Abstract
The saturation of negative charges of zeolites by specific cations to modify their physicochemical and catalytic properties has broadened the applications of zeolites. The adsorption behavior of H+ to Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+ and Cs+-saturated Linde-type A, Na-P1, mordenite, X type and Y type zeolites was evaluated at different pH-pM, where pH-pM is equal to log {(M+)/(H+)} and M+ represents either Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+, or Cs+. In all cases, with decreasing pH-pM, the amounts of alkali metal retention decreased due to the adsorption of H+ via cation exchange reaction. The adsorption selectivity of H+ into the zeolites had a negative correlation with the Si/Al ratio of the zeolites. In each zeolite species, Cs+-saturated zeolite showed the lowest H+ selectivity, and this suggested that Cs+ had the strongest adsorption energy in the alkali metal cations. The adsorption of H+ was strongly affected by diameter and hydration energy of the alkali metal cations, and was also affected by the framework type and Si/Al ratio of the zeolites. The adsorption of H+ into zeolites decreases the amount of cation retention other than with H+ and may cause the elution of Si and Al into aqueous solutions.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the utilization of zeolites as adsorbents and catalysts has increasingly broadened in both aqueous and gaseous systems. The variety of zeolites’ applications has been achieved through modifications of their physicochemical properties [1], and, in most cases, zeolites’ modifications are possible through the incorporation of specific cations with different properties such as ionic radius and hydration energy [2]. Usually, saturation of the negative charges of zeolites by a specific cation species causes changes in their pore sizes and geometry (e.g., length and angle of Al-O-Si) [3,4], location of cation sites [5], nature of hydration water or other ligands [6], and variations in acid strength of Brønsted or Lewis acid-basic sites [7]. These changes improve their adsorptive and catalytic activities and enable them to have specific adsorption and catalytic properties toward certain ions or molecules of a particular interest. This causes zeolites to be more effective, selective, and superior adsorbents and catalysts for separating specific ions in aqueous systems or molecules from the air [8,9,10].
The applications of cation saturated zeolites include: Li+-saturated Y and ZSM used as a catalyst for a number of hydrocarbon conversion processes such as in oil refining and the petrochemical industry [11,12,13]; K+, NH4+, Mg2+ or Ca2+ saturated zeolites used as fertilizers and for the amelioration of acid soils in agriculture [14,15]; Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, etc. saturated zeolites such as mordenite, clinoptilolite, P, A, and X are used in environmental remediation such as mine acid water treatment, removal of radionuclides such as Cs+, Sr2+ from nuclear waste effluents [4,9], and for Na+ saturated nano-composite-magnetic zeolites such as Na-P1 used in soil radionuclide decontamination [16,17,18]; Na+ saturated Linde-type A, mordenite, Na-P1, X and Y zeolites in remediation of heavy metals [19]; industrial applications such as detergency and water treatment [20,21]; Fe saturated zeolites used in nano-organic composites as pesticides, etc. [22]; Ag+ or in combination with its coexisting mixtures of Cs+, Li+, Zn2+ saturated in zeolite X or Y are used in photoluminescence or fluorescence [23,24,25]; coexistent cations such as Ag+, Na+, Cs+, Li+ with S compounds in zeolite coloring [25,26,27]; and Ag+ zeolites used as antibacterial agents in the food and medical industry [28,29].
In some of the aforementioned applications, zeolites are used in a wide range of pH from acidic to alkaline conditions in aqueous media. However, our recent study showed that cation exchange capacity (CEC) Na+ retention by zeolites is greatly affected by the adsorption of H+, even in the neutral pH region [30]. The adsorption of H+ into zeolites results in the loss of the negative charge due to neutralization forming covalent bonds from the Lewis acid-base reaction [29,31]. This finding has been contrary to what has been thought all along: that the CEC of zeolites does not change with change in aqueous pH. This concept has been inferred from the fact that the CEC of 2:1 type layer silicate clay minerals such as montmorillonite is constant even at acidic conditions such as pH 4 [30,32]. Such logic possibly led to the determination of CEC without considering the effect of H+ adsorption. Consequently, most CEC studies in zeolites have focused on looking at factors such as Si/Al ratio (i.e., low Si/Al ratio leads to high CEC), the nature of exchangeable cation species, temperature, concentration or activity of cations in solutions, and structural characteristics of the particular zeolites in ion exchange dynamics [33,34].
On the other hand, H+ adsorption selectivity in various cation saturated zeolites at different pH levels is likely to vary and to be influenced by a number of factors such as saturated cation type, negative charge density, Si/Al ratio, ordering of Si-O-Al linkage, and type of crystal structure. However, there is currently scarce information and it is not well known how the saturation by different cations affects H+ adsorption selectivity in relation to a CEC decrease of the various cation saturated zeolites at different aqueous pH levels. Therefore, this research work was carried out to bridge the information gap and to understand how the saturation by different cations in various zeolite species with different Si/Al ratio affects their H+ adsorption selectivity.
2. Experimental Section
The experiments were conducted in the Laboratory of Applied Chemistry for Environmental Industry, Faculty of Agriculture, Ehime University in Matsuyama, Japan. Linde-type A, Na-P1, mordenite, X type and Y type zeolite species with different Si/Al ratios, crystal structures, and amount of charge densities were used in this study. All standard analytical chemical reagents and zeolites samples used in this study were purchased from Wako Chemicals Ltd, Japan except for the Na-P1 zeolite samples that were synthesized in this study [19].
2.1. Preparation of Li+, K+, Rb+, and Cs+ Saturated Zeolites
In respective 250 mL centrifuge bottles, 10 g of each added zeolite sample was washed five times with 150 mL of 1 M chloride solutions of Li+, K+, Rb+, or Cs+ to saturate the zeolites with the alkali metal cation. Thereafter, the contents were washed twice with 150 mL of water and then washed once with 100 mL of acetone, air-dried, and used as samples. Cations contained in the samples were exchangeable alkali metal cations, and free Li+, K+, Rb+ or Cs+ as chloride salt. The sum of exchangeable and free Li+, K+, Rb+ or Cs+ content of the sample (hereafter, Li+, K+, Rb+ or Cs+ content) were determined by washing 1 g of the sample with 30 mL of 1 M NH4Cl in a 50 mL centrifuge bottle seven times. The water content of the samples was determined by heating it at 105 °C for 3 h. The content of Si and Al of the samples was determined after dissolution with hydrofluoric acid.
2.2. Determination of CEC of Zeolites at Different pH Levels
One gram of Li+, K+, Rb+ or Cs+ saturated Linde-type A, Na-P1, mordenite, X type or Y type zeolite samples were put into a 250 mL centrifuge bottle, and 200 mL of 0 to 7.5 mM HCl solution was added. To obtain CEC values at higher pH, 200 mL of 0 to 5 mM LiOH, KOH, RbOH or CsOH solution was added instead of HCl solution. The mixture was shaken for 3 h at 25 ± 0.5 °C, centrifuged at 2000 g, and the concentration of the alkali metal and pH of the supernatant was measured. Preliminary experiments revealed that the Na+ concentration and pH of the supernatant became constant within 3 h, and the measured Li+, K+, Rb+ or Cs+ concentration and pH are hereafter referred to as equilibrium Li+, K+, Rb+ or Cs+ concentration and equilibrium pH, respectively. The CEC (the amount of alkali metal cation retention) of the respective samples were simply calculated from the difference between the content of each alkali metal cation of the samples and the amount of the alkali metal cation in the supernatant solution. Al and Si concentrations were also measured in the supernatant to check the dissolution of zeolite samples. The quantification of the metals was done by using an atomic absorption spectrophotometer (Hitachi Z-5000). Powder X-ray diffraction patterns of the samples before and after the CEC determination were obtained with a Rigaku Ultima IV X-ray diffractometer with Cu-Kα radiation generated at 40 kV and 40 mA, between 3–60° of 2θ angles with a sampling width of 0.02° and a scanning rate of 2° min−1.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Stability of Zeolites with CEC Measurement
The determination of the CEC of zeolites was conducted in a pH range of moderately acidic to moderately alkaline, and so we checked the stability of zeolites, i.e., if they underwent dissolution or not in aqueous solution. We analyzed XRD patterns for each treated zeolite sample after CEC measurement, and the results for the water (lower) and highest HCl concentration (upper) treated samples are given in Figure 1. We also quantified the percentage of Si and Al dissolved from zeolites’ structural framework and the amounts was less than 2% for Si and 0.5% Al. The dissolution was very minimal, possibly because the reaction time was only 3 h. Analysis of XRD patterns in Figure 1 of all zeolite samples indicated that there was neither a change in their structures nor formation of new materials. Comparison of the XRD patterns indicated that there was an increase in peak intensities of most samples after CEC measurement.
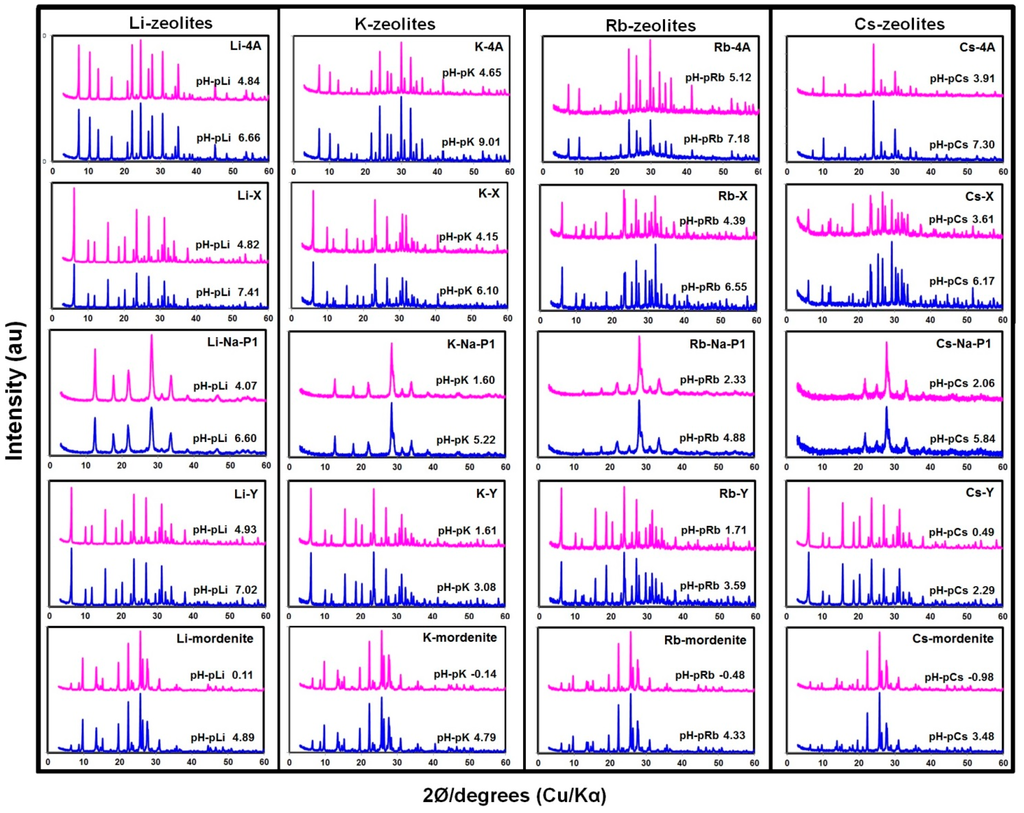
Figure 1.
XRD patterns of zeolites after CEC measurement.
This means that the amounts of Si and Al dissolved in the samples were possibly due to dissolution of amorphous materials such as precursors of zeolites contained in the samples. It is also possible that the dissolution of minuscule amounts of the zeolites’ framework might have taken place. In this case, Al and Si were dissolved simultaneously, and the dissolved Al species, probably hydroxy-Al cations, might be readily absorbed in zeolites. This is the reason why the observed amount of Al dissolution was very low (<0.5%). Therefore, we concluded that the amounts of dissolution of Al and Si from zeolites were very small compared to the changes in CEC (Figure 2). However, in other preliminary experiments, we found that samples of Linde-type A when reacting at pH 6 for seven days resulted into almost total dissolution and formation of amorphous aluminosilicate materials. The results suggest that there is a need to study the dissolution dynamics of various zeolites at different pH levels in depth.

Figure 2.
Change in CEC of zeolites with pH-pM. (A) Li-zeolites, (B) K-zeolites, (C) Rb-zeolites, (D) Cs-zeolites. cmol in the unit of CEC is centimole.
3.2. Effect of pH-pM on CEC of Zeolites
In this experiment, CEC, or the amount of retention of a zeolite’s alkali metal cation, is affected not only by pH, but also by the concentration of the alkali metal cation in the solution phase. On one hand, the CEC of clays in a monovalent cation system is known to be dependent on the value of pH-pM (M: activity of Na+ or NH4+) [35], and this means CEC is dependent on the ratio of activities of the monovalent cation to H+. Therefore, we plotted measured CEC values against pH-pM (M: activity of Li+, K+, Rb+ or Cs+), and the plots are shown in Figure 2.
In all cation saturated zeolites, CEC values decreased with a decrease in pH-pM, and their change within and among zeolites was dependent on both the types of saturated cations and zeolite species. At high pH-pM regions, CEC values did not change with increasing pH-pM and became constant. The constant values of CEC at high pH-pM regions correspond to the amounts of negative charge due to isomorphous substitution of Si by Al. The curves for Li, and K+ zeolites (Figure 2A,B) are sigmoidal, while the curves for Rb+ and Cs+ zeolites (Figure 2C,D) are linear from the points where CEC began to decrease. The points at which the CEC of zeolites began to decrease were different by the alkali metal species saturation. This suggested that there are differences in the degree of H+ adsorption selectivity among the cation species.
The pH-pM values were highest for Linde-type A among the K+, Rb+ and Cs+ saturated zeolites, and, for Li+ saturated zeolites, it was X that had the highest pH-pM value. Among all the cation saturated zeolites, the lowest pH-pM values were in mordenite. Among Li+, K+, Rb+, and Cs+ saturated Linde-type A zeolites, the highest pH-pM value was in Rb+ saturated Linde-type A, while the lowest was in K+ saturated Linde-type A. In the case of mordenite, the highest pH-pM value was in Li+ saturated mordenite, while the lowest was in Rb+ saturated mordenite. The results suggest that ion exchangeability of H+ in the replacement of alkali metal cations on the charge sites of various zeolites favored those zeolites with higher CEC than zeolites with lower CEC. In other words, the alkali metal cations were adsorbed more strongly by zeolites with higher Si/Al ratio. It is reported that monovalent cations are more preferable in adsorption by high Si/Al zeolites than low Si/Al zeolites [36].
On the other hand, when we express the acidity of a monovalent acid, a pKa value is used. The pKa value is equal to the pH value at 50% dissociation, and greater pKa value indicates weaker acidity and stronger H+ adsorption selectivity of the monovalent acid. By then plotting the degree of dissociation of a monovalent acid against pH, we get a sigmoid curve. In our results (Figure 2), we obtained similar sigmoid curves, although the horizontal axes were pH-pM. Then, to express the H+ adsorption selectivity of the zeolites more quantitatively, we introduced a (pH-pM)90 value. The (pH-pM)90 value is equal to the pH-pM value when 90% of the zeolites negative charge due to isomorphous substitution of Si by Al is occupied by the alkali metal cations. The amount of the isomorphous substitution was assumed to be equal to the CEC value obtained when distilled water was added in the CEC measurement. Because the measurement of CEC under very low pH-pM was not carried out due to the dissolution of the zeolites, we adopted (pH-pM)90 instead of (pH-pM)50 to compare the H+ adsorption selectivity among Li+, K+, Rb+ and Cs+ saturated Linde-type A, Na-P1, mordenite, X type and Y type zeolites. We plotted (pH-pM)90 values against Si/Al ratios of respective zeolites in Figure 3. The results show that there was a negative correlation between Si/Al ratio and (pH-pM)90 of the zeolites. That is to say, with an increase in Si/Al ratios, a decrease in H+ selectivity resulted. The negative correlations observed in the four zeolites, despite having different structural frameworks, imply the H+ adsorption selectivity was closely related to Si/Al ratios of zeolites. The deviation of some data points from the lines shows that there were other factors that influenced the H+ adsorption selectivity, and they are discussed in Section 3.4.
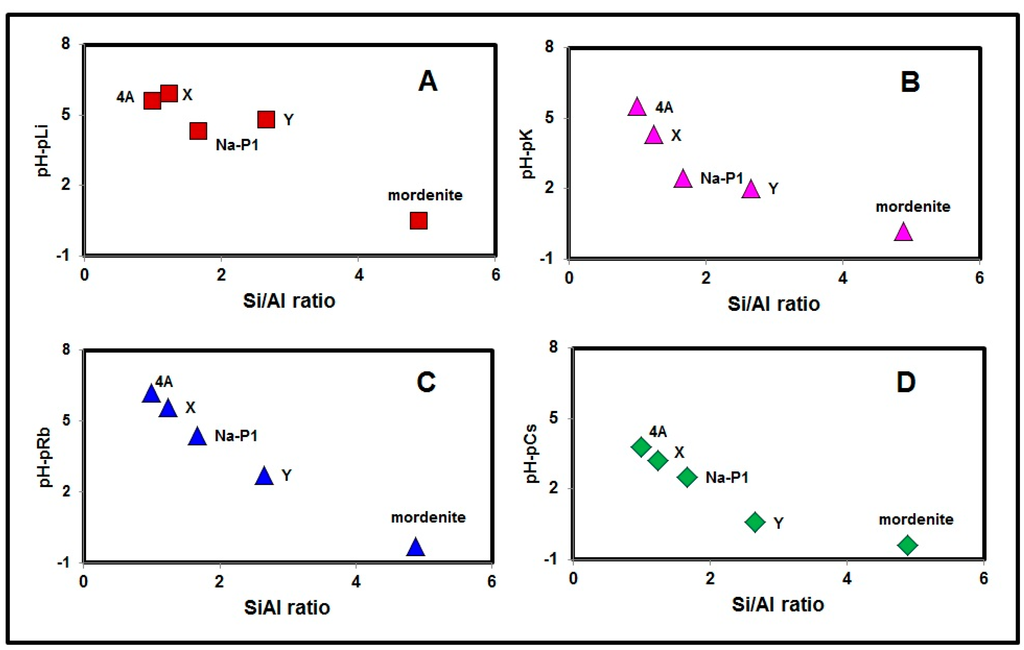
Figure 3.
Correlation between (pH-pM)90 and Si/Al ratio of zeolites. (A) Li-zeolites, (B) K-zeolites, (C) Rb-zeolites, (D) Cs-zeolites.
3.3. Effect of Cation and Zeolite Species on Proton Adsorption
The degree of H+ adsorption selectivity varied greatly and was influenced by alkali metal cation species and by zeolite species (Figure 3). We compared the (pH-pM)90 values for each cation saturated zeolite and the results are summarized in Table 1. The results indicated that (pH-pM)90 values were different among alkali metal cation species and also among zeolite species. In general, Cs+ saturated zeolites had the lowest (pH-pM)90 values, and this indicated that H+ adsorption selectivity was lowest for the Cs+ saturated zeolite. In other words, among alkali metal cations, Cs+ had the highest adsorption selectivity toward zeolites. This result is partly explained by the hydration diameter sequence order of the alkali metal cations, but the other four cations did not follow this order: for example, Rb+ saturated zeolites had higher (pH-pM)90 values than K+ saturated zeolites except for mordenite.

Table 1.
Effect of saturation cation of zeolites on (pH-pM)90 value. Data of (pH-pNa)90 were cited from a reference [34].
| Zeolite | (pH-pLi)90 | (pH-pNa)90 | (pH-pK)90 | (pH-pRb)90 | (pH-pCs)90 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linde-type A | 5.61 | 5.38 | 5.64 | 6.23 | 3.80 |
| faujasite X | 5.90 | 5.75 | 4.30 | 5.59 | 3.21 |
| Na-P1 | 4.34 | 3.64 | 2.47 | 4.42 | 2.53 |
| faujasite Y | 4.79 | 3.06 | 2.02 | 2.71 | 0.57 |
| mordenite | 0.51 | 0.92 | 0.18 | −0.33 | −0.42 |
The (pH-pCs)90 value of Cs-Na-P1 was 2.53, and the (pH-pRb)90 value of Rb-Na-P1 was 4.42. In the case of faujasite Y, the (pH-pLi)90 value was 4.79 for Li-Y, while for Cs-Y the (pH-pCs)90 value was 0.57. A similar trend was observed in mordenite where the (pH-pLi)90 value was 0.51 for Li-mordenite, while for Rb-mordenite the (pH-pRb)90 value was −0.33. The trends were similar for the other cation zeolites. It appears that the differences in zeolite structural frameworks also affected the H+ adsorption selectivity. A good example is faujasite X and faujasite Y. The two zeolites have the same structural framework but have different Si/Al ratios and CEC. Now considering faujasite X and faujasite Y, the (pH-pCs)90 value of faujasite X was 3.21, while for faujasite Y, the value was 0.57. These results suggest that faujasite X has a higher H+ adsorption selectivity than faujasite Y, possibly due to its lower Si/Al and higher CEC [37].
By using the data in Table 1, for each saturation cation type, the H+ adsorption selectivity sequence among the zeolite species is summarized in Table 2. In K+-, Rb+- and Cs+-types, Linde-type A had the greatest H+ adsorption selectivity, while in the case of Li+- and Na+-types, the strongest H+ adsorption selectivity was in faujasite X. On one hand, in all saturation cation species, mordenite had the lowest H+ adsorption selectivity. The H+ adsorption selectivity sequence of the zeolite species is also summarized in Table 3, in which the effect of the saturation cation species was evaluated in each zeolite species. As has been described earlier, in most zeolite species, Cs+-type showed the lowest H+ adsorption selectivity. The positions of the other saturation cation types at the sequences were varied, but the sequences of faujasite X and faujasite Y were identical. This indicated that H+ and alkali metal cation selectivity sequences were affected by the type of zeolite framework.

Table 2.
Proton adsorption selectivity sequences of zeolites: the effect of zeolite species.
| Saturation Cation | H+ Adsorption Selectivity Sequence |
|---|---|
| Li+ | faujasite X > Linde-type A > faujasite Y > Na-P1 > mordenite |
| Na+ | faujasite X > Linde-type A > Na-P1 > faujasite Y > mordenite |
| K+ | Linde-type A > faujasite X > Na-P1 > faujasite Y > mordenite |
| Rb+ | Linde-type A > faujasite X > Na-P1 > faujasite Y > mordenite |
| Cs+ | Linde-type A > faujasite X > Na-P1 > faujasite Y > mordenite |

Table 3.
Proton adsorption selectivity sequences of zeolites: the effect of saturation cation species.
| Zeolite | H+ Adsorption Selectivity Sequence |
|---|---|
| Linde-type A | Rb+-type > K+-type > Li+-type > Na+-type > Cs+-type |
| faujasite X | Li+-type > Na+-type > Rb+-type > K+-type > Cs+-type |
| Na-P1 | Rb+-type > Li+-type > Na+-type > Cs+-type > K+-type |
| faujasite Y | Li+-type > Na+-type > Rb+-type > K+-type > Cs+-type |
| mordenite | Na+-type > Li+-type > K+-type > Rb+-type > Cs+-type |
3.4. Factors Affecting Proton Adsorption Selectivity of Zeolites
3.4.1. Si/Al Ratio and Charge Density
Considering the arrangement of Si-O-Al links and values of Si/Al ratios of the zeolites (mordenite: 4.88; Linde-type A: 1.00; Na-P1: 1.67; faujasite X: 1.24; and faujasite Y: 2.66) [19], they are causing variations in geometrical assemblies and physicochemical properties. Usually, the variations in Si-O-Al angles and bond lengths, differences in crystal structures and amounts of Si-O-Si or Si-O-Al affect the ion adsorptions of H+, Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+ and Cs+ on surface charge sites within and among zeolites [38]. The presence of Si-O-Si and Si-O-Al links determines the occurrence of a number of acidic sites, and the adsorption of H+ to zeolites leads to the occurrence of Brönsted acid sites [7]. Adsorption of Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+ and Cs+ in negative charge sites and the surrounding atoms affects the degree of Lewis basic strength differently [7,39] that, in turn, affects the H+ selectivity. The attachment of Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+ and Cs+ as a balancing charge cation in zeolites causes variations in the H+ selectivity and Lewis acidity [40]. This explains why the H+ selectivity was different among Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+ and Cs+ saturated zeolites. Furthermore, the difference in the Si/Al ratio among zeolites resulted in variations in the amount of negative charge or cation exchange capacity (CEC) of mordenite (179 cmol·kg−1), Linde-type A (565 cmol·kg−1), Na-P1 (429 cmol·kg−1), faujasite X (461 cmol·kg−1) and faujasite Y (250 cmol·kg−1) [37].
Zeolites with high Si/Al ratios such as mordenite usually have low negative charge density, and this implies that their negative charge sites are far away from each other, while in zeolites with low Si/Al ratios such as Linde-type A, their negative charge sites are close to each other. In other words, the separation distance between the negative charge sites determines the cation selectivity of zeolites [41]. When the separation distances are short, the adsorption of two or more cations close to each other is unfavorable due to electrostatic repulsion. In case of H+, such an electrostatic repulsion is weaker than the case of other cations, because H+ binds to the negative charge site in the form of covalent bonding as Si-OH-Al [42]. This explains why the H+ adsorption selectivity was higher in high CEC zeolites such as Linde-type A rather than in low CEC zeolites such as mordenite. Another good example is faujasite X and faujasite Y, which have the same structural framework. In this case, the negative charge sites are closer to each other in faujasite X than faujasite Y and so the H+ is more strongly adsorbed in faujasite X than in faujasite Y [43]. When alkali metal cations adsorb into zeolites, the binding energy and the resultant electrostatic potential fields are different between cations [44]. The difference possibly occurs due to the variations in the ionic size of the cations occupying different pores of zeolites with different electrical attractions on their charge sites [2,33,45].
3.4.2. Nature of Cations and Zeolite Pore Sizes
The difference in the H+ adsorption selectivity among different cation saturated zeolites could be well understood if we look at the diameter of the cations: Cs+ (3.3 Å) > Rb+ (2.9 Å) > K+ (2.7 Å) > Na+ (1.9 Å) > Li+ (1.4 Å). The expected order of their polarities were as follows: Li+ > Na+ > K+ > Rb+ > Cs+ [46,47,48]. The occupancy of the cations on the negative charge sites within zeolite cavities is usually greatly influenced by the type of coexisting extra framework cations and the presence or absence of hydration water [6,33]. The cations had different strengths of hydration water due to the differences in the relative charge-to-radius ratios in aqueous solutions and relative ionic field strengths of zeolites [47]. For instance, Na+, K+ and Cs+ have diameters of 1.90, 2.60, and 3.34 Å with hydration energies of −365, −295 and −280 kJ·mole−1, respectively [45,48,49,50]. Sodium ions with large hydrated radii have charge centers far away from the surface of contact causing weak solid-cation electrostatic interactions [45]. On the other hand, Cs+ has low hydration energy and so is strongly attached on the negative charge site of zeolites [51]. This is one of the reasons why Cs+ was more strongly adsorbed by the zeolites than the other cations, as has been described earlier.
Depending on the location of adsorption, cations may be bound as hydrated forms (e.g., Li+), partially hydrated or not hydrated (e.g., Cs+) indicating that on some negative charge sites there could be no water molecules interposed between the fixed anionic sites and the counterions [47]. Therefore, the binding energy of the alkali metal cations is affected by the hydration state of the cations and size of the zeolite pores. The exchange of the alkali metal cations to H+ is the net result of free energy due to coulombic interactions (between partially dehydrated alkali metal cation and negatively charged lattice) and the free energy of partial dehydration. The distribution of the alkali metal cations in different zeolite pore spaces causes a heterogeneous character of adsorption of the cations [52]. The cation with great permanent quadrupole moments might interact strongly with the gradient of the electric field induced by the zeolite pore spaces. In other words, pore sizes of zeolites have a crucial role in determining the adsorption behavior of the cations.
Furthermore, considering a single zeolite species, the pores are not homogeneous and have different sizes. For instance, Linde type A has cavities of 11.4 Å, 6.6 Å, and 2.2 Å [53] while faujasite X and faujasite Y have supercages of 13.0 Å and 8.0 Å and small cages [47]. Now, when alkali metal cations are adsorbed as charge balancing cations, they influence the electric field gradient differently depending on the size and shape of the pores [54,55]. Some cations may be weakly bound in a large pore as hydrated ions, while in a small pore the same cation may be strongly adsorbed. This implies that the adsorption of H+ by exchange with the cations depends on the hydration diameter of the cations and the pore size [56,57]. Although H+ can penetrate more easily into most of the pores, its adsorption selectivity is affected by the differences in the adsorption strength of the alkali metal cations to be replaced. For instance, in faujasite Y, Li+ may be weakly bound in the large supercage as fully hydrated cations, and, therefore, may be easily replaced by H+. The cation selectivity follows the relative order of free energies of reactions for different cations, favoring the reaction with the most negative free energy of reactions [55]. The effect of lattice interactions on the polarizabilities of the component cations increased in the crystal and that of the negative ions decreased, relative to the values that characterize the free ions [58,59].
4. Conclusions
In all examined combinations of zeolite species and alkali metal cation species, the amount of adsorption of the alkali metal cations decreased with decreasing pH-pM, due to the adsorption of H+. The adsorption selectivity of H+ was affected by zeolite species and also by alkali metal cation species. The highest H+ selectivity was observed in Rb+-saturated Linde-type A, and the lowest was observed in Cs+-saturated mordenite. There was a negative correlation between Si/Al of zeolites and (pH-pM)90 value, implying that H+ selectivity was mainly dependent on the Si/Al ratio and negative charge density of zeolites. The H+ selectivity was also influenced by alkali metal cation species and zeolite pore sizes. Proton adsorption in various zeolites caused the loss of cation retention capacity and could lead to the dissolution of zeolites.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Seki Scholarship and Saibikai Scholarship for their support.
Author Contributions
Moses Wazingwa Munthali and Erni Johan performed the research and data analysis. Moses Wazingwa Munthali drafted the manuscript. Naoto Matsue designed the research and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Global inorganic geochemistry. In Frontiers in Geochemistry: Konrad Krauskopf; Ernst, W.G. (Ed.) The Sheridan Press: Hanover, PA, USA, 2002; Volume 1.
- Mon, J.; Deng, Y.; Flury, M.; Harsh, J.B. Cesium incorporation and diffusion in cancrinite, sodalite, zeolite and allophane. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 86, 277–286. [Google Scholar]
- Bonenfant, D.; Kharoune, M.; Niquette, P.; Mimeault, M.; Hausler, R. Advances in principal factors influencing carbon dioxide adsorption on zeolites. Sci. Tehcnol. Adv. Mater. 2008, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuronen, M.; Harjula, R.; Jernstrom, J.; Vestenius, M.; Lehto, J. Effect of the framework charge density on zeolite ion exchange selectivities. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 2655–2659. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Kim, H.S.; Seo, S.M.; Ko, S.O.; Suh, J.M.; Kim, G.H.; Lim, W.T. Location of Na+ ions in fully dehydrated Na+-saturated zeolite Y (FAU, Si/Al-1.56). Bull. Kor. Chem. Soc. 2012, 33, 2785–2788. [Google Scholar]
- Mortier, W.J.; Bosmans, H.J.; Uytterhoeven, J.B. Location of univalent cations in synthetic zeolites of the Y and X type with varying Silicon to aluminum ratio. II dehydrated potassium exchanged forms. J. Phys. Chem. 1972, 1, 650–656. [Google Scholar]
- Katada, N.; Suzuki, K.; Noda, T.; Sastre, G.; Niwa, M. Correlation between BrØnsted Acid strength and local structure in zeolites. J. Phys. Chem. 2009, 113, 19208–19217. [Google Scholar]
- Bonelli, B.; Civalleri, B.; Fubini, B.; Ugliengo, P.; Areán, C.O.; Garrone, E. Experimental and quantum chemical studies on the adsorption of carbondioxide on alkali-metal-exchanged ZSM-5 zeolites. J. Phys. Chem. 2000, 104, 10978–10988. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Rahman, R.O.; Ibrahium, H.A.; Yung-Tse, H. Liquid radioactive wastes treatment: A review. Water 2011, 3, 551–565. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J. Li+- and H+-exchanged low-silica X zeolite as selective N adsorbent for air separation. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2003, 24, 1814–1818. [Google Scholar]
- Nilchi, A.; Maalek, B.; Khanchi, A.; Ghanadi, M.M.; Bagheri, A.; Savoji, K. Ion exchangers in radioactive waste management: Natural Iranian zeolites. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2006, 64, 138–143. [Google Scholar]
- Busca, G. Acid catalysts in industrial hydrocarbon chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5366–5410. [Google Scholar]
- Degnan, T.F. The implications of the fundamentals of shape selectivity for the development of catalysts for the petroleum and petrochemical industries. J. Catal. 2003, 216, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Pickering, H.W.; Menzies, N.W.; Hunter, M.N. Zeolite/rock phosphate—A novel slow release phosphorus fertiliser for potted plant production. Sci. Hortic. 2002, 94, 333–343. [Google Scholar]
- Rabai, K.A.; Ahmed, O.H.; Kasim, S. Use of formulated nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium compound fertilizer using clinoptilolite zeolite in maize (Zea mays L.) cultivation. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2013, 25, 713–722. [Google Scholar]
- Aono, H.; Tamura, K.; Johan, E.; Yamauchi, R.; Yamamoto, T.; Matsue, N.; Henmi, T. Preparation of composite material of Na-P1-type zeolite and magnetic for Cs decontamination. Che. Lett. 2013, 42, 589–591. [Google Scholar]
- Macasek, F.; Navratil, J.D.; Dulanska, S. Magnetic sorbent for soil remediation—A new waste for waste treatment. Separ. Sci Technol. 2002, 37, 3673–3692. [Google Scholar]
- Dyer, A.; Miki-iail, K.Y. The use of zeolites for the treatment of radioactive waste. Mineral. Mag. 1985, 49, 203–210. [Google Scholar]
- Kabwadza-Corner, P.; Munthali, M.W.; Johan, E.; Matsue, N. Comparative study of copper adsorptivity and selectivity toward zeolites. Amer. J. Analyt. Chem. 2014, 5, 395–405. [Google Scholar]
- Fruijtier-Pölloth, C. The safety of synthetic zeolites used in detergents. Arch. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 23–35. [Google Scholar]
- Dyer, A. An Introduction to Zeolite Molecular Sieves; John Wiley and Sons, Bath Press Ltd.: Bath, Avon, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Yousef, R.; El-Eswed, B. The effect of pH on the adsorption of phenol and chlorophenols onto natural zeolite. Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 2009, 334, 92–99. [Google Scholar]
- Seifert, R.; Rytz, R.; Calzaferri, G. Colors of Ag+-Exchanged Zeolite A. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 104, 7473–7483. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Wang, Z.; Lin, L.; Lin, J.; Su, M. Photostimulated luminescence of silver clusters in zeolite-Y. Physics Lett. A 1997, 232, 391–394. [Google Scholar]
- Menezes, R.A.; Paz, S.P.R.; Angélica, R.S.; Neves, R.F.; Pergher, S.B.C. Color and shade parameters of ultramarine zeolitic pigments synthesized from kaolin waste. Mater. Res. 2014, 17 (Suppl. 1), 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska, A.; Kowalak, S. Cesium bearing ultramarine prepared from zeolites. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2008, 174, 193–196. [Google Scholar]
- Calzaferri, G.; Leiggener, C.; Glaus, S.; Schürcha, D.; Kuge, K. The electronic structure of Cu+, Ag+, and Au+ zeolites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2003, 32, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, T.V. Applications of nanotechnology in food packaging and food safety: Barrier materials, antimicrobials and sensors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 363, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, A.; Harrison, A.; Sabbani, S.; Munson, R.S.; Dutta, P.K.; Waldman, W.J. Silver nanoparticles embedded in zeolite membranes: Release of silver ions and mechanism of antibacterial action. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 1833–1852. [Google Scholar]
- Munthali, M.W.; Kabwadza-Corner, P.; Johan, E.; Matsue, N. Decrease in cation exchange capacity of zeolites at neutral pH: Examples and proposal of a determination method. J. Mater. Sci. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Santen, A.R.V.; Neurock, M. Molecular Heterogeneous Catalysis: A Conceptual and Computational Approach; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- McBride, M.B. Minerals in Soil Environments; Dixon, J.B., Weed, S.B., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1989; pp. 35–88. [Google Scholar]
- Kirov, G.; Filizova, L. Cationic hydration impact on zeolite formation and properties: A review and discussion. Geochem. Miner. Petrol. Sofia 2012, 49, 65–82. [Google Scholar]
- Barrer, R.M.; Klinowski, J. Influence of framework charge density on ion exchange properties of zeolites. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 1972, 68, 1956–1963. [Google Scholar]
- Wada, S.; Kawabata, K. Ion adsorption on variable charge materials and thermodynamics of ion exchange. Soil Sci. Plant. Nutr. 1991, 37, 191–200. [Google Scholar]
- Fogg, A.M. Simple and mixed metal oxides and hydroxides: Solids with extended structures of different dimensionalities and porosity. In The group 13 metals, Aluminium, Gallium, Indium and Thallium: Chemical patterns and peculiarities; Aldridge, S., Downs, A.J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 503–506. [Google Scholar]
- Munthali, M.W.; Elsheik, M.A.; Johan, E.; Matsue, N. Proton adsorption selectivity of zeolites in aqueous media: Effect of Si/Al ratio of zeolites. Molecules 2014, 19, 20468–20481. [Google Scholar]
- Noda, T.; Suzuki, K.; Katada, N.; Niwa, M. Combined study of IRMS-TPD measurement and DFT calculation on Brønstedacidity and catalytic cracking activity of cation-exchanged Y zeolites. J. Catalysis. 2008, 259, 203–210. [Google Scholar]
- Sastre, G.; Katada, N.; Niwa, M. Computational study of BrØnsted acidity of mordenite. Effect of the electric field on the infrared OH stretching frequencies. J. Phys. Chem. 2010, 114, 15424–15431. [Google Scholar]
- Hiromi, Y.; Masakazi, A. Photofunctional Zeolites: Synthesis, Characterization, Photocatalytic Reactions, Light Harvesting; Nova Science publishers: Huntington, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- van Santen, R.A.; Neurock, M. Molecular Heterogeneous Catalysis: A Conceptual and Computational Approach; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Beran, S.; Dubskÿ, J. Quantum chemical study of the electronic structure of Na-X and Na-Y zeolites. J. Phys. Chem. 1979, 83, 2538–2543. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S.; Choi, S.Y.; Lim, W.T. Complete Li+ exchange into zeolite X (FAU, Si/Al=1.09) from undried methanol solution. J. Porous Mater. 2013, 20, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Herron, N.; Corbin, D.R. Inclusion Chemistry with Zeolites: Nanoscale Materials by Design; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Tansel, B. Significance of thermodynamic and physical characteristics on permeation of ions during membrane separation: Hydrated radius, hydration free energy and viscous effects. Separ. Purif. Tech. 2012, 86, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Querol, X.; Moreno, N.; Umana, J.C.; Alastuey, A.; Hernandez, E.; Lopez-Soler, A.; Plana, F. Synthesis of zeolites from coal fly ash: An overview. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2002, 50, 413–423. [Google Scholar]
- Sherry, H.S. The ion-exchange properties of zeolites. In Ion Exchange; Manisky, J.A., Dekker, M., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1969; pp. 89–133. [Google Scholar]
- Sienko, M.; Plan, R.; Hester, R. Structural Inorganic Chemistry; Mir Publishers: Moscow, Russia, 1968; p. 344. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Nightingale, E.R., Jr. Phenomenological theory of ion solvation. Effective radii of hydrated ions. J. Phys. Chem. 1959, 63, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar]
- Binder, H.; Zschornig, O. The effect of metal cations on the phase behavior and hydration characteristics of phospholipid membranes. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2002, 115, 39–61. [Google Scholar]
- Woods, R.M.; Gunter, M.E. Na-and Cs-exchange in a clinoptilolite-rich rock: Analysis of the outgoing cations in solution. Am. Mineral. 2001, 86, 424–430. [Google Scholar]
- Breck, D.W. Zeolites Molecular Sieves. Structure, Chemistry, and Use; Wiley-Interscience Publication: New York, NY, USA, 1974; p. 82. [Google Scholar]
- Loera, S.; Llewellyn, P.L.; Lima, E. Na+ charge tuning through encapsulation of sulfur chromophores in zeolite A and the consequences in adsorbent properties. J. Phys. Chem. 2010, 114, 7880–7887. [Google Scholar]
- Breck, D.W. Zeolite Molecular Sieves; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.T. Adsorbents: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, D.; Siriwardane, R.; Biegler, L.T. Optimization of pressure swing adsorption and fractionated vacuum pressure swing adsorption processes for CO2 capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 8084–8094. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Navrotsky, A.; Wilkin, R. Thermodynamics of ion exchanged and natural clinoptilolite. Am. Mineral. 2001, 86, 438–447. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.N.; Curtis, R.M. Dipole polarizabilities of ions in alkali halide crystals. J. Phys. Chem. 1970, 74, 187–196. [Google Scholar]
- Legras, B.; Polaert, I.; Estel, L. Effect of alcaline cations in zeolites on their dielectric properties. J. Microw. Power Electromagn. Energy 2012, 46, 2011–2013. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).