Abstract
Rapid population growth and climate change have created challenges for managing water quality. Protecting water sources and devising practical solutions are essential for restoring impaired inland rivers. Traditional water quality monitoring and forecasting methods rely on labor-intensive sampling and analysis, which are often costly. In recent years, real-time monitoring, remote sensing, and machine learning have significantly improved the accuracy of water quality forecasting. This paper categorizes machine learning approaches into traditional, deep learning, and hybrid models, evaluating their performance in forecasting water quality parameters. In recent years, the long short-term memory (LSTMs), gated recurrent units (GRUs) and LSTM- and GRU-based hybrid models have been widely used in forecasting inland river water quality. Combining remote sensing with a real-time water quality monitoring network has enhanced data collection efficiency by capturing spatial variability within the river network, complementing the high temporal resolution of in situ measurements, and improving the overall robustness of predictive deep learning models. Additionally, leveraging weather prediction models can further enhance the accuracy of water quality forecasting and better decision-making for water resource management.
1. Introduction
Water quality is a critical indicator of ecosystem health, human well-being, and socioeconomic development. Inland rivers, as vital freshwater sources, play a fundamental role in supporting ecosystems and providing water for agriculture, industry, and human consumption. However, concerns over the deterioration of river water quality have grown significantly in recent decades, driven by both natural and human factors [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13].
1.1. Problem Statement
Major contributors to inland river water pollution include industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, urbanization, and climate change [13,14,15,16,17]. Untreated or poorly treated effluents from manufacturing, mining, and chemical industries introduce hazardous pollutants into rivers [14]. Through the widespread use of fertilizers and pesticides, agricultural activities lead to nutrient pollution and trigger eutrophication and harmful algal blooms [18,19,20,21]. Rapid urban growth increases domestic wastewater discharge and stormwater runoff [22]. Meanwhile, variations in rainfall patterns, rising temperatures, and extreme weather events further exacerbate water quality issues by altering river flow regimes and pollutant transport mechanisms [13,23,24,25].
These factors have degraded river ecosystems, reduced aquatic biodiversity, and created dead zones that severely impact aquatic life [26,27]. Consequently, there is an urgent need to develop accurate and efficient inland river water quality forecasting models to support proactive water resource management.
Between 2000 and 2010, traditional machine learning models were widely used in river water quality forecasting. However, traditional water quality assessment methods relating to physical sampling and analysis are often time-consuming, costly, and geographically limited. After that, big data techniques and neural networks also started gaining traction in this domain. By the 2020s, deep learning models emerged as the most popular choice, owing to their superior performance in handling spatial and temporal river datasets. More recently, hybrid models have surpassed standalone deep learning approaches, offering greater accuracy and efficiency. These advanced hybrid models are now becoming the dominant choice in river water quality forecasting. This progression, synthesized from a critical review of the recent literature [28,29], highlights the evolving methodological landscape in river water quality forecasting.
In recent years, machine learning techniques have emerged as effective tools for forecasting river water quality because they can process large datasets and non-linear relationships to provide timely predictions [30,31]. While significant progress has been made, the current body of research lacks a comprehensive ynthesis of the methods applied, as well as their respective strengths, limitations, and areas for improvement.
1.2. Contribution
This review focuses on inland rivers, including a wide range of river types from major river basins to smaller rivers, streams, and tributaries. It narratively categorizes machine learning approaches for inland river water quality forecasting, including traditional, deep learning, and hybrid models. It analyzes the characteristics, limitations, and challenges of recent methods, guiding the selection of model inputs tailored to river system features. Furthermore, it proposes future research directions such as hybrid model integration, addressing data sparsity through real-time forecasting, incorporating remote sensing for near-real-time monitoring, and enhancing model interpretability for decision-making support. By synthesizing current research, this review fosters the development of robust, scalable tools for sustainable water quality management, and lays the groundwork for future innovations in the field.
2. Materials and Methods
In inland river water quality forecasting, key elements include essential water quality indicators and performance metrics. The water quality indicators are categorized into physical, chemical, and biological parameters. Additionally, this paper highlights commonly used performance indicators to evaluate forecasting models effectively.
To ensure the review captures the latest advancements, the papers collected were mainly published between 2000 and 2025, reflecting the most recent research in the field. However, foundational and highly cited studies published before 2000 and those from 2000 to 2020 were also incorporated to provide historical context and deepen insights into the evolution of water quality forecasting methodologies. With the rise of machine learning, machine learning models have been commonly applied across many fields, including river water quality prediction.
A comprehensive literature search was conducted using Google Scholar to identify relevant studies published until 2025. Figure 1 shows the process of the review. The search strategy incorporated a combination of keywords, including “real-time monitoring water quality”, “inland river water quality forecasting”, “water management”, “inland river water quality deep learning”, “water quality hybrid machine learning”, “water quality machine learning”, “water quality urbanization agriculture”, and “water quality remote sensing”.
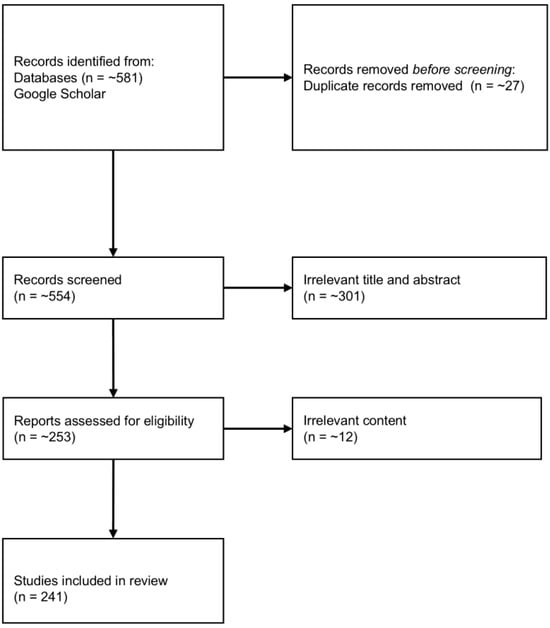
Figure 1.
The process of the review. This diagram illustrates the conceptual logic of literature selection for this narrative review. The numerical values are approximate and not derived from a formal systematic review process.
In addition to studies directly applying machine learning techniques for inland river water quality forecasting, additional references were incorporated during the writing process to provide essential background information. These included studies related to water quality indicators, pollution sources, hydrological processes, and remote sensing technologies. As a result, the final synthesis reflects foundational knowledge necessary for a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
2.1. Hydrology Background
River water quality detection is important for water management and protects water resources. Water quality forecasting offers an early warning for polluted water bodies. For example, the dynamic forecasting model helps determine whether the water body has a high risk of pollution. Water management has become an urgent issue due to the increasing pressure from human activities, such as urbanization and globalization, and the impacts of climate change on water resources [32,33]. Water is crucial for agriculture and energy production, while urban and industrial sectors continue to drive growing demand, further intensifying the need for effective water resource management [33].
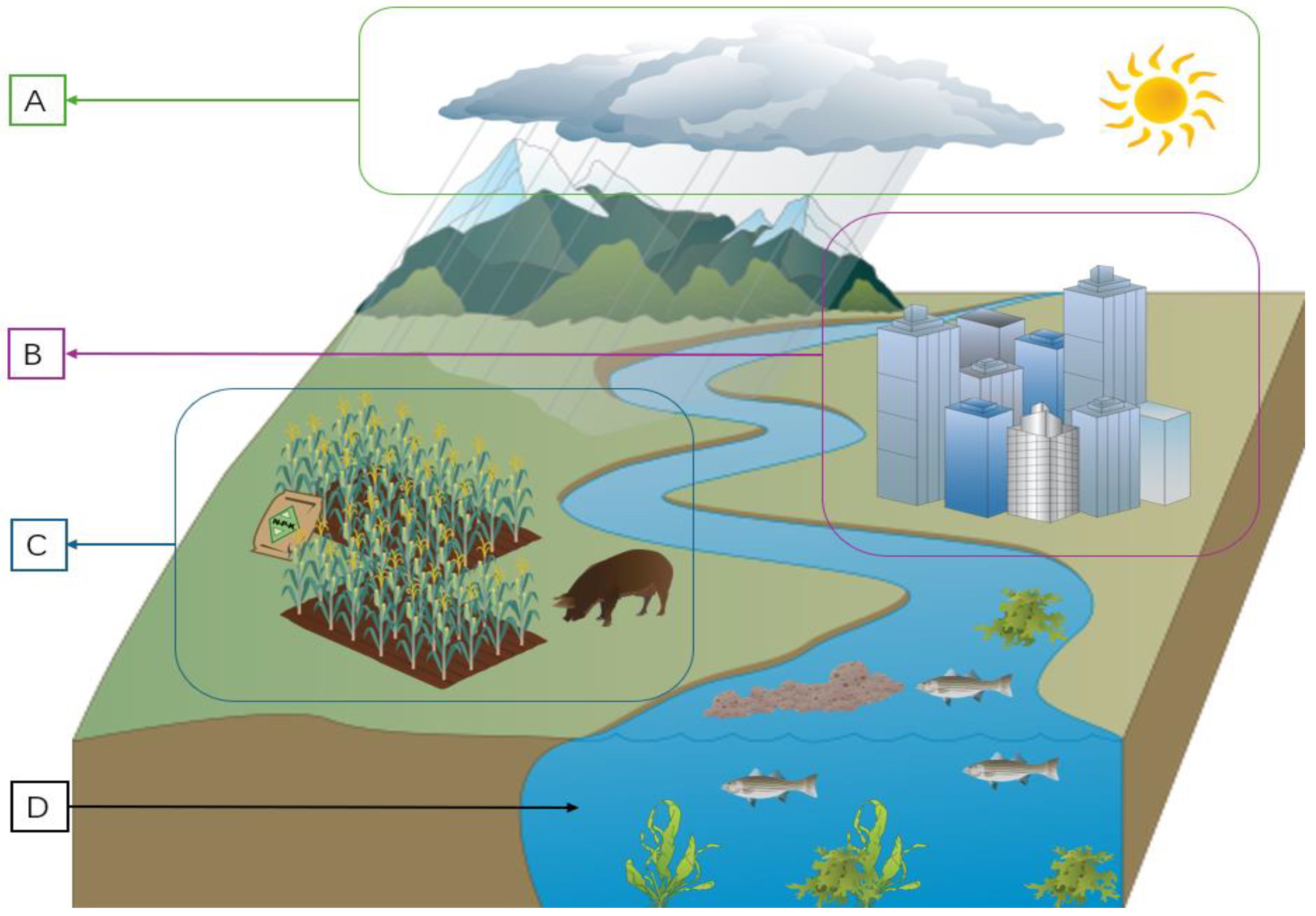
Figure 2 presents a conceptual diagram illustrating the key factors influencing inland river water quality. As depicted, three primary drivers—weather, urbanization, and agriculture—play significant roles in shaping water quality dynamics [34,35,36,37]. Section A outlines the water quality impacts driven by precipitation. During periods of low precipitation and drought, river discharge decreases. Under such conditions, pollutants such as nutrients and heavy metals tend to accumulate due to limited dilution and slower flow. This accumulation can promote eutrophication and lead to increased concentrations of dissolved and suspended solids in the water column. Human activities are a major contributor to these changes, influencing nutrient loading, pollution levels, and hydrological conditions. Sections B and C highlight the impacts of urbanization and agricultural activities, respectively. Urbanization increases domestic wastewater discharge and industrial effluents, while agriculture contributes to nutrient enrichment through fertilizer runoff and animal waste. Although the climatic influences are not explicitly illustrated in Figure 2, they are further discussed in the following paragraph, with particular attention to the impacts of ice cover and road salt on river water quality.
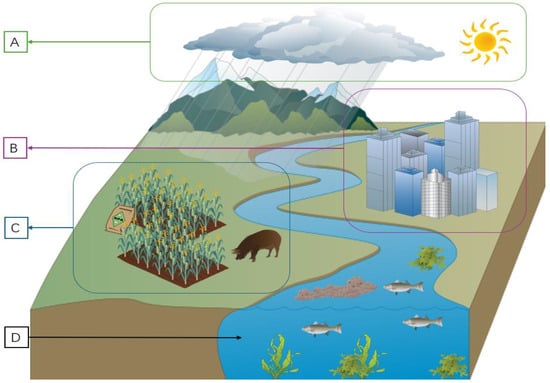
Figure 2.
Conceptual diagram of river water quality influences. The labels refer to the following: (A) Increased river discharge, resulting from precipitation, leads to reduced turbidity and residence time, and consequently increases dissolved oxygen levels. (B) Urbanization increases pollution inputs, elevating nutrient levels, suspended solids, and organic contaminants. (C) Agricultural runoff delivers fertilizers and pesticides into rivers, leading to nutrient enrichment, turbidity increase, and dissolved oxygen decrease. (D) Eutrophication promotes algal blooms, which consume dissolved oxygen, causing hypoxia and the death of aquatic life. Figure made using icons from Integration and Application Network (ian.umces.edu/media-library; accessed on 9 May 2025).
In northern areas, seasonal ice formation significantly impacts river water quality. During winter, ice cover restricts gas exchange between water and air, leading to oxygen depletion. Moreover, ice formation alters turbidity and algal dynamics, which are key indicators of water quality [38,39]. Notably, the widespread use of road salt to accelerate ice melt leads to elevated chloride concentrations, which can disrupt aquatic ecosystems [40,41]. These seasonal variations underscore the complex interplay between climatic factors and river water quality, warranting further investigation into predictive modeling and management strategies.
Human activities contribute to water pollution, significantly impacting water quality. Pollution is generally categorized into two types—diffuse pollution and point source pollution [42]. Diffuse pollution is primarily caused by surface runoff and interflow, while wastewater emissions represent point source pollution. Unlike point source pollution, diffuse pollution arises over a broad area, making it more challenging to monitor and control. Multiple factors influence river water quality forecasting, including the interaction between groundwater and surface water. For instance, rainfall can transport fertilizers into the soil, where they gradually infiltrate into groundwater [43]. When groundwater interacts with surface water, these nutrients are transferred into rivers, impacting water quality and potentially leading to eutrophication.
2.2. Water Quality Indicators
Water quality indicators are measurable parameters that provide critical information about water’s physical, chemical, and biological characteristics. These indicators are used to assess, monitor, and predict the condition of river systems. Accurate water quality forecasting heavily relies on selecting and analyzing the most relevant indicators. Water quality indicators serve as fundamental parameters in river water quality forecasting, providing essential insights into aquatic ecosystems’ physical, chemical, and biological conditions. Temperature, discharge, turbidity, total dissolved solid (TDS) and total suspended solids (TSS) are regarded as physical indicators. Dissolved oxygen (DO), biological oxygen demand (BOD), chemical oxygen demand (COD), pH, nutrient levels and heavy metals are chemical indicators. The biological indicators include algae and coliform bacteria amount [44]. Table 1 introduces detailed information for each indicator. While this table summarizes the most frequently reported water quality parameters, future investigations could extend the scope by including a broader range of dissolved organic compounds. Other dissolved organic components, such as artificial sweeteners and iodinated X-ray contrast media, antibiotics and pesticides, are also important water quality indicators. These compounds primarily originate from wastewater discharge and runoff, and their concentration can serve as useful markers for detecting pollution in inland river systems [45,46].

Table 1.
Detailed information for water quality indicators.
Water quality indicators exhibit both temporal and spatial variations and are influenced by other environmental factors. The table shows that temperature and turbidity affect DO, while discharge impacts turbidity. In water quality forecasting, correlation analysis is commonly used to determine relationships between different indicators. Indicators with higher correlation coefficients are considered more influential in predicting the target water quality parameter [48], making them essential for improving forecasting accuracy.
These are the typical water quality indicators used in recent research. However, water quality indicators are inherently variable, as all components entering the water system contribute to changes in water quality. The following section provides an overview of recent advancements in river water quality forecasting.
2.3. River Water Quality Forecasting in Recent Years
Traditional monitoring methods rely on physical sampling and laboratory analysis, which are time-consuming, costly, and spatially limited, making it difficult to provide real-time assessments and early warnings for pollution events [30]. Furthermore, using machine learning, river water quality forecasting supports proactive decision-making in pollution control and disaster management. By identifying trends and predicting potential contamination events, machine learning models help policymakers implement targeted mitigation strategies, optimize wastewater treatment, and ensure drinking water supply safety [64]. Integrating hybrid machine learning models, combining deep learning and physics-based hydrological models, has further improved forecasting capabilities by capturing both temporal and spatial variations in river ecosystems [66].
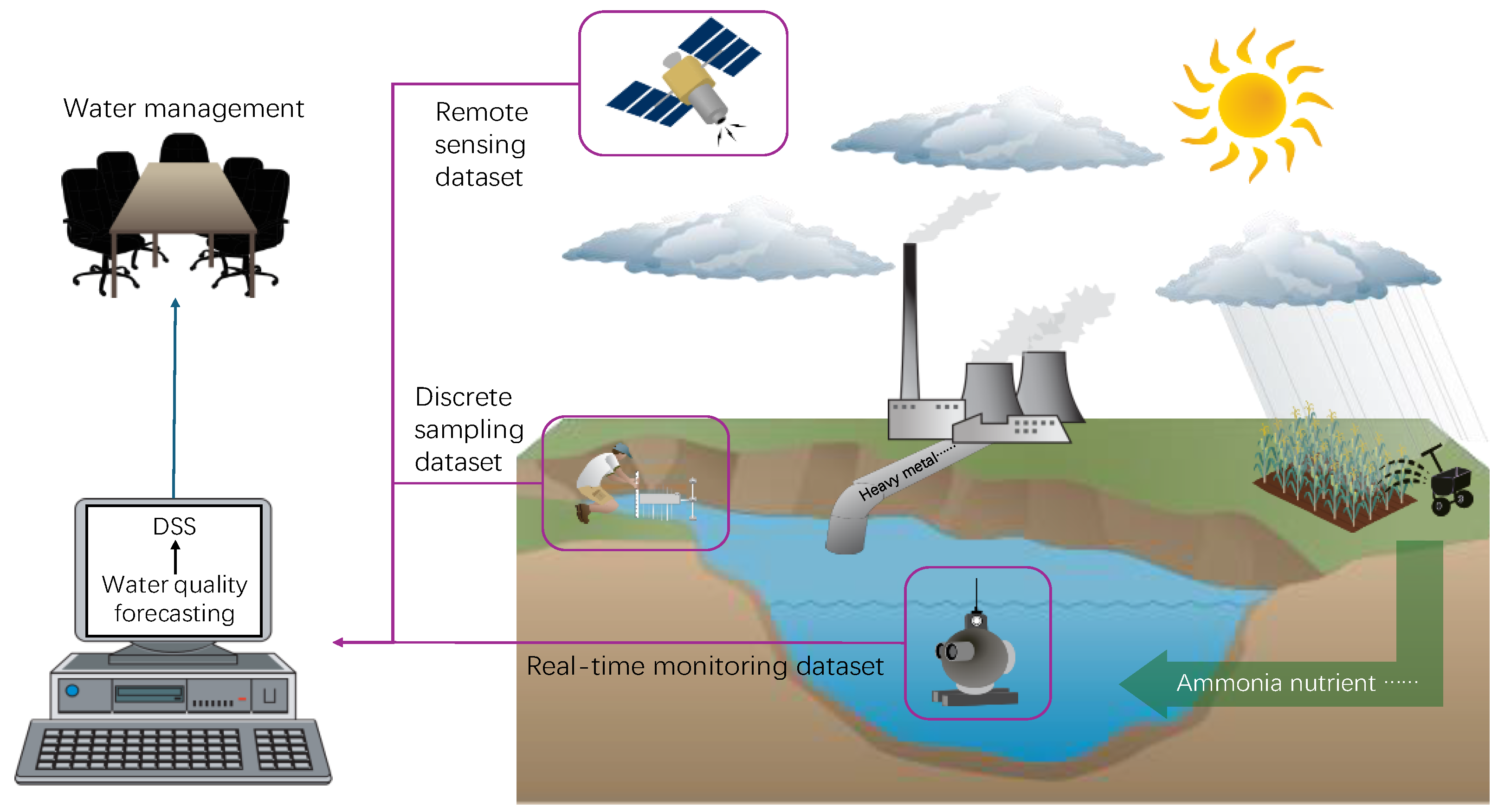
Figure 3 shows that weather conditions, diffuse pollution, and point source pollution influence river water quality. Machine learning methods use remote sensing, discrete sampling, and real-time monitoring datasets to forecast river water quality. The predicted water quality data are then utilized in decision-support systems (DSS) to inform decision-making. Water management strategies, including policy development, are based on insights derived from DSS, enabling more effective and sustainable water resource management.
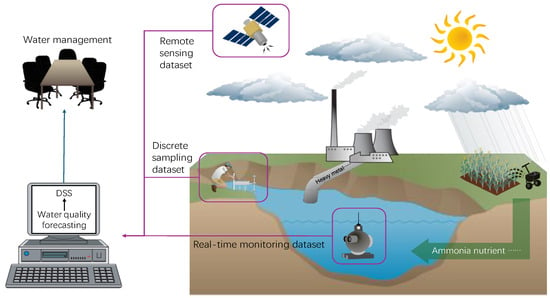
Figure 3.
A schematic diagram of water quality monitoring. Figure made using icons from Integration and Application Network (ian.umces.edu/media-library; accessed on 9 May 2025).
Traditional methods face challenges such as the lack of real-time data, limited large-scale coverage, and low efficiency. Recent advancements incorporating real-time monitoring, remote sensing, and DSS help address these issues, enhancing the performance and effectiveness of water quality assessment and management.
2.3.1. Real-Time Monitoring for Water Quality
Real-time monitoring enables the collection of continuous, high-frequency water quality datasets [90], identifying water quality trends with greater accuracy. These datasets are particularly valuable for spatial models [91]. While real-time monitoring provides strong temporal resolution and operational efficiency [92], it may have some spatial limitations due to localized sensor deployment.
Some common indicators that apply real-time monitoring include TDS [93,94,95], temperature [93,96], pH [93,96], DO [89], and turbidity [96]. Monitoring spikes in these parameters can help detect various upland sources of industrial effluent discharges, agricultural non-point source pollution runoff, municipal wastewater discharges in combined sewer systems and stormwater runoff pollution to urban streams using well-established modelling tools [97]. These indicators provide an instant reflection of water quality changes, offering real-time insights into the health of aquatic ecosystems. Implementing real-time monitoring for these parameters enhances assessment and response to fluctuations in water quality, ensuring more effective water resource management and ecosystem protection.
2.3.2. Advances in Remote Sensing and Machine Learning for River Water Quality Prediction
River water quality prediction is essential for environmental management and public health. Integrating remote sensing and machine learning offers a promising alternative, enabling large-scale assessment of key water quality parameters.
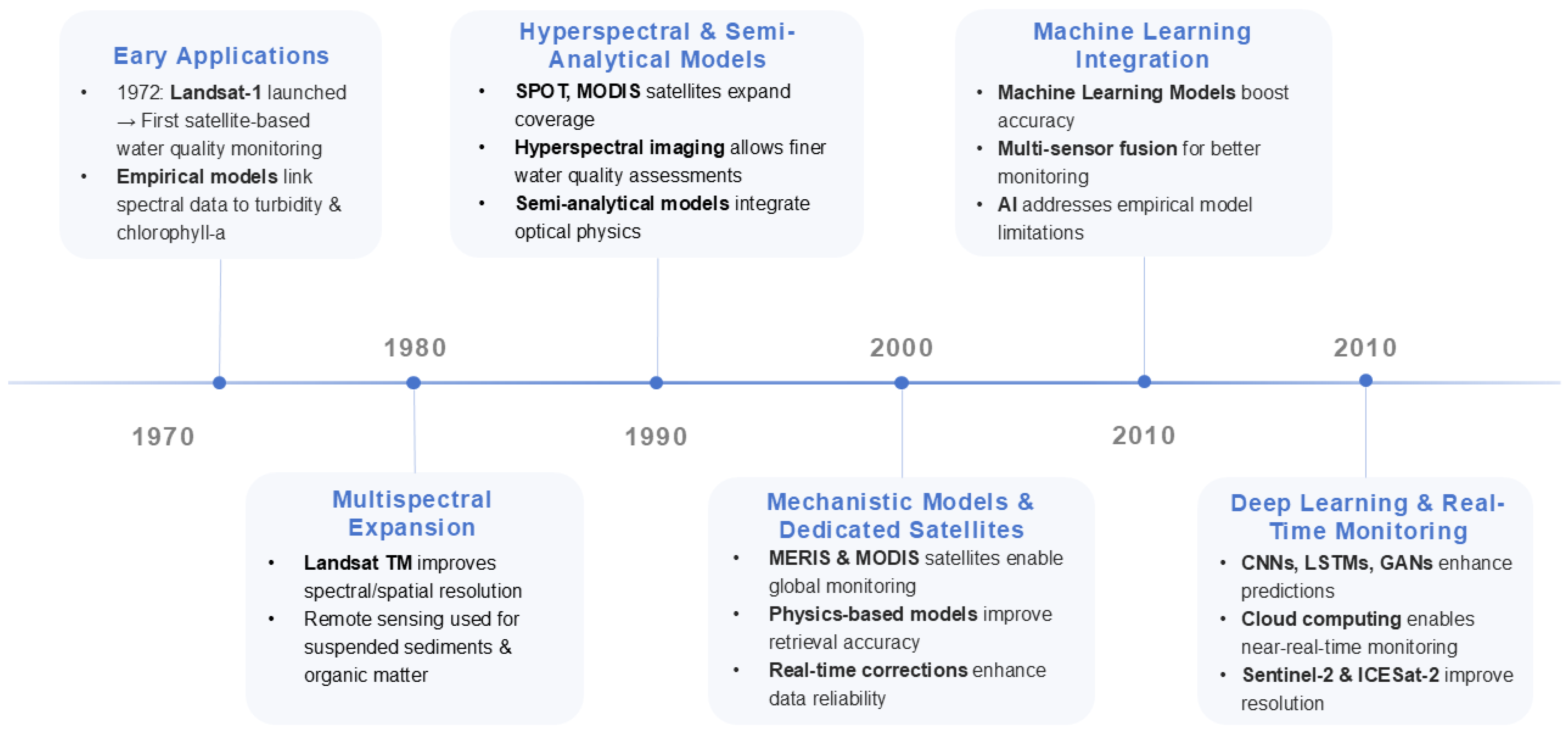
Remote sensing has facilitated the collection of large-scale datasets, such as chlorophyll-a measurements spanning from 1970 to 2023 [98,99]. Traditional in situ sampling often requires more than a day to produce comprehensive contamination mapping. In contrast, the integration of satellite data with machine learning significantly reduced detection times to within a few hours [98]. As shown in Figure 4, dating back to the 1970s, the launch of Landsat-1 enabled the first satellite-based observations of inland and coastal waters [100]. Early studies demonstrated that satellite spectral measurements could be empirically correlated with water quality indicators such as turbidity and chlorophyll-a, establishing remote sensing as a viable supplement to in situ sampling. Throughout the 1980s, advancements in multispectral sensors, such as the Landsat Thematic Mapper, expanded spectral coverage and spatial resolution, enabling more accurate access to water quality parameters [101]. The 1990s saw the introduction of new satellites, including SPOT and MODIS [102], alongside hyperspectral imaging [103], significantly enhancing the ability to detect subtle water quality signals. Concurrently, retrieval models evolved from purely empirical regressions to semi-analytical approaches [104] that integrated optical physics, ultimately leading to fully analytical (mechanistic) radiative transfer models. By the early 2000s, dedicated satellite missions, including MERIS and MODIS, were operational, and improvements in inversion algorithms, supported by increased computational power, yielded more accurate and globally applicable water quality estimates. In the 2010s, machine learning methods began to be applied to water quality prediction [105,106], capturing complex nonlinear relationships between spectral reflectance and water quality parameters. These data-driven approaches outperformed traditional empirical and semi-analytical models in predictive accuracy.
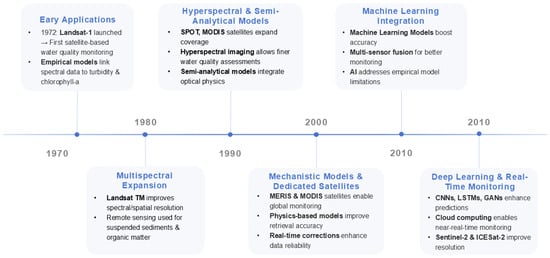
Figure 4.
The timeline of remote sensing and machine learning for water quality monitoring.
More recently, deep learning techniques have emerged, leveraging high-dimensional data from hyperspectral imagery and temporal records to further enhance retrieval accuracy and enable near-real-time monitoring. Such advancements underscore the disruptive potential of merging spectral data with computational intelligence. This section examines three pivotal innovations that are reshaping the field while addressing unresolved technical bottlenecks.
Multi-sensor data fusion for water quality prediction: Multi-sensor data fusion made river water quality prediction more accurate. Chen et al. [107] demonstrated that UAV-based multispectral imaging combined with CatBoost regression performed better than traditional machine learning models in predicting turbidity, TN, and TP. Cheng et al. [108] further improved prediction accuracy using a stacked ensemble learning model (Stacked-RF), integrating gradient boosting, CatBoost, and Adaboost techniques. Despite these advancements, challenges remain in synchronizing multi-sensor data and addressing discrepancies in spatial and temporal resolutions. Future work should focus on optimizing sensor calibration and data harmonization techniques.
Innovations in spatiotemporal modeling: Spatiotemporal modeling is important in addressing the dynamic nature of river water quality. Zhu et al. [109] proposed a sub-regional inversion method using Gaofen-1 satellite data, significantly enhancing prediction accuracy in complex river networks. Zhao et al. [110] utilized Google Earth Engine (GEE) with a stacked generalization learning approach, achieving 91.67% accuracy in water quality classification for the Songhua River Basin. While these models enhance prediction reliability, their computational complexity and generalizability across diverse hydrological conditions remain challenges. The further exploration of hybrid physics-based deep learning models may address these limitations.
Few-shot learning for water quality prediction: It addresses data scarcity issues in river water quality prediction. Villota-González et al. [111] achieved scores of 0.72 for total suspended solids estimation using superlearner algorithms on limited Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 datasets. Further, transfer learning approaches, such as those by Ueda et al. [112], demonstrated that for four peak water-level scenarios, the transfer learning model delivered 6 h forecasts with a Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE) of 0.86, matching the performance of traditional upstream-based methods (NSE = 0.84). Notably, prediction accuracy remained stable when training data for specific storm events were reduced from 12 to 3 periods, highlighting the framework’s resilience in data-limited conditions. These approaches effectively circumvent data poverty but face trade-offs: model adaptation to new regions typically requires retraining 65–70% of network layers, eroding computational efficiency.
The selection of remote sensing platforms for river water quality monitoring must align with the spatial and temporal resolution requirements of target river reaches. For instance, Landsat-8/9 (30 m spatial resolution, 16-day revisit) is well-suited for large rivers (>50 m width) to monitor chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) and turbidity trends, as demonstrated in nutrient monitoring studies for major basins [107,113]. Sentinel-2 (10–60 m resolution, 5-day revisit) offers a balance between spatial detail and temporal frequency, making it ideal for medium-sized rivers (20–50 m width) to track algal bloom dynamics and suspended sediment transport [107]. In contrast, MODIS (250–1000 m resolution, daily coverage) provides macroscale insights for estuaries and large river systems, despite its limited ability to resolve narrow channels [107,114]. Emerging technologies like UAV-based hyperspectral imaging (0.1–1 m resolution) enable the high-precision mapping of pollution sources in small tributaries or urban channels, such as pinpointing industrial discharge points or localized nutrient hotspots [115]. This multi-scale synergy ensures comprehensive monitoring, where coarse-resolution satellites capture basin-wide trends, while UAVs and high-resolution sensors address site-specific challenges [113].
The focus on remote sensing in this review stems from its transformative ability to overcome limitations inherent to traditional monitoring methods. Unlike labor-intensive in situ sampling, which lacks spatial coverage and temporal continuity, remote sensing enables large-scale, real-time assessments of optically active parameters (e.g., Chl-a, turbidity) across entire watersheds [114]. For example, Sentinel-2’s frequent revisit cycle allows the near-real-time detection of harmful algal blooms (HABs), triggering timely interventions to mitigate public health risks [99,113]. Furthermore, remote sensing reduces operational costs by up to 60% compared to manual sampling, particularly in remote or hazardous regions [113]. While traditional methods remain critical for ground-truth validation, remote sensing provides unparalleled scalability for global water quality management. Future advancements in hyperspectral sensors (e.g., PRISMA, DESIS) and AI explainability frameworks will further bridge gaps in monitoring non-optically active parameters, solidifying remote sensing as a cornerstone of sustainable water resource management.
Although this review focuses on remote sensing methods due to their broad spatial coverage and scalability, it is also recognized that artificial intelligence (AI) models have proven effective when applied to high-frequency water column observations collected via sensor networks [116]. Combining those two methods will improve predictions across diverse spatial and temporal scales.
Integrating remote sensing and machine learning has significantly advanced river water quality prediction, providing unprecedented spatial and temporal coverage. Despite these advances, challenges remain in optimizing remote sensing methodologies, improving model generalization, and addressing discrepancies in multi-sensor data integration. Continued research is necessary to refine hybrid modeling approaches that incorporate physics-based constraints, enhance the interpretability of deep learning predictions, and develop more robust calibration techniques for non-optically active water quality parameters.
2.3.3. Decision-Support Systems for Water Management
DSS for water management is a system applied to water resources and datasets to make decisions [117]. These water resources include water quality datasets from predictive models and weather variations. DSS is crucial in decision-making, policy formulation, and in guiding research in related fields [118]. One example of DSS implementation is the SMART method [119]. The SMART method is successfully applied to issue warnings for the Bedog and Sembung Rivers, where water quality is deemed unsuitable for daily use. Another successful DSS application is the WATERMAN DSS, which integrates geographical information systems (GIS) with satellite imagery to effectively monitor the Strymon River [120].
AI DSS has become a prominent research topic in recent years. Unlike traditional DSS, AI DSS incorporates machine learning techniques, including deep learning methods, to generate datasets for decision-making. These AI-driven models enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs [121]. In water quality management, AI DSS utilizes AI models to predict water quality indices, enabling more accurate assessments. AI DSS and DSS are particularly effective in handling complex, variable, and extreme water bodies [122,123].
Despite these advancements, accurately forecasting water quality trends remains a complex challenge, as it involves nonlinear interactions between physical, chemical, and biological processes influenced by climatic variability, human activities, and hydrological dynamics. To address these challenges, machine learning models are powerful tools for water quality prediction, offering the ability to detect patterns in large datasets and provide highly accurate, data-driven forecasts.
3. Machine Learning Models Used in River Water Quality Forecasting
Machine learning models have been increasingly applied to forecast inland river water quality in recent years. As a vast and dynamic field, machine learning encompasses a wide variety of models.
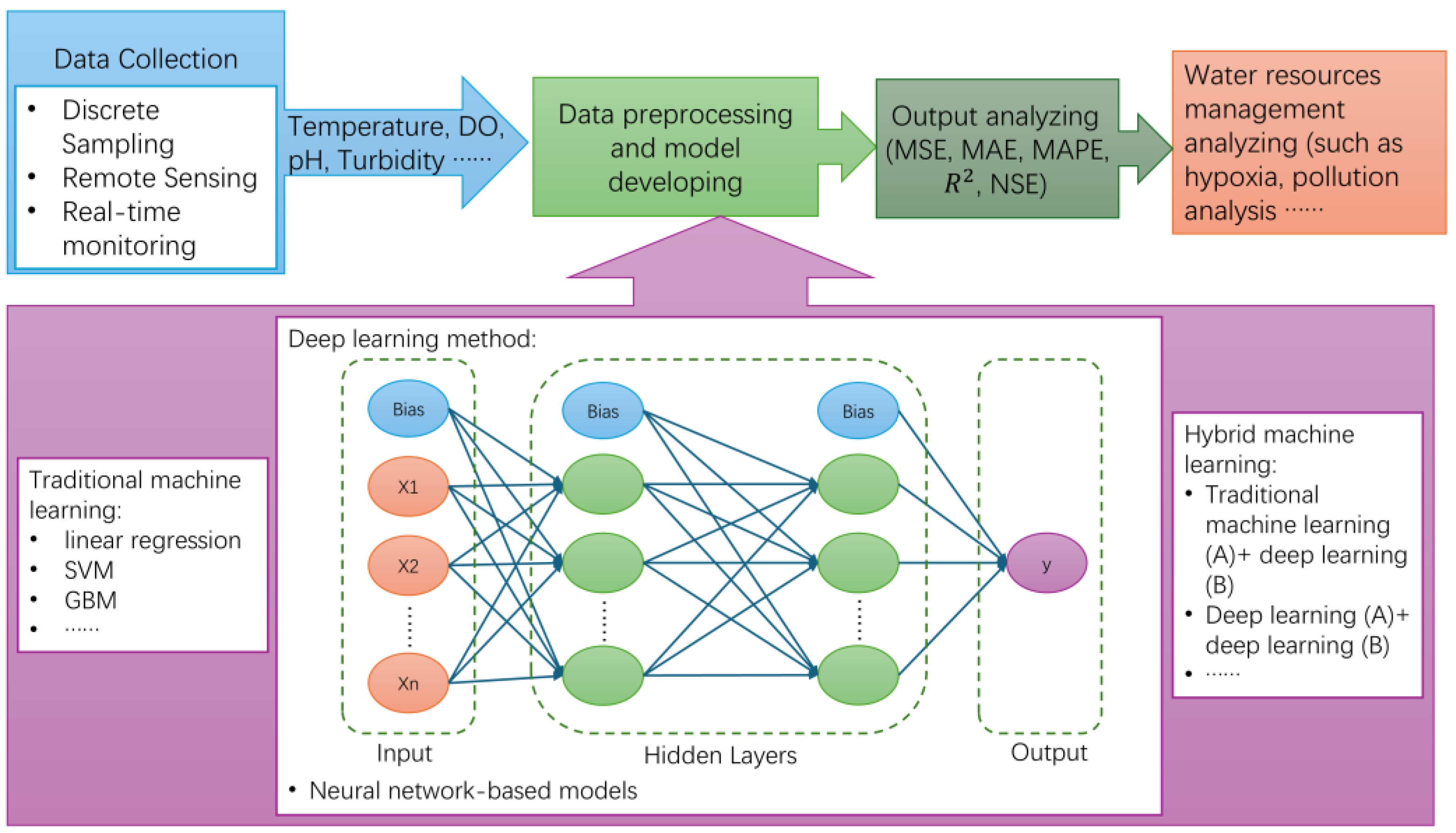
As presented in Figure 5, the river water quality forecasting process is mainly divided into four steps. The methods of data preprocessing and model development have been continuously evolving in recent years, incorporating advanced techniques to improve accuracy and efficiency in water quality forecasting.
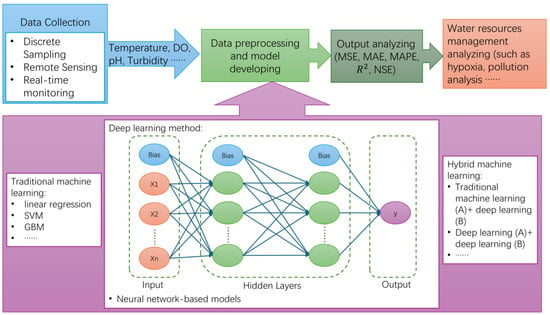
Figure 5.
The flowchart of river water quality forecasting.
Besides the model development process, the output analysis is also important for water quality forecasting. In this step, performance indicators are metrics used to evaluate machine learning models’ effectiveness, accuracy, and reliability. These indicators are crucial for assessing how well models predict parameters in river water quality prediction.
Mean square error (MSE) highlights model performance, especially in the presence of outliers. The root means squared error (RMSE) expresses errors in the same units as the target variable, enhancing interpretability. Mean absolute error (MAE) is more robust against outliers, making it a reliable accuracy measure. Mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) provides insights into relative performance. Lower values for MSE, RMSE, MAE, and MAPE indicate better model effectiveness, ensuring clarity and confidence in real-world applications.
The Coefficient of Determination () is close to 1, which indicates better performance. NSE is commonly used in hydrology to evaluate prediction accuracy relative to the mean observed value. NSE measures predictive skill relative to observed variability. measures the goodness of fit and explained variance.
Understanding the performance indicators helps to determine the machine learning performance. This section illustrates the machine learning models used nowadays for river water quality forecasting. Three primary categories of models stand out: traditional machine learning models, deep learning models, and hybrid machine learning models. This section highlights examples of machine learning applications in predicting river water quality.
3.1. Traditional Machine Learning Models
Traditional machine learning models were popular for river water quality prediction because they can process structured datasets, uncover patterns, and make predictions. Unlike deep learning models, traditional machine learning uses manual feature engineering and is generally more interpretable. It is particularly effective for datasets with limited complexity or size, making it useful for many water quality prediction tasks.
Multi linear regression models are the fundamental models used in river water quality forecasting [124]. As predicted, river water quality over a certain period of time is a regression problem. Support vector machines (SVMs) use hyperplanes to classify data points [125,126]. They can predict discrete water quality classes. The gradient boosting machines (GBMs) sequentially build an ensemble of weak learners, focusing on correcting errors from previous iterations. XGBoost, LightGBM and CatBoost are popular variants of GBMs [127,128,129].
Traditional machine learning models are relatively simple, and they can be explained. They are effective for small datasets. However, traditional machine learning methods are not as popular as complex machine learning methods as more machine learning models are being developed.
3.2. Deep Learning Models
Deep learning has revolutionized the field of data-driven modeling by effectively handling large, complex and unstructured datasets. Deep learning models in river water quality prediction excel at capturing non-linear relationships and temporal dependencies between multiple water quality indicators, making them particularly suitable for dynamic and complex river ecosystems.
They can handle complex datasets better than traditional machine learning models. They are used for high-dimensional datasets with different temporal and spatial information. In recent times, the most common deep learning models include artificial neural networks (ANNs), recurrent neural networks (RNNs), convolutional neural networks (CNNs), long short-term memory networks (LSTMs) and transformer models.
3.2.1. Artificial Neural Networks
ANNs are the foundational deep learning models. They are highly versatile and have been applied in water quality prediction due to their ability to capture non-linear relationships in data [130,131,132,133,134,135]. ANNs predict critical water quality indicators such as DO, BOD, pH, and turbidity [136,137,138,139]. ANNs analyze large and high-dimensional spatial and temporal water quality data to find pollution sources and predict their downstream impacts. This makes them suitable for modern water monitoring systems involving remote sensing [140].
ANNs are flexible and can be tailored to various prediction tasks, including regression and multi-output problems. They automatically learn relevant relationships from raw data, reducing manual preprocessing demand. However, the accuracy of the ANN-predicted water quality parameters depends on the availability of a comprehensive and extensive monitoring program to provide a suitable training/testing dataset, which should include extreme events and significant effluent discharges and spills that would cause spikes in water quality parameters.
3.2.2. Recurrent Neural Networks
RNNs are designed to process sequential and time-series data. RNNs incorporate feedback loops, allowing them to maintain information about previous inputs (memory) in their computations. This makes RNNs particularly suitable for water quality prediction, where the temporal relationships between parameters are critical [141,142].
RNNs have a similar structure to ANNs. The input layer accepts sequential data such as time-series measurements of water quality parameters. The recurrent hidden layers are more complex than ANNs [143]. The hidden layers process inputs sequentially, using feedback loops to maintain a state that captures previous time step information. Each hidden state is computed as
where is the hidden state at the time step t, is the input, and is an activation function. The output layer predicts the current or next time step for different water quality research. RNNs have recurrent hidden layers that serve as memory, which maintains temporal dependencies in the data.
RNNs are used in river water quality forecasting, including time-series forecasting [144]. RNNs predict future water quality indicators based on historical data. Meanwhile, they are used to predict algae bloom. The algae bloom can be used to reveal the trend of eutrophication in the river [145] by modeling the progression of nutrient levels and their impacts on algal growth over time. RNNs also integrate real-time sensor data to provide dynamic predictions of water quality parameters.
The most apparent advantage of RNNs is that they are temporal dependency models. The recurrent structure allows RNNs to account for the order of water quality events, making them ideal for time-series prediction tasks. RNNs can process multiple water quality parameter inputs simultaneously to predict various outputs.
3.2.3. Convolutional Neural Networks
CNNs excel at extracting spatial patterns and features from structured data, making them efficient for tasks like analyzing satellite imagery of rivers, detecting pollution sources, and studying spatial variations in water quality [146].
CNNs are mainly used for spatial pattern analysis. They analyze spatial variations in water quality parameters by processing gridded datasets [147]. CNNs have a strong capacity for image analysis [148,149]. In this case, they can analyze the satellite imagery [150]. The satellite images contain pollution sources, and algae blooms are used to analyze river water quality [146]. CNNs can combine spatial data from sensors to predict water quality at different locations in a river system.
For CNNs, they automatically learn spatial patterns and relationships, reducing the need for manual feature engineering. CNNs efficiently handle large datasets, including high-resolution imagery and multi-sensor spatial data. They are also robust to noise and variations in the data, making them well-suited for diverse environmental conditions.
3.2.4. Long Short-Term Memory Networks
By incorporating memory cells and gates, LSTMs can effectively capture both short-term and long-term dependencies. There is a special type of LSTM that shows an advanced ability for river water quality forecasting, called gated recurrent units (GRUs) [127,151,152,153,154]. GRUs are similar to LSTM networks but with a simplified architecture [155]. LSTMs and GRUs are particularly effective for river water quality prediction, where temporal relationships are essential, and computational efficiency is often required.
Both LSTMs and GRUs are special RNNs. The main difference with them is that the cells’ structures are different. The information derived from the previous cells will be new for the following cells. The equations for LSTMs are shown below:
where is the forget gate output; and are the outputs for the input and output gate, respectively; is the time step; is the memory cell state; is the candidate cell state;, and represent the weight matrix for the forget, input and output state, respectively; is the hidden state; is the current input; and are the bias for different gates; is the sigmoid activation function.
For GRUs, the equations are similar. The equations can be represented as
where is the update gate output; is the reset gate output. is the candidate activation. The other letters have the same meanings as LSTM equations.
LSTMs and GRUs are robust to sequential data challenges [155]. They overcome the vanishing gradient problem, allowing for stable training and improved performance on long time-series data. They are suitable for real-time applications where continuous data streams from sensors need to be analyzed dynamically. As they have different structures, they are also advanced in different fields. Table 2 lists the different characteristics of LSTMs and GRUs.

Table 2.
The comparison between LSTMs and GRUs.
Models excel in sequential data analysis and are useful for water quality prediction. LSTMs are more powerful for analyzing long-term information but are computationally heavier. GRUs are simpler, faster, and more effective for tasks with moderate temporal dependencies.
3.2.5. Transformer Models
Transformer models have been applied for forecasting water quality in the recent years [156,157]. The self-attention mechanism is a commonly used transformer model [158,159]. It enables the model to concentrate on the important sections of the input sequence when generating predictions. Multi-head attention models are also a kind of transformer model [160]. They enhance the model’s ability to recognize various patterns by utilizing multiple attention mechanisms simultaneously.
Transformer models allow themselves to capture relationships over long sequences without the vanishing gradient problem [161]. They process all input elements simultaneously, significantly speeding up training and inference. Transformers can also integrate multivariate data, including temporal, spatial, and contextual information, making them versatile for water quality prediction tasks. The attention weights provide insights into the input sequence that is most relevant to the prediction. This improves the explainability.
Time-series forecasting and spatiotemporal analysis are the applications of transformers in river water quality prediction [162]. They forecast water quality indicators based on historical data with time and space information. They can also identify and attribute water quality changes to specific pollution sources using multivariate data.
Deep learning models have significantly advanced the river water quality prediction field by offering superior capabilities in handling large, complex, and unstructured datasets. Each model contributes unique strengths to water quality prediction, providing researchers with flexible tools to address various aspects of river system dynamics. The integration of temporal, spatial, and multivariate data into deep learning models has made them indispensable for modern environmental management.
3.3. Hybrid Machine Learning Models
Hybrid machine learning models combine the strengths of different modeling techniques, including traditional machine learning, deep learning, and statistical methods, to enhance predictive accuracy, robustness, and adaptability. These models are particularly valuable in river water quality prediction, where the data are often complex, multivariate, and span both temporal and spatial dimensions. By leveraging multiple approaches, hybrid models can address the limitations of individual models and improve performance across diverse tasks.
The hybrid machine learning models combine different models. One example is the integration of statistical and machine learning methods. Statistical models capture linear trends, while machine learning models address non-linear relationships [30,163,164,165,166]. Combining different machine learning models is commonly used to develop hybrid models. As an example, hybrid models often combine algorithms such as random forests, SVMs, and gradient boosting with deep learning techniques like LSTMs or CNNs [167,168]. Spatiotemporal models can also be combined [168,169,170,171,172]. Ensemble approaches, such as stacking, boosting, or bagging, combine multiple models to improve generalization and reduce errors.
The hybrid machine learning models are complex but more accurate than simple models. Combining models helps to capture both linear and non-linear relationships, leading to more precise predictions. Meanwhile, hybrid models are able to adapt to a variety of data types and tasks. For example, CNNs are not good at dealing with temporal datasets. If we use CNN-LSTM, this hybrid model can deal with spatial and temporal datasets [173]. Besides this, hybrid models do not easily overfit when they are dealing with noisy datasets.
3.4. Overview of the Useful Machine Learning Method for River Water Quality Forecasting
River water quality forecasting has evolved significantly over the years, moving from traditional monitoring techniques to advanced data-driven approaches that leverage machine learning and artificial intelligence. Early efforts primarily focused on manual sampling and empirical statistical methods to predict water quality parameters like DO, BOD, and nutrient levels [64]. These methods, while foundational, were limited in their ability to handle complex datasets or predict water quality in dynamic environments.
The advent of machine learning marked a turning point in water quality forecasting. Techniques such as ANNs began to be applied, enabling the modeling of non-linear relationships and improving prediction accuracy. ANNs demonstrated their ability to forecast key parameters such as turbidity, pH, and TSS, but their reliance on high-quality datasets and computational resources presented challenges.
In recent years, hybrid models combining machine learning algorithms with data preprocessing techniques have gained prominence. For instance, hybrid decision tree-based models have been shown to enhance short-term water quality predictions by reducing noise and capturing critical features. These models, integrating tools like wavelet transforms and ensemble learning, have significantly improved the robustness of predictions, especially in rivers affected by urbanization and industrial activities.
Deep learning further revolutionized the field, with models such as LSTMs and CNNs widely adopted for spatio-temporal water quality forecasting. These models capture temporal dependencies and spatial heterogeneity, as demonstrated in studies focusing on complex river systems like the Burnett River in Australia and the Kelantan River Basin in Malaysia [174].
More recently, transformer models have emerged as a cutting-edge approach in water quality forecasting, offering advanced capabilities in handling long-term dependencies and large datasets. For example, the temporal fusion transformer has been applied to model and forecast water quality indexes in multi-site river networks, showcasing its potential for integrating diverse data sources [78].
The evolution of river water quality forecasting reflects a shift from manual and statistical methods to sophisticated machine learning and deep learning models driven by the availability of large datasets. Although there are advancements, challenges such as data quality, interpretability, and model generalization remain areas for future development.
Table 3 lists recent years’ research on river water quality forecasting. According to Table 3, hybrid models are widely adopted by researchers, with LSTM-based models being the most commonly used. In recent years, real-time monitoring has become a prevalent method for data collection, resulting in datasets that are both temporal and spatial in nature. LSTM-based models, including those using GRU architectures, demonstrate strong capabilities in analyzing and forecasting such real-time datasets. Those models fulfil the modern water quality prediction tasks.

Table 3.
The summary of machine learning models used for water quality forecasting.
The most commonly used and predicted parameters are oxygen indicators, such as DO, BOD and COD. These parameters are frequently investigated due to their importance in maintaining aquatic life, with DO being particularly vital for the survival of aquatic organisms [48]. The table also shows that the nutrient level is the most common water quality parameter that researchers have assessed recently (especially in 2025). As for the previous research, most water bodies face eutrophication. This is mainly caused by substantial nutrients in the water, including ammonia, TP and TN.
Another key finding is that total coliform levels are influenced by multiple external factors, making precise prediction challenging. To address this complexity, advanced modeling techniques are required. Hybrid models integrate multiple predictive approaches and are the most effective choice for capturing these influencing factors and improving prediction accuracy.
Meanwhile, this provides more water quality indicators, which might help with accurate water quality forecasting. In this case, many indicators are used to find the source of pollution, like river basin-specific pollutants (RBSPs) [202,213,214,215], aromatic compounds [216] and other organic or inorganic substances of origin. Compared with other water quality indicators, they show specific characteristics and can be related to local point source pollution. Many data collection methods, such as satellite images, can also be related to diffuse pollution.
Table 4 compiles representative case studies, listing not only the predictive models and their associated performance metrics (e.g., RMSE, MAE, ), but also the corresponding climate zones and major anthropogenic stressors affecting river water quality. The selection of models for inclusion is guided by the need to capture a diverse range of climatic conditions and temperate continental zones.

Table 4.
The climate zone and model performances of different models.
Based on the analysis in Table 4, model effectiveness appears closely linked to environmental conditions. As rivers traverse diverse landscapes, they are subjected to varying climatic regimes and anthropogenic influences. Agricultural runoff emerges as a common and significant threat across many river systems. In cold regions, snowmelt processes introduce additional complexities by causing substantial variations in river discharge, which, in turn, affect water quality dynamics.
Typically, as rivers flow through different climatic zones, they are influenced by multiple interacting factors. However, most existing studies tend to focus on specific river segments or localized regions, which helps to reduce the confounding effects of mixed climatic and anthropogenic interactions.
Forecasting river water quality in a specific area can serve as a valuable reference for shaping future governmental strategies. Consequently, temporal and spatial–temporal water quality forecasting has recently gained increasing attention. Hybrid models are commonly employed to enhance predictive accuracy, leveraging the strengths of multiple approaches to enhance model performance.
4. Limitations of the Present River Water Quality Forecasting Methods
The river water quality models discussed in the previous section demonstrate strong performance. However, they still have certain limitations, some of which are influenced by environmental factors.
4.1. Disadvantages of Machine Learning Models for Forecasting
Challenges inherent to these models, such as suboptimal performance and overfitting, present significant issues for researchers in this section. Additionally, improving machine learning models’ interpretability continues to be a critical area of concern.
4.1.1. Traditional Machine Learning Models
As mentioned above, the traditional machine learning methods are simple. This brings a lot of benefits. However, this also causes some limitations. Small and simple traditional machine learning methods struggle with high-dimensional, large-scale datasets or datasets with complex temporal and spatial structures. They are unable to handle complex features in the dataset. Based on the important water quality indicators section, there are many indicators that make the dataset non-linear [30,174,217]. Some simple traditional machine learning models, like linear regression, cannot capture non-linear interactions between water quality indicators.
4.1.2. Deep Learning Models
For deep learning models, ANNs restrict data requirements. They require large, high-quality datasets for training to avoid overfitting and ensure reliable predictions [136,218]. Training the ANN models requires significant time and equipment. ANNs models are black box models [130]. The models lack interpretability. This makes it hard for ANNs to understand how predictions are made. This can hinder trust in decisions based on ANN outputs. ANNs may memorize training data instead of generalizing, particularly when the dataset is small or noisy.
During backpropagation, gradients can shrink to near zero. Learning long-term dependencies is hard [141]. This limitation often necessitates using advanced RNN architectures like LSTM or GRU. There are many recurrent hidden layers in the RNNs. This increases computational complexity [219]. Training RNNs can be computationally demanding, particularly when dealing with long sequences and extensive datasets. RNNs require extensive and high-quality datasets for effective training.
CNNs have similar limitations to the previous models [219]. They also need large datasets for training to prevent overfitting and achieve generalization. CNNs are also limited temporal models. They are primarily designed for spatial data and lack the inherent ability to capture temporal relationships, requiring integration with time-series models like RNNs [133,173].
LSTMs and GRUs are useful machine-learning models for river water quality forecasting. There are still some disadvantages of the models. Both models require high-quality datasets for effective performance [219,220]. They require careful and time-consuming tuning for optimal performance [221]. If there are missing data and noisy datasets, they still cannot perform well.
Given the limitations of transformer models, they still need large datasets. As they analyze and forecast based on historical information, the limited and small dataset causes the model to not perform well, and the architecture is complex. This requires expertise in model design and hyperparameter tuning. The self-attention mechanism makes transformers memory-intensive for very long sequences [222].
Based on the previous analysis, the dataset is the biggest challenge for deep learning. Most of the models require high-quality datasets, and the neural network models are complex. This makes them expensive and raises the challenges of overfitting, as most of the models are black box models. It is challenging to understand how predictions are made.
4.1.3. Hybrid Machine Learning Models
Although hybrid machine learning models perform well, their complexity also increases. Designing and implementing hybrid models require expertise and the careful tuning of multiple components. This increases the cost as it increases computational resource requirements and training time. Integrating multiple models can make it difficult to explain predictions or identify the contributions of individual components.
4.2. Summary of the Machine Learning Models Used for River Water Quality
Based on the previous sections, we can use Table 5 to summarize the characteristics of river water quality forecasting. To put it simply, traditional machine learning models are ideal for simple physical indicators analysis, but lack the capacity to handle complex dynamic systems. Deep learning models excel in accuracy and spatial–temporal dynamics modeling, but are resource-intensive and challenging to interpret. They can learn and find the relationship between time and parameters. Hybrid models represent a key future direction, combining multiple approaches. Hybrid models represent improvements in the performance of simple deep learning models.

Table 5.
The characteristics of machine learning (ML) models for river water quality forecasting.
There are some challenges for the river water quality field. River water quality forecasting using current machine learning models faces several challenges that hinder its accuracy, reliability, and practical application. One significant issue is data availability and quality, as many regions lack comprehensive, high-resolution datasets due to limited monitoring infrastructure, leading to gaps and inconsistencies that affect model training and validation [223].
Additionally, handling complex spatiotemporal dependencies remains a challenge, as current models often struggle to simultaneously account for the interactions between spatial pollution patterns and temporal variations in water quality indicators [224]. Model interpretability is another critical limitation. The black box function of machine learning makes it hard to know the rationale behind predictions and trust their outcomes [225]. Furthermore, computational costs associated with advanced models like deep learning can be prohibitive, especially for resource-constrained settings requiring real-time predictions [226]. Models also face difficulties in adapting to climate change impacts, introducing new uncertainties in water quality dynamics [164]. Finally, the generalizability of models across different river systems is limited, as each system’s unique hydrological, geographical, and anthropogenic factors often necessitate extensive retraining and fine-tuning [174]. Addressing these challenges improves the effectiveness and adoption of machine learning models in river water quality forecasting.
4.3. Challenges in Data Collection for River Water Quality Forecasting
In addition to model-related challenges, data collection is another significant obstacle in river water quality forecasting. The factors contributing to river water quality deterioration are complex, with climate change and human activities being the primary drivers.
Extreme weather events, such as severe droughts and floods caused by climate change, significantly influence river discharge patterns, introducing considerable uncertainty into water quality forecasting [227,228]. Climate change also affects air temperature and wind patterns, further altering key water quality parameters [229,230]. Moreover, the inherent difficulty of accurately forecasting long-term weather conditions presents an additional layer of complexity, as these uncertainties directly impact the reliability of river water quality predictions.
Also, the river discharge brings another difficulty, called lag time. The lag time is the delay between pollutant input and observable changes in water quality parameters. Weather changes and agricultural runoff always cause a lag time. The lag time problem affects the accuracy of water quality forecasting [231].
Human activities like mining, industrial expansion, urbanization and agriculture introduce pollutants and alter river ecosystems, making water quality prediction increasingly complex. The interplay between diverse pollution sources and natural processes introduces nonlinearity and high variability in water quality parameters. This makes it challenging to develop models that can accurately account for both temporal and spatial variations [232]. Human activity also affects climate [233]. Global warming is a typical example. This further influences the prediction of river water quality.
While machine learning has greatly advanced river water quality forecasting, challenges remain in model reliability, data dependency, and computational costs. Traditional models struggle with complex, non-linear relationships, deep learning requires extensive data and resources, and hybrid models, though more accurate, are often complex and less interpretable. The following section explores these limitations, highlighting key data quality, model generalization, and scalability obstacles, and providing insights into future improvements.
5. Conclusions
In recent years, inland river water quality forecasting has significantly advanced, transitioning from traditional monitoring methods to hybrid remote-sensing, real-time monitoring and sophisticated machine learning-based approaches. While conventional monitoring methods provide critical insights, they are often labor-intensive, costly, and lack real-time forecasting with adequate spatial coverage to capture spatiotemporal variability. Machine learning techniques have emerged as powerful tools for water quality forecasting, offering the ability to process large datasets, model non-linear relationships, and generate accurate predictions across spatial and temporal scales.
This review examined various machine learning approaches, including traditional models, deep learning techniques, and hybrid frameworks. The emergence of deep learning and hybrid models, particularly LSTMs, GRUs and LSTM, and GRU-based models, has improved the ability to capture spatiotemporal dependencies in river water quality data. These models have proven highly effective in handling large-scale datasets and improving prediction accuracy. However, they also pose challenges, including high computational costs, reliance on large training datasets, and limited interpretability. Current methods cannot provide long real-time forecasts to meet water management requirements for timely early warnings, and there is a lack of updated datasets relevant to improved forecast accuracy. All of this is based on the current literature and the gaps we have identified.
Hybrid deep learning models are widely used; however, their complexity often makes them difficult to interpret. Attention-based deep learning models provide a potential solution to this issue. For instance, STA-GRU models have been used for water-level forecasting, demonstrating strong predictive performance [221]. Additionally, graph neural networks (GNNs), which leverage graph topology [234], have been effectively used for river water quality forecasting by modeling the diffusion of pollutants.
Another direction is the development of hybrid modeling approaches, combining machine learning techniques with data preprocessing tools. Multi-source data integration is crucial, incorporating information from satellite imagery and hydrological models to build comprehensive datasets for improved spatial and temporal analysis [235]. The availability and completeness of datasets often limit advanced machine learning models. Integrating remote sensing imagery and monitoring data enhances dataset comprehensiveness, providing a more robust foundation for accurate water quality predictions. For human-affected, complex, non-linear datasets like mine water datasets, thermodynamic models have been employed to perform predictions in mining-impacted regions [236]. Combining these physics-based models with machine learning techniques could allow for more robust and adaptive water quality forecasting frameworks in complex geological and hydrogeological conditions.
Applying explainable AI is also vital for improving stakeholder trust and the interpretability of predictions, especially in decision-making scenarios that require transparency [237]. Techniques such as Shapley Additive Explanations (SHAP) [48,128,238,239] and Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations (LIME) [238,239] provide feature-level interpretability by quantifying the contribution of each input variable to the model’s prediction.
Future models could focus on adapting to climate change impacts, such as increasing extreme weather events and shifting precipitation patterns, by incorporating dynamic inputs into predictive frameworks [240]. Moreover, real-time forecasting systems powered by edge computing and advanced neural networks, such as CNNs and LSTMs, could enhance responsiveness and accuracy in operational water quality monitoring [241].
Finally, one potential avenue for further improvement is to enhance existing machine learning methods while optimizing the data collection process. This could involve leveraging remote sensing technology for more efficient data acquisition and integrating advanced weather forecasting models to obtain highly accurate meteorological information. Beyond technical improvements, future research could also expand the range of water quality indicators and the scope of forecasting applications. In particular, these approaches could be extended to tidal rivers and estuarine environments. By addressing both methodological enhancements and broader application domains, this review is expected to serve as a reference for developing more resilient and adaptive forecasting systems under increasing climatic and anthropogenic pressures. It contributes both to academic discourse and to the practical foundation for deploying intelligent water quality monitoring systems worldwide.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.P.; methodology, D.P.; formal analysis, D.P.; investigation, D.P.; resources, D.P.; writing—original draft preparation, D.P.; writing—review and editing, Y.D., S.X.Y. and B.G.; supervision, S.X.Y. and B.G.; project administration, S.X.Y. and B.G.; funding acquisition, S.X.Y. and B.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of 535 Canada (NSERC) Alliance Grant #401643.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gani, M.A.; Sajib, A.M.; Siddik, M.A.; Moniruzzaman, M. Assessing the impact of land use and land cover on river water quality using water quality index and remote sensing techniques. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfram, J.; Stehle, S.; Bub, S.; Petschick, L.L.; Schulz, R. Water quality and ecological risks in European surface waters–Monitoring improves while water quality decreases. Environ. Int. 2021, 152, 106479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.G.; Diganta, M.T.M.; Sajib, A.M.; Rahman, A.; Nash, S.; Dabrowski, T.; Olbert, A.I. Assessing the impact of COVID-19 lockdown on surface water quality in Ireland using advanced Irish water quality index (IEWQI) model. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 336, 122456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortuna, A.M.; Starks, P.J.; Moriasi, D.N.; Steiner, J.L. Use of archived data to derive soil health and water quality indicators for monitoring shifts in natural resources. J. Environ. Qual. 2023, 52, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, A.; Biswas, D. Assessment of drinking water quality using water quality index: A review. Water Conserv. Sci. Eng. 2023, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajib, A.M.; Diganta, M.T.M.; Rahman, A.; Dabrowski, T.; Olbert, A.I.; Uddin, M.G. Developing a novel tool for assessing the groundwater incorporating water quality index and machine learning approach. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 23, 101049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, R.; Maqsood, A.; Baig, A.; Pande, C.B.; Zahra, S.M.; Saad, A.; Singh, S.K. A comprehensive review on water pollution, South Asia Region: Pakistan. Urban Clim. 2023, 48, 101413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, R.; Villanueva, C.M.; Beene, D.; Cradock, A.L.; Donat-Vargas, C.; Lewis, J.; Deziel, N.C. US drinking water quality: Exposure risk profiles for seven legacy and emerging contaminants. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2024, 34, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.D.; Staddon, C.; Salzberg, A.; Lucks, J.B.; Bruine de Bruin, W.; Young, S.L. Self-reported anticipated harm from drinking water across 141 countries. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Zhang, F.; Shi, J.; Kung, H.T. What is the relationship between land use and surface water quality? A review and prospects from remote sensing perspective. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 56887–56907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.I.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Sullivan, C.A. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karr, J.R.; Chu, E.W. Introduction: Sustaining living rivers. In Assessing the Ecological Integrity of Running Waters, Proceedings of the International Conference, Vienna, Austria, 9–11 November 1998; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Knapp, J.L.; Lintern, A.; Ng, G.H.C.; Perdrial, J.; Sullivan, P.L.; Zhi, W. River water quality shaped by land–river connectivity in a changing climate. Nat. Clim. Change 2024, 14, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.M.B.; do Valle Junior, R.F.; de Melo, M.M.A.P.; Pissarra, T.C.T.; de Melo, M.C.; Valera, C.A.; Fernandes, L.F.S. A framework model to integrate sources and pathways in the assessment of river water pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 347, 123661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Goyal, M.K.; Surampalli, R.Y.; Zhang, T.C. River pollution in India: Exploring regulatory and remedial paths. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2024, 26, 2777–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglou, A.N.; Nazari, R.; Karimi, M.; Museru, M.L.; Opare, K.N.; Nikoo, M.R. Future eco-hydrological dynamics: Urbanization and climate change effects in a changing landscape: A case study of Birmingham’s river basin. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 447, 141320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalińska, E.; Jarosińska, E.; Orlińska-Woźniak, P.; Jakusik, E.; Warzecha, W.; Ogar, W.; Wilk, P. Total nitrogen and phosphorus loads in surface runoff from urban land use (city of Lublin) under climate change. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 48135–48153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, P.J.; Neal, C.; Jarvie, H.P.; Doody, D.G. Agriculture and eutrophication: Where do we go from here? Sustainability 2014, 6, 5853–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viviano, G.; Valsecchi, S.; Polesello, S.; Capodaglio, A.; Tartari, G.; Salerno, F. Combined use of caffeine and turbidity to evaluate the impact of CSOs on river water quality. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menberu, Z.; Mogesse, B.; Reddythota, D. Evaluation of water quality and eutrophication status of Hawassa Lake based on different water quality indices. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakade, A.; Salama, E.S.; Han, H.; Zheng, Y.; Kulshrestha, S.; Jalalah, M.; Li, X. World eutrophic pollution of lake and river: Biotreatment potential and future perspectives. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, T.; Zhu, Z.; Kuang, Y. Assessing impact of urbanization on river water quality in the Pearl River Delta Economic Zone, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 120, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vliet, M.T.; Thorslund, J.; Strokal, M.; Hofstra, N.; Flörke, M.; Ehalt Macedo, H.; Mosley, L.M. Global river water quality under climate change and hydroclimatic extremes. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.J.; Bierkens, M.F.; van Vliet, M.T. Impacts of droughts and heatwaves on river water quality worldwide. J. Hydrol. 2024, 629, 130590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Qi, W. Assessing the water quality in urban river considering the influence of rainstorm flood: A case study of Handan city, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallin, M.A.; Johnson, V.L.; Ensign, S.H.; MacPherson, T.A. Factors contributing to hypoxia in rivers, lakes, and streams. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51 Pt 2, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, R.; Chan, F.; Conley, D.J.; Garnier, J.; Doney, S.C.; Marino, R.; Billen, G. Coupled biogeochemical cycles: Eutrophication and hypoxia in temperate estuaries and coastal marine ecosystems. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frincu, R.M. Artificial intelligence in water quality monitoring: A review of water quality assessment applications. Water Qual. Res. J. 2025, 60, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.; Durlik, I.; Kostecka, E.; Kozlovska, P.; Łobodzińska, A.; Sokołowska, S.; Nowy, A. Integrating artificial intelligence agents with the Internet of Things for enhanced environmental monitoring: Applications in water quality and climate data. Electronics 2025, 14, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.N.; Othman, F.B.; Afan, H.A.; Ibrahim, R.K.; Fai, C.M.; Hossain, M.S.; Elshafie, A. Machine learning methods for better water quality prediction. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghiabi, A.H.; Nasrolahi, A.H.; Parsaie, A. Water quality prediction using machine learning methods. Water Qual. Res. J. 2018, 53, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milly, P.C.; Betancourt, J.; Falkenmark, M.; Hirsch, R.M.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Stouffer, R.J. Stationarity is dead: Whither water management? Science 2008, 319, 573–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrove, W.J.; Loucks, D.P. Water management: Current and future challenges and research directions. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 4823–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, W.; Pan, S.; Parthum, B.M. When It Rains, It Pours: Severe Weather Events, Flooding, and Drinking Water Quality; US Environmental Protection Agency National Center for Environmental Economics: Washington, DC, USA, 2025.
- Zhou, L.; Appiah, R.; Boadi, E.B.; Ayamba, E.C.; Larnyo, E.; Antwi, H.A. The impact of human activities on river pollution and health-related quality of life: Evidence from Ghana. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billen, G.; Garnier, J.; Ficht, A.; Cun, C. Modeling the response of water quality in the Seine river estuary to human activity in its watershed over the last 50 years. Estuaries 2001, 24, 977–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidis, M.O.; Markantonatos, P.G.; Bacalis, N.C. Impact of human activities on the quality of river water: The case of Evrotas River catchment basin, Greece. Environ. Monit. Assess. 1995, 35, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, N.; Chun, K.P.; Wheater, H.; Lindenschmidt, K.E. Parameter sensitivity of a surface water quality model of the lower South Saskatchewan River—Comparison between ice-on and ice-off periods. Environ. Model. Assess. 2017, 22, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Pavelsky, T.M.; Allen, G.H. The past and future of global river ice. Nature 2020, 577, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenschmidt, K.E.; Baulch, H.M.; Cavaliere, E. River and lake ice processes—Impacts of freshwater ice on aquatic ecosystems in a changing globe. Water 2018, 10, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsi, S.R.; De Cicco, L.A.; Lutz, M.A.; Hirsch, R.M. River chloride trends in snow-affected urban watersheds: Increasing concentrations outpace urban growth rate and are common among all seasons. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 508, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A.M.; Klein, C.; Fünfrocken, E.; Kautenburger, R.; Beck, H.P. Real-time monitoring of water quality to identify pollution pathways in small and middle scale rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2323–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, N.; Fukushima, T.; Harasawa, H.; Kojiri, T.; Kawashima, K.; Ono, M. Statistical analyses on the effects of air temperature fluctuations on river water qualities. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 2837–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, N.H. Water quality parameters. In Water Quality—Science, Assessments and Policy; InTech Open: Rijeka, Croatia, 2019; Volume 18, pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, A.; He, Y.; Jekel, M.; Reinhard, M.; Gin, K.Y.H. Emerging contaminants of public health significance as water quality indicator compounds in the urban water cycle. Environ. Int. 2014, 71, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, S.M.; Ray, A.K.; Barghi, S. Water pollution and agriculture pesticide. Clean Technol. 2022, 4, 1088–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, D.M.; Garner, G. River water temperature in the United Kingdom: Changes over the 20th century and possible changes over the 21st century. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2015, 39, 68–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Van Griensven Thé, J.; Yang, S.X.; Gharabaghi, B. Dissolved oxygen forecasting for Lake Erie’s Central Basin using hybrid long short-term memory and gated recurrent unit networks. Water 2024, 16, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Thé, J.V.G.; Yang, S.X.; Gharabaghi, B. The discharge forecasting of multiple monitoring stations for Humber River by hybrid LSTM models. Water 2022, 14, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, D.; Van Griensven, J.; Yang, S.X.; Gharabaghi, B. Intelligent flood forecasting and warning: A survey. Intell. Robot. 2023, 3, 190–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Lee, Y.C.; Chiang, H.M. Abrupt state change of river water quality (turbidity): Effect of extreme rainfalls and typhoons. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huey, G.M.; Meyer, M.L. Turbidity as an indicator of water quality in diverse watersheds of the Upper Pecos River Basin. Water 2010, 2, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.L.; Ho, C.R.; Huang, C.C.; Srivastav, A.L.; Tzeng, J.H.; Lin, Y.T. Hyperspectral sensing for turbid water quality monitoring in freshwater rivers: Empirical relationship between reflectance and turbidity and total solids. Sensors 2014, 14, 22670–22688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies-Colley, R.J.; Smith, D.G. Turbidity, suspended sediment, and water clarity: A review. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 37, 1085–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarbøvik, E.; Roseth, R. Use of sensor data for turbidity, pH and conductivity as an alternative to conventional water quality monitoring in four Norwegian case studies. Acta Agric. Scand. B Soil Plant Sci. 2015, 65, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Zhuang, W.; Qian, Y.; Xia, B.; Yang, Y.; Qian, X. Estimating and predicting metal concentration using online turbidity values and water quality models in two rivers of the Taihu Basin, Eastern China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrabadi, T.; Ruegner, H.; Sirdari, Z.Z.; Schwientek, M.; Grathwohl, P. Using total suspended solids (TSS) and turbidity as proxies for evaluation of metal transport in river water. Appl. Geochem. 2016, 68, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, R.; Amini, H.; Fakheri, F.; Lam, M.Y.; Zahraie, B. Comparative analysis of correlation and causality inference in water quality problems with emphasis on TDS Karkheh River in Iran. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, E.O. Effect of temperature on DO and TDS: A measure of ground and surface water interaction. Water Sci. 2021, 35, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewangan, S.K.; Shrivastava, S.; Kadri, M.; Saruta, S.; Yadav, S.; Minj, N. Temperature effect on electrical conductivity (EC) & total dissolved solids (TDS) of water: A review. Int. J. Res. Anal. Rev. 2023, 10, 514–520. [Google Scholar]
- Adjovu, G.E.; Stephen, H.; Ahmad, S. Spatiotemporal variability in total dissolved solids and total suspended solids along the Colorado River. Hydrology 2023, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjovu, G.E.; Stephen, H.; James, D.; Ahmad, S. Measurement of total dissolved solids and total suspended solids in water systems: A review of the issues, conventional, and remote sensing techniques. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Y.; Gao, X. Analyzing the correlations of long-term seasonal water quality parameters, suspended solids and total dissolved solids in a shallow reservoir with meteorological factors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 6746–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannel, P.R.; Kanel, S.R.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.S.; Gan, T.Y. A review of public domain water quality models for simulating dissolved oxygen in rivers and streams. Environ. Model. Assess. 2011, 16, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, E.; Colmenarejo, M.F.; Vicente, J.; Rubio, A.; García, M.G.; Travieso, L.; Borja, R. Use of the water quality index and dissolved oxygen deficit as simple indicators of watershed pollution. Ecol. Indic. 2007, 7, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, M.; Willems, P.; El-Sadek, A.; Berlamont, J. Modelling of dissolved oxygen and biochemical oxygen demand in river water using a detailed and a simplified model. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2003, 1, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacar, S.; Mete, B.; Bayram, A. Estimation of daily dissolved oxygen concentration for river water quality using conventional regression analysis, multivariate adaptive regression splines, and TreeNet techniques. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaszczak, J.R.; Koenig, L.E.; Mejia, F.H.; Gómez-Gener, L.; Dutton, C.L.; Carter, A.M.; Cohen, M.J. Extent, patterns, and drivers of hypoxia in the world’s streams and rivers. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2023, 8, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, A.M.; Blaszczak, J.R.; Heffernan, J.B.; Bernhardt, E.S. Hypoxia dynamics and spatial distribution in a low gradient river. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 2251–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Gan, J.; Dai, M.; Hui, C.R.; Lu, Z.; Li, D. Modeling the role of riverine organic matter in hypoxia formation within the coastal transition zone off the Pearl River Estuary. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 452–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yu, L.; Yang, X.; Gan, J.; Yin, H.; Li, J. Sediment oxygen uptake and hypoxia in coastal oceans, the Pearl River Estuary region. Water Res. 2024, 267, 122499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geeraert, N.; Archana, A.; Xu, M.N.; Kao, S.J.; Baker, D.M.; Thibodeau, B. Investigating the link between Pearl River-induced eutrophication and hypoxia in Hong Kong shallow coastal waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, W.S. Progression of river BOD/DO modeling for water quality management. Water Environ. Res. 2023, 95, e10864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amira, S.; Soesilo, T.E.; Moersidik, S.S. BOD and DO Models of Krukut River, Jakarta. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 716, 012021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razif, M. BOD, COD, and TSS Predictions from DO measurement results for the Surabaya River, Indonesia. J. Civ. Eng. Plan. Des. 2022, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tian, C.; Sheng, Y. Fluxes of chemical oxygen demand and nutrients in coastal rivers and their influence on water quality evolution in the Bohai Sea. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2022, 52, 102322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojbasic, S.; Dmitrasinovic, S.; Kostic, M.; Turk Sekulic, M.; Radonic, J.; Dodig, A.; Stojkovic, M. Application of machine learning in river water quality management: A review. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 88, 2297–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Luo, W.; Guo, L. Water quality prediction in the Yellow River source area based on the DeepTCN-GRU model. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 59, 105052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, X.; Meng, M.; Zhai, L.; Zhang, B.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, J. The use of Biolog Eco microplates to compare the effects of sulfuric and nitric acid rain on the metabolic functions of soil microbial communities in a subtropical plantation within the Yangtze River Delta region. Catena 2021, 198, 105039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bing, H.; Peng, J.; Dong, F.; Gao, J.; Arhonditsis, G.B. Characterizing the river water quality in China: Recent progress and ongoing challenges. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokarram, M.; Saber, A.; Sheykhi, V. Effects of heavy metal contamination on river water quality due to the release of industrial effluents. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, R.; Bhardwaj, R.; Kumar Thukral, A.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Assessment of heavy-metal pollution in three different Indian water bodies by combination of multivariate analysis and water pollution indices. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2020, 26, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treuer, G.; Kirchhoff, C.; Lemos, M.C.; McGrath, F. Challenges of managing harmful algal blooms in US drinking water systems. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinck, M.P.; L’Ecuyer-Sauvageau, C.; Leroux, J.; Kermagoret, C.; Dupras, J. Risk, drinking water and harmful algal blooms: A contingent valuation of water bans. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 3933–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, R.; Wahid, K.A.; Dinh, A. Estimation of the chlorophyll-a concentration of algae species using electrical impedance spectroscopy. Water 2021, 13, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, P.; Yang, Z.; Ding, S.; Qian, C. River algal blooms are well predicted by antecedent environmental conditions. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safitri, A.; Arisanty, D.; Saputra, A.N. Content of fecal coliform bacteria as an indicator of water quality in the Sungai Jingah, Banjarmasin City. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Social Sciences Education (ICSSE 2020), Virtual, 24–27 September 2020; Atlantis Press: Paris, France, 2021; pp. 414–416. [Google Scholar]
- Some, S.; Mondal, R.; Mitra, D.; Jain, D.; Verma, D.; Das, S. Microbial pollution of water with special reference to coliform bacteria and their nexus with the environment. Energy Nexus 2021, 1, 100008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aram, S.A.; Saalidong, B.M.; Osei Lartey, P. Comparative assessment of the relationship between coliform bacteria and water geochemistry in surface and groundwater systems. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, P.; Mehta, P. Emerging trends in real-time water quality monitoring and sanitation systems. In Sustaining Water Quality—From Local Challenges to Global Solutions; InTech Open: Rijeka, Croatia, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Syafriadi, S.; Sarminingsih, A.; Juliani, H.; Budihardjo, M.A.; Sani, M.T.; Wati, H.R. A review of watershed-scale water quality monitoring: Integrating real-time systems monitoring and spatial modeling for sustainable water resource management. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2025, 12, 12–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Fu, G.; Butler, D. Cost-effective river water quality management using integrated real-time control technology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9876–9886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgantas, I.; Mitropoulos, S.; Katsoulis, S.; Chronis, I.; Christakis, I. Integrated low-cost water quality monitoring system based on LoRa network. Electronics 2025, 14, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, A.J.; Martín, C.; Torres, L.L.; Díaz, M.; Fernández-Ortega, J.; Barberá, J.A.; Andreo, B. A soft sensor open-source methodology for inexpensive monitoring of water quality: A case study of NO₃⁻ concentrations. J. Comput. Sci. 2025, 85, 102522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.M.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Krishnakumar, A.; Sedaghat, S.; Sarnaik, D.; Zareei, A.; Rahimi, R. Real-time monitoring of fertilizer runoff at the watershed scale using a low-cost solar-powered Lego-like electrochemical water quality monitoring system. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 232, 110064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baena-Navarro, R.; Carriazo-Regino, Y.; Torres-Hoyos, F.; Pinedo-López, J. Intelligent prediction and continuous monitoring of water quality in aquaculture: Integration of machine learning and Internet of Things for sustainable management. Water 2025, 17, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Flynn, B.; Regan, F.; Lawlor, A.; Wallace, J.; Torres, J.; O’Mathuna, C. Experiences and recommendations in deploying a real-time, water quality monitoring system. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 124004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahvaran, A.R.; Kheyrollah Pour, H.; Van Cappellen, P. Comparative evaluation of semi-empirical approaches to retrieve satellite-derived chlorophyll-a concentrations from nearshore and offshore waters of a large lake (Lake Ontario). Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahvaran, A.R.; Pour, H.K.; Binding, C.; Van Cappellen, P. Mapping satellite-derived chlorophyll-a concentrations from 2013 to 2023 in Western Lake Ontario using Landsat 8 and 9 imagery. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 968, 178881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.L. Monitoring Water Quality by Remote Sensing; No. NASA-CR-154259; National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA): Moffett Field, CA, USA, 1977.
- Khorram, S.; Cheshire, H.; Geraci, A.L.; La Rosa, G. Water quality mapping of Augusta Bay, Italy from Landsat-TM data. In Proceedings of the 12th Canadian Symposium on Remote Sensing/Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–14 July 1989; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1989; Volume 1, pp. 335–338. [Google Scholar]
- Salomonson, V.V. Earth observations through the Earth Observing System (EOS)/Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) multispectral capability and combined observations with other EOS instruments. In Proceedings of the IEEE Topical Symposium on Combined Optical, Microwave, Earth and Atmosphere Sensing, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 22–25 March 1994; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri, S. Evaluation of the potential of the GER airborne imaging spectrometer for marine application. In Proceedings of the IGARSS’93—IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Tokyo, Japan, 18–21 August 1993; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 491–493. [Google Scholar]
- Barducci, A.; Pippi, I. Environmental monitoring of the Venice lagoon using MIVIS data. In IGARSS’97. 1997 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium Proceedings. Remote Sensing—A Scientific Vision for Sustainable Development, Singapore, 3–8 August 1997; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 2, pp. 888–890. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Fu, L.; He, C. Applying support vector regression to water quality modelling by remote sensing data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 8615–8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binding, C.E.; Stumpf, R.P.; Shuchman, R.A.; Sayers, M.J. Advances in remote sensing of Great Lakes algal blooms. In Contaminants of the Great Lakes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 217–232. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Yao, K.; Zhu, B.; Gao, Z.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Lin, F.; Zhang, X. Water quality inversion of a typical rural small river in Southeastern China based on UAV multispectral imagery: A comparison of multiple machine learning algorithms. Water 2024, 16, 40553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Xie, Z.; Jin, X.; Peng, C.; Ren, C.; Mao, Y.; Zhou, K.; Li, Y. Urban fine-grained water quality monitoring based on a stacked machine learning approach. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 77156–77170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wen, Y.; Li, X.; Yan, F.; Zhao, S. Remote sensing inversion of typical water quality parameters of a complex river network: A case study of Qidong’s rivers. Sustainability 2023, 15, 86948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wan, L.; Wang, L.; Che, L. Remote sensing inversion of water quality grades using a stacked generalization approach. Sensors 2024, 24, 6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villota-González, F.H.; Sulbarán-Rangel, B.; Zurita-Martínez, F.; Gurubel-Tun, K.J.; Zúñiga-Grajeda, V. Assessment of machine learning models for remote sensing of water quality in Lakes Cajititlán and Zapotlán, Jalisco—Mexico. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 35505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, T.; Tanouchi, T. A transfer learning approach based on radar rainfall for water level prediction. Water 2024, 16, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, Q. The application of remote sensing technology in inland water quality monitoring and water environment science: Recent progress and perspectives. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, Q.; Huang, C. Application of remote sensing technology in water quality monitoring: From traditional approaches to artificial intelligence. Water Res. 2024, 267, 122546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H. Satellite and Drone Remote Sensing Models and Tools for Water Quality Monitoring and Ecological Assessment of Fresh Water Resources; WaterRF Project 5174; The Water Research Foundation: Denver, CO, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Driscol, J.; Sarigai, S.; Wu, Q.; Lippitt, C.D.; Morgan, M. Towards synoptic water monitoring systems: A review of AI methods for automating water body detection and water quality monitoring using remote sensing. Sensors 2022, 22, 2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, D.G.; Fedra, K. The ‘WaterWare’ decision-support system for river-basin planning. 1. Conceptual design. J. Hydrol. 1996, 177, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, N.W.; Dinar, A.; Sridharan, V. Decision support tools for water quality management. Water 2022, 14, 3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumarlin, M.Z.; Rahayu, S. Decision support system for urban river water quality as a source of clean water using the SMART method. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 10-13 December 2023; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2024; Volume 1372, p. 012038. [Google Scholar]
- Manos, B.; Bournaris, T.; Silleos, N.; Antonopoulos, V.; Papathanasiou, J. A decision support system approach for rivers monitoring and sustainable management. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2004, 96, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soori, M.; Jough, F.K.G.; Dastres, R.; Arezoo, B. AI-based decision support systems in Industry 4.0: A review. J. Econ. Technol. 2024, 216, 119456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzana, S.Z.; Paudyal, D.R.; Chadalavada, S.; Alam, M.J. Decision support framework for water quality management in reservoirs integrating artificial intelligence and statistical approaches. Water 2024, 16, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardropper, C.; Brookfield, A. Decision-support systems for water management. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, T.M.; Yaseen, Z.M. A survey on river water quality modelling using artificial intelligence models: 2000–2020. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124670. [Google Scholar]
- Najwa Mohd Rizal, N.; Hayder, G.; Mnzool, M.; Elnaim, B.M.; Mohammed, A.O.Y.; Khayyat, M.M. Comparison between regression models, support vector machine (SVM), and artificial neural network (ANN) in river water quality prediction. Processes 2022, 10, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Qiao, Q.; Tavares, A.; Liang, Y. Water quality prediction based on machine learning and comprehensive weighting methods. Entropy 2023, 25, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, M.Y.; Kim, Y.W.; Hyung, J.S.; Koo, J.Y. Development of a short-term water quality prediction model for urban rivers using real-time water quality data. Water Supply 2022, 22, 4082–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peng, H.; Liang, S. Prediction of estuarine water quality using an interpretable machine learning approach. J. Hydrol. 2022, 605, 127320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.M.; Kim, J.; Kim, K. Ensemble machine learning of gradient boosting (XGBoost, LightGBM, CatBoost) and attention-based CNN-LSTM for harmful algal blooms forecasting. Toxins 2023, 15, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Song, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, D. A review of the artificial neural network models for water quality prediction. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palani, S.; Liong, S.Y.; Tkalich, P. An ANN application for water quality forecasting. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Pandey, P. River water quality modelling using artificial neural network technique. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 4, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegar, R.; Adamowski, J.; Moghaddam, A.A. Application of wavelet-artificial intelligence hybrid models for water quality prediction: A case study in Aji-Chay River, Iran. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2016, 30, 1797–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Basant, A.; Malik, A.; Jain, G. Artificial neural network modeling of the river water quality—A case study. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, A.K.; Singh, R.; Bhutiani, R.; Bhatt, A. Artificial neural network-based water quality forecasting model for Ganga River. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2019, 8, 2778–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.E.; Seo, I.W. Artificial neural network ensemble modeling with conjunctive data clustering for water quality prediction in rivers. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2015, 9, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubah, J.I.; Orakwe, L.C.; Ogbu, K.N.; Awu, J.I.; Ahaneku, I.E.; Chukwuma, E.C. Forecasting water quality parameters using artificial neural network for irrigation purposes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Stanley, S.J. Forecasting raw-water quality parameters for the North Saskatchewan River by neural network modeling. Water Res. 1997, 31, 2340–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, A.K.; Wagh, V.M.; Muley, A.A.; Umrikar, B.N.; Sankhua, R.N. Prediction of water quality index using artificial neural network and multiple linear regression modelling approach in Shivganga River basin, India. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 5, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, H.M.; Mustapha, A.; Hayder, G.; Salisu, A. Applications of IoT and artificial intelligence in water quality monitoring and prediction: A review. In Proceedings of the 2021 6th International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT), Coimbatore, India, 20–22 January 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 968–975. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Jiang, P.; Xu, H.; Lin, G.; Guo, D.; Wu, H. Water quality prediction based on recurrent neural network and improved evidence theory: A case study of Qiantang River, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 19879–19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Yang, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, J. River water quality parameters prediction method based on LSTM-RNN model. In Proceedings of the 2019 Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Nanchang, China, 3–5 June 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 3024–3028. [Google Scholar]
- Salehinejad, H.; Sankar, S.; Barfett, J.; Colak, E.; Valaee, S. Recent advances in recurrent neural networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1801.01078. [Google Scholar]
- Moghadam, S.V.; Sharafati, A.; Feizi, H.; Marjaie, S.M.S.; Asadollah, S.B.H.S.; Motta, D. An efficient strategy for predicting river dissolved oxygen concentration: Application of deep recurrent neural network model. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, Q.V.; Nguyen, X.C.; Lê, N.C.; Truong, T.D.; Hoang, T.H.T.; Park, T.J.; Hur, J. Application of machine learning for eutrophication analysis and algal bloom prediction in an urban river: A 10-year study of the Han River, South Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, J.; Park, L.J.; Pachepsky, Y.; Baek, S.S.; Kim, K.; Cho, K.H. Using convolutional neural network for predicting cyanobacteria concentrations in river water. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, M.V.; Sohitha, C.; Saraswathi, G.N.; Lavanya, G.V. Water quality prediction using CNN. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2484, 012051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattenborn, T.; Leitloff, J.; Schiefer, F.; Hinz, S. Review on convolutional neural networks (CNN) in vegetation remote sensing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 173, 24–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, F.; Ding, C.; Chao, Z.; Yu, Y.; Xu, X. Water-quality classification of inland lakes using Landsat8 images by convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Chen, J.; Dou, X.; Xing, Q. Using machine learning algorithms with in situ hyperspectral reflectance data to assess comprehensive water quality of urban rivers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y. Comparative analysis of water quality prediction performance based on LSTM in the Haihe River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 7498–7509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, N.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, N.; Liang, C. Prediction of river water quality based on neural network model. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 6th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 11–14 December 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 2075–2079. [Google Scholar]
- Loc, H.H.; Do, Q.H.; Cokro, A.A.; Irvine, K.N. Deep neural network analyses of water quality time series associated with water-sensitive urban design (WSUD) features. J. Appl. Water Eng. Res. 2020, 8, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H. Comparison of deep learning models on time series forecasting: A case study of dissolved oxygen prediction. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.08414. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Han, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, M.; Lin, Q. Short-term runoff prediction with GRU and LSTM networks without requiring time step optimization during sample generation. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jitha, P.; Vijaya, M.S. Temporal fusion transformer: A deep learning approach for modeling and forecasting river water quality index. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. Eng. 2023, 11, 277–293. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.; Wu, H.; Gao, M.; Yi, H.; Xiong, Q.; Yang, L.; Cheng, S. TLT: Recurrent fine-tuning transfer learning for water quality long-term prediction. Water Res. 2022, 225, 119171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Lyu, L.; Wang, N.; Zhou, X.; Fang, M. Long-term prediction of multiple river water quality indexes based on hybrid deep learning models. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024, 35, 125803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, J.; Fu, X.; Zheng, Q.; Song, X.; Fu, Z.; Yang, X. Water quality prediction based on LSTM and attention mechanism: A case study of the Burnett River, Australia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, H.; Felix, M.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, K. Water quality prediction of artificial intelligence model: A case of Huaihe River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 14610–14640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Qiu, X. A survey of transformers. AI Open 2022, 3, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Lin, Y.; Bi, J.; Yuan, H.; Wang, G.; Zhou, M. Attention-Based Spatiotemporal Graph Fusion Convolution Networks for Water Quality Prediction. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2024, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, D.T.; Khosravi, K.; Tiefenbacher, J.; Nguyen, H.; Kazakis, N. Improving prediction of water quality indices using novel hybrid machine-learning algorithms. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y. Real-time probabilistic forecasting of river water quality under data missing situation: Deep learning plus post-processing techniques. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadollah, S.B.H.S.; Sharafati, A.; Motta, D.; Yaseen, Z.M. River water quality index prediction and uncertainty analysis: A comparative study of machine learning models. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melesse, A.M.; Khosravi, K.; Tiefenbacher, J.P.; Heddam, S.; Kim, S.; Mosavi, A.; Pham, B.T. River water salinity prediction using hybrid machine learning models. Water 2020, 12, 2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Yao, L.; Hua, C.; Ni, Q. A water quality prediction model based on variational mode decomposition and the least squares support vector machine optimized by the sparrow search algorithm (VMD-SSA-LSSVM) of the Yangtze River, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbasi, M.; Ali, M.; Bateni, S.M.; Jun, C.; Jamei, M.; Farooque, A.A.; Yaseen, Z.M. Multi-step ahead forecasting of electrical conductivity in rivers by using a hybrid CNN-LSTM model enhanced by Boruta-XGBoost feature selection algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15051. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, S.S.; Pyo, J.; Chun, J.A. Prediction of water level and water quality using a CNN-LSTM combined deep learning approach. Water 2020, 12, 3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, Z.; He, S.; Duan, J.; Wang, P.; Zhou, T. Study on water quality prediction of urban reservoir by coupled CEEMDAN decomposition and LSTM neural network model. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 3715–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satish, N.; Anmala, J.; Rajitha, K.; Varma, M.R. A stacking ANN ensemble model of ML models for stream water quality prediction of Godavari River Basin, India. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 80, 102500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omeka, M.E.; Igwe, O.; Onwuka, O.S.; Nwodo, O.M.; Ugar, S.I.; Undiandeye, P.A.; Anyanwu, I.E. Efficacy of GIS-based AHP and data-driven intelligent machine learning algorithms for irrigation water quality prediction in an agricultural-mine district within the Lower Benue Trough, Nigeria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 54204–54233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhong, S.; Chen, K. W-WaveNet: A multi-site water quality prediction model incorporating adaptive graph convolution and CNN-LSTM. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0276155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, N.; Yaacob, W.; Nasir, S.; Shaadan, N. Prediction of water quality classification of the Kelantan River Basin, Malaysia, using machine learning techniques. Water 2022, 14, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callegari, M.; Mazzoli, P.; De Gregorio, L.; Notarnicola, C.; Pasolli, L.; Petitta, M.; Pistocchi, A. Seasonal river discharge forecasting using support vector regression: A case study in the Italian Alps. Water 2015, 7, 2494–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stajkowski, S.; Zeynoddin, M.; Farghaly, H.; Gharabaghi, B.; Bonakdari, H. A methodology for forecasting dissolved oxygen in urban streams. Water 2020, 12, 2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhartybayeva, M.; Muntayev, N.; Tulegenova, S.; Oralbekova, Z.; Lamasheva, Z.; Iskakov, K. Monitoring and forecasting of water pollution by heavy metals. IEEE Access 2022, 11, 1593–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnahit, A.O.; Mishra, A.K.; Khan, A.A. Stream water quality prediction using boosted regression tree and random forest models. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 36, 2661–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoi, D.N.; Quan, N.T.; Linh, D.Q.; Nhi, P.T.T.; Thuy, N.T.D. Using machine learning models for predicting the water quality index in the La Buong River, Vietnam. Water 2022, 14, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lai, T.; Jahan, S.; Farid, F.; Bello, A. A machine learning predictive model to detect water quality and pollution. Future Internet 2022, 14, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medupe, M.; Letshwenyo, M.W. Investigation of self-purification and water quality index during dry and rainy seasons in the Khurumela Stream (Botswana). J. Ecohydraul. 2025, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, K.; Shi, H.; Wu, Y.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Ji, X.; Yang, M.; Guan, Y. Impact of landscape patterns on river water quality: Spatial-scale effects across an agricultural-urban interface. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 170, 113019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, U.; Mumtaz, R.; Anwar, H.; Shah, A.A.; Irfan, R.; García-Nieto, J. Efficient water quality prediction using supervised machine learning. Water 2019, 11, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, K.T.; Sagan, V.; Sloan, J.J. Deep learning-based water quality estimation and anomaly detection using Landsat-8/Sentinel-2 virtual constellation and cloud computing. GISci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 510–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeinzadeh, H.; Jegakumaran, P.; Yong, K.T.; Withana, A. Efficient water quality prediction by synthesizing seven heavy metal parameters using deep neural network. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 56, 104349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigl, M.; Lebiedzinski, K.; Herrnegger, M.; Schulz, K. Machine-learning methods for stream water temperature prediction. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 2951–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh Khozani, Z.; Iranmehr, M.; Wan Mohtar, W.H.M. Improving Water Quality Index prediction for water resources management plans in Malaysia: Application of machine learning techniques. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 10058–10075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, Y. An ensemble model for accurate prediction of key water quality parameters in rivers based on deep learning methods. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Z.; Xu, X.; Hu, L.; Liu, J.; Yan, X.; Han, M. A study on long-term forecasting of water quality data using self-attention with correlation. J. Hydrol. 2025, 650, 132390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Ma, X. Hybrid decision tree-based machine learning models for short-term water quality prediction. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noori, N.; Kalin, L.; Isik, S. Water quality prediction using SWAT-ANN coupled approach. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Xu, H. Water quality prediction in the Luan River based on 1-DRCNN and BiGRU hybrid neural network model. Water 2021, 13, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sulttani, A.O.; Al-Mukhtar, M.; Roomi, A.B.; Farooque, A.A.; Khedher, K.M.; Yaseen, Z.M. Proposition of new ensemble data-intelligence models for surface water quality prediction. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 108527–108541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, H.; Jiang, P.; Yu, S.; Lin, G.; Bychkov, I.; Liu, Z. A transfer learning-based LSTM strategy for imputing large-scale consecutive missing data and its application in a water quality prediction system. J. Hydrol. 2021, 602, 126573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Yao, L.; Hua, C.; Ni, Q. A novel hybrid model for water quality prediction based on synchrosqueezed wavelet transform technique and improved long short-term memory. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.I.; Javed, M.F.; Alqahtani, A.; Aldrees, A. Environmental assessment-based surface water quality prediction using hyper-parameter optimized machine learning models based on consistent big data. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 151, 324–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xiong, Q.; Wu, C.; Zou, Q.; Yu, Y.; Yi, H.; Gao, M. A study on water quality prediction by a hybrid CNN-LSTM model with attention mechanism. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 55129–55139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.L. Comparison of forecasting models for real-time monitoring of water quality parameters based on hybrid deep learning neural networks. Water 2021, 13, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoudi, S.; Roushangar, K. Innovative approaches to surface water quality management: Advancing nitrate (NO₃) forecasting with hybrid CNN-LSTM and CNN-GRU techniques. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2025, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Z. A hybrid model for water quality prediction based on an artificial neural network, wavelet transform, and long short-term memory. Water 2022, 14, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Xu, R.; Zhang, M.; Cai, Y.; Li, J.; Shen, X. A novel model for water quality prediction caused by non-point source pollution based on deep learning and feature extraction methods. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khullar, S.; Singh, N. Water quality assessment of a river using deep learning Bi-LSTM methodology: Forecasting and validation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 12875–12889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wu, T. A novel hybrid model for water quality prediction based on VMD and IGOA optimized for LSTM. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2023, 17, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Lyu, L.; Wang, N.; Zhou, X.; Fang, M. Application of hybrid improved temporal convolution network model in time series prediction of river water quality. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, T.; Liu, Z.; Luo, H.; Pei, H. A novel deep learning ensemble model based on two-stage feature selection and intelligent optimization for water quality prediction. Environ. Res. 2023, 224, 115560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Santos, V.; Costa Rocha, P.A.; Scott, J.; Thé, J.V.G.; Gharabaghi, B. A new graph-based deep learning model to predict flooding with validation on a case study on the Humber River. Water 2023, 15, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafsin, N.; Li, J. Prediction of total organic carbon and E. coli in rivers within the Milwaukee River basin using machine learning methods. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2023, 2, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Kong, J.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, D. The optimal method for water quality parameter retrieval of an urban river based on machine learning algorithms using remote sensing images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2024, 45, 7297–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talnikar, M.; Anmala, J.; Venkateswarlu, T.; Parimi, C. Support vector machine (SVM) model development for prediction of fecal coliform of Upper Green River Watershed, Kentucky, USA. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2024, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xiong, W.; Zhang, G. Application of deep learning models with spectral data augmentation and denoising for predicting total phosphorus concentration in water pollution. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2025, 167, 105852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, T.; Chen, C.; Xu, L. A water quality prediction model based on modal decomposition and hybrid deep learning models. Water 2025, 17, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroudi, S.; Kheyruri, Y.; Sharafati, A.; Hameed, A.S. Enhancing prediction of dissolved oxygen over Santa Margarita River: Long short-term memory incorporated with multi-objective observer-teacher-learner optimization. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 70, 106969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.M.; Gupta, R.; Sekhri, S. Superposition learning-based model for prediction of E. coli in groundwater using physico-chemical water quality parameters. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 13, 100580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolkefli, N.; Sharuddin, S.S.; Yusoff, M.Z.M.; Hassan, M.A.; Maeda, T.; Ramli, N. A review of current and emerging approaches for water pollution monitoring. Water 2020, 12, 3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenburger, R.; Brack, W.; Burgess, R.M.; Busch, W.; Escher, B.I.; Focks, A.; Krauss, M. Future water quality monitoring: Improving the balance between exposure and toxicity assessments of real-world pollutant mixtures. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019, 31, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, M.V.; Van der Gaag, B.; Burns, B.P. Advances in on-line drinking water quality monitoring and early warning systems. Water Res. 2011, 45, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogo, E.; Nwulu, N.; Twala, B.; Aigbavboa, C. A survey of machine learning methods applied to anomaly detection on drinking-water quality data. Urban Water J. 2019, 16, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustam, F.; Ishaq, A.; Kokab, S.T.; de la Torre Diez, I.; Mazón, J.L.V.; Rodríguez, C.L.; Ashraf, I. An artificial neural network model for water quality and water consumption prediction. Water 2022, 14, 3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, K.R.A.; Harigovindan, V.P. Water quality prediction for smart aquaculture using hybrid deep learning models. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 60078–60098. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Zou, R.; Chen, X.; Ren, T.; Su, H.; Liu, Y. Simulating the forecast capacity of a complicated water quality model using the long short-term memory approach. J. Hydrol. 2020, 581, 124432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Van Griensven Thé, J.; Yang, S.X.; Gharabaghi, B. Flood forecasting using hybrid LSTM and GRU models with lag time preprocessing. Water 2023, 15, 3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiray, B.Z.; Sit, M.; Mermer, O.; Demir, I. Enhancing hydrological modeling with transformers: A case study for 24-h streamflow prediction. Water Sci. Technol. 2024, 89, 2326–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khullar, S.; Singh, N. Machine learning techniques in river water quality modeling: A research travelogue. Water Supply 2021, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharib, A.; Davies, E.G. A workflow to address pitfalls and challenges in applying machine learning models to hydrology. Adv. Water Resour. 2021, 152, 103920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, A.; Shah, M.I.; Aldrees, A.; Javed, M.F. Comparative assessment of individual and ensemble machine learning models for efficient analysis of river water quality. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, Z.M.; Sulaiman, S.O.; Deo, R.C.; Chau, K.W. An enhanced extreme learning machine model for river flow forecasting: State-of-the-art, practical applications in water resource engineering area, and future research direction. J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilby, R.; Whitehead, P.; Wade, A.; Butterfield, D.; Davis, R.; Watts, G. Integrated modeling of climate change impacts on water resources and quality in a lowland catchment: River Kennet, UK. J. Hydrol. 2006, 330, 204–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, M.; Williams, R.; Prudhomme, C.; Bowes, M.; Brown, H.; Waylett, A.; Loewenthal, M. Projections of future deterioration in UK river quality are hampered by climatic uncertainty under extreme conditions. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 2818–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, P.; Wilby, R.; Battarbee, R.; Kernan, M.; Wade, A. A review of the potential impacts of climate change on surface water quality. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducharne, A. Importance of stream temperature to climate change impact on water quality. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 12, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meals, D.W.; Dressing, S.A.; Davenport, T.E. Lag time in water quality response to best management practices: A review. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, G.; Liu, Q.; Huang, C.; Li, H. Studies on the Spatiotemporal Variability of River Water Quality and Its Relationships with Soil and Precipitation: A Case Study of the Mun River Basin in Thailand. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, M.; Abesser, C.; Prudhomme, C.; Elliott, J.; Bloomfield, J.; Mansour, M.; Hitt, O. Combined impacts of future land-use and climate stressors on water resources and quality in groundwater and surface water bodies of the Upper Thames River Basin, UK. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 962–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, M.; De Brouwer, E.; Moor, M.; Moreau, Y.; Rieck, B.; Borgwardt, K. Topological graph neural networks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.07835. [Google Scholar]
- Alizadeh, M.J.; Kavianpour, M.R.; Danesh, M.; Adolf, J.; Shamshirband, S.; Chau, K.W. Effect of river flow on the quality of estuarine and coastal waters using machine learning models. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2018, 12, 810–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinrath, G.; May, P.M. Thermodynamic prediction in the mine water environment. Mine Water Environ. 2002, 21, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaivude, P. Artificial Intelligence for Water Quality. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2023, 11, 1521–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, S.; Shahfahad; Ahmed, I.A.; Rihan, M.; Rahman, A. Integrating explainable artificial intelligence and machine learning for understanding water pollution and its management. In Environmental Risk and Resilience in the Changing World: Integrated Geospatial AI and Multidimensional Approach; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 115–128. [Google Scholar]
- Ramya, S.; Srinath, S.; Tuppad, P. Comprehensive analysis of multiple classifiers for enhanced river water quality monitoring with explainable AI. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 10, 100822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Chen, H.; Zhou, C.; Huang, Y.; Qi, X.; Shen, R.; Ren, H. Comparative analysis of surface water quality prediction performance and identification of key water parameters using different machine learning models based on big data. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiacchiera, A.; Sai, F.; Salvetti, A.; Guariso, G. Neural structures to predict river stages in heavily urbanized catchments. Water 2022, 14, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).