Comparative Toxicological Evaluation of Solubilizers and Hydrotropic Agents Using Daphnia magna as a Model Organism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Toxicity Assay
2.3. Physiological Activity Assessment
2.3.1. Recording of Heart Rate
2.3.2. Recording of Thoracic Appendages and Post-Abdominal Claw Movement
2.3.3. Motion Recording and Swimming Speed Evaluation
2.4. Embryotoxicity
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Toxicity Evaluation
3.2. Physiological Activity Assessment
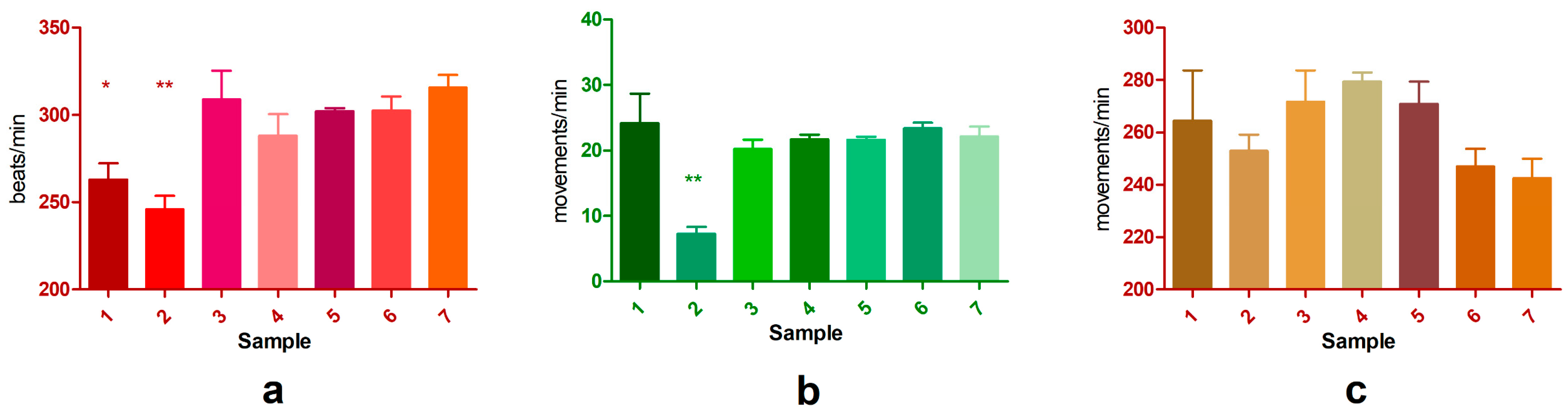
3.2.1. Heart Rate
3.2.2. Claw Movement
3.2.3. Appendages Movement
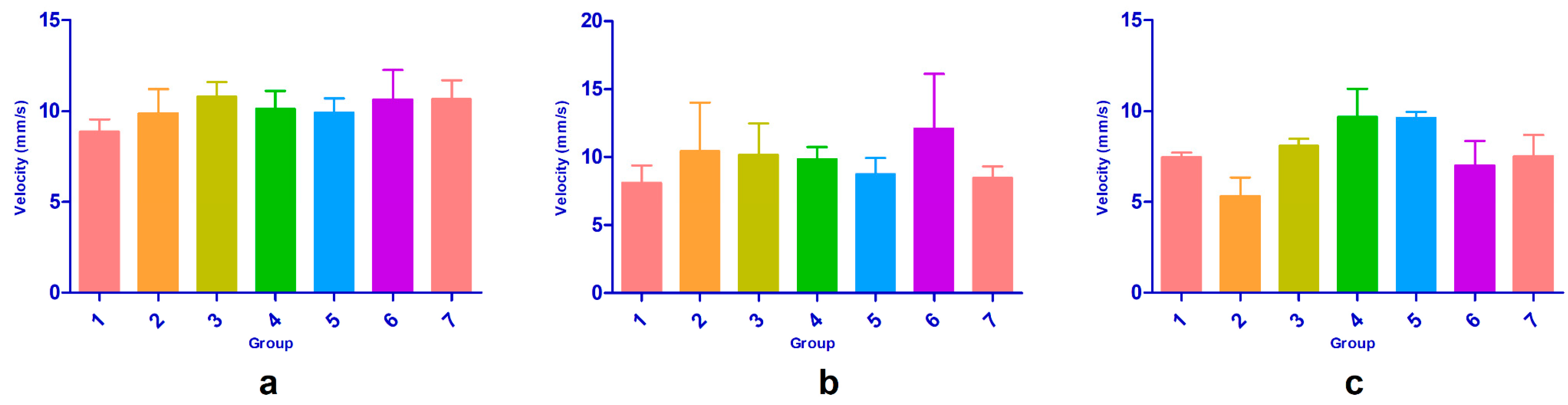
3.2.4. Behavioral Evaluation
3.2.5. D. magna Embryotoxicity
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koivisto, S. Is Daphnia magna an Ecologically Representative Zooplankton Species in Toxicity Tests? Environ. Pollut. 1995, 90, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, D. Daphnia as a Versatile Model System in Ecology and Evolution. EvoDevo 2022, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, B.G.; Jenkins, J.C. A Time Study of Events in the Life Span of Daphnia magna. Biol. Bull. 1942, 83, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.; Ferrando, M.D.; Sancho, E.; Andreu-Moliner, E.; Sánchez, M.; Ferrando, M.D.; Sancho, E.; Andreu-Moliner, E. Evaluation of a Daphnia magna Renewal Life-Cycle Test Method with Diazinon. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 1998, 33, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebeker, A.V. Evaluation of a Daphnia magna Renewal Life-Cycle Test Method with Silver and Endosulfan. Water Res. 1982, 16, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasik, P.; Warren, D.M. The Use of Daphnia in Studies of Metal Pollution of Aquatic Systems. Environ. Rev. 2011, 4, 25–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Yim, B.; Bae, C.; Lee, Y.M. Acute Toxicity and Antioxidant Responses in the Water Flea Daphnia magna to Xenobiotics (Cadmium, Lead, Mercury, Bisphenol A, and 4-Nonylphenol). Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2017, 9, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, M.T.K.; Wang, W.X. Biokinetics and Tolerance Development of Toxic Metals in Daphnia magna. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullahi, M.; Li, X.; Abdallah, M.A.E.; Stubbings, W.; Yan, N.; Barnard, M.; Guo, L.H.; Colbourne, J.K.; Orsini, L. Daphnia as a Sentinel Species for Environmental Health Protection: A Perspective on Biomonitoring and Bioremediation of Chemical Pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 14237–14248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkaczyk, A.; Bownik, A.; Dudka, J.; Kowal, K.; Ślaska, B. Daphnia magna Model in the Toxicity Assessment of Pharmaceuticals: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 143038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M. Daphnia magna as a Model Organism to Predict the Teratogenic Effect of Different Compounds. Methods Mol. Biol. 2024, 2753, 261–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, G.A.; Mu, X.; Rider, C.V. Embryotoxicity of the Alkylphenol Degradation Product 4-Nonylphenol to the Crustacean Daphnia magna. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weichert, F.G.; Floeter, C.; Meza Artmann, A.S.; Kammann, U. Assessing the Ecotoxicity of Potentially Neurotoxic Substances—Evaluation of a Behavioural Parameter in the Embryogenesis of Danio rerio. Chemosphere 2017, 186, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittlerová, M.; Jírová, G.; Vlková, A.; Kejlová, K.; Maly, M.; Heinonen, T.; Wittlingerová, Z.; Zimová, M. Sensitivity of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos to Hospital Effluent Compared to Daphnia magna and Aliivibrio fischeri. Physiol. Res. 2020, 69, S681–S691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, K.; Ellis, L.J.A.; Davoudi, H.H.; Supian, S.; Maia, M.T.; Silva, G.H.; Guo, Z.; Martinez, D.S.T.; Lynch, I. Daphnia as a Model Organism to Probe Biological Responses to Nanomaterials—From Individual to Population Effects via Adverse Outcome Pathways. Front. Toxicol. 2023, 5, 1178482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakka, Y.; Koeser, J.; Filser, J. How Test Vessel Properties Affect the Fate of Silver Nitrate and Sterically Stabilized Silver Nanoparticles in Two Different Test Designs Used for Acute Tests with Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 2495–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, R.L.; Moser, E.M.; Kimerle, R.A.; McKenzie, D.E.; McKee, M. Use of a Miniaturized Test System for Determining Acute Toxicity of Toxicity Identification Evaluation Fractions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1996, 35, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küster, E.; Addo, G.G.; Aulhorn, S.; Kühnel, D. Miniaturisation of the Daphnia magna Immobilisation Assay for the Reliable Testing of Low Volume Samples. UCL Open Environ. 2025, 7, e3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.P.; Rees, S.S.; Kalindjian, S.B.; Philpott, K.L. Principles of Early Drug Discovery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products As Sources of New Drugs over the 30 Years from 1981 to 2010. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 311–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, L.; Choudhari, Y.; Patel, P.; Gupta, G.D.; Singh, D.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Bansal, K.K.; Kurmi, B. Das Advancement in Solubilization Approaches: A Step towards Bioavailability Enhancement of Poorly Soluble Drugs. Life 2023, 13, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerns, E.; Di, L.; Carter, G. In Vitro Solubility Assays in Drug Discovery. Curr. Drug Metab. 2008, 9, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvao, J.; Davis, B.; Tilley, M.; Normando, E.; Duchen, M.R.; Cordeiro, M.F. Unexpected Low-Dose Toxicity of the Universal Solvent DMSO. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kais, B.; Schneider, K.E.; Keiter, S.; Henn, K.; Ackermann, C.; Braunbeck, T. DMSO Modifies the Permeability of the Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Chorion-Implications for the Fish Embryo Test (FET). Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 140–141, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, K.; Tibazarwa, C.; Certa, H.; Greggs, W.; Hillebold, D.; Jovanovich, L.; Woltering, D.; Sedlak, R. Environmental Risk Assessment of Hydrotropes in the United States, Europe, and Australia. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2010, 6, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMille, C.M.; Arnott, S.E.; Pyle, G.G. Variation in Copper Effects on Kairomone-Mediated Responses in Daphnia Pulicaria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 126, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, B.P.; Abranches, D.O.; Sintra, T.E.; Leal-Duaso, A.; García, J.I.; Pires, E.; Shimizu, S.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Glycerol Ethers as Hydrotropes and Their Use to Enhance the Solubility of Phenolic Acids in Water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 5742–5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaud, A.; Lebeuf, R.; Laguerre, M.; Nardello-Rataj, V. Improved Hydrotropic Extraction of Carnosic Acid from Rosemary and Sage with Short-Chain Monoalkyl Glycerol Ethers. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 3673–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bownik, A.; Jasieczek, M.; Kosztowny, E. Ketoprofen Affects Swimming Behavior and Impairs Physiological Endpoints of Daphnia magna. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, M.N.; Kuptsova, T.S.; Semenov, V.V. Toxicity of Organic Solvents and Surfactants to the Sea Urchin Embryos. Chemosphere 2024, 353, 141589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, M.; Palma, M.; Tavares, L.C.; Panserat, S.; Viegas, I.; Magnoni, L.J. Glycerol Supplementation in Farmed Fish Species: A Review from Zootechnical Performance to Metabolic Utilisation. Rev. Aquac. 2024, 16, 1901–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.I.; Pires, E.; Aldea, L.; Lomba, L.; Perales, E.; Giner, B. Ecotoxicity Studies of Glycerol Ethers in Vibrio Fischeri: Checking the Environmental Impact of Glycerol-Derived Solvents. Green. Chem. 2015, 17, 4326–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.A.; De Mora, S.J.; Levasseur, M. A Review of Dimethylsulfoxide in Aquatic Environments. Atmos. Ocean 1999, 37, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncaglioni, A.; Toropov, A.A.; Toropova, A.P.; Benfenati, E. In Silico Methods to Predict Drug Toxicity. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2013, 13, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freires, I.A.; Morelo, D.F.C.; Soares, L.F.F.; Costa, I.S.; de Araújo, L.P.; Breseghello, I.; Abdalla, H.B.; Lazarini, J.G.; Rosalen, P.L.; Pigossi, S.C.; et al. Progress and Promise of Alternative Animal and Non-Animal Methods in Biomedical Research. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 2329–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaru, O.T.; Nitulescu, G.M.; Codreanu, A.M.; Calmuc, V.A.; Venables, L.; van de Venter, M.; Gird, C.E.; Duta-Bratu, C.G.; Nitulescu, G. Inhibitory Effects on Staphylococcus aureus Sortase A by Aesculus Sp. Extracts and Their Toxicity Evaluation. Plants 2024, 13, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajir, S.; Jobst, K.J.; Kleywegt, S.; Simpson, A.J.; Simpson, M.J. Do Co-Solvents Used in Exposure Studies Equally Perturb the Metabolic Profile of Daphnia magna? Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2025, vgaf068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, K.; Oda, N.; Miyoshi, K.; Funaki, T.; Ida, Y. Solubilization Behavior of a Poorly Soluble Drug under Combined Use of Surfactants and Cosolvents. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 28, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheleski, J.; Wiggers, H.J.; Citadini, A.P.; da Costa Filho, A.J.; Nonato, M.C.; Montanari, C.A. Kinetic Mechanism and Catalysis of Trypanosoma cruzi Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase Enzyme Evaluated by Isothermal Titration Calorimetry. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 399, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, M.; Pitts, W.; Dewprashad, B. Using Videography to Study the Effects of Stimulants on Daphnia magna. Am. Biol. Teach. 2017, 79, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracker® Software. Available online: https://opensourcephysics.github.io/tracker-website/ (accessed on 3 February 2025).
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.S.; Lu, C.Y.; Chang, S.H. Evaluation of Acute Toxicity and Teratogenic Effects of Plant Growth Regulators by Daphnia magna Embryo Assay. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivan, I.M.; Popovici, V.; Chițescu, C.L.; Popescu, L.; Luță, E.A.; Ilie, E.I.; Brașoveanu, L.I.; Hotnog, C.M.; Olaru, O.T.; Nițulescu, G.M.; et al. Phytochemical Profile, Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Potential of Capsicum annuum (L.) Dry Hydro-Ethanolic Extract. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corotto, F.; Ceballos, D.; Lee, A.; Vinson, L. Making the Most of the Daphnia Heart Rate Lab: Optimizing the Use of Ethanol, Nicotine & Caffeine. Am. Biol. Teach. 2010, 72, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bownik, A.; Stępniewska, Z.; Skowroński, T. Effects of Ectoine on Behavioural, Physiological and Biochemical Parameters of Daphnia magna. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 168, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, F.; Farhan, A.; Suryanto, M.E.; Kurnia, K.A.; Chen, K.H.C.; Vasquez, R.D.; Roldan, M.J.M.; Huang, J.C.; Lin, Y.K.; Hsiao, C. Der Automated Cardiac Chamber Size and Cardiac Physiology Measurement in Water Fleas by U-Net and Mask RCNN Convolutional Networks. Animals 2022, 12, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lari, E.; Steinkey, D.; Pyle, G.G. A Novel Apparatus for Evaluating Contaminant Effects on Feeding Activity and Heart Rate in Daphnia spp. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 135, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, S.W.; Wood, D.C. Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) Toxicology, Pharmacology, and Clinical Experience. Am. J. Surg. 1967, 114, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci, M.; Maione, F.; Bonito, M.C.; Piscopo, A.; Di Giannuario, A.; Pieretti, S. New Insights of Dimethyl Sulphoxide Effects (DMSO) on Experimental in Vivo Models of Nociception and Inflammation. Pharmacol. Res. 2008, 57, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyberghs, J.; Bars, C.; Ayuso, M.; Van Ginneken, C.; Foubert, K.; Van Cruchten, S. DMSO Concentrations up to 1% Are Safe to Be Used in the Zebrafish Embryo Developmental Toxicity Assay. Front. Toxicol. 2021, 3, 804033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade-Vieira, L.F.; Bojic, C.; Santana Alvarenga, I.F.; de Carvalho, T.S.; Masfaraud, J.F.; Cotelle, S. Ecotoxic Effects of the Vehicle Solvent Dimethyl Sulfoxide on Raphidocelis subcapitata, Daphnia magna and Brachionus calyciflorus. Chem. Ecol. 2022, 38, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haap, T.; Triebskorn, R.; Köhler, H.R. Acute Effects of Diclofenac and DMSO to Daphnia magna: Immobilisation and Hsp70-Induction. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelizaro, B.I.; Braga, F.C.; Crispim, B.d.A.; de Barros, L.G.M.L.; Pessatto, L.R.; Oliveira, E.J.T.; Vani, J.M.; de Souza, A.P.; Grisolia, A.B.; Antoniolli-Silva, A.C.M.B.; et al. Assessment of Acute Toxicity and Cytotoxicity of Fluorescent Markers Produced by Cardanol and Glycerol, Which Are Industrial Waste, to Different Biological Models. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 9193–9202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, R.; Kim, S.W.; An, Y.J. Polystyrene Nanoplastics Inhibit Reproduction and Induce Abnormal Embryonic Development in the Freshwater Crustacean Daphnia Galeata. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verge, C.; Moreno, A. Effects of Anionic Surfactants on Daphnia magna. Tenside Surfactants Deterg. 2000, 37, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Long, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhou, F.; Liu, C.; Chen, L.; Pan, Y. Ecological Impact of Surfactant Tween-80 on Plankton: High-Scale Analyses Reveal Deeper Hazards. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Min, P.; Liu, W.; Li, L.; Yi, P.; Guo, R.; Chen, J. Ecological Risks of High-Ammonia Environment with Inhibited Growth of Daphnia magna: Disturbed Energy Metabolism and Oxidative Stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechuga, M.; Fernández-Serrano, M.; Jurado, E.; Núñez-Olea, J.; Ríos, F. Acute Toxicity of Anionic and Non-Ionic Surfactants to Aquatic Organisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 125, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| LC50 (%) | 95%CI of LC50 (%) | r2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substance | 24 h | 48 h | 24 h | 48 h | 24 h | 48 h | |
| 1 | SXS | 1.569 | 0.0863 | 1.023–2.405 | 0.0536–0.1390 | 0.8605 | 0.8162 |
| 2 | SBS | 2.078 | 0.0928 | 1.447–2.983 | 0.0750–0.1148 | 0.8536 | 0.9555 |
| 3 | PTS | 1.153 | 0.0606 | 0.6764–1.965 | 0.0553–0.0664 | 0.7838 | 0.962 |
| 4 | SBDS | 2.516 | 0.4823 | 1.824–3.473 | 0.2127–1.094 | 0.8371 | 0.722 |
| 5 | DMBA | 0.1358 | ND * | ND *** | ND | 0.998 | ND |
| 6 | DENA | 1.083 | 0.1491 | 0.8912–1.316 | 0.0780–0.2849 | 0.9525 | 0.8074 |
| 7 | DMU | 2.664 | 0.3909 | 1.477–4.807 | 0.2097–0.7285 | 0.9489 | 0.8307 |
| 8 | Urea | 3.27 | 0.9286 | 2.369–4.516 | 0.5688–1.516 | 0.6624 | 0.7353 |
| 9 | DMF | 2.464 | 0.305 | 0.1717–0.5418 | 0.9213 | 0.8575 | |
| 10 | DMSO | ND ** | ND ** | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 11 | Tween 20 | ND * | ND * | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 12 | Tween 80 | ND * | ND * | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 13 | SLS | ND * | ND * | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 14 | GLY | ND ** | ND ** | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 15 | PDO | ND ** | 2.725 | ND | 2.086–3.559 | ND | 0.7268 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olaru, I.I.; Mihai, D.P.; Olaru, O.T.; Gird, C.E.; Zanfirescu, A.; Stancov, G.; Andrei, C.; Luta, E.-A.; Nitulescu, G.M. Comparative Toxicological Evaluation of Solubilizers and Hydrotropic Agents Using Daphnia magna as a Model Organism. Environments 2025, 12, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050172
Olaru II, Mihai DP, Olaru OT, Gird CE, Zanfirescu A, Stancov G, Andrei C, Luta E-A, Nitulescu GM. Comparative Toxicological Evaluation of Solubilizers and Hydrotropic Agents Using Daphnia magna as a Model Organism. Environments. 2025; 12(5):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050172
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlaru, Iulia Ioana, Dragos Paul Mihai, Octavian Tudorel Olaru, Cerasela Elena Gird, Anca Zanfirescu, Gheorghe Stancov, Corina Andrei, Emanuela-Alice Luta, and George Mihai Nitulescu. 2025. "Comparative Toxicological Evaluation of Solubilizers and Hydrotropic Agents Using Daphnia magna as a Model Organism" Environments 12, no. 5: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050172
APA StyleOlaru, I. I., Mihai, D. P., Olaru, O. T., Gird, C. E., Zanfirescu, A., Stancov, G., Andrei, C., Luta, E.-A., & Nitulescu, G. M. (2025). Comparative Toxicological Evaluation of Solubilizers and Hydrotropic Agents Using Daphnia magna as a Model Organism. Environments, 12(5), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050172









