Smartphone Distraction and Academic Anxiety: The Mediating Role of Academic Procrastination and the Moderating Role of Time Management Disposition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Smartphone Distraction and Academic Anxiety
2.2. The Mediating Role of Academic Procrastination
2.3. The Moderating Role of Time Management Disposition
2.4. The Present Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Participants
3.2. Design and Measures
3.2.1. Smartphone Distraction
3.2.2. Academic Anxiety
3.2.3. Academic Procrastination
3.2.4. Time Management Disposition
3.3. Procedure
3.4. Data Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Preliminary Analyses
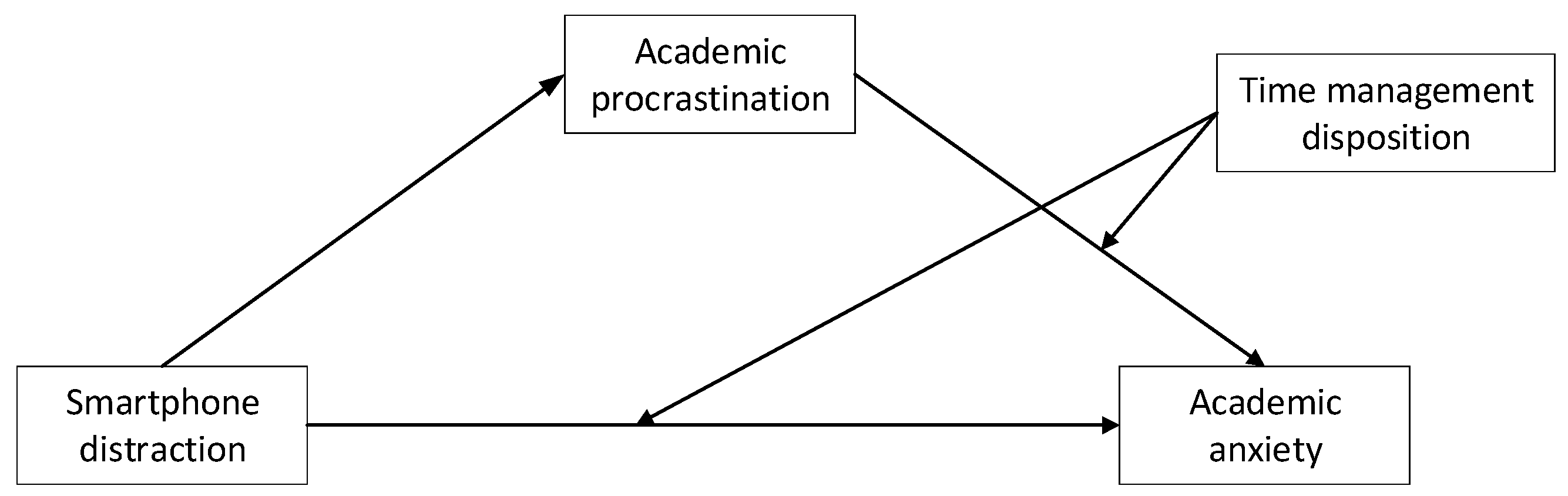
4.2. Testing the Mediation of Academic Procrastination
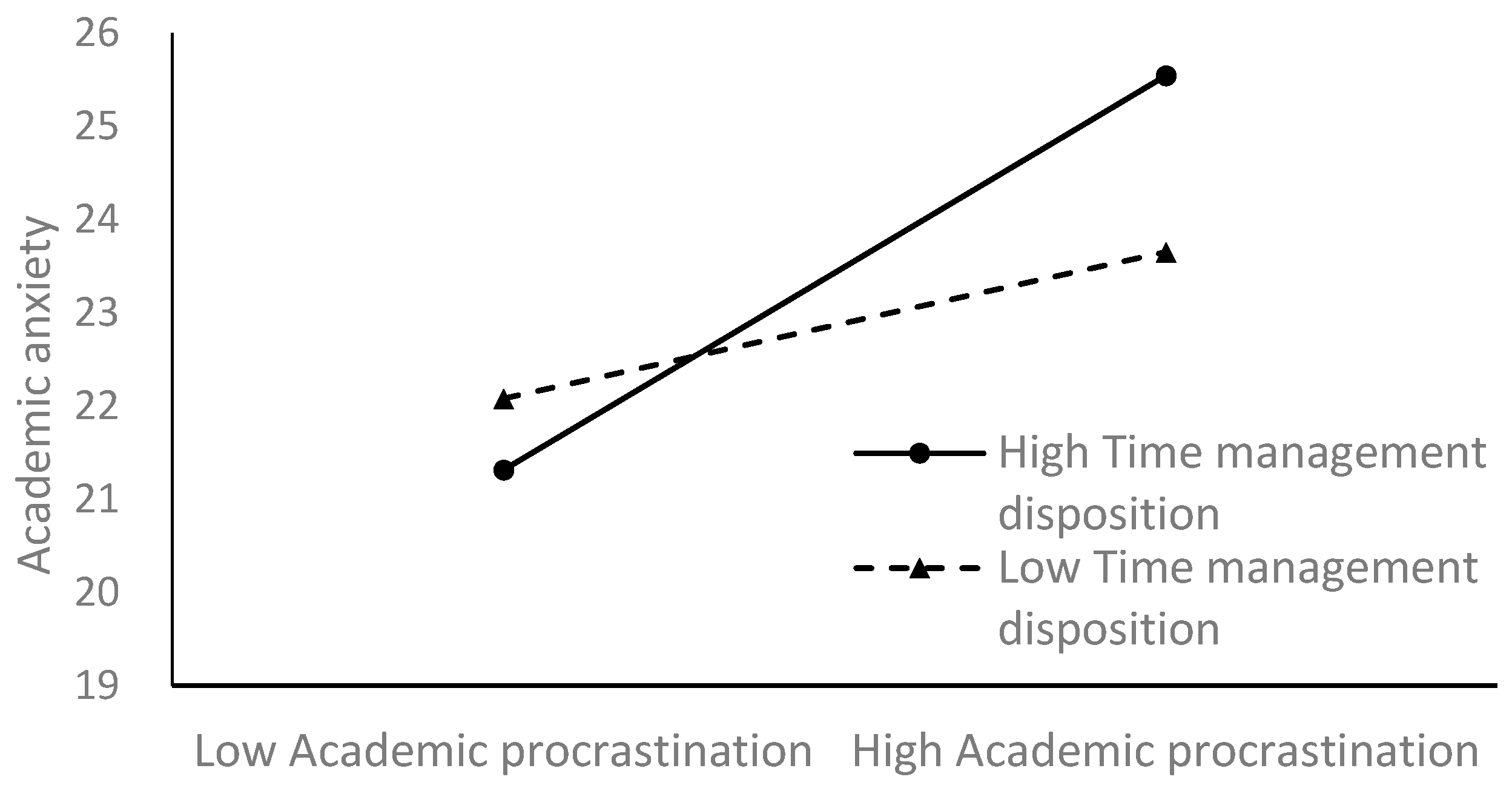
4.3. Testing the Moderated Mediation Model
5. Discussion
5.1. Summary of the Findings
5.2. Theoretical and Practical Implications
5.2.1. The Predicting Effects of Smartphone Distraction
5.2.2. Academic Procrastination as a Mediator
5.2.3. Time Management Dispositions Moderate the Mediation Model
5.2.4. Procrastination and Time Management
5.3. Limitations and Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Statista. Smartphone Mobile Network Subscriptions Worldwide 2016–2028. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/330695/number-of-smartphone-users-worldwide/ (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- Hussain, Z.; Wegmann, E.; Yang, H.; Montag, C. Social Networks Use Disorder and Associations with Depression and Anxiety Symptoms: A Systematic Review of Recent Research in China. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinci, T. Determination of Predictive Relationships between Problematic Smartphone Use, Self-Regulation, Academic Procrastination and Academic Stress through Modelling. Int. J. Progress. Educ. 2021, 17, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, P.A.; McCarthy, S. Antecedents and consequences of problematic smartphone use: A systematic literature review of an emerging research area. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2021, 114, 106414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Liu, R.D.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yang, X.; Sheng, X. Academic procrastination precedes problematic mobile phone use in Chinese adolescents: A longitudinal mediation model of distraction cognitions. Addict. Behav. 2021, 121, 106993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalbers, G.; vanden Abeele, M.M.; Hendrickson, A.T.; De Marez, L.; Keijsers, L. Caught in the moment: Are there person-specific associations between momentary procrastination and passively measured smartphone use? Mob. Media Commun. 2022, 10, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, A.; Liaquat, A.W.; Shahid, H. Mediating Effect of Academic Amotivation between Smartphone Addiction and Academic Procrastination among University Students. Online Media Soc. 2022, 3, 202–212. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, L.S.; Valentini, J.P.; Monteiro, T.H.; Costacurta, M.C.D.F.; Soares, L.O.N.; Telfar-Barnard, L.; Nunes, P.V. Problematic social media use and its relationship with depression or anxiety: A systematic review. Cyberpsychology Behav. Soc. Netw. 2022, 25, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Throuvala, M.A.; Pontes, H.M.; Tsaousis, I.; Griffiths, M.D.; Rennoldson, M.; Kuss, D.J. Exploring the Dimensions of Smartphone Distraction: Development, Validation, Measurement Invariance, and Latent Mean Differences of the Smartphone Distraction Scale (SDS). Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 642634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yan, Z.; Hussain, Z. The relationships between smartphone distraction, problematic smartphone use and mental health issues amongst a Chinese sample. Soc. Sci. J. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozgonjuk, D.; Kattago, M.; Täht, K. Social media use in lectures mediates the relationship between procrastination and problematic smartphone use. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 89, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Gao, H.; Xu, Y. The mediating and buffering effect of academic self-efficacy on the relationship between smartphone addiction and academic procrastination. Comput. Educ. 2020, 159, 104001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, R.; Li, L.; Ding, Y.; Hong, W.; Liu, R.D. How does mobile phone dependency impair academic engagement among Chinese left-behind children? Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020, 116, 105169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xu, X.; Zhu, L. Media multitasking and psychological wellbeing in Chinese adolescents: Time management as a moderator. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 53, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Gu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R. Smartphone addiction and depression, anxiety: The role of bedtime procrastination and self-control. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 293, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, J.; Qaisar, S.; Shah, Z.; Jalil, A. Attention or distraction? The impact of mobile phone on users’ psychological well-being. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 612127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billieux, J.; Maurage, P.; Lopez-Fernandez, O.; Kuss, D.J.; Griffiths, M.D. Can disordered mobile phone use be considered a behavioral addiction? An update on current evidence and a comprehensive model for future research. Curr. Addict. Rep. 2015, 2, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Asbury, K.; Griffiths, M.D. “A cancer in the minds of youth?” A qualitative study of problematic smartphone use among undergraduate students. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2021, 19, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhai, J.D.; Dvorak, R.D.; Levine, J.C.; Hall, B.J. Problematic smartphone use: A conceptual overview and systematic review of relations with anxiety and depression psychopathology. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 207, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oraison, H.; Nash-Dolby, O.; Wilson, B.; Malhotra, R. Smartphone distraction-addiction: Examining the relationship between psychosocial variables and patterns of use. Aust. J. Psychol. 2020, 72, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielberger, C.D. The nature and measurement of anxiety. In Anxiety: Current Trends in Theory and Research; Spielberger, C.D., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1972; pp. 23–49. [Google Scholar]
- Pekrun, R. The control-value theory of achievement emotions: Assumptions, corollaries, and implications for educational research and practice. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2006, 18, 315–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraw, G.; Wadkins, T.; Olafson, L. Doing the things we do: A grounded theory of academic procrastination. J. Educ. Psychol. 2007, 99, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzsche, B.A.; Young, B.R.; Hickson, K.C. Individual differences in academic procrastination tendency and writing success. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2003, 35, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klassen, R.M.; Ang, R.P.; Chong, W.H.; Krawchuk, L.L.; Huan, V.S.; Wong, I.Y.; Yeo, L.S. A cross-cultural study of adolescent procrastination. J. Res. Adolesc. 2009, 19, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soysa, C.K.; Weiss, A. Mediating perceived parenting styles–test anxiety relationships: Academic procrastination and maladaptive perfectionism. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2014, 34, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerdelen, S.; McCaffrey, A.; Klassen, R.M. Longitudinal examination of procrastination and anxiety, and their relation to self-efficacy for self-regulated learning: Latent growth curve modeling. Educ. Sci. Theory Pract. 2016, 16, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, A.; Polizzi, C.P.; Mattson, R.E. Mindfulness, procrastination, and anxiety: Assessing their interrelationships. Psychol. Conscious. Theory Res. Pract. 2023, 10, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Asbury, K.; Griffiths, M.D. An exploration of problematic smartphone use among Chinese university students: Associations with academic anxiety, academic procrastination, self-regulation and subjective wellbeing. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2019, 17, 596–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Academic procrastination and test anxiety: A cross-lagged panel analysis. J. Psychol. Couns. Sch. 2021, 31, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przepiorka, A.; Blachnio, A.; Cudo, A. Procrastination and problematic new media use: The mediating role of future anxiety. Curr. Psychol. 2023, 42, 5169–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintrich, P.R.; Smith, D.A.F.; Garcia, T.; Mckeachie, W.J. Reliability and predictive validity of the Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire (MSLQ). Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1993, 53, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintrich, P.R. Multiple goals, multiple pathways: The role of goal orientation in learning and achievement. J. Educ. Psychol. 2000, 92, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, Z. The compiling of adolescence time management disposition inventory. Acta Psychol. Sin. 2001, 33, 338–343. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Sun, P.; Wang, R.; Fang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, X. Moderating Role of Time Management Disposition to the Relation Between Stress and Anxiety. Chin. J. Clin. Psychol. 2011, 19, 660–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.S.; Li, J.; Kim, S.-Y. Structural Relationship among Mobile Phone Dependence, Self-Efficacy, Time Management Disposition, and Academic Procrastination in College Students. Iran. J. Public Health 2021, 50, 2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Xu, Y.; Yang, T.; Li, Z.; Dong, Y.; Chen, L.; Sun, X. The Mediating Roles of Time Management and Learning Strategic Approach in the Relationship Between Smartphone Addiction and Academic Procrastination. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2022, 15, 2639–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghiasvand, A.M.; Naderi, M.; Tafreshi, M.Z.; Ahmadi, F.; Hosseini, M. Relationship between time management skills and anxiety and academic motivation of nursing students in Tehran. Electron. Physician 2017, 9, 3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Yu, G. The development and application of an academic emotions questionnaire. Acta Psychol. Sin. 2007, 39, 852–860. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, L.J.; Rothblum, E.D. Academic procrastination: Frequency and cognitive-behavioral correlates. J. Couns. Psychol. 1984, 31, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X. The Effects of Temporal Discounting and Task Character on Academic Procrastination. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Research on the Relationship between Emotion Regulation and Learning Effect of Undergraduates Majoring in Tourism Management under the Tendency of Time Management. Master’s Thesis, Shenyang Normal University, Shenyang, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.N.; Moran, S.V. Why not procrastinate? Development and validation of a new active procrastination scale. J. Soc. Psychol. 2009, 149, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Fernandez, S.; Terrier, L. Procrastination, personality traits, and academic performance: When active and passive procrastination tell a different story. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2017, 108, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Mean | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Gender | 1.85 | 0.36 | - | |||||
| 2. Age | 21.25 | 2.04 | 0.01 | - | ||||
| 3. Smartphone distraction | 53.61 | 9.98 | 0.13 ** | 0.10 * | - | |||
| 4. Academic anxiety | 23.02 | 5.71 | 0.10 * | −0.07 | 0.40 *** | - | ||
| 5. Academic procrastination | 36.52 | 7.83 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.42 *** | 0.39 *** | - | |
| 6. Time management disposition | 77.05 | 11.16 | 0.00 | 0.07 | −0.07 | −0.03 | −0.23 *** | - |
| Predictors | Model 1 (Academic Anxiety) | Model 2 (Academic Procrastination) | Model 3 (Academic Anxiety) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | t | B | t | B | t | |
| Gender | 0.75 | 1.11 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.73 | 1.14 |
| Age | −0.30 | −2.57 | 0.06 | 0.36 | −0.32 | −2.77 ** |
| Smartphone distraction | 0.23 | 9.54 *** | 0.33 | 9.84 *** | 0.17 | 6.45 *** |
| Academic procrastination | 0.20 | 6.23 *** | ||||
| R2 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.24 | |||
| F | 33.08 *** | 33.53 *** | 36.49 *** | |||
| Predictors | R2 | F | B | t |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model (academic anxiety) | 0.26 | 23.02 *** | ||
| Gender | 0.66 | 1.03 | ||
| Age | −0.31 | −2.77 ** | ||
| Smartphone distraction | 0.47 | 3.06 ** | ||
| Academic procrastination | −0.40 | −2.05 * | ||
| Time management disposition | −0.05 | −0.48 | ||
| Smartphone distraction × Time management disposition | −0.004 | −2.01 * | ||
| Academic procrastination × Time management disposition | 0.008 | 3.19 ** |
| Time Management Disposition | Effect | SE | LLCI | ULCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M − 1SD (65.89) | 0.22 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.29 |
| M (77.05) | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.22 |
| M + 1SD (88.21) | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.19 |
| Time Management Disposition | Effect | BootSE | BootLLCI | BootULCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M − 1SD (65.89) | 0.03 | 0.02 | −0.01 | 0.07 |
| M (77.05) | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.09 |
| M + 1SD (88.21) | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Hussain, Z. Smartphone Distraction and Academic Anxiety: The Mediating Role of Academic Procrastination and the Moderating Role of Time Management Disposition. Behav. Sci. 2024, 14, 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14090820
Jin Y, Zhou W, Zhang Y, Yang Z, Hussain Z. Smartphone Distraction and Academic Anxiety: The Mediating Role of Academic Procrastination and the Moderating Role of Time Management Disposition. Behavioral Sciences. 2024; 14(9):820. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14090820
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Yuanting, Wanqi Zhou, Yueling Zhang, Zeyang Yang, and Zaheer Hussain. 2024. "Smartphone Distraction and Academic Anxiety: The Mediating Role of Academic Procrastination and the Moderating Role of Time Management Disposition" Behavioral Sciences 14, no. 9: 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14090820
APA StyleJin, Y., Zhou, W., Zhang, Y., Yang, Z., & Hussain, Z. (2024). Smartphone Distraction and Academic Anxiety: The Mediating Role of Academic Procrastination and the Moderating Role of Time Management Disposition. Behavioral Sciences, 14(9), 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14090820






