Nature-Based Therapeutic Intervention for Individuals with Post-Concussion Symptoms
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Clinical Guidelines
1.2. Enriched and Natural Environments
1.3. Attention Restoration
1.4. Pilot Study
1.5. Aim
2. Materials and Methods
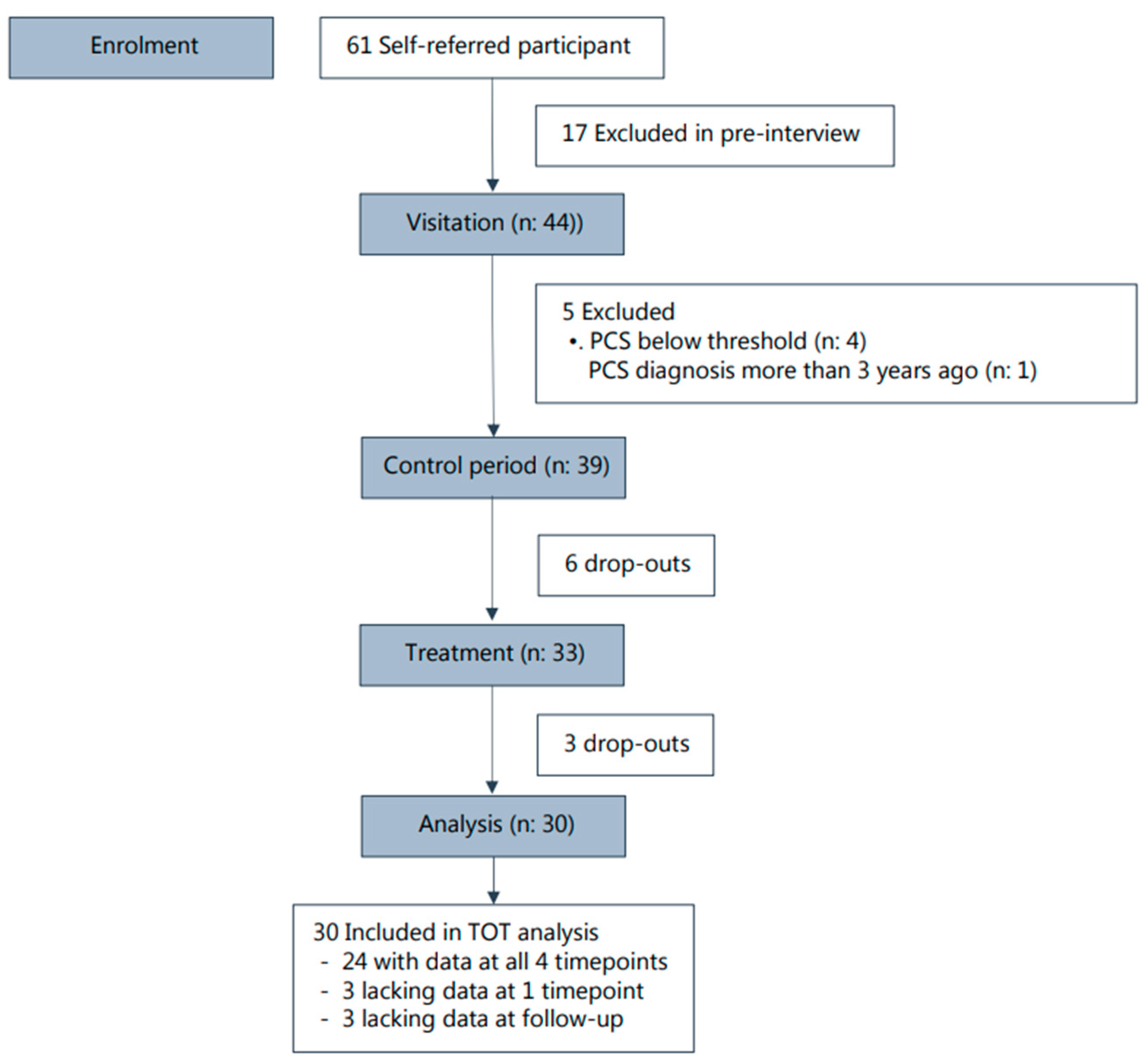
2.1. Trial Design and Sample Size
2.2. Recruitment
2.3. Inclusion
2.4. Nature-Based Intervention
2.4.1. The Therapy Garden Nacadia
2.4.2. The Therapeutic Concept
2.4.3. Structure and Content of the 10 Sessions
2.5. Data Collection
2.6. Primary Outcome Measure
2.7. Secondary Outcome Measures
2.8. Likert Scales on Session Level
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
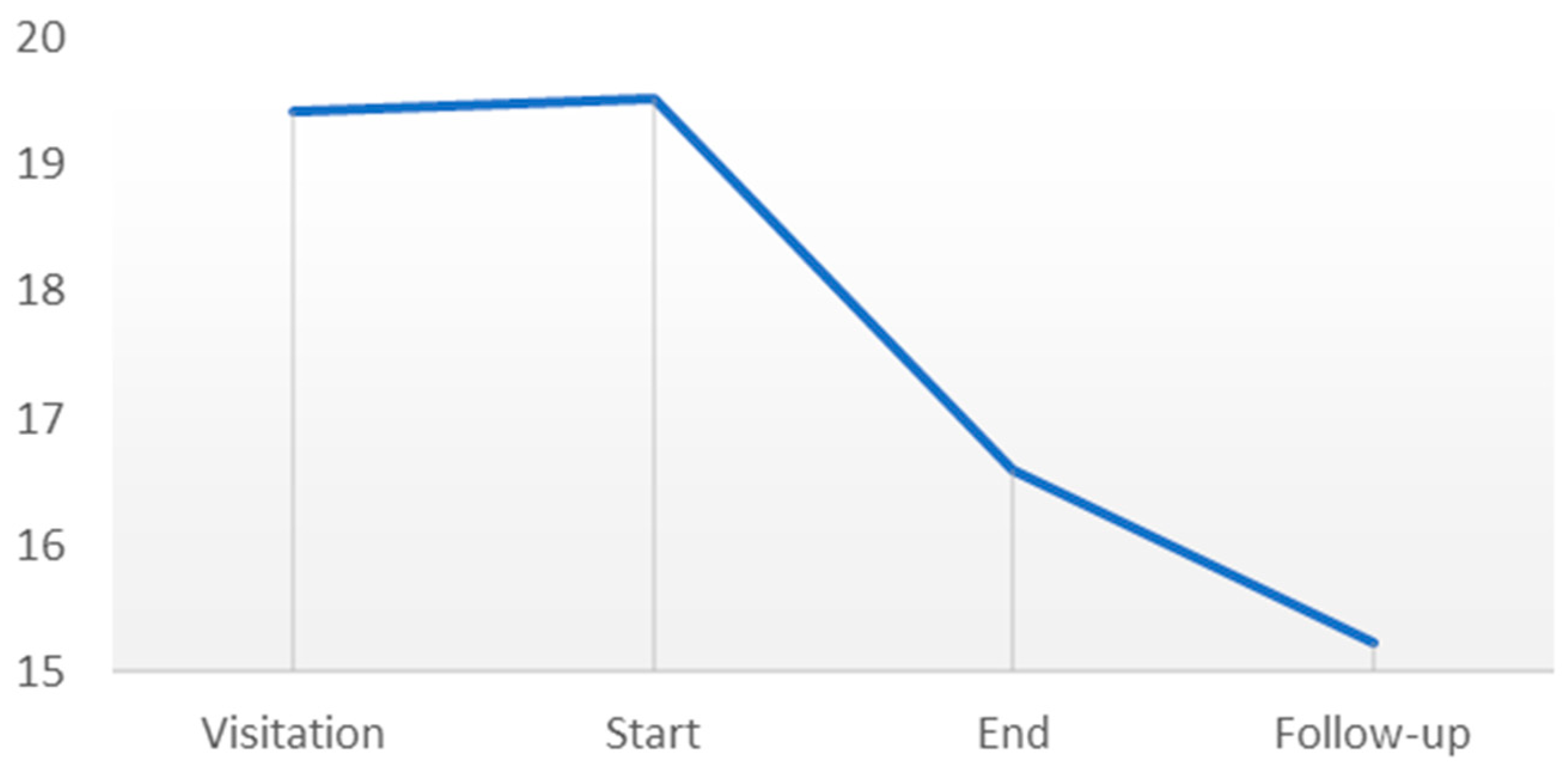
3.2. Primary Outcome: The Mental Fatigue Scale
3.3. Secondary Outcomes
3.4. Correlation between Primary and Secondary Outcomes
3.5. Likert Scale Outcomes from Single Sessions
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lefevre-Dognin, C.; Cogné, M.; Perdrieau, V.; Granger, A.; Heslot, C.; Azouvi, P. Definition and epidemiology of mild traumatic brain injury. Neurochirurgie 2021, 67, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyder, A.A.; Wunderlich, C.A.; Puvanachandra, P.; Gururaj, G.; Kobusingye, O.C. The impact of traumatic brain injuries: A global perspective. NeuroRehabilitation 2007, 22, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daugherty, J.; DePadilla, L.; Sarmiento, K.; Breiding, M.J. Self-Reported Lifetime Concussion Among Adults: Comparison of 3 Different Survey Questions. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2020, 35, E36–E143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, L.J.; Cassidy, J.D.; Peloso, P.; Borg, J.; von Holst, H.; Holm, L.; Paniak, C.; Pépin, M. Prognosis of mild traumatic brain injury: Results of the WHO Collaborating Centre Task Force on Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Rehabil. Med. 2004, 43, 84–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polinder, S.; Cnossen, M.C.; Ruben, G.L.; Real, R.; Covic, A.; Gorbunova, A.; Voormolen, D.C.; Master, C.L.; Haagsma, J.A.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; et al. A Multidimensional Approach to Post-concussion Symptoms in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. The ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders: Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Guidelines; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, L.M.; Warden, D.L. Post concussion syndrome. Int. Rev. Psychiatry 2003, 15, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, L.J.; Cassidy, J.D.; Cancelliere, C.; Côté, P.; Hincapié, C.A.; Kristman, V.L.; Holm, L.W.; Borg, J.; Nygren-de Boussard, C.; Hartvigsen, J. Systematic review of the prognosis after mild traumatic brain injury in adults: Cognitive, psychiatric, and mortality outcomes: Results of the International Collaboration on Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Prognosis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, S152–S173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palm, S.; Rönnbäck, L.; Johansson, B. Long-term mental fatigue after traumatic brain injury and impact on employment status. J. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 49, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langlois, J.A.; Rutland-Brown, W.; Wald, M.M. The epidemiology and impact of traumatic brain injury: A brief overview. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2006, 21, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiploylee, C.; Dufort, P.A.; Davis, H.S.; Wennberg, R.A.; Tartaglia, M.C.; Mikulis, D.; Hazrati, L.N.; Tator, C.H. Longitudinal study of post-concussion syndrome: Not everyone recovers. J. Neurotrauma 2016, 34, 1511–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, A.N.; Rytter, H.M. Vidensrapport om let Hovedtraume, Herunder Hjernerystelse—Voksne; Dansk Center for Hjernerystelse: København, Denmark, 2024. (In Danish) [Google Scholar]
- Rytter, H.M.; Graff, H.J.; Henriksen, H.K.; Aaen, N.; Hartvigsen, J.; Hoegh, M.; Nisted, I.; Næss-Schmidt, E.T.; Pedersen, L.L.; Schytz, H.W.; et al. Nonpharmacological Treatment of Persistent Post-concussion Symptoms in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis and Guideline Recommendation. JAMA 2021, 4, e2132221. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, S.; Bayley, M.; McCullagh, S.; Velikonja, D.; Berrigan, L.; Ouchterlony, D.; Weegar, K. Updated clinical practice guidelines for concussion/mild traumatic brain injury and persistent symptoms. Brain Inj. 2015, 29, 688–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, B.; Bjuhr, H.; Rönnbäck, L. Mindfulness based stress reduction improves long-term mental fatigue after stroke or traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2012, 26, 1621–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayegh, A.; Sandfor, D.; Carlson, A.J. Psychological approaches to treatment of post-concussion syndrome: A systematic review. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2010, 81, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, T.K.A.; Carey, L.M.; Nilsson, M. Motivation, mood and the right environment. In Stroke Rehabilitation; Carey, L.M., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, M.; Pekny, M.; Pekna, M. Modulation of neural plasticity as a basis for stroke rehabilitation. Stroke 2012, 43, 2819–2828. [Google Scholar]
- Vibholm, A.P.; Christensen, J.R.; Pallesen, H. Nature-based rehabilitation for adults with acquired brain injury: A scoping review. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2020, 30, 661–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, S. The restorative benefits of nature: Toward an integrative framework. J. Environ. Psychol. 1995, 16, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohly, H.; White, M.P.; Wheeler, B.W.; Bethel, A.; Ukoumunne, O.C.; Nikolaou, V.; Garside, R. Attention Restoration Theory: A systematic review of the attention restoration potential of exposure to natural environments. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2016, 19, 305–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stigsdotter, U.K. Nature, health and design. Alam Cipta 2015, 8, 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Corazon, S.S.; Olsen, L.J.; Olsen, A.M.; Sidenius, U. Nature-based therapy for people suffering from post-concussion syndrome—A pilot study. Health 2019, 11, 1501–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stigsdotter, U.K.; Corazon, S.S.; Sidenius, U.; Nyed, P.K.; Larsen, H.B.; Fjorback, L.O. Efficacy of nature-based therapy for individuals with stress-related illnesses: Randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Psychiatry 2018, 213, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, B.; Rönnbäck, L. Evaluation of the Mental Fatigue Scale and its relation to Cognitive and Emotional Functioning after Traumatic Brain Injury or Stroke. Int. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 2, 182. [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan, D.V.; Lecrubier, Y.; Sheehan, K.H.; Amorim, P.; Janavs, J.; Weiller, E.; Hergueta, T.; Baker, R.; Dunbar, G.C. The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (M.I.N.I.): The development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1998, 59 (Suppl. S20), 22–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stigsdotter, U.K. Nacadia healing forest garden, Hoersholm Arboretum, Copenhagen, Denmark. In Therapeutic Landscapes: An Evidence-Based Approach to Designing Healing Gardens and Restorative Outdoor Spaces; Marcus, C.C., Sachs, N.A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 198–205. [Google Scholar]
- Corazon, S.S.; Stigsdotter, U.K.; Jensen, A.G.C.; Nilsson, K. Development of the nature-based therapy concept for patients with stress-related illness at the Danish Healing Forest Garden Nacadia. J. Ther. Hortic. 2010, 20, 34–51. [Google Scholar]
- Corazon, S.S.; Poulsen, D.V.; Sidenius, U.; Gramkow, M.C.; Djernis, D.; Stigsdotter, U.K. Konceptmanual for Naturbaseret Terapi; Institut for Geovidenskab & Naturforvaltnng: Frederiksberg, Denmark, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Corazon, S.S.; Schilbah, T.S.S.; Stigsdotter, U.K. Developing the therapeutic potential of embodied cognition and metaphors in nature-based therapy: Lessons from theory to practice. J. Adventure Educ. Outdoor Learn. 2011, 11, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M. Nature and Therapy. Understanding Counselling Fand Psychotherapy in Outdoor Spaces; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Corazon, S.S.; Kæreby, N.; Olsen, L.J.; Poulsen, D.V.; Bekke-Hansen, S.; Sidenius, U. Naturbaseret Manual til Mennesker med Senfølger efter Hjernerystelse; Institut for Geovidenskab & Naturforvaltning: Frederiksberg, Denmark, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Johannson, B.; Starmark, A.; Berglund, P.; Rödholm, M.; Rönnbäck, L. A self-assessment questionnaire for mental fatigue and related symptoms after neurological disorders and injuries. Brain Inj. 2010, 24, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, N.; Crawford, S.; Wenden, F.; Moss, N.; Wade, D.J. The Rivermead post-concussion symptoms questionnaire: A measure of symptoms commonly experienced after head injury and its reliability. J. Neurol. 1995, 242, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennant, R.; Hiller, L.; Fishwick, R.; Platt, S.; Joseph, S.; Weich, S.; Parkinson, J.; Secker, J.; Stewart-Brown, S. The Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Wellbeing Scale (WEMWBS): Development and UK validation. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2007, 5, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart-Brown, S.L.; Platt, S.; Tennant, A.; Maheswaran, H.; Parkinson, J.; Weich, S.; Tennant, R.; Taggart, F.; Clarke, A. The Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Wellbeing Scale (WEMWBS): A valid and reliable tool for measuring mental wellbeing in diverse populations and projects. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2011, 65 (Suppl. S2), A38–A39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Steinbuechel, N.; Wilson, L.; Gibbons, H.; Hawthorne, G.; Höfer, S.; Schmidt, S.; Bullinger, M.; Maas, A.; Neugebauer, E.; Powell, J.; et al. Quality of Life after Brain Injury (QOLIBRI): Scale validity and correlates of quality of life. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Steinbuechel, N.; Wilson, L.; Gibbons, H.; Muehlan, H.; Schmidt, H.; Schmidt, S.; Sasse, N.; Koskinen, S.; Sarajuuri, J.; Hofer, S.; et al. QOLIBRI Overall Scale: A brief index of health-related quality of life after traumatic brain injury. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2012, 83, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gignac, G.E.; Szodorai, E.T. Effect size guidelines for individual differences researchers. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2016, 102, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, L.; Marsden-Loftus, I.; Koskinen, S.; Bakx, W.; Bullinger, M.; Formisano, R.; Maas, A.; Neugebauer, E.; Powell, J.; Sarajuuri, J.; et al. Interpreting Quality of Life after Brain Injury Scores: Cross-Walk with the Short Form-36. J. Neurotrauma 2017, 1, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gender: Female/Male, n | 23/7 |
| Age, n | |
| 20–29 | 2 |
| 30–39 | 4 |
| 40–49 | 7 |
| 50–59 | 10 |
| 60–69 | 3 |
| 70–79 | 3 |
| Education, n | |
| Primary/secondary school | 2 |
| Vocational training | 3 |
| University bachelor’s degree | 12 |
| University master’s degree | 11 |
| Employment status n | |
| Full-time employed | 2 |
| Reduced time/Part-time sick leave | 5 |
| Full-time sick leave | 7 |
| Unemployed | 1 |
| Student | 2 |
| Retired | 4 |
| Municipal subsidized employment | 7 |
| (job trial, internship, flex job) | |
| Concussion incident | |
| 2019 | 3 |
| 2020 | 10 |
| 2021 | 10 |
| 2022 | 5 |
| 2023 | 2 |
| Do you enjoy being in nature? | |
| Very much | 29 |
| To some extent | 0 |
| Somewhat | 0 |
| To a low extent | 0 |
| Not really | 0 |
| How often do you spend time in nature? | |
| Every day | 19 |
| A few times a week | 8 |
| Once a week | 2 |
| Once a month or more | 0 |
| Rarely | 0 |
| To what degree do you consider the time spent in nature to benefit… | |
| Your physical health? | |
| Very much | |
| To some extent | 19 |
| Somewhat | 10 |
| To a low extent | 0 |
| Not really | 0 |
| Your mental health | |
| Very much | 25 |
| To some extent | 4 |
| Somewhat | 0 |
| To a low extent | 0 |
| Not really | 0 |
| 0 |
| Data Points | Mean | SD | p Value * | Cohen’s d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visitation | 19.42 | 3.21 | ||
| Control period | ||||
| Start | 19.52 | 4.41 | 0.525 | NA |
| Intervention period | ||||
| End | 16.59 | 6.06 | 0.005 | 0.553 |
| Follow-up | 15.83 | 6.71 | 0.544 | NA |
| Data Points | Mean | SD | p Value * | Cohen’s d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visitation | 45.00 | 6.55 | ||
| Control period | ||||
| Start | 43.62 | 7.54 | 0.094 | NA |
| Intervention period | ||||
| End | 47.00 | 7.43 | 0.006 | 0.452 |
| Follow up | 47.84 | 8.98 | 0.676 | NA |
| Data Points | Value% | SD | p Value * | Cohen’s d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| visitation | 39.74 | 18.68 | ||
| Control period | ||||
| Start | 41.24 | 20.42 | 0.958 | NA |
| Intervention period | ||||
| End | 48.56 | 22.67 | 0.012 | 0.339 |
| Follow up | 49.36 | 26.21 | 0.879 | NA |
| Data Points | Mean | SD | p Value | Pearsons r |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level of mental fatigue | ||||
| Pre-session | 4.60 | 1.84 | ||
| Post-session | 5.12 | 2.02 | 0.000 | 0.351 |
| Level of well-being | ||||
| Pre-session | 5.08 | 1.81 | ||
| Post-session | 6.01 | 1.95 | 9.029 × 10−11 | 0.564 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corazon, S.S.; Olsen, L.J.; Kæreby, N.; Poulsen, D.V.; Sidenius, U.; Bekke-Hansen, S.; Marschner, L. Nature-Based Therapeutic Intervention for Individuals with Post-Concussion Symptoms. Behav. Sci. 2024, 14, 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14070594
Corazon SS, Olsen LJ, Kæreby N, Poulsen DV, Sidenius U, Bekke-Hansen S, Marschner L. Nature-Based Therapeutic Intervention for Individuals with Post-Concussion Symptoms. Behavioral Sciences. 2024; 14(7):594. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14070594
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorazon, Sus Sola, Lisbeth Jul Olsen, Natasha Kæreby, Dorthe Varning Poulsen, Ulrik Sidenius, Stine Bekke-Hansen, and Linda Marschner. 2024. "Nature-Based Therapeutic Intervention for Individuals with Post-Concussion Symptoms" Behavioral Sciences 14, no. 7: 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14070594
APA StyleCorazon, S. S., Olsen, L. J., Kæreby, N., Poulsen, D. V., Sidenius, U., Bekke-Hansen, S., & Marschner, L. (2024). Nature-Based Therapeutic Intervention for Individuals with Post-Concussion Symptoms. Behavioral Sciences, 14(7), 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14070594








