The Impact of Noise Pollution on Cognitive Function in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: Empirical Evidence from the CHARLS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Cognitive Function
2.2.2. Noise Pollution
2.2.3. Covariates
2.2.4. Mediated Variables
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Participants
3.2. Correlation Analysis
3.3. Results of Multistep Regression Analysis of Noise Pollution on Cognitive Function
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis
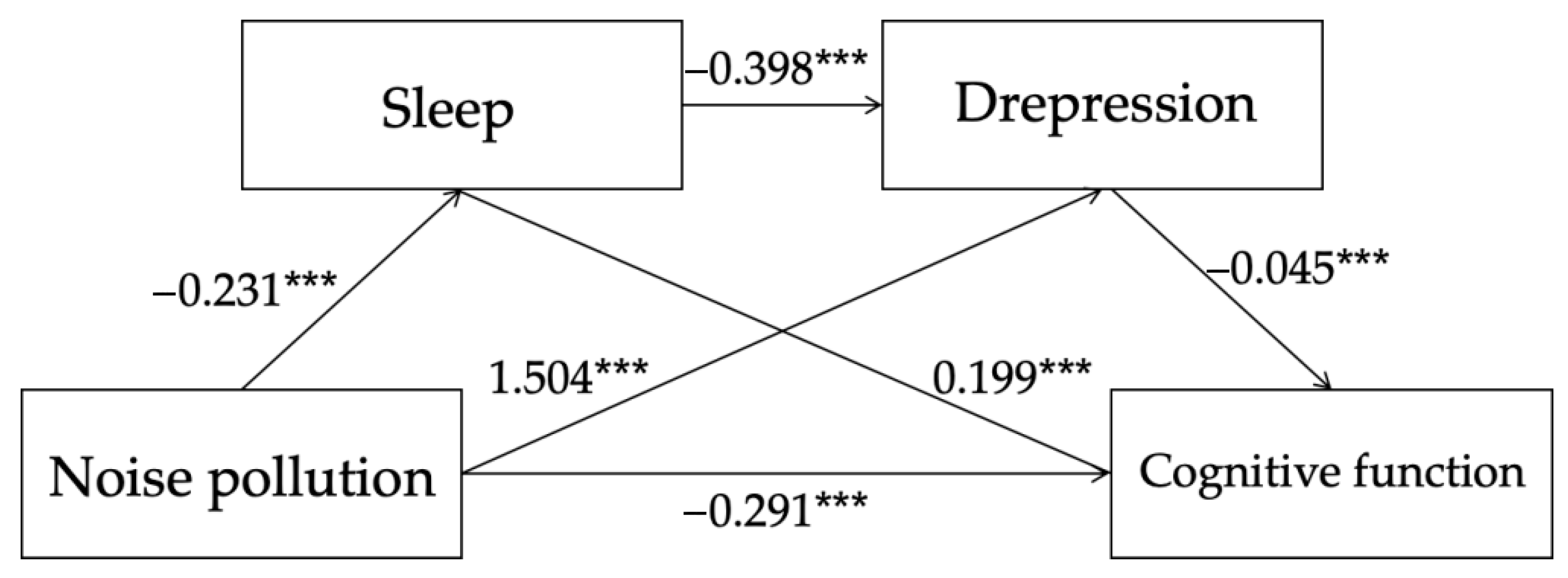
3.5. Analysis of the Mediating Effects of Sleep and Depression
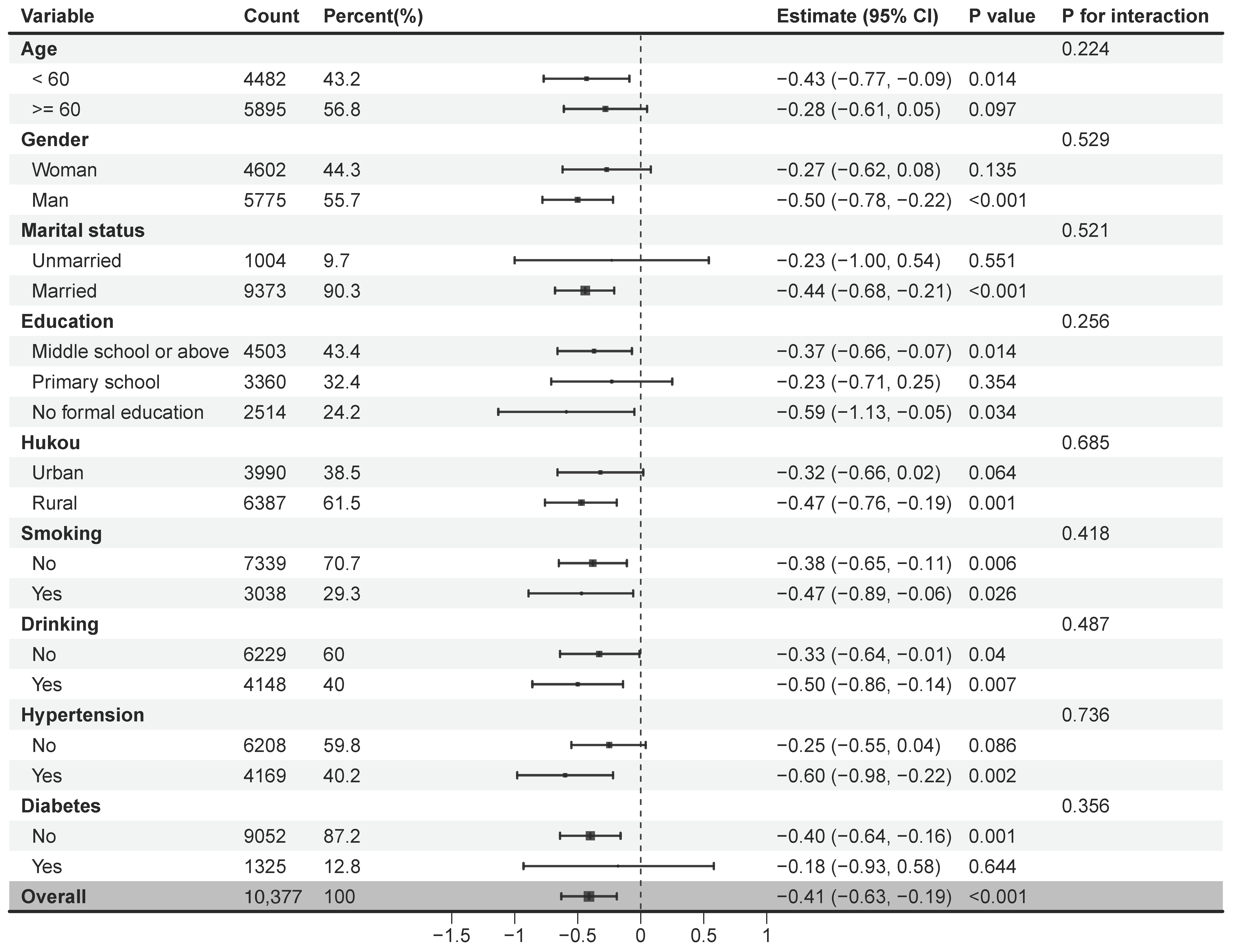
3.6. Subgroup Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andersson, J., Oudin, A., Sundström, A., Forsberg, B., Adolfsson, R., & Nordin, M. (2018). Road traffic noise, air pollution, and risk of dementia—Results from the Betula project. Environmental Research, 166, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocancea, D. I., Svenningsson, A. L., Van Loenhoud, A. C., Groot, C., Barkhof, F., Strandberg, O., Smith, R., for the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, Weiner, M. W., Aisen, P., Petersen, R., Aisen, P., Petersen, R., Jack, C. R., Jagust, W., Trojanowki, J. Q., Toga, A. W., Beckett, L., Green, R. C., … Ossenkoppele, R. (2023). Determinants of cognitive and brain resilience to tau pathology: A longitudinal analysis. Brain, 146(9), 3719–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braithwaite, I., Zhang, S., Kirkbride, J. B., Osborn, D. P. J., & Hayes, J. F. (2019). Air pollution (particulate matter) exposure and associations with depression, anxiety, bipolar, psychosis and suicide risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environmental Health Perspectives, 127(12), 126002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, M., Wilcox, R., Chou, C.-P., Chang, M., Yang, F., Blanchard, J., Marterella, A., Kuo, A., & Clark, F. (2011). Psychometric properties of reverse-scored items on the CES-D in a sample of ethnically diverse older adults. Psychological Assessment, 23(2), 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, N. M., Xue, Q.-L., McAdams-DeMarco, M. A., Carlson, M. C., Bandeen-Roche, K., & Gross, A. L. (2021). Frailty—A risk factor of global and domain-specific cognitive decline among a nationally representative sample of community-dwelling older adult U.S. Medicare beneficiaries. Age and Ageing, 50(5), 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C., Liu, L., Qi, Y., Han, N., Xu, H., Wang, Z., Shang, X., Han, T., Zha, Y., Wei, X., & Wu, Z. (2024). Joint association of TyG index and high sensitivity C-reactive protein with cardiovascular disease: A national cohort study. Cardiovascular Diabetology, 23(1), 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, G. W. (2021). The physical context of child development. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 30(1), 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H., Yu, W., Rong, H., & Geng, X. (2025). Associations between sleep duration and activity of daily living disability among older adults in China: Cross-sectional study. Interactive Journal of Medical Research, 14, e65075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X., Kou, C., Wu, S., Zhang, W., Li, B., Yu, G., Shen, Y., Gao, J., Li, W., & Bai, W. (2025). The mediating effect of depressive symptoms between frailty and cognitive impairment in the Northeast Chinese older adults. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders, 54(4), 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goines, L., & Hagler, L. (2007). Noise pollution: A modern plague. Southern Medical Journal, 100(3), 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S., & Zheng, X.-Y. (2023). New evidence of trends in cognitive function among middle-aged and older adults in China, 2011–2018: An age-period-cohort analysis. BMC Geriatrics, 23(1), 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahad, O., Kuntic, M., Al-Kindi, S., Kuntic, I., Gilan, D., Petrowski, K., Daiber, A., & Münzel, T. (2025). Noise and mental health: Evidence, mechanisms, and consequences. Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology, 35(1), 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahad, O., Schmidt, F. P., Hübner, J., Foos, P., Al-Kindi, S., Schmitt, V. H., Hobohm, L., Keller, K., Große-Dresselhaus, C., Schmeißer, J., Koppe-Schmeißer, F., Vosseler, M., Gilan, D., Schulz, A., Chalabi, J., Wild, P. S., Daiber, A., Herzog, J., & Münzel, T. (2023). Acute exposure to simulated nocturnal traffic noise and cardiovascular complications and sleep disturbance—Results from a pooled analysis of human field studies. Clinical Research in Cardiology, 112(11), 1690–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halperin, D. (2014). Environmental noise and sleep disturbances: A threat to health? Sleep Science, 7(4), 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, M. S., Swinburn, T. K., & Neitzel, R. L. (2014). Environmental noise pollution in the united states: Developing an effective public health response. Environmental Health Perspectives, 122(2), 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, T. S., Wu, A. W., Sharma, D., Illing, E. A., Rubel, K., Ting, J. Y., & Snot Force Alliance. (2020). Correlations of online search engine trends with coronavirus disease (COVID-19) incidence: Infodemiology study. JMIR Public Health and Surveillance, 6(2), e19702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C., Zhao, Y., Zhao, X., Zhu, B., & Qin, H. (2021). Correlation between sleep characteristics and cognitive decline in the elderly people: A cross-sectional study in China. International Journal of Clinical Practice, 75(7). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C., Yan, Y., Tam, W. W. S., Sun, W., Ye, Y., Wang, N., Shi, Y., Zhu, Z., Chen, D., Chen, L., Zhao, J., Lin, R., & Li, H. (2025). Effects of an integrated social-art intervention on cognitive and psychosocial outcomes among older adults with mild cognitive impairment in nursing homes: A mixed methods study. BMC Medicine, 23(1), 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, R.-R., Zhai, L., Liao, Q., & You, X.-M. (2023). Changes in the triglyceride glucose-body mass index estimate the risk of stroke in middle-aged and older Chinese adults: A nationwide prospective cohort study. Cardiovascular Diabetology, 22(1), 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jak, A. J., Preis, S. R., Beiser, A. S., Seshadri, S., Wolf, P. A., Bondi, M. W., & Au, R. (2016). Neuropsychological criteria for mild cognitive impairment and dementia risk in the framingham heart study. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 22(9), 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L., Du, Y., Chu, L., Zhang, Z., Li, F., Lyu, D., Li, Y., Li, Y., Zhu, M., Jiao, H., Song, Y., Shi, Y., Zhang, H., Gong, M., Wei, C., Tang, Y., Fang, B., Guo, D., Wang, F., … Qiu, Q. (2020). Prevalence, risk factors, and management of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in adults aged 60 years or older in China: A cross-sectional study. The Lancet Public Health, 5(12), e661–e671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M., Chen, Z., Pei, N., Li, J., & Ren, Z. (2024). Nonlinear effect of urban noise pollution on depression of the elderly in China based on the Bayesian machine learning method. Applied Acoustics, 225, 110207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavayuth, D., Liang, Y., & Zikos, V. (2018). An active lifestyle and cognitive function: Evidence from China. The Journal of the Economics of Ageing, 12, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-J., Jeon, T.-Y., & Lee, Y.-C. (2024). Impact of ship noise on seafarers’ sleep disturbances and daily activities: An analysis of fatigue increase and maritime accident risk through a survey. Applied Sciences, 14(9), 3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leger, D., Ferini-Strambi, L., Han, F., Poyares, D., Uchiyama, M., & Zee, P. C. (2024). Novel perspective of ‘poor sleep’ in public health: A narrative review. BMJ Public Health, 2(2), e000952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F., Wu, T., Zhao, J., Ji, L., Song, A., Zhang, M., & Huang, G. (2016). Prevalence of mild cognitive impairment and its subtypes among chinese older adults: Role of vascular risk factors. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders, 41(5–6), 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac Domhnaill, C., Douglas, O., Lyons, S., Murphy, E., & Nolan, A. (2021). Road traffic noise and cognitive function in older adults: A cross-sectional investigation of The Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing. BMC Public Health, 21(1), 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, K., Thandavan, S. P., Mohebbi, M., Pasco, J. A., Williams, L. J., Walder, K., Ng, B. L., & Gupta, V. B. (2022). Depression and bone loss as risk factors for cognitive decline: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Research Reviews, 76, 101575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedema, H. M. E., & Vos, H. (2007). Associations between self-reported sleep disturbance and environmental noise based on reanalyses of pooled data from 24 studies. Behavioral Sleep Medicine, 5(1), 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. (2022). 2022 China noise pollution prevention report. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/hjzywr/202211/t20221116_1005052.shtml (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. (2023). 2022 China environmental quality bulletin. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/sthjtjnb/202301/t20230118_1013682.shtml (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. (2025). Environmental status—Major pollutants. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/hjzywr/ (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Münzel, T., Schmidt, F. P., Steven, S., Herzog, J., Daiber, A., & Sørensen, M. (2018). Environmental noise and the cardiovascular system. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 71(6), 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. (2025). Statistical communiqué of the People’s Republic of China on the 2024 national economic and social development. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/english/PressRelease/202502/t20250228_1958822.html (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Ogurtsova, K., Soppa, V. J., Weimar, C., Jöckel, K.-H., Jokisch, M., & Hoffmann, B. (2023). Association of long-term air pollution and ambient noise with cognitive decline in the Heinz Nixdorf Recall study. Environmental Pollution, 331, 121898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W., Lu, P., Wang, Y., & Hong, X.-C. (2024). Understanding the association between urban noise and nighttime light in China. Scientific Reports, 14(1), 31472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S., Yu, L., Li, J., Wu, J., Huang, X., Xie, Z., Xue, T., Li, Y., & Su, L. (2025). Insulin resistance quantified by estimated glucose disposal rate predicts cardiovascular disease incidence: A nationwide prospective cohort study. Cardiovascular Diabetology, 24(1), 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R., Smith, R. B., Bou Karim, Y., Shen, C., Drummond, K., Teng, C., & Toledano, M. B. (2022). Noise pollution and human cognition: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of recent evidence. Environment International, 158, 106905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, A. P. L., Lee, C. K., & Chan, S. C. Y. (2025). A cross-lagged panel analysis of social participation in the relationship between functional limitations and cognitive functioning: Evidence from CHARLS. Journal of Applied Gerontology, 44(4), 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzivian, L., Winkler, A., Dlugaj, M., Schikowski, T., Vossoughi, M., Fuks, K., Weinmayr, G., & Hoffmann, B. (2015). Effect of long-term outdoor air pollution and noise on cognitive and psychological functions in adults. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 218(1), 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, J. N., & Newhouse, P. A. (2014). Mild cognitive impairment: Diagnosis, longitudinal course, and emerging treatments. Current Psychiatry Reports, 16(10), 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-M., Kang, D. W., Um, Y. H., Kim, S., Lee, C. U., & Lim, H. K. (2023). Depression is associated with the aberration of resting state default mode network functional connectivity in patients with amyloid-positive mild cognitive impairment. Brain Sciences, 13(7), 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weuve, J., D’Souza, J., Beck, T., Evans, D. A., Kaufman, J. D., Rajan, K. B., De Leon, C. F. M., & Adar, S. D. (2021). Long-term community noise exposure in relation to dementia, cognition, and cognitive decline in older adults. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 17(3), 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. (2024). Guidance on environmental noise. Compendium of WHO and other UN guidance on health and environment. World Health Organization. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X., Tang, Y., He, Y., Wang, Q., Wang, Y., & Qin, X. (2024). Prevalence of cognitive impairment and its related factors among Chinese older adults: An analysis based on the 2018 CHARLS data. Frontiers in Public Health, 12, 1500172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiangli, J., Chang, L., Sheng, R., Lou, N., Chen, X., Tu, J., & Lin, H. (2025). The u-shape association between noise and individual depression: Nationwide longitudinal evidence from three waves of CHARLS. Journal of Urban Health, 102(3), 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H., Wang, Z., Liu, F., & Unger, J. M. (2023). Excess all-cause mortality in china after ending the zero COVID policy. JAMA Network Open, 6(8), e2330877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y., Su, J., Jerrett, M., Paul, K. C., Lee, E., Shih, I.-F., Haan, M., & Ritz, B. (2023). Air pollution and traffic noise interact to affect cognitive health in older Mexican Americans. Environment International, 173, 107810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekveld, A. A., Kramer, S. E., & Festen, J. M. (2011). Cognitive load during speech perception in noise: The influence of age, hearing loss, and cognition on the pupil response. Ear & Hearing, 32(4), 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B., & Jiang, S. (2022). Heterogeneity in longitudinal trajectories of cognitive performance among middle-aged and older individuals with hypertension: Growth mixture modeling across an 8-year cohort study. Hypertension Research, 45(6), 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K., Yi, L., Su, X., & Sun, Y. (2023). Environmental noise pollution prevention and control law. In K. Zhou, L. Yi, X. Su, & Y. Sun (Eds.), Environmental and Resource Protection Law (pp. 195–209). Springer Nature. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

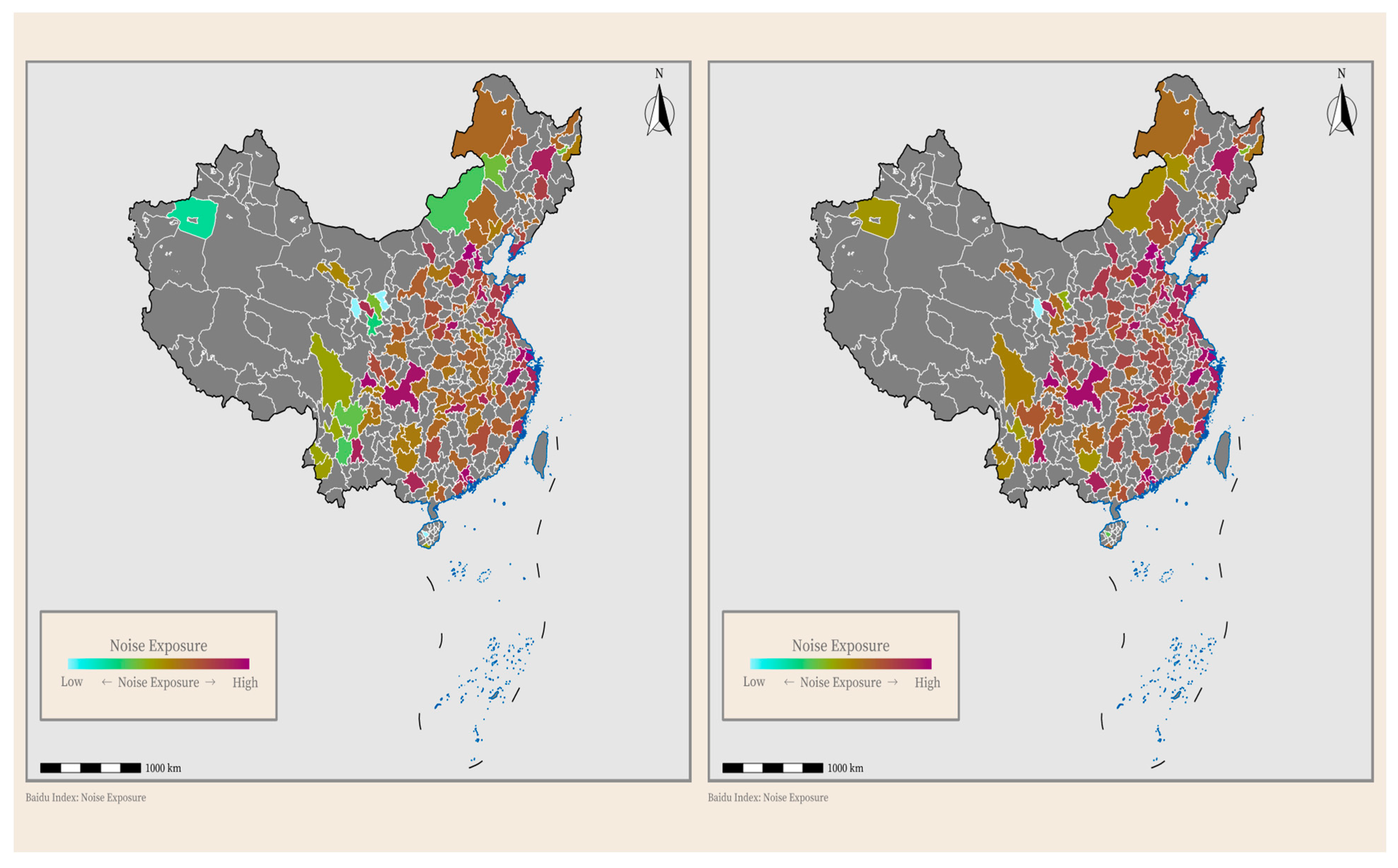
| Variable | Total (n = 3459) | Low Exposure (n = 1692) | High Exposure (n = 1767) | Statistic | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cognitive function score | 12.24 ± 3.55 | 12.39 ± 3.42 | 12.09 ± 3.67 | 2.45 | 0.01 |
| Age (years) | 59.14 ± 7.94 | 58.71 ± 7.90 | 59.55 ± 7.95 | −3.09 | <0.01 |
| Depression | 7.10 ± 5.80 | 7.43 ± 5.87 | 6.78 ± 5.72 | 3.28 | <0.01 |
| Sleep (hours) | 6.42 ± 1.67 | 6.42 ± 1.70 | 6.41 ± 1.65 | 0.14 | 0.89 |
| ADL | 0.22 ± 0.69 | 0.24 ± 0.70 | 0.21 ± 0.67 | 1.13 | 0.26 |
| Consumption | 3.32 ± 4.76 | 3.41 ± 5.38 | 3.24 ± 4.07 | 1.02 | 0.31 |
| Gender | 1.18 | 0.28 | |||
| Woman | 1534 (44.35) | 734 (43.38) | 800 (45.27) | ||
| Man | 1925 (55.65) | 958 (56.62) | 967 (54.73) | ||
| Marital status | 0.00 | 1.00 | |||
| Non-married | 268 (7.75) | 131 (7.74) | 137 (7.75) | ||
| Married | 3191 (92.25) | 1561 (92.26) | 1630 (92.25) | ||
| Education | 15.53 | <0.01 | |||
| Middle school or above | 1461 (42.24) | 707 (41.78) | 754 (42.67) | ||
| Primary school | 826 (23.88) | 395 (23.35) | 431 (24.39) | ||
| No formal education | 1086 (31.40) | 530 (31.32) | 556 (31.47) | ||
| Hukou | 7.47 | <0.01 | |||
| Urban | 1330 (38.45) | 611 (36.11) | 719 (40.69) | ||
| Rural | 2129 (61.55) | 1081 (63.89) | 1048 (59.31) | ||
| Smoking | 4.11 | 0.04 | |||
| No | 2406 (69.56) | 1149 (67.91) | 1257 (71.14) | ||
| Yes | 1053 (30.44) | 543 (32.09) | 510 (28.86) | ||
| Drinking | 1.08 | 0.30 | |||
| No | 2021 (58.43) | 973 (57.51) | 1048 (59.31) | ||
| Yes | 1438 (41.57) | 719 (42.49) | 719 (40.69) | ||
| Hypertension | 0.06 | 0.81 | |||
| No | 2085 (60.28) | 1016 (60.05) | 1069 (60.50) | ||
| Yes | 1374 (39.72) | 676 (39.95) | 698 (39.50) | ||
| Diabetes | 6.05 | 0.01 | |||
| No | 3137 (90.69) | 1556 (91.96) | 1581 (89.47) | ||
| Yes | 322 (9.31) | 136 (8.04) | 186 (10.53) |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cognitive function score | 1.000 | |||
| Depression score | −0.240 *** | 1.000 | ||
| Sleep duration | 0.091 *** | −0.290 *** | 1.000 | |
| Noise pollution | −0.094 *** | 0.023 ** | −0.028 *** | 1.000 |
| β | (95%CI) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | −0.408 | [−0.629, −0.187] | <0.001 |
| Model 2 | −0.408 | [−0.629, −0.187] | <0.001 |
| Model 3 | −0.410 | [−0.631, −0.189] | <0.001 |
| Model 4 | −0.410 | [−0.631, −0.189] | <0.001 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression | Regression | Cox | Regression | |
| Equivalent sound | −0.379 *** | |||
| Road traffic noise | −0.379 *** | |||
| Noise pollution | 1.0623 ** | |||
| Noise pollution | −0.219 *** |
| Effect Type | Effect Value | Boot SE | Boot LLCI | Boot ULCI | Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Effect | −0.413 | 0.076 | −0.562 | −0.270 | |
| Direct Effect | −0.291 | 0.076 | −0.443 | −0.146 | 70.480 |
| Total Indirect Effect | −0.122 | 0.014 | −0.150 | −0.096 | 29.520 |
| Noise→Sleep→Cognition | −0.046 | 0.008 | −0.063 | −0.032 | 11.149 |
| Noise→Depression→Cognition | −0.072 | 0.010 | −0.091 | −0.052 | 17.371 |
| Noise→Sleep→Depression→Cognition | −0.004 | 0.001 | −0.006 | −0.003 | 1.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Han, Y.; Guan, K. The Impact of Noise Pollution on Cognitive Function in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: Empirical Evidence from the CHARLS. Behav. Sci. 2025, 15, 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15101404
Zhang Y, Han Y, Guan K. The Impact of Noise Pollution on Cognitive Function in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: Empirical Evidence from the CHARLS. Behavioral Sciences. 2025; 15(10):1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15101404
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yanzhe, Yushun Han, and Kaiyu Guan. 2025. "The Impact of Noise Pollution on Cognitive Function in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: Empirical Evidence from the CHARLS" Behavioral Sciences 15, no. 10: 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15101404
APA StyleZhang, Y., Han, Y., & Guan, K. (2025). The Impact of Noise Pollution on Cognitive Function in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: Empirical Evidence from the CHARLS. Behavioral Sciences, 15(10), 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15101404






