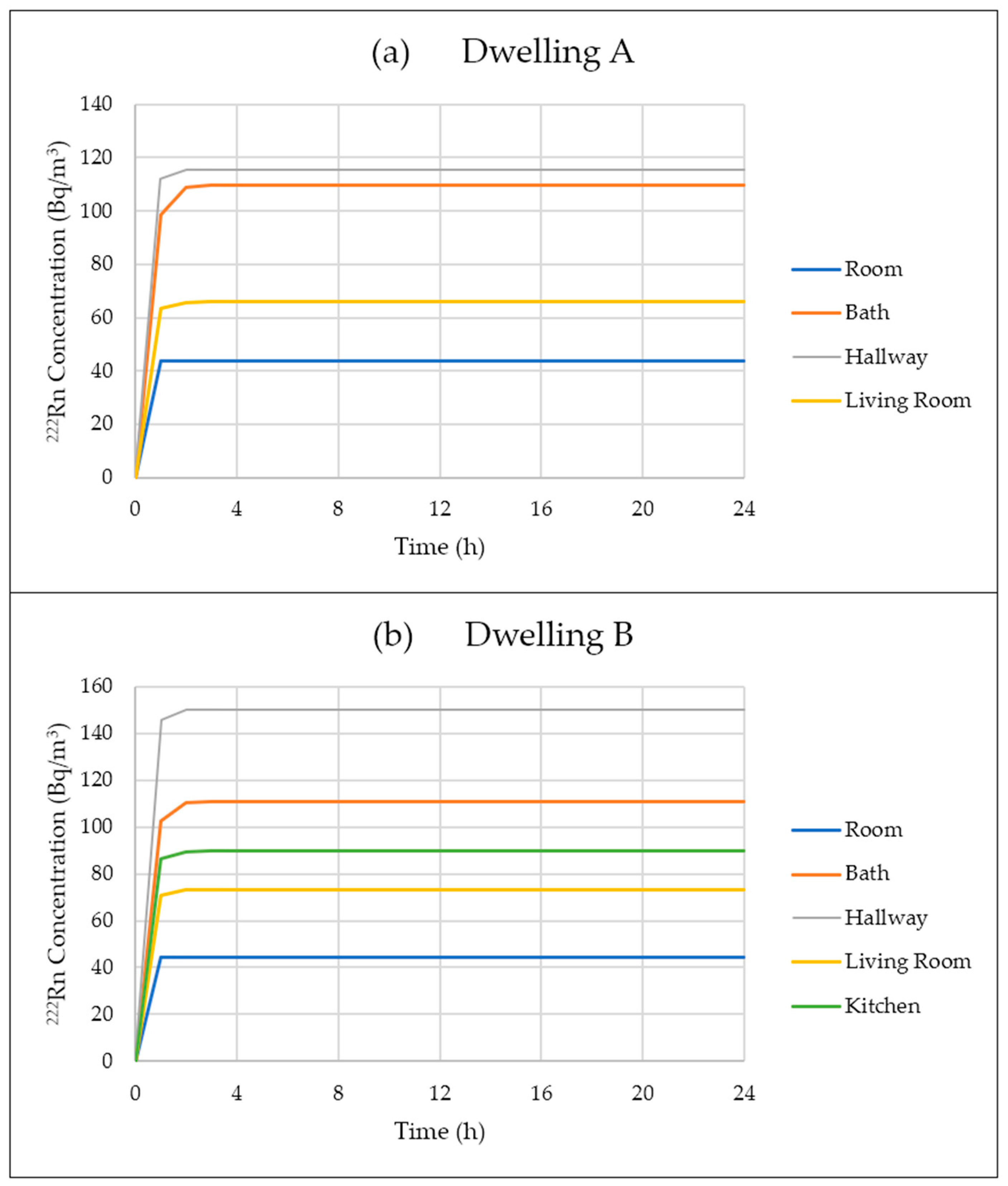
3.2. Comparison between Two Dwellings with Similar Radon Sources
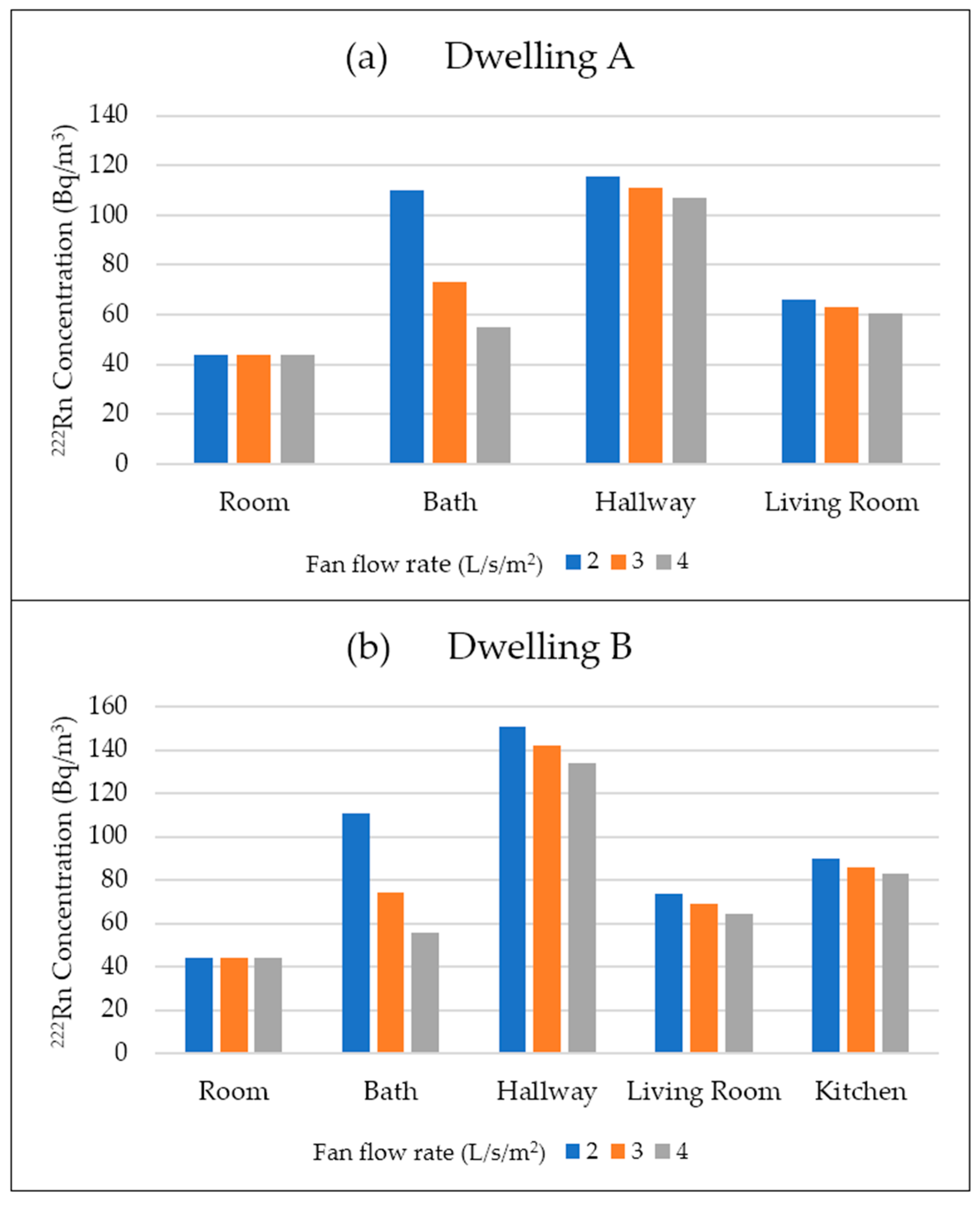
3.3. Impact of Ventilation on Radon Concentration
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation. Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation; UNSCEAR 2000 Report to the General Assembly, with Scientific Annexes; United Nations Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Stranden, E.; Berteig, L. Radon in Dwellings and Influencing Factors. Health Phys. 1980, 39, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, A.G. Effect of Indoor Radon Variability on the Duration and Interpretation of Radon Measurements; EPA Symposium on Radon and Radon Reduction Technology: Denver, CO, USA, 1988.
- European Council Directive 2013/59/Euratom of 5 December 2013 Laying down Basic Safety Standards for Protection against the Dangers Arising from Exposure to Ionising Radiation, and Repealing Directives 89/618/Euratom, 90/641/Euratom, 96/29/Euratom, 97/43/Euratom and 2003/122/Euratom. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2013/59/oj (accessed on 9 May 2018).
- IAEA Safety Standards Series No. GSR Part 3, Radiation Protection and Safety of Radiation Sources: International Basic Safety Standards, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna 2014. Available online: https://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/publications/PDF/Pub1578_web-57265295.pdf (accessed on 9 May 2018).
- Zeeb, H.; Shannoun, F.; World Health Organization. WHO Handbook on Indoor Radon: A Public Health Perspective; Zeeb, H., Shannoun, F., Eds.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dols, W.S.; Polidoro, B.J. CONTAM User Guide and Program Documentation Version 3.2; Technical Note (NIST TN)—1887; National Institute for Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Tobar, J.; Mazadiego, L.F.; Quindos-Poncela, L.S. A Comparison of Preliminary Results of Indoor Radon Behaviour between One Occupied and One Unoccupied Dwelling in Madrid, Spain. Solid State Phenom. 2015, 238, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive 2010/31/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Energy Performance of Buildings. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2010:153:0013:0035:EN:PDF (accessed on 19 May 2010).
- Derbez, M.; Berthineau, B.; Cochet, V.; Lethrosne, M.; Pignon, C.; Riberon, J.; Kirchner, S. Indoor Air Quality and Comfort in Seven Newly-Built, Energy-Efficient Houses in France. Build. Environ. 2014, 72, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quindós Poncela, L.S.; Fernández, P.L.; Gómez Arozamena, J.; Sainz, C.; Fernández, J.A.; Suarez Mahou, E.; Martin Matarranz, J.L.; Cascón, M.C. Natural gamma radiation map (MARNA) and indoor radon levels in Spain. Environ. Int. 2004, 29, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainz-Fernandez, C.; Fernandez-Villar, A.; Fuente-Merino, I.; Gutierrez-Villanueva, J.L.; Martin-Matarranz, J.L.; Garcia-Talavera, M.; Casal-Ordas, S.; Quindós-Poncela, L.S. The Spanish Indoor Radon Mapping Strategy. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2014, 162, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dols, W.S.; Walton, G.N.; Denton, K.R. CONTAMW 1.0 User Manual, NISTIR 6476; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000.
- Musser, A. Multizone Modelling as an Indoor Air Quality Design Tool. In Proceedings of the Healthy Buildings 2000 Conference, Espoo, Finland, 6–10 August 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Leprince, V.; Carrie, F.R. Comparative Analysis of Window Airing Models Proposed in prEN 16798-7 and Influence of Internal Resistances. In Proceedings of the CLIMA 2016-12th REHVA World Congress, Aalborg, Denmark, 22–25 May 2016; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Temenos, N.; Nikolopoulos, D.; Petraki, E.; Yannakopoulos, P. Modelling of Indoor Air Quality of Greek Apartments Using CONTAM (W) Software. J. Phys. Chem. Biophys. 2015, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Chauhan, R.P.; Joshi, M.; Sahoo, B.K. Modelling of Indoor Radon Concentration from Radon Exhalation Rates of Building Materials and Validation through Measurements. J. Environ. Radioact. 2014, 127, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgoni, R.; De Francesco, D.; De Bartolo, D.; Tzavidis, N. Hierarchical Modelling of Indoor Radon Concentration: How Much do Geology and Building Factors Matter? J. Environ. Radioact. 2014, 138, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
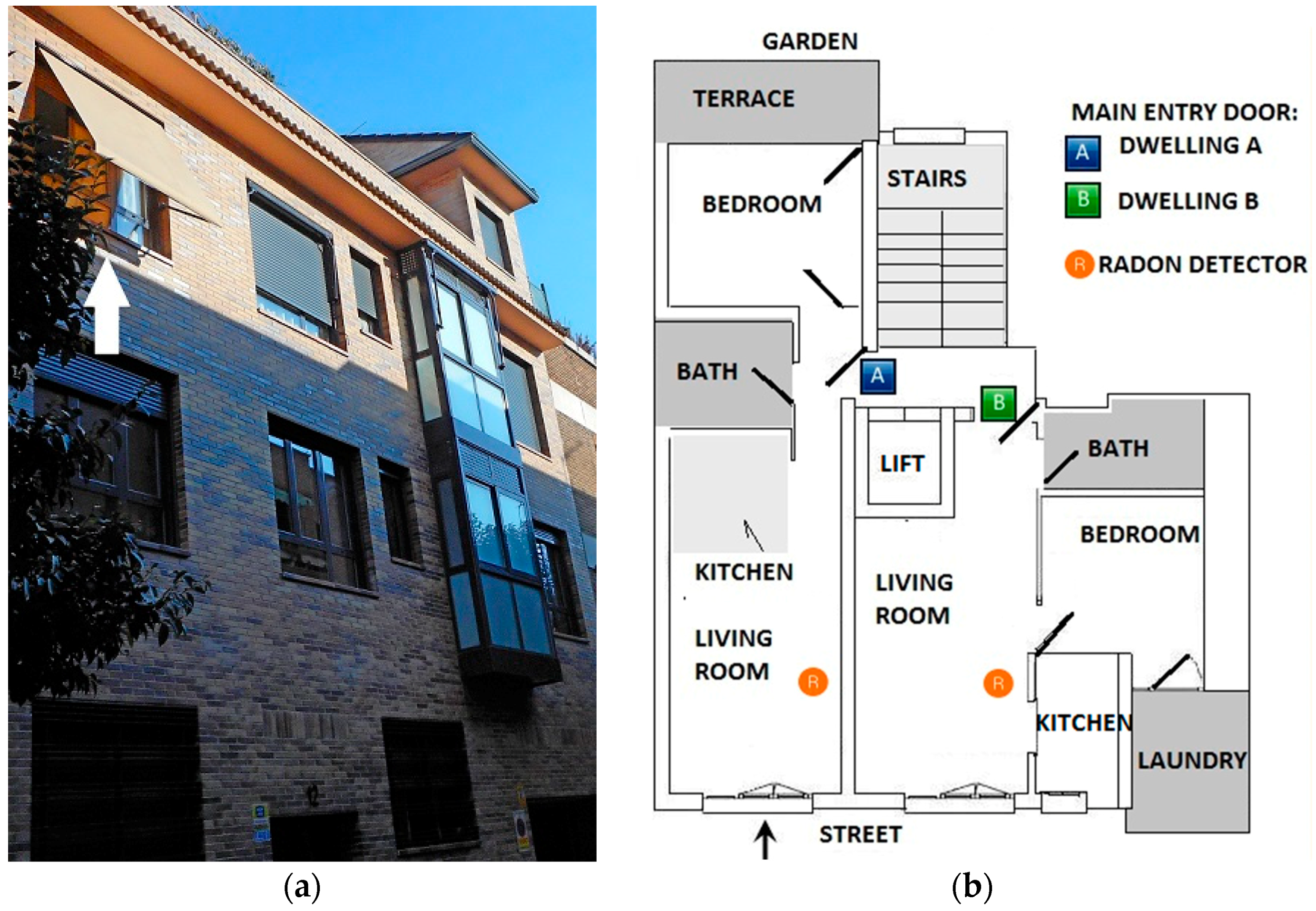
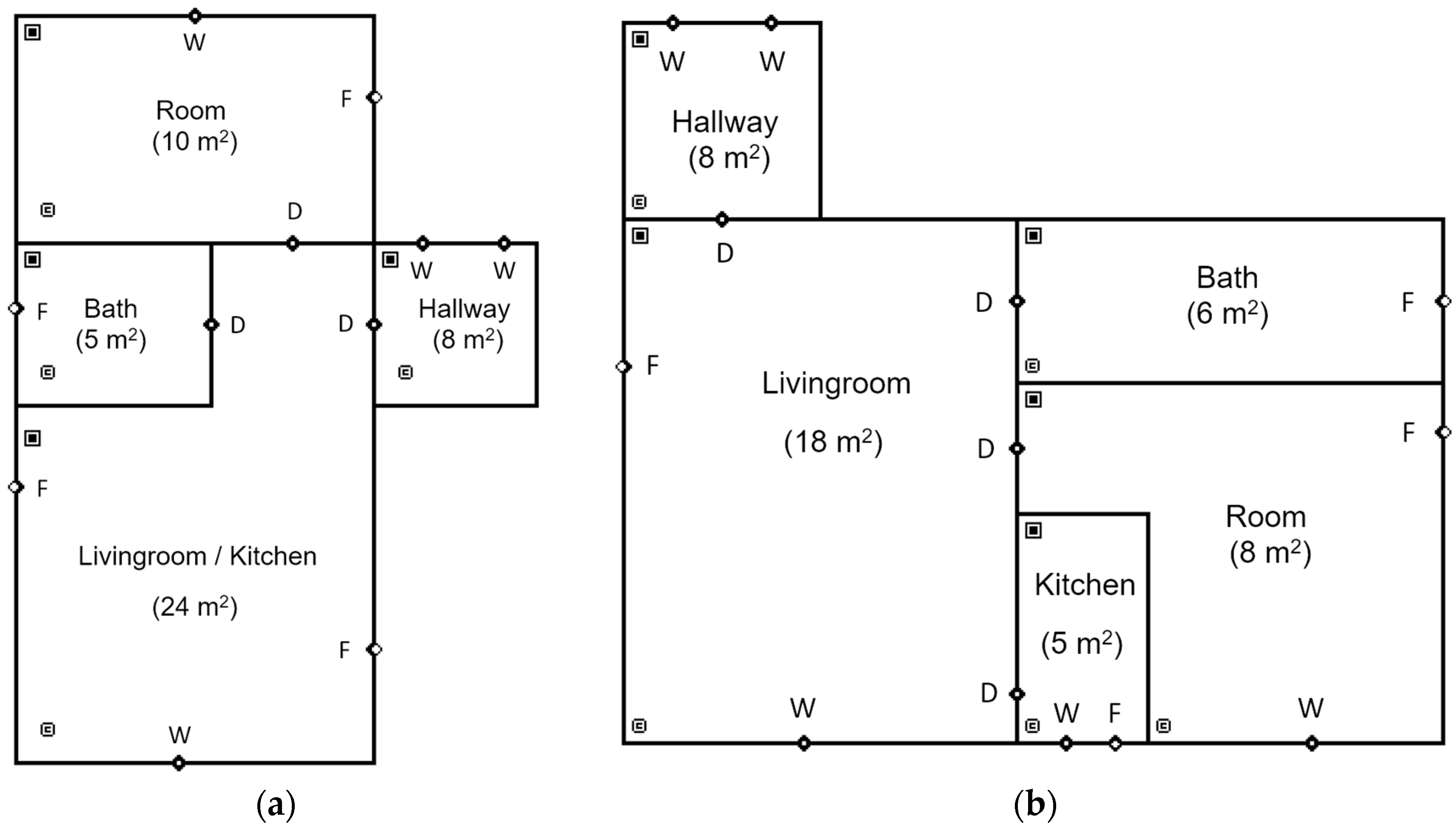
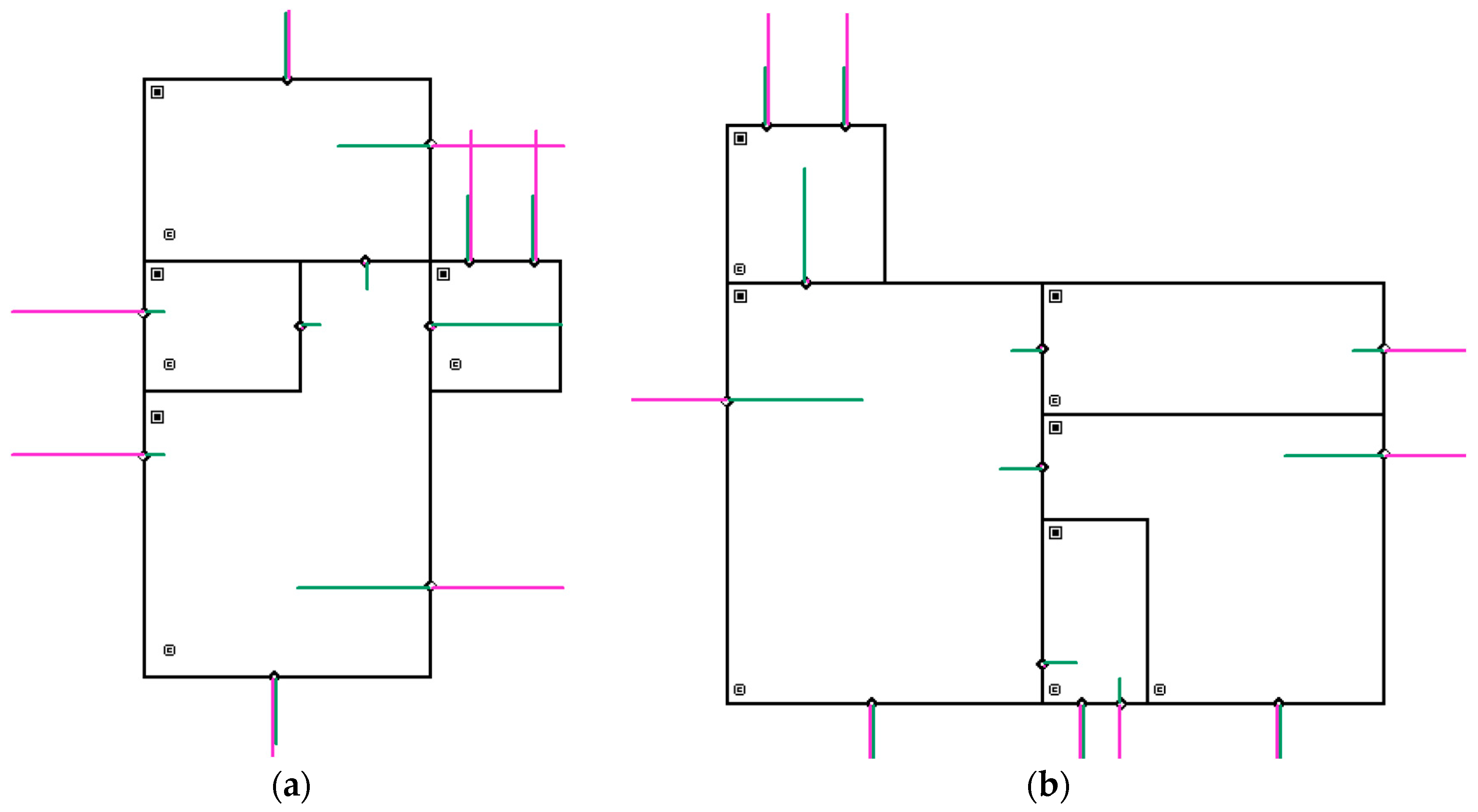
| Airflow Elements (Maximum Flow Rate (Number of Elements)) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (39 m2) | ID room | Surface (m2) | Sources (Bq/h) | Window | Door | Fan |
| Bedroom | 10 | 8000 | (1) | (1) | 50 L/s * (1) | |
| Living room (includes kitchen) | 24 | 19,200 | (1) | (1) | Kitchen: 10 L/s (1) Living room: 72 L/s (1) | |
| Bath | 5 | 4000 | (1) | (0) | 10 L/s (1) | |
| Hallway | 8 | 12,800 | (2) | (1) | (0) | |
| Bedroom | 8 | 6400 | (1) | (1) | 40 L/s (1) | |
| Living room | 18 | 14,400 | (1) | (3) | 54 L/s (1) | |
| B (37 m2) | Bath | 6 | 4800 | (1) | (0) | 12 L/s (1) |
| Kitchen | 5 | 4000 | (1) | (1) | 10 L/s (1) | |
| Hallway | 8 | 12,800 | (2) | (1) | (0) | |
| Window | Door | |
|---|---|---|
| Type of model | One-way flow using power law | |
| Formula | Orifice area data | |
| Cross-sectional data (cm2) | 5 | 80 |
| Hydraulic diameter (cm) | 2.52 | 10.09 |
| Transition Reynolds number | 30 | 30 |
| Discharge coefficient | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Flow exponent | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Room Type | Flow Rates (L/s/m2) |
|---|---|
| Kitchen/bath | 2 |
| Bedroom | 5 |
| Living room | 3 |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Tobar, J. A Comparative Study of Indoor Radon Levels between Two Similar Dwellings Using CONTAM Software . Environments 2018, 5, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5050059
García-Tobar J. A Comparative Study of Indoor Radon Levels between Two Similar Dwellings Using CONTAM Software . Environments. 2018; 5(5):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5050059
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Tobar, Javier. 2018. "A Comparative Study of Indoor Radon Levels between Two Similar Dwellings Using CONTAM Software " Environments 5, no. 5: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5050059
APA StyleGarcía-Tobar, J. (2018). A Comparative Study of Indoor Radon Levels between Two Similar Dwellings Using CONTAM Software . Environments, 5(5), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5050059





