Social Undermining and Promotive Voice: The Moderating Effects of Procedural Justice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Hypothesis Development
2.1. Social Undermining
2.2. Employee Voice
2.3. Supervisor Social Undermining and Employee Promotive Voice
2.4. Moderating Role of Procedural Justice
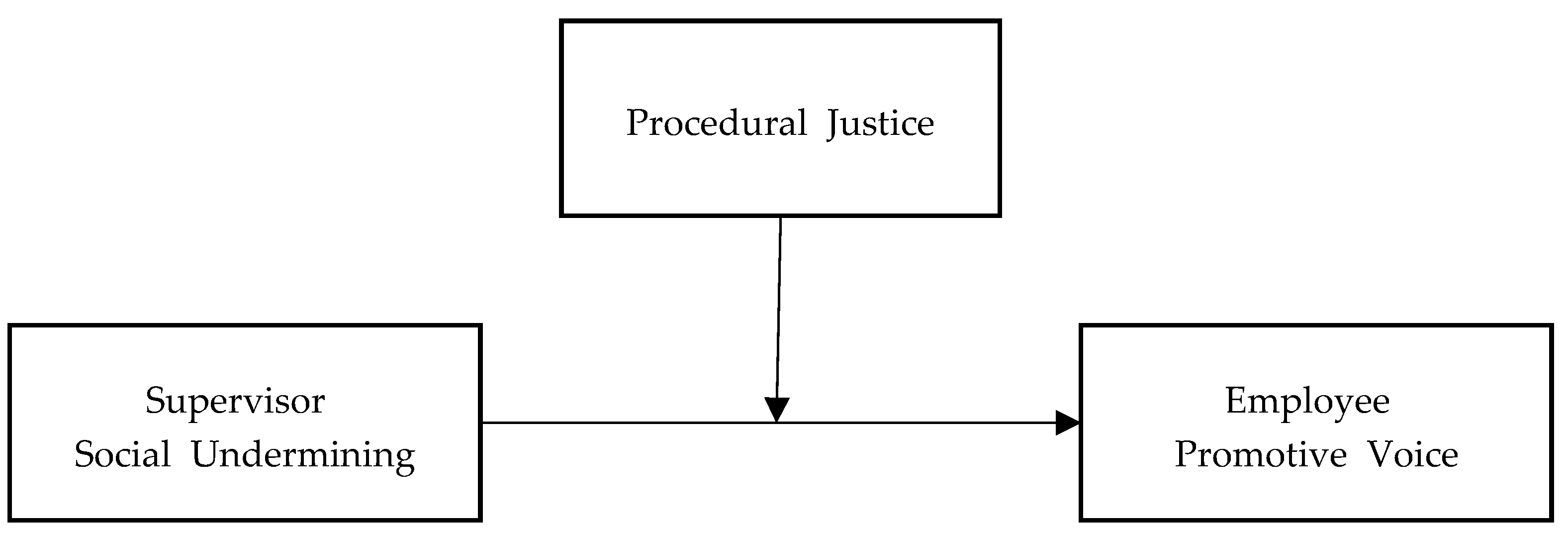
3. Methods
3.1. Sample and Procedure
3.2. Measures
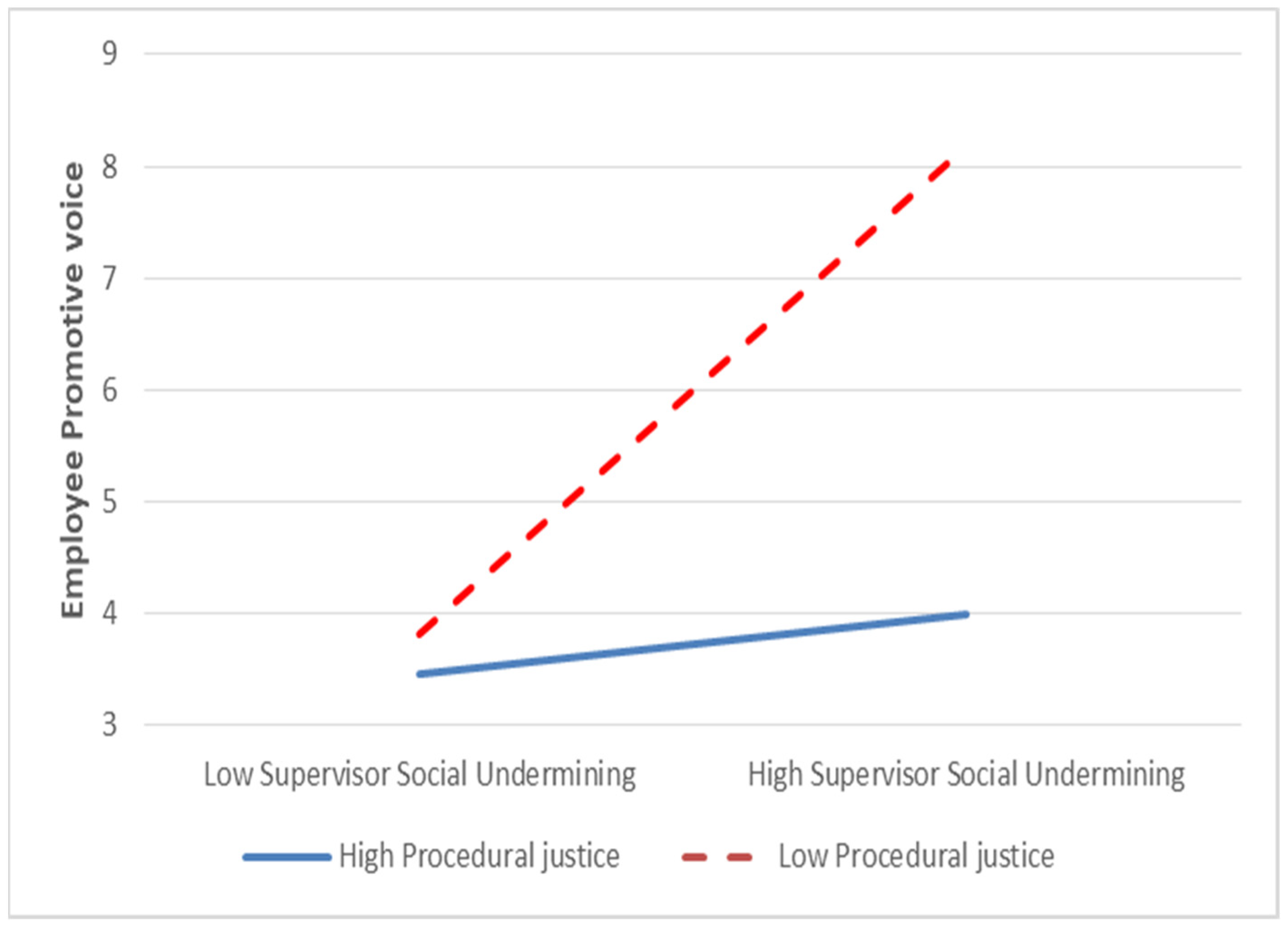
4. Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Theoretical Discussion
5.2. Managerial Implications
5.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shin, D.; Woodwark, M.J.; Konrad, A.M.; Jung, Y. Innovation strategy, voice practices, employee voice participation, and organizational innovation. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 147, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choi, D.; Cheong, M. Leader Boundary-Spanning Behavior and Employee Voice Behavior: The Job Demands–Resources Perspective. Behav. Sci. 2023, 13, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Van de Vliert, E.; Van der Vegt, G. Breaking the silence culture: Stimulation of participation and employee opinion withholding cross-nationally. Manag. Organ. Rev. 2005, 1, 459–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyne, L.; Ang, S.; Botero, I.C. Conceptualizing employee silence and employee voice as multidimensional constructs. J. Manag. Stud. 2003, 40, 1359–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.J.; Johnson, R.E. A suggestion to improve a day keeps your depletion away: Examining promotive and prohibitive voice behaviors within a regulatory focus and ego depletion framework. J. Appl. Psychol. 2015, 100, 1381–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Farh, C.I.C.; Farh, J.-L. Psychological antecedents of promotive and prohibitive voice: A two wave examination. Acad. Manag. J. 2012, 55, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Hou, M. The multilevel influence of supervisor helping behavior on employee voice behavior: A moderated mediation model. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 955288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detert, J.R.; Treviño, L.K. Speaking up to higher-ups: How supervisors and skip-level leaders influence employee voice. Organ. Sci. 2010, 21, 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedahanov, A.T.; Fayzullaev, A.K.U.; Abdurazzakov, O.S. Supervisor incivility and employee voice: The roles of cognitive reappraisal and psychological distress. Leadersh. Organ. Dev. J. 2022, 43, 689–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, H.; Shah, S.M.M.; Umrani, W.A.; Syed, J.; Afshan, G. Employee state paranoia: Linking abusive supervision with employee voice behavior. Leadersh. Organ. Dev. J. 2021, 42, 1053–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Dedahanov, A.T.; Fayzullaev, A.K.U.; Abdurazzakov, O.S. Abusive supervision and employee voice: The roles of positive reappraisal and employee cynicism. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 927–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.E.; Chen, W.X.Y.; Huang, J. Supervisor incivility and employee silence: Does Chinese traditionality matter. Int. J. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2018, 9, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-F.; Tian, Y.-Z. Influence of workplace ostracism on employee voice behavior. Am. J. Math. Manag. Sci. 2016, 35, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sun, M.; Guan, Y.-W.; Liu, C.-Y.; Ren, B.; Yang, Q. How leadership ostracism influences public servants’ promotive voice: Public service motivation as a moderator. Soc. Behav. Personal. 2023, 51, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, M.L.; Bowler, W.M. Voice climate, supervisor undermining, and work outcomes: A group-level examination. J. Manag. 2015, 41, 841–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.S.; Yoon, H.H. The effects of social undermining on employee voice and silence and on organizational deviant behaviors in the hotel industry. J. Serv. Theory Pract. 2019, 29, 213–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.K.; Ganster, D.C.; Pagon, M. Social undermining in the workplace. Acad. Manag. J. 2002, 45, 331–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; DiRenzo, M.S.; Xu, M.; Duan, Y. When do emotionally exhausted employees speak up? Exploring the potential curvilinear relationship between emotional exhaustion and voice. J. Organ. Behav. 2014, 35, 1018–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.; Shi, J. The voice link: A moderated mediation model of how ethical leadership affects individual task performance. J. Bus. Ethics 2016, 152, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, J.B.; Barnett, T.; Hester, K.; Relyea, C.; Frey, L. An exploratory examination of voice behavior from an impression management perspective. J. Manag. Issues 2007, 19, 134–151. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/40601197 (accessed on 11 April 2024).
- Hsiung, H.H. Authentic leadership and employee voice behavior: A multi-level psychological process. J. Bus. Ethics 2012, 107, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangirala, S.; Ramanujam, R. Employee silence on critical work issues: The cross level effects of procedural justice climate. Pers. Psychol. 2008, 61, 37–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colquitt, J.A. Does the justice of the one interact with the justice of the many? Reactions to procedural justice in teams. J. Appl. Psychol. 2004, 89, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobfoll, S.E. Social and psychological resources and adaptation. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 2002, 6, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.W.H.; Feldman, D.C. Employee voice behavior: A meta-analytic test of the conservation of resources framework. J. Organ. Behav. 2012, 33, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershcovis, M.S. “Incivility, social undermining, bullying...oh my!”: A call to reconcile constructs within workplace aggression research. J. Occup. Health Psychol. 2011, 32, 499–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenbaum, R.L.; Mawritz, M.B.; Eissa, G. Bottom-line mentality as an antecedent of social undermining and the moderating roles of core self-evaluations and conscientiousness. J. Appl. Psychol. 2012, 97, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuman, J.; Baron, R. Aggression in the workplace. In Antisocial Behavior in Organizations; Giacalone, R., Greenberg, J., Eds.; Sage: London, UK, 1997; pp. 37–67. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Zhao, Z. Social undermining and interpersonal rumination among employees: The mediating role of being the subject of envy and the moderating role of social support. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, M.K.; Ganster, D.C.; Shaw, J.D.; Johnson, J.L.; Pagon, M. The social context of undermining behavior at work. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 2006, 101, 105–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.K.; Scott, K.L.; Shaw, J.D.; Tepper, B.J.; Aquino, K. A Social Context Model of Envy and Social Undermining. Acad. Manag. J. 2012, 55, 643–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyne, L.; LePine, J.A. Helping and voice extra-role behaviors: Evidence of construct and predictive validity. Acad. Manag. J. 1998, 41, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyne, L.; Cummings, L.L.; McLean Parks, J. Extrarole behaviors: In pursuit of construct and definitional clarity (a bridge over muddied waters). Res. Organ. Behav. 1995, 17, 215–285. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, E.W. Employee voice behavior: Integration and directions for future research. Acad. Manag. Ann. 2011, 5, 373–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.-K.; Ravlin, E.C.; Klaas, B.S.; Ployhart, R.E.; Buchan, N.R. When do high-context communicators speak up? Exploring contextual communication orientation and employee voice. J. Appl. Psychol. 2016, 101, 1498–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, E.W. Employee voice and silence: Taking stock a decade later. Annu. Rev. Organ. Psychol. Organ. Behav. 2023, 10, 79–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedahanov, A.T.; Rhee, C.; Yoon, J. Organizational structure and innovation performance: Is employee innovative behavior a missing link? Career Dev. Int. 2017, 22, 334–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detert, J.R.; Burris, E.R. Leadership behavior and employee voice: Is the door really open? Acad. Manag. J. 2007, 50, 869–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burris, E.R.; Detert, J.R.; Chiaburu, D.S. Quitting before leaving: The mediating effects of psychological attachment and detachment on voice. J. Appl. Psychol. 2008, 93, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blau, P.M. Exchange and Power in Social Life; Routledge: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberger, R.; Cotterell, N.; Marvel, J. Reciprocation ideology. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1987, 53, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilies, R.; Nahrgang, J.D.; Morgeson, F.P. Leader-member exchange and citizenship behaviors: A meta-analysis. J. Appl. Psychol. 2007, 92, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Paine, J.B.; Bachrach, D.G. Organizational citizenship behaviors: A critical review of the theoretical and empirical literature and suggestions for future research. J. Manag. 2000, 26, 513–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kim, E.; Bhave, D.P.; Duffy, M.K. Why victims of undermining at work become perpetrators of undermining: An integrative model. J. Appl. Psychol. 2016, 101, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.; Frankwick, G.L. Exploring the impact of social undermining on salesperson deviance: An integrated model. J. Pers. Sell. Sales Manag. 2013, 33, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepper, B.J.; Carr, J.C.; Breaux, D.M.; Geider, S.; Hu, C.; Wie, H. Abusive supervision, intentions to quit, and employees’ workplace deviance: A power/dependence analysis. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 2009, 109, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zellars, K.L.; Tepper, B.J.; Duffy, M.K. Abusive supervision and subordinates’ organizational citizenship behavior. J. Appl. Psychol. 2002, 87, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leventhal, G.S. What should be done with equity theory? New approaches to the study of fairness in social relationships. In Social Exchange: Advances in Theory and Research; Gergen, K., Greenberg, M., Willis, R., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 27–55. [Google Scholar]
- Dietz, J.; Robinson, S.L.; Folger, R.; Baron, R.A.; Schulz, M. The impact of community violence and an organization’s procedural justice climate on workplace aggression. Acad. Manag. J. 2003, 46, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liao, H.; Rupp, D. The impact of justice climate and justice orientation on work outcomes: A cross-level multifoci framework. J. Appl. Psychol. 2005, 90, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinder, C.C.; Harlos, K.P. Employee silence: Quiescence and acquiescence as responses to perceived injustice. Res. Pers. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2001, 20, 331–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, T.R.; Lind, E.A. A relational model of authority in groups. Adv. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 1992, 25, 115–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.Y.; Barron, K. Employee voice behavior revisited: Its forms and antecedents. Manag. Res. Rev. 2016, 39, 1720–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lou, M.; Guan, H. How and when perceived leader narcissism impacts employee voice behavior: A social exchange perspective. J. Manag. Organ. 2022, 28, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, B.; Shafique, I.; Kalyar, M.N. A moderated mediation model of the association between coworker social undermining and knowledge hiding. VINE J. Inform. Knowl. Manag. Syst. 2022, 52, 763–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobfoll, S.E. Conservation of resources: A new attempt at conceptualizing stress. Am. Psychol. 1989, 44, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luria, G.; Gal, I.; Yagil, D. Employees’ willingness to report service complaints. J. Serv. Res. 2009, 12, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, K.v.D.; Vermunt, R.; Wilke, H.A.M. Procedural and distributive justice: What is fair depends more on what comes first than on what comes next. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1997, 72, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bos, K.; Lind, E.A.; Wilke, H.A. The psychology of procedural and distributive justice viewed from the perspective of fairness heuristic theory. In Justice in the Workplace; Cropanzano, R., Ed.; Erlbaum: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2001; Volume 2, pp. 49–66. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, M.S.; Bernerth, J.B.; Walter, F.; Holt, D.T. Organizational justice and individuals’ withdrawal: Unlocking the influence of emotional exhaustion. J. Manag. Stud. 2010, 47, 367–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-J.; Lu, C.-Q.; Siu, O.-L. Job insecurity and job performance: The moderating role of organizational justice and the mediating role of work engagement. J. Appl. Psychol. 2015, 100, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, S.E.; Kraimer, M.L.; Crant, J.M. What do proactive people do? A longitudinal model linking proactive personality and career success. Pers. Psychol. 2001, 54, 845–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, E.L.; Gellatly, I.R.; Feeney, J.R.; Inness, M. Social Undermining and Three Forms of Organizational Commitment. J. Personal. Psychol. 2022, 22, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; May, D.R.; Schwoerer, C.E.; Deeg, M. “Called” to speak out: Employee career calling and voice behavior. J. Career Dev. 2023, 50, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brislin, R. Understanding Culture’s Influence on Behavior; Harcourt Brace College Publishers: Fort Worth, TX, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Colquitt, J.A. On the dimensionality of organizational justice: A construct validation of a measure. J. Appl. Psychol. 2001, 86, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, B.M. Structural Equation Modeling with AMOS; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.-Y.; Podsakoff, N.P. Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement errors. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunnally, J.C. Psychometric Theory; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Afshan, G.; Kashif, M.; Sattayawaksakul, D.; Cheewaprakobkit, P.; Wijenayake, S. Abusive supervision, supervisor undermining, and turnover intentions: Mediation of quiescent silence and desire to seek revenge among Thai banking frontliners. Manag. Res. Rev. 2022, 45, 1479–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Malik, O.F.; Shahzad, A. Social undermining and employee creativity: The mediating role of interpersonal distrust and knowledge hiding. Behav. Sci. 2022, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Huang, W. Interactional justice and employee silence: The roles of procedural justice and affect. Soc. Behav. Personal. 2016, 44, 837–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouichou, S.I.; Wang, L.; Feroz, H.M.B. How corporate social responsibility perceptions affect employees’ positive behavior in the hospitality industry: Moderating role of responsible leadership. Int. Rev. Public Nonproft Mark. 2022, 19, 413–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, G.; Wyland, R.; Gupta, R. Supervisor to coworker social undermining: The moderating roles of bottom-line mentality and self-efficacy. J. Manag. Organ. 2020, 26, 756–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Mean | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Gender | 0.713 | 0.454 | 1 | ||||||
| 2. Age | 2.287 | 0.734 | 0.091 | 1 | |||||
| 3. Education level | 2.078 | 0.623 | −0.044 | 0.429 ** | 1 | ||||
| 4. Tenure | 3.252 | 1.626 | 0.039 | 0.497 ** | 0.067 | 1 | |||
| 5. Supervisor Social Undermining | 1.667 | 0.799 | −0.187 * | 0.049 | 0.109 | 0.055 | 1 | ||
| 6. Procedural Justice | 2.628 | 0.851 | 0.028 | 0.095 | 0.026 | 0.176 | −0.250 ** | 1 | |
| 7. Employee Promotive Voice | 3.706 | 0.854 | 0.151 | 0.060 | 0.063 | 0.000 | −0.362 ** | 0.283 ** | 1 |
| AVE | 0.610 | 0.562 | 0.651 | ||||||
| CR | 0.933 | 0.774 | 0.903 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.152 | 0.086 | 0.092 | 0.063 |
| Age | 0.036 | 0.034 | 0.034 | 0.009 |
| Education level | 0.056 | 0.092 | 0.083 | 0.081 |
| Tenure | −0.028 | −0.007 | −0.047 | −0.004 |
| Supervisor social undermining | −0.357 *** | −0.301 *** | −0.218 * | |
| Procedural justice | 0.208 * | 0.244 ** | ||
| interaction: Super. Soc. Under. X Proced. Justice | 0.232 ** | |||
| R2 | 0.029 | 0.150 | 0.189 | 0.233 |
| Adjusted R2 | −0.007 | 0.111 | 0.144 | 0.183 |
| Change in R2 | 0.029 | 0.121 | 0.039 | 0.044 |
| F | 0.813 | 3.853 | 4.199 | 4.637 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fayzullaev, A.K.u.; Shin, S.Y. Social Undermining and Promotive Voice: The Moderating Effects of Procedural Justice. Behav. Sci. 2024, 14, 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14060447
Fayzullaev AKu, Shin SY. Social Undermining and Promotive Voice: The Moderating Effects of Procedural Justice. Behavioral Sciences. 2024; 14(6):447. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14060447
Chicago/Turabian StyleFayzullaev, Abdulkhamid Komil ugli, and Soo Young Shin. 2024. "Social Undermining and Promotive Voice: The Moderating Effects of Procedural Justice" Behavioral Sciences 14, no. 6: 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14060447
APA StyleFayzullaev, A. K. u., & Shin, S. Y. (2024). Social Undermining and Promotive Voice: The Moderating Effects of Procedural Justice. Behavioral Sciences, 14(6), 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14060447








