Abstract
Nutrient removal in conventional wastewater treatment systems is expensive due to the high aeration costs. An alternative method for effective and sustainable nitrogen removal in wastewater treatment is anaerobic ammonium oxidation (Anammox) implemented with other innovative technologies, such as membrane-aerated biofilm reactors (MABRs). A major challenge associated with the Anammox process is effective control of nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB). High temperature operation in wastewater treatment systems can promote Anammox bacterial growth and inhibit NOB activity. This research aims to investigate the feasibility of integrating Anammox processes with a lab-scale MABR and to examine the effects of high temperature aeration supplied to MABR systems on Anammox bacterial growth and NOB suppression. Experimental results indicate that the membrane’s air permeability was a critical parameter for the successful operation of Anammox-integrated MABR systems due to its influence on the system’s dissolved oxygen concentration (0.41 ± 0.39 mg O2/L). The ammonia removal by AOB and Anammox bacteria was determined to be 7.53 mg N/L·d (76.5%) and 2.12 mg N/L·d (23.5%), respectively. High temperature aeration in MABRs with the Anammox process shows a promising potential for improving energy consumption and sustainable nitrogen removal in wastewater treatment systems.
1. Introduction
The presence of nutrients, such as nitrogenous compounds, in wastewater can pose serious environmental concerns to water systems, leading to reduced water quality and potential risks to public health [1,2]. Nitrogen removal in wastewater treatment is often associated with extensive energy consumption and high treatment costs [2,3,4]. Conventional wastewater treatment typically includes nitrification and denitrification processes, which are associated with high oxygen requirements, long hydraulic retention times, and a large footprint of land [5,6]. These factors all contribute to the high treatment costs in conventional wastewater treatment systems. Additionally, the sludge that is produced needs to be managed for disposal and can account for up to 40% of the overall wastewater treatment management costs [3,4,7].
Anaerobic ammonium oxidation (Anammox) is an emerging technology first discovered in the 1990s that can convert ammonia (NH3) and nitrite (NO2) into nitrogen gas under anoxic conditions [8]. In comparison to conventional wastewater treatment processes involving two-step nitrification by ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB) followed by denitrification by denitrifying bacteria, the Anammox process can be operated with less aeration and a reduced footprint while producing less sludge, which can reduce overall wastewater treatment costs by providing more sustainable and efficient nutrient removal [3,7,9,10]. However, Anammox bacteria cultivation must be coupled with other bacterial groups due to its dependence on nitrite substrates, which are not commonly found in natural waters [9,11]. The biological reactions for AOB, Anammox bacteria, NOB, and denitrifying bacteria can be described by Equations (1)–(4), respectively [9,10].
The Anammox process can be integrated with other innovative technologies such as membrane-aerated biofilm reactors (MABR) to provide an ideal environment for simultaneous nitrification and denitrification (SND) biological reactions [12,13,14]. For Anammox–MABR systems to thrive, the four groups of bacteria (AOB, Anammox, NOB, and denitrifying bacteria) must coexist. The expected biofilm profile (Figure 1) consists of an inner aerobic layer to support AOB and NOB growth and an outer anoxic layer to support Anammox and denitrifying bacterial growth [12]. The nitrogen gas produced by both Anammox bacteria and denitrifying bacteria helps to maintain low dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration or anoxic conditions in the bulk solution.
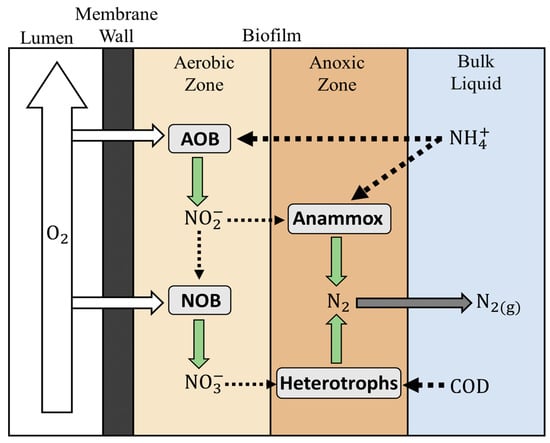
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the expected biological reactions in the biofilm profile for Anammox–MABR systems.
A major challenge for successful integration of Anammox and MABR technologies is the effective control of NOB while accomplishing sufficient treatment [15,16,17]. Operational parameters that can inhibit NOB activity include DO concentration, aeration patterns, pH, hydraulic retention time (HRT), temperature, and substrate concentration [9,18,19,20]. Studies with MABR systems have shown low DO concentration and intermittent aeration strategies to enhance AOB activity and reduce NOB activity [15,21,22,23,24]. The AOB can outcompete NOB and function in oxygen-limited environments primarily due to their higher oxygen affinity in comparison to NOB [20,25,26,27]. A recent study demonstrated that a relatively higher DO concentration (up to 0.8 mg O2/L) can support NOB suppression in the presence of Anammox bacteria [22]. Furthermore, operating with a shorter HRT can be beneficial for controlling NOB inhibition by promoting NOB washout since AOB has a shorter doubling time (7–8 h) than NOB (10–13 h) [9,28].
The operational temperature of wastewater treatment processes can impact the metabolism of the bacteria in the system [29,30]. A higher maximum growth rate for AOB compared to NOB is observed at higher temperatures than 20 °C [26,31]. Due to the dominant growth rate of AOB over NOB at higher temperatures, the operation of bioreactors at temperatures higher than 30 °C was reported to be feasible for NOB elimination in nitrification processes [31,32]. Recent studies demonstrated that operation at high temperatures (30 °C to 40 °C) could maintain stable nitrite accumulation with low nitrate concentrations [28,31,33]. Furthermore, high-temperature operation affects the solubility of oxygen, which may reduce the DO concentration and create desirable growth conditions for Anammox-integrated systems [30]. For most Anammox bacterial species, the optimal temperature for growth is 30 °C to 40 °C [3,7,34,35]. The operation of high-temperature wastewater treatment could primarily control NOB suppression while also promoting Anammox bacterial growth. However, high-temperature operation is still unreliable since large energy requirements are associated with maintaining high water temperatures, leading to increased operational costs [32].
High-temperature reactor operation can be reliably incorporated in MABRs by supplying high-temperature aeration through the lumen of the membranes. In comparison to maintaining high water temperatures for wastewater treatment, managing aeration temperature supplied to MABRs is more feasible and requires less energy consumption because the energy for heating air is significantly small compared to that for heating wastewater of the same volume. Since MABRs support an inner aerobic layer, the high temperature aeration supplied could inhibit NOB activity by providing more favourable growth conditions for AOB, allowing AOB to outcompete NOB. Operation of Anammox–MABR systems with high-temperature aeration can effectively control and suppress NOB while reducing the competition for nitrite substrates between Anammox bacteria and NOB. This study aims to demonstrate NOB suppression using heated air aeration in an MABR for effective nitrogen removal by Anammox bacteria in a lab-scale experiment. Another objective of this work was to investigate the effect of the heated air aeration on the microbial communities in MABR biofilms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Anammox–MABR Configuration
The membranes used in the Anammox–MABR system are polymeric hollow fiber membranes designed for oxygen transfer. A lab-scale Anammox–MABR operating under a partial nitritation–Anammox process (PN-A) was constructed using 4 membrane fibers, each 7.5 cm long (Figure 2). It should be noted that all 4 membrane fibers were placed in a single and well-mixed reactor (600 mL) so that the experimental variable (air temperature) can be emphasized in the reactor operation. The preferred length of the membrane in the Anammox–MABR system was determined to be less than 10 cm from the results of a preliminary MABR system (Figure S1 and Table S1) [Section S1, see Supplementary Information]. Air at two different aeration temperatures was supplied through the membranes of the Anammox–MABR system: 20 °C (ports 1 and 3) and 60 °C (ports 2 and 4). The air was maintained at the desired temperature by directing air flow through copper tubing in a heated water bath kept at a constant temperature. The tubing from the water bath to the reactor was insulated to minimize the heat loss in the tubing.
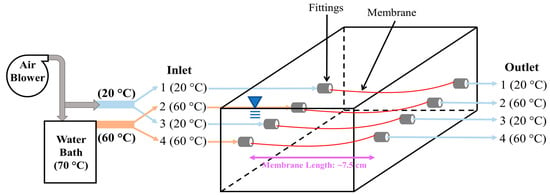
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of Anammox–MABR configuration with 20 °C (ports 1 and 3) and 60 °C (ports 2 and 4) aeration fibers placed in a single well-mixed reactor.
The Anammox–MABR system was enriched with a seed inoculum from an existing Anammox-integrated MABR fed with downstream wastewater. The synthetic feed solution provided to the Anammox–MABR system included 38 mg N/L NH4Cl, 50 mg N/L NaNO2, 500 mg/L NaHCO3, 50 mM PBS (i.e., 8.66 g/L Na2HPO4·7H2O, 2.14 g/L NaH2PO4, 0.13 g/L KCl), 0.1 mL of 100× Vitamins, and 2.5 mL of 10× minerals. The composition of the vitamins and minerals can be found in Cheng et al., 2005 [36].
2.2. Experimental Methods
The Anammox–MABR system was operated for 111 days in continuous fed-batch mode for a hydraulic retention time (HRT) of 14 days. One half of the solution (300 mL out of 600 mL) was replaced every 7 days with a fresh synthetic solution. The fresh feed solution was purged with nitrogen (N2) gas before its addition to the Anammox–MABR system. Samples from the bulk solution were collected from a port at the top of the Anammox–MABR system and analyzed. The pH (SevenMulti, Mettler-Toledo International Inc., Columbus, OH, USA), DO concentration (OX 4100H, VWR International, Mississauga, ON, Canada), and temperature were monitored daily. The reactor pH was maintained at 7.0–7.5 with periodic NaOH injections, and the temperature was kept consistently at 24.4 ± 1.0 °C. The samples were analyzed daily for ammonia (NH4-N TNT832, HACH, Romeoville, IL, USA), nitrite (NO2-N TNT840, HACH, Romeoville, IL, USA), and nitrate (NO3-N TNT835, HACH, Romeoville, IL, USA). The total suspended solids (TSS) and volatile suspended solids (VSS) were analyzed weekly according to Baird et al., 2017; Section 2540 [37].
The daily nitrogen removal rate (mg N/L·d) by each specific bacterial group (AOB, Anammox bacteria, NOB, and denitrifying bacteria) can be estimated by deriving theoretical mass balance equations from Equations (1)–(4) [Section S2, see Supplementary Information]. Since no organic substrates were provided to the synthetic feed solution, the activity of denitrifying bacteria was assumed to be negligible.
2.3. Quantifying Airflow Characteristics
The air flow rate can be used to estimate the average effluent air linear velocity through the membrane to determine if sufficient aeration was provided (Equation (5)). Furthermore, the residence time of the air can be determined (Equation (6)).
2.4. 16S Amplicon Sequencing Methods
Biofilm membrane samples for the two temperature conditions (20 °C and 60 °C) and for the bulk solution in the Anammox–MABR system were prepared for 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing (Surette Laboratory, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada) (Table S2) [Section S3, see Supplementary Information]. The microbial species were then assigned to a target bacterial group of interest: AOB, Anammox bacteria, NOB, denitrifying bacteria, and others.
2.5. qPCR Methods
The DNA from the biofilm membrane samples was extracted using the Soil DNA Isolation Kit (Norgen Biotek Corp., Thorold, ON, Canada). Each biofilm membrane sample was 2 cm in length and was weighed prior to DNA extraction. The specific targets of interest were the 16S rRNA genes for general bacteria, AOB, Anammox bacteria, and NOB (Table 1). Each target bacterial group of interest for qPCR analysis can be described from 16S rRNA with single-copy genes; therefore, the abundance can be directly compared [38,39].

Table 1.
Specific target amplicons for qPCR and primers with associated sequences used in this study.
The PCR protocols were conducted for each primer pair (Table 2). The PCR components included 12.5 µL iTaq Universal SYBR Green Supermix (BioRad Laboratories (Canada) Ltd., Mississauga, ON, Canada), 9.5 µL DI water, 1 µL forward primer, 1 µL reverse primer, and 1 µL DNA template. The PCR products were purified using the PCR Kleen Spin Columns (BioRad, Laboratories (Canada) Ltd., Mississauga, ON, Canada) and then analyzed using a Nanodrop Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The DNA concentration of purified PCR product was quantified using Qubit dsDNA Quantification Assays (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).

Table 2.
PCR protocols for the primers used in this study.
Standard curves (Figure S2, see Supplementary Information) were constructed by conducting qPCR for 10-fold dilutions of the purified PCR product (Table 3). The qPCR components included 10 µL iTaq Universal SYBR Green Supermix (BioRad, Laboratories (Canada) Ltd., Mississauga, ON, Canada), 6 µL DI water, 1 µL forward primer, 1 µL reverse primer, and 2 µL DNA template.

Table 3.
qPCR protocols for the primers used in this study.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Anammox–MABR Performance
The overall performance of the Anammox–MABR system was determined by monitoring key operational parameters throughout the 111 days of the operational period. From day 0 to day 20, there was a rapid ammonia consumption attributed to AOB growth and an indication of low NOB levels due to nitrite accumulation and stable nitrate concentrations in the system (Figure 3a). However, after day 20, nitrite decreased, while nitrate increased drastically, implying NOB activity. Following day 40, the nitrite concentration was maintained consistently at ~45 mg N/L despite the rapid increase in nitrate. This observation demonstrates NOB suppression in the reactor, although it was not sufficient. Furthermore, the optimal growth of Anammox bacteria is dependent on the ratio of substrate available for utilization. The optimal nitrite to ammonia molar ratio for Anammox bacteria under anoxic conditions is 1.32 [9,10]. During day 0 to day 40, the nitrite-to-ammonia molar ratio was unstable, indicating that the growth of the Anammox bacteria may not have been ideal; however, from day 40 onwards, the nitrite-to-ammonia molar ratio was stable at 1.17 ± 0.45. Note that the small fluctuations were induced by injections of NH4Cl into the reactor (Figure 3b). The average time between each injection period was 3 days, and the average ammonia removal efficiency was 59.2 ± 17.5% (Figure 3d). It should be noted that the reactor was not operated for high ammonia removal efficiencies because the primary objective of this study was to examine the effects of aeration temperature on NOB control in MABR systems. Since no organic substrates were supplied to the Anammox–MABR system, denitrification was negligible, with an average COD concentration of 11.4 ± 5.3 mg O2/L (Figure S3, see Supplementary Information).
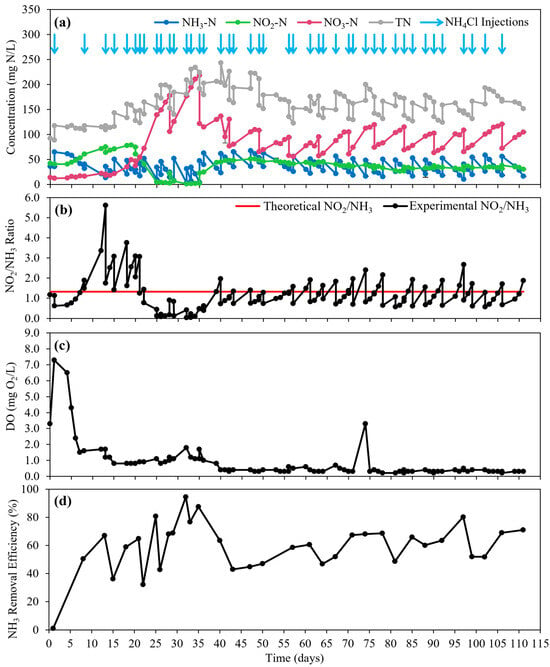
Figure 3.
(a) Nitrogen concentrations, (b) comparison of theoretical and experimental nitrite-to-ammonia molar ratio, (c) dissolved oxygen concentration, and (d) ammonia removal efficiency for Anammox–MABR performance throughout the 111-day operational period.
3.2. Oxygen Transfer through Membranes
The DO concentration in the reactor was relatively high until day 40 (1.78 ± 1.62 mgO2/L), but it was maintained at a low level afterwards (0.36 ± 0.14 mgO2/L) (Figure 3c). This high DO until day 40 resulted in a high nitrate concentration by boosted NOB activity (Figure 3a). On day 35, a simple test was conducted by turning off the aeration blower and monitoring the DO change with time in the reactor. When the aeration was turned off, the DO dropped rapidly from 2.1 mg O2/L to below 0.5 mg O2/L within 120 min (Figure S4, see Supplementary Information), indicating that the aeration membrane allows significant oxygen transfer only with four pieces of 7.5 cm-long hollow fiber membranes. This result shows that membranes for high oxygen transfer may not be suitable for Anammox–MABR systems.
To reduce the oxygen transfer in the reactor, from day 35 onwards, the air blower was operated at the lowest setting (Table 4), and the DO concentration was maintained at 0.41 ± 0.39 mg O2/L. As a result, the nitrite concentration was restored immediately after reduced aeration, indicating controlled NOB activity. The linear velocity and mean air residence time of air through the membrane () for each temperature aeration condition before and after day 35 can be used as an indication of whether the air supplied will maintain sufficient heat (Table 4). In full-scale MABR systems, the mean residence time can be even longer with longer membrane fibers; thus, the DO concentration can be even lower than 0.4 mg O2/L. Since typical Anammox processes operate with a DO < 0.1 mg O2/L [3], a lower DO concentration would be even more effective for controlling NOB activity in Anammox–MABR systems.

Table 4.
Effluent air linear velocity and air residence time () in Anammox–MABR system throughout the 111-day operational period for 20 °C and 60 °C aeration conditions.
3.3. Nitrogen Removal by Specific Bacterial Groups
For ammonia removal, AOB and Anammox bacteria had an average daily removal rate of 7.53 mg N/L·d (76.5%) and 2.12 mg N/L·d (23.5%), respectively (Figure 4a). While AOB was predominantly responsible for ammonia removal in the Anammox–MABR system, there was minor or no competition between AOB and Anammox bacteria, as both groups of bacteria are associated with a slow growth rate [3]. Since the ammonia concentrations in the Anammox–MABR reactor were not depleted with periodic injections of NH4Cl, the ammonia substrate was sufficient for both AOB and Anammox bacteria. Likewise, for nitrite removal, Anammox bacteria and NOB had an average daily removal rate of 2.38 mg N/L·d (37.2%) and 6.05 mg N/L·d (62.8%), respectively (Figure 4b). For days 20–35, nitrite removal was achieved predominantly by NOB due to the high oxygen supply; however, the Anammox contribution to nitrite removal was restored after day 40 with reduced aeration. This observation implies that the MABR membranes should be designed for moderate oxygen transfer to avoid the outgrowth of NOB.
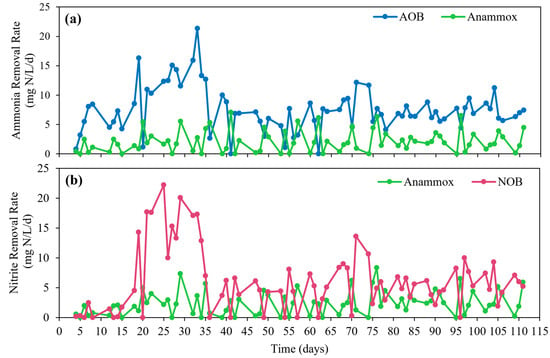
Figure 4.
Estimated daily removal rate for (a) ammonia removal and (b) nitrite removal contributions for target bacterial groups based on theoretical mass balance in the Anammox–MABR throughout the 111-day operational period.
3.4. Microbial Communities
The microbial communities from 16S amplicon sequencing were organized in five target bacterial groups of interest: AOB; Anammox bacteria; NOB; denitrifying bacteria; and others. The relative abundance for these bacterial groups of interest was compared for the two different aeration temperature conditions (Figure 5a,b) and the bulk solution (Figure 5c). The most abundant bacterial group in the biofilm was AOB at 20 °C and 60 °C, with an increasing relative abundance from 3.9% to 47.3 ± 10.9% and 40.4 ± 23.1%, respectively. For Anammox bacteria, the relative abundance in the biofilm decreased from 8.5% to less than 0.001% at both 20 °C and 60 °C, indicating a decrease in Anammox bacterial activity and a shift towards full nitrification with primarily AOB and NOB in the system. The low levels of Anammox bacteria detected by 16S amplicon sequencing analysis could also be due to poor amplification of the 16S rRNA gene with the universal bacterial primers [45]. For NOB, the relative abundance increased from 0.2% to 15.7 ± 8.9% (20 °C) and 19.81 ± 15.08% (60 °C). In comparison to both of the temperature aeration conditions, the relative abundance of AOB in the bulk solution was also highest (Figure 5c), indicating that AOB was dominant for both attached and suspended growth conditions with negligible repercussions. However, the relative abundance of NOB in the bulk solution was less than 2%, indicating that a majority of the NOB preferred to attach to the membrane, which supports a higher DO concentration in the aerobic biofilm. This suggests that the membrane’s oxygen transfer and air permeability resulted in the outgrowth of NOB in the biofilm compared to that in the bulk solution.
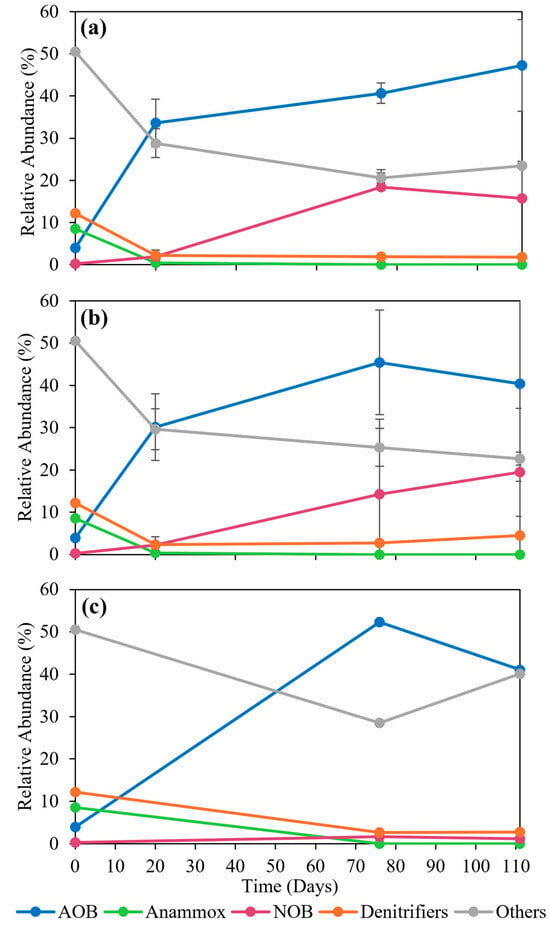
Figure 5.
Relative abundance of microbial communities from 16S amplicon sequencing analysis for the V4 region of 16S rRNA gene in Anammox–MABR system for (a) T = 20 °C, (b) T = 60 °C, and (c) bulk solution.
Compared to 16S amplicon sequencing, the qPCR method was found to provide more accurate detection and representation of the microbial community in the Anammox–MABR reactor. In this method, the relative abundance of each bacterial group of interest was normalized by the general bacteria, DNA concentration, and the effective total surface area of each membrane sample (Table 5). Comparing the two temperature conditions, the abundance of Anammox bacteria and NOB in the MABR biofilm was higher at 60 °C than at 20 °C, while the opposite was observed for AOB. The ratio between AOB and Anammox bacteria (AOB: Anammox) was 30.9 (20 °C) and 25.6 (60 °C), indicating that MABR operation with low-temperature air promotes the growth of AOB over Anammox bacteria. Conversely, the ratio between NOB and Anammox bacteria (NOB: Anammox) was 0.05 (20 °C) and 0.12 (60 °C). However, considering the magnitude of normalized gene copies, Anammox bacteria made significant contributions to nitrite removal regardless of the aeration temperatures, indicating that MABR membranes are suitable for Anammox bacterial attachment.

Table 5.
Relative abundance of target bacterial groups quantified using qPCR assays on Day 111 and normalized using general bacteria in Anammox–MABR system for 20 °C and 60 °C air temperature conditions.
4. Conclusions
For the successful integration of the Anammox process with MABR technologies, there are still challenges associated with controlling the DO concentrations in the system’s bulk solution. Controlling the DO concentration in the system’s bulk solution was difficult since the membrane used in this study had a characteristically high air permeability. Other materials with a lower air permeability can be considered for membrane aeration with Anammox in the future.
The estimated daily removal rate in an ideal PN-A process was estimated to be 12.03 mg N/L·d (70.9%), while for AOB and Anammox bacteria, it was estimated to be 7.53 mg N/L·d (42.8%) and 4.50 mg N/L·d (28.1%), respectively. The nitrogen removal rate and contributions from each target bacterial group were good indicators of the system’s performance and were comparable to the relative abundance of the bacterial groups of interest. For the quantification of relative abundance, the primers used in this study only targeted specific genetic markers for the detection of bacteria in each bacterial group of interest. Future investigations should consider functional gene analysis to improve the accuracy of the representation of the microbial communities in the system.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/environments11070155/s1; Figure S1: (a) Nitrogen concentrations and (b) dissolved oxygen concentrations for the preliminary Anammox–MABR.; Table S1: Effluent air linear velocity and residence time (τair) for the membranes in the preliminary Anammox–MABR.; Table S2: PCR protocol for 16S amplicon sequencing used in this study.; Figure S2: Standard curves constructed from qPCR methods for each primer pair for (a) General Bacteria, (b) AOB, (c) Anammox bacteria (AMX809f/1066r), (d) Anammox bacteria (AMX368f/820r), and (e) NOB.; Figure S3: Suspended Solids concentrations for Anammox–MABR performance throughout 111 days operational period.; Figure S4: Dissolved oxygen concentrations for MABR system with no aeration conducted on Day 35 for 120 min. References [46,47,48,49] are cited in the Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.G. and Y.K.; methodology, N.S., H.G. and Y.K.; formal analysis, N.S.; investigation, N.S.; data curation, N.S.; writing—original draft preparation, N.S.; writing—review and editing, H.G. and Y.K.; visualization, N.S.; supervision, H.G. and Y.K.; project administration, Y.K.; funding acquisition, Y.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (Discovery Grants, RGPIN-2019-06747 and Alliance Grants, ALLRP 588364-23) and the Ontario Ministry of Research and Innovation (Ontario Research Fund-Research Excellence, RE09-077).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hu, Z.; Houweling, D.; Dold, P. Biological nutrient removal in municipal wastewater treatment: New Directions in Sustainability. J. Environ. Eng. 2012, 138, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, S.; Modin, O.; Mijakovic, I. Technologies for biological removal and recovery of nitrogen from wastewater. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 43, 107570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shourjeh, M.S.; Kowal, P.; Lu, X.; Xie, L.; Drewnowski, J. Development of strategies for AOB and NOB competition supported by mathematical modeling in terms of successful Deammonification implementation for energy-efficient wwtps. Processes 2021, 9, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, N.L.; Williams, A.P.; Styles, D. Pitfalls in international benchmarking of energy intensity across wastewater treatment utilities. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Gu, J.; Liu, Y. Environmental sustainability: A pressing challenge to Biological Sewage Treatment Processes. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2019, 12, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Batstone, D.J.; Keller, J. Operating aerobic wastewater treatment at very short sludge ages enables treatment and energy recovery through anaerobic sludge digestion. Water Res. 2013, 47, 6546–6557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.; Kambey, C.; Nguyen, V. Performance of Anammox Processes for wastewater treatment: A critical review on effects of operational conditions and environmental stresses. Water 2020, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, A.; Graaf, A.A.; Robertson, L.A.; Kuenen, J.G. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation discovered in a denitrifying fluidized bed reactor. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1995, 16, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, M.; Eldyasti, A. Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB): Opportunities and applications—A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2018, 17, 285–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, H.P.; Lee, S.-H.; Jeong, G.; Yoon, H.; Park, H.-D. Recent developments of the mainstream anammox processes: Challenges and opportunities. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.-Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.-G.; Du, X.-N.; Huang, B.-C.; Jin, R.-C. A review of anammox-based nitrogen removal technology: From Microbial Diversity to engineering applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 363, 127896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landes, N.; Rahman, A.; Morse, A.; Jackson, W.A. Performance of a lab-scale membrane aerated biofilm reactor treating nitrogen dominant space-based wastewater through simultaneous nitrification-denitrification. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Terada, A.; Tsuneda, S. Modeling of membrane-aerated biofilm: Effects of C/N ratio, biofilm thickness and surface loading of oxygen on feasibility of simultaneous nitrification and Denitrification. Biochem. Eng. J. 2007, 37, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, Z.; Sun, M.; Liang, D.; Hou, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, J. Optimization of nitrogen and carbon removal with simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification in membrane bioreactor. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 200584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunse, P.; Orschler, L.; Agrawal, S.; Lackner, S. Membrane aerated biofilm reactors for mainstream partial nitritation/anammox: Experiences using real municipal wastewater. Water Res. X 2020, 9, 100066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Bao, P.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, G.; Yuan, Z.; Peng, Y. Suppressing nitrite-oxidizing bacteria growth to achieve nitrogen removal from domestic wastewater via ANAMMOX using intermittent aeration with low dissolved oxygen. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, S.; Wang, S.; Janka, E. Achieving partial nitritation in anammox start-up environment. Water 2022, 14, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Ye, L.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, M.; Lu, X.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Z. Nitrite oxidizing bacteria (NOB) contained in influent deteriorate mainstream nob suppression by sidestream inactivation. Water Res. 2019, 162, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Park, Y.-G. Light as a novel inhibitor of nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB) for the mainstream partial nitrification of wastewater treatment. Processes 2021, 9, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Guo, X.; Park, H.-S. Comparison study of the effects of temperature and free ammonia concentration on nitrification and nitrite accumulation. Process Biochem. 2008, 43, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Domingo-Félez, C.; Plósz, B.G.; Smets, B.F. Intermittent aeration suppresses nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in membrane-aerated biofilms: A model-based explanation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6146–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, T.; Niu, C.; Duan, H.; Zheng, M.; Hu, S.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, H.; Guo, J. Challenges of suppressing nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in membrane aerated biofilm reactors by low dissolved Oxygen Control. Water Res. 2023, 247, 120754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, C.; Ying, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, M.; Guo, J.; Yuan, Z.; Hu, S.; Liu, T. Superior mainstream partial nitritation in an acidic membrane-aerated biofilm reactor. Water Res. 2024, 257, 121692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrabi, S.; Houweling, D.; Dagnew, M. MABR process development downstream of a carbon redirection unit: Opportunities and challenges in Nitrogen Removal Processes. Environ. Technol. 2022, 44, 4084–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackburne, R.; Yuan, Z.; Keller, J. Partial nitrification to nitrite using low dissolved oxygen concentration as the main selection factor. Biodegradation 2007, 19, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; He, C.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Pérez, J. Selection of ammonium oxidizing bacteria (AOB) over nitrite oxidizing bacteria (NOB) based on conversion rates. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 304, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Feng, M.; Zheng, S.; Zhao, W.; Xu, X.; Yu, X. The membrane aerated biofilm reactor for nitrogen removal of wastewater treatment: Principles, performances, and Nitrous Oxide Emissions. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 460, 141693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbavarsad, M.S.; Jalalieh, B.J.; Landes, N.; Jackson, W.A. Impact of free ammonia and free nitrous acid on nitritation in membrane aerated bioreactors fed with high strength nitrogen urine dominated wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzeminski, P.; Iglesias-Obelleiro, A.; Madebo, G.; Garrido, J.M.; van der Graaf, J.H.J.M.; van Lier, J.B. Impact of temperature on raw wastewater composition and activated sludge filterability in full-scale MBR systems for Municipal Sewage treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 423–424, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alisawi, H.A. Performance of wastewater treatment during variable temperature. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureni, M.; Weissbrodt, D.G.; Villez, K.; Robin, O.; de Jonge, N.; Rosenthal, A.; Wells, G.; Nielsen, J.L.; Morgenroth, E.; Joss, A. Biomass segregation between biofilm and flocs improves the control of nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in mainstream partial nitritation and Anammox Processes. Water Res. 2019, 154, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H. Nitrite accumulation stability evaluation for low-strength ammonium wastewater by adsorption and biological desorption of zeolite under different operational temperature. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougard, D.; Bernet, N.; Chèneby, D.; Delgenès, J.-P. Nitrification of a high-strength wastewater in an inverse turbulent bed reactor: Effect of temperature on nitrite accumulation. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Xing, D.; Call, D.F.; Logan, B.E. Direct biological conversion of electrical current into methane by electromethanogenesis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3953–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotti, T.; Kleerebezem, R.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Effect of temperature change on ANAMMOX activity. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2014, 112, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Almeida Fernandes, L.; Pereira, A.D.; Leal, C.D.; Davenport, R.; Werner, D.; Filho, C.R.; Bressani-Ribeiro, T.; de Lemos Chernicharo, C.A.; de Araújo, J.C. Effect of temperature on microbial diversity and nitrogen removal performance of an ANAMMOX reactor treating anaerobically pretreated municipal wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 258, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D.; Rice, E.W.; Bridgewater, L. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; Section 2540 Solids; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Speth, D.R.; in’t Zandt, M.H.; Guerrero-Cruz, S.; Dutilh, B.E.; Jetten, M.S. Genome-based microbial ecology of anammox granules in a full-scale wastewater treatment system. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Zhang, I.H.; Jayakumar, A.; Ward, B.B.; Babbin, A.R. Age, Metabolisms, and Potential Origin of Dominant Anammox Bacteria in the Global Oxygen Deficient Zones. ISME Commun. 2024, 4, ycae060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonthiphand, P.; Neufeld, J.D. Evaluating primers for profiling anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria within freshwater environments. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, M.; Twachtmann, U.; Klein, M.; Strous, M.; Juretschko, S.; Jetten, M.; Metzger, J.W.; Schleifer, K.-H.; Wagner, M. Molecular evidence for genus level diversity of bacteria capable of catalyzing anaerobic ammonium oxidation. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 23, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, M.; Walsh, K.; Webb, R.; Rijpstra, W.I.; van de Pas-Schoonen, K.; Verbruggen, M.J.; Hill, T.; Moffett, B.; Fuerst, J.; Schouten, S.; et al. Candidatus “Scalindua Brodae”, sp. nov., Candidatus “Scalindua Wagneri”, sp. nov., two new species of anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacteria. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 26, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Liu, G.; Fan, Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H.; et al. Effects of gibberellin on the activity of anammox bacteria. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 225, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionisi, H.M.; Layton, A.C.; Harms, G.; Gregory, I.R.; Robinson, K.G.; Sayler, G.S. Quantification of Nitrosomonas oligotropha-like ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and Nitrospira spp. from full-scale wastewater treatment plants by competitive PCR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Gu, J.-D. Advances in methods for detection of anaerobic ammonium oxidizing (anammox) bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 90, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stearns, J.C.; Davidson, C.J.; McKeon, S.; Whelan, F.J.; Fontes, M.E.; Schryvers, A.B.; Bowdish, D.M.E.; Kellner, J.D.; Surette, M.G. Culture and Molecular-Based Profiles Show Shifts in Bacterial Communities of the Upper Respiratory Tract That Occur with Age. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1246–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartram, A.K.; Lynch, M.D.J.; Stearns, J.C.; Moreno-Hagelsieb, G.; Neufeld, J.D. Generation of Multimillion-Sequence 16S RRNA Gene Libraries from Complex Microbial Communities by Assembling Paired-End Illumina Reads. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3846–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences from High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).