Comparison of Geometrical Layouts for a Multi-Box Aerosol Model from a Single-Chamber Dispersion Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Model
2.1.1. Source
2.1.2. Transport and Ventilation
2.1.3. Coagulation
2.1.4. Deposition
2.1.5. Solving the General Dynamics Equation
2.2. Experimental Work
2.3. Description of Geometries Considered
Mixing and Transport
3. Results
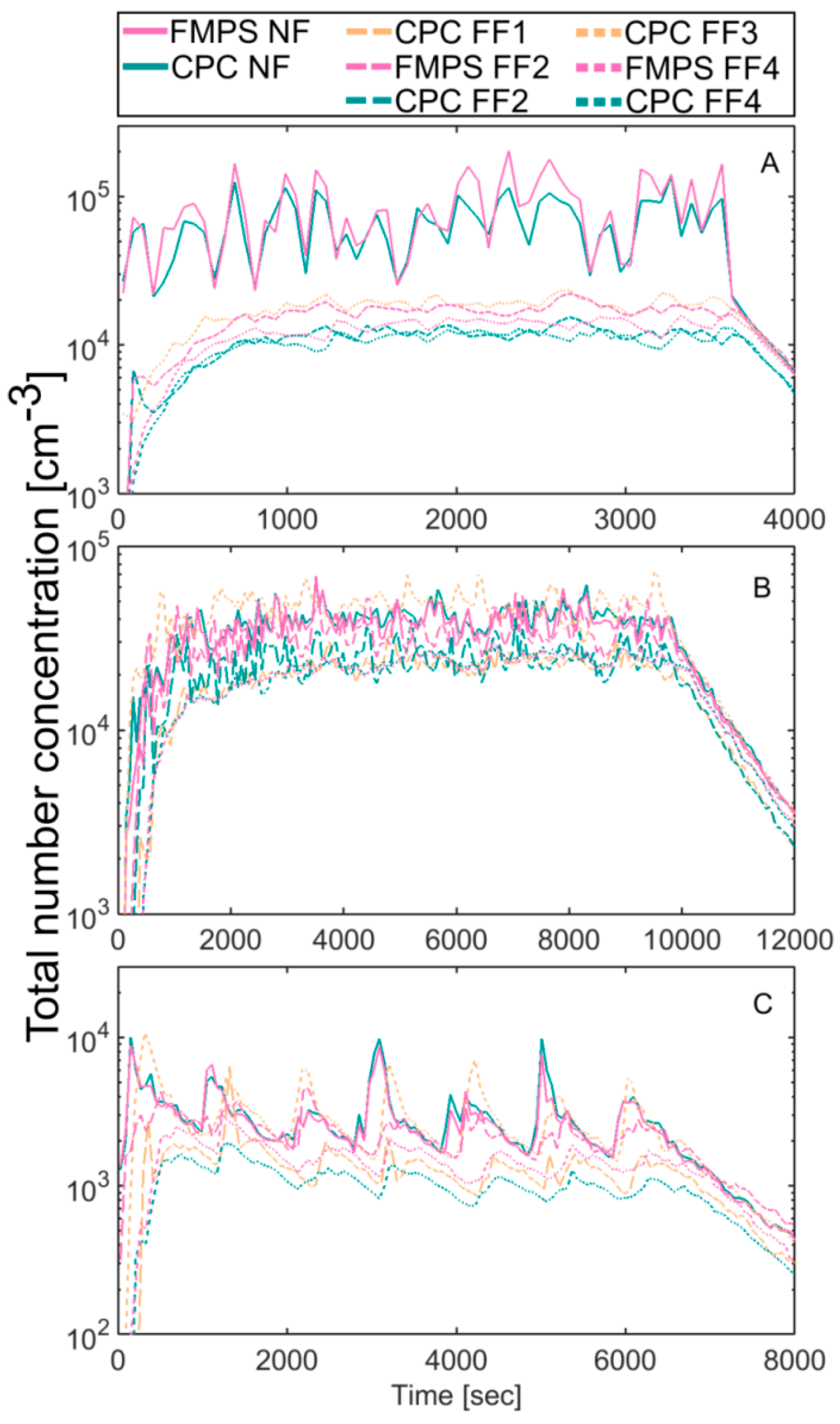
3.1. Particle Concentration Measurements
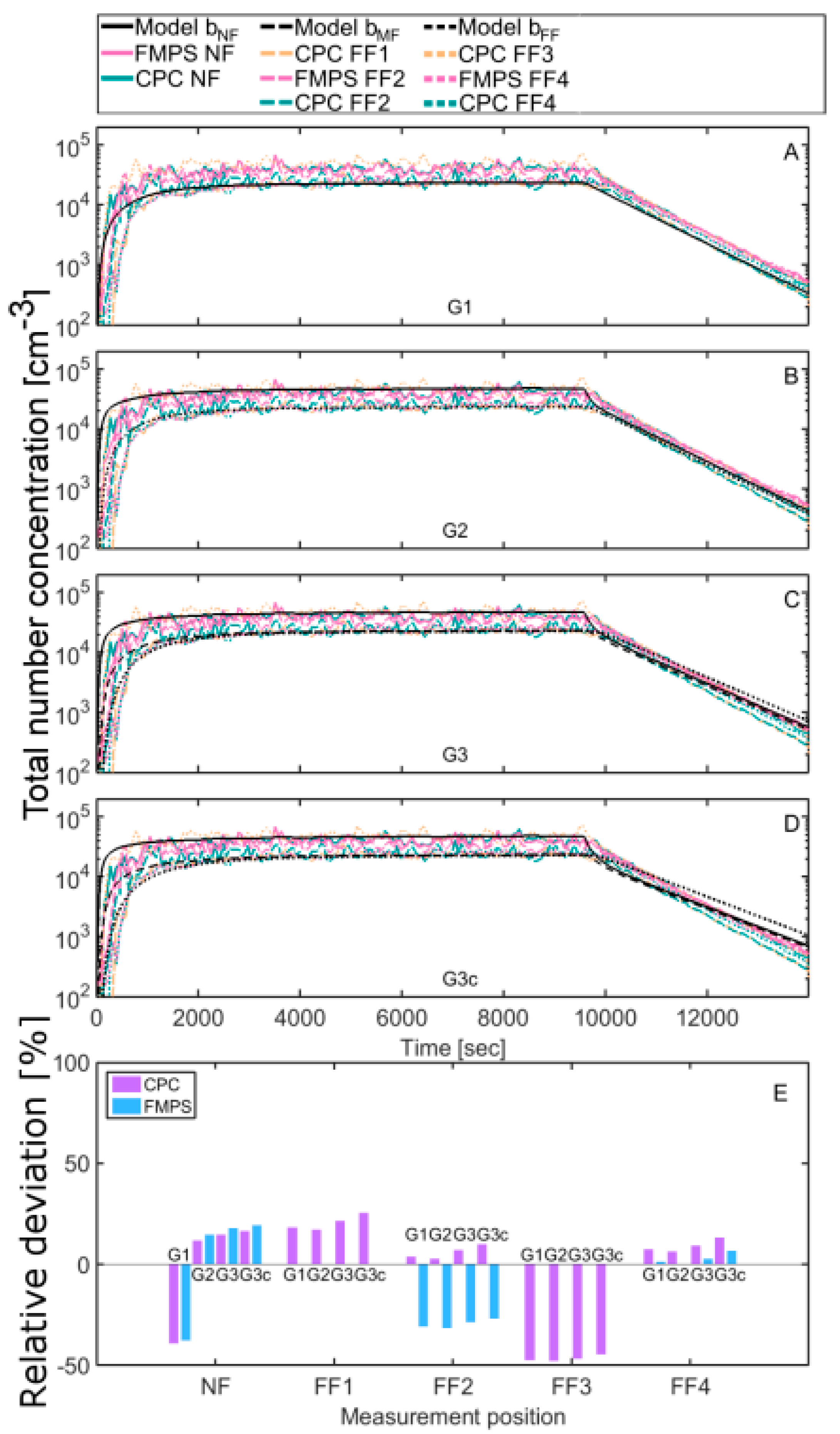
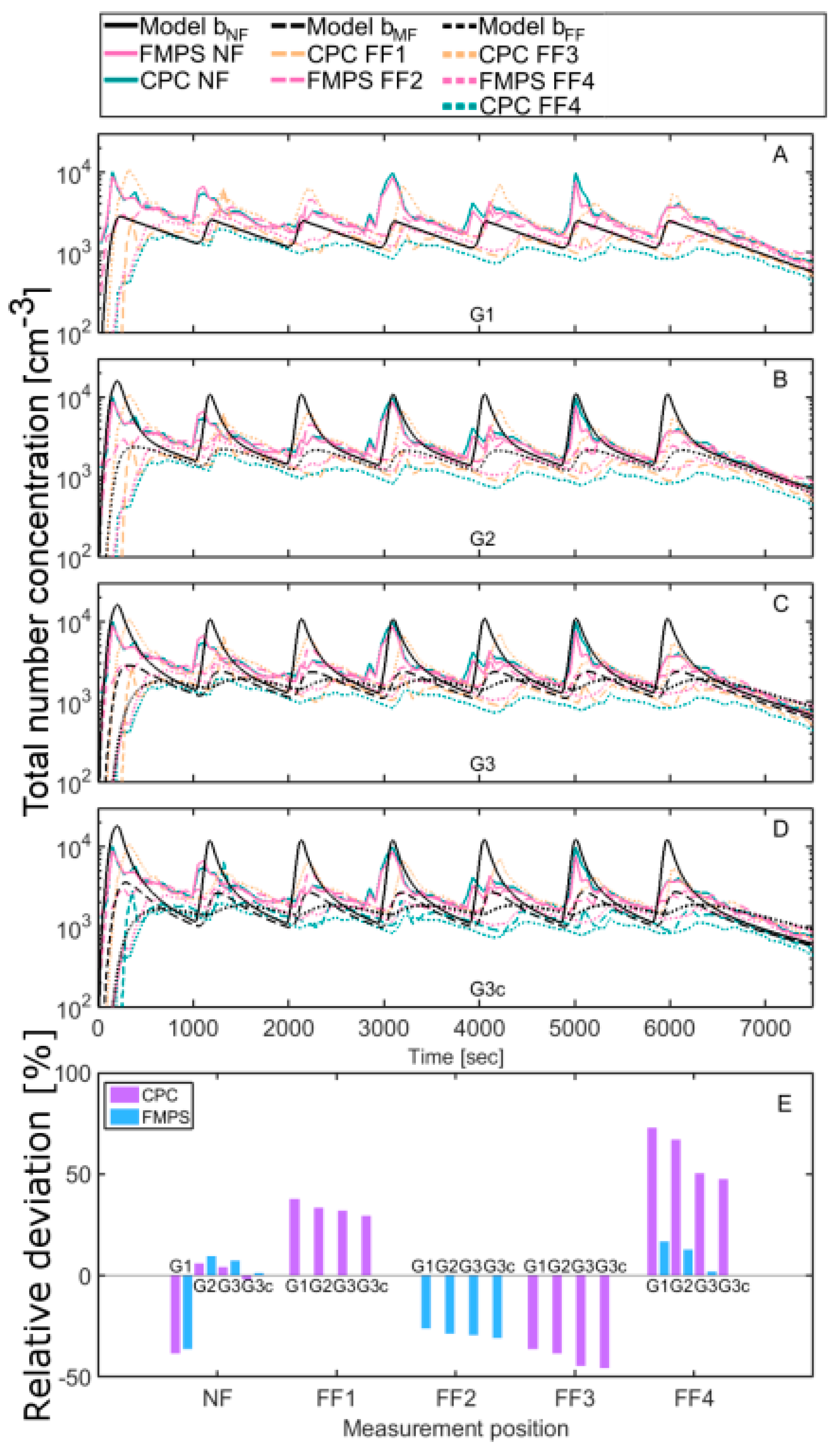
3.2. Modelled Concentrations
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with the Modelled Concentrations
4.2. Geometrical Layouts
4.3. Measurements
4.4. Outlook
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piccinno, F.; Gottschalk, F.; Seeger, S.; Nowack, B. Industrial production quantities and uses of ten engineered nanomaterials in Europe and the world. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, S.; Olveria, S.; Seeger, S. Nanotechnology in the market: Promises and realities. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 2011, 8, 592–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendren, C.; Mesnard, X.; Droge, J.; Wiesner, M. Estimating production data for five engineered nanomaterials as a basis for exposure assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2562–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, S.F.; Heggelund, L.R.; Besora, P.R.; Mackevica, A.; Boldrin, A.; Baun, A. Nanoproducts—What is actually available to European consumers? Environ. Sci. Nano 2016, 3, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koivisto, A.J.; Jensen, A.C.Ø.; Kling, K.I.; Nørgaard, A.; Brinch, A.; Christensen, F.; Jensen, K.A. Quantitative material releases from products and articles containing manufactured nanomaterials: Towards a release library. NanoImpact 2017, 5, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, P.A.; Geraci, C.L.; Murashov, V.; Kuempel, E.D.; Zumwalde, R.D.; Castranova, V.; Hoover, M.D.; Hodson, L.; Martinez, K.F. Occupational safety and health criteria for responsible development of nanotechnology. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roldin, P.; Liao, L.; Mogensen, D.; Dal Maso, M.; Rusanen, A.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Mentel, T.F.; Wildt, J.; Kleist, E.; Kiendler-Scharr, A.; et al. Modelling the contribution of biogenic volatile organic compounds to new particle formation in the Jülich plant atmosphere chamber. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 10777–10798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, M.; Lam, N.; Brant, S.; Gray, C.; Pennise, D. Modeling indoor air pollution from cookstove emissions in developing countries using a Monte Carlo single-box model. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 3237–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Banerjee, S.; Yang, R.; Lungu, C.; Ramachandran, G. Bayesian modeling of exposure and airflow using two-zone models. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2009, 53, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazaroff, W.W.; Cass, G.R. Mathematical modeling of indoor aerosol dynamics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1989, 23, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Niu, J.; Gao, N. Spatial distribution of human respiratory droplet residuals and exposure risk for the co-occupant under different ventilation methods. HVAC&R Res. 2011, 17, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.S. Condensation detection and diffusion size separation techniques. In Aerosol Measurements: Principles, Techniques and Applications; Baron, P.A., Willeke, K., Eds.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 569–601. [Google Scholar]
- Drivas, P.J.; Valberg, P.A.; Murphy, B.L.; Wilson, R. Modeling indoor air exposure from short-term point source releases. Indoor Air 1996, 6, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.Y.H.; Wan, M.P. A study of the dispersion of expiratory aerosols in unidirectional downward and ceiling-return type airflows using a multiphase approach. Indoor Air 2006, 16, 296–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, N.; Niu, J. Modeling particle dispersion and deposition in indoor environments. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 3862–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, W.; Lin, C.-H.; Chen, Q. Comparing the Markov chain model with the Eulerian and Lagrangian models for indoor transient particle transport simulations. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayjock, M.A.; Armstrong, T.; Taylor, M. The Daubert standard as applied to exposure assessment modeling using the two-zone (NF/FF) model estimation of indoor air breathing zone concentration as an example. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2011, 8, D114–D122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtaw, E.J.; Pandian, M.D.; Nelson, D.R.; Behar, J.V. Modeling indoor air concentrations near emission sources in imperfectly mixed rooms. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1996, 46, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicas, M. Estimating exposure intensity in an imperfectly mixed room. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1996, 57, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherrie, J.W.; Schneider, T. Validation of a new method for structured subjective assessment of past concentrations. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 1999, 43, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, T.; Korhonen, H.; Herrmann, E.; Hämeri, K.; Lehtinen, K.E.J.; Kulmala, M. Emission rates due to indoor activities: Indoor aerosol model development, evaluation, and applications. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1111–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mølgaard, B.; Viitanen, A.K.; Kangas, A.; Huhtiniemi, M.; Larsen, S.T.; Vanhala, E.; Hussein, T.; Boor, B.E.; Hämeri, K.; Koivisto, A.J. Exposure to airborne particles and volatile organic compounds from polyurethane molding, spray painting. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 3756–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherrie, J.W.; MacCalman, L.; Fransman, W.; Tielemans, E.; Tischer, M.; Van Tongeren, M. Revisiting the effect of room size and general ventilation on the relationship between near- and far-field air concentrations. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2011, 55, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganser, G.H.; Hewett, P. Models for nearly every occasion: Part II—Two box models. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2017, 14, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koivisto, A.J.; Jensen, A.C.Ø.; Levin, M.; Kling, K.I.; Dal Maso, M.; Nielsen, S.H.; Jensen, K.A.; Koponen, I.K. Testing the near field/far field model performance for prediction of particulate matter emissions in a paint factory. Environ. Sci. Processes Impacts 2015, 17, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- ECETOC Targeted Risk Assessment; Technical Report No. 93; European Centre for Ecotoxicology and Toxicology of Chemicals: Brussels, Belgium, 2004.
- Marquart, H.; Heussen, H.; Le Feber, M.; Noy, D.; Tielemans, E.; Schinkel, J.; West, J.; Van Der Schaaf, D. ‘Stoffenmanager’, a web-based control banding tool using an exposure process model. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2008, 52, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fransman, W.; Cherrie, J.; van Tongeren, M.; Schneider, T.; Tischer, M.; Schinkel, J.; Kromhout, H.; Warren, N.; Goede, H.; Tielemans, E. Advanced Reach Tool (ART): Development of the Mechanistic Model. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2011, 55, 957–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, A.C.Ø.; Levin, M.; Koivisto, A.J.; Kling, K.I.; Saber, A.T.; Koponen, I.K. Exposure assessment of particulate matter from abrasive treatment of carbon and glass fibre-reinforced epoxy-composites—Two case studies. Aerosol. Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 1906–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, M.Z. Fundamentals of Atmospheric Modeling, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, N.A. The Mechanics of Aerosols; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK; The Macmillan Company: New York, NY, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, A.C.K.; Nazaroff, W.W. Modeling indoor particle deposition from turbulent flow onto smooth surfaces. J. Aerosol Sci. 2000, 31, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Zhao, B. Deposition of Indoor Airborne Particles onto Human Body Surfaces: A Modeling Analysis and Manikin-Based Experimental Study. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shampine, L.F.; Reichelt, M.W. The MATLAB ODE Suite. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 1997, 18, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormand, J.R.; Prince, P.J. A family of embedded Runge-Kutta formulae. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1980, 6, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltelli, A.; Ratto, M.; Andres, T.; Campolongo, F.; Cariboni, J.; Gatelli, D.; Gatelli, D.; Saisana, M.; Tarantola, S. Global Sensitivity Analysis. The Primer; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: West Sussex, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer-Plath, A.; Koponen, I.K.; Jensen, A.C.Ø.; Koivisto, A.J.; Belut, E.; Sánchez, A.; van Tongeren, M.; MacCalman, L.; Tuinman, I.; Fransman, W.; et al. NANoREG Report D3.4. Available online: http://www.rivm.nl/en/About_RIVM/International_Affairs/International_Projects/Completed/NANoREG/deliverables/NANoREG_D3_04_DR_Improved_data_for_the_modelling_of_the_exposure_to_MNMs.pdf (accessed on 8 February 2018).
- Levin, M.; Gudmundsson, A.; Pagels, J.H.; Fierz, M.; Mølhave, K.; Löndahl, J.; Jensen, K.A.; Koponen, I.K. Limitations in the Use of Unipolar Charging for Electrical Mobility Sizing Instruments: A Study of the Fast Mobility Particle Sizer. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelzer, J.; Schumacher, C. Nano Exposure & Contextual Information Database. Available online: http://www.perosh.eu/research-projects/perosh-projects/necid/ (accessed on 8 February 2018).
- CaLIBRAte Project, EU Horizon 2020 Grant Agreement 686239. Available online: www.nanocalibrate.eu (accessed on 8 February 2018).
- Koponen, I.K.; Koivisto, A.J.; Jensen, K.A. Worker Exposure and High Time-Resolution Analyses of Process-Related Submicrometre Particle Concentrations at Mixing Stations in Two Paint Factories. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2015, 59, 749–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koivisto, A.J.; Palomäki, J.E.; Viitanen, A.-K.; Siivola, K.M.; Koponen, I.K.; Yu, M.; Kanerva, T.S.; Norppa, H.; Alenius, H.T.; Hussein, T.; et al. Range-Finding Risk Assessment of Inhalation Exposure to Nanodiamonds in a Laboratory Environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 5382–5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koivisto, A.J.; Brostrøm, A.; Kling, K.I.; Fonseca, A.S.; Redant, E.; Andrade, F.; Hougaard, K.S.; Krepker, M.; Prinz, O.S.; Segal, E.; et al. Occupational exposure during handling and loading of halloysite nanotubes—A case study of counting nanofibers. Nanoimpact 2018. accepted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivisto, A.J.; Kling, K.I.; Fonseca, A.S.; Bluhme, A.B.; Moreman, M.; Yu, M.; Costa, A.L.; Giovanni, B.; Ortelli, S.; Fransman, W. Dip coating of air purifier ceramic honeycombs with photocatalytic TiO2 nanoparticles: A case study for occupational exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, A.S.; Viitanen, A.-K.; Koivisto, A.J.; Kangas, A.; Huhtiniemi, M.; Hussein, T.; Vanhala, E.; Viana, M.; Querol, X.; Hämeri, K. Characterization of exposure to carbon nanotubes in an industrial setting. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2015, 59, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, A.S.; Kuijpers, E.; Kling, K.I.; Levin, M.; Koivisto, A.J.; Nielsen, S.H.; Fransman, W.; Fedutik, Y.; Jensen, K.A.; Koponen, I.K. Particle release and control of worker exposure during laboratory-scale synthesis, handling and simulated spills of manufactured nanomaterials in fume-hoods. J. Nanopart. Res. 2018, 20, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| bNF | bMF | bFF | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | V [m3] | 80.7 | - | - |
| AU [m2] | 30.4 | - | - | |
| AD [m2] | 30.4 | - | - | |
| AV [m2] | 59.2 | - | - | |
 | V [m3] | 8 | - | 72.7 |
| AU [m2] | 0 | - | 30.4 | |
| AD [m2] | 0 | - | 30.4 | |
| AV [m2] | 0 | - | 59.2 | |
 | V [m3] | 8 | 45.8 | 26.9 |
| AU [m2] | 0 | 20.3 | 10.1 | |
| AD [m2] | 0 | 20.3 | 10.1 | |
| AV [m2] | 0 | 35.3 | 23.9 | |
 | V [m3] | 6.4 | 34.7 | 39.6 |
| AU [m2] | 2.4 | 13.1 | 14.9 | |
| AD [m2] | 2.4 | 13.1 | 14.9 | |
| AV [m2] | 0 | 20.9 | 38.3 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jensen, A.C.Ø.; Dal Maso, M.; Koivisto, A.J.; Belut, E.; Meyer-Plath, A.; Van Tongeren, M.; Sánchez Jiménez, A.; Tuinman, I.; Domat, M.; Toftum, J.; et al. Comparison of Geometrical Layouts for a Multi-Box Aerosol Model from a Single-Chamber Dispersion Study. Environments 2018, 5, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5050052
Jensen ACØ, Dal Maso M, Koivisto AJ, Belut E, Meyer-Plath A, Van Tongeren M, Sánchez Jiménez A, Tuinman I, Domat M, Toftum J, et al. Comparison of Geometrical Layouts for a Multi-Box Aerosol Model from a Single-Chamber Dispersion Study. Environments. 2018; 5(5):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5050052
Chicago/Turabian StyleJensen, Alexander C. Ø., Miikka Dal Maso, Antti J. Koivisto, Emmanuel Belut, Asmus Meyer-Plath, Martie Van Tongeren, Araceli Sánchez Jiménez, Ilse Tuinman, Maida Domat, Jørn Toftum, and et al. 2018. "Comparison of Geometrical Layouts for a Multi-Box Aerosol Model from a Single-Chamber Dispersion Study" Environments 5, no. 5: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5050052
APA StyleJensen, A. C. Ø., Dal Maso, M., Koivisto, A. J., Belut, E., Meyer-Plath, A., Van Tongeren, M., Sánchez Jiménez, A., Tuinman, I., Domat, M., Toftum, J., & Koponen, I. K. (2018). Comparison of Geometrical Layouts for a Multi-Box Aerosol Model from a Single-Chamber Dispersion Study. Environments, 5(5), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5050052







