Decision-Making in Repeated Games: Insights from Active Inference
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Game Theory and Repeated Games
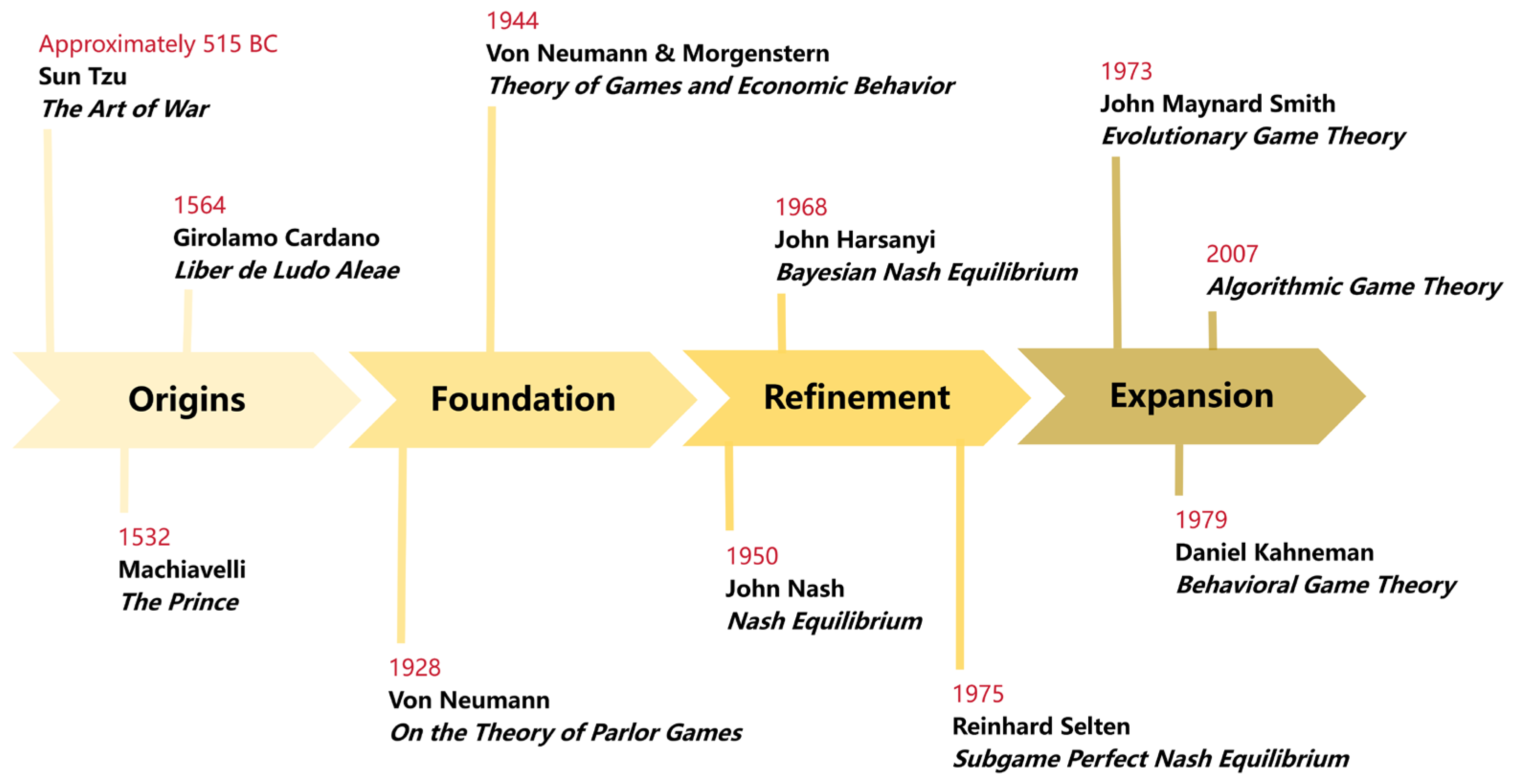
2.1. The History of Game Theory Development
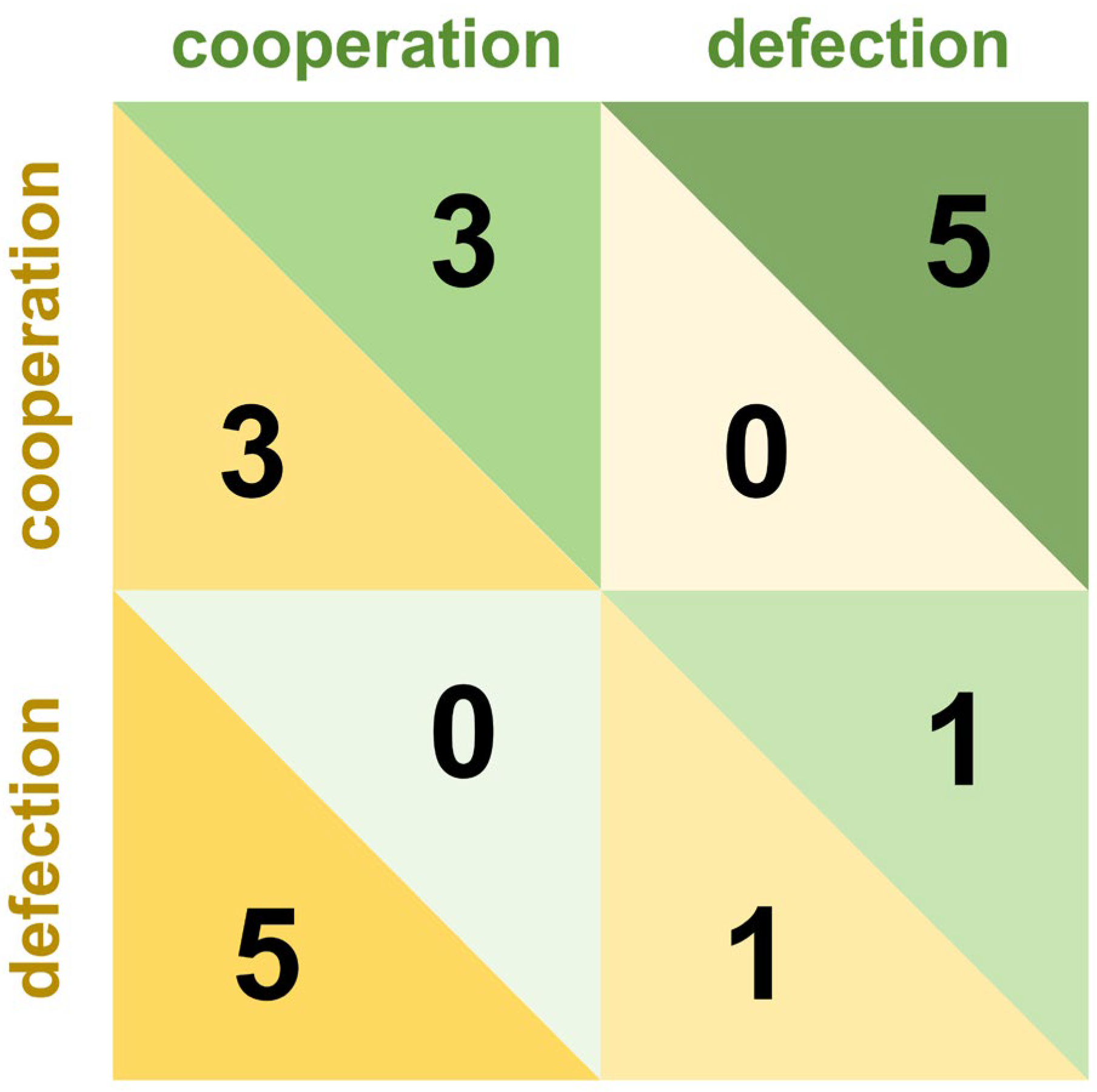
2.2. Repeated Games
3. Decision-Making in Repeated Games
4. Computational Modeling for Decision-Making
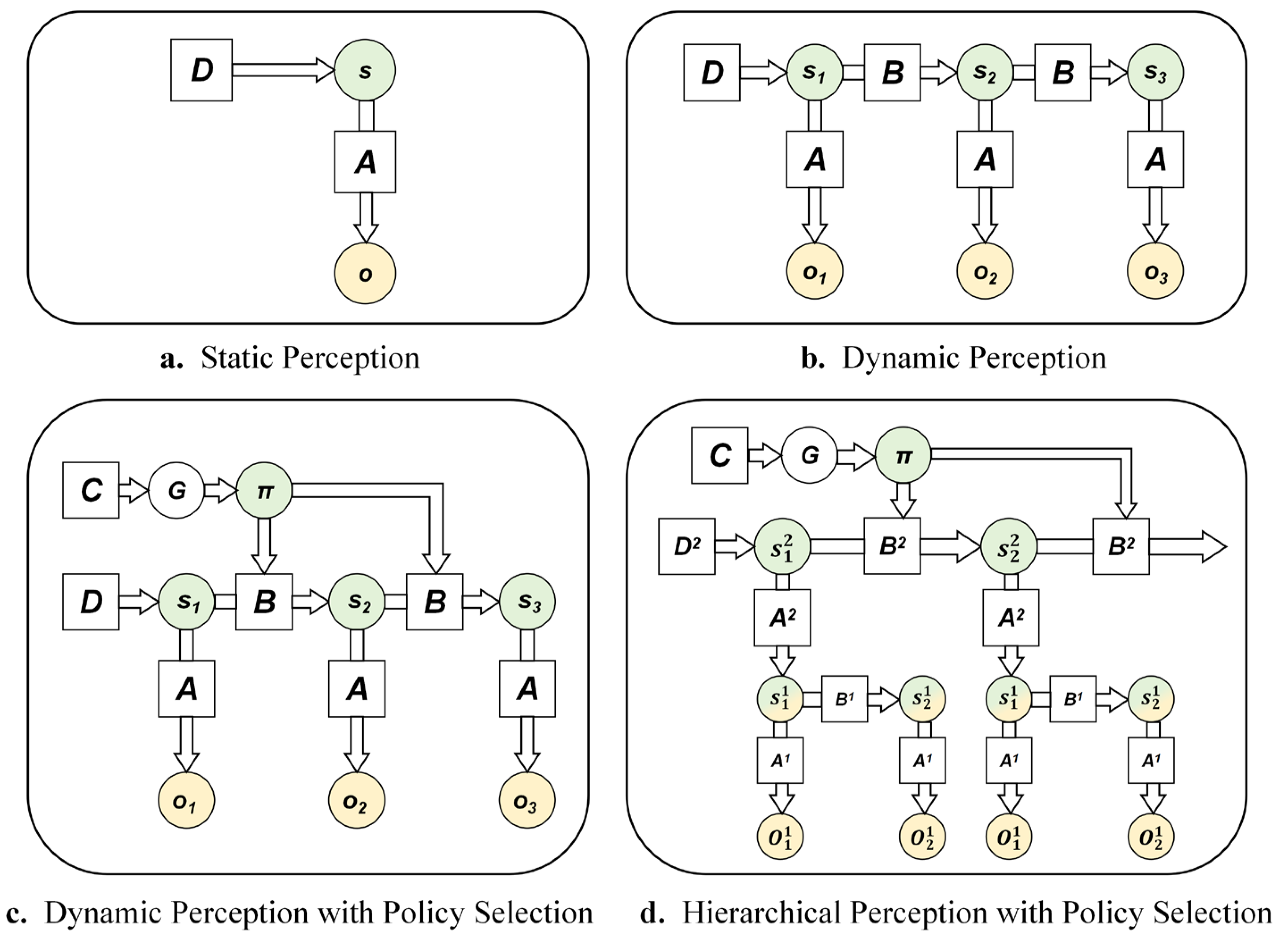
5. Basic Concepts of Active Inference
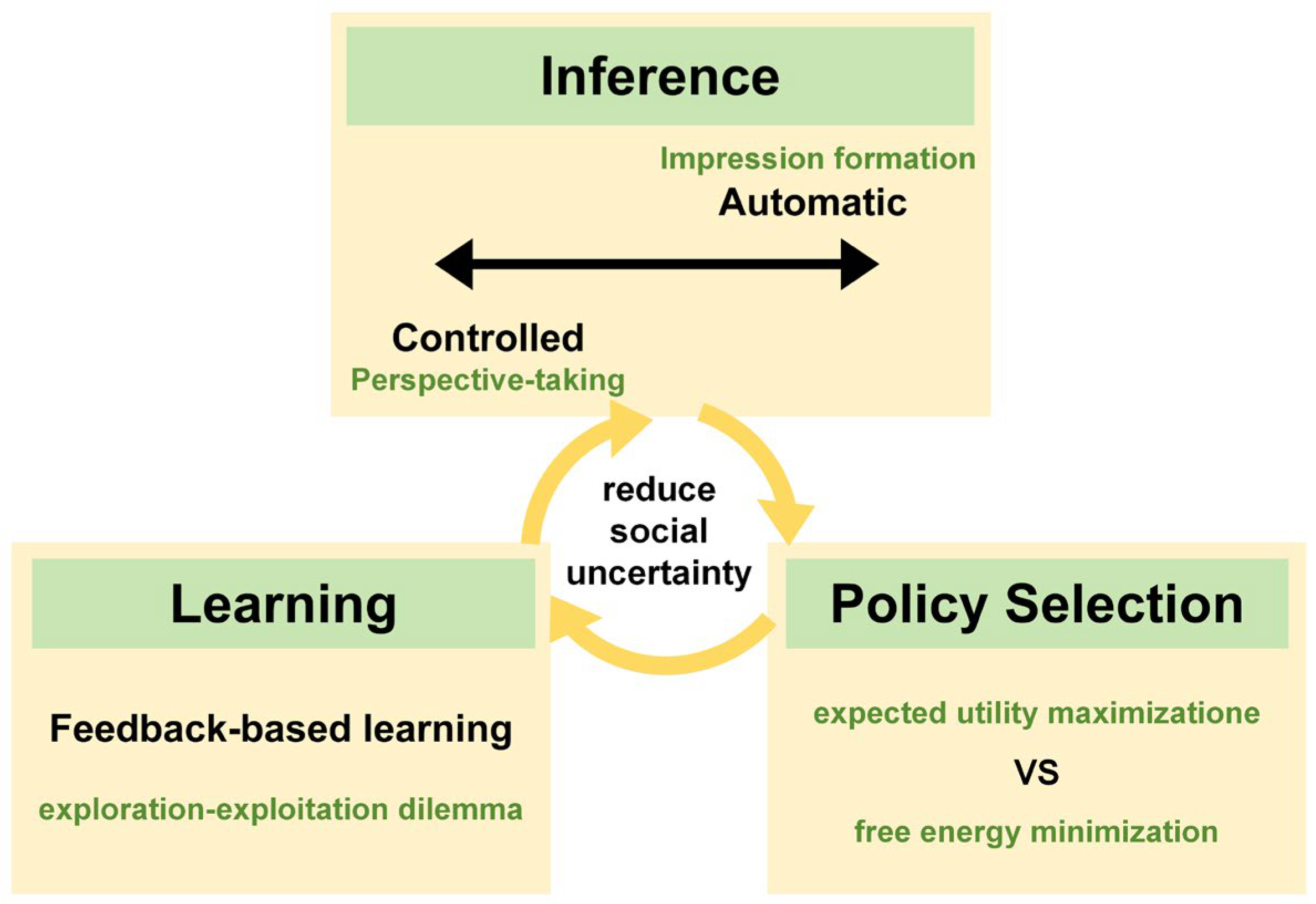
6. Why Active Inference? Advantages for Decision-Making in Repeated Games
6.1. The Free-Energy Principle: A Unified Framework for Cognitive Integration and Behavioral Optimization
6.2. Simulating the Nature of Social Interaction
6.3. Future Directions: Model Simulation and Behavioral Fitting
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahn, W.-Y., Busemeyer, J. R., Wagenmakers, E.-J., & Stout, J. C. (2008). Comparison of decision learning models using the generalization criterion method. Cognitive Science, 32(8), 1376–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akata, E., Schulz, L., Coda-Forno, J., Oh, S. J., Bethge, M., & Schulz, E. (2025). Playing repeated games with large language models. Nature Human Behaviour, 9, 1380–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alchian, A. A. (1950). Uncertainty, evolution, and economic theory. Journal of Political Economy, 58(3), 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumann, R. J. (1981). Survey of repeated games. In Essays in game theory and mathematical economics in honor of oskar morgenstern (pp. 11–42). Bibliographisches Institut. [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod, R. (1980). Effective choice in the prisoner’s dilemma. The Journal of Conflict Resolution, 24(1), 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, T. E. J., Woolrich, M. W., Walton, M. E., & Rushworth, M. F. S. (2007). Learning the value of information in an uncertain world. Nature Neuroscience, 10(9), 1214–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonowski, T., & Minnameier, G. (2022). Morality and trust in impersonal relationships. Journal of Economic Psychology, 90, 102513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camerer, C. (2003). Behavioural studies of strategic thinking in games. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 7(5), 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochard, F., Van, P., & Willinger, M. (2004). Trusting behavior in a repeated investment game. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization, 55(1), 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colman, A. (2003). Cooperation, psychological game theory, and limitations of rationality in social interaction. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 26(2), 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colman, A. M., Pulford, B. D., & Krockow, E. M. (2018). Persistent cooperation and gender differences in repeated prisoner’s dilemma games: Some things never change. Acta Psychologica, 187, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M., & Wright, C. (2021). First principles in the life sciences: The free-energy principle, organicism, and mechanism. Synthese, 198(Suppl. S14), 3463–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courville, A. C., Daw, N. D., & Touretzky, D. S. (2006). Bayesian theories of conditioning in a changing world. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 10(7), 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X., Bryant, D. M., & Reiss, A. L. (2012). NIRS-based hyperscanning reveals increased interpersonal coherence in superior frontal cortex during cooperation. Neuroimage, 59(3), 2430–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, F. (2024). Computational social psychology. Annual Review of Psychology, 75, 625–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, F., & Gershman, S. (2019). Editors’ introduction: Computational approaches to social cognition. Topics in Cognitive Science, 11(2), 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaine, M., Hollard, G., & Daunizeau, J. (2014). The social bayesian brain: Does mentalizing make a difference when we learn? PLoS Computational Biology, 10(12), e1003992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman Hall, O., & Shenhav, A. (2019). Resolving uncertainty in a social world. Nature Human Behaviour, 3(5), 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischhut, N., Artinger, F. M., Olschewski, S., & Hertwig, R. (2022). Not all uncertainty is treated equally: Information search under social and nonsocial uncertainty. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 35(2), e2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K., FitzGerald, T., Rigoli, F., Schwartenbeck, P., O’Doherty, J., & Pezzulo, G. (2016). Active inference and learning. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 68, 862–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friston, K., Rigoli, F., Ognibene, D., Mathys, C., Fitzgerald, T., & Pezzulo, G. (2015). Active inference and epistemic value. Cognitive Neuroscience, 6(4), 187–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friston, K. J. (2010). The free-energy principle: A unified brain theory? Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 11(2), 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K. J., Editor, R. R. G., Parr, T., Price, C., & Bowman, H. (2017). Deep temporal models and active inference. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 77, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K. J., Kilner, J., & Harrison, L. (2006). A free energy principle for the brain. Journal of Physiology-Paris, 100(1–3), 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galinsky, A., Ku, G., & Wang, C. (2005). Perspective-taking and self-other overlap: Fostering social bonds and facilitating social coordination. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations, 8(2), 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershman, S. J. (2019). Uncertainty and exploration. Decision, 6(3), 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijsen, S., Grundei, M., & Blankenburg, F. (2022). Active inference and the two-step task. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 17682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackel, L. M., & Amodio, D. M. (2018). Computational neuroscience approaches to social cognition. Current Opinion in Psychology, 24, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, D. J., Arthur, T., Broadbent, D. P., Wilson, M. R., Vine, S. J., & Runswick, O. R. (2022). An active inference account of skilled anticipation in sport: Using computational models to formalise theory and generate new hypotheses. Sports Medicine, 52(9), 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, D. J., North, J. S., & Runswick, O. R. (2023). A bayesian computational model to investigate expert anticipation of a seemingly unpredictable ball bounce. Psychological Research-Psychologische Forschung, 87(2), 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsanyi, J. C. (1968). Part ii: Bayesian equilibrium points. Management Science, 14, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchcock, P. F., Fried, E. I., & Frank, M. J. (2022). Computational psychiatry needs time and context. Annual Review of Psychology, 73, 243–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, R., Mehta, M., & Smith, R. (2024). The empirical status of predictive coding and active inference. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 157, 105473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, B. L., Zaki, J., & Ambady, N. (2017). Motivation alters impression formation and related neural systems. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 12(1), 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, H., & Nakamura, K. (2007). Partially observable markov decision processes with imprecise parameters. Artificial Intelligence, 171(8), 453–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahneman, D., & Tversky, A. (1979). Prospect theory: An analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica, 47(2), 263–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappes, A., Nussberger, A.-M., Siegel, J. Z., Rutledge, R. B., & Crockett, M. J. (2019). Social uncertainty is heterogeneous and sometimes valuable. Nature Human Behaviour, 3(8), 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, D. A., & Albright, L. (1987). Accuracy in interpersonal perception: A social relations analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 102, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsh, D., & Maglio, P. (1994). On distinguishing epistemic from pragmatic action. Cognitive Science, 18(4), 513–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krafft, P. M., Shmueli, E., Griffiths, T. L., Tenenbaum, J. B., & Pentland, A. (2021). Bayesian collective learning emerges from heuristic social learning. Cognition, 212, 104469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacomba, J. A., Lagos, F., Reuben, E., & van Winden, F. (2017). Decisiveness, peace, and inequality in games of conflict. Journal of Economic Psychology, 63, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, D. (2008). Game theory and neural basis of social decision making. Nature Neuroscience, 11(4), 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loennqvist, J.-E., & Walkowitz, G. (2019). Experimentally induced empathy has no impact on generosity in a monetarily incentivized dictator game. Frontiers in Psychology, 10, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewenstein, G. (1994). The psychology of curiosity: A review and reinterpretation. Psychological Bulletin, 116(1), 75–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, C., Chambon, V., Bourgeois-Gironde, S., Leboyer, M., & Zalla, T. (2018). The influence of prior reputation and reciprocity on dynamic trust-building in adults with and without autism spectrum disorder. Cognition, 172, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller Moya, L. M. (2007). Coordination and collective action. Revista Internacional De Sociologia, 65(46), 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montague, P. R. (2018). Computational phenotypes revealed by interactive economic games. In Computational psychiatry: Mathematical modeling of mental illness (pp. 273–292). Academic Press. [Google Scholar]
- Montague, P. R., Dolan, R. J., Friston, K. J., & Dayan, P. (2012). Computational psychiatry. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 16(1), 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J. F. (1950). Equilibrium points in n-person games. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 36(1), 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, J. v. (1928). Zur theorie der gesellschaftsspiele. Mathematische Annalen, 100(1), 295–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, G. T. T., & Au, W. T. (2016). Expectation and cooperation in prisoner’s dilemmas: The moderating role of game riskiness. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 23(2), 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisan, N., Roughgarden, T., Tardos, E., & Vazirani, V. V. (Eds.). (2007). Algorithmic game theory. Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y., Cheng, X., Zhang, Z., Li, X., & Hu, Y. (2017). Cooperation in lovers: An fNIRS-based hyperscanning study. Human Brain Mapping, 38(2), 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, T., & Friston, K. J. (2017). Uncertainty, epistemics and active inference. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 14(136), 20170376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, T., & Friston, K. J. (2019). Generalised free energy and active inference. Biological Cybernetics, 113(5–6), 495–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W. H., & Dyson, F. J. (2012). Iterated prisoner’s dilemma contains strategies that dominate any evolutionary opponent. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(26), 10409–10413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proietti, R., Parr, T., Tessari, A., Friston, K., & Pezzulo, G. (2025). Active inference and cognitive control: Balancing deliberation and habits through precision optimization. Physics of Life Reviews, 54, 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proietti, R., Pezzulo, G., & Tessari, A. (2023). An active inference model of hierarchical action understanding, learning and imitation. Physics of Life Reviews, 46, 92–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puterman, M. L. (1994). Markov decision processes: Discrete stochastic dynamic programming. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. [Google Scholar]
- Qinglin, G., & Yuan, Z. (2021). Psychological and neural mechanisms of trust formation: A perspective from computational modeling based on the decision of investor in the trust game [计算模型视角下信任形成的心理和神经机制--基于信任博弈中投资者的角度]. Advances in Psychological Science, 29(1), 178–189. [Google Scholar]
- Ruff, C. C., & Fehr, E. (2014). The neurobiology of rewards and values in social decision making. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 15(8), 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelling, T. (1960). The strategy of conflict. Harvard University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Selten, R. (1975). Reexamination of the perfectness concept for equilibrium points in extensive games. International Journal of Game Theory, 4(1), 25–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J. M., & Price, G. R. (1973). The logic of animal conflict. Nature, 246(5427), 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R., Friston, K. J., & Whyte, C. J. (2022). A step-by-step tutorial on active inference and its application to empirical data. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 107, 102632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R., Kirlic, N., Stewart, J. L., Touthang, J., Kuplicki, R., McDermott, T. J., Taylor, S., Khalsa, S. S., Paulus, M. P., & Aupperle, R. L. (2021). Long-term stability of computational parameters during approach-avoidance conflict in a transdiagnostic psychiatric patient sample. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 11783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R., Kuplicki, R., Feinstein, J., Forthman, K. L., Stewart, J. L., Paulus, M. P., Tulsa 1000 Investigators & Khalsa, S. S. (2020a). A bayesian computational model reveals a failure to adapt interoceptive precision estimates across depression, anxiety, eating, and substance use disorders. PLoS Computational Biology, 16(12), e1008484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R., Schwartenbeck, P., Stewart, J. L., Kuplicki, R., Ekhtiari, H., Paulus, M. P., & Tulsa 1000 Investigators. (2020b). Imprecise action selection in substance use disorder: Evidence for active learning impairments when solving the explore-exploit dilemma. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 215, 108208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speekenbrink, M., & Konstantinidis, E. (2015). Uncertainty and exploration in a restless bandit problem. Topics in Cognitive Science, 7(2), 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speekenbrink, M., & Shanks, D. R. (2010). Learning in a changing environment. Journal of Experimental Psychology-General, 139(2), 266–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojic, H., Orquin, J. L., Dayan, P., Dolan, R. J., & Speekenbrink, M. (2020a). Uncertainty in learning, choice, and visual fixation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 117(6), 3291–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojic, H., Schulz, E., Analytis, P., & Speekenbrink, M. (2020b). It’s new, but is it good? How generalization and uncertainty guide the exploration of novel options. Journal of Experimental Psychology-General, 149(10), 1878–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, R. S., & Barto, A. G. (1998). Reinforcement learning: An introduction. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 9(5), 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomov, M. S., Schulz, E., & Gershman, S. J. (2021). Multi-task reinforcement learning in humans. Nature Human Behaviour, 5(6), 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tump, A. N., Deffner, D., Pleskac, T. J., Romanczuk, P., & Kurvers, R. H. J. M. (2024). A cognitive computational approach to social and collective decision-making. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 19(2), 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, E., & De Dreu, C. K. W. (2021). Experimental games and social decision making. Annual Review of Psychology, 72, 415–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermorel, J., & Mohri, M. (2005). Multi-armed bandit algorithms and empirical evaluation. In J. Gama, R. Camacho, P. Brazdil, A. Jorge, & L. Torgo (Eds.), Lecture notes in computer science: Vol 3720. Machine learning: ECML 2005 (pp. 437–448). Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Von Neumann, J., & Morgenstern, O. (1944). Theory of games and economic behavior. Princeton University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Vorauer, J. D., Hodges, S. D., & Hall, J. A. (2025). Thought-feeling accuracy in person perception and metaperception: An integrative perspective. Annual Review of Psychology, 76, 413–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A. R., Luque, D., Le Pelley, M. E., & Beesley, T. (2019). The role of uncertainty in attentional and choice exploration. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 26(6), 1911–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H., & Kwan, A. C. (2023). Competitive and cooperative games for probing the neural basis of social decision-making in animals. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 149, 105158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Way, N., & Taffe, R. (2025). Interpersonal curiosity: A missing construct in the field of human development. Human Development, 69(2), 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthy, D. A., Pang, B., & Byrne, K. A. (2013). Decomposing the roles of perseveration and expected value representation in models of the iowa gambling task. Frontiers in Psychology, 4, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yifrah, B., Ramaty, A., Morris, G., & Mendelsohn, A. (2021). Individual differences in experienced and observational decision-making illuminate interactions between reinforcement learning and declarative memory. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M., Liu, T., Pelowski, M., & Yu, D. (2017). Gender difference in spontaneous deception: A hyperscanning study using functional near-infrared spectroscopy. Scientific Reports, 7, 7508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, H.; Wang, L.; Gao, W.; Tao, T.; Fan, C. Decision-Making in Repeated Games: Insights from Active Inference. Behav. Sci. 2025, 15, 1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15121727
Yuan H, Wang L, Gao W, Tao T, Fan C. Decision-Making in Repeated Games: Insights from Active Inference. Behavioral Sciences. 2025; 15(12):1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15121727
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Hui, Ligang Wang, Wenbin Gao, Ting Tao, and Chunlei Fan. 2025. "Decision-Making in Repeated Games: Insights from Active Inference" Behavioral Sciences 15, no. 12: 1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15121727
APA StyleYuan, H., Wang, L., Gao, W., Tao, T., & Fan, C. (2025). Decision-Making in Repeated Games: Insights from Active Inference. Behavioral Sciences, 15(12), 1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15121727





