How Educational Background Influences Recruitment Evaluation: Evidence from Event-Related Potentials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Design
2.3. Stimuli
2.4. Procedure
2.5. EEG Recording and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Results
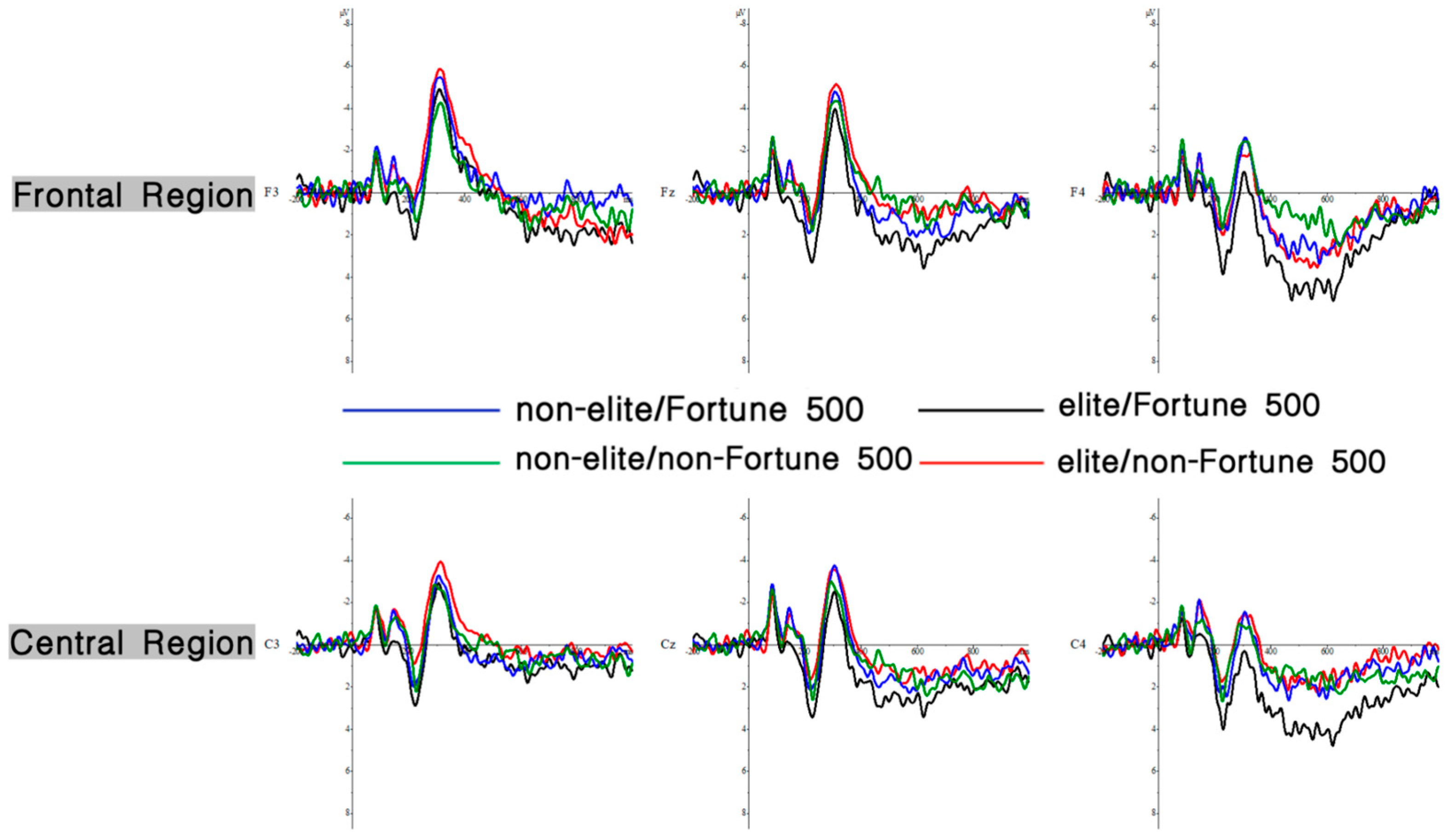
3.2. ERPs Results
3.2.1. P200 (210~280 ms)
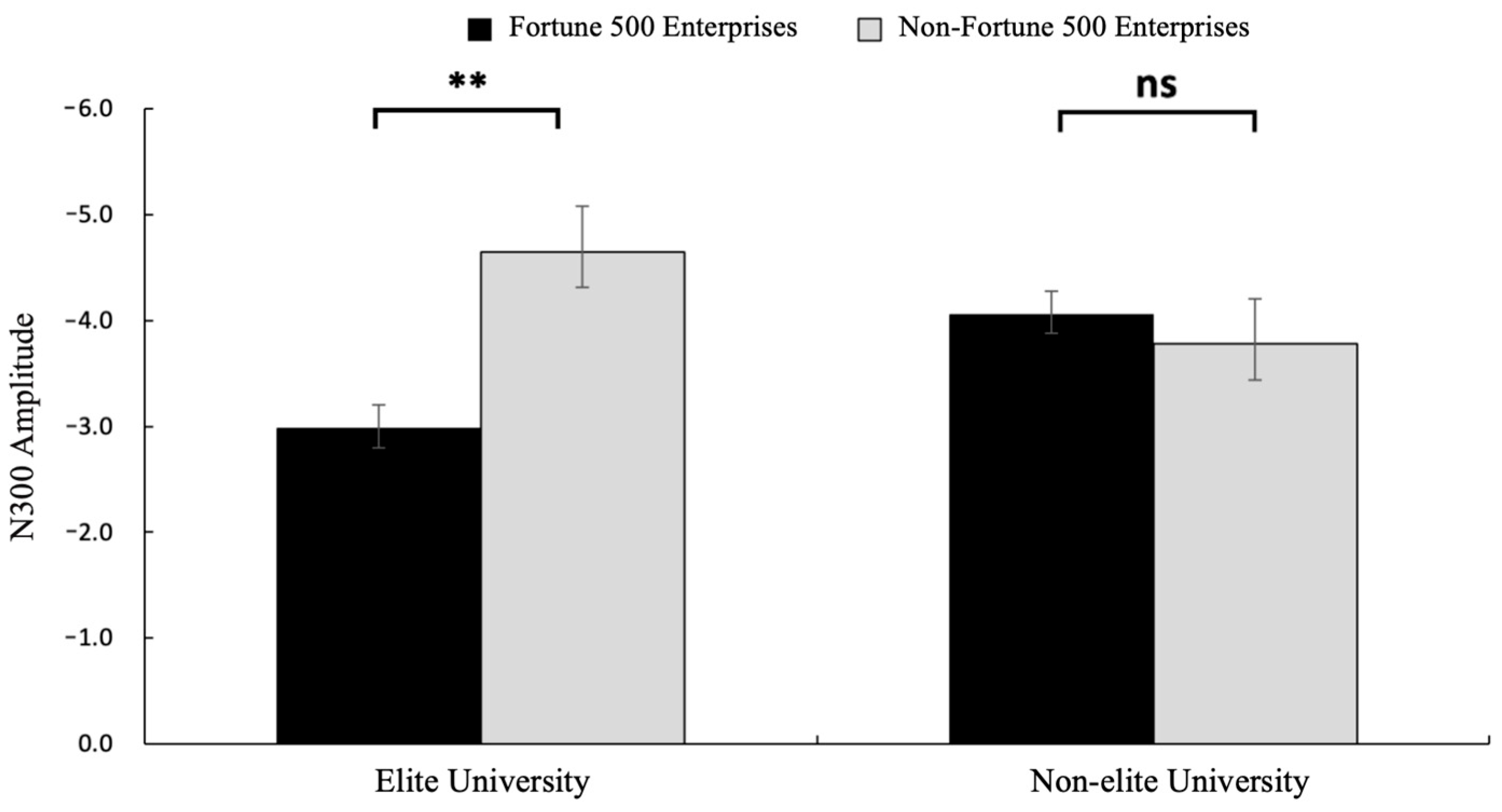
3.2.2. N300 (300~350 ms)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions, Limitations and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
Appendix A
| Enterprise Name | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fortune 500 | Wangyi | China Telecom | Jing Dong | Alibaba | Gree | Baidu | Xiaomi | Huawei |
| Non-Fortune 500 | Youwo | Yanding | Yingzhi | Boying | Netrong | Jiayu | Wenkuang | Fuyuan |
| Enterprise Name | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fortune 500 | 网易有道 | 中国电信 | 京东贸易 | 阿里巴巴 | 格力电器 | 百度科技 | 小米科技 | 华为技术 |
| Non-Fortune 500 | 优渥农业 | 言鼎企业 | 硬制合金 | 博盈科技 | 牛创汽车 | 佳裕农业 | 文旷咨询 | 富源企业 |
Appendix B
| University Name | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elite University | Xi’an Jiaotong University | Renmin University of China | Beijing Normal University | Nankai University | Xiamen University | Zhong shan University | Jilin University | Southeast University |
| Non-Elite University | Anhui University | Hebei University | Shanxi University | Liaoning University | Hechi University | Ankang University | Hainan University | Guizhou University |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | |
| Tsinghua University | Sichuan University | Zhejiang University | Tongji University | Peking University | Fudan University | Nanjing University | Wuhan University | |
| Yunnan University | Tibet University | Qinghai University | Ningxia University | Pu’er University | Changji University | Zhongbei University | Kashgar University |
| University Name | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elite University | 西安交通大学 | 中国人民大学 | 北京师范大学 | 南开大学 | 厦门大学 | 中山大学 | 吉林大学 | 东南大学 |
| Non-Elite University | 安徽大学 | 河北大学 | 山西大学 | 辽宁大学 | 河池学院 | 安康学院 | 海南大学 | 贵州大学 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | |
| 清华大学 | 四川大学 | 浙江大学 | 同济大学 | 北京大学 | 复旦大学 | 南京大学 | 武汉大学 | |
| 云南大学 | 西藏大学 | 青海大学 | 宁夏大学 | 普洱学院 | 昌吉学院 | 中北大学 | 喀什大学 |
| 1 | Double First-Class Universities refer to a group of elite Chinese institutions selected and supported by the government to develop into world-class universities and disciplines. |
References
- Addante, R. J., Lopez-Calderon, J., Allen, N., Luck, C., Muller, A., Sirianni, L., Inman, C. S., & Drane, D. L. (2023). An ERP measure of non-conscious memory reveals dissociable implicit processes in human recognition using an open-source automated analytic pipeline. Psychophysiology, 60(10), e14334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amodio, D. M. (2019). Social Cognition 2.0: An interactive memory systems account. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 23(1), 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellucci, G. (2023). The organizational principles of impression formation. Cognition, 239, 105550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benati, K., Lindsay, S., O’Toole, J., & Fischer, J. (2023). Career planning and workforce preparation during economic downturn: Perceptions of graduating business students. Education + Training, 65(3), 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J., Fu, H., & Jin, J. (2020). Are we sensitive to different types of safety signs? Evidence from ERPs. Psychology Research and Behavior Management, 13, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowyer, C., Brush, C. J., Threadgill, H., Harmon-Jones, E., Treadway, M., Patrick, C. J., & Hajcak, G. (2021). The effort-doors task: Examining the temporal dynamics of effort-based reward processing using ERPs. NeuroImage, 228, 117656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C. M., Jimenez, M., & Arrozal, C. A. N. (2019). Prestige or education: College teaching and rigor of courses in prestigious and non-prestigious institutions in the US. Higher Education, 77, 717–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X., Liu, M., Huang, T., Wu, M., Li, J., Zhao, X., Yan, T., Song, Y., & Zhang, Y.-X. (2023). Neurophysiological evidence for goal-oriented modulation of speech perception. Cerebral Cortex, 33(7), 3910–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L., Cichy, R. M., & Kaiser, D. (2022). Semantic scene-object consistency modulates N300/400 EEG components, but does not automatically facilitate object representations. Cerebral Cortex, 32(16), 3553–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derous, E., & Ryan, A. M. (2019). When your resume is (not) turning you down: Modelling ethnic bias in resume screening. Human Resource Management Journal, 29(2), 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Russo, F., Berchicci, M., Bianco, V., Perri, R. L., Pitzalis, S., Quinzi, F., & Spinelli, D. (2019). Normative event-related potentials from sensory and cognitive tasks reveal occipital and frontal activities prior and following visual events. NeuroImage, 196, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraga, F. J., Mamani, G. Q., Johns, E., Tavares, G., Falk, T. H., & Phillips, N. A. (2018). Early diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s with event-related potentials and event-related desynchronization in N-back working memory tasks. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 164, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, J. B., & Ambady, N. (2011). A dynamic interactive theory of person construal. Psychological Review, 118(2), 247–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghani, U., Signal, N., Niazi, I. K., & Taylor, D. (2020). ERP based measures of cognitive workload: A review. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 118, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Naranjo, J. E., Alfonso-Alfonso, M., Grass-Fernandez, D., Morales-Chacón, L. M., Pedroso-Ibáñez, I., Ricardo-de La Fe, Y., & Padrón-Sánchez, A. (2019). Analysis of sleep macrostructure in patients diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease. Behavioral Sciences, 9(1), 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, T. (2020). The relationship between language control, semantic control and nonverbal control. Behavioral Sciences, 10(11), 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, L., Dawel, A., Greenwood, L., Monaghan, C., Berryman, K., & Jack, B. N. (2023). Estimating statistical power for ERP studies using the auditory N1, Tb, and P2 components. Psychophysiology, 60(11), e14363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irak, M., Soylu, C., Turan, G., & Çapan, D. (2019). Neurobiological basis of feeling of knowing in episodic memory. Cognitive Neurodynamics, 13(3), 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y., Cui, L., Pollmann, S., & Wei, P. (2021). The interactive effects of reward expectation and emotional interference on cognitive conflict control: An ERP study. Physiology & Behavior, 234, 113369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X., & Lu, Y. (2023). Education–occupation mismatch and nativity inequality among highly educated US workers. Demography, 60(1), 201–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, B., Dong, B., & Cai, F. (2024). Applicants’ fairness perception of human and AI collaboration in resume screening. International Journal of Human–Computer Interaction, 2024, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P., Yang, X., & Tan, J. X. Y. (2024). Trial-level ERPs predicted behavioral responses during self-referential processing in late childhood. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 19(1), nsae011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y., & Li, X. (2021). Vertical education-occupation mismatch and wage inequality by race/ethnicity and nativity among highly educated US workers. Social Forces, 100(2), 706–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S., & Yu, J. (2024). ESGNet: A multimodal network model incorporating entity semantic graphs for information extraction from Chinese resumes. Information Processing & Management, 61(1), 103524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, B. M., Koenig, B. L., Wan, K. S., Laine, T., Gupta, S., & Ortony, A. (2018). Re-examining dominance of categories in impression formation: A test of dual-process models. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 115(1), 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, O. A., Livingston, B., & Susskind, A. M. (2023). Résumé screening heuristic outcomes: An examination of hiring manager evaluation bias. Equality, Diversity and Inclusion: An International Journal, 42(1), 104–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pina, A., Petersheim, C., Cherian, J., Lahey, J. N., Alexander, G., & Hammond, T. (2023). Using machine learning with eye-tracking data to predict if a recruiter will approve a resume. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction, 5(3), 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, L. H., Portugal, R., & Viana, P. (2024). What is in your résumé? The effects of multiple social categories in résumé screening. Personnel Review, 53(5), 1331–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisanelli, E. (2022). Your resume is your gatekeeper: Automated resume screening as a strategy to reduce gender gaps in hiring. Economics Letters, 221, 110892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurthy, S., & Sedgley, N. (2019). A note on school quality, educational attainment and the wage gap. Eastern Economic Journal, 45, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, L. A. (2020). Employer decision making. Annual Review of Sociology, 46(1), 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, T., Homan, A. C., & Lancee, B. (2024). Impression formation of majority and minority applicants during resume screening—Does processing more information reduce prejudice? Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 54(7), 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S., & Gray, K. (2021). Feeling empathy for organizations: Moral consequences, mechanisms, and the power of framing. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 96, 104147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpert-Esmond, H. I., & Bartholow, B. D. (2019). Explicit categorization goals affect attention-related processing of race and gender during person construal. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 85, 103839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessel, J. R. (2018). An adaptive orienting theory of error processing. Psychophysiology, 55(3), e13041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeineldin, M., Patel, A. G., & Dyer, M. A. (2022). Neuroblastoma: When differentiation goes awry. Neuron, 110(18), 2916–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X., Jia, H., & Wang, E. (2024). Exploring attention bias mechanisms in sub-threshold depression: ERP insights into biased orientation and disengagement. Behavioral Sciences, 14(9), 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ling, B.; Wang, Y. How Educational Background Influences Recruitment Evaluation: Evidence from Event-Related Potentials. Behav. Sci. 2025, 15, 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15060832
Ling B, Wang Y. How Educational Background Influences Recruitment Evaluation: Evidence from Event-Related Potentials. Behavioral Sciences. 2025; 15(6):832. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15060832
Chicago/Turabian StyleLing, Bin, and Yihan Wang. 2025. "How Educational Background Influences Recruitment Evaluation: Evidence from Event-Related Potentials" Behavioral Sciences 15, no. 6: 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15060832
APA StyleLing, B., & Wang, Y. (2025). How Educational Background Influences Recruitment Evaluation: Evidence from Event-Related Potentials. Behavioral Sciences, 15(6), 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15060832





