Effects of Sampling Time and Depth on Phytoplankton Metrics in Agricultural Irrigation Ponds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sites, Field, and Laboratory
2.2. Microscopy
2.3. Statistics and Graphics
3. Results
3.1. Data Summary
3.2. Diurnal Vertical Variations in Phytoplankton Pigments
3.3. Diurnal Vertical Variations in Phytoplankton Cell Counts
3.4. Diurnal and Vertical Variations in Water Quality Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhattarai, S.P.; Midmore, D.J.; Pendergast, L. Yield, Water-Use Efficiencies and Root Distribution of Soybean, Chickpea and Pumpkin under Different Subsurface Drip Irrigation Depths and Oxygation Treatments in Vertisols. Irrig. Sci. 2008, 26, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestre-Valero, J.F.; Martínez-Alvarez, V. Effects of Drip Irrigation Systems on the Recovery of Dissolved Oxygen from Hypoxic Water. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1806–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbel, S.; Mougin, C.; Nélieu, S.; Delarue, G.; Bouaïcha, N. Evaluation of the Transfer and the Accumulation of Microcystins in Tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum Cultivar MicroTom) Tissues Using a Cyanobacterial Extract Containing Microcystins and the Radiolabeled Microcystin-LR ((14)C-MC-LR). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saqrane, S.; Oudra, B. CyanoHAB Occurrence and Water Irrigation Cyanotoxin Contamination: Ecological Impacts and Potential Health Risks. Toxins 2009, 1, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USDA. 2018 Irrigation and Water Management Survey; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- Downing, J.A.; Prairie, Y.T.; Cole, J.J.; Duarte, C.M.; Tranvik, L.J.; Striegl, R.G.; McDowell, W.H.; Kortelainen, P.; Caraco, N.F.; Melack, J.M.; et al. The Global Abundance and Size Distribution of Lakes, Ponds, and Impoundments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 2388–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, R.; Ye, J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C. Monitoring and Research of Microcystins and Environmental Factors in a Typical Artificial Freshwater Aquaculture Pond. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 5921–5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, K.; Vrba, J.; Kaushik, S.J.; Mraz, J. Feed-Based Common Carp Farming and Eutrophication: Is There a Reason for Concern? Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1736–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Lai, D.Y.F.; Jin, B.; Bastviken, D.; Tan, L.; Tong, C. Dynamics of Dissolved Nutrients in the Aquaculture Shrimp Ponds of the Min River Estuary, China: Concentrations, Fluxes and Environmental Loads. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 603–604, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Harada, M.; Hiramatsu, K. Evaluation of the Water-Quality Dynamics in a Eutrophic Agricultural Pond by Using a One-Box Ecosystem Model Considering Several Algal Groups. Paddy Water Environ. 2010, 8, 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Onodera, S.I.; Shiimizu, Y. Effects of Residence Time and Nutrient Load on Eutrophic Conditions and Phytoplankton Variations in Agricultural Reservoirs. In Proceedings of the 2013 Symposium H04: Understanding Freshwater Quality Problems in a Changing World, Gothenburg, Sweden, 22–26 July 2013; pp. 197–203. [Google Scholar]
- Usio, N.; Imada, M.; Nakagawa, M.; Akasaka, M.; Takamura, N. Effects of Pond Draining on Biodiversity and Water Quality of Farm Ponds. Conserv. Biol. 2013, 27, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malerba, M.E.; Lindenmayer, D.B.; Scheele, B.C.; Waryszak, P.; Yilmaz, I.N.; Schuster, L.; Macreadie, P.I. Fencing Farm Dams to Exclude Livestock Halves Methane Emissions and Improves Water Quality. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 4701–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.E.; Chislock, M.F.; Yang, Z.; Barros, M.U.G.; Roberts, J.F. Pond Bank Access as an Approach for Managing Toxic Cyanobacteria in Beef Cattle Pasture Drinking Water Ponds. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, K.J.; Clark, D.R.; Mitra, A.; Fabian, H.; Hansen, P.J.; Glibert, P.M.; Wheeler, G.L.; Stoecker, D.K.; Blackford, J.C.; Brownlee, C. Ocean Acidification with (de)Eutrophication Will Alter Future Phytoplankton Growth and Succession. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20142604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z.; Feng, M.; Li, R.; Zhang, J.; Tian, X.; Zhang, W. Characteristics of Phytoplankton Community Structure and Indication to Water Quality in the Lake in Agricultural Areas. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 833409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, L.M.; Soares, M.C.S.; Paiva, R.; Silva, L.H.S. Morphology-Based Functional Groups as Effective Indicators of Phytoplankton Dynamics in a Tropical Cyanobacteria-Dominated Transitional River–Reservoir System. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 64, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimet, F.; Druart, J.-C. A Trait Database for Phytoplankton of Temperate Lakes. Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Lim. 2018, 54, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, M. Phytoplankton Functional Groups in a Monomictic Reservoir: Seasonal Succession, Ecological Preferences, and Relationships with Environmental Variables. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 20439–20453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nankabirwa, A.; De Crop, W.; Van der Meeren, T.; Cocquyt, C.; Plisnier, P.-D.; Balirwa, J.; Verschuren, D. Phytoplankton Communities in the Crater Lakes of Western Uganda, and Their Indicator Species in Relation to Lake Trophic Status. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 107, 105563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Duan, L.; Wen, X.; Li, H.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Effects of Seasonal Variation on Water Quality Parameters and Eutrophication in Lake Yangzong. Water 2022, 14, 2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twiss, M.R.; Brahmstedt, E.S.; Cabana, G.; Guillemette, F. Proliferation of Phytoplankton along a 500 Km Transect of the St. Lawrence River from Its Outflow at Lake Ontario. J. Great Lakes Res. 2022, 48, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.E.; Stocker, M.D.; Wolny, J.L.; Hill, R.L.; Pachepsky, Y.A. Intraseasonal Variation of Phycocyanin Concentrations and Environmental Covariates in Two Agricultural Irrigation Ponds in Maryland, USA. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.E.; Wolny, J.L.; Stocker, M.D.; Hill, R.L.; Pachepsky, Y.A. Temporal Stability of Phytoplankton Functional Groups within Two Agricultural Irrigation Ponds in Maryland, USA. Front. Water 2021, 3, 724025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gámez, T.E.; Groeger, A.W.; Manning, S.R. Dynamic Phytoplankton Community Structure in a Subtropical Reservoir during an Extended Drought, Central Texas, USA. Aquat. Sci. 2022, 85, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Lou, I.; Zhang, Y.; Lou, C.U.; Mok, K.M. Using an online phycocyanin fluorescence probe for rapid monitoring of cyanobacteria in Macau freshwater reservoir. Hydrobiologia 2014, 741, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio Medrano, E.; Uittenbogaard, R.E.; Dionisio Pires, L.M.; van de Wiel, B.J.H.; Clercx, H.J.H. Coupling Hydrodynamics and Buoyancy Regulation in Microcystis aeruginosa for Its Vertical Distribution in Lakes. Ecol. Model. 2013, 248, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Hu, C.; Visser, P.M.; Ma, R. Diurnal Changes of Cyanobacteria Blooms in Taihu Lake as Derived from GOCI Observations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 1711–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Kong, F.; Wu, X.; Xing, P. Different Photochemical Responses of Phytoplankters from the Large Shallow Taihu Lake of Subtropical China in Relation to Light and Mixing. Hydrobiologia 2008, 603, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.; Rigosi, A.; Hoyer, A.; Escot, C.; Rueda, F.J. Spatial Distribution of Phytoplankton Cells in Small Elongated Lakes Subject to Weak Diurnal Wind Forcing. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 76, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.M.; Saggio, A.A.; Silva, T.L.R.; Negreiros, N.F.; Rocha, O. Short-Term Thermal Stratification and Partial Overturning Events in a Warm Polymictic Reservoir: Effects on Distribution of Phytoplankton Community. Braz. J. Biol. 2015, 75, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, V.; de Souza Cardoso, L.; Huszar, V.L.M. Diel Variation of Phytoplankton Functional Groups in a Subtropical Reservoir in Southern Brazil during an Autumnal Stratification Period. Aquat. Ecol. 2009, 43, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, G.; Wilson, K.K. The Influence of the Diel Climatic Cycle on the Depth-Time Distribution of Phytoplankton and Photosynthesis in a Shallow Equatorial Lake (Lake Baringo, Kenya). Hydrobiologia 1995, 304, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.; Moreno-Ostos, E.; Escot, C.; Quesada, R.; Rueda, F. The Effects of Diel Changes in Circulation and Mixing on the Longitudinal Distribution of Phytoplankton in a Canyon-Shaped Mediterranean Reservoir. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 1945–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossetti, L.O.; Becker, V.; de Souza Cardoso, L.; Rodrigues, L.R.; da Costa, L.S.; da Motta-Marques, D. Is Phytoplankton Functional Classification a Suitable Tool to Investigate Spatial Heterogeneity in a Subtropical Shallow Lake? Limnologica 2013, 43, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.-J.; He, W.; Liu, W.-X.; Qin, N.; Ouyang, H.-L.; Wang, Q.-M.; Kong, X.-Z.; He, Q.-S.; Yang, C.; Yang, B.; et al. The Seasonal and Spatial Variations of Phytoplankton Community and Their Correlation with Environmental Factors in a Large Eutrophic Chinese Lake (Lake Chaohu). Ecol. Indic. 2014, 40, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, R.; Imberger, J. Spatial Distribution of Motile Phytoplankton in a Stratified Reservoir: The Physical Controls on Patch Formation. J. Plankton Res. 2009, 31, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.S.; Shao, N.F.; Yang, S.T.; Ren, H.; Ge, Y.R.; Feng, P.; Dong, B.E.; Zhao, Y. Predicting Cyanobacteria Bloom Occurrence in Lakes and Reservoirs before Blooms Occur. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touchart, L.; Bouny, J. Phytoplankton Geographic Spatialization in Two Ponds in Limousin (France). Appl. Geogr. 2008, 28, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Jewel, M.A.S.; Akhi, M.M.; Atique, U.; Paul, A.K.; Iqbal, S.; Islam, M.S.; Das, S.K.; Alam, M.M. Seasonal Dynamics of Phytoplankton Community and Functional Groups in a Tropical River. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Xia, J.; Cai, W.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhu, X.; Li, C. Seasonal and Spatial Distributions of Morpho-Functional Phytoplankton Groups and the Role of Environmental Factors in a Subtropical River-Type Reservoir. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 2316–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Y.; Kong, L.; Tan, L. Vertical distribution patterns of phytoplankton in summer microcystis bloom period of Xiangxi Bay, Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2011, 20, 553–560. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, B.B.; Bailey, M.C.; Hamilton, D.P. Simulation of Vertical Position of Buoyancy Regulating Microcystis Aeruginosa in a Shallow Eutrophic Lake. Aquat. Sci. 2000, 62, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, L.D.S.; Marques, D.D.M. The Influence of Hydrodynamics on the Spatial and Temporal Variation of Phytoplankton Pigments in a Large, Sub-Tropical Coastal Lake (Brazil). Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2004, 47, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.S.; Churnside, J.H.; Sullivan, J.M.; Twardowski, M.S.; Nayak, A.R.; McFarland, M.N.; Stockley, N.D.; Gould, R.W.; Johengen, T.H.; Ruberg, S.A. Vertical Distributions of Blooming Cyanobacteria Populations in a Freshwater Lake from LIDAR Observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 347–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Holbach, A.; Wilhelms, A.; Qin, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zou, H.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Norra, S. Highly Time-Resolved Analysis of Seasonal Water Dynamics and Algal Kinetics Based on in-Situ Multi-Sensor-System Monitoring Data in Lake Taihu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevindik, T.O.; Çelik, K.; Naselli-Flores, L. Spatial Heterogeneity and Seasonal Succession of Phytoplankton Functional Groups along the Vertical Gradient in a Mesotrophic Reservoir. Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Lim. 2017, 53, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Perkins, K.R.; Rollwagen-Bollens, G.; Bollens, S.M.; Harrison, J.A. Variability in the Vertical Distribution of Chlorophyll in a Spill-Managed Temperate Reservoir. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2019, 35, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, K.A.; Murdock, J.N.; Lizotte, R.E., Jr. Water Depth Influences Algal Distribution and Productivity in Shallow Agricultural Lakes. Ecohydrology 2021, 14, e2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declerck, S.; De Bie, T.; Ercken, D.; Hampel, H.; Schrijvers, S.; Van Wichelen, J.; Gillard, V.; Mandiki, R.; Losson, B.; Bauwens, D.; et al. Ecological Characteristics of Small Farmland Ponds: Associations with Land Use Practices at Multiple Spatial Scales. Biol. Conserv. 2006, 131, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro Berman, M.; O’ Farrell, I.; Huber, P.; Marino, D.; Zagarese, H. A Large-Scale Geographical Coverage Survey Reveals a Pervasive Impact of Agricultural Practices on Plankton Primary Producers. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 325, 107740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Felices, B.; Aznar-Sánchez, J.A.; Velasco-Muñoz, J.F.; Piquer-Rodríguez, M. Contribution of Irrigation Ponds to the Sustainability of Agriculture. A Review of Worldwide Research. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qin, B.; Teubner, K.; Dokulil, M.T. Long-Term Dynamics of Phytoplankton Assemblages: Microcystis-Domination in Lake Taihu, a Large Shallow Lake in China. J. Plankton Res. 2003, 25, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Pan, B.; Zhao, G.; Sun, C.; Han, X.; Li, M. Geo-Climatic Factors Weaken the Effectiveness of Phytoplankton Diversity as a Water Quality Indicator in a Large Sediment-Laden River. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Yang, K.; Che, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhou, L.; Chen, L. Spatial and Temporal Assessment of the Initial Pattern of Phytoplankton Population in a Newly Built Coastal Reservoir. Front. Earth Sci. 2016, 10, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Hou, C.; Liu, Q.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yi, Y. Spatial and Temporal Variations in the Plankton Community Because of Water and Sediment Regulation in the Lower Reaches of Yellow River. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 120972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srichandan, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kumar, A.; Mishra, D.R.; Bhadury, P.; Muduli, P.R.; Pattnaik, A.K.; Rastogi, G. Interannual and Cyclone-Driven Variability in Phytoplankton Communities of a Tropical Coastal Lagoon. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocker, M.D.; Smith, J.E.; Pachepsky, Y.A. Depth-Dependent Concentrations of E. coli in Agricultural Irrigation Ponds. Water 2022, 14, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, H.G.; Alden, R.W. A Comparison of Phytoplankton Assemblages and Environmental Relationships in Three Estuarine Rivers of the Lower Chesapeake Bay. Estuaries 1990, 13, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, M.; Wolny, J.; Truby, E.; Heil, C.; Kovach, C. Harmful Algal Bloom Species and Phosphate-Processing Effluent: Field and Laboratory Studies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, D.M.; Whitton, B.A.; Brook, A.J. The Freshwater Algal Flora of the British Isles: An Identification Guide to Freshwater and Terrestrial Algae; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 2011; 724p, ISBN 978-0-521-19375-7. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Bd. 19/3: Cyanoprokaryota. Tiel/3rd Part: Heterocystous Genera; Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Spektrum Academischer Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J.; Anagnostidis, K. Cyanoprokaryota: Chroococcales; Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Spektrum Akademischer Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; ISBN 978-3-7482-2111-1. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, C.H.; Coughlan, A.; Hallegraeff, G.; Ajani, P.; Armbrecht, L.; Atkins, N.; Bonham, P.; Brett, S.; Brinkman, R.; Burford, M.; et al. A Database of Marine Phytoplankton Abundance, Biomass and Species Composition in Australian Waters. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Gregor, J.; Maršálek, B.; Šípková, H. Detection and Estimation of Potentially Toxic Cyanobacteria in Raw Water at the Drinking Water Treatment Plant by in Vivo Fluorescence Method. Water Res. 2007, 41, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasinak, J.M.E.; Holt, B.M.; Chislock, M.F.; Wilson, A.E. Benchtop Fluorometry of Phycocyanin as a Rapid Approach for Estimating Cyanobacterial Biovolume. J. Plankton Res. 2015, 37, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, J.; Geriš, R.; Maršálek, B.; Heteša, J.; Marvan, P. In Situ Quantification of Phytoplankton in Reservoirs Using a Submersible Spectrofluorometer. Hydrobiologia 2005, 548, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozina, T.; Eleršek, T.; Justin, M.Z.; Meglič, A. Combined Use of Chlorophyll a and Phycocyanin Fluorescence Sensors for Quantification and Differentiation of Phytoplankton: A Useful Approach for Small Surface Water Bodies. Acta Biol. Slov. 2018, 61, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.W.; Howell, E.T.; Watson, S.B.; Smith, R.E.H. Improved Estimates of Phytoplankton Community Composition Based on in Situ Spectral Fluorescence: Use of Ordination and Field-Derived Norm Spectra for the Bbe FluoroProbe. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 73, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godhe, A.; Cusack, C.; Pedersen, J.; Andersen, P.; Anderson, D.M.; Bresnan, E.; Cembella, A.; Dahl, E.; Diercks, S.; Elbrächter, M.; et al. Intercalibration of Classical and Molecular Techniques for Identification of Alexandrium fundyense (Dinophyceae) and Estimation of Cell Densities. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venrick, E.L. How Many Cells to Count? Phytopalnkton Man. 1978, 167–180. [Google Scholar]
- Liefer, J.D.; Robertson, A.; MacIntyre, H.L.; Smith, W.L.; Dorsey, C.P. Characterization of a Toxic Pseudo-Nitzschia spp. Bloom in the Northern Gulf of Mexico Associated with Domoic Acid Accumulation in Fish. Harmful Algae 2013, 26, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, A.A.; Wolny, J.; Leone, E.; Ivey, J.; Murasko, S. Drivers of Phytoplankton Dynamics in Old Tampa Bay, FL (USA), a Subestuary Lagging in Ecosystem Recovery. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2017, 185, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoveská, L. Study of the Seasonality and Hydrology as Drivers of Phytoplankton Abundance and Composition in a Shallow Estuary, Weeks Bay, Alabama (USA). JAMB 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertone, E.; Burford, M.A.; Hamilton, D.P. Fluorescence Probes for Real-Time Remote Cyanobacteria Monitoring: A Review of Challenges and Opportunities. Water Res. 2018, 141, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.-W.; Hobson, P.; Burch, M.; Lin, T.-F. Measurement of Cyanobacteria Using In-Vivo Fluoroscopy—Effect of Cyanobacterial Species, Pigments, and Colonies. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5037–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, A.; Rimet, F.; Jacquet, S. A 2-Year Survey of Phytoplankton in the Marne Reservoir (France): A Case Study to Validate the Use of an in Situ Spectrofluorometer by Comparison with Algal Taxonomy and Chlorophyll a Measurements. Knowl. Managt. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2010, 398, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonazzi, M.; Pezzolesi, L.; Guerrini, F.; Vanucci, S.; Graziani, G.; Vasumini, I.; Pandolfi, A.; Servadei, I.; Pistocchi, R. Improvement of In Vivo Fluorescence Tools for Fast Monitoring of Freshwater Phytoplankton and Potentially Harmful Cyanobacteria. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latasa, M.; Scharek, R.; Morán, X.A.G.; Gutiérrez-Rodríguez, A.; Emelianov, M.; Salat, J.; Vidal, M.; Estrada, M. Dynamics of Phytoplankton Groups in Three Contrasting Situations of the Open NW Mediterranean Sea Revealed by Pigment, Microscopy, and Flow Cytometry Analyses. Progress Oceanogr. 2022, 201, 102737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlüter, L.; Møhlenberg, F.; Havskum, H.; Larsen, S. The Use of Phytoplankton Pigments for Identifying and Quantifying Phytoplankton Groups in Coastal Areas: Testing the Influence of Light and Nutrients on Pigment/Chlorophyll a Ratios. Mar. Ecol. Progress Ser. 2000, 192, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uitz, J.; Claustre, H.; Morel, A.; Hooker, S.B. Vertical Distribution of Phytoplankton Communities in Open Ocean: An Assessment Based on Surface Chlorophyll. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2006, 111, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, S.E.; Gray, D.K.; Izmest’eva, L.R.; Moore, M.V.; Ozersky, T. The Rise and Fall of Plankton: Long-Term Changes in the Vertical Distribution of Algae and Grazers in Lake Baikal, Siberia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivey, J.E.; Wolny, J.L.; Heil, C.A.; Murasko, S.M.; Brame, J.A.; Parks, A.A. Urea Inputs Drive Picoplankton Blooms in Sarasota Bay, Florida, USA. Water 2020, 12, 2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowling, L.C.; Zamyadi, A.; Henderson, R.K. Assessment of in Situ Fluorometry to Measure Cyanobacterial Presence in Water Bodies with Diverse Cyanobacterial Populations. Water Res. 2016, 105, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahnenstiel, G.L.; Carrick, H.J. Phototrophic Picoplankton in Lakes Huron and Michigan: Abundance, Distribution, Composition, and Contribution to Biomass and Production. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1992, 49, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steitz, A.; Velimirov, B. Contribution of Picocyanobacteria to Total Primary Production and Community Respiratory Losses in a Backwater System. J. Plankton Res. 1999, 21, 2341–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoane, S.; Garmendia, M.; Revilla, M.; Borja, Á.; Franco, J.; Orive, E.; Valencia, V. Phytoplankton Pigments and Epifluorescence Microscopy as Tools for Ecological Status Assessment in Coastal and Estuarine Waters, within the Water Framework Directive. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1484–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, M.L.; Kemp, A.E.S.; Nimmo-Smith, W.A.M.; Purdie, D.A. Total Water Column Analysis Shows the Importance of a Single Species in Subsurface Chlorophyll Maximum Thin Layers in Stratified Waters. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 733799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brient, L.; Lengronne, M.; Bertrand, E.; Rolland, D.; Sipel, A.; Steinmann, D.; Baudin, I.; Legeas, M.; Rouzic, B.L.; Bormans, M. A Phycocyanin Probe as a Tool for Monitoring Cyanobacteria in Freshwater Bodies. J. Environ. Monit. 2008, 10, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, R.P.; Johnson, L.T.; Wynne, T.T.; Baker, D.B. Forecasting Annual Cyanobacterial Bloom Biomass to Inform Management Decisions in Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hašler, P.; Štěpánková, J.; Špačková, J.; Neustupa, J.; Kitner, M.; Hekera, P.; Veselá, J.; Burian, J.; Poulíčková, A. Epipelic Cyanobacteria and Algae: A Case Study from Czech Ponds. Fottea 2008, 8, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinta-Kanto, J.M.; Saxton, M.A.; DeBruyn, J.M.; Smith, J.L.; Marvin, C.H.; Krieger, K.A.; Sayler, G.S.; Boyer, G.L.; Wilhelm, S.W. The Diversity and Distribution of Toxigenic Microcystis spp. in Present Day and Archived Pelagic and Sediment Samples from Lake Erie. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, S.; Villeneuve, V.; Vincent, W.F. Benthic and Planktonic Algal Communities in a High Arctic Lake: Pigment Structure and Contrasting Responses to Nutrient Enrichment. J. Phycol. 2005, 41, 1120–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henesy, J.; Wolny, J.; Mullican, J.; Rosales, D.; Pitula, J.; Love, J. Identification of Planktothrix (Cyanobacteria) Blooms and Effects on the Aquatic Macroinvertebrate Community in the Non-Tidal Potomac River, USA. Va. J. Sci. 2020, 72, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, J.; Wang, L.; Guislain, A.; Shatwell, T. Influence of Vertical Mixing on Light-Dependency of Phytoplankton Growth. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öterler, B.; Elipek, B.; Arat, S.M. Influence of Environmental Conditions on the Phytoplankton Community Assemblages in Süloğlu Reservoir (Edirne, Turkey). Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 18, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Uyl, P.A.; Harrison, S.B.; Godwin, C.M.; Rowe, M.D.; Strickler, J.R.; Vanderploeg, H.A. Comparative Analysis of Microcystis Buoyancy in Western Lake Erie and Saginaw Bay of Lake Huron. Harmful Algae 2021, 108, 102102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Feng, G.; Chen, H.; Wang, R.; Tan, Y.; Zhao, H. Modelling the Vertical Migration of Different-Sized Microcystis Colonies: Coupling Turbulent Mixing and Buoyancy Regulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 30339–30347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, L.M.; Silva, L.H.S.; Arcifa, M.S.; Perticarrari, A. Driving Forces of the Diel Distribution of Phytoplankton Functional Groups in a Shallow Tropical Lake (Lake Monte Alegre, Southeast Brazil). Braz. J. Biol. 2009, 69, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.-J.; Liu, D.-F.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.-J.; Khu, S.-T.; Ji, D.-B.; Song, L.-X.; Long, L.-H. Diel Migration of Microcystis during an Algal Bloom Event in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrlack, T. The Diel Vertical Migration of the Nuisance Alga Gonyostomum semen Is Controlled by Temperature and by a Circadian Clock. Limnologica 2020, 80, 125746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagman, C.H.C.; Skjelbred, B.; Thrane, J.-E.; Andersen, T.; Wit, H.A. de Growth Responses of the Nuisance Algae Gonyostomum semen (Raphidophyceae) to DOC and Associated Alterations of Light Quality and Quantity. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 82, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamura, N.; Yasuno, M. Diurnal Changes in the Vertical Distribution of Phytoplankton in Hypertrophic Lake Kasumigaura, Japan. Hydrobiologia 1984, 112, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joniak, T.; Klimaszyk, P.; Kraska, M. Diel Dynamics of Vertical Changes of Chlorophyll and Bacteriochlorophyll in Small Humic Lakes. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2010, 39, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergkemper, V.; Weisse, T. Do Current European Lake Monitoring Programmes Reliably Estimate Phytoplankton Community Changes? Hydrobiologia 2018, 824, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefort, T.; Gasol, J.M. Short-Time Scale Coupling of Picoplankton Community Structure and Single-Cell Heterotrophic Activity in Winter in Coastal NW Mediterranean Sea Waters. J. Plankton Res. 2014, 36, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, C.; Huang, S.; Wu, M.; Du, S.; Scholz, M.; Gao, F.; Lin, C.; Guo, Y.; Dong, Y. Comparison of Relationships Between pH, Dissolved Oxygen and Chlorophyll a for Aquaculture and Non-Aquaculture Waters. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 219, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolini, J.C.; Moresco, G.A.; de Paula, A.C.M.; Jati, S.; Rodrigues, L.C. Functional Approach Based on Morphology as a Model of Phytoplankton Variability in a Subtropical Floodplain Lake: A Long-Term Study. Hydrobiologia 2016, 767, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraco, N.F.; Cole, J.J. Contrasting Impacts of a Native and Alien Macrophyte on Dissolved Oxygen in a Large River. Ecol. Appl. 2002, 12, 1496–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand-Jensen, K.; Prahl, C.; Stokholm, H. Oxygen Release from Roots of Submerged Aquatic Macrophytes. Oikos 1982, 38, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas, M.P.; Marti, C.L.; Adams, M.P.; Oldham, C.E.; Hipsey, M.R. Invasive Macrophytes Control the Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen in a Shallow Lake: A Proposed Feedback Mechanism of Macrophyte Loss. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 270779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, R.I.; Rengefors, K. Life Cyle and Sexuality of the Freshwater Raphidophyte Gonyostomum semen (Raphidophyceae). J. Phycol. 2006, 42, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidmiller, D.R.; Avery, C.W.; Easterling, D.R.; Kunkel, K.E.; Lewis, K.L.M.; Maycock, T.K.; Stewart, B.C. Impacts, Risks, and Adaptation in the United States: The Fourth National Climate Assessment, Volume II; U.S. Global Change Research Program: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [CrossRef]




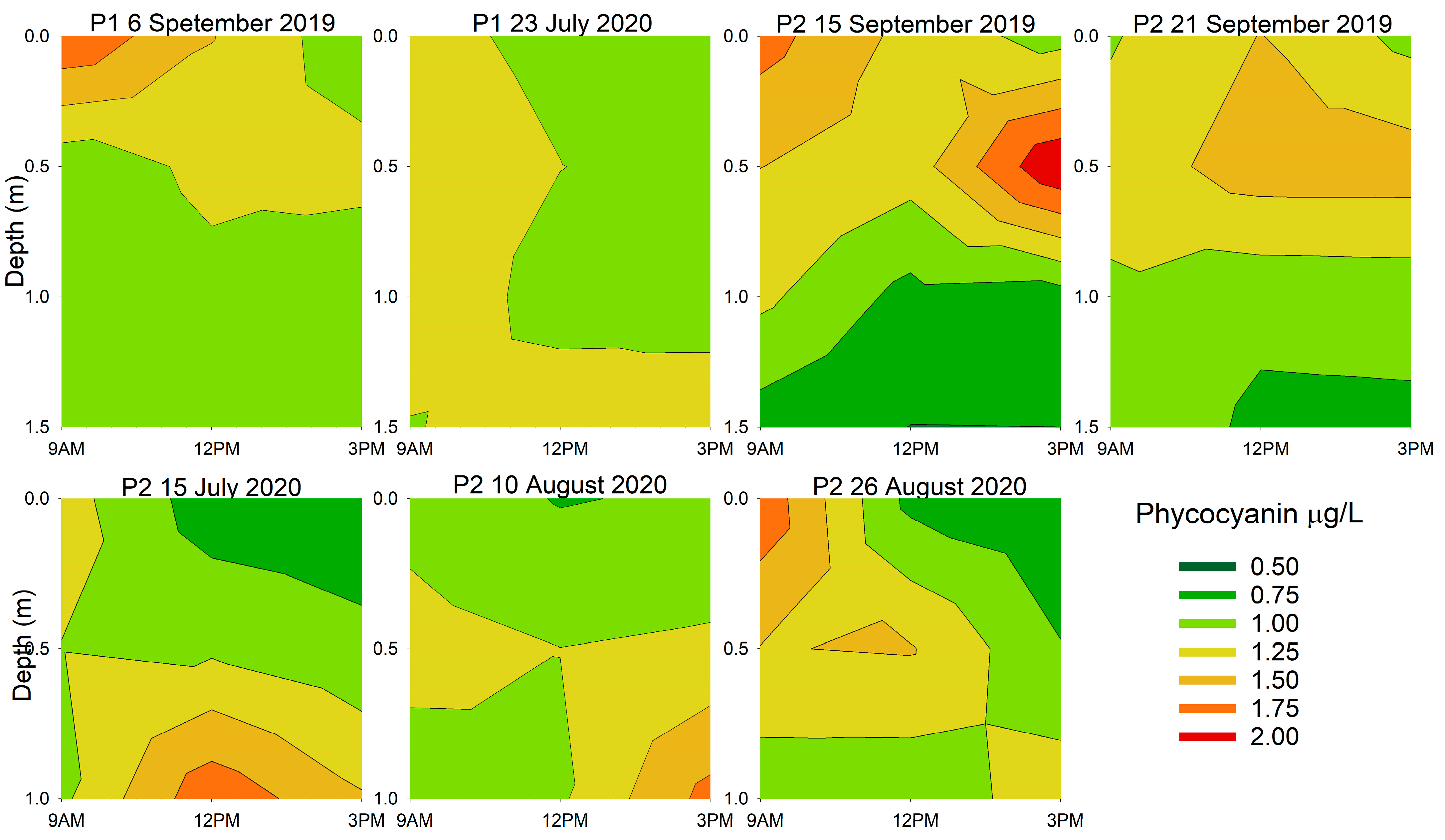
| Location and Date | Chlorophyll-a | Phycocyanin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Depth | Time | Depth | |
| Pond 1 | ||||
| 6 September 2019 | 0.021 | 0.006 | 0.718 | 0.098 |
| 23 July 2020 | 0.478 | 0.023 | 0.268 | 0.361 |
| Pond 2 | ||||
| 15 September 2019 | 0.097 | 0.006 | 0.324 | <0.001 |
| 21 September 2019 | 0.767 | 0.043 | 0.865 | 0.012 |
| 15 July 2020 | 0.046 | <0.001 | 0.104 | <0.001 |
| 10 August 2020 | 0.003 | <0.001 | 0.026 | 0.001 |
| 26 August 2020 | 0.050 | 0.269 | 0.049 | 0.679 |
| Dates | Diatoms | Flagellates | Chlorophytes | Cyanobacteria | Total Cell Count | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Depth | Time | Depth | Time | Depth | Time | Depth | Time | Depth | |
| Pond 1 | ||||||||||
| 6 September 2019 | 0.706 | 0.319 | 0.839 | 0.604 | 0.845 | 0.592 | 0.616 | 0.708 | 0.542 | 0.963 |
| 23 July 2020 | <0.001 | 0.251 | <0.001 | 0.305 | <0.001 | 0.311 | 0.116 | 0.358 | <0.001 | 0.340 |
| Pond 2 | ||||||||||
| 15 September 2019 | 0.479 | 0.179 | 0.047 | 0.236 | 0.043 | 0.228 | 0.633 | 0.140 | 0.054 | 0.052 |
| 21 September 2019 | 0.179 | 0.981 | 0.643 | 0.186 | 0.665 | 0.182 | 0.556 | 0.608 | 0.6965 | 0.760 |
| 15 July 2020 | 0.787 | 0.131 | 0.015 | 0.841 | 0.013 | 0.836 | 0.809 | 0.897 | 0.237 | 0.726 |
| 10 August 2020 | 0.002 | 0.339 | 0.002 | 0.226 | <0.001 | 0.228 | 0.319 | 0.589 | <0.001 | 0.240 |
| 26 August 2020 | 0.491 | 0.880 | 0.025 | 0.547 | 0.757 | 0.408 | ND | ND | 0.533 | 0.394 |
| Two-Way PERMANOVA | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEMP | DO | SPC | pH | NTU | FDOM | CDOM | TC | TOC | TIC | TNB | ||||||||||||
| Time | Depth | Time | Depth | Time | Depth | Time | Depth | Time | Depth | Time | Depth | Time | Depth | Time | Depth | Time | Depth | Time | Depth | Time | Depth | |
| Pond 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 September 2019 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.041 | 0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.995 | 0.099 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.091 | 0.239 | 0.025 | 0.884 | 0.008 | 0.591 | 0.021 | 0.957 | 0.042 | 0.629 |
| 23 July 2020 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.396 | 0.021 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.302 | <0.001 | 0.402 | 0.003 | 0.527 | 0.002 | 0.023 | 0.260 | 0.073 | 0.918 | 0.022 | 0.025 | 0.014 | 0.136 |
| Pond 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15 September 2019 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.004 | <0.001 | 0.457 | <0.001 | 0.018 | <0.001 | 0.589 | 0.220 | 0.634 | <0.001 | 0.432 | 0.003 | 0.085 | 0.448 | 0.941 | 0.078 | 0.023 | 0.932 | 0.063 | 0.903 |
| 21 September 2019 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.335 | 0.019 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.641 | 0.002 | 0.472 | <0.001 | 0.976 | 0.017 | <0.001 | 0.567 | 0.008 | 0.181 | 0.001 | 0.887 | 0.002 | 0.813 |
| 15 July 2020 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.107 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.256 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.693 | <0.001 | 0.519 | <0.001 | 0.911 | <0.001 | 0.422 |
| 10 August 2020 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.173 | 0.095 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.043 | 0.129 | 0.152 | 0.058 | 0.013 | <0.001 | 0.073 | 0.834 | 0.113 | 0.927 | 0.015 | 0.012 | 0.098 | 0.668 |
| 26 August 2020 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.983 | 0.033 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.959 | 0.023 | 0.522 | <0.001 | 0.017 | 0.172 | 0.001 | 0.903 | 0.004 | 0.680 | 0.017 | 0.020 | 0.003 | 0.896 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smith, J.E.; Wolny, J.L.; Stocker, M.D.; Pachepsky, Y. Effects of Sampling Time and Depth on Phytoplankton Metrics in Agricultural Irrigation Ponds. Environments 2024, 11, 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040074
Smith JE, Wolny JL, Stocker MD, Pachepsky Y. Effects of Sampling Time and Depth on Phytoplankton Metrics in Agricultural Irrigation Ponds. Environments. 2024; 11(4):74. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040074
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmith, Jaclyn E., Jennifer L. Wolny, Matthew D. Stocker, and Yakov Pachepsky. 2024. "Effects of Sampling Time and Depth on Phytoplankton Metrics in Agricultural Irrigation Ponds" Environments 11, no. 4: 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040074
APA StyleSmith, J. E., Wolny, J. L., Stocker, M. D., & Pachepsky, Y. (2024). Effects of Sampling Time and Depth on Phytoplankton Metrics in Agricultural Irrigation Ponds. Environments, 11(4), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11040074






