Legacy Phosphorus in Sediments of Lowland Waterways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
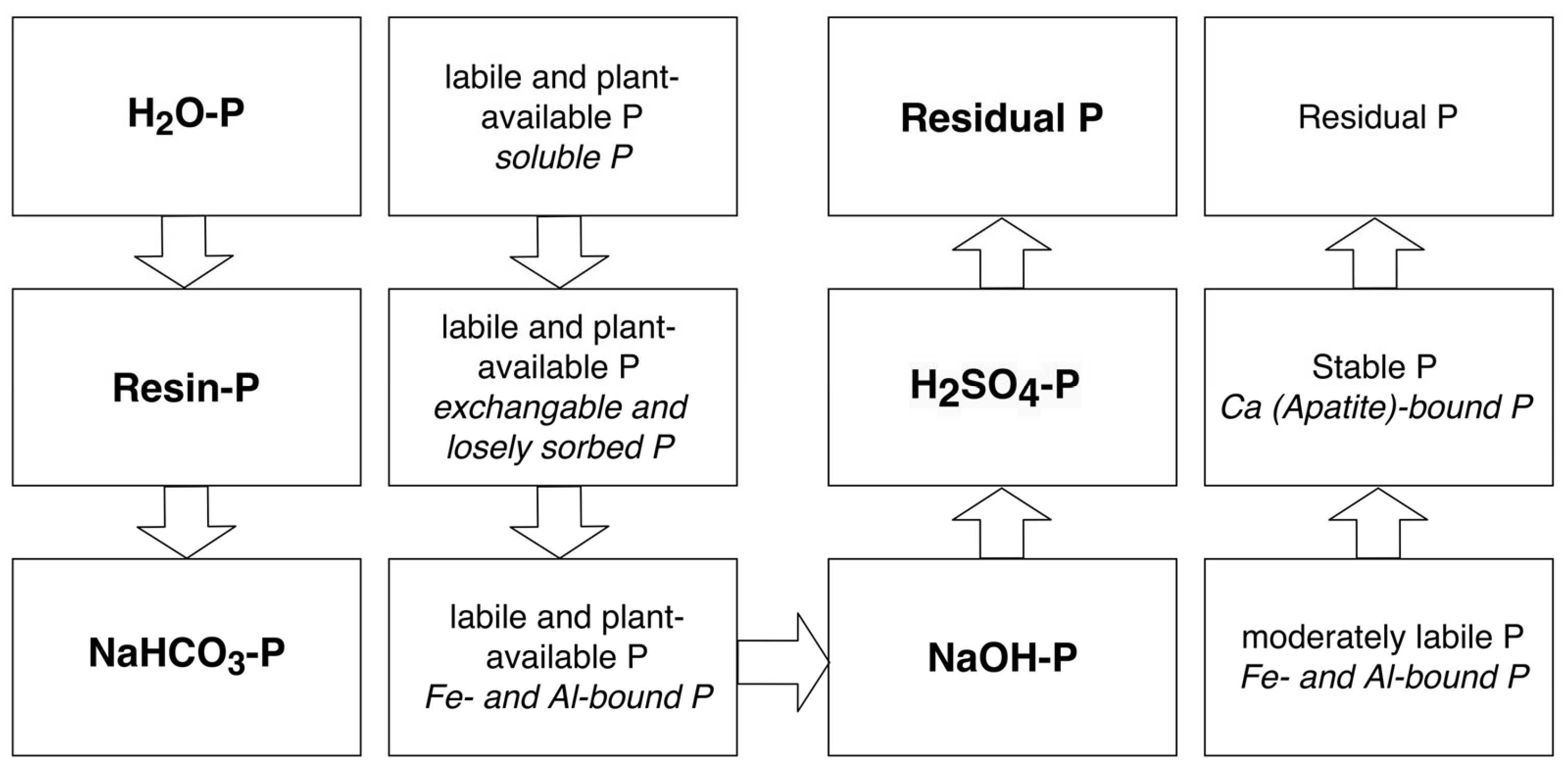
2.1. Conceptual Design of the Study
2.2. Study Site
2.3. Sampling, In Situ, and Laboratory Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Total P Contents of the Warnow River Basin
| Source | Catchment | Region | TP Levels mg P kg−1 Sediment−1 | Main Land Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [17] | Recknitz River | Europe, Northern Germany | 912–3974 | Agriculture |
| [43] | River Swale | Europe, England, Yorkshire | 500–1500 | Agriculture, Moorland |
| [11] | Sävjaån River | Europe, central Sweden | 73–1568 | Permanent Forest |
| [44] | West Holland River | North America, Canada | 1600–2000 | Agriculture |
| [45] | Hadlock Brook | North America, USA | 211–223 | Forest |
| [46] | Agudo River | South America, Brazil, Rio Grande du sol | 622–992 | Permanent Forest |
| [47] | Mekong River | Asia, China, Yunnan Province | 500–800 | Non-Agricultural |
| [12] | Yangtze River | Asia, China, | 550–844 | Urban, Agriculture |
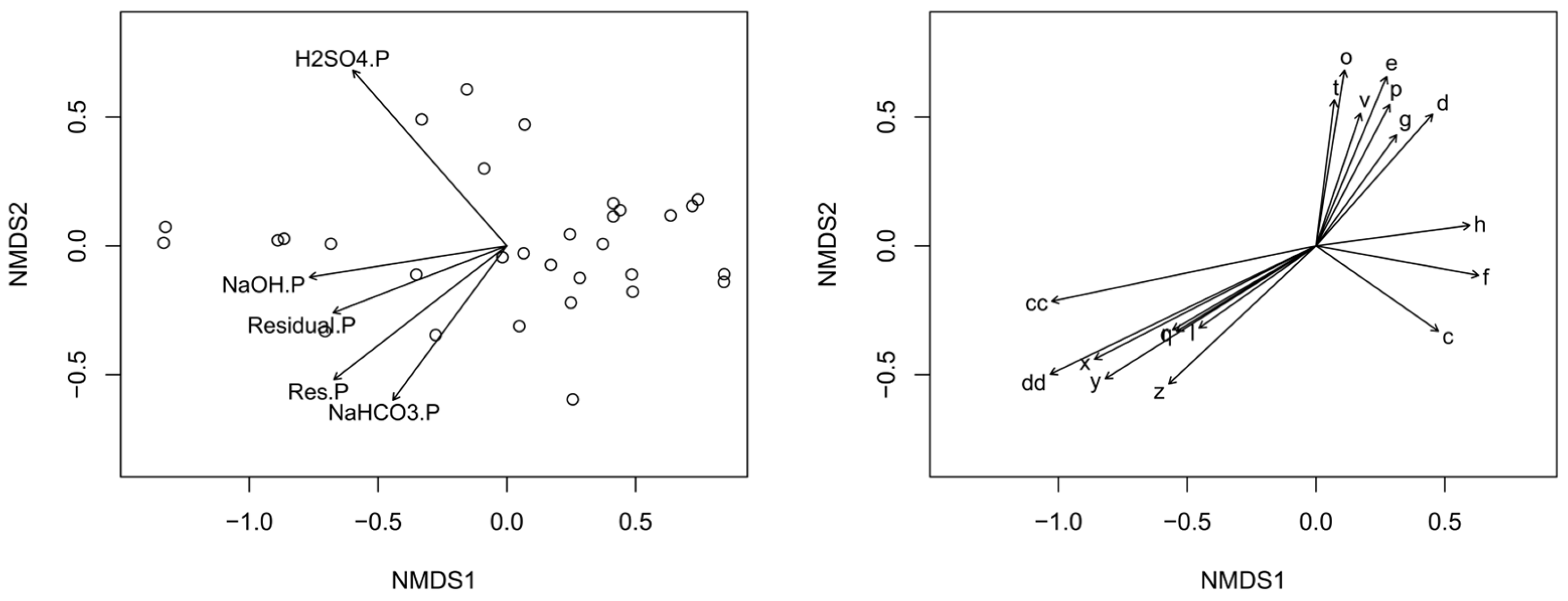
3.2. P Fractionation and Controlling Factors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rowe, H.; Withers, P.J.A.; Baas, P.; Chan, N.I.; Doody, D.; Holiman, J.; Jacobs, B.; Li, H.; MacDonald, G.K.; McDowell, R.; et al. Integrating legacy soil phosphorus into sustainable nutrient management strategies for future food, bioenergy and water security. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2016, 104, 393–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordell, D.; Drangert, J.-O.J.O.; White, S. The story of phosphorus: Global food security and food for thought. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2009, 19, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V. Eutrophication of freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems a global problem. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2003, 10, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mccrackin, M.L.; Muller-Karulis, B.; Gustafsson, B.G.; Howarth, R.W.; Humborg, C.; Svanbäck, A.; Swaney, D.P. A Century of Legacy Phosphorus Dynamics in a Large Drainage Basin. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2018, 32, 1107–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekholm, P.; Rankinen, K.; Rita, H.; Räike, A.; Sjöblom, H.; Raateland, A.; Vesikko, L.; Cano Bernal, J.E.; Taskinen, A. Phosphorus and nitrogen fluxes carried by 21 Finnish agricultural rivers in 1985–2006. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, S.; Kahle, P.; Lennartz, B. Spatio-temporal analysis of phosphorus concentrations in a North-Eastern German lowland watershed. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 15, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.N.; Jarvie, H.P.; Buda, A.; May, L.; Spears, B.; Kleinman, P. Phosphorus Legacy: Overcoming the Effects of Past Management Practices to Mitigate Future Water Quality Impairment. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 1308–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haygarth, P.M.; Jarvie, H.P.; Powers, S.M.; Sharpley, A.N.; Elser, J.J.; Shen, J.; Peterson, H.M.; Chan, N.I.; Howden, N.J.K.; Burt, T.; et al. Sustainable phosphorus management and the need for a long-term perspective: The legacy hypothesis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8417–8419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.M.; Bruulsema, T.W.; Burt, T.P.; Chan, N.I.; Elser, J.J.; Haygarth, P.M.; Howden, N.J.K.; Jarvie, H.P.; Lyu, Y.; Peterson, H.M.; et al. Long-term accumulation and transport of anthropogenic phosphorus in three river basins. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvie, H.P.; Sharpley, A.N.; Brahana, V.; Simmons, T.; Price, A.; Neal, C.; Lawlor, A.J.; Sleep, D.; Thacker, S.; Haggard, B.E. Phosphorus retention and remobilization along hydrological pathways in karst terrain. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4860–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannergård, E.E.; Agstam-Norlin, O.; Huser, B.J.; Sandström, S.; Rakovic, J.; Futter, M.N. New Insights Into Legacy Phosphorus From Fractionation of Streambed Sediment. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2020, 125, e2020JG005763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; He, Y.; Kirumba, G.; Hassan, Y.; Li, J. Phosphorus fractions and phosphate sorption-release characteristics of the sediment in the Yangtze River estuary reservoir. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 55, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temporetti, P.; Beamud, G.; Nichela, D.; Baffico, G.; Pedrozo, F. The effect of pH on phosphorus sorbed from sediments in a river with a natural pH gradient. Chemosphere 2019, 228, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydin, E. Potentially mobile phosphorus in Lake Erken sediment. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2037–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, E.T.; Schlesinger, W.H. A comparison of fractionation methods for forms of phosphorus in soils. Biogeochemistry 1999, 47, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauke, S.L.; Landl, M.; Koch, M.; Hofmann, D.; Nagel, K.A.; Siebers, N.; Schnepf, A.; Amelung, W. Macropore effects on phosphorus acquisition by wheat roots—A rhizotron study. Plant Soil 2017, 416, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prüter, J.; Leipe, T.; Michalik, D.; Klysubun, W.; Leinweber, P. Phosphorus speciation in sediments from the Baltic Sea, evaluated by a multi-method approach. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 1676–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, M.J.; Stewart, J.W.B.; Chauhan, B.S. Changes in Inorganic and Organic Soil Phosphorus Fractions Induced by Cultivation Practices and by Laboratory Incubations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1982, 46, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bol, R.; Julich, D.; Brödlin, D.; Siemens, J.; Kaiser, K.; Dippold, M.A.; Spielvogel, S.; Zilla, T.; Mewes, D.; von Blanckenburg, F.; et al. Dissolved and colloidal phosphorus fluxes in forest ecosystems—An almost blind spot in ecosystem research. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2016, 179, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauke, S.L.; von Sperber, C.; Siebers, N.; Tamburini, F.; Amelung, W. Biopore effects on phosphorus biogeochemistry in subsoils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 111, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinweber, P. Phosphorus fractions in soils from an area with high density of livestock population. Z. Pflanz. Bodenkd. 1996, 159, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Yost, R.S.; Hue, N.V.; Evensen, C.I.; Silva, J.A. Changes in Phosphorus Fractions in Soils under Intensive Plant Growth. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.N.; Mcdowell, R.W.; Kleinman, P.J.A. Amounts, Forms, and Solubility of Phosphorus in Soils Receiving Manure. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fytianos, K.; Kotzakioti, A. Sequential fractionation of phosphorus in lake sediments of Northern Greece. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2005, 100, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, L.; Jarosch, K.A.; Schneider, T.; Grosjean, M. Phosphorus fractions in sediments and their relevance for historical lake eutrophication in the Ponte Tresa basin (Lake Lugano, Switzerland) since 1959. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, C.; Heathwaite, A.L. Nutrient mobility within river basins: A European perspective. J. Hydrol. 2005, 304, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selig, U.; Schlungbaum, G. Longitudinal patterns of phosphorus and phosphorus binding in sediment of a lowland lake-river system. Hydrobiologia 2002, 472, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, F.; Küchler, A.; Mehl, D.; Hoffmann, T.G. Ermittlung von Art und Intensität Künstlicher Entwässerung von Landwirtschaftlichen Nutzflächen in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. In Aktuelle Probleme im Wasserhaushalt von Nordostdeutschland: Trends, Ursachen, Lösungen; Scientific Technical Report 10/10; Deutsches GeoForschungsZentrum: Potsdam, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, S.; Bauwe, A.; Lennartz, B. Application of the SWAT Model for a Tile-Drained Lowland Catchment in North-Eastern Germany on Subbasin Scale. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 791–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitschofsky, F.; Nausch, M. Spatial and seasonal variations in phosphorus speciation along a river in a lowland catchment (Warnow, Germany). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, V.; Degen, B.; Kasper, D. Erarbeitung Einer Methodik zur Fließgewässerstrukturgütekartierung in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Endbericht. Landesamt für Umwelt, Naturschutz und Geologie Mecklenburg-Vorpommern: Güstrow, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tiessen, H.; Moir, J.O. Characterization of available P by sequential extraction. In Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis; Carter, M.R., Ed.; Canadian Society of Soil Science: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; pp. 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Do Nascimento, C.A.C.; Pagliari, P.H.; Schmitt, D.; He, Z.; Waldrip, H. Phosphorus concentrations in sequentially fractionated soil samples as affected by digestion methods. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruttenberg, K.C. Development of a sequential extraction method for different forms of phosphorus in marine sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 1460–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copernicus. CLC 2018—Copernicus Land Monitoring Service. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european/corine-land-cover/clc2018 (accessed on 26 August 2022).
- R Core Development Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Development Team: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kassambara, A.; Mundt, F. Factoextra: Extract and Visualize the Results of Multivariate Data Analyses 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=factoextra (accessed on 9 September 2021).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.B.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Simpson, G.L.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; et al. vegan: Community Ecology Package 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 9 September 2021).
- Prüter, J.; McLaren, T.I.; Pätzig, M.; Hu, Y.; Leinweber, P. Phosphorus Speciation Along a Soil to Kettle Hole Transect: Sequential P Fractionation, P Xanes, and 31p Nmr Spectroscopy. SSRN Electron. J. 2022, 429, 116215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prüter, J.; Schumann, R.; Klysubun, W.; Leinweber, P. Characterization of Phosphate Compounds along a Catena from Arable and Wetland Soil to Sediments in a Baltic Sea lagoon. Soil Syst. 2023, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, K.; Shaheen, S.M.; Hu, Y.; Gros, P.; Heilmann, E.; Morshedizad, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.L.; Rinklebe, J.; Leinweber, P. Speciation and sorption of phosphorus in agricultural soil profiles of redoximorphic character. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 3231–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, P.N.; Walling, D.E. The phosphorus content of fluvial sediment in rural and industrialized river basins. Water Res. 2002, 36, 685–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audette, Y.; O’Halloran, I.P.; Nowell, P.M.; Dyer, R.; Kelly, R.; Voroney, R.P. Speciation of Phosphorus from Agricultural Muck Soils to Stream and Lake Sediments. J. Environ. Qual. 2018, 47, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SanClements, M.D.; Fernandez, I.J.; Norton, S.A. Soil and sediment phosphorus fractions in a forested watershed at Acadia National Park, ME, USA. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 258, 2318–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiecher, T.; Schenato, R.B.; Santanna, M.A.; Caner, L.; dos Santos, D.R. Phosphorus forms in sediments as indicators of anthropic pressures in an agricultural catchment in Southern Brazil. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2017, 41, e0160569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhao, H.; Deng, L.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Dong, S. The phosphorus speciations in the sediments up- and down-stream of cascade dams along the middle Lancang River. Chemosphere 2015, 120, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persaud, D.; Jaagumagi, R.; Hayton, A. Guidelines for the Protection and Management of Aquatic Sediment Quality in Ontario Ministry of Environment and Energy; Ontario Ministry of the Environment: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Katsaounos, C.Z.; Giokas, D.L.; Leonardos, I.D.; Karayannis, M.I. Speciation of phosphorus fractionation in river sediments by explanatory data analysis. Water Res. 2007, 41, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemeyer, B.; Kahle, P.; Lennartz, B. Phosphorus losses from an artificially drained rural lowland catchment in North-Eastern Germany. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandström, S.; Futter, M.N.; Kyllmar, K.; Bishop, K.; O’Connell, D.W.; Djodjic, F. Particulate phosphorus and suspended solids losses from small agricultural catchments: Links to stream and catchment characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darch, T.; Blackwell, M.S.A.; Hawkins, J.M.B.; Haygarth, P.M.; Chadwick, D. A meta-analysis of organic and inorganic phosphorus in organic fertilizers, soils, and water: Implications for water quality. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 2172–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, S.; Kahle, P.; Lennartz, B. Biogas Digestate Application Modifies Solute Transport Conditions in Soils and Increases the Release of Phosphorus. Vadose Zone J. 2019, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacha, K.M.; Papanicolaou, A.N.T.; Abban, B.K.; Wilson, C.G.; Giannopoulos, C.P.; Hou, T.; Filley, T.R.; Hatfield, J.L. The impact of tillage row orientation on physical and chemical sediment enrichment. Agrosyst. Geosci. Environ. 2020, 3, e20007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, D.; Kahle, P.; Baum, C. Loss of soil phosphorus by tile drains during storm events. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 167, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, G.A.; Purvis, R.A.; Penn, C.J. Streambanks: A net source of sediment and phosphorus to streams and rivers. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 602–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, T.N.; Christensen, V.G.; Richardson, W.B.; Frey, J.W.; Gellis, A.C.; Kieta, K.A.; Fitzpatrick, F.A. Stream Sediment Sources in Midwest Agricultural Basins with Land Retirement along Channel. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43, 1624–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Cheng, P.D.; Zhong, B.C.; Wang, D.Z. Total phosphorus release from bottom sediments in flowing water. J. Hydrodyn. 2012, 24, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Batalla, R.J.; Birgand, F.; Esteves, M.; Gentile, F.; Harrington, J.R.; Navratil, O.; López-Tarazón, J.A.; Vericat, D. Influences of catchment and river channel characteristics on the magnitude and dynamics of storage and re-suspension of fine sediments in river beds. Water 2019, 11, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, A.; Exner-Kittridge, M.; Strauss, P.; Blöschl, G. Re-suspension of bed sediment in a small stream – Results from two flushing experiments. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; He, J.; Luo, X.; Zheng, Z. Phosphorus mobility among sediments, water and cyanobacteria enhanced by cyanobacteria blooms in eutrophic Lake Dianchi. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negassa, W.; Leinweber, P. How does the hedley sequential phosphorus fractionation reflect impacts of land use and management on soil phosphorus: A review. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2009, 172, 305–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bol, R.; Gruau, G.; Mellander, P.E.; Dupas, R.; Bechmann, M.; Skarbøvik, E.; Bieroza, M.; Djodjic, F.; Glendell, M.; Jordan, P.; et al. Challenges of reducing phosphorus based water eutrophication in the agricultural landscapes of Northwest Europe. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, E.; Baetens, E.; Verbeeck, M.; Nawara, S.; Diels, J.; Verdievel, M.; Peeters, B.; De Cooman, W.; Baken, S. Internal Loading and Redox Cycling of Sediment Iron Explain Reactive Phosphorus Concentrations in Lowland Rivers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2584–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, W.; Didenko, J.; Uri, E.; Eldar, D. Spatial and temporal variability of particulate phosphorus fractions in seston and sediments of Lake Kinneret under changing loading scenario. In The Interactions between Sediments and Water; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 223–229. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Livi, K.J.T.; Arenberg, M.R.; Chen, A.; Chen, K.Y.; Gentry, L.; Li, Z.; Xu, S.; Arai, Y. High flow event induced the subsurface transport of particulate phosphorus and its speciation in agricultural tile drainage system. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, S.-C.; Whalen, J.K.; Michaud, A.R. Bioavailable Phosphorus in Fine-Sized Sediments Transported from Agricultural Fields. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


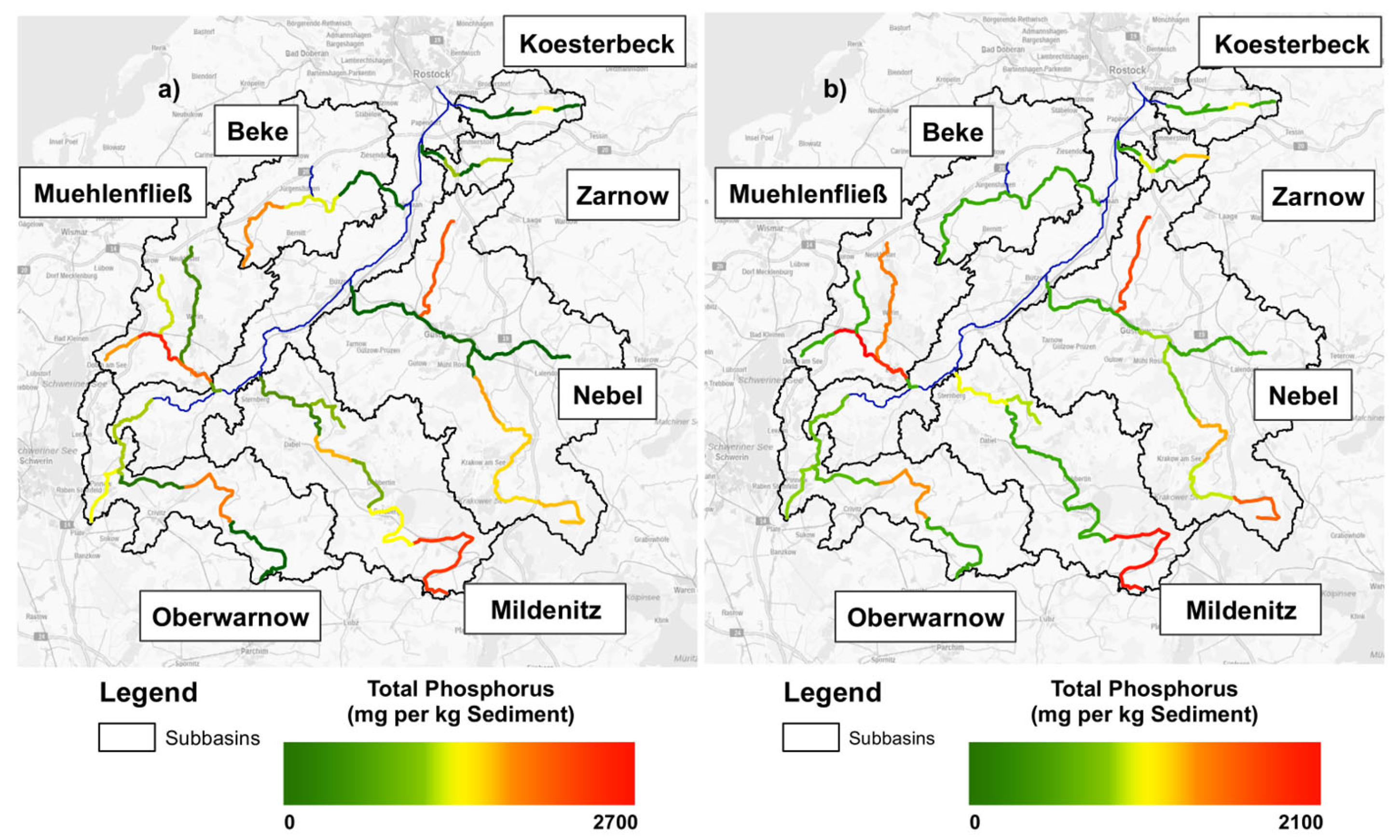
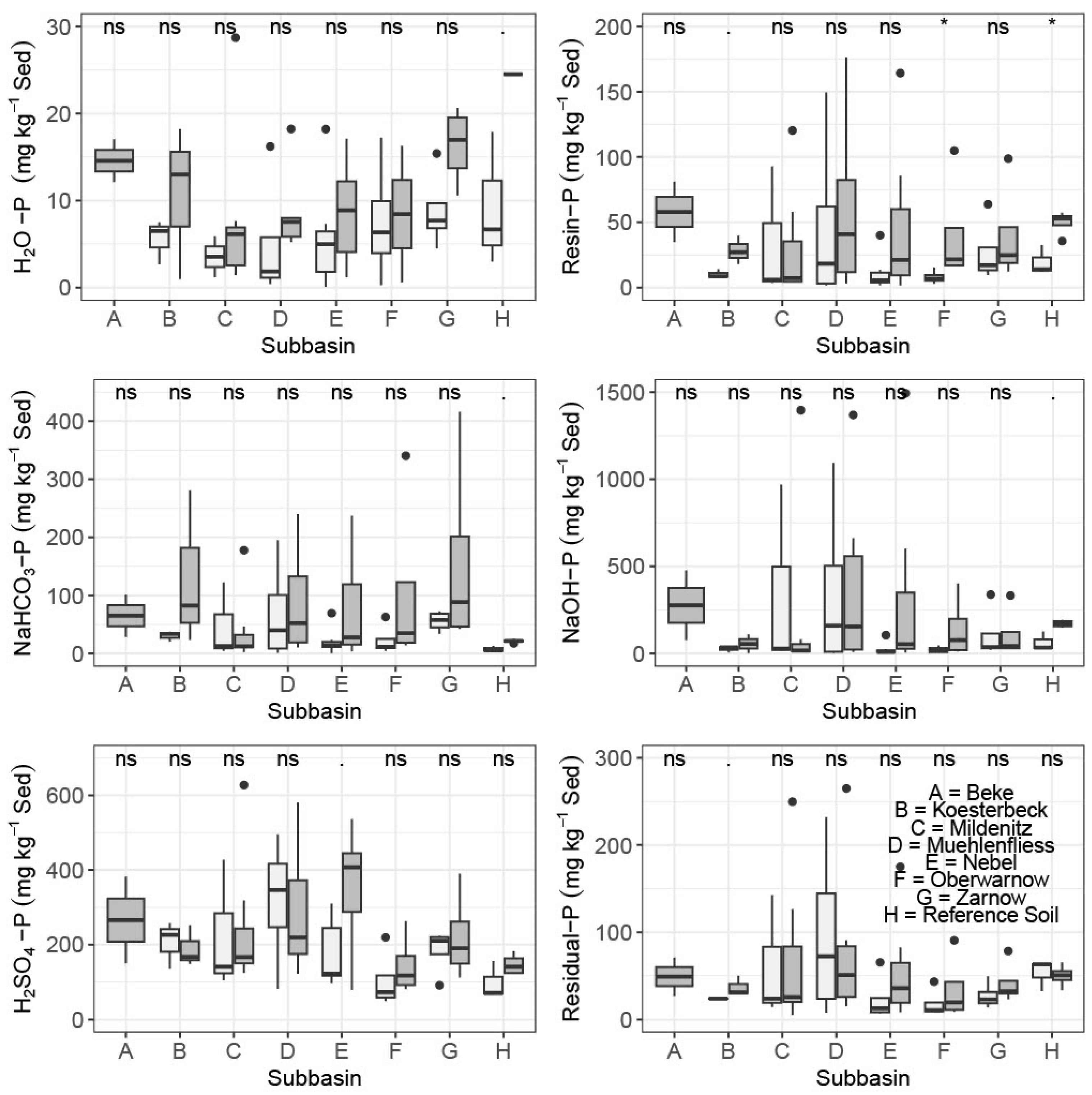
| H2O-P | NaHCO3-P | Resin-P | NaOH-P | H2SO4-P | Residual P | Total P | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subbasin | M ± sd | Range | M ± sd | Range | M ± sd | Range | M ± sd | Range | M ± sd | Range | M ± sd | Range | M ± sd | Range |
| Beke | 15 ± 3 | 12–17 | 65 ± 51 | 28–101 | 58 ± 32 | 35–81 | 276 ± 283 | 76–476 | 266 ± 163 | 150–382 | 49 ± 30 | 27–71 | 728 ± 558 | 333–1123 |
| Koesterbeck | 11 ± 9 | 1–18 | 129 ± 134 | 23–281 | 28 ± 11 | 18–40 | 55 ± 52 | 3–109 | 189 ± 54 | 149–251 | 37 ± 11 | 30–50 | 449 ± 147 | 350–619 |
| Mildenitz | 8 ± 9 | 1–29 | 40 ± 63 | 3–178 | 30 ± 44 | 4–120 | 222 ± 518 | 7–1397 | 244 ± 181 | 124–628 | 70 ± 88 | 5–250 | 613 ± 874 | 161–2578 |
| Muehlenfliess | 9 ± 5 | 5–18 | 87 ± 91 | 10–240 | 60 ± 65 | 3–176 | 393 ± 538 | 9–1369 | 287 ± 175 | 122–580 | 82 ± 93 | 15–265 | 918 ± 964 | 164–2648 |
| Nebel | 9 ± 19 | 1–17 | 77 ± 87 | 4–237 | 47 ± 59 | 2–164 | 329 ± 555 | 5–1493 | 355 ± 158 | 79–536 | 55 ± 58 | 9–175 | 872 ± 790 | 155–2429 |
| Oberwarnow | 23 ± 19 | 1–46 | 106 ± 157 | 14–341 | 41 ± 42 | 17–105 | 142 ± 181 | 12–402 | 144 ± 82 | 81–263 | 35 ± 38 | 9–91 | 491 ± 467 | 158–1182 |
| Zarnow | 16 ± 5 | 11–21 | 159 ± 176 | 42–416 | 40 ± 39 | 12–99 | 111 ± 147 | 29–333 | 220 ± 121 | 112–390 | 42 ± 24 | 23–78 | 589 ± 506 | 257–1334 |
| Whole watershed | 12 ± 9 | 1–46 | 88 ± 105 | 3–416 | 43 ± 45 | 2–176 | 241 ± 401 | 3–1493 | 257 ± 150 | 79–628 | 57 ± 61 | 5–265 | 698 ± 676 | 155–2648 |
| Reference topsoils | 31 ± 18 | 24–34 | 21 ± 23 | 17–24 | 50 ± 24 | 36–57 | 171 ± 54 | 151–193 | 147 ± 56 | 123–182 | 50 ± 23 | 34–65 | 469 ± 198 | 417–515 |
| Reference subsoils | 9 ± 8 | 3–18 | 7 ± 5 | 4–13 | 20 ± 14 | 12–32 | 63 ± 32 | 29–125 | 99 ± 28 | 69–156 | 53 ± 12 | 33–63 | 250 ± 123 | 149–407 |
| Beke | Koesterbeck | Mildenitz | Muehlenfliess | Nebel | Warnow | Zarnow | Whole Watershed | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | sd | Mean | sd | Mean | sd | Mean | sd | Mean | sd | Mean | sd | Mean | sd | Mean | sd | |
| Fe (mg kg−1) | 0.7 | 0.4 | 1.4 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
| Ca (mg kg−1) | 1.2 | 0.8 | 2.1 | 1.8 | 3.6 | 4.0 | 3.7 | 2.0 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.9 | 2.3 | 1.9 | 1.6 | 2.5 | 2.4 |
| Al (mg kg−1) | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| C (%) | 0.6 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 1.4 | 4.6 | 7.7 | 6.2 | 8.0 | 3.5 | 5.5 | 3.3 | 5.8 | 1.7 | 1.2 | 3.7 | 5.7 |
| N (%) | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| S (%) | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| C:N ratio (1) | 9.8 | 5.3 | 26.3 | 17.0 | 19.8 | 11.5 | 12.6 | 2.2 | 15.0 | 13.2 | 13.2 | 9.9 | 12.9 | 6.9 | 15.8 | 10.6 |
| openwater (km2) | 1.2 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 17.0 | 12.8 | 3.4 | 3.4 | 15.0 | 11.8 | 3.9 | 4.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | - | - |
| agriculture (km2) | 46.4 | 13.2 | 27.5 | 32.5 | 139.9 | 107.3 | 63.6 | 53.6 | 112.6 | 97.3 | 172.9 | 74.9 | 29.9 | 15.2 | - | - |
| forest (km2) | 8.5 | 1.5 | 4.2 | 3.3 | 75.3 | 57.9 | 23.5 | 19.3 | 71.5 | 51.5 | 44.1 | 30.2 | 3.4 | 1.2 | - | - |
| drainage_area (km2) | 39.4 | 19.0 | 34.6 | 34.1 | 112.9 | 55.7 | 48.7 | 54.1 | 49.6 | 54.7 | 76.2 | 49.4 | 46.4 | 19.1 | - | - |
| area (km2) | 57.1 | - | 34.1 | - | 241.0 | - | 94.2 | - | 206.8 | - | 228.2 | - | 34.6 | - | - | - |
| water_level (m) | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| SO42− (mg L−1) | 108.1 | 23.8 | 65.6 | 16.1 | 87.1 | 51.3 | 77.2 | 39.8 | 101.1 | 81.8 | 95.1 | 35.6 | 160.2 | 54.4 | 97.2 | 54.4 |
| NO3− (mg L−1) | 5.8 | 1.7 | 6.9 | 5.2 | 4.5 | 7.6 | 2.8 | 2.2 | 6.1 | 9.8 | 2.6 | 2.0 | 10.7 | 4.7 | 5.2 | 6.1 |
| Cl− (mg L−1) | 57.0 | 27.8 | 47.5 | 4.9 | 29.0 | 2.7 | 150.1 | 255.0 | 40.3 | 12.3 | 30.8 | 1.0 | 36.5 | 12.3 | 57.6 | 110.7 |
| velocity (m s−1) | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| oxygen (mg L−1) | 9.0 | 0.1 | 4.1 | 4.8 | 8.9 | 1.7 | 6.6 | 2.9 | 6.8 | 2.2 | 6.0 | 2.9 | 7.2 | 1.5 | 7.0 | 2.7 |
| pH (1) | 7.6 | 0.0 | 7.1 | 0.4 | 7.7 | 0.3 | 7.3 | 0.2 | 7.3 | 0.3 | 7.3 | 0.2 | 7.3 | 0.1 | 7.4 | 0.3 |
| conductivity (µS cm−1) | 629.1 | 32.0 | 563.6 | 82.5 | 419.0 | 110.9 | 744.7 | 676.6 | 556.6 | 308.4 | 470.9 | 91.7 | 656.3 | 123.2 | 565.5 | 323.6 |
| redox (mV) | 33.5 | 27.3 | −4.7 | 128.9 | 63.3 | 50.4 | 39.6 | 46.8 | 24.8 | 39.1 | 58.7 | 53.0 | 51.0 | 24.7 | 41.3 | 54.0 |
| PO43− (mg L−1) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| TP (mg L−1) | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| P from WWT (kg a−1) | 116.0 | 0.0 | 48.3 | 83.7 | 127.6 | 157.1 | 49.2 | 105.5 | 319.3 | 98.7 | 522.4 | 664.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 188.6 | 305.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koch, S.; Rosewig, E.I.; Lennartz, B. Legacy Phosphorus in Sediments of Lowland Waterways. Environments 2023, 10, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10030043
Koch S, Rosewig EI, Lennartz B. Legacy Phosphorus in Sediments of Lowland Waterways. Environments. 2023; 10(3):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10030043
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoch, Stefan, Ellen Iva Rosewig, and Bernd Lennartz. 2023. "Legacy Phosphorus in Sediments of Lowland Waterways" Environments 10, no. 3: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10030043
APA StyleKoch, S., Rosewig, E. I., & Lennartz, B. (2023). Legacy Phosphorus in Sediments of Lowland Waterways. Environments, 10(3), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10030043