Communicating Nutritional Knowledge to the Chinese Public: Examining Predictive Factors of User Engagement on TikTok in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Account Selection
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Operationalization of Variables
2.4. Coding Method
Coders and Reliability Test
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analysis
3.1.1. Frequency Distribution of Content Themes
3.1.2. Descriptive Analysis of User Engagement
3.2. Negative Binomial Regression
3.2.1. Research Question 1
3.2.2. Research Question 2
3.2.3. Research Question 3
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, J.; Zhang, P. China’s Public Health Policies in Response to COVID-19: From an “Authoritarian” Perspective. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 756677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Council of PRC. Outline of the Healthy China 2030 Plan Issued by the State Council; State Council of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2016-10/25/content_5124174.htm (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- State Council of PRC. Notice on Issuing the National Nutrition Plan (2017–2030); General Office of the State Council of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017; No. 000014349/2017-00138. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2017-07/13/content_5210134.htm (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Che, S.P.; Zhang, S.N.; Kim, J.H. How public health agencies communicate with the public on TikTok under the normalization of COVID-19: A case of 2022 Shanghai’s outbreak. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1039405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Business of Apps. Available online: https://www.businessofapps.com/data/tik-tok-statistics/ (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Wang, H.; Yin, H.; Feng, S.; Ren, D.Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Ji, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; et al. China Internet Audio & Video Research Development Report, 1st ed.; China Netcasting Services Association: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Global Times. TikTok Released the Health Science Popularization Data Report, and 35000 Certified Doctors Created 4.43 million Science Popularization Articles. Available online: https://m.huanqiu.com/article/4CRpUxR2rhf (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Zou, P.; Yang, H.; Lin, W.; Jiang, L.; Bai, Z.; Pu, Y. Consumer demand and new changesL increasing health awareness. In 2021 China Emerging Brands Development Study, 1st ed.; Ocean Insights: Beijing, China, 2021; Volume 1, p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, D.; Shi, Y.; Tang, W.; Li, D.; Han, K.; Shi, C.; Li, G.; Zhu, F. The influencing factors of nutrition and diet health knowledge dissemination using the WeChat official account in health promotion. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 775729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.S.; Looil, J.; Leung, Y.W.; Goh, T.J. Public engagement by researchers of different disciplines in Singapore: A qualitative comparison of macro- and meso-level concerns. Public Underst. Sci. 2020, 29, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.D.; Cohen, N.L.; Fulgoni, V.L.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Wellman, N.S. From nutrition scientist to nutrition communicator: Why you should take the leap. Am. J. Clin. 2006, 83, 1272–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakopoulos, M. Pandora’s box or panacea? Using metaphors to create the public representations of biotechnology. Public Underst. Sci. 2022, 11, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, M. More about metaphor. In Metaphor and Thought, 2nd ed.; Ortony, A., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993; pp. 19–41. [Google Scholar]
- Leggett, M.; Finlay, M. Science, story, and image: A new approach to crossing the communication barrier posed by scientific jargon. Public Underst. Sci. 2001, 10, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perra, M.; Brinkman, T. Seeing science: Using graphics to communicate research. Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, C.; Eathorne, A.; Semprini, A.; Braithwaite, I.; Beasley, R. Public engagement with clinical research on social media; which visual medium works best? A 5-year retrospective analysis. J. Vis. Commun. Med. 2021, 44, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, C.M.; Murray, E.J.; Beard, J.; Schnoes, A.M.; Wang, M.L. Science Communication in the Age of Misinformation. Ann. Behav. Med. 2020, 54, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Milkman, K.L. What makes online content viral? J. Mark. Res. 2012, 49, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplette, M.E.; Provencher, V.; Bissonnette-Maheux, V.; Dugrenier, M.; Lapointe, A.; Gagnon, M.; Straus, S.; Desroches, S. Increasing fruit and vegetable consumption through a healthy eating blog: A feasibility study. JMIR Res. Protocs 2016, 6, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, T.; Joseph, J.; Yardley, L.; Michie, S. Using the internet to promote health behavior change: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the impact of theoretical basis, use of behavior change techniques, and mode of delivery on efficacy. J. Med. Internet Res. 2010, 12, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jane, M.; Hagger, M.; Foster, J.; Ho, S.; Kane, R.; Pal, S. Effects of a weight management program delivered by social media on weight and metabolic syndrome risk factors in overweight and obese adults: A randomised controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhabash, S.; McAlister, A.R.; Hagerstrom, A.; Quilliam, E.T.; Rifon, N.J.; Richards, J.I. Between likes and shares: Effects of emotional appeal and virality on the persuasiveness of anticyberbullying messages on Facebook. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2013, 16, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahbaznezhad, H.; Dolan, R.; Rashidirad, M. The role of social media content format and platform in users’ engagement behavior. J. Interact. Mark. 2021, 53, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barklamb, A.M.; Molenaar, A.; Brennan, L.; Evans, S.; Choong, J.; Herron, E.; Reid, M.; McCaffrey, T.A. Learning the language of social media: A comparison of engagement metrics and social media strategies used by food and nutrition-related social media accounts. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welbourne, D.J.; Grant, W.J. Science communication on YouTube: Factors that affect channel and video popularity. Public Underst. Sci. 2015, 25, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durbano, A.; Bert, F.; Pivi, A.; Moro, G.L.; Scaioli, G.; Siliquini, R. Use of TikTok by nutrition healthcare professionals: Analysis of the Italian context. Eur. J. Public Health 2022, 32, ckac131.333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortune. Available online: https://fortune.com/company/cofco/global500/ (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- COFCO Nutrition Research Institute. Available online: http://www.cofconhri.com/Introduction.html (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Baram-Tsabari, A.; Wolfson, O.; Yosef, R.; Chapnik, N.; Brill, A.; Segev, E. Jargon use in Public Understanding of Science papers over three decades. Public Underst. Sci. 2020, 29, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowiec, B.G. Ten simple rules for scientists engaging in science communication. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2023, 19, e1011251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez Estrada, F.C.; Davis, L.S. Improving visual communication of science through the incorporation of graphic design theories and practices into science communication. Sci. Commun. 2015, 37, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessel, P.V.; Toor, S.; Smith, A. A Week in the Life of Popular YouTube Channels. Available online: https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2019/07/25/a-week-in-the-life-of-popular-youtube-channels/ (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Bhattacharya, S.; Srinivasan, P.; Polgreen, P. Social media engagement analysis of U.S. Federal health agencies on Facebook. MC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2017, 17, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Min, C.; Zhang, W.; Ma, X.; Evans, R. Factors Driving Citizen Engagement with Government TikTok Accounts During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Model Development and Analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e21463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Wang, L.; Song, S.; Dong, M.; Xu, Y.; Zuo, X.; Zhang, J.; Adrian, S.A.; Ehsan, J.; Ma, J.; et al. Quality and Audience Engagement of Takotsubo Syndrome–Related Videos on TikTok: Content Analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2022, 24, e39360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
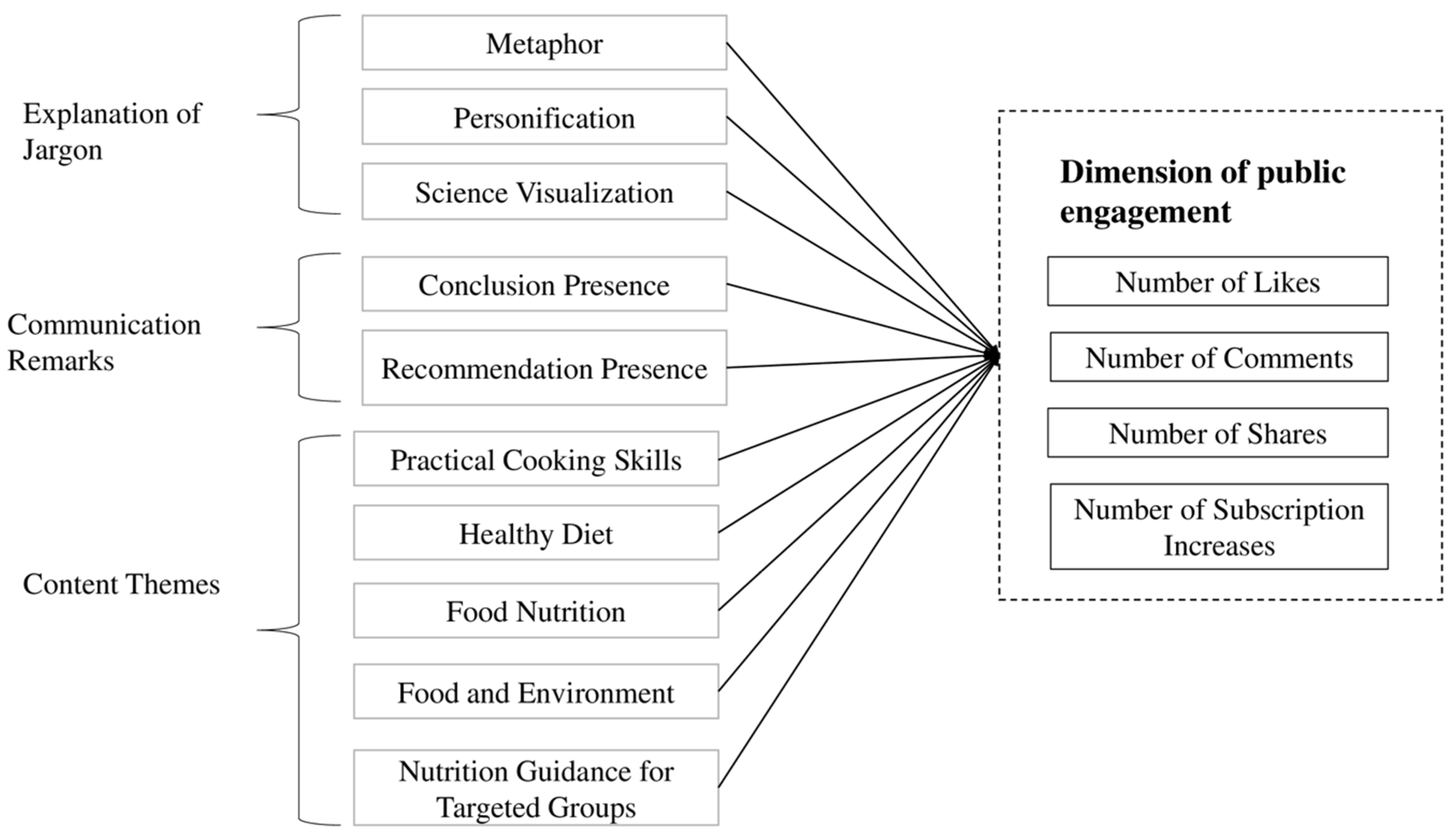
| Variables | Operational Definition | Examples | Intercoder Reliability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation of Jargon | 1.00 | ||
| Metaphor | Using parallel concepts to help illustrate science terminology | Lutein resides within the macula of the eye, serving as a shield that absorbs 40% to 90% of incoming blue light, similarly to equipping the eyes with a protective filter. | 1.00 |
| Personification | Applying human attributes to discuss a scientific term | L-arabinose can compete with sucrose in the intestines, taking the enzyme that digests sucrose away from sucrose and preventing this absorption trip. | 1.00 |
| Science Visualization | Usage of visual tools such as infographics and images to illustrate jargons | N/A | 1.00 |
| Scientific Message Attributes | 1.00 | ||
| Conclusion Presence | Science communicator gives definite and scientific conclusion | Natural vitamin E is better than synthetic vitamin E in every way. | 1.00 |
| Recommendation Presence | Science communicator offers tangible advice to the audience | The intake of natural vitamin E is also recommended in the daily diet. | 1.00 |
| Content Themes | 1.00 | ||
| Practical Cooking Skills | Giving recipes, cooking methods and culinary tips | How do you determine the temperature of the oil for stir-frying without a thermometer? | 1.00 |
| Healthy Diet | Providing knowledge about healthy eating habits, debunking myths, and encouraging diverse food intake | I’ve heard that the delicious taste you get from frying things in palm oil is something we trade for our health! Is this a rumor? | 1.00 |
| Food Nutrition | Educating the public about functions of different nutrients | The chemical structure of plant sterols and cholesterol is very similar, only because of the side chain structure of the C24 position on the extra group, the two on the human body’s role, is a world of difference. | 1.00 |
| Food and Environment | The impact of nutrients on the environment and the broader social context of sustainability eating | The Green Magic of Biofuels: Why Ethanol Reduces Carbon Emissions | 1.00 |
| Nutrition Guidance for Targeted groups | Addressing nutrition-related topics and giving tailored advice to a specific group | Scientists have discovered klotho, a protein that may be able to awaken memories which could be a huge benefit for Alzheimer’s patients. | 1.00 |
| Theme Unrelated to Food and Nutrition Popularization | Content unrelated to food, diet, nutrients and science popularization | Do sensory evaluators just keep tasting new foods? | 1.00 |
| Content Themes | Frequency | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Practical Cooking Skills | 10 | 12.35 |
| Healthy Diet | 33 | 40.74 |
| Food Nutrition | 14 | 17.28 |
| Food and Environment | 13 | 16.05 |
| Nutrition Guidance for Targeted Groups | 11 | 13.58 |
| Total | 81 | 100.00 |
| Engagement Metrics | Count | Min. | Max. | SD. | Median |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Likes | 81 | 50.00 | 7207.000 | 1423.941 | 726.000 |
| Number of Shares | 81 | 2.000 | 1940.000 | 236.991 | 42.000 |
| Number of Comments | 81 | 4.000 | 904.000 | 172.643 | 46.000 |
| Number of Subscription Increases | 81 | 0.000 | 3589.000 | 567.367 | 23.000 |
| Content Theme | Engagement Metrics | Min. | Max. | SD. | Median |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Practical Cooking Skills | Number of Likes | 77 | 7207 | 2508.037 | 1529.5 |
| Number of Shares | 4 | 1940 | 603.248 | 80.5 | |
| Number of Comments | 4 | 800 | 237.765 | 58 | |
| Number of Subscription Increases | 4 | 3589 | 120.626 | 81 | |
| Healthy Diet | Number of Likes | 50 | 4631 | 1106.952 | 561 |
| Number of Shares | 3 | 211 | 67.784 | 45 | |
| Number of Comments | 7 | 687 | 126.811 | 34 | |
| Number of Subscription Increases | 1 | 1461 | 352.122 | 20 | |
| Food Nutrition | Number of Likes | 59 | 3017 | 958.839 | 469.5 |
| Number of Shares | 5 | 159 | 39.224 | 22 | |
| Number of Comments | 10 | 510 | 129.973 | 35 | |
| Number of Subscription Increases | 3 | 1143 | 301.99 | 16.5 | |
| Food and Environment | Number of Likes | 105 | 5572 | 1549.103 | 929 |
| Number of Shares | 2 | 541 | 150.671 | 54 | |
| Number of Comments | 12 | 904 | 249.23 | 114 | |
| Number of Subscription Increases | 1 | 2696 | 751.944 | 29 | |
| Nutrition Guidance for Targeted Groups | Number of Likes | 59 | 2355 | 755.548 | 479 |
| Number of Shares | 9 | 518 | 153.130 | 29 | |
| Number of Comments | 6 | 547 | 158.261 | 61 | |
| Number of Subscription Increases | 0 | 576 | 170.418 | 11 |
| Variables | Model 1: Number of Subscription Increases | Model 2: Number of Shares | Model 3: Number of Comments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression Coefficient | OR Value | Regression Coefficient | OR Value | Regression Coefficient | OR Value | |
| Explanation of Jargon | ||||||
| Metaphor | −0.974 ** (−3.647) | 0.378 | -------- | |||
| Personification | 0.441 * (2.262) | 1.554 | -------- | |||
| Science Visualization | 0.478 ** (3.534) | 1.613 | -------- | |||
| Intercept | 5.201 | 43.408 | -------- | |||
| Likelihood Ratio | X2 (3) = 24.073 p = 0.000 | -------- | ||||
| McFadden R2 | 0.023 | -------- | ||||
| Scientific Message Attributes | ||||||
| Conclusion Presence | -------- | −0.582 * (−2.511) | 0.559 | 0.44 (1.876) | 1.544 | |
| Recommendation Presence | -------- | 0.190 (0.830) | 1.209 | 0.924 ** (4.025) | 2.518 | |
| Intercept | -------- | 5.097 (9.690) | 163.540 | 2.459 (4.663) | 11.698 | |
| Likelihood Ratio | -------- | X2 (2) = 7.670 p = 0.022 | X2 (2) = 19.341 p = 0.000 | |||
| McFadden R2 | -------- | 0.008 | 0.021 | |||
| Content Themes | Number of Likes | Number of Shares | Number of Comments | Number of Subscription Increases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 5.894 ** (58.150) | 3.795 ** (37.227) | 3.909 ** (38.405) | 4.430 ** (43.581) |
| Practical Cooking Skills | 1.866 ** (6.799) OR = 6.595 | 1.960 ** (7.051) OR = 7.098 | 1.064 ** (3.824) OR = 2.899 | 2.010 ** (7.239) OR = 7.463 |
| Healthy Diet | 0.959 ** (5.493) OR = 2.610 | 0.511 ** (2.909) OR = 1.667 | 0.398 * (2.267) OR = 1.489 | 0.772 ** (4.412) OR = 2.165 |
| Food Nutrition | 0.915 ** (3.801) OR = 2.497 | −0.221 (−0.907) OR = 0.802 | 0.363 (1.498) OR = 1.437 | 0.414 (1.713) OR = 1.513 |
| Food and Environment | 1.357 ** (5.468) OR = 3.884 | 0.782 ** (3.138) OR = 2.187 | 1.311 ** (5.269) OR = 3.710 | 1.395 ** (5.611) OR = 4.033 |
| Nutrition guidance for Targeted Group | 0.777 ** (2.916) OR = 2.175 | 0.762 ** (2.848) OR = 2.143 | 0.772 ** (2.888) OR = 2.165 | −0.161 (−0.600) OR = 0.851 |
| Likelihood ratio McFadden R2 | X2 (4) = 10.790, p = 0.029 0.008 | X2 (4) = 33.267, p = 0.000 0.036 | X2 (4) = 11.473, p = 0.022 0.013 | X2 (4)= 32.755, p = 0.000 0.031 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, M.; Che, S. Communicating Nutritional Knowledge to the Chinese Public: Examining Predictive Factors of User Engagement on TikTok in China. Behav. Sci. 2024, 14, 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14030201
Zhu M, Che S. Communicating Nutritional Knowledge to the Chinese Public: Examining Predictive Factors of User Engagement on TikTok in China. Behavioral Sciences. 2024; 14(3):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14030201
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Min, and ShaoPeng Che. 2024. "Communicating Nutritional Knowledge to the Chinese Public: Examining Predictive Factors of User Engagement on TikTok in China" Behavioral Sciences 14, no. 3: 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14030201
APA StyleZhu, M., & Che, S. (2024). Communicating Nutritional Knowledge to the Chinese Public: Examining Predictive Factors of User Engagement on TikTok in China. Behavioral Sciences, 14(3), 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14030201







