Rumble: Prevalence and Correlates of Group Fighting among Adolescents in the United States
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Sample and Procedures
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Group Fighting
2.2.2. Sensation Seeking.
2.2.3. Parental Disengagement
2.2.4. School Disengagement
2.2.5. Violence and Delinquency
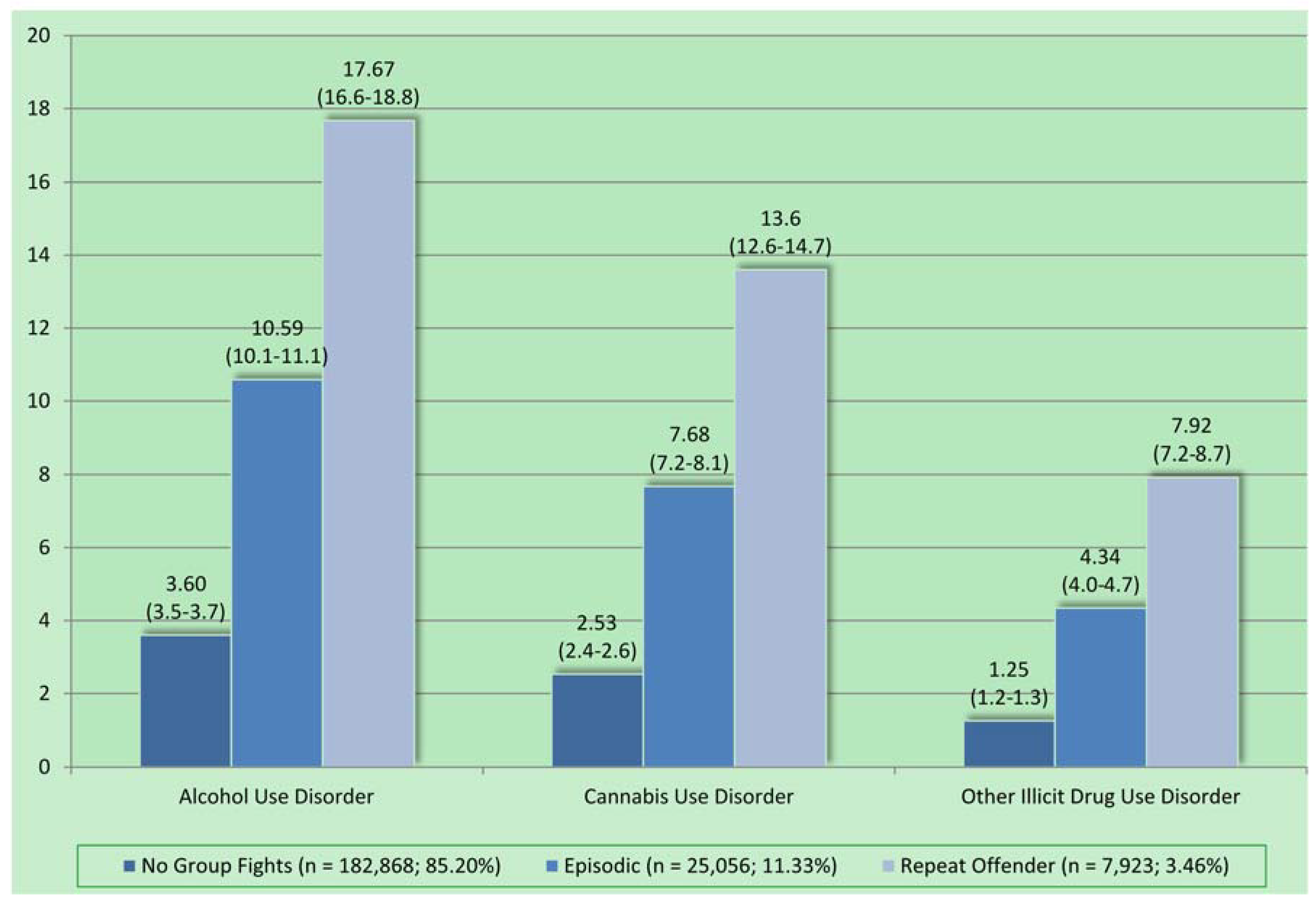
2.2.6. Substance Use Disorders
2.2.7. Sociodemographic Factors
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. What are the Sociodemographic Characteristics of Group Fighters in the United States?
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gannon, T.M. Emergence of the defensive gang. Fed. Probat. 1966, 30, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Hoover, J.E. The school and juvenile delinquency. Educ. Forum 1960, 25, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, J.C. Youth gang homicides: A literature review. Crime Delinq. 1999, 45, 208–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.B. The rumble this time. Psychol. Today 1977, 10, 52–88. [Google Scholar]
- Yablonsky, L. The delinquent gang as a near-group. Soc. Probl. 1959, 7, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffitt, T.E. Adolescence-limited and life-course-persistent antisocial behavior: A developmental taxonomy. Psychol. Rev. 1993, 100, 674–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffitt, T.E.; Caspi, A. Childhood predictors differentiate life-course persistent and adolescence-limited antisocial pathways among males and females. Dev. Psychopathol. 2001, 13, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffitt, T.E.; Caspi, A.; Dickson, N.; Silva, P.; Stanton, W. Childhood-onset versus adolescent-onset antisocial conduct problems in males: Natural history from ages 3 to 18 years. Dev. Psychopathol. 1996, 8, 399–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Adams, M. Are teen delinquency abstainers social introverts? A test of Moffitt’s theory. J. Res. Crime Delinq. 2010, 47, 439–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piquero, A.R.; Brezina, T.; Turner, M.G. Testing Moffitt’s account of delinquency abstention. J. Res. Crime Delinq. 2005, 42, 27–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, M.G.; Fu, Q.; Wernet, S.J.; DeLisi, M.; Beaver, K.M.; Perron, B.E.; Howard, M.O. Characteristics of abstainers from substance use and antisocial behavior in the United States. J. Crim. Justice 2011, 39, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughn, M.G.; Salas-Wright, C.P.; DeLisi, M.; Maynard, B.R. Violence and externalizing behavior among youth in the United States: Is there a severe 5%? Youth Violence Juv. Justice 2014, 12, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnken, M.P.; DeLisi, M.; Trulson, C.R.; Vaughn, M.G. The traumatic brain injury association with career criminality withstands powerful confounds. In Routledge International Handbook of Biosocial Criminology; DeLisi, M., Vaughn, M.G., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 418–424. [Google Scholar]
- Malek, M.K.; Chang, B.H.; Davis, T.C. Self-reported characterization of seventh-grade students’ fights. J. Adolesc. Health 1998, 23, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, J.A.; Beaver, K.M. Serious fighting-related injuries produce a significant reduction in intelligence. J. Adolesc. Health 2013, 53, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trulson, C.R.; Caudill, J.W.; Haerle, D.R.; DeLisi, M. Cliqued up: The postincarceration recidivism of young gang-related homicide offenders. Crim. Justice Rev. 2012, 37, 174–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Results from the 2012 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Summary of National Findings; Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration: Rockville, MD, USA, 2013.
- Herman-Stahl, M.A.; Krebs, C.P.; Kroutil, L.A.; Heller, D.C. Risk and protective factors for nonmedical use of prescription stimulants and methamphetamine among adolescents. J. Adolesc. Health 2006, 39, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merianos, A.L.; King, K.A.; Vidourek, R.A.; Nabors, L.A. Recent alcohol use and binge drinking based on authoritative parenting among Hispanic youth nationwide. J. Child Family Stud. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, M.G.; Maynard, B.R.; Salas-Wright, C.P.; Perron, B.E.; Abdon, A. Prevalence and correlates of truancy in the US: Results from a national sample. J. Adolesc. 2013, 36, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. In DSM-IV-TR Fourth Edition (Text Revision); American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Grucza, R.A.; Abbacchi, A.M.; Przybeck, T.R.; Gfroerer, J.C. Discrepancies in estimates of prevalence and correlates of substance use and disorders between two national surveys. Addiction 2007, 102, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, B.K.; Karg, R.S.; Batts, K.R.; Epstein, J.F.; Wiesen, C. A clinical validation of the National Survey on Drug Use and Health assessment of substance use disorders. Addict. Behav. 2008, 33, 782–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLisi, M. Career Criminals in Society; SAGE: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn, M.G.; DeLisi, M.; Gunter, T.; Fu, Q.; Beaver, K.M.; Perron, B.E.; Howard, M.O. The severe 5%: A latent class analysis of the externalizing behavior spectrum in the United States. J. Crim. Justice 2011, 39, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLisi, M.; Piquero, A.R. New frontiers in criminal careers research, 2000–2011: A state-of-the-art review. J. Crim. Justice 2011, 39, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynam, D.R. Early identification of chronic offenders: Who is the fledgling psychopath? Psychol. Bull. 1996, 120, 209–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagin, D.; Tremblay, R.E. Trajectories of boys’ physical aggression, opposition, and hyperactivity on the path to physically violent and nonviolent juvenile delinquency. Child Dev. 1999, 70, 1181–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newsome, J.; Boisvert, D.; Wright, J.P. Genetic and environmental influences on the co-occurrence of early academic achievement and externalizing behavior. J. Crim. Justice 2014, 42, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piquero, A.R.; Jennings, W.G.; Piquero, N.L.; Schubert, C.A. Human but not social capital is better able to distinguish between offending trajectories in a sample of serious adolescent Hispanic offenders. J. Crim. Justice 2014, 42, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shook, J.J.; Vaughn, M.G.; Salas-Wright, C.P. Exploring the variation in drug selling among adolescents in the United States. J. Crim. Justice 2013, 41, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzoumakis, S.; Lussier, P.; Corrado, R.R. The persistence of early childhood physical aggression: Examining maternal delinquency and offending, mental health, and cultural differences. J. Crim. Justice 2014, 42, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, G.D. Pathways to early delinquency: Exploring the individual and collective contributions of difficult temperament, low maternal involvement, and externalizing behavior. J. Crim. Justice 2014, 42, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottfredson, M.R.; Hirschi, T. A General Theory of Crime; Stanford University Press: Stanford, CA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- DeLisi, M.; Vaughn, M.G. Foundation for a temperament-based theory of antisocial behavior and criminal justice system involvement. J. Crim. Justice 2014, 42, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
DeLisi, M.; Vaughn, M.G.; Salas-Wright, C.P. Rumble: Prevalence and Correlates of Group Fighting among Adolescents in the United States. Behav. Sci. 2015, 5, 214-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs5020214
DeLisi M, Vaughn MG, Salas-Wright CP. Rumble: Prevalence and Correlates of Group Fighting among Adolescents in the United States. Behavioral Sciences. 2015; 5(2):214-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs5020214
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeLisi, Matt, Michael G. Vaughn, and Christopher P. Salas-Wright. 2015. "Rumble: Prevalence and Correlates of Group Fighting among Adolescents in the United States" Behavioral Sciences 5, no. 2: 214-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs5020214
APA StyleDeLisi, M., Vaughn, M. G., & Salas-Wright, C. P. (2015). Rumble: Prevalence and Correlates of Group Fighting among Adolescents in the United States. Behavioral Sciences, 5(2), 214-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs5020214