Parental Educational Expectations and Academic Achievement of Left-Behind Children in China: The Mediating Role of Parental Involvement
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Parents’ Educational Expectations and Parental Involvement
1.2. Parents’ Educational Expectations and Children’s Academic Performance
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research and Analysis Methods
2.2. Sample Selection
2.3. Measurements
2.3.1. Parental Educational Expectations
2.3.2. Parental Education Involvement
2.3.3. Academic Performances
3. Results
3.1. Difference Analysis of Left-Behind Children
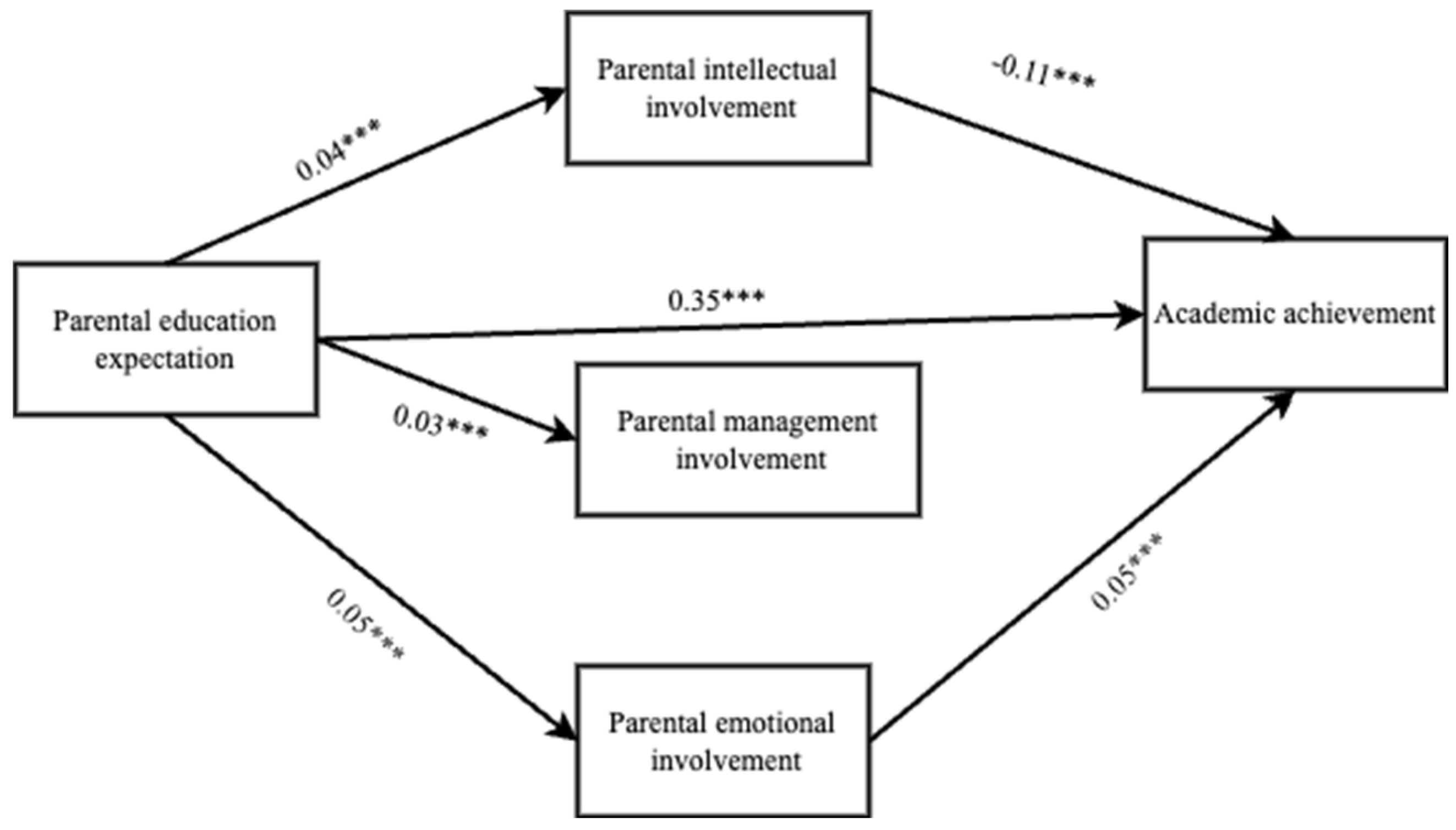
3.2. Mediating Roles of Parental Intellectual, Management and Emotional Involvement
3.3. Influence of Parents’ Involvement on the Academic Achievement of Left-Behind Children
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. The Practical Implications and Future Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. List of Survey Items
| Variables | Question of Investigation | |
| parents’ educational expectations | What are your parents’ educational expectations for you? | |
| Types of left-behind children | Are there any immediate family members who are not currently living with you at home? | |
| Parental education involvement | Parental intellectual involvement | Last week, did your parents urge you to study? “Check your homework”, “guide your homework”. |
| Parental management involvement | Are your parents strict with you about the following things? Homework, tests, performance in school, going to school every day, what time you come home every day, who you are friends with, how you dress, how much time you spend online, how much time you watch TV. | |
| Parental emotional involvement | “How often do your parents discuss the following with you”—what’s going on at school, your relationship with your friends, your relationship with your teachers, your mind, your mind or troubles. | |
| Academic achievement | Students’ midterm scores for the fall 2013 semester | |
References
- Chan, Y.Y.; Li, J. An early look at parental expectation towards early childhood education among Pakistani parents in Hong Kong: The role of culture and acculturation. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020, 119, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Elliott, W.; Wang, K.; Zhang, A.; Zheng, H. Examining parental educational expectations in one of the oldest children’s savings account programs in the country: The Harold Alfond College Challenge. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020, 108, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chiu, S.W.K.; Zhu, J.; So, W.W.M. Maintaining secondary school students’ STEM career aspirations: The role of perceived parental expectations, self-efficacy, and cultural capital. Int. J. Sci. Educ. 2022, 44, 434–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Yang, K. The Left-behind children in rural China. Popul. Res. 2008, 32, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Fellmeth, G.; Rose-Clarke, K.; Zhao, C.; Busert, L.K.; Zheng, Y.; Massazza, A.; Sonmez, H.; Eder, B.; Blewitt, A.; Lertgrai, W.; et al. Health impacts of parental migration on left-behind children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2018, 392, 2567–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, P.; Wang, L. China boom leaves children behind. Nature 2016, 529, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, M.; Zang, L.; Zhang, H. The Effects of Parental Absence on Children Development: Evidence from Left-Behind Children in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Lin, L.; Lu, J.; Cai, J.; Xu, J.; Zhou, X. Mental health and substance use in urban left-behind children in China: A growing problem. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020, 116, 105135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuang, M.; Yiqing, W.; Ling, J.; Guanzhen, O.; Jing, G.; Zhiyong, Q.; Xiaohua, W. Relationship between parent–child attachment and depression among migrant children and left-behind children in China. Public Health 2022, 204, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Zhao, C.; Dou, Y.; Duan, X.; Shi, H.; Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J. Caregivers’ depressive symptoms and social–emotional development of left-behind children under 3 years old in poor rural China: The mediating role of home environment. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020, 116, 105109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Chen, B. Parental migration and non-cognitive abilities of left-behind children in rural China: Causal effects by an instrumental variable approach. Child Abus. Negl. 2022, 123, 105389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Oubibi, M.; Liang, A.; Zhou, Y. Parents’ Educational Anxiety Under the “Double Reduction” Policy Based on the Family and Students’ Personal Factors. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2022, 15, 2067–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, R.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, K. Education fever in China: Children’s academic performance and parents’ life satisfaction. J. Happiness Stud. Interdiscip. Forum Subj. Well-Being 2021, 22, 927–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canelo, E. Perceptions of animal assisted reading and its results reported by involved children, parents and teachers of a Portuguese elementary school. Hum.-Anim. Interact. Bull. 2020, 8, 92–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.; Son, H.; Ham, K.A. Understanding the experiences of mothers with academic socialization in South Korea: A phenomenological approach. J. Child Fam. Stud. 2023, 32, 1962–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dockery, A.M.; Koshy, P.; Li, I.W. Parental expectations of children’s higher education participation in Australia. Br. Educ. Res. J. 2022, 48, 617–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Huang, J.; Wu, S.; Jin, M.; Kim, Y.; Henrichsen, C. Family assets, parental expectation, and child educational achievement in china: A validation of mediation analyses. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020, 112, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Cai, Z.; Wu, J. What Influences the Self-Educational Expectations of China’s Migrant Children in the Post-Pandemic Era. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbins, V.; Otero, G. Determinants of parental involvement in primary school: Evidence from Chile. Educ. Rev. 2020, 72, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hascoët, M.; Giaconi, V.; Jamain, L. Family socioeconomic status and parental expectations affect mathematics achievement in a national sample of Chilean students. Int. J. Behav. Dev. 2021, 45, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbins, V.; Otero, G. Parental involvement and low-SES children’s academic achievement in early elementary school: New evidence from Chile. Educ. Stud. 2020, 46, 548–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmerechts, K.; Kavadias, D.; Boone, S. The effects of neighborhood and parental educational expectations on teacher judgments of children in the fifth and sixth grades of primary school. Urban Educ. 2022, 57, 842–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yeh, T.; Liu, H.; Lee, T. Parental experiences of educational supports offered during their child’s cancer treatment. Child Care Health Dev. 2022, 48, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonk, L.; Gijselaers, H.J.M.; Ritzen, H.; Brand-Gruwel, S. A review of the relationship between parental involvement indicators and academic achievement. Educ. Res. Rev. 2018, 24, 10–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilder, S. Effects of parental involvement on academic achievement: A meta-synthesis. Educ. Rev. 2014, 66, 377–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinquart, M.; Ebeling, M. Parental Educational Expectations and Academic Achievement in Children and Adolescents—A Meta-analysis. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2020, 32, 463–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Chen, M. Parental Involvement and Students’ Academic Achievement: A Meta-Analysis. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2001, 13, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benner, A.D.; Fernandez, C.C.; Hou, Y.; Gonzalez, C.S. Parent and teacher educational expectations and adolescents’ academic performance: Mechanisms of influence. J. Community Psychol. 2021, 49, 2679–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silinskas, G.; Niemi, P.; Lerkkanen, M.-K.; Nurmi, J.-E. Children’s poor academic performance evokes parental homework assistance—But does it help? Int. J. Behav. Dev. 2013, 37, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froiland, J.M.; Peterson, A.; Davison, M.L. The long-term effects of early parent involvement and parent expectation in the USA. Sch. Psychol. Int. 2018, 31, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patall, A.; Cooper, H.; Robinson, J.C. Parent involvement in homework: A research synthesis. Rev. Educ. Res. 2008, 78, 1039–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.J.; Ford, J.R.; James, B.A.; Schleiden, C.A.; Harris-McKoy, D.; Holcomb, J.E. Expect the best; not the worst: The impact of parental expectation on Black males’ math scores. J. Black Stud. 2020, 51, 767–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeynes, W.H. A Meta-Analysis: The Relationship Between the Parental Expectations Component of Parental Involvement with Students’ Academic Achievement. Urban Educ. 2024, 59, 63–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.M.; Newman, L.A.; Cawthon, S.W.; Javitz, H. Parent expectations, deaf youth expectations, and transition goals as predictors of postsecondary education enrollment. Career Dev. Transit. Except. Individ. 2022, 45, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez, S.W.; Chaparro, G.; Rios-Aguilar, C.; Guarneros, N. Parental expectations of postsecondary outcomes for diverse students with learning disabilities: A funds of knowledge and social capital approach to transition planning. J. Lat. Educ. 2023, 22, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katherine, M.; Peterson, E.G.; Green, A.E.; Kolvoord, R.A.; Uttal, D.H. Parents’ Beliefs about High School Students’ Spatial Abilities: Gender Differences and Associations with Parent Encouragement to Pursue a STEM Career and Students’ STEM Career Intentions. Sex Roles 2020, 82, 570–583. [Google Scholar]
- Keung, C.P.C.; Ho, E.S.C. Structure and agency in adolescents’ expectations of pursuing post-secondary education. Res. High. Educ. 2020, 61, 270–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, A.V.; Holmes, L.G.; Persch, A.C. Longitudinal change in parent postsecondary expectations for youth with disabilities. Disability and Rehabilitation: An International. Multidiscip. J. 2021, 43, 2829–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, J.W. Expectations of a promise: The psychological contracts between students, the state, and key actors in a tuition-free college environment. Educ. Eval. Policy Anal. 2022, 44, 759–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, X.; Wu, D.; Li, H. Effects of attending preschool on adolescents’ reading literacy: Evidence from the ethnic minority children in China. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020, 116, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, S.E.; Vail, C.O.; Roulston, K.; Clees, T.J. Examining the expectations of parents of young children with disabilities from a “care” perspective. Exceptionality 2021, 29, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, R.J.; Baltodano-Van Ness, H.M.; Mathur, S.R. Improving engagement in the virtual environment through culturally relevant expectations and parent collaboration for students with emotional and behavioral disorders. Beyond Behav. 2023, 32, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbhiza, H.; Nkambule, T. Reimagining the Needs of Rural Schools: Teachers’ and Parents’ Experiences of Parental Involvement in School Activities. Afr. Educ. Rev. 2022, 19, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Z.; Hu, S. Unequal childhoods in china: Parental education and children’s time use. J. Community Psychol. 2021, 51, 695–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumeyer, S.; Olczyk, M.; Schmaus, M.; Will, G. Reducing or widening the gap? How the educational aspirations and expectations of Turkish and majority families develop during lower secondary education in Germany. Kölner Z. Für Soziologie Sozialpsychologie 2022, 74, 259–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoku, M.P.; Nketsia, W.; Banye, M.A.; Mprah, W.K.; Dogbe, J.A.; Badu, E. Caregiving experiences and expectations of parents with in-school children with intellectual disability in Ghana. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2020, 96, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, Y.; Ding, D.; Xu, X. Problem Behaviors of Adolescents: The Role of Family Socioeconomic Status, Parental Educational Expectations, and Adolescents’ Confidence in the Future. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rispoli, K.M.; Lee, G.K.; Okyere, C.; Nelson, S.R.; Norman, M.Z. Parent expectations for postsecondary transition among youth with asd: Exploring the role of family mental health. Contemp. Sch. Psychol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.C.; Liao, K.Y. Educational channeling, internalized stereotyping, expectations fulfillment and major choice on Asian Americans’ major satisfaction: A moderated mediation model. J. Vocat. Behav. 2022, 132, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, E. Shaping educational expectations: The perspectives of 13-year-olds and their parents. Educ. Rev. 2020, 72, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollars, V. Children’s achievements in ECEC: Parents’ expectations. Int. J. Early Years Educ. 2023, 31, 627–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Petracchi, H.E. The effects of college savings on college enrollment and the mediating role of parental expectations and discussions about college among students from low-income households. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020, 108, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Yu, F.; Zhang, W. Profiles and Developmental Transitions of Educational Future Orientation among Senior High School Students in China. J. Youth Adolesc. 2023, 52, 2214–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starr, C.R.; Ramos Carranza, P.; Simpkins, S.D. Stability and changes in high school students’ STEM career expectations: Variability based on STEM support and parent education. J. Adolesc. 2022, 94, 906–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takriti, R.; Atkinson, S.; Alhosani, N.; Schofield, L.; Elhoweris, H. Starting school—Parental perspectives in the United Arab Emirates in the first year. Educ. 3-13 2022, 50, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wu, X.; Zhao, M. Work-family conflict, enrichment, and adolescent academic adjustment in dual-earner family. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson-Forsberg, S.; Oliver, M.; Edward, S.; Ginette, L.; Mfoafo-M’Carthy, M. Great Expectations: Perspectives of Young West African Immigrant Men Transitioning to the Canadian Labour Market Without Postsecondary Education. J. Int. Migr. Integr. 2020, 21, 1309–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Womack, T.A.; Johnson, A.H. Examining the likelihood of parents’ homework involvement with elementary-age students with individualized education programs. Remedial Spec. Educ. 2022, 43, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lawrence, J.F.; Grøver, V. Parental Expectations and Home Literacy Environment: A Questionnaire Study of Chinese-Norwegian Dual Language Learners: JRCE. J. Res. Child. Educ. 2023, 37, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, J.W.K.; Xia, L.L.L. Family and Individual Contexts of Middle-School Years and Educational Achievement of Youths in Middle-Aged Adulthood. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Inoue, T.; Cao, G.; Li, L.; Georgiou, G.K. Unpacking the effects of parents on their children’s emergent literacy skills and word reading: Evidence from urban and rural settings in China. Sci. Stud. Read. 2023, 27, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Q.W.; Ronka, A.; Perala-Littunen, S. Rural Children’s Perceptions of Parental Involvement in Their Education in Pakistan. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladsani, H.; Al-Abdullatif, A.; Almuhanna, M.; Gameil, A. Ethnographic Reflections of K-12 Distance Education in Saudi Arabia: Shaping the Future of Post-Pandemic Digital Education. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladsani, H.K. The perceptions of female breadwinner parents regarding their children’s distance learning during the COVID-19 pandemic. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2022, 27, 4817–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.J. Bangladesh’s Early Childhood Education Settings’ School Preparation Depends on Parental Socioeconomic Status: An Empirical Study. Int. J. Early Child. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldosari, M. The Influence of Parental Characteristics on Parental Involvement in Programs for Students with Intellectual Disabilities. Int. J. Disabil. Dev. Educ. 2023, 70, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hail, M.A.; Al-Fagih, L.; Koc, M. Partnering for Sustainability: Parent-Teacher-School (PTS) Interactions in the Qatar Education System. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthi, M. Parental Involvement in Children’s Online Education During COVID-19; A Phenomenological Study in Saudi Arabia. Early Child. Educ. J. 2023, 51, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, N.; Mukhtar, S.; Khan, Y.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, Z.U. Analysis of Secondary School Students’ Academic Performance and Parental Involvement in Children Education at Home. Obraz. I Nauka-Educ. Sci. 2022, 24, 118–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata-Akturk, A.; Demircan, H.O. Supporting Preschool Children’s STEM Learning with Parent-Involved Early Engineering Education. Early Child. Educ. J. 2021, 49, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahcekapili, E.; Karaman, S. A path analysis of five-factor personality traits, self-efficacy, academic locus of control and academic achievement among online students. Knowl. Manag. E-Learn. 2020, 12, 191–208. [Google Scholar]
- Bakac, E. Investigation of the Relationship between Teacher Candidates’ E- Learning Styles, Academic Achievements and Educational Technology Self-Efficiency Perceptions. Cukurova Univ. Fac. Educ. J. 2022, 51, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banda, H.J.; Nzabahimana, J. The Impact of Physics Education Technology (PhET) Interactive Simulation-Based Learning on Motivation and Academic Achievement Among Malawian Physics Students. J. Sci. Educ. Technol. 2023, 32, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barattucci, M.; Zakariya, Y.F.; Ramaci, T. Academic Achievement and Delay: A Study with Italian Post-Graduate Students in Psychology. Int. J. Instr. 2021, 14, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardach, L.; Daumiller, M.; Lueftenegger, M. Multiple Social and Academic Achievement Goals: Students’ Goal Profiles and Their Linkages. J. Exp. Educ. 2023, 91, 655–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becirovic, S.; Brdarevic-Celjo, A.; Polz, E. Exploring the Relationship Between Language Learning Strategies, Academic Achievement, Grade Level, and Gender. J. Lang. Educ. 2021, 7, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C.; Puckett, T. I Want To Learn But They Won’t Let Me: Exploring the Impact of School Discipline on Academic Achievement. Urban Educ. 2023, 58, 2658–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, E.; Bulca, Y.; Demirhan, G. Relationships Between Physical Activity Level, Health-Related Fitness, Academic Achievement, and Academic Self-Concept. Egit. Ve Bilim-Educ. Sci. 2020, 45, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanca Ibanez, M.; Uriarte Portillo, A.; Zatarain Cabada, R.; Lucia Btarron, M. Impact of augmented reality technology on academic achievement and motivation of students from public and private Mexican schools. A case study in a middle-school geometry course. Comput. Educ. 2020, 145, 103734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolat, Y.I.; Tas, N. A meta-analysis on the effect of gamified-assessment tools’ on academic achievement in formal educational settings. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 28, 5011–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshoff-Knoetze, A.; Duminy, L.; Du Toit, Y. Examining the effect of self-regulation failure on academic achievement in emergency remote teaching and learning versus face-to-face. J. Appl. Res. High. Educ. 2023, 15, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, T.; Ge, T.; Auden, E. The relationship between home-based parental involvement, parental educational expectation and academic performance of middle school students in mainland China: A mediation analysis of cognitive ability. Int. J. Educ. Res. 2019, 97, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seginer, R. Parents’ educational involvement: A developmental ecology perspective. Parent. Sci. Pract. 2006, 6, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comer, J.P. School Power: Implications of an Intervention Project; Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, J.L. Toward a theory of family-school connections: Teacher practices and parent involvement. In Social Intervention: Potential and Constraints; Hurrelman, K., Kaufman, F.X., Losel, F., Eds.; Walter de Gruyter: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 121–136. [Google Scholar]
- Bing, S. The Relationship of Parental Involvement to Achievement Goal Orientation, Test Anxiety, and Academic Achievement in Middle School Students. Master’s Thesis, Hebei Normal University, Shijiazhuang, China, 2010. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Nie, P.; Sousa-Poza, A. The Effect of Parental Educational Expectations on Adolescent Subjective Well-Being and the Moderating Role of Perceived Academic Pressure: Longitudinal Evidence for China. Child Indic. Res. 2021, 14, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.S.; Pomerantz, E.M. Why does parents’ involvement enhance children’s achievement? The role of parent-oriented motivation. J. Educ. Psychol. 2012, 104, 820–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strayhorn, T.L. The role of schools, families, and psychological variables on math achievement of black high school students. High Sch. J. 2010, 93, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, I. Parental involvement and the academic achievement of Mexican American youths: What kinds of involvement in youths’ education matter most? Soc. Work Res. 2011, 35, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, J.C.; Suarez, N.; Rosario, P.; Vallejo, G.; Valle, A.; Epstein, J.L. Relationships between perceived parental involvement in homework, student homework behaviors, and academic achievement: Differences among elementary, junior high, and high school students. Metacognition Learn. 2015, 10, 375–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, R.A.; Bush, K.R.; McKenry, P.C.; Wilson, S.M. The impact of parental support, behavioral control, and psychological control on the academic achievement and self-esteem of African American and European American adolescents. J. Adolesc. Res. 2003, 18, 523–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, C.R.; DeGarmo, D.S.; Eddy, J.M. Promoting academic success among Latino youths. Hisp. J. Behav. Sci. 2004, 26, 128–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Ho, H.Z. Direct and indirect longitudinal effects of parental involvement on student achievement: Second-order latent growth modeling across ethnic groups. J. Educ. Psychol. 2005, 97, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houtenville, A.J.; Conway, K.S. Parental effort, school resources, and student achievement. J. Hum. Resour. 2008, 43, 437–453. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.B.; Gregory, A. Parental involvement as a protective factor during the transition to high school. J. Educ. Res. 2010, 103, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.S.; Cui, M. The effects of school-specific parenting processes on academic achievement in adolescence and young adulthood. Fam. Relat. 2012, 61, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Tadesse, E.; Khalid, S. Word of Mouth from Left-Behind Children in Rural China: Exploring Their Psychological, Academic and Physical Well-being During COVID-19. Child Indic. Res. 2022, 15, 1719–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Benner, A.D. Parent–Child Discrepancies in Educational Expectations: Differential Effects of Actual Versus Perceived Discrepancies. Child Dev. 2014, 85, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Mother | Father | |
|---|---|---|
| Parental intellectual involvement | Mother studying middle school textbooks or tutorials on her own in order to tutor you Your mother buys books on educating children Your mother attends lectures on education Your mother tutors you in your studies Your mother takes you to libraries, museums, cultural centers, etc. Your mother watches educational TV programs Mother helps you when you have problems with your studies. Your mother participates in parent activities organized by the school | Father studying middle school textbooks or tutorials on his own in order to tutor you Father buys books on educating children Your father attends lectures on education Father buys study books or materials for you Father assigns a study plan for you Father participates in parent activities organized by the school Father watches educational TV programs Father hires a tutor or finds someone to help you with your homework/Father does homework with you |
| Parental emotional engagement | Mothers encourage you when you do not do well on exams. | Your father encourages you when you do not do well on a test. |
| Mother’s channeling of the difficult emotions you are experiencing in your studies Mother understands how you feel at school Your mother encourages you to do well in your exams. Your mother talks to you about how you approach your studies Your mother talks to you about things you are interested in at school. | Your father encourages you to study by using moral encouragement such as praise. Your father encourages you to do well in exams. Your father encourages you to study with material rewards Your father emphasizes the importance of learning through his own experiences or lessons. Your father tells you stories or philosophies about the importance of learning. | |
| Parental management engagement | Mothers manage the time you spend watching TV Mother manages the time you spend playing with your friends Your mother manages the time you spend on the internet Mother asks you how you are doing with your homework Mother manages what you watch on TV Your mother manages your work schedule | Fathers manage the time you spend watching TV. Fathers manage the time you spend playing with your friends Father manages the time you spend on the internet Father asks you how your homework is done Father manages what you watch on TV Father manages your work and rest time |
| Variable | Frequency | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Student gender | Male | 2618 | 52.6 |
| Female | 2357 | 47.4 | |
| Grade | Grade 7 | 2729 | 53.7 |
| Grade 9 | 2349 | 46.3 | |
| Only child | Yes | 1789 | 35.2 |
| No | 3289 | 64.8 | |
| Left-behind type | Absent mother | 710 | 14.0 |
| Absent father | 2228 | 43.9 | |
| Both parents absent | 2140 | 42.1 |
| Variable | Left-Behind Children | F | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absent Mother (n = 710) | Absent Father (n = 2228) | Both Parents Absent (n = 2140) | Non-Left-Behind Children (n = 9769) | |||
| Parental educational expectation | 6.33 ± 1.72 | 6.48 ± 1.67 | 6.42 ± 1.61 | 6.66 ± 1.58 | 23.58 ** | <0.01 |
| Academic standard achievement | 68.05 ± 9.09 | 69.62 ± 8.64 | 69.93 ± 8.47 | 70.33 ± 8.55 | 17.91 ** | <0.01 |
| Parental intellectual involvement | 2.06 ± 0.99 | 2.13 ± 0.96 | 1.87 ± 0.99 | 2.29 ± 1.03 | 104.79 ** | <0.01 |
| Parental management involvement | 2.27 ± 0.42 | 2.34 ± 0.38 | 2.33 ± 0.39 | 2.35 ± 0.39 | 13.48 ** | <0.01 |
| Parental emotional involvement | 1.93 ± 0.53 | 1.96 ± 0.50 | 1.93 ± 0.53 | 2.03 ± 0.51 | 33.66 ** | <0.01 |
| Family economic condition | 2.85 ± 0.62 | 2.89 ± 0.58 | 2.84 ± 0.59 | 3.04 ± 0.54 | 103.44 | <0.01 |
| Mother’s level of education | 3.53 ± 1.87 | 3.69 ± 1.94 | 3.14 ± 1.62 | 3.99 ± 2.05 | 115.16 | <0.01 |
| Father’s level of education | 3.83 ± 1.89 | 4.10 ± 1.93 | 3.49 ± 1.57 | 4.35 ± 2.06 | 118.62 | <0.01 |
| Relationship with mother | 2.47 ± 0.68 | 2.71 ± 0.50 | 2.61 ± 0.58 | 2.74 ± 0.47 | 91.93 | <0.01 |
| Relationship with father | 2.50 ± 0.61 | 2.44 ± 0.66 | 2.53 ± 0.60 | 2.61 ± 0.55 | 64.93 | <0.01 |
| Self-education expectation | 3.91 ± 2.65 | 3.92 ± 2.48 | 3.89 ± 2.46 | 3.83 ± 2.52 | 1.04 | 0.38 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Academic standard achievement | 1 | ||||
| 2. Parental intellectual involvement | −0.73 *** | 1 | |||
| 3. Parental management involvement | 0.02 | 0.34 *** | 1 | ||
| 4. Parental emotional involvement | 0.06 *** | 0.32 *** | 0.35 *** | 1 | |
| 5. Parental educational expectation | 0.35 *** | 0.07 *** | 0.15 *** | 0.15 *** | 1 |
| Regression Equation | Overall Fitting Coefficient | Significance of Regression Coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Result Variable | Predictor | R2 | β | t |
| Academic standard achievement | Parental educational expectation | 0.18 | 0.35 | 25.87 *** |
| Parental intellectual involvement | −0.11 | −0.72 *** | ||
| Parental management involvement | −0.01 | −0.72 | ||
| Parental emotional involvement | 0.05 | 3.18 *** | ||
| Types of left-behind children | 0.04 | 2.72 ** | ||
| Gender | 0.19 | 14.5 *** | ||
| Grade | 0.04 | 2.77 ** | ||
| Only child | 0.04 | 2.83 *** | ||
| Parental intellectual involvement | Parental educational expectation | 0.06 | 0.04 | 4.98 *** |
| Parental management involvement | Parental educational expectation | 0.03 | 0.03 | 10.16 *** |
| Parental emotional involvement | Parental educational expectation | 0.04 | 0.05 | 10.74 *** |
| Intermediate Path | Effect Size | Boot Standard Error | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
| Total effect | 1.80 | 0.07 | 1.67 | 1.94 |
| Direct effect | 1.82 | 0.07 | 1.68 | 1.95 |
| Total indirect effect | −0.01 | −0.01 | −0.04 | −0.02 |
| Indirect effect 1 | −0.04 | −0.04 | −0.06 | −0.02 |
| Indirect effect 2 | −0.01 | −0.01 | −0.03 | 0.01 |
| Indirect effect 3 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.06 |
| C1 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.001 | 0.06 |
| C2 | −0.05 | 0.02 | −0.08 | −0.01 |
| C3 | −0.08 | 0.02 | −0.11 | −0.05 |
| Regression Equation | Overall Fitting Coefficient | Significance of Regression Coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Result Variable | Predictor | R2 | β | t |
| Academic standard achievement | Parental educational expectation | 0.18 | 0.34 | 25.50 *** |
| Parental intellectual involvement | −0.12 | −8.28 *** | ||
| Parental management involvement | 0.03 | 2.41 * | ||
| Parental emotional involvement | 0.04 | 2.62 ** | ||
| Types of left-behind children | 0.03 | 2.48 * | ||
| Gender | 0.19 | 14.42 *** | ||
| Grade | 0.04 | 2.85 ** | ||
| Only child | 0.04 | 2.73 *** | ||
| Parental intellectual involvement | Parental educational expectation | 0.06 | 0.07 | 4.98 *** |
| Parental management involvement | Parental educational expectation | 0.04 | 0.15 | 10.47 *** |
| Parental emotional involvement | Parental educational expectation | 0.04 | 0.15 | 10.74 *** |
| Intermediate Path | Effect Size | Boot Standard Error | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
| Total effect | 1.80 | 0.07 | 1.67 | 1.94 |
| Direct effect | 1.79 | 0.07 | 1.65 | 1.93 |
| Total indirect effect | 0.01 | 0.02 | −0.02 | 0.04 |
| Indirect effect 1 | −0.04 | 0.01 | −0.07 | −0.02 |
| Indirect effect 2 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.05 |
| Indirect effect 3 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.05 |
| C1 | −0.01 | 0.003 | −0.02 | −0.01 |
| C2 | −0.01 | 0.003 | −0.02 | −0.01 |
| C3 | −0.0006 | 0.003 | −0.01 | −0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Xue, E.; You, H. Parental Educational Expectations and Academic Achievement of Left-Behind Children in China: The Mediating Role of Parental Involvement. Behav. Sci. 2024, 14, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14050371
Li J, Xue E, You H. Parental Educational Expectations and Academic Achievement of Left-Behind Children in China: The Mediating Role of Parental Involvement. Behavioral Sciences. 2024; 14(5):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14050371
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jian, Eryong Xue, and Huiyuan You. 2024. "Parental Educational Expectations and Academic Achievement of Left-Behind Children in China: The Mediating Role of Parental Involvement" Behavioral Sciences 14, no. 5: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14050371
APA StyleLi, J., Xue, E., & You, H. (2024). Parental Educational Expectations and Academic Achievement of Left-Behind Children in China: The Mediating Role of Parental Involvement. Behavioral Sciences, 14(5), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14050371








