Water for Energy and Food: A System Modelling Approach for Blue Nile River Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
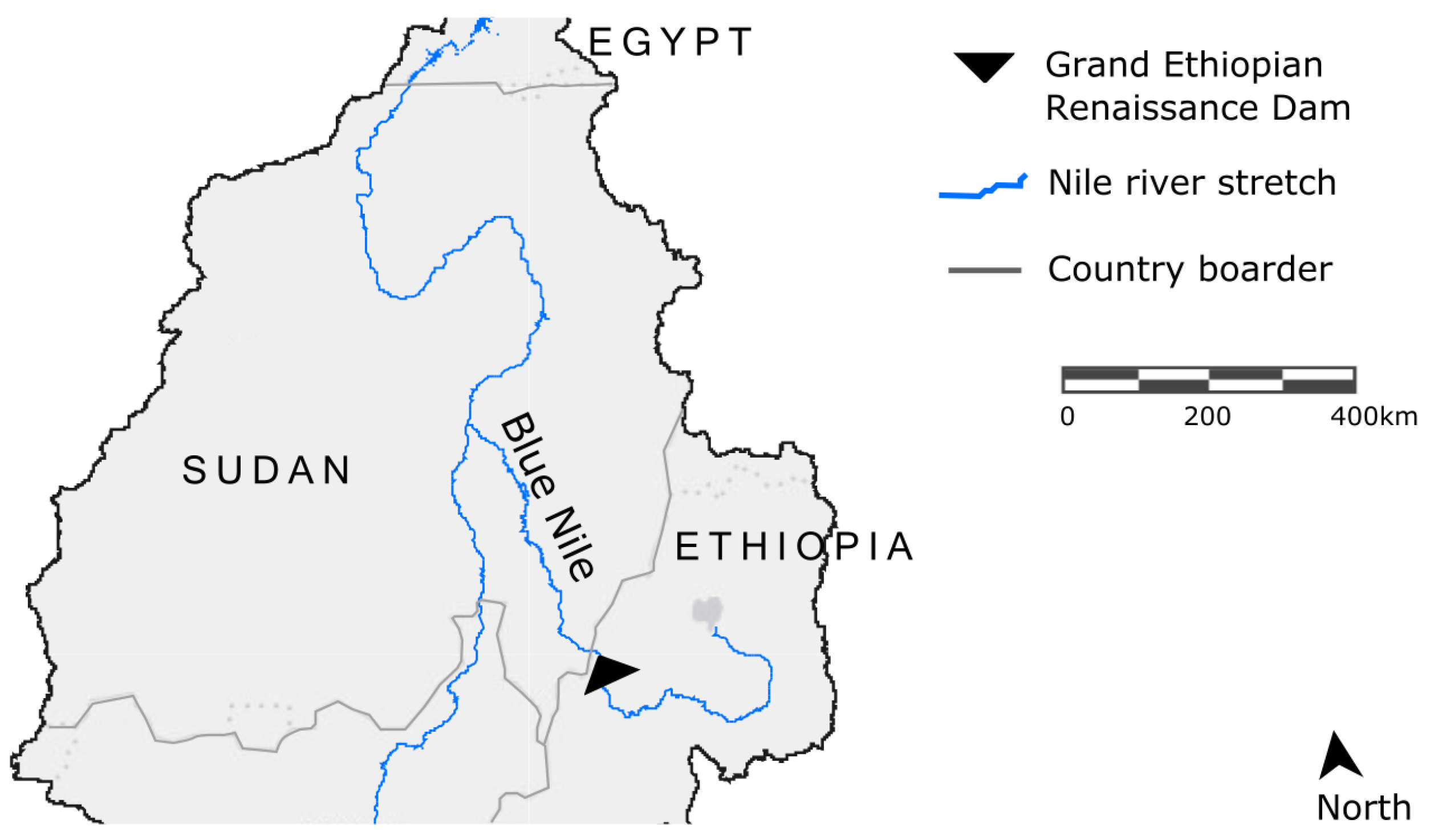
2. Case Study Description: Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam
3. Model Development
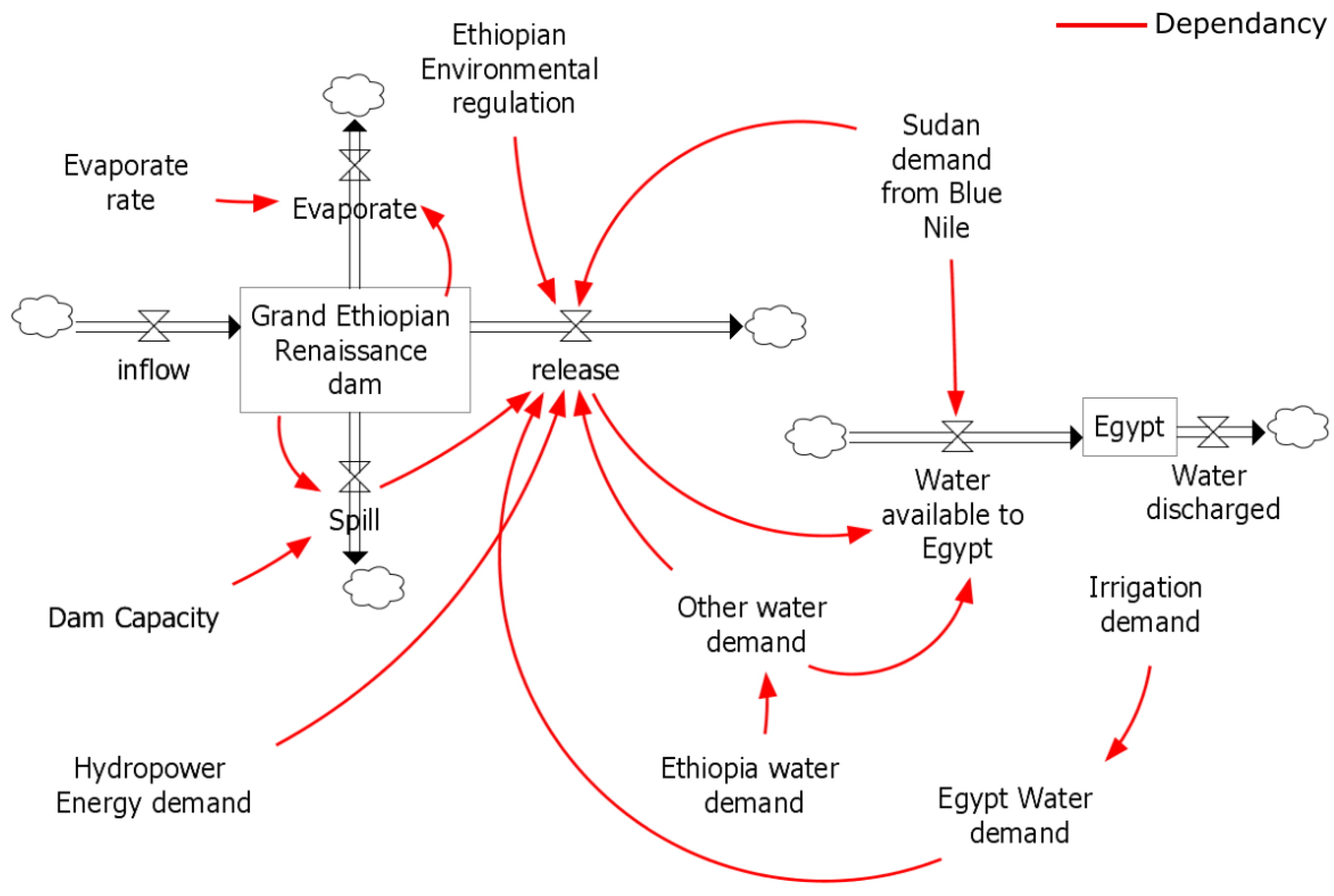
3.1. System Dynamic Model
3.2. Optimisation Linkage
3.3. Management Options
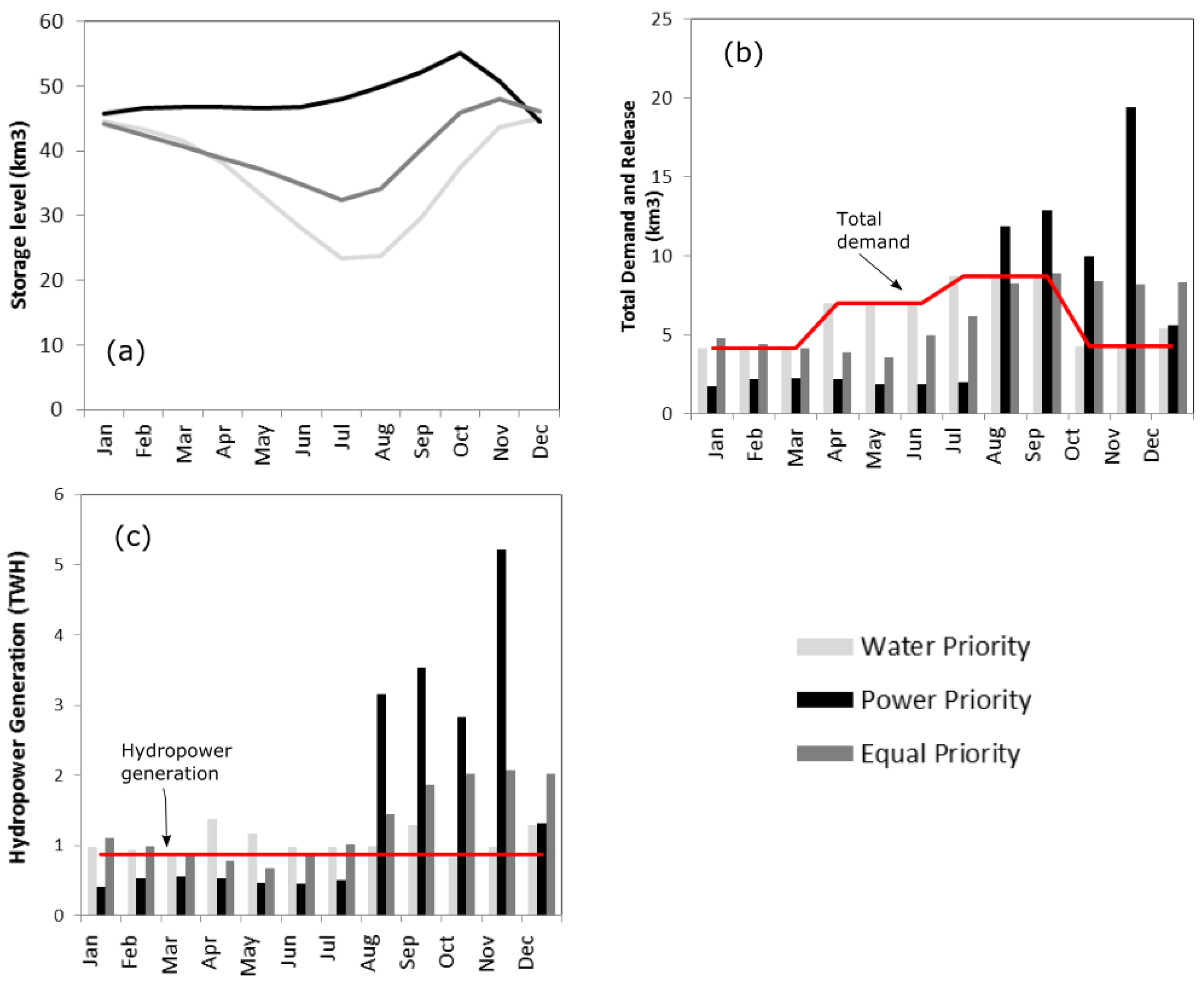
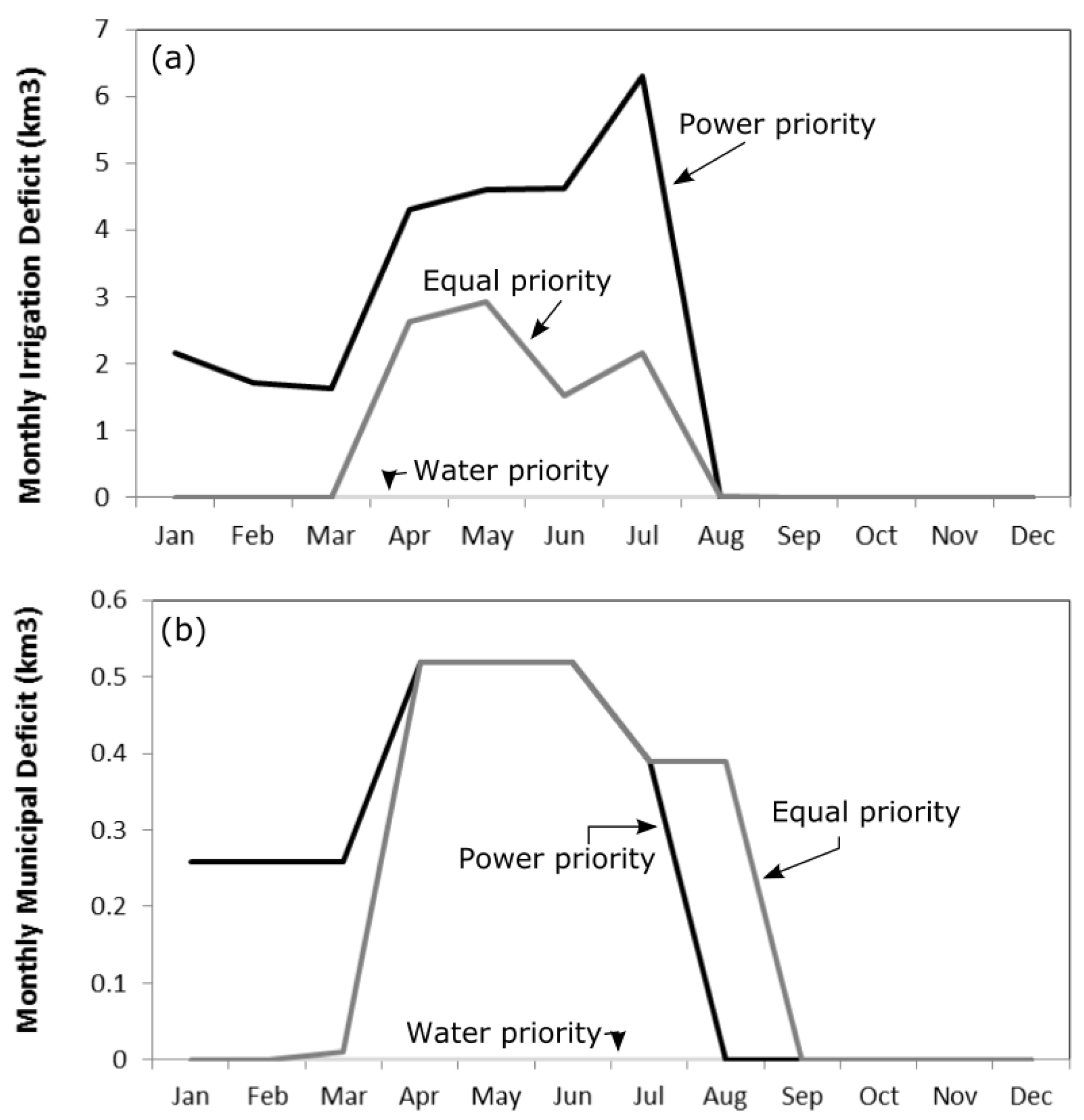
4. Results and Discussion
5. Perturbation Analysis
5.1. Sensitivity Due to Inflow
5.2. Reliability Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Howell, P.P.; Allan, J.A. The Nile: Sharing a Scarce Resource: A Historical and Technical Review of Water Management and of Economical and Legal Issues; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Shiklomanov, I.A.; Rodda, J.C. World Water Resources at the Beginning of the Twenty-First Century; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Grey, D.; Sadoff, C.W. Sink or swim? Water security for growth and development. Water Policy 2007, 9, 545–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jägerskog, A.; Granit, J.; Risberg, A.; Yu, W. Transboundary Water Management as a Regional Public Good. Financing Development—An Example from the Nile Basin; Technical Report; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Speed, R.; Yuanyuan, L.; Zhiwei, Z.; Le Quesne, T.; Pegram, G. Basin Water Allocation Planning: Principles, Procedures and Approaches for Basin Allocation Planning; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tesfaye, A.; Brouwer, R. Exploring the scope for transboundary collaboration in the Blue Nile river basin: Downstream willingness to pay for upstream land use changes to improve irrigation water supply. Environ. Dev. Econ. 2016, 21, 180–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCartney, M.P.; Menker Girma, M. Evaluating the downstream implications of planned water resource development in the Ethiopian portion of the Blue Nile River. Water Int. 2012, 37, 362–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirumachi, N.; Allan, J.A. Revisiting transboundary water governance: Power, conflict cooperation and the political economy. In Proceedings of the CAIWA International Conference on Adaptive and Integrated Water Management: Coping with Scarcity, Basel, Switzerland, 12–15 November 2007; Volume 1215.
- Moller, L.C. Transboundary Water Conflicts over Hydropower and Irrigation: Can Multilateral Development Banks Help? Centre for Research in Economic Development and International Trade (CREDIT), University of Nottingham: Nottingham, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Erfani, T.; Erfani, R. An evolutionary approach to solve a system of multiple interrelated agent problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 37, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukmehmetoglu, M. A game theoretic approach to assess the impacts of major investments on transboundary water resources: The case of the Euphrates and Tigris. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 3069–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibaroglu, A.; Ünver, I.O. An institutional framework for facilitating cooperation in the Euphrates-Tigris river basin. Int. Negot. 2000, 5, 311–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukmehmetoglu, M.; Guldmann, J.M. Multiobjective allocation of transboundary water resources: Case of the Euphrates and Tigris. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2009, 136, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoudy, M. Asymmetric power: Negotiating water in the Euphrates and Tigris. Int. Negot. 2009, 14, 361–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukmehmetoglu, M.; Guldmann, J.M. International water resources allocation and conflicts: The case of the Euphrates and Tigris. Environ. Plan. A 2004, 36, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliot, N.; Shmueli, D.; Shamir, U. Institutions for management of transboundary water resources: Their nature, characteristics and shortcomings. Water Policy 2001, 3, 229–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitoun, M.; Mirumachi, N. Transboundary water interaction I: Reconsidering conflict and cooperation. Int. Environ. Agreem. Politics Law Econ. 2008, 8, 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Erfani, R.; Mokhtar, H.; Erfani, T. Agent based modelling for water resource allocation in the transboundary Nile River. Water 2016, 8, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degefu, D.M.; He, W.; Yuan, L.; Zhao, J.H. Water Allocation in Transboundary River Basins under Water Scarcity: A Cooperative Bargaining Approach. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 4451–4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinar, A.; Nigatu, G.S. Distributional considerations of international water resources under externality: The case of Ethiopia, Sudan and Egypt on the Blue Nile. Water Resour. Econ. 2013, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Block, P.; Hammond, M.; King, A. Ethiopia’s Grand Renaissance Dam: Implications for downstream riparian countries. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2015, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Erkyihum, S.T.; Block, P. Filling the GERD: Evaluating hydroclimatic variability and impoundment strategies for Blue Nile riparian countries. Water Int. 2016, 41, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.M.; Varis, O. Integrated water resources management: Evolution, prospects and future challenges. Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 2005, 1, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Jaspers, F.G. Institutional arrangements for integrated river basin management. Water Policy 2003, 5, 77–90. [Google Scholar]
- Bazilian, M.; Rogner, H.; Howells, M.; Hermann, S.; Arent, D.; Gielen, D.; Steduto, P.; Mueller, A.; Komor, P.; Tol, R.S.; et al. Considering the energy, water and food nexus: Towards an integrated modelling approach. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 7896–7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawford, R.; Bogardi, J.; Marx, S.; Jain, S.; Wostl, C.P.; Knüppe, K.; Ringler, C.; Lansigan, F.; Meza, F. Basin perspectives on the water-energy-food security nexus. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, A.; Burnett, K.; Orencio, P.M.; Kumazawa, T.; Wada, C.A.; Ishii, A.; Tsurita, I.; Taniguchi, M. Methods of the water-energy-food nexus. Water 2015, 7, 5806–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfani, T.; Erfani, R. Fair Resource Allocation Using Multi-population Evolutionary Algorithm. In Applications of Evolutionary Computation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 214–224. [Google Scholar]
- Block, P.J. Integrated Management of the Blue Nile Basin in Ethiopia: Hydropower and Irrigation Modeling; Technical Report; International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI): Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Awulachew, S.B.; McCartney, M.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Ahmed, A.A. A Review of Hydrology, Sediment and Water Resource Use in the Blue Nile Basin; International Water Management Institute (IWMI): Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2009; Volume 131. [Google Scholar]
- Hammond, M. The Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam and the Blue Nile: Implications for Transboundary Water Governance; Global Water Forum Discussion Paper; Global Water Forum: Canberra, Australia, 2013; Volume 1307. [Google Scholar]
- Sterman, J.D. Business Dynamics: Systems Thinking and Modeling for a Complex World; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mirchi, A.; Madani, K.; Watkins, D., Jr.; Ahmad, S. Synthesis of system dynamics tools for holistic conceptualization of water resources problems. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 2421–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonovic, S.P. Managing Water Resources: Methods and Tools for a Systems Approach; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Initiative, N.B. Hydrologic Regime in the Nile Basin; Technical Report; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nile Basin Initiative. The Water Resources of the Nile Basin—-Nile Information System; Technical Report; Nile Basin Initiative: Entebbe, Uganda, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe, J.V.; Parks, Y.P. The Hydrology of the Nile; International Association of Hydrological Sciences Wallingford: Oxfordshire, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. FAO Statistical Yearbook 2014 Africa Food and Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Regional Office for Africa: Accra, Ghana, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Price, K.V.; Lampinen, J.A.; Storn, R.M. Differential Evolution: A Practical Approach to Global Optimization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Postle-Floyd, H.; Erfani, T. A reliability and robustness analysis of the Masinga dam under uncertainty. Climate 2017, in press. [Google Scholar]
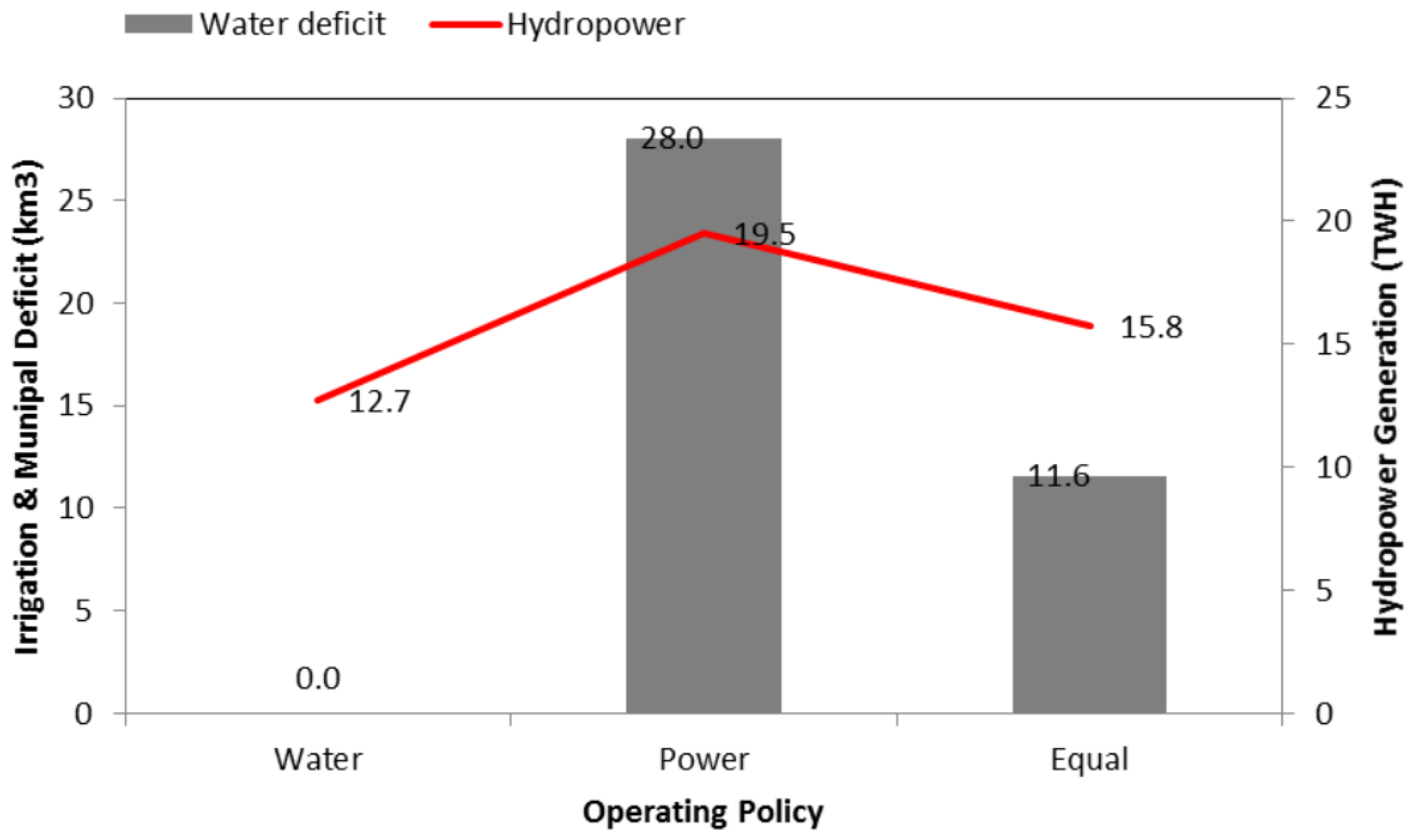
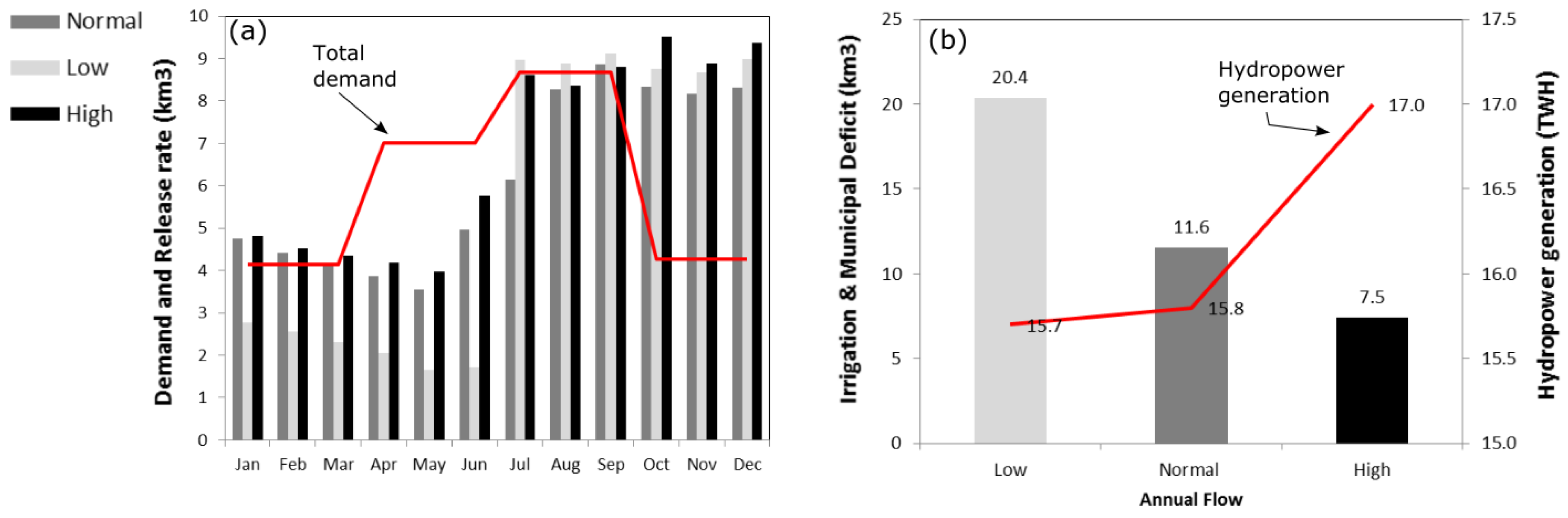
| Period | Inflow into | Irrigation | Municipal | Hydropower |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| the Reservoir (%) | Demand (%) | Demand (%) | Demand (%) | |
| January–March | 11 | 15 | 20 | 25 |
| April–June | 8 | 30 | 30 | 25 |
| July–August | 63 | 40 | 25 | 25 |
| October–December | 18 | 15 | 25 | 25 |
| Month | Rate (km) | r = 1 | 0.9 | 0.85 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | R1 | 4.147 | 4.21 | 4.755 | 3.845 | 2.281 | 1.736 |
| February | R2 | 4.152 | 3.905 | 4.412 | 3.456 | 2.475 | 2.181 |
| March | R3 | 4.147 | 4.168 | 4.137 | 3.373 | 2.408 | 2.259 |
| April | R4 | 6.998 | 4.567 | 3.86 | 3.431 | 2.229 | 2.168 |
| May | R5 | 6.998 | 5.13 | 3.557 | 3.513 | 1.873 | 1.881 |
| June | R6 | 6.998 | 7.393 | 4.963 | 3.599 | 1.88 | 1.863 |
| July | R7 | 8.683 | 8.976 | 6.143 | 7.845 | 10.675 | 1.996 |
| August | R8 | 8.683 | 8.99 | 8.279 | 9.02 | 11.839 | 11.844 |
| September | R9 | 8.683 | 7.738 | 8.875 | 9.095 | 10.616 | 12.894 |
| October | R10 | 4.277 | 5.829 | 8.347 | 8.893 | 9.24 | 9.97 |
| November | R11 | 4.277 | 6.471 | 8.158 | 8.775 | 8.783 | 19.399 |
| December | R12 | 5.425 | 6.423 | 8.314 | 8.954 | 9.501 | 5.609 |
| Power (TWH) | 12.72 | 14 | 15.76 | 16.5 | 17.5 | 19.53 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, C.C.; Erfani, T.; Erfani, R. Water for Energy and Food: A System Modelling Approach for Blue Nile River Basin. Environments 2017, 4, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments4010015
Tan CC, Erfani T, Erfani R. Water for Energy and Food: A System Modelling Approach for Blue Nile River Basin. Environments. 2017; 4(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments4010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Cho Chia, Tohid Erfani, and Rasool Erfani. 2017. "Water for Energy and Food: A System Modelling Approach for Blue Nile River Basin" Environments 4, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments4010015
APA StyleTan, C. C., Erfani, T., & Erfani, R. (2017). Water for Energy and Food: A System Modelling Approach for Blue Nile River Basin. Environments, 4(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments4010015





