Abstract
Drinking water, in addition to the best-known chemical and biological agents, contains radionuclides of both natural and artificial origin, which can contribute significantly to the overall effective dose received by the population. The Italian Decree Law 28/2016, implementing the 2013/51/EURATOM Directive, establishes the activities for risk management and the parameter values for different radionuclide activity concentrations. In addition to the institutions involved, the National Inspectorate for Nuclear Safety and Radiation Protection (ISIN) annually publishes monitoring reports of environmental radioactivity in Italy, including radioactivity in drinking water. The purpose of the study was to integrate ISIN reports with 2018–2020 data by collecting measurements performed by institutional laboratories to obtain more complete information and adding, for the Campania region, some data not yet published. This new updated report was not significantly different from ISIN’s one, meaning that those publications are nevertheless extremely representative of the radioactivity in Italian drinking water. However, the study allowed us to obtain more detailed data, including measurements not considered in ISIN reports, for instance, radon-222 activity concentrations. This may be of great usefulness for all radiation protection stakeholders in order to ensure environmental protection, pollution prevention, and population safety.
1. Introduction
Radionuclides can be found in air, water, soil, and living organisms as a consequence of natural and artificial contamination [1]. However, sources of natural origin mostly contribute to environmental radioactivity. In particular, radioisotopes in soil and rocks are those from uranium-238 (U-238) and thorium-232 (Th-232) chains, and potassium-40 (K-40). These nuclides, together with any artificial radionuclides due to accidental contamination [2], are also released into groundwater through erosion and dissolution processes [3,4]. Given the great heterogeneity of radionuclides in drinking water, radiological risk management is done by performing measurements of gross alpha and gross beta activity concentrations [5,6,7,8]. Moreover, particular attention is also given to the activity concentrations of radon (Rn-222) and tritium (H-3) [9].
The impact on human health is due to stochastic events peculiar to carcinogenic substances; therefore, there is no dose-response relationship, but the onset of the effect can occur for any dose, with severity not dependent on the dose and being random in the exposed population. However, as the dose increases, the probability of the effect occurring increases, and the latency period can also be very long. For this reason, the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) recommends adopting a linear no-treshold-LNT model [10]. Paying particular attention to the radiometric characterization of drinking water, even the measurement and monitoring of radionuclides required by law have a biological impact, particularly concerning the internal exposure of the representative individual.
Rn-222, originating from the U-238 series, is dissolved in water given its physio-chemical characteristics [11]. The biological hazard associated with radon exposure is related to inhalation and ingestion since the alpha particles generated by the decay of radon and its daughters can damage the cells of the bronchioles and intestinal tract [12,13,14,15,16]. Despite these two different internal exposure scenarios, it has been concluded that the most important mechanism of exposure to Rn-222 in drinking water is inhalation [17] because of the propriety of the gas to exhale from the water itself. H-3 is a radioisotope of hydrogen with a mainly cosmogenic origin formed in the high atmosphere that reaches the ground with rain [18,19]. A small fraction is H-3 of artificial origin, produced by human activities such as research and nuclear power plants. Even if its radiotoxicity is low compared to other radionuclides, there is an interest in the biological consequences of low-dose H-3 exposures since it can occur in three different forms: tritium water, tritium gas, and bounded organic molecules, each with a different contribution to tissue irradiation because of different distribution modes inside the organism [20,21]. However, given the few data available in literature regarding the risk correlated with tritium exposure, it is hard to assess the related biological effects [22,23].
In this complex framework, it appears essential to regulate and monitor radioactivity in drinking water in order to ensure radiological safety. Despite the origin of radioactivity, the intake of radionuclides by drinking water is considered a planned exposure situation rather than a source of environmental background radiation [24,25]. Globally, the World Health Organization (WHO) [26] and the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) [10] advise an Individual Dose Criterion (IDC) of 0.1 mSv/year as an effective dose limit, a value considered sufficiently low to pose minimal risk and not lead to any detrimental health consequences compared to the total exposure to environmental radioactivity. In order not to exceed the IDC of 0.1 mSv/year, the WHO recommends screening levels of 0.5 Bq/L and 1 Bq/L for gross alpha and beta activities, respectively [27]. If the gross beta activity is higher than 1 Bq/L, the K-40′s contribution is evaluated, and the residual beta activity is calculated by subtraction. The result of this additional assessment might indicate that no action is needed, or it may suggest that further evaluation is necessary before the implementation of measures to decrease the dose. For low-energy beta emitters, such as H-3, no monitoring guidelines are given. Even about Rn-222, WHO does not provide instructions on radiological risk management related to water ingestion, while it only highlights the need for monitoring the radon concentration in the air and the hazards associated with its inhalation. Consequently, screening levels for radon concentration in drinking water must be based on those currently valid for indoor air activities.
By EURATOM Council Directive n°51 of 2013 [28], the European Union adopted a parameter value, i.e., screening level, of 100 Bq/L for Rn-222 and, accordingly, for H-3 too, with an Indicative Dose (ID) of 0.1 mSv/year, which takes into account the annual effective dose from ingestion resulting from all natural and artificial nuclides but H-3, K-40, and Rn-222 [29]. Furthermore, compared to WHO, the European Commission recommends a more severe parameter value for gross alpha activity and the same for gross beta activity. These are, in fact, set to 0.1 and 1.0 Bq/L respectively. In Italy, the legislative framework that regulates the radioactivity in drinking water is given by Decree Law n°28 of 2016 [30], which implemented the 51/2013/EURATOM Directive [28], lowering the screening level for gross beta activity to 0.5 Bq/L. If the measured gross alpha and beta activity concentrations are lower than their parameter values, no further actions are required since ID < 0.1 mSv. In case one of these two parameter values is exceeded, it is required to determine the activity concentration of specific nuclides to calculate the ID, which is evaluated assuming an annual water intake of 730 L with Equation (1):
with n being the number of radionuclides, while and are the measured and derived (tabulated) activity concentrations for the i-th nuclide, respectively. If ID < 0.1 mSv, no further actions are required. In cases where ID > 0.1 mSv, corrective actions are required in order to decrease the activity concentration and make them in compliance with the law. The whole control program, including risk management, is carried out by the Ministry of Health in collaboration with the Istituto Superiore di Sanità (ISS), which, through the measurement and control activities of the territorial Regional Agencies for Environmental Protection (ARPAs) and Autonomous Provinces Agencies for Environmental Protection (APPAs), can check compliance with the provisions of the law and apply any activities for public health protection.
Furthermore, in addition to the provisions of current legislation, the National Inspectorate for Nuclear Safety and Radiation Protection (ISIN), for each annual campaign of monitoring, publishes a report summarizing all the collected information and measured values about environmental radioactivity, including drinking water. Data are presented cohesively, but measurements are performed independently by 19 ARPAs, 2 APPAs, and 10 Experimental Zooprophylactic Institutes (IIZZSSs). However, published reports do not always include data regarding all 20 Italian regions, especially for radionuclides in drinking water, where the measurements are typically inhomogeneous and partially lacking. In addition, ISIN does not provide any information on Rn-222 activity concentrations in drinking water but only gross alpha, gross beta, and H-3 activity concentrations. The purpose of this work is to implement and integrate the latest reports published by ISIN by adding, whenever available, lacking data from missing regions provided by institutional laboratories (IL) to obtain a more complete outline of radioactivity in Italian drinking water.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Institutional Data Collection
Data published by ISIN about environmental radioactivity monitoring in Italy were considered. The reports are freely available online on the official website (www.isinucleare.it (accessed on 19 August 2023). To date, these reports contain measurements performed in 2018 [31], 2019 [32], and 2020 [33]. In each of these reports, the average of measured values of gross alpha, gross beta, and H-3 activity concentrations in drinking water performed by individual regions is presented. In these documents, the total number of measurements, including those with a value lower than the Minimum Detectable Activity (MDA), is reported. Activity concentration values from missing regions were added by searching for official data published independently by individual ARPAs and APPAs. By accessing the publication section for each official ARPA/APPA’s website, data over radionuclides in drinking water were sorted, whenever available, according to:
- Type of parameter (gross alpha, gross beta, H-3, Rn-222, and other radioisotope activity concentrations);
- Measurement year;
- Type of data (average activity concentration values, total number of measurements, number of measurements with values lower than the MDA);
- Presentation of data (tabular format, spreadsheet, histogram/graphical, interactive map).
For this work, gross alpha, gross beta, H-3, and Rn-222 activity concentrations measured during the three-year period 2018–2020 were considered. Given a specific parameter, if the average activity concentration values were available, all types of data were collected; otherwise, they were excluded. Moreover, some of the ARPAs and APPAs also give a description of the methodology used to perform the measurements, along with the provided data.
For the Campania region, measurements carried out in a UNI EN ISO 9001:2015 laboratory [34] by La Verde et al. [35,36,37] during the years 2018 and 2019 were considered. For the year 2020, given the lack of data, measurements performed by the same authors with the same methodology were included despite not being published. Details on materials and methods for gross alpha, gross beta, H-3, and Rn-222 activity concentration measurements in Campania are given in Section 2.2.
After all the data had been collected, weighted average activity concentration values were calculated, considering the total number of measurements for each Italian macro-area. According to ISIN reports, the three macro-areas are defined as follows:
- (a)
- North: Emilia-Romagna, Friuli-Venezia Giulia, Liguria, Lombardy, Piedmont, Trentino-Alto Adige, Aosta Valley, and Veneto.
- (b)
- Center: Lazio, the Marches, Tuscany, Umbria, and Sardinia.
- (c)
- South: Abruzzo, Basilicata, Calabria, Campania, Molise, Apulia, and Sicily.
2.2. Sampling and Radionuclide Activity Concentration Measurement in Campania
The same methodology described in the work by La Verde et al. [35] has been used to perform measurements in 2020 in Campania.
2.2.1. Sample Preparation
During 2020, a total of 13 samples were collected from sites (dwells) distributed in three water subsystems in the Campania region [35]. Additionally, 7 more samples were collected only for Rn-222 measurements from the same sampling points. Sample preparation was performed according to standard techniques and procedures [38,39,40], as summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Procedures and techniques used to perform measurements of gross alpha, gross beta, H-3, and Rn-222 activity concentrations in Campania. The calculated detection limits for each parameter are lower or equal to those required by Decree Law 28/2016 [30].
2.2.2. Activity Concentration Measurements
For details on the instruments and methods used to perform the measurements, refer to La Verde et al. [35]. Some specifications are as follows: 1. For gross alpha activity concentration Aα measurements, the Ortec® Alpha Duo spectrometer (Peschiera Borromeo, Milan, Italy) and the detector ULTRA-AS, with an efficiency of 0.0332, were used. For gross beta activity concentration Aβ measurements, the proportional counter Berthold Technologies Umo LB 123, with an efficiency of 0.105, was used. Both activities were calculated with Equation (2):
where V = 0.05 l is the sample volume and CPSnet is the net counts per second obtained after background count subtraction.
2. For H-3 activity concentration AH-3 measurements, the PerkinElmer® Wallac 1220 Quantulus liquid scintillator was used. After having determined the background counts, ABKG Equation (3) was used to evaluate the net H-3 activity after measuring the activity in the sample AT.
3. For Rn-222 in water activity concentration and measurements, the Electret Ion Chamber (EIC) E-Perm® system was used. Equations (4)–(6) were used for the evaluation:
where is the radon concentration in the air inside the jar; B1 considers the delay period between the collection of the sample and the start of the measurement. B2 is a constant based on the analysis period. B3 is the ratio between the jar and water sample volumes. Vi and Vf are the electret voltages before and after the exposure, respectively. T is the exposure time. Gγ is the background signal due to gamma radiation, and C1 = 0.097, C2 = 1.670, and C3 = 5.742 × 10−4 are constants provided by the instrumentation manufacturer; CF is the calibration factor.
3. Results and Discussions
Among all the 21 ARPAs and APPAs, only 12 of them have published the results of at least one measurement campaign since 2016 (i.e., the year of the Italian Decree Law n°28 [30]). However, among these 12, only 6 met the following criteria for at least one parameter:
- To provide the precise result of average activity concentration for at least one year between 2018 and 2020;
- To provide the total number of measurements;
- Not to be included in any considered ISIN report.
Subsections with summarized data for each parameter will follow. More specifically, the average activity concentration values (A), the total number of measurements performed (N), and the number of measurements with values lower than the MDA (N < MDA) (annex III Table 2 of [30]) will be reported for each parameter, relative to the years 2018, 2019, and 2020. The average activity concentration values for each region and each parameter were computed as the arithmetic mean of measurements performed and published by single ARPA/APPAs, as previously explained; in cases of measures lower than the MDA, the MDA value was considered for the calculation.

Table 2.
Measurements of Gross alpha activity concentrations in Italian drinking water in 2018–2020. “N” indicates the total number of measurements, “N < MDA” indicates the total number of measurements with activity lower than the MDA of 0.04 Bq/L as indicated in annex III, Table 2 of [30], and “A” indicates the average activity concentration values. The sign “-“ indicates that data were already published by ISIN; “na” stands for “not available”; colored in gray are data published by ARPAs indicated in the “Ref.” column that are not included in ISIN reports for a specific year. Data by La Verde et al. [35] for the Campania region are also colored gray. All other values are taken from ISIN reports.
3.1. Gross Alpha Activity Concentration
For gross alpha activity concentrations, data from four regions was added with respect to ISIN reports. Measurements performed in Veneto [41], Tuscany [42], Sardinia [43], and Campania [35] between 2018 and 2020, together with values provided by ISIN for gross alpha activity concentration, are shown in Table 2.
3.2. Gross Beta Activity Concentration
For gross beta activity concentrations, data from three regions was added with respect to ISIN reports. Measurements performed in Tuscany [42], Sardinia [43], and Campania [35] between 2018 and 2020, together with values provided by ISIN for gross beta activity concentration, are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Measurements of Gross beta activity concentrations in Italian drinking water in 2018–2020. “N” indicates the total number of measurements, “N < MDA” indicates the total number of measurements with activity lower than the MDA of 0.2 Bq/L as indicated in annex III, Table 2 of [30], and “A” indicates the average activity concentration values. The sign “-“ indicates that data were already published by ISIN; “na” stands for “not available”; colored in gray are data published by ARPAs indicated in the “Ref.” column that are not included in ISIN reports for a specific year. Data by La Verde et al. [35] for the Campania region are also colored gray. All other values are taken from ISIN reports.
3.3. Tritium Activity Concentration
For H-3 activity concentrations, no data was found from all the ARPAs and APPAs websites; therefore, only measurements performed by La Verde et al. [35] were included for years 2019 and 2020. Table 4 presents all the reported values of H-3 activity concentration in the three years. Given that most measured values are lower than the MDA of 10 Bq/L indicated in annex III, Table 2 of [30], we considered MDA values reported by ISIN.

Table 4.
Measurements of H-3 activity concentrations in Italian drinking water in 2018–2020. “N” indicates the total number of measurements, and “A” indicates the average activity concentration values. The sign “-“ indicates that data were already published by ISIN; “na” stands for “not available”; colored in gray are data published by La Verde et al. [35] for the Campania region. All other values are taken from ISIN reports.
3.4. Radon Activity Concentration
For Rn-222 activity concentrations, data from seven regions were included. Measurements performed in Lombardy [44,45], Veneto [41], Lazio [46], The Marches [47], Tuscany [42], Sardinia [43], and Campania [35] between 2018 and 2020 are shown in Table 5. Note that none of these measurements are reported in any ISIN report. Given that most measured values are lower than the MDA of 10 Bq/L indicated in annex III, Table 2 of [30], we considered MDA values reported by ISIN.

Table 5.
Measurements of Rn-222 activity concentrations in Italian drinking water in 2018–2020. “N” indicates the total number of measurements, and “A” indicates the average activity concentration values. “na” stands for “not available." All data are from ARPAs and La Verde et al. [35], given that Rn-222 activity concentration is not included in ISIN reports.
3.5. Comparisons between ISIN and Institutional Laboratories Data
To perform a comparison between measurements provided by ISIN and institutional laboratories (ARPAs and, for the Campania region, La Verde et al. [35]), the weighted average for each parameter in all three Italian macro-areas was calculated using the total number of measurements as weights. Results are shown in Table 6, which presents data reported in ISIN publications and data obtained by integrating ISIN ones with IL ones (ISIN + IL).

Table 6.
Values of weighted average H-3, gross alpha, gross beta, and Rn-222 activity concentrations in Italian drinking water in 2018–2020 for individual macro-areas. The sign “-“for Rn-222 values in ISIN columns indicates that data is lacking in reports. Institutional laboratories (IL) are ARPAs and La Verde et al. (details on single regions for each Macro-area are listed in Table 2, Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5).
As can be seen from the values in Table 6, integrated values are not significantly different from the ones published by ISIN. This highlights how, despite not including measurements from all the 20 Italian regions, those reports are extremely effective and representative of the radioactivity distribution in drinking water. However, results indicate that small variations are still present, meaning that including more regions, that is, more measurements for each macro-area, allows for more detailed information on parameter values with higher statistics. Furthermore, independent research of official published data allowed us to collect additional information, such as the Rn-222 distribution in Italian drinking water, which was missing in ISIN reports.
Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4 represent data from Table 6 in graphical format. Each figure shows a bar graph of activity concentration for a specific parameter in the three-year period considered (2018–2020) and for each Macro-area.
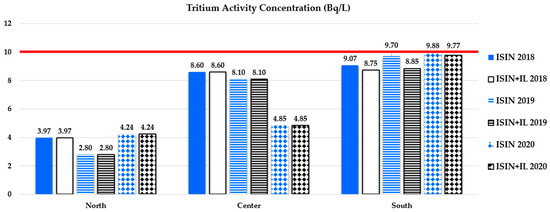
Figure 1.
Bar graph of data from Table 6 on H-3 average activity concentration (Bq/L) in the three years 2018–2020 and for each Italian macro-area. Both ISIN reported and ISIN + IL values are shown. Institutional laboratories (IL) are ARPAs and La Verde et al. (details on single regions for each Macro-area are listed in Table 4). The red line represents the MDA of 10 Bq/L for H-3, as indicated in Italian law [30].
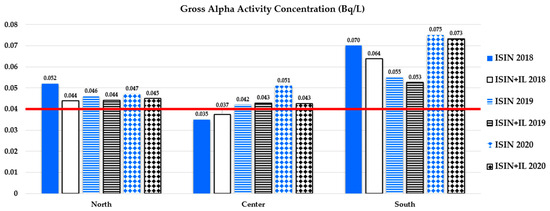
Figure 2.
Bar graph of data from Table 6 on gross alpha average activity concentration (Bq/L) in the three years 2018–2020 and for each Italian macro-area. Both ISIN reported and ISIN + IL values are shown. Institutional laboratories (IL) are ARPAs and La Verde et al. (details on single regions for each Macro-area are listed in Table 2). The red line represents the MDA of 0.04 Bq/L for gross alpha, as indicated in Italian law [30].
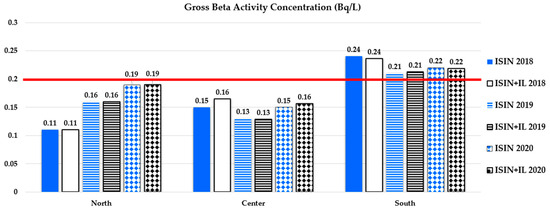
Figure 3.
Bar graph of data from Table 6 on gross beta average activity concentration (Bq/L) in the three years 2018–2020 and for each Italian macro-area. Both ISIN reported and ISIN + IL values are shown. Institutional laboratories (IL) are ARPAs and La Verde et al. (details on single regions for each Macro-area are listed in Table 3). The red line represents the MDA of 0.2 Bq/L for gross beta, as indicated in Italian law [30].
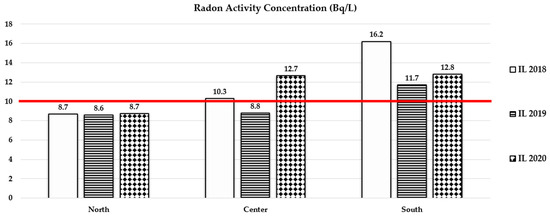
Figure 4.
Bar graph of data from Table 6 on Rn-222 average activity concentration (Bq/L) in the three years 2018–2020 and for each Italian macro-area. Only Institutional laboratories (IL) data from Table 5 since ISIN does not provide any information on these radionuclide measurements in drinking water. The red line represents the MDA of 10 Bq/L for Rn-222, as indicated in Italian law [30].
As can be seen from Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4, the average activity concentrations for each parameter are greater in the south of Italy compared to the center and north, probably due to the peculiar hydrogeological features of the macro-area, which is characterized by volcanic soils and territories with singular lithological traits that strongly influence environmental radioactivity. However, all average activity concentrations are lower than the screening levels/parameter values indicated in the law [30]. Also, the majority of results are even lower than the MDAs given in the law [30]: as shown in Figure 2, the only exception relies on the gross alpha average measurements, which are all above 0.04 Bq/L, excluding data from the center of Italy obtained in 2018.
3.6. Comparisons with Literature Data
Results found in the literature over radioactivity measurements in Italian drinking waters are in good agreement with both ISIN and the upgraded scenarios presented in Table 6. In the Calabria region, gross alpha and gross beta measurements vary in the ranges <0.04–0.16 and <0.20–0.34 Bq/L, respectively [48], in line with values obtained from South Italy. In addition, in the Calabria region, the average reported Rn-222 activity concentration is 24.4 Bq/L (1.6–94.0 Bq/L) [49]. These values are higher compared to the ones reported in this study, but very few data are available about Rn-222. Moreover, they’re always lower than the legislative limit. Still in South Italy, some measurements of Rn-222 are reported to be on average equal to 4.6 Bq/L (1.0–12.7 Bq/L) for Sicily [50] and 17 Bq/L (3.0–45.0 Bq/L) for Campania [51]. In the Umbria region of central Italy, Rn-222 measurements ranged between 5.9 and 65.8 Bq/L [52], still higher than the ones in this study. The same authors also provided data on H-3 activity concentration, with values lower than the calculated MDA of 8.6 Bq/L [52]. Measurements performed in The Marchs are in good agreement with all parameters reported in Table 6: Gross alpha and beta values are reported to be in the ranges <0.018–0.128 Bq/L and <0.042–0.259 Bq/L, respectively [53], while average Rn-222 and H-3 activity concentrations are 6.12 Bq/L (0.69–20.3 Bq/L) and <6.75 Bq/L, respectively [54].
Measurements performed in 13 cities in Lombardy are reported to be, on average, 0.062 Bq/L (<0.008–0.349 Bq/L), 0.144 Bq/L (<0.025–0.273 Bq/L), and <6.8 Bq/L for gross alpha, gross beta, and Radon activity concentrations, respectively [55]. The accordance for gross alpha, gross beta, and H-3 concentrations between the literature and the data reported in this study is fairly good [29]. However, it is advisable to perform a higher number of measurements, especially of Rn-222 activity concentrations in drinking water, given the low number of available statistics.
4. Conclusions
This work integrates official data on radioactivity monitoring in Italian drinking water. For the specific case, measurements elaborated and published by ISIN in annual reports were implemented with values taken from institutional sources and laboratories. Comparisons between ISIN and updated values showed that published reports are representative of the Italian framework on radionuclides in drinking water, although the same reports are incomplete since many regions are not included. In the future, it could be interesting to create a network of information flows in order to merge them into a single document that could be continuously updated to obtain a more detailed distribution of radioactivity in Italian drinking water. Institutional laboratories, for example, could have access to a database and upload data. Given this scenario, an intrinsic limitation of such a network could be the lack of data published by laboratories. The unavailability of measurements, together with a poor description of methodology and other missing information, could make collecting and updating data on radioactivity in drinking water challenging. Nevertheless, the creation of this kind of database would also promote more in-depth investigations for Italian regions with few/no measurements, providing not only for regulatory compliance but also for a more extensive radio protection program.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.M., M.P. and G.L.V.; methodology, F.M., M.P., F.A., M.T., A.G. and G.L.V.; validation, F.M., M.P., F.A., M.T., A.G. and G.L.V.; formal analysis, F.M. and G.L.V.; investigation, F.M., M.P. and G.L.V.; resources, M.P. and M.T.; data curation, F.M. and G.L.V.; writing—original draft preparation, F.M. and G.L.V.; writing—review and editing, F.M., M.P., F.A., M.T., A.G. and G.L.V.; visualization, M.P.; supervision, M.P. and G.L.V.; project administration, M.P. and M.T.; funding acquisition, M.P. and M.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR). RADIATION EFFECTS and SOURCES What Is Radiation? What Does Radiation Do to Us? Where Does Radiation Come from? United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Altıkulaç, A.; Turhan, Ş.; Gümüş, H. The natural and artificial radionuclides in drinking water samples and consequent population doses. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2015, 8, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanovich, M.; Harmon, R.S. Uranium-Series Disequilibrium, 2nd ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Semkow, T.M. Mobilization of thorium, radium and radon radionuclides in ground water by successive alpha-recoils. J. Hydrol. 1998, 205, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semkow, T.M.; Parekh, P.P. Principles of gross alpha and beta radioactivity detection in water. Health Phys. 2001, 81, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonotto, D.M.; Bueno, T.O.; Tessari, B.W.; Silva, A. The natural radioactivity in water by gross alpha and beta measurements. Radiat. Meas. 2009, 44, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobbágy, V.; Wätjen, U.; Meresova, J. Current status of gross alpha/beta activity analysis in water samples: A short overview of methods. J. Radioanal. Nucl. 2010, 286, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.L.; Minh, V.T.; Van Chinh, D.; Thanh, T.T.; Van Tao, C. Simultaneous determination of gross alpha/beta activities in groundwater for ingestion effective dose and its associated public health risk prevention. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Management of Radioactivity in Drinking-Water; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP). The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection; ICRP Publication 103; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, M.; Paschke, A.; Lieberman, E.; Burnett, W.C. Air-water partitioning of 222Rn and its dependence on water temperature and salinity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3905–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-González, M.; Torres-Durán, M.; Barbosa-Lorenzo, R.; Provencio-Pulla, M.; Barros-Dios, J.M.; Ruano-Ravina, A. Radon exposure: A major cause of lung cancer. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2019, 13, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Health Risks from Exposure to Low Levels of Ionizing Radiation (BEIR VII); Committee on the Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiations; Board of Radiation Effects Research; Committee on Life Sciences; National Research Council; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Khursheed, A. Doses to systemic tissues from radon gas. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2000, 88, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford-Brown, D.J. The biokinetics and dosimetry of radon-222 in the human body following ingestion of groundwater. Environ. Geochem. Health 1989, 11, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, G.M.; Smith, T.J. Doses to organs and tissues from radon and its decay products. J. Radiol. Prot. 2002, 22, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR). Chapter III RADON. In Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation. UNSCEAR 1993 Report to the General Assembly with Scientific Annexes; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 1993; Annex A; pp. 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, S.; Momoshima, N. Overview of tritium: Characteristics, sources, and problems. Health Phys. 1993, 65, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairlie, I. The hazards of tritium–revisited. Med. Confl. Surviv. 2008, 24, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyrolle, F.; Ducros, L.; Le Dizès, S.; Beaugelin-Seiller, K.; Charmasson, S.; Boyer, P.; Cossonnet, C. An updated review on tritium in the environment. J. Environ. Radioact. 2018, 181, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingwall, S.; Mills, C.E.; Phan, N.; Taylor, K.; Boreham, D.R. Human health and the biological effects of tritium in drinking water: Prudent policy through science–addressing the ODWAC new recommendation. Dose-Response 2011, 9, 6–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, M.P.; Wakeford, R. Systematic review of epidemiological studies of exposure to tritium. J. Radiol. Prot. 2008, 28, 9–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health Protection Agency (HPA). Report of Independent Advisory Group on Ionising Radiation, Review of Risks from Tritium, Documents of HPA RCE-4; Health Protection Agency (HPA): Oxfordshire, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP). Protection of the Public in Situations of Prolonged Radiation Exposure, 1st ed.; Valentin, J., Ed.; ICRP Publication 82; Ann. ICRP 1999, Annex A; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1999; pp. 78–79. [Google Scholar]
- Joint FAO/IAEA & World Health Organization (WHO). Key Radiation Protection Concepts Relating to Radionuclides in Food and Drinking Water. In Criteria for Radionuclide Activity Concentrations for Food and Drinking Water; IAEA-TECDOC-1788; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2016; pp. 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Radiological aspects. In Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Incorporating the First and Second Addenda; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 219–236. [Google Scholar]
- The Council of the European Union. Council Directive 2013/51/EURATOM of 22 October 2013 Laying Down Requirements for the Protection of the Health of the General Public with Regard to Radioactive Substances in Water Intended for Human Consumption; Official Journal of the European Union, L 296/12, 7.11.2013; European Council: Brussels, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, M.; Suursoo, S.; Martin-Sanchez, N.; Vaasma, T.; Leier, M. Natural radioactivity in European drinking water: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 53, 198–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italian Government. Decreto Legislativo 15 Febbraio 2016, N. 28 Attuazione Della Direttiva 2013/51/Euratom Del Consiglio, Del 22 Ottobre 2013, Che Stabilisce Requisiti per la Tutela Della Salute Della Popolazione Relativamente Alle Sostanze Radioattive Presenti Nelle Acque Destinate Al Consumo Umano; Gazzetta Ufficiale, Serie Generale n.55, 07-03-2016; Italian Parliament: Roma, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ispettorato Nazionale per la Sicurezza Nucleare e la radioprotezione (ISIN). La Sorveglianza Della Radioattività Ambientale in Italia; Rapporto ISIN; Ispettorato Nazionale per la Sicurezza Nucleare e la Radioprotezione: Roma, Italy, 2019; Available online: https://www.isinucleare.it/sites/default/files/contenuto_redazione_isin/rapp_radamb_2019.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2023).
- Ispettorato Nazionale per la Sicurezza Nucleare e la Radioprotezione (ISIN). La Sorveglianza Della Radioattività Ambientale in Italia; Rapporto 2/2021; Ispettorato Nazionale per la Sicurezza Nucleare e la Radioprotezione: Roma, Italy, 2021; Available online: https://www.isinucleare.it/sites/default/files/contenuto_redazione_isin/la_sorveglianza_della_radioattivita_ambientale_5-2021.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2023).
- Ispettorato nazionale per la sicurezza nucleare e la radioprotezione (ISIN). La Sorveglianza della Radioattività Ambientale in Italia; Rapporto 08/2022; Ispettorato Nazionale per la Sicurezza Nucleare e la Radioprotezione: Roma, Italy, 2022; Available online: https://www.isinucleare.it/sites/default/files/contenuto_redazione_isin/la_sorveglianza_della_radioattivita_ambientale.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2023).
- La Verde, G.; Roca, V.; Pugliese, M. Quality assurance in planning a radon measurement survey using PDCA cycle approach: What improvements? Int. J. Metrol. Qual. Eng. 2019, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Verde, G.; Artiola, V.; D’Avino, V.; La Commara, M.; Panico, M.; Polichetti, S.; Pugliese, M. Measurement of Natural Radionuclides in Drinking Water and Risk Assessment in a Volcanic Region of Italy, Campania. Water 2021, 13, 3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Verde, G.; Desiderio, A.; La Commara, M.; D’Avino, V.; Roca, V. Radon measurements in drinking water using electret according to Italian legislation and mapping of Campania region (Southern Italy). Nuovo Cimento C 2020, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- La Verde, G.; Roca, V.; Sabbarese, C.; Ambrosino, F.; Pugliese, M. The equilibrium factor in the radon dose calculation in the archaeological site of Acquedotto Augusteo del Serino in Naples. Nuovo Cimento C 2018, 41, 218. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA National Exposure Research Laboratory, EPA 900. Gross Alpha and Gross Beta Radioactivity in Drinking Water; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- EN ISO 9698:2015; Water Quality—Determination of Tritium Activity Concentration—Liquid Scintillation Counting Method. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2015.
- EN ISO 13164-1:2013; Water quality—Radon-222—Part 1: General Principles. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2013.
- Agenzia Regionale per la Prevenzione e Protezione Ambientale del Veneto (ARPAV). Available online: https://www.arpa.veneto.it/temi-ambientali/radioattivita/approfondimenti/la-radioattivita-nellacqua-potabile-approfondimento (accessed on 19 August 2023).
- Agenzia Regionale per la Protezione Ambientale della Toscana (ARPAT). Available online: https://www.arpat.toscana.it/datiemappe/dati/concentrazione-di-attivita-alfa-totale-beta-totale-e-radon-222-acqua-destinata-consumo-umano (accessed on 19 August 2023).
- Agenzia Regionale per la Protezione dell’Ambiente della Sardegna (ARPAS). Available online: https://www.sardegnaambiente.it/index.php?xsl=612&s=335047&v=2&c=5013&idsito=21 (accessed on 19 August 2023).
- Agenzia Regionale per la Protezione dell’Ambiente della Lombardia (ARPA Lombardia). Available online: https://www.arpalombardia.it/dati/2019/radioattivita/rete-di-monitoraggio-della-radioattivita-ambientale/ (accessed on 19 August 2023).
- Agenzia Regionale per la Protezione dell’Ambiente della Lombardia (ARPA Lombardia). Available online: https://www.arpalombardia.it/indicatori/2020/radioattivita/radioattivita-nell-acqua-potabile/ (accessed on 19 August 2023).
- Agenzia Regionale Protezione Ambientale del Lazio (ARPA Lazio). https://www.arpalazio.it. Available online: https://www.arpalazio.it/ambiente/radioattivita/dati-radioattivit%C3%A0 (accessed on 19 August 2023).
- Agenzia Regionale Protezione Ambientale delle Marche (ARPAM). https://www.arpa.marche.it. Available online: https://www.arpa.marche.it/radiazioni-ionizzanti/monitoraggi-ambientali (accessed on 19 August 2023).
- Caridi, F.; Belmusto, G. Gross alpha and beta radioactivity evaluation in drinking water: Results from the Calabria Region, Southern Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2021, 15, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caridi, F.; Belmusto, G. Assessment of the public effective dose due to the 222Rn radioactivity in drinking water: Results from the Calabria region, southern Italy. J. Instrum. 2021, 16, P02033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozłowska, B.; Morelli, D.; Walencik, A.; Dorda, J.; Altamore, I.; Chieffalo, V.; Giammanco, S.; Immè, G.; Zipper, W. Radioactivity in waters of Mt. Etna (Italy). Radiat. Meas. 2009, 44, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faella, E.; Mancini, S.; Guida, M.; Cuomo, A.; Guida, D. Alpha spectrometry of radon short-lived progeny in drinking water and assessment of the public effective dose: Results from the cilento area, province of salerno, southern Italy. Materials 2020, 13, 5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borio, R.; Rongoni, A.; Saetta, D.M.S.; Desideri, D.; Roselli, C. Radon and tritium measurements in drinking water in a region of central Italy (Umbria). J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2005, 266, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desideri, D.; Roselli, C.; Meli, M.A.; Feduzi, L.; Rongoni, A.; Saetta, D. Radioactivity measurements and radiation dose evaluation in tap waters of Central Italy. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desideri, D.; Roselli, C.; Feduzi, L.; Meli, M.A. Radiological characterization of drinking waters in Central Italy. Microchem. J. 2007, 87, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, M.; Rusconi, R.; Bellinzona, S.; Cazzaniga, M.T.; Sgorbati, G. A wide range monitoring of drinking water natural radioactivity in northern Italy. In Proceedings of the 11th IRPA Congress, Madrid, Spain, 23–28 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).