Hard Evidence from Turtle Shells: Tracing Metal and Non-Metallic Elements Bioaccumulation in Freshwater Ecosystems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
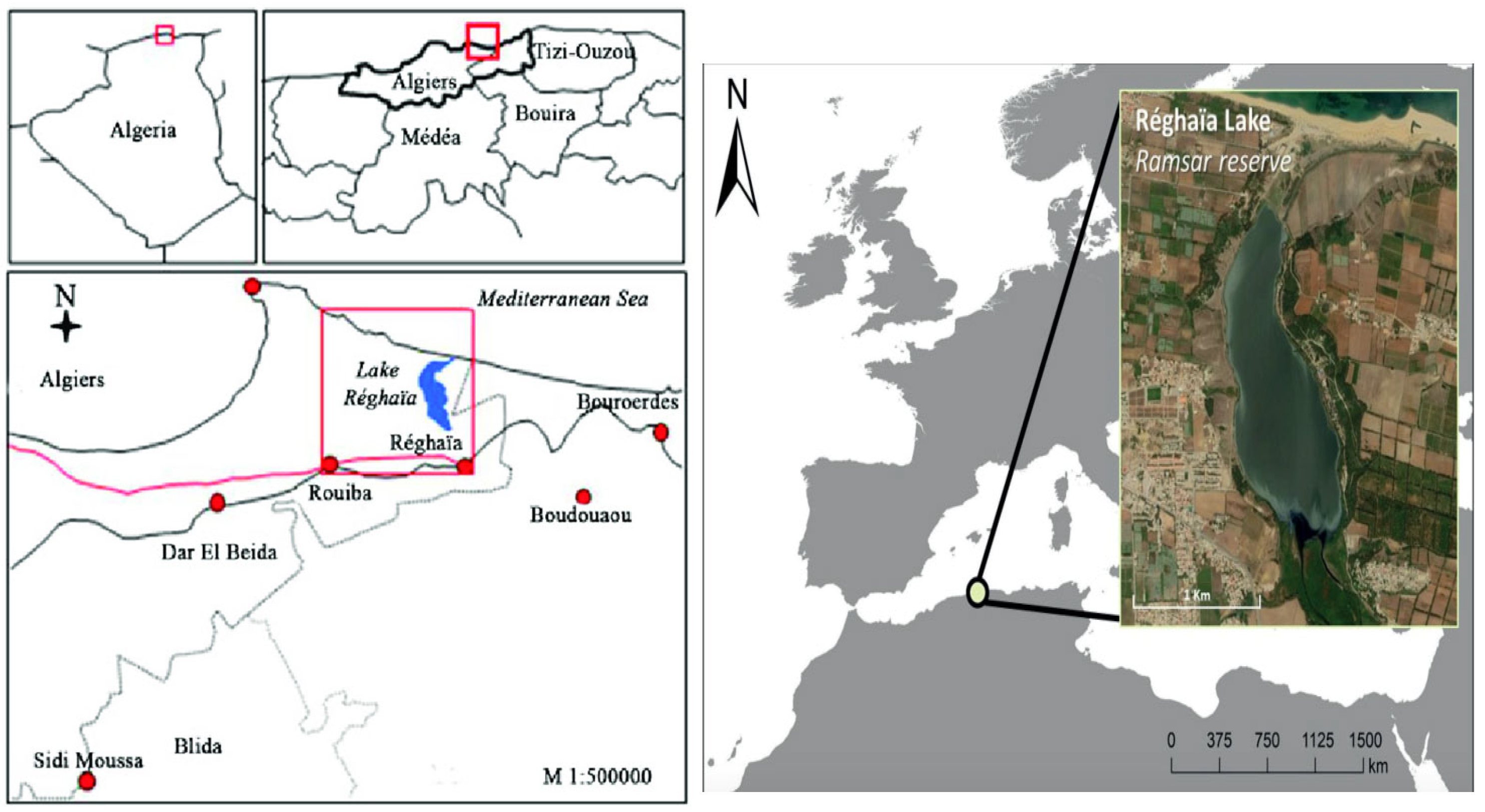
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Environmental Sampling, Preservation, and Acid Digestion
2.4. Turtle Shell Preparation and Analysis
2.4.1. Shell Morphometric Analysis
2.4.2. Analytical Techniques
2.5. Quality Assurance and Quality Control (QA/QC)
2.6. Data Analysis
2.7. Shell–Environment Correlations and Multiple Testing Correction
3. Results
3.1. Morphometric Parameters
3.2. Elemental Composition
3.3. Sex-Based Differences
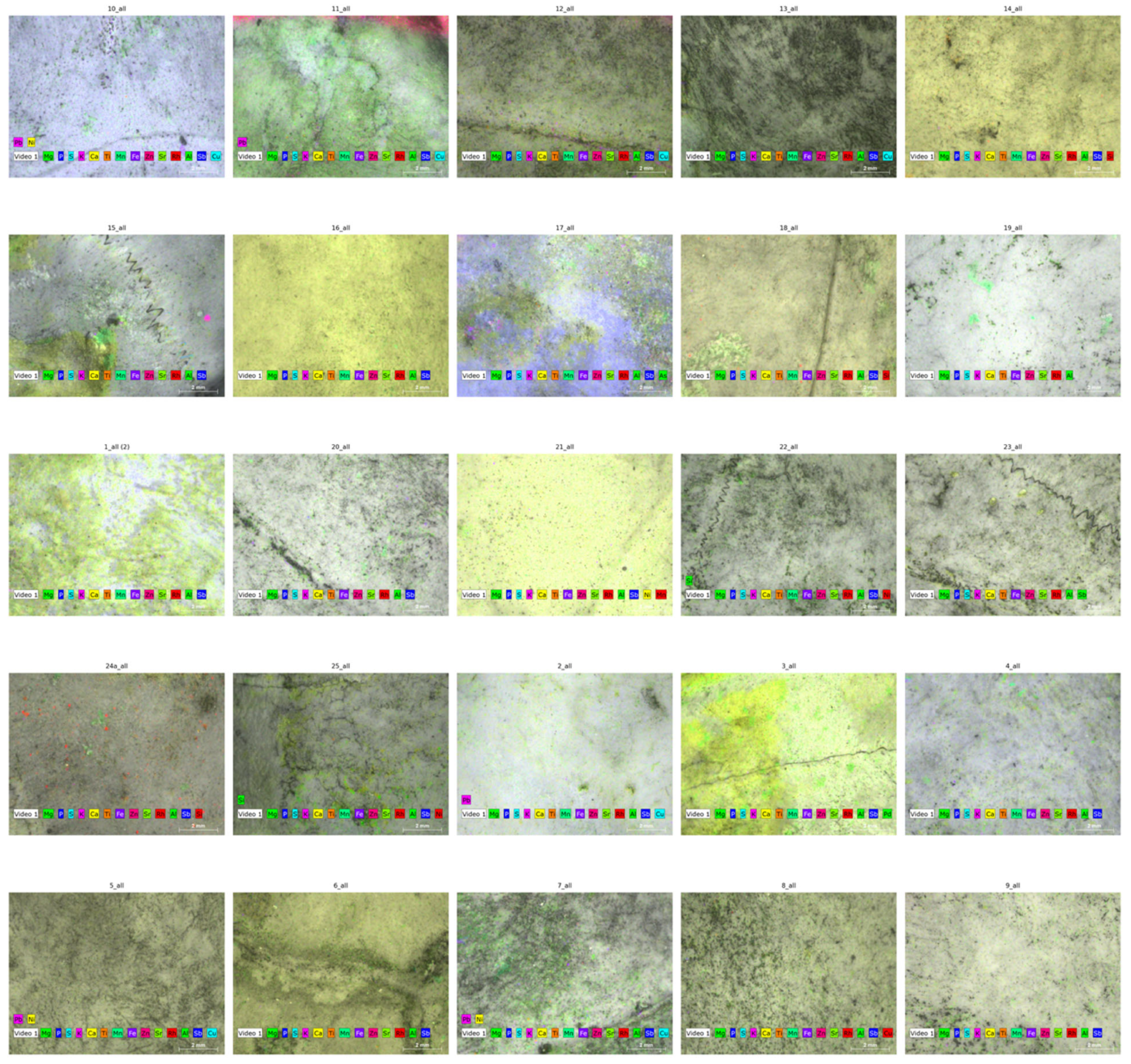
3.4. Micro-XRF Elemental Mapping
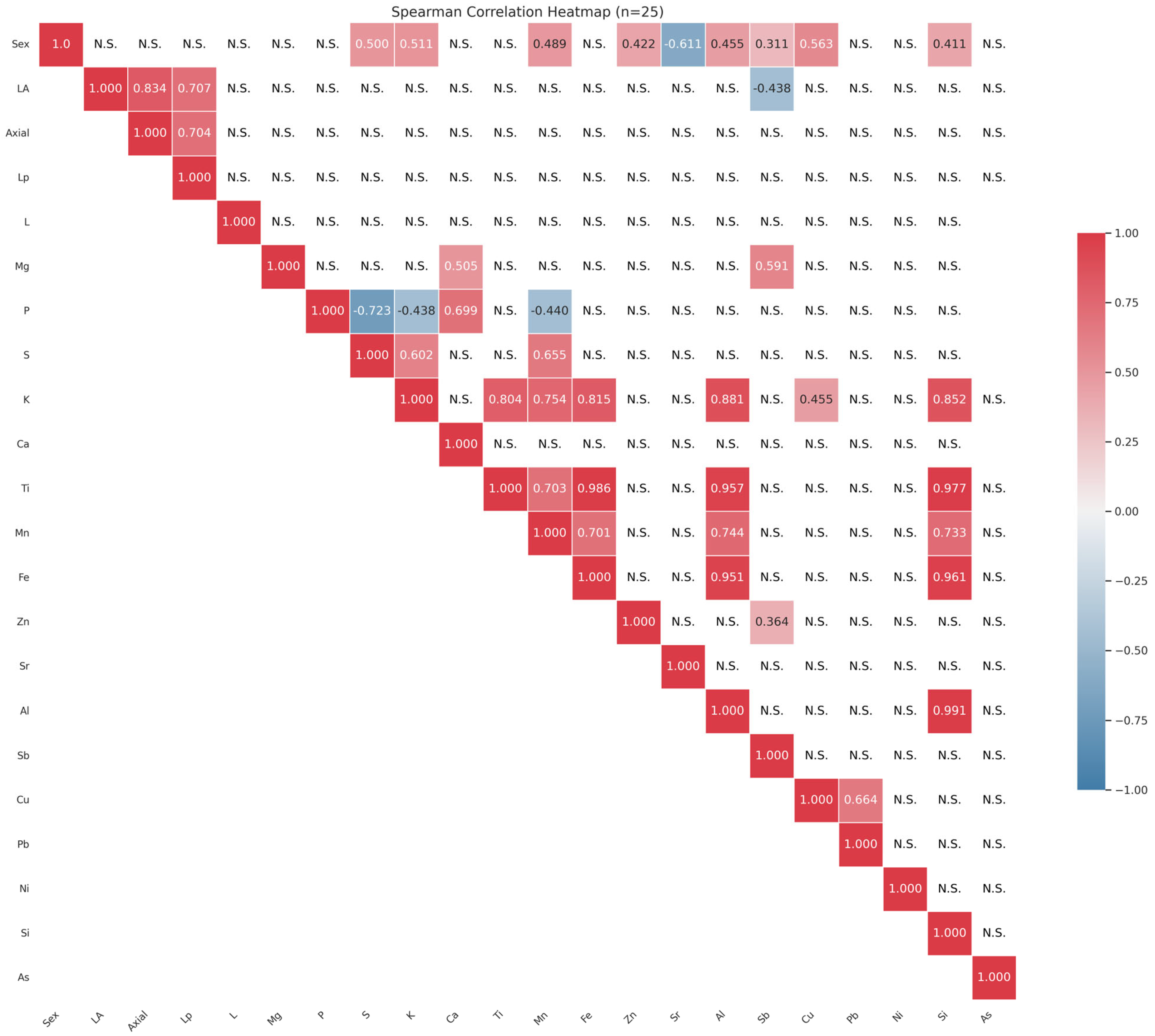
3.5. Correlation Patterns Among Shell Elements
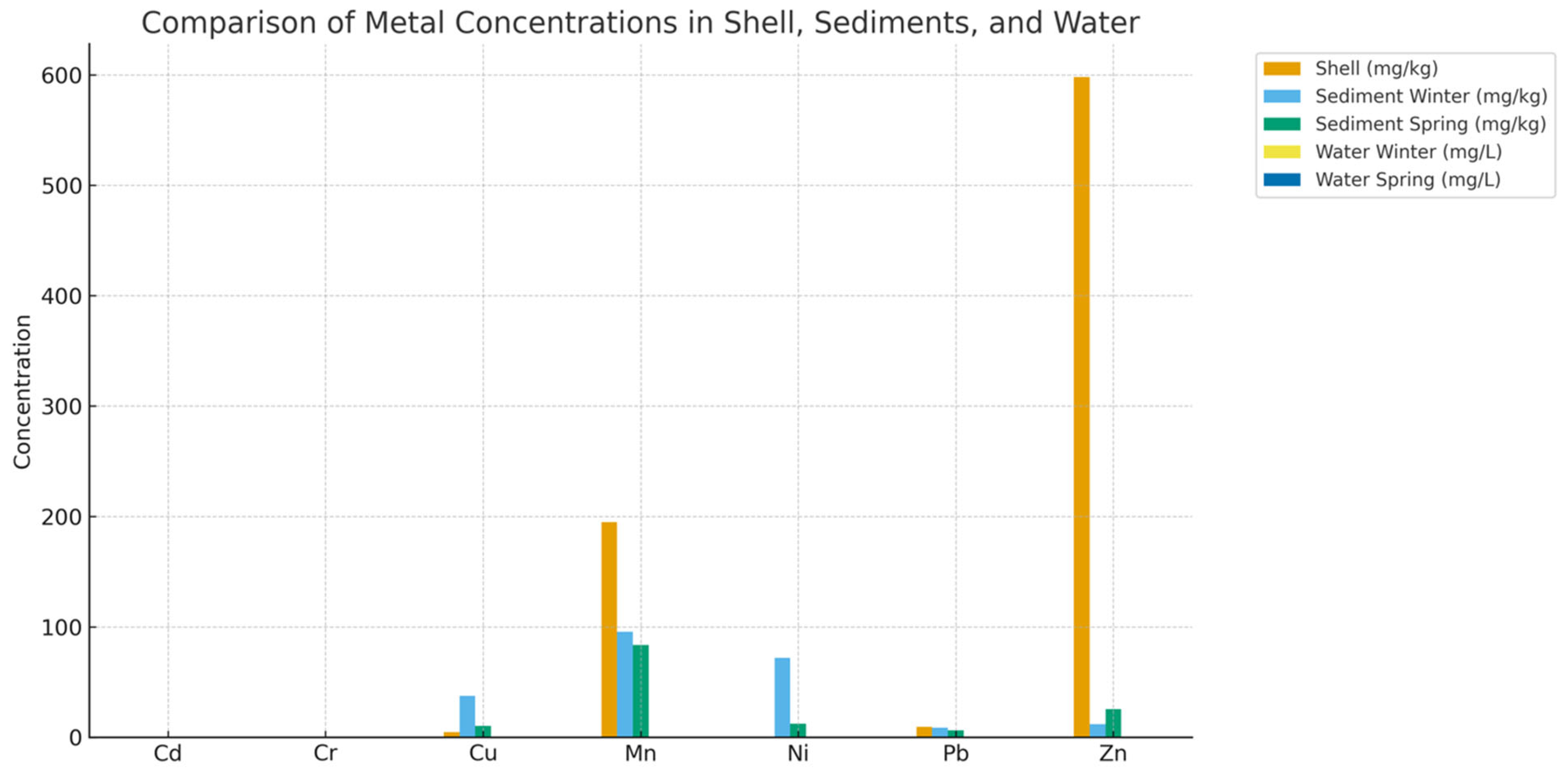
3.6. Seasonal Variation in Heavy Metals in Sediments and Water
3.7. Bioindicator Relationships Between Shell and Environmental Concentrations
4. Discussion
4.1. Elemental Composition of Turtle Shells
4.2. Sex-Based Differences in Metal Accumulation
4.3. Elemental Mapping
4.4. Relationships with Morphometrics
4.5. Environmental Correlations and Bioindicator Potential
4.6. Ecological and Conservation Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malaj, E.; Von der Ohe, P.C.; Grote, M.; Kühne, R.; Mondy, C.P.; Usseglio-Polatera, P.; Brack, W.; Schäfer, R.B. Organic chemicals jeopardize the health of freshwater ecosystems on the continental scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9549–9554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Sajad, M.A. Phytoremediation of heavy metals—Concepts and applications. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, M.A.; Nur-A-Tomal, M.S.; Mondal, N.R.; Rahman, M.A. Hair burning and liming in tanneries is a source of pollution by arsenic, lead, zinc, manganese and iron. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2017, 15, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aib, H.; Czédli, H.; Baranyai, E.; Sajtos, Z.; Döncző, B.; Parvez, M.S.; Berta, C.; Varga, Z.; Benhizia, R.; Nyeste, K. Fish Scales as a Non-Invasive Method for Monitoring Trace and Macroelement Pollution. Biology 2025, 14, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebol, E.L.; Donoso, C.H.; Saura, R.B.D.; Ferol, R.J.C.; Mozar, J.R.D.; Bermon, A.N.; Manongas, J.; Libot, J.C.H.; Matabilas, C.J.; Jumawan, J.C.; et al. Heavy Metals Accumulation in Surface Waters, Bottom Sediments and Aquatic Organisms in Lake Mainit, Philippines. Int. Lett. Nat. Sci. 2020, 79, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda Toxicity, K.N. mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboob, S.; Al-Balwai, H.F.A.; Al-Misned, F.; Al-Ghanim, K.A.; Ahmad, Z. A study on the accumulation of nine heavy metals in some important fish species from a natural reservoir in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2014, 96, 783–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csuros, M.; Csuros, C. Environmental Sampling and Analysis for Metals; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 1–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffus, J.H. ‘Heavy metals’—A meaningless term? (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E. What are heavy metals? Long-standing controversy over the scientific use of the term ‘heavy ’metals’—proposal of a comprehensive definition. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2018, 100, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloway, B.J. Heavy Metals in Soils “‘Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and their Bioavailability’”. In Environmental Pollution; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förstner, U.; Wittmann, G.T.W. Metal Pollution in the Aquatic Environment; Springer Nature: Durham, NC, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, G.R.; Burchett, M.D. Cellular distribution of copper, lead and zinc in the grey mangrove, Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. Aquat. Bot. 2000, 68, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baby, J.; Raj, J.S.; Biby, E.T.; Sankarganesh, P.; Jeevitha, M.V.; Ajisha, S.U.; Rajan, S.S. Toxic effect of heavy metals on aquatic environment. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2010, 4, 62976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiwan, S.; Ajay, K. Effects of Heavy Metals on Soil, Plants, Human Health and Aquatic Life. Int. J. Res. Chem. Environ. 2011, 1, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Hesham, A.E.L.; Qiao, M.; Rehman, S.; He, J.Z. Effects of Cd and Pb on soil microbial community structure and activities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2010, 17, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.S.; Cai, S.S.; Mo, C.H.; Chu, B.; Peng, L.H.; Yang, F.B. Toxic effects of heavy metals and their accumulation in vegetables grown in a saline soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, G.; Li, X. Heavy metal contamination in soils and vegetables near an e-waste processing site, south China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaynab, M.; Al-Yahyai, R.; Ameen, A.; Sharif, Y.; Ali, L.; Fatima, M.; Khan, K.A.; Li, S. Health and environmental effects of heavy metals. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Tareq, A.M.; Emran, T.B.; Nainu, F.; Khusro, A.; Idris, A.M.; Khandaker, M.U.; Osman, H.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; et al. Impact of heavy metals on the environment and human health: Novel therapeutic insights to counter the toxicity. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology of Hazardous Heavy Metals: Environmental Persistence, Toxicity, and Bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhezila, F.; Hacene, H. Water quality assessment in Réghaïa (North of Algeria) lake basin by using traditional approach and water quality indices. Kuwait J. Sci. 2020, 47, 57–71. [Google Scholar]
- Network, M.M. Lake Réghaïa—The MedWet Managers Network. Available online: https://medwetmanagers.net/marine-and-coastal-wetlands/reghaia-lake-algeria (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Le Gal, A.S.; Priol, P.; Georges, J.Y.; Verneau, O. Population structure and dynamics of the Mediterranean Pond Turtle Mauremys leprosa (Schweigger, 1812) in contrasted polluted aquatic environments. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 330, 121746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luiselli, L. Mauremys leprosa, IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, January 2023. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/158468/207995085 (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Mediterranean Turtle (Mauremys leprosa). 2023. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Mediterranean_Pond_Turtle (accessed on 13 November 2025).
- Hassani, M.S.E.L.; El Hassan, E.M.; Slimani, T.; Bonnet, X. Morphological and physiological assessments reveal that freshwater turtle (Mauremys leprosa) can flourish under extremely degraded-polluted conditions. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H.; Saeki, K.; Ichihashi, H.; Suganuma, H.; Tanabe, S.; Tatsukawa, R. Species-specific distribution of heavy metals in tissues and organs of loggerhead turtle (Caretta caretta) and green turtle (Chelonia mydas) from Japanese coastal waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisa, Z.U.; Sultana, S.; Al-Ghanim, K.; Ghazla; Khan, Q.F.; Al-Misned, F.; Atique, U.; Ahmed, Z.; Mahboob, S. Comparative assessment of heavy metal bioaccumulation in skeletal muscles of softshell and hard-shell freshwater turtles. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2021, 33, 101463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Solla, S.R.; Fernie, K.J. Characterization of contaminants in snapping turtles (Chelydra serpentina) from Canadian Lake Erie Areas of Concern: St. Clair River, Detroit River, and Wheatley Harbour. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 132, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, J.; Jeitner, C.; Schneider, L.; Vogt, R.; Gochfeld, M. Arsenic; cadmium; chromium; lead; mercury, and selenium levels in blood of four species of turtles from the Amazon in brazil. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health-Part A Curr. Issues 2010, 73, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers-Schöne, L.; Shugart, L.R.; Walton, B.T.; Beauchamp, J.J. Comparison of two freshwater turtle species as monitors of radionuclide and chemical contamination: DNA Damage and residue analysis. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1993, 12, 1487–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahmous, S.A.; Tiar, G.; Tiar-Saadi, M.; Bouslama, Z.; Široký, P. Reproductive Traits Demonstrate How Well the Mediterranean Stripe-Necked Turtle Mauremys leprosa Can Flourish under Highly Degraded–Polluted Conditions. Biology 2022, 11, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhouche, B.; Ghoulem, T.; Imed, D.; Khalil, D.; Escoriza, D. Phenology and population structure of the mediterranean stripe-necked terrapin Mauremys leprosa (Schweigger, 1812) in the Reghaïa Lake (northern Algeria). Basic Appl. Herpetol. 2019, 33, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, N.; Chanson, J.; Stuart, S. The Status and Distribution of Reptiles and Amphibians of the Mediterranean Basin; The World Conservation Union (IUCN): Gland, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Salvador, A.; Pleguezuelos, J.M. Reptiles españoles: Identificación, historia natural y distribución. Ichthyol. Herpetol. 2003, 2003, 201–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djitli, Y.; Boix, D.; Milla, A.; Marniche, F.; Tornero, I.; Cunillera-Montcusí, D.; Sala, J.; Gascón, S.; Quintana, X.D.; Daoudi-Hacini, S. Annual cycle of water quality and macroinvertebrate composition in Algerian wetlands: A case study of lake Réghaïa (Algeria). Limnetica 2021, 40, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, R. Detection Limit and Estimate of Uncertainty of Analytical XRF Results. Rigak J. 2001, 18. Available online: https://www.scribd.com/document/481280444/Detection-limit-and-estimate-of-uncertainty-of-analytical-XRF-results (accessed on 27 October 2025).
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, N.; Bisht, N.; Chauhan, S.; Singh, D. Exploring the Functionality and Diversity of Biological Materials. In Mechanics and Materials Science of Biological Materials; Springer: Singapore, 2025; Volume Part F558; pp. 203–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothschild, B.M.; Schultze, H.P.; Pellegrini, R. Osseous and Other Hard Tissue Pathologies in Turtles and Abnormalities of Mineral Deposition. In Morphology and Evolution of Turtles; Vertebrate Paleobiology and Paleoanthropology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 501–534. ISBN 9789400743083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.H.; Preskitt, C.; Gresham-Fiegel, C.J.I.B.R. Chemical and Physiological Change from Calcium Carbonate to Calcium Phosphate in Skeletal Structures. Insights Biomed. Res. 2021, 5, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, D.N.; Brown, D.J.; Hubbart, J.A.; Anderson, J.T. Environmental factors influencing bioaccumulation of xenobiotic metals in freshwater turtles. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2025, 37, 2474007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, J.; Naureen, I. Benefit of Egg Shell as Calcium Source in Egg Production and Bone Development. Sch. Int. J. Anat. Physiol. 2021, 4, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair-Black, M.; Garcia, R.A.; Ellestad, L.E. Physiological regulation of calcium and phosphorus utilization in laying hens. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1112499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, T.-G. The Role of The Skeleton in Egg-Shell Formation. Ann. De Biol. Anim. Biochim. Biophys. 1970, 10, 83–91. Available online: https://hal.science/hal-00896581v1 (accessed on 13 November 2025). [CrossRef]
- Naghilou, Z.; Rajaei, F.; Behrooz, R.D.; Chakraborty, P. Trace elements in barnacle, egg contents, and egg shells of the critically endangered hawksbill turtle (Eretmochelys imbricata) from the Persian Gulf Iran. Environ. Res. 2025, 282, 122032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.M.; Butler, M.A.; John-Alder, H.B. The evolution of sexual size dimorphism in reptiles. Sex Size Gend. Roles: Evol. Stud. Sex. Size Dimorphism 2007, 5, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katona, G.; Vági, B.; Végvári, Z.; Liker, A.; Freckleton, R.P.; Bókony, V.; Székely, T. Are evolutionary transitions in sexual size dimorphism related to sex determination in reptiles? J. Evol. Biol. 2021, 34, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, J.W.; Lovich, J. Sexual Dimorphism in Turtles with Emphasis on the slider turtle (Trachemys scripta). Herpetol. Monogr. 1990, 4, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.M.; McClellan-Green, P.D.; Kucklick, J.R.; Keil, D.E.; Peden-Adams, M.M. Effects of Organochlorine Contaminants on Loggerhead Sea Turtle Immunity: Comparison of a Correlative Field Study and In Vitro Exposure Experiments. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, B.C.; Hopkins, W.A.; Moore, I.T.; Hawley, D.M. Mercury Bioaccumulation and Adverse Reproductive Effects in Snapping Turtles Inhabiting a Historically Contaminated River; Virginia Tech: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, B.C.; Willson, J.D.; Hopkins, W.A. Mercury exposure is associated with negative effects on turtle reproduction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2416–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.R.; Ecay, T.W. Patterns of maternal provision and embryonic mobilization of calcium in oviparous and viviparous squamate reptiles. Herpetol. Conserv. Biol. 2010, 5, 341–359. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, B.E.; Savitzky, B.A.; Abdel-Fattah, T. Lead bioaccumulation in emydid turtles of an urban lake and its relationship to shell disease. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccolini, É. Nutrition for Aquatic Turtles. Vet et Nous. 2024. Available online: https://www.vetetnous.com/en/tips/nutrition-for-aquatic-turtles/ (accessed on 18 September 2025).
- Wilczek, G.; Babczyńska, A.; Wilczek, P. Antioxidative responses in females and males of the spider Xerolycosa nemoralis (Lycosidae) exposed to natural and anthropogenic stressors. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 157, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilczek, G.; Rost-Roszkowska, M.; Wilczek, P.; Babczyńska, A.; Szulińska, E.; Sonakowska, L.; Marek-Swędzioł, M. Apoptotic and necrotic changes in the midgut glands of the wolf spider Xerolycosa nemoralis (Lycosidae) in response to starvation and dimethoate exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 101, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparling, D.W.; Linder, G.; Bishop, C.A.; Krest, S.K. Ecotoxicology of Amphibians and Reptiles. In Ecotoxicology of Amphibians and Reptiles. In Ecotoxicology of Amphibians and Reptiles, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 1–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-López, E.; Gómez-Ramírez, P.; Espín, S.; Aldeguer, M.P.; García-Fernández, A.J. Influence of a Former Mining Area in the Heavy Metals Concentrations in Blood of Free-Living Mediterranean Pond Turtles (Mauremys leprosa). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 99, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolini, M.; Sturini, M.; Maraschi, F.; Profumo, A.; Costanzo, A.; Caprioli, M.; Rubolini, D.; Ambrosini, R.; Canova, L. Trace elements fingerprint of feathers differs between breeding and non-breeding areas in an Afro-Palearctic migratory bird, the barn swallow (Hirundo rustica). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 28, 15828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushie, M.J.; Pickering, I.J.; Korbas, M.; Hackett, M.J.; George, G.N. Elemental and Chemically Specific X-ray Fluorescence Imaging of Biological Systems. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 8499–8541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushie, M.J.; Sylvain, N.J.; Hou, H.; Hackett, M.J.; Kelly, M.E.; Webb, S.M. X-ray fluorescence microscopy methods for biological tissues. Metallomics 2022, 14, mfac032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, L.; Zhang, T.; Lin, L.; Xiong, J.; Shi, H.; Wang, J. Transfer and accumulation of trace elements in seawater, sediments, green turtle forage, and eggshells in the Xisha Islands, South China Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 50832–50844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, A.; Ariel, E.; van de Merwe, J.; Brodie, J. Green Turtle (Chelonia mydas) Blood and Scute Trace Element Concentrations in the Northern Great Barrier Reef. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2023, 42, 2375–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, L.; Guo, R.; Zheng, X.; Shi, H.; Wang, J. Trace elements in green turtle eggshells and coral sand sediments from the Xisha Islands, South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 164, 112036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adel, M.; Cortés-Gómez, A.A.; Dadar, M.; Riyahi, H.; Girondot, M. A comparative study of inorganic elements in the blood of male and female Caspian pond turtles (Mauremys caspica) from the southern basin of the Caspian Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 24965–24979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pounds, J.G. Effect of lead intoxication on calcium homeostasis and calcium-mediated cell function: A review. Neurotoxicology 1984, 5, 295–331. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Rawahy, S.H. Accumulation of metals in the egg yolk and liver of hatchling of green turtles Chelonia mydas at Ras Al Hadd, Sultante of Oman. J. Biol. Sci. 2007, 7, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, K.; Kamala, K.; Ramasamy, P.; Musthafa, M.S.; Almujri, S.S.; Asdaq, S.M.B.; Sivaperumal, P. Unveiling the silent threat: Heavy metal toxicity devastating impact on aquatic organisms and DNA damage. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 200, 116139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhardt, J.; Butler, P.G.; Carroll, M.L.; Hartley, J. The application of long-lived bivalve sclerochronology in environmental baseline monitoring. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, S.; Baskar, A.; Geevarghese, D.M.; Ali, M.N.V.S.; Bahubali, P.; Choudhary, R.; Lvov, V.; Tovar, G.I.; Senatov, F.; Koppala, S.; et al. Bioaccumulation of lead (Pb) and its effects in plants: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2022, 3, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Cabral-Pinto, M.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Shabnam, A.A.; Subrahmanyam, G.; Mondal, R.; Gupta, D.K.; Malyan, S.K.; Kumar, S.S.; et al. Lead Toxicity: Health Hazards, Influence on Food Chain, and Sustainable Remediation Approaches. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yin, Z.; Yan, W.; Hao, J.; Tian, F.; Shi, J. Nitrate-dependent antimony oxidase in an uncultured Symbiobacteriaceae member. ISME J. 2024, 18, wrae204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Li, L.; He, M.; Ouyang, W.; Lin, C.; Liu, X. Toxicity and bioavailability of antimony to the earthworm (Eisenia fetida) in different agricultural soils. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, A.; Martínez-Silvestre, A.; Podkowa, D.; Woźniakiewicz, A.; Woźniakiewicz, M.; Pabijan, M. The chemistry and histology of sexually dimorphic mental glands in the freshwater turtle, Mauremys leprosa. PeerJ 2020, 2020, e9047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenet, T.; Schwarz, G.; Neff, C.; Hattendorf, B.; Günther, D.; Martucci, A.; Cescon, M.; Baldi, A.; Pasti, L. Scallop shells as biosorbents for water remediation from heavy metals: Contributions and mechanism of shell components in the adsorption of cadmium from aqueous matrix. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.A.; Abdullah, N.A.; Chowdhury, A.J.K.; Yunus, K. Fish Scales as a Bioindicator of Potential Marine Pollutants and Carcinogens in Asian Sea Bass and Red Tilapia within the Coastal Waters of Pahang, Malaysia. J. Coast. Res. 2018, 82, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvat-Leal, I.; Cortés-Gómez, A.A.; Romero, D.; Girondot, M. New Method for Imputation of Unquantifiable Values Using Bayesian Statistics for a Mixture of Censored or Truncated Distributions: Application to Trace Elements Measured in Blood of Olive Ridley Sea Turtles from Mexico. Animals 2022, 12, 2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, W.A.; Bodinof, C.; Budischak, S.; Perkins, C. Nondestructive indices of mercury exposure in three species of turtles occupying different trophic niches downstream from a former chloralkali facility. Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Héritier, L.; Meistertzheim, A.L.; Verneau, O. Oxidative stress biomarkers in the Mediterranean pond turtle (Mauremys leprosa) reveal contrasted aquatic environments in Southern France. Chemosphere 2017, 183, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| n | Sex | LA (mm) | Lp (mm) | L |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 124.4 | NA | NA |
| 2 | M | 110.1 | NA | NA |
| 3 | M | 83 | NA | NA |
| 4 | F | 96 | NA | NA |
| 5 | M | 116.1 | 134 | 193 |
| 6 | M | 139.2 | 158.1 | 200 |
| 7 | M | 111 | NA | 189 |
| 8 | M | 127 | 131 | 195 |
| 9 | M | 116 | 132 | 199 |
| 10 | F | 126 | NA | NA |
| 11 | M | 115 | 129 | 193 |
| 12 | M | 112 | 126 | 189 |
| 13 | M | 112 | 130 | 189 |
| 14 | F | 124 | 144 | 207 |
| 15 | M | 112 | 128 | 186 |
| 16 | F | NA | 149 | NA |
| 17 | F | NA | 121 | NA |
| 18 | F | 118 | 129 | 195.5 |
| 19 | F | 122.9 | 134.9 | 187 |
| 20 | F | 114.2 | 126 | 195.5 |
| 21 | F | 111 | NA | NA |
| 22 | F | 110 | 128 | 184 |
| 23 | F | 111 | 124 | 179 |
| 24 | F | 122 | 144 | 216 |
| 25 | F | 118.9 | 140 | 207.5 |
| Variable | Overall (mm) | Male (mm) | Female (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LA | 115 ± 11 | 115 ± 13 | 116.1 ± 8.0 |
| Axial length | 134.1 ± 9.3 | 133.5 ± 9.6 | 134.5 ± 9.0 |
| Lp | 195.1 ± 9.4 | 192.6 ± 4.5 | 198 ± 12 |
| Element | Overall | Male | Female | Test | p-Value | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-normally distributed elements | ||||||
| Mg | 3622 (3184–4105) | 4026 (3550–4460) | 3275 (2900–3600) | Mann–Whitney U | 0.04 | * |
| K | 1096 (820–1370) | 1268 (970–1600) | 952 (700–1150) | Mann–Whitney U | 0.07 | n.s. |
| Ti | 346 (190–470) | 389 (210–540) | 307 (180–410) | Mann–Whitney U | 0.29 | n.s. |
| Mn | 195 (85–310) | 277 (130–420) | 122 (55–210) | Mann–Whitney U | 0.05 | * |
| Fe | 2151 (950–3200) | 2397 (1200–3650) | 1942 (800–2800) | Mann–Whitney U | 0.31 | n.s. |
| Zn | 598 (410–760) | 632 (450–780) | 569 (400–730) | Mann–Whitney U | 0.42 | n.s. |
| Sr | 1622 (1200–2050) | 1690 (1300–2200) | 1560 (1100–1900) | Mann–Whitney U | 0.66 | n.s. |
| Al | 3975 (2300–5200) | 4813 (3100–6100) | 3216 (1900–4100) | Mann–Whitney U | 0.03 | * |
| Si | 8943 (5100–12,400) | 11,06 (6800–15,000) | 6938 (4200–9400) | Mann–Whitney U | 0.06 | n.s. |
| Normally distributed elements | ||||||
| P | 101,461 ± 11,594.13 | 100,015 ± 11,916 | 102,700 ± 11,163 | t-test | 0.55 | n.s. |
| S | 3126 ± 1160 | 3493 ± 1230 | 2806 ± 961 | t-test | 0.09 | n.s. |
| Ca | 415,698 ± 17,697 | 414,450 ± 18,059 | 416,799 ± 17,607 | t-test | 0.48 | n.s. |
| Sb | 1491 ± 1082 | 2109 ± 1156 | 904 ± 704 | t-test | 0.02 | * |
| Cu | 4.6 ± 9.7 | 7.3 ± 12.4 | 2.3 ± 6.4 | Mann–Whitney U | 0.08 | n.s. |
| Pb | 9.6 ± 20.4 | 14.3 ± 24.3 | 5.4 ± 15.8 | Mann–Whitney U | 0.04 | * |
| Ni | 0.23 ± 0.78 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.42 ± 0.99 | Mann–Whitney U | 0.15 | n.s. |
| As | Excluded (>30% missing) | — | — | — | — | — |
| Sex | LA | Axial | Lp | L | Mg | P | S | K | Ca | Ti | Mn | Fe | Zn | Sr | Al | Sb | Cu | Pb | Ni | Si | As | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 1.000 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | 0.500 | 0.511 | N.S. | N.S. | 0.489 | N.S. | 0.422 | −0.611 | 0.455 | 0.311 | 0.563 | N.S. | N.S. | 0.411 | N.S. |
| LA | 1.000 | 0.834 | 0.707 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | −0.438 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | |
| Axial | 1.000 | 0.704 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | ||
| Lp | 1.000 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | |||
| L | 1.000 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | ||||
| Mg | 1.000 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | 0.505 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | 0.591 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | |||||
| P | 1.000 | −0.723 | −0.438 | 0.699 | N.S. | −0.440 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | ||||||
| S | 1.000 | 0.602 | N.S. | N.S. | 0.655 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | |||||||
| K | 1.000 | N.S. | 0.804 | 0.754 | 0.815 | N.S. | N.S. | 0.881 | N.S. | 0.455 | N.S. | N.S. | 0.852 | N.S. | ||||||||
| Ca | 1.000 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | |||||||||
| Ti | 1.000 | 0.703 | 0.986 | N.S. | N.S. | 0.957 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | 0.977 | N.S. | ||||||||||
| Mn | 1.000 | 0.701 | N.S. | N.S. | 0.744 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | 0.733 | N.S. | |||||||||||
| Fe | 1.000 | N.S. | N.S. | 0.951 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | 0.961 | N.S. | ||||||||||||
| Zn | 1.000 | N.S. | N.S. | 0.364 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | |||||||||||||
| Sr | 1.000 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | ||||||||||||||
| Al | 1.000 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | 0.991 | N.S. | |||||||||||||||
| Sb | 1.000 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | ||||||||||||||||
| Cu | 1.000 | 0.664 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | |||||||||||||||||
| Pb | 1.000 | N.S. | N.S. | N.S. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ni | 1.000 | N.S. | N.S. | |||||||||||||||||||
| Si | 1.000 | N.S. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| As | 1.000 |
| Cadmium | Chromium | Copper | Manganese | Nickel | Lead | Zinc | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sediments (mg/kg) | Winter | 0 | 0 | 37.51 | 95.47 | 72.04 | 8.73 | 12.14 |
| spring | 0 | 0 | 10.55 | 83.79 | 12.33 | 6.26 | 25.58 | |
| Water (mg/L) | Winter | 0 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 |
| spring | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0 |
| Comparison | Spearman’s Rho | p-Value | FDR-Adjusted p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sediment Winter | −0.20 | 0.747 | 1.00 |
| Sediment Spring | 0.50 | 0.391 | 1.00 |
| Water Winter | −0.26 | 0.668 | 1.00 |
| Water Spring | −0.05 | 0.935 | 0.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aib, H.; Bakhouche, B.; Nyeste, K.; Döncző, B.; Chabani, S.; Saadi, A.; Varga, Z.; Czédli, H.M. Hard Evidence from Turtle Shells: Tracing Metal and Non-Metallic Elements Bioaccumulation in Freshwater Ecosystems. Environments 2025, 12, 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12110445
Aib H, Bakhouche B, Nyeste K, Döncző B, Chabani S, Saadi A, Varga Z, Czédli HM. Hard Evidence from Turtle Shells: Tracing Metal and Non-Metallic Elements Bioaccumulation in Freshwater Ecosystems. Environments. 2025; 12(11):445. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12110445
Chicago/Turabian StyleAib, Haithem, Badis Bakhouche, Krisztián Nyeste, Boglárka Döncző, Selmane Chabani, Amina Saadi, Zsolt Varga, and Herta Mária Czédli. 2025. "Hard Evidence from Turtle Shells: Tracing Metal and Non-Metallic Elements Bioaccumulation in Freshwater Ecosystems" Environments 12, no. 11: 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12110445
APA StyleAib, H., Bakhouche, B., Nyeste, K., Döncző, B., Chabani, S., Saadi, A., Varga, Z., & Czédli, H. M. (2025). Hard Evidence from Turtle Shells: Tracing Metal and Non-Metallic Elements Bioaccumulation in Freshwater Ecosystems. Environments, 12(11), 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12110445







