Greenhouse Gas Emission Assessment from Electricity Production in the Czech Republic
Abstract
1. Introduction
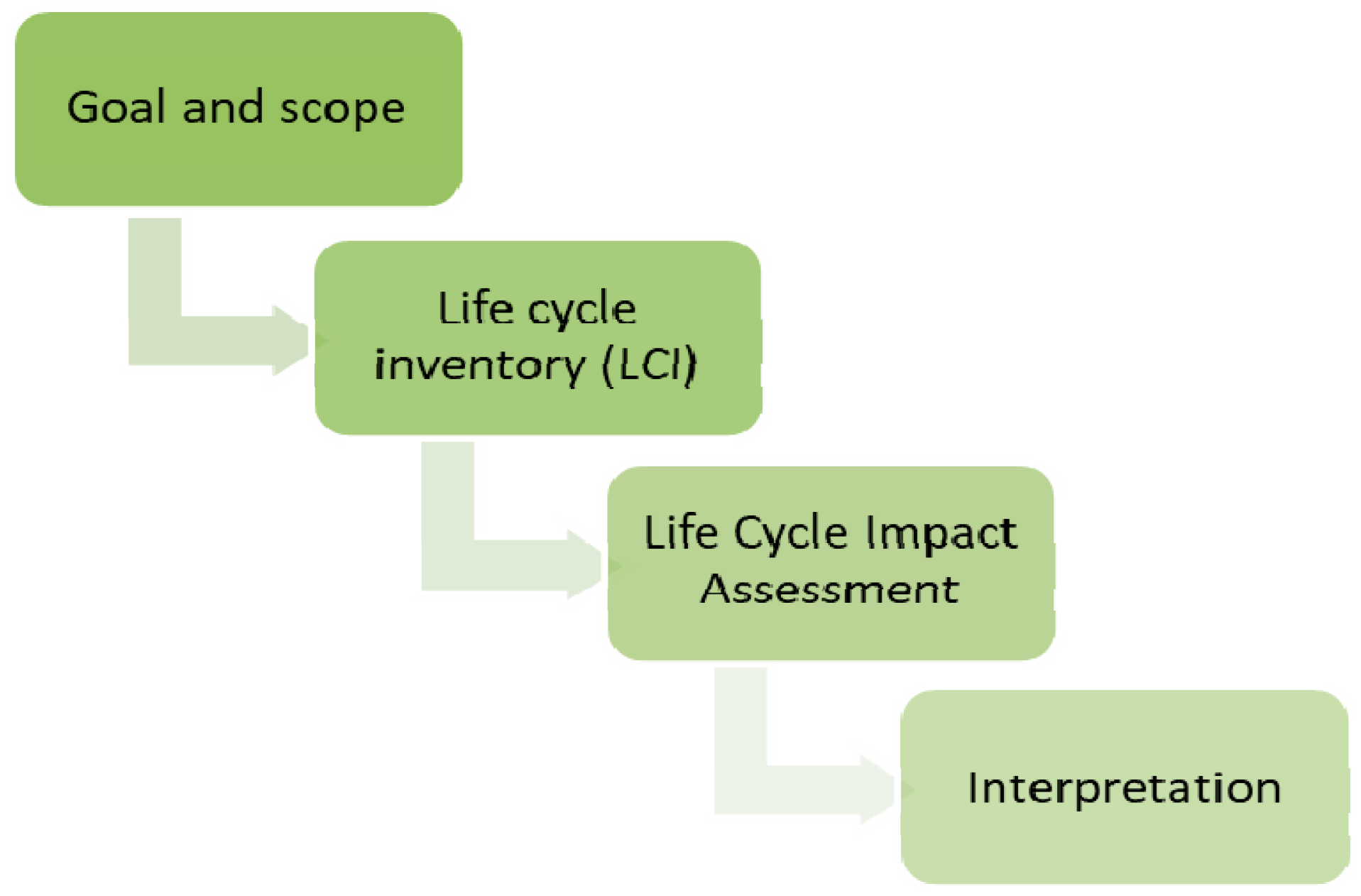
2. Materials and Methods
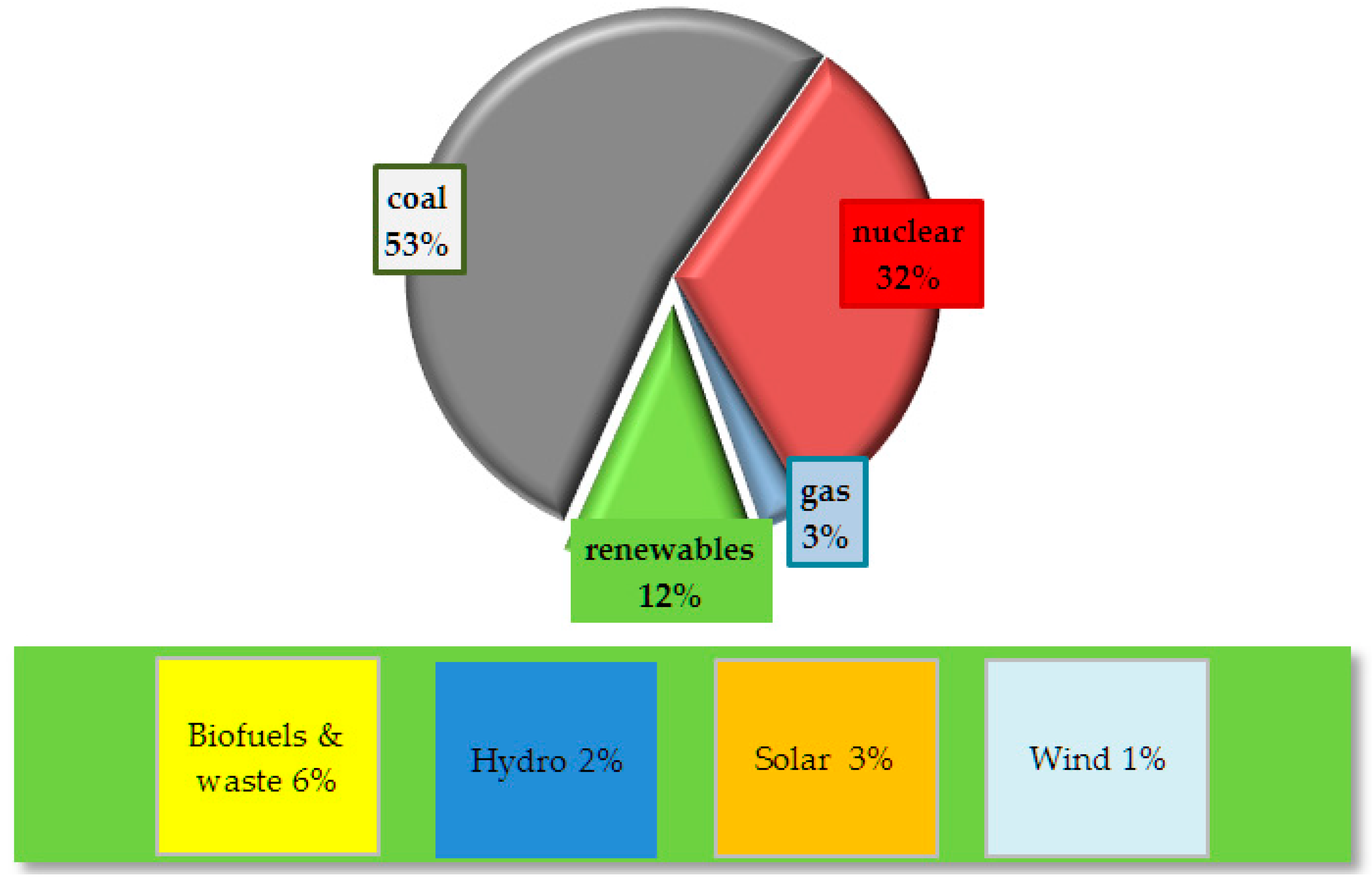
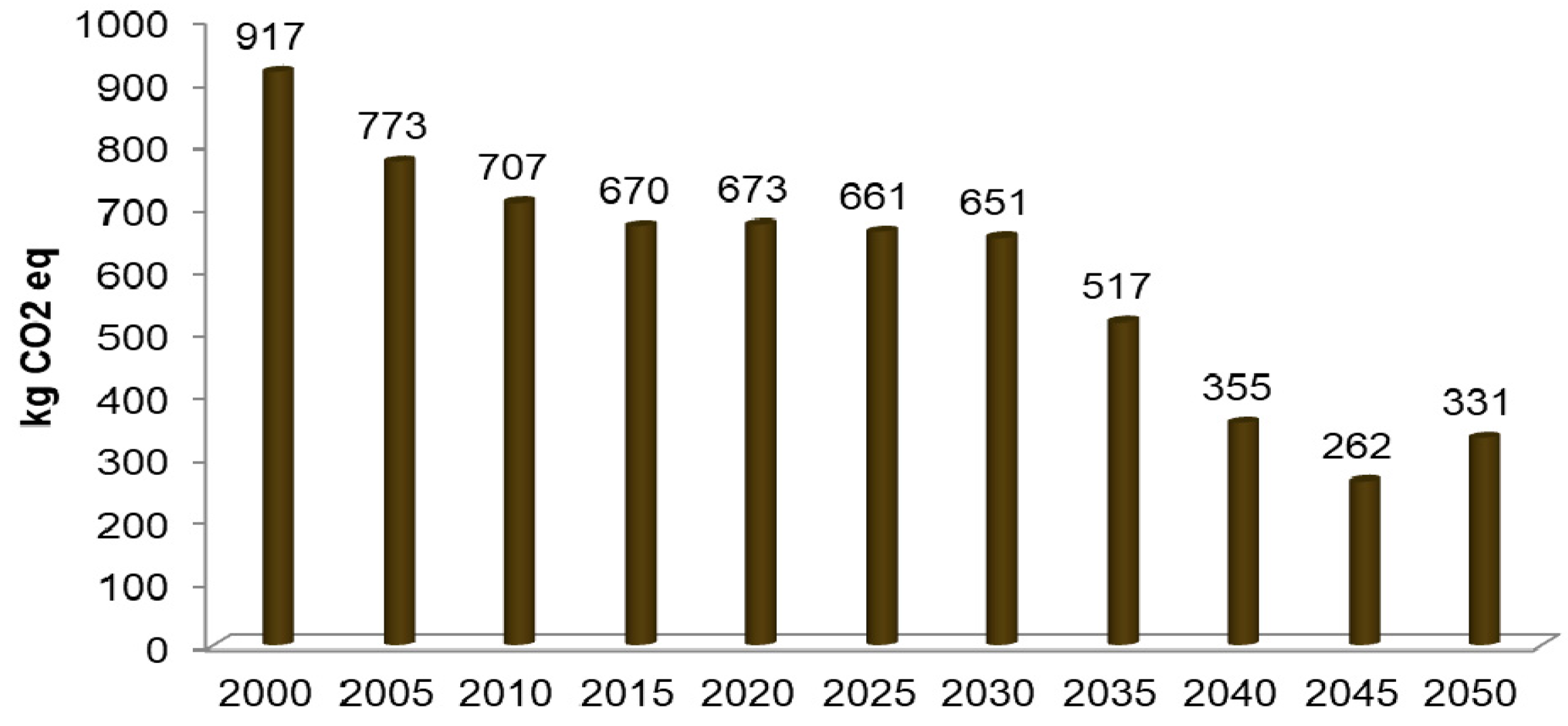
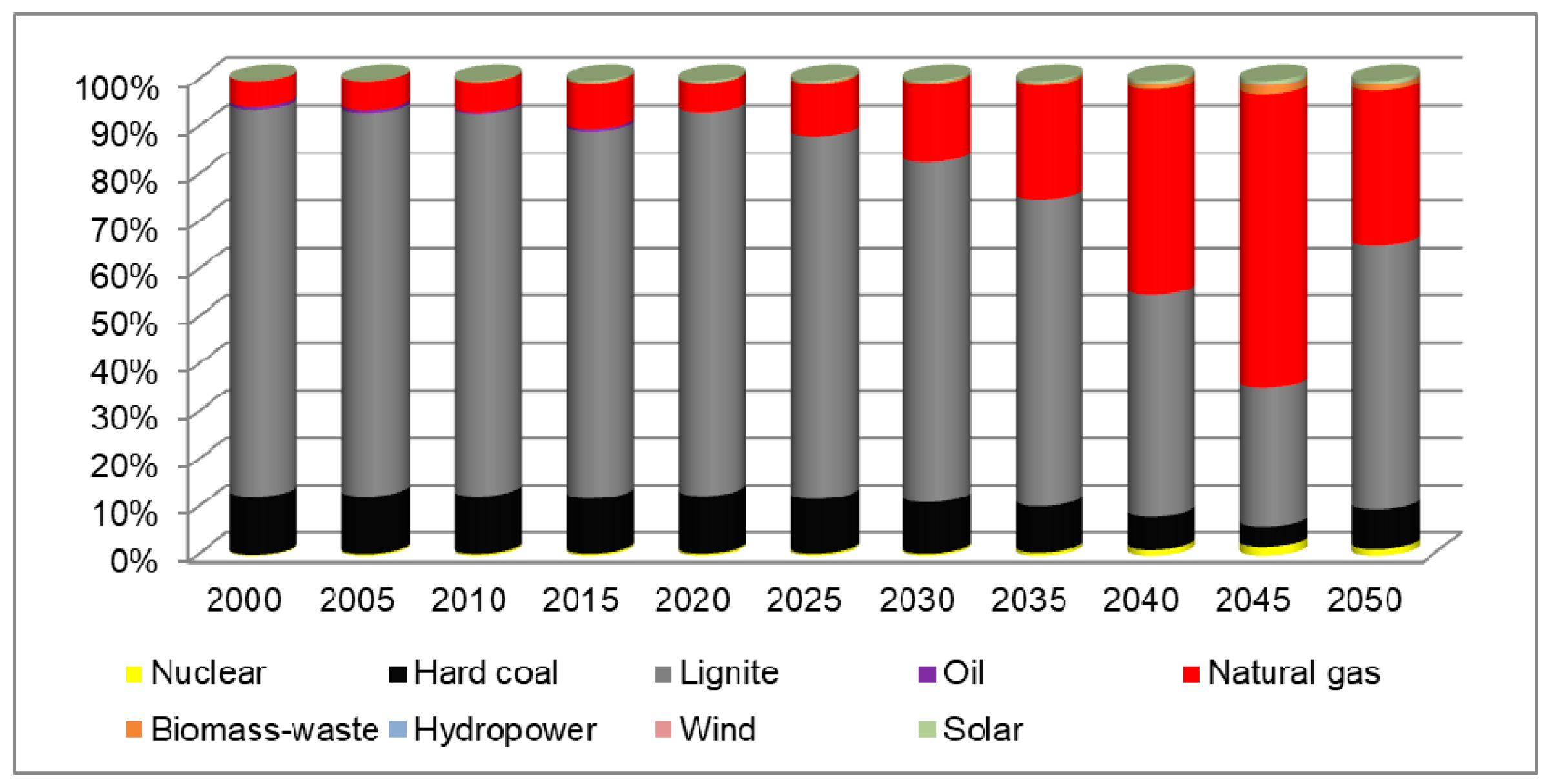
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weldu, Y.W.; Assefa, G. The search for most cost-effective way of achieving environmental sustainability status in electricity generation: Environmental life cycle cost analysis of energy scenarios. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 2296–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astudillo, M.F. Life cycle inventories of electricity supply through the lens of data quality: Exploring challenges and opportunities. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2017, 22, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treyer, K.; Bauer, C. Life cycle inventories of electricity generation and power supply in version 3 of the ecoinvent database—Part II: Electricity markets. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Dehwah, A.H.A.; Ashraf, F.; Khan, H.S.; Shaukat, M.M.; Hassan, M.T. Life Cycle Assessment of a Three-Bedroom House in Saudi Arabia. Environments 2017, 4, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raugei, M.; Leccisi, E. A comprehensive assessment of the energy performance of the full range of electricity generation technologies deployed in the United Kingdom. Energy Policy 2016, 9, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Václavík, V.; Valíček, J.; Dvorský, T.; Hryniewicz, T.; Rokosz, K.; Harničárová, M.; Kušnerová, M.; Daxner, J.; Bendová, M. A method of utilization of polyurethane after the end of its life cycle. Rocznik Ochrony Środowiska 2012, 14, 96–106. [Google Scholar]
- Dvorský, T.; Václavík, V.; Šimíček, V.; Břenek, A. Research of the Use of Waste Rigid Polyurethane Foam in the Segment of Lightweight Concretes. Inzynieria Mineralna 2015, 36, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Břenek, A.; Öchsner, A.; Václavík, V.; Altenbach, H.; Dvorský, T.; Daxner, J.; Dirner, V.; Bendová, M.; Harničárová, M.; Valíček, J. Capillary Active Insulations Based on Waste Calcium Silicates. Adv. Struct. Mater. 2015, 70, 177–188. [Google Scholar]
- Günkaya, Z.; Özdemir, A.; Özkan, A.; Banar, M. Environmental Performance of Electricity Generation Based on Resources: A Life Cycle Assessment Case Study in Turkey. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, A.; Espinosa, N. Environmental impacts of electricity generation at global, regional and national scales in 1980–2011: What can we learn for future energy planning? Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.; Yan, X.; Zhang, X. Life-cycle energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions for electricity generation and supply in China. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, R.; Marques, P.; Freire, F. Life-cycle assessment of electricity in Portugal. Appl. Energy 2014, 134, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamford, L.; Azapagic, A. Life cycle sustainability assessment of UK electricity scenarios to 2070. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2014, 23, 194–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiu, N. Life cycle inventory study of the electrical energy production in Romania. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2007, 12, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, M.; Gheewala, S.H. Environmental assessment of electricity production in Tanzania. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2012, 16, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoyo-Castelazo, E.; Gujba, H.; Azapagic, A. Life cycle assessment of electricity generation in Mexico. Energy 2011, 36, 1488–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizmohun, R.; Ramjeawon, T.; Azapagic, A. Life cycle assessment of electricity generation in Mauritius. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 16, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Gilbert, P.; Raugei, M.; Mander, S.; Leccisi, E. An approach to prospective consequential life cycle assessment and net energy analysis of distributed electricity generation. Energy Policy 2017, 100, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hondo, H. Life cycle GHG emission analysis of power generation systems: Japanese case. Energy 2005, 30, 2042–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, R.; Leong, K.C.; Osman, R.; Ho, H.K. Life cycle energy, emissions and cost inventory of power generation technologies in Singapore. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2007, 11, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantin, V.; Giuliano, A.; Manfredi, M.; Ottaviano, G.; Stefanova, M.; Masoni, P. Environmental assessment of electricity generation from an Italian anaerobic digestion plant. Biomass Bioenergy 2015, 83, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasini-Montenegro, C.; Santoyo-Castelazo, E.; Gujba, H.; Romero, R.J.; Santoyo, E. Life cycle assessment of geothermal power generation technologies: An updated review. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 114, 1119–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turconi, R.; O’Dwyer, C.; Flynn, D.; Astrup, T. Emissions from cycling of thermal power plants in electricity systems with high penetration of wind power: Life cycle assessment for Ireland. Appl. Energy 2014, 131, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehtiwesh, I.A.S.; Coelho, M.C.; Sousa, A.C.M. Exergetic and environmental life cycle assessment analysis of concentrated solar power plants. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 56, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peric, M.; Komatina, M.; Bugarski, B.; Antonijevic, D. Best Practices of Biomass Energy Life Cycle Assessment and Possible Applications in Serbia. Croat. J. For. Eng. 2016, 37, 375–390. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, H.M.; Bergman, R. Cradle-to-grave life cycle assessment of syngas electricity from woody biomass residues. Wood Fiber Sci. 2017, 49, 177–192. [Google Scholar]
- Honus, S.; Kumagai, S.; Němček, O.; Yoshioka, T. Replacing conventional fuels in USA, Europe, and UK with plastic pyrolysis gases—Part I: Experiments and graphical interchangeability methods. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 126, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honus, S.; Kumagai, S.; Yoshioka, T. Replacing conventional fuels in USA, Europe, and UK with plastic pyrolysis gases—Part II: Multi-index interchangeability methods. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 126, 1128–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Cen, K. Up-to-date life cycle assessment and comparison study of clean coal power generation technologies in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 39, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchart-Korol, D.; Korol, J.; Czaplicka-Kolarz, K. Life cycle assessment of heat production from underground coal gasification. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2016, 21, 1391–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyder, Z.; Ripepi, N.S.; Karmis, M.E. A life cycle comparison of greenhouse emissions for power generation from coal mining and underground coal gasification. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2016, 21, 515–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koci, V.; Trecakova, T. Mixed municipal waste management in the Czech Republic from the point of view of the LCA method. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2011, 16, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luňáčková, P.; Průša, J.; Janda, K. The merit order effect of Czech photovoltaic plants. Energy Policy 2017, 106, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Europe Commission. EU Reference Scenario 2016—Energy, Transport and GHG Emissions—Trends to 2050; The European Commission Report; Europe Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO). 14044:2006—Environmental Management. Life Cycle Assessment. Requirements and Guidelines. Available online: https://www.saiglobal.com/pdftemp/previews/osh/iso/updates2006/wk26/iso_14044-2006.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2006).
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC Fifth Assessment Report. The Physical Science Basis. 2007. Available online: http://www.ipcc.ch (accessed on 15 November 2017).
- Energy Policies of IEA Countries—Czech Republic 2016. Review The International Energy Agency. Available online: http://www.iea.org (accessed on 8 November 2017).
- The Voice of Coal in Europe. Available online: https://euracoal.eu/info/country-profiles/czech-republic/ (accessed on 8 January 2018).
- State Energy Policy of the Czech Republic. Available online: https://www.mzp.cz/C125750E003B698B/en/climate_energy/$FILE/OEOK-State_Energy_Policy-20160310.pdf (accessed on 24 November 2017).
- Ministry of Agriculture of the Czech Republic. Action Plan for Biomass in the Czech Republic for the Period 2012–2020; Ministry of Agriculture: Prague, Czech Republic, 2016.
- Czech Republic—Energy System Overview. Available online: http://www.iea.org/media/countries/CzechRepublic.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2017).
| Year | Total | Nuclear | Hard Coal | Lignite | Oil | Natural Gas | Biomass Waste | Hydro | Wind | Solar |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 917 | 1.45 | 112.69 | 746.98 | 6.15 | 48.97 | 0.43 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 2005 | 773 | 2.35 | 94.15 | 624.03 | 4.79 | 47.01 | 0.53 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 2010 | 707 | 2.56 | 86.02 | 570.10 | 2.24 | 44.14 | 1.50 | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.62 |
| 2015 | 670 | 2.62 | 77.99 | 516.98 | 3.39 | 65.17 | 1.58 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 2.25 |
| 2020 | 673 | 2.69 | 81.97 | 543.32 | 0.00 | 41.13 | 0.80 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 2.39 |
| 2025 | 661 | 2.58 | 76.08 | 504.22 | 0.00 | 73.27 | 1.95 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 2.33 |
| 2030 | 651 | 2.51 | 70.36 | 466.33 | 0.00 | 107.05 | 2.50 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 2.28 |
| 2035 | 517 | 3.30 | 50.23 | 332.96 | 0.00 | 124.62 | 2.98 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 2.27 |
| 2040 | 355 | 4.12 | 25.02 | 165.80 | 0.00 | 153.58 | 4.27 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 2.28 |
| 2045 | 262 | 4.53 | 11.57 | 76.65 | 0.00 | 161.37 | 5.14 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 2.22 |
| 2050 | 331 | 4.22 | 27.81 | 184.39 | 0.00 | 107.67 | 4.43 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 2.54 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jursová, S.; Burchart-Korol, D.; Pustějovská, P.; Korol, J.; Blaut, A. Greenhouse Gas Emission Assessment from Electricity Production in the Czech Republic. Environments 2018, 5, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5010017
Jursová S, Burchart-Korol D, Pustějovská P, Korol J, Blaut A. Greenhouse Gas Emission Assessment from Electricity Production in the Czech Republic. Environments. 2018; 5(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleJursová, Simona, Dorota Burchart-Korol, Pavlína Pustějovská, Jerzy Korol, and Agata Blaut. 2018. "Greenhouse Gas Emission Assessment from Electricity Production in the Czech Republic" Environments 5, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5010017
APA StyleJursová, S., Burchart-Korol, D., Pustějovská, P., Korol, J., & Blaut, A. (2018). Greenhouse Gas Emission Assessment from Electricity Production in the Czech Republic. Environments, 5(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5010017







