The Impact of Air Pollution on Stone Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Air Pollution and Stone
3. The Study of Black Crusts
3.1. The Sampling Methodology
3.2. Structure and Main Components
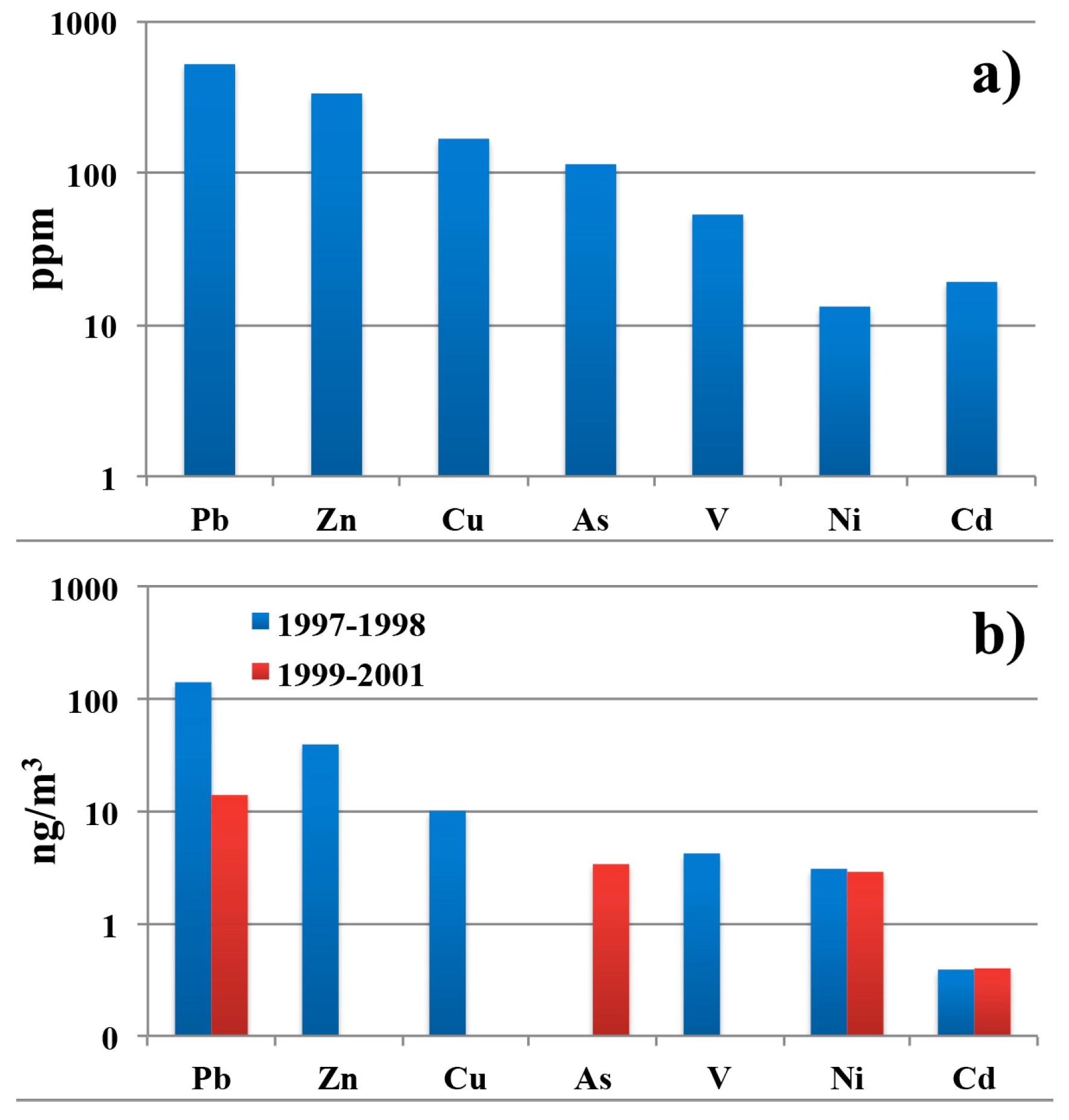
3.3. Analysis of Metals
| Sampling | Country | As | Ba | Cd | Cr | Cu | Mn | Ni | Pb | Sb | Sn | V | Zn | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tower of London | England | 57.2 | 4.4 | 41.2 | 185.6 | 275.0 | 56.5 | 807.6 | 20.2 | 38.2 | 116.8 | 384.1 | [52] | |
| Mechelen Cathedral | Belgium | 35.6 | 0.2 | 58.6 | 182.2 | 120.9 | 29.7 | 1721.3 | 10.1 | 9.7 | 320.2 | 3436.8 | [53] | |
| St. Eustache Paris | France | 58.1 | 12.2 | 15.0 | 89.4 | 68.4 | 33.2 | 813.3 | 17.0 | 165.7 | 66.8 | 451.8 | [53] | |
| Seville Cathedral | Spain | 85.5 | 15.3 | 213.7 | 125.1 | 255.0 | 18.4 | 378.2 | 8.7 | 819.3 | 43.5 | 226.7 | [54] | |
| La Galea Fortress, Getxo, Basque Country | Spain | 16.3 | 110.7 | 0.3 | 20.3 | 19.0 | 74.0 | 10.0 | 299.3 | 2.0 | 6.7 | 19.0 | 184.7 | [21] |
| Altenberg Cathedral | Germany | 28.0 | 890.0 | 12.0 | [45] | |||||||||
| Cologne Cathedral | Germany | 365.0 | 1849.0 | 37.0 | [45] | |||||||||
| Xanten Cathedral | Germany | 50.0 | 1944.0 | 16.0 | [45] | |||||||||
| Corner Palace in Venice | Italy | 125.4 | 4.2 | 54.2 | 98.3 | 327.9 | 49.5 | 2613.1 | 41.7 | 31.1 | 106.4 | 712.5 | [53] | |
| Fontana di Trevi Rome | Italy | 58.2 | 620.3 | 49.3 | 122.8 | 26.8 | 557.3 | 34.0 | 45.4 | 103.9 | 337.0 | [62] | ||
| Monza Cathedral | Italy | 240.0 | 2415.5 | 72.0 | 2567.5 | 217.0 | 221.0 | 9009.0 | 399.5 | 546.5 | 302.5 | 2047.0 | [31] | |
| Historical center of Naples | Italy | 21.5 | 532.2 | 0.9 | 16.4 | 89.8 | 7.9 | 1395.1 | 9.6 | 22.9 | 628.0 | [34] | ||
| Historical center of Venice | Italy | 170.2 | 836.2 | 8.1 | 65.2 | 160.8 | 179.9 | 696.5 | 40.7 | 604.0 | 98.6 | 1848.2 | [35] | |
| St. Cosimato Cloister, Rome | Italy | 34.5 | 772.9 | 2.6 | 21.3 | 60.1 | 248.5 | 9.2 | 598.4 | 7.1 | 25.3 | 56.1 | 210.7 | [51] |
| Cemetery Pessago con Bornago (Milan) | Italy | 44.8 | 202.7 | 19.0 | 55.1 | 64.6 | 250.1 | 13.0 | 2821.2 | 62.0 | 222.7 | 123.5 | 414.2 | [51] |
| Renaissance city walls of Padua | Italy | 47.8 | 8.7 | 68.9 | 489.8 | 46.4 | 6738.2 | 17.8 | 38.7 | 143.1 | 4171.3 | [44] |
3.4. Particulate Matter and Organic Fraction
4. Intervention Strategies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- La Russa, M.F.; Ruffolo, S.A. Mortars and plasters—How to characterize mortar and plaster degradation. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2021, 13, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hees, R.P.J.; Binda, L.; Papayianni, I.; Toumbakari, E. Characterisation and damage analysis of old mortars. Mater. Struct. 2004, 37, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurenbrecher, P. Water-Shedding Details Improve Masonry Performance; Construction Technology Update 23; Institute for Research in Construction, National research Council: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Fassina, V. 46-Influenza dell’inquinamento atmosferico sui processi di degrado dei materiali lapidei. In Bollettino d’Arte “Materiali Lapidei-Problemi Relativi Allo Studio Del Degrado e Conservazione; Ministero per i beni e le attività culturali: Rome, Italy, 1987; pp. 19–47. [Google Scholar]
- Fassina, V.; Favaro, M.; Crivellari, F.; Naccari, A. The stone decay of monuments in relation to atmospheric environment. Ann. Di Chim. 2001, 91, 767–774. [Google Scholar]
- The Early Keeling Curve Scripps CO2 Program. Available online: scrippsco2.ucsd.edu (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Zeldovich, Y.B. The Oxidation of Nitrogen in Combustion Explosions. Acta Physicochim. USSR 1946, 21, 577–628. [Google Scholar]
- Hegg, D.A.; Hobbs, P.V. Oxidation of sulfur dioxide in aqueous systems with particular reference to the atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 1967, 12, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Yuan, Z.; Griffith, S.M.; Yu, X.; Lau, A.K.H.; Yu, J.Z. Sulfate Formation Enhanced by a Cocktail of High NOx, SO2, Particulate Matter, and Droplet pH during Haze-Fog Events in Megacities in China: An Observation-Based Modeling Investigation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7325–7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Ye, J.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, D.; Nie, D.; Shen, F.; Huang, X.; et al. Fast sulfate formation from oxidation of SO2 by NO2 and HONO observed in Beijing haze. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P. China’s air pollution policies: Progress and challenges. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2021, 19, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betha, R.; Behera, S.N.; Balasubramanian, R. 2013 Southeast Asian smoke haze: Fractionation of particulate-bound elements and associated health risk. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4327–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Particulate Matter|Air & Radiation|US EPA. US Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/pm/ (accessed on 6 July 2011).
- Amoroso, G.; Fassina, V. Stone Decay and Conservation. Atmospheric Pollution, Cleaning, Consolidation and Protection; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1983; p. 474. [Google Scholar]
- Vergès-Belmin, V. Illustrated Glossary on Stone Deterioration Patterns; ICOMOS: Pairs, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Török, A.; Licha, T.; Simon, K.; Siegesmund, S. Urban and rural limestone weathering; the contribution of dust to black crust formation; examples from Germany and Hungary. Environ. Earth Sci. 2008, 63, 675–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonazza, A.; Sabbioni, C.; Ghedini, N.; Hermosin, B.; Jurado, V.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Saiz-Jimenez, C. Did smoke from Kuwait oil well fires affect Iranian archeological heritage? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2378–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antill, S.J.; Viles, H.A. Deciphering the impacts of traffic on stone decay in Oxford: Some preliminary observations from old limestone walls. In Aspects of Stone Weathering, Decay and Conservation; Jones, M.S., Wakefield, R.D., Eds.; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 1999; pp. 28–42. [Google Scholar]
- Török, A. Surface strength and mineralogy of weathering crusts on limestone buildings in Budapest. Build. Environ. 2003, 38, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Török, A. Black crusts on travertine: Factors controlling development and stability. Environ. Geol. 2008, 56, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillas, H.; Maguregui, M.; García-Florentino, C.; Carrero, J.A.; Salcedo, I.; Madariaga, J.M. The cauliflower-like black crusts on sandstones: A natural passive sampler to evaluate the surrounding environmental pollution. Environ. Res. 2016, 147, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, E.M. Important agents of weathering for building and monumental stone. Eng. Geol. 1966, 1, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartarelli, R.; Davini, P.; Morelli, F.; Corsi, P. Interactions between SO2 and carbonaceous particulates. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1978, 12, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spedding, D.J. Sulphur dioxide uptake by limestone. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1969, 3, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, R.C.; Wilson, M.J.G. The removal of atmospheric sulphur by building stones. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1970, 4, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Monte, M.; Sabbioni, C.; Vittori, O. Airborne carbon particles and marble deterioration. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1981, 15, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Mo, T.; Chen, T. Deterioration of stony cultural relics and their geochemical characteristics. Chin. J. Geochem. 1986, 5, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Monte, M.; Vittori, O. Air pollution and stone decay: The case of Venice. Endeavour 1985, 9, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.J.; Castillo, R. A Study of Marble Deterioration an City Hall, Schenectady, New York. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1984, 34, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maravelaki-Kalaitzaki, P.; Biscontin, G. Origin, characteristics and morphology of weathering crusts on Istria stone in Venice. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 1699–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comite, V.; Pozo-Antonio, J.S.; Cardell, C.; Rivas, T.; Randazzo, L.; La Russa, M.F.; Fermo, P. Environmental impact assessment on the Monza Mathedral (Italy): A multi-analytical approach. Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2020, 11, 291–304. [Google Scholar]
- Vidorni, G.; Sardella, A.; De Nuntiis, P.; Volpi, F.; Dinoi, A.; Contini, D.; Comite, V.; Vaccaro, C.; Fermo, P.; Bonazza, A. Air pollution impact on carbonate building stones in Italian urban sites. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2019, 134, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovella, N.; Aly, N.; Comite, V.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Ricca, M.; Fermo, P.; Alvarez de Buergo, M.; La Russa, M.F. A methodological approach to define the state of conservation of the stone materials used in the Cairo historical heritage (Egypt). Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2020, 12, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comite, V.; Ricca, M.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Graziano, S.F.; Rovella, N.; Rispoli, C.; Gallo, C.; Randazzo, L.; Barca, D.; Cappelletti, P.; et al. Multidisciplinary approach for evaluating the geochemical degradation of building stone related to pollution sources in the historical center of Naples (Italy). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Russa, M.F.; Comite, V.; Aly, N.; Barca, D.; Fermo, P.; Rovella, N.; Antonelli, F.; Tesser, E.; Aquino, M.; Ruffolo, S.A. Black crusts on Venetian built heritage, investigation on the impact of pollution sources on their composition. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2018, 133, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbioni, C. Contribution of atmospheric deposition to the formation of damage layers. Sci. Total Environ. 1995, 167, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte, M.D.; Sabbioni, C. Weddellite on Limestone in the Venice Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1983, 17, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulotta, D.; Bertoldi, M.; Bortolotto, S.; Fermo, P.; Piazzalunga, A.; Toniolo, L. The Angera stone: A challenging conservation issue in the polluted environment of Milan (Italy). Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampazzi, L.; Andreotti, A.; Bonaduce, I.; Colombini, M.P.; Colombo, C.; Toniolo, L. Analytical investigation of calcium oxalate films on marble monuments. Talanta 2004, 63, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbioni, C.; Zappia, G. Oxalate patinas on ancient monuments: The biological hypothesis. Aerobiologia 1991, 7, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadd, G.M.; Bahri-Esfahani, J.; Li, Q.; Rhee, Y.J.; Wei, Z.; Fomina, M.; Liang, X. Oxalate production by fungi: Significance in geomycology, biodeterioration and bioremediation. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2014, 28, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaylarde, C.C.; Morton, L.H.G. Deteriogenic biofilms on buildings and their control: A review. Biofouling 1999, 14, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjurjo Sánchez, J.; Alves, C.A.S.; Vidal Romani, J.R.; Fernández Mosquera, D. Origin of gypsum-rich coatings on historic buildings. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2009, 204, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germinario, L.; Siegesmund, S.; Maritan, L.; Simon, K.; Mazzoli, C. Trachyte weathering in the urban built environment related to air quality. Herit. Sci. 2017, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graue, B.; Siegesmund, S.; Oyhantcabal, P.; Naumann, R.; Licha, T.; Simon, K. The effect of air pollution on stone decay: The decay of the Drachenfels trachyte in industrial, urban, and rural environments—A case study of the Cologne, Altenberg and Xanten cathedrals. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 1095–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, M.; Pironti, C.; Motta, O.; Fiorillo, R.; Camin, F.; Faggiano, A.; Proto, A. Investigations on historical monuments’ deterioration through chemical and isotopic analyses: An Italian case study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 29409–29418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetintas, S.; Akboga, Z. Investigation of resistance to ageing by SO2 on some building stone. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, M.Y.; Ersoy, M.; Sert, M.; Arsoy, Z.; Yesilkaya, L. Investigation of some atmospheric effects in the laboratory tests on deterioration of andesite (Iscehisar-Turkey) used as the building stone of cultural heritages. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, C.; Du, H.; Huang, J.; Guo, X.; Luo, Q.; Ren, J. Investigation into the Gaseous SO2 Attack on Sandstone in the Yungang Grottoes. Minerals 2023, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo-Antonio, J.S.; Pereira, M.F.C.; Rocha, C.S.A. Microscopic characterisation of black crusts on different substrates. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barca, D.; Belfiore, C.M.; Crisci, G.M.; la Russa, M.F.; Pezzino, A.; Ruffolo, S.A. Application of laser ablation ICP-MS and traditional techniques to the study of black crusts on building stones: A new methodological approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2010, 17, 1433–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Russa, M.F.; Belfiore, C.M.; Comite, V.; Barca, D.; Bonazza, A.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Crisci, G.M.; Pezzino, A. Geochemical study of black crusts as a diagnostic tool in cultural heritage. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2013, 113, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfiore, C.M.; Barca, D.; Bonazza, A.; Comite, V.; la Russa, M.F.; Pezzino, A.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Sabbioni, C. Application of spectrometric analysis to the identification of pollution sources causing cultural heritage damage. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 8848–8859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffolo, S.A.; Comite, V.; La Russa, M.F.; Belfiore, C.M.; Barca, D.; Bonazza, A.; Crisci, G.M.; Pezzino, A.; Sabbioni, C. An analysis of the black crusts from the Seville Cathedral: A challenge to deepen the understanding of the relationships among microstructure, microchemical features and pollution sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geller, M.D.; Ntziachristos, L.; Mamakos, A.; Samaras, Z.; Schmitz, D.A.; Froines, J.R.; Sioutas, C. Physicochemical and redox characteristics of particulate matter (PM) emitted from gasoline and diesel passenger cars. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 6988–7004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmens, H.; Norris, D.A. The Participants of the Moss Survey Spatial and Temporal Trends in Heavy Metal Accumulation in Mosses in Europe (1990–2005) Programme Coordination Centre for the ICP Vegetation; Centre for Ecology & Hydrology, Natural Environment Research Council: Bangor, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Winther, M.; Slentø Neri, E. (Eds.) Heavy Metal Emissions for Danish Road Transport; Technical Report; National Environmental Research Institute, University Aarhus: Aarhus, Denmark, 2010; p. 780. [Google Scholar]
- Sternbeck, J.; Sjödin, A.; Andréasson, K. Metal emissions from road traffic and the influence of resuspension—Results from two tunnel studies. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 4735–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongarrà, G.; Manno, E.; Varrica, D. Possible markers of traffic-related emissions. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 154, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmens, H.; Norris, D.A.; Koerber, G.R.; Buse, A.; Steinnes, E.; Rühling, Å. Temporal trends in the concentration of arsenic, chromium, copper, iron, nickel, vanadium and zinc in mosses across Europe between 1990 and 2000. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 6673–6687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlister, J.J.; Smith, B.J.; Török, A. Transition metals and water-soluble ions in deposits on a building and their potential catalysis of stone decay. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7657–7668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Russa, M.F.; Fermo, P.; Comite, V.; Belfiore, C.M.; Barca, D.; Cerioni, A.; De Santis, M.; Barbagallo, L.F.; Ricca, M.; Ruffolo, S.A. The Oceanus statue of the Fontana di Trevi (Rome): The analysis of black crust as a tool to investigate the urban air pollution and its impact on the stone degradation. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 593–594, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermo, P.; Turrion, R.G.; Rosa, M.; Omegna, A. A new approach to assess the chemical composition of powder deposits damaging the stone surfaces of historical monuments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 6262–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belis, C.A.; Cancelinha, J.; Duane, M.; Forcina, V.; Pedroni, V.; Passarella, R.; Tanet, G.; Douglas, K.; Piazzalunga, A.; Bolzacchini, E.; et al. Sources for PM air pollution in the Po Plain, Italy: I. Critical comparison of methods for estimating biomass burning contributions to benzo(a)pyrene. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 7266–7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidblad, J.; Kucera, V.; Ferm, M.; Kreislova, K.; Brüggerhoff, S.; Doytchinov, S.; Screpanti, A.; Grøntoft, T.; Yates, T.; De La Fuente, D.; et al. Effects of air pollution on materials and cultural heritage: ICP materials celebrates 25 years of research. Int. J. Corros. 2012, 2012, 496321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo-Antonio, J.S.; Cardell, C.; Comite, V.; Fermo, P. Characterization of black crusts developed on historic stones with diverse mineralogy under different air quality environments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 29438–29454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, O.; Siegesmund, S.; Licha, T.; Török, Á. Geochemical and mineralogical composition of black weathering crusts on limestones from seven different European countries. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orecchio, S. Analytical method, pattern and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the stone of the Temples of Agrigento (Italy). J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, M.; Faggiano, A.; Pironti, C.; Motta, O.; Carotenuto, M.; Comite, V.; Fermo, P.; Proto, A. Analysis of PAHs (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons) and other main components in black crusts collected from the Monumental Cemetery of Milan (Italy). J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2204, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Arkarazo, I.; Angulo, M.; Bartolomé, L.; Etxebarria, N.; Olazabal, M.A.; Madariaga, J.M. An integrated analytical approach to diagnose the conservation state of building materials of a palace house in the metropolitan Bilbao (Basque Country, North of Spain). Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 584, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.L.; Farrington, J.W.; Reddy, C.M. Combustion-derived polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the environment—A review. Environ. Forensics 2005, 6, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoneit, B.R.T. Biomass burning—A review of organic tracers for smoke from incomplete combustion. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 129–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianguzza, A.; Governanti, M.; Orecchio, S.; Piazzese, D. Identification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHS) in the black crusts of Sicilian stone monuments: Distribution and sources. Sci. Technol. Cult. Herit. 2004, 13, 53–61. [Google Scholar]
- Pozo-Antonio, J.S.; Alonso-Villar, E.M.; Rivas, T. Efficacy of mechanical procedures for removal of a lichen and a gypsum black crust from granite. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 102986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, J.; Wain, A.; Rode, A.V.; Madden, S.; Rappet, L. Towards safe and effective femtosecond laser cleaning for the preservation of historic monuments. Appl. Phys. A 2023, 129, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranalli, G.; Zanardini, E. Biocleaning on Cultural Heritage: New frontiers of microbial biotechnologies. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 583–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo, S.; Barreiro, P.; Rivas, T.; González, P.; Fiorucci, M.P. Effectiveness and harmful effects of removal sulphated black crust from granite using Nd:YAG nanosecond pulsed laser. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 302, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappitelli, F.; Toniolo, L.; Sansonetti, A.; Gulotta, D.; Ranalli, G.; Zanardini, E.; Sorlini, C. Advantages of using microbial technology over traditional chemical technology in removal of black crusts from stone surfaces of historical monuments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5671–5675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, R.; Palla, F. Plant Essential Oils as Biocides in Sustainable Strategies for the Conservation of Cultural Heritage. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Russa, M.F.; Rovella, N.; Alvarez de Buergo, M.; Belfiore, C.M.; Pezzino, A.; Crisci, G.M.; Ruffolo, S.A. Nano-TiO2 coatings for cultural heritage protection: The role of the binder on hydrophobic and self-cleaning efficacy. Prog. Org. Coat. 2016, 91, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Russa, M.F.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Rovella, N.; Belfiore, C.M.; Palermo, A.M.; Guzzi, M.T.; Crisci, G.M. Multifunctional TiO2coatings for cultural heritage. Prog. Org. Coat. 2012, 74, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruffolo, S.A.; La Russa, M.F.; Rovella, N.; Ricca, M. The Impact of Air Pollution on Stone Materials. Environments 2023, 10, 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10070119
Ruffolo SA, La Russa MF, Rovella N, Ricca M. The Impact of Air Pollution on Stone Materials. Environments. 2023; 10(7):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10070119
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuffolo, Silvestro Antonio, Mauro Francesco La Russa, Natalia Rovella, and Michela Ricca. 2023. "The Impact of Air Pollution on Stone Materials" Environments 10, no. 7: 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10070119
APA StyleRuffolo, S. A., La Russa, M. F., Rovella, N., & Ricca, M. (2023). The Impact of Air Pollution on Stone Materials. Environments, 10(7), 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10070119








