The Need for Status, Organizational Citizenship Behavior, and Overall Evaluation: Focusing on the Moderating Effects of Political Skill and Task Visibility
Abstract
1. Introduction
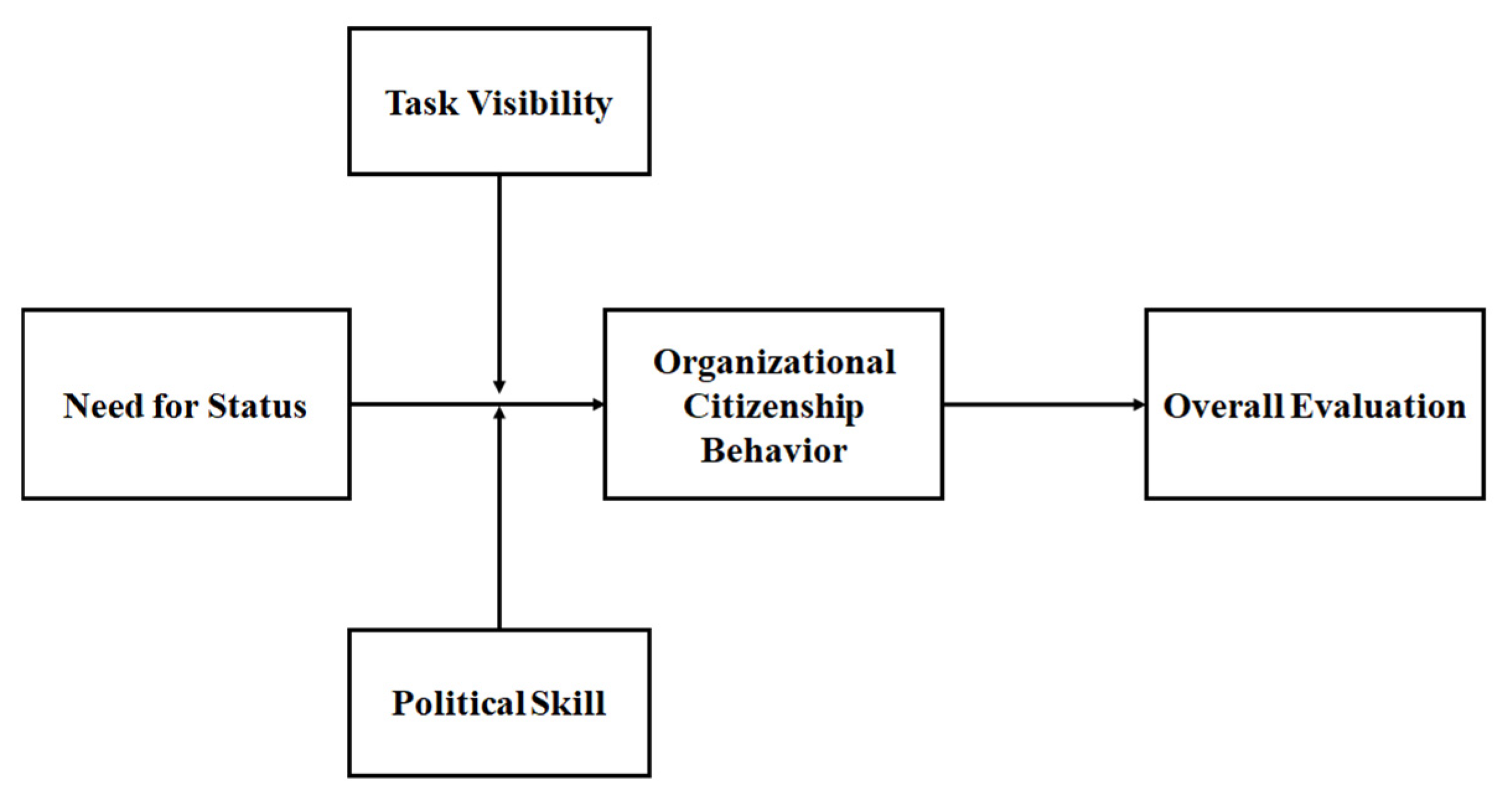
2. Theoretical Background and Hypotheses
2.1. Costly Signaling Theory
2.2. Need for Status, Organizational Citizenship Behavior, and Overall Evaluation
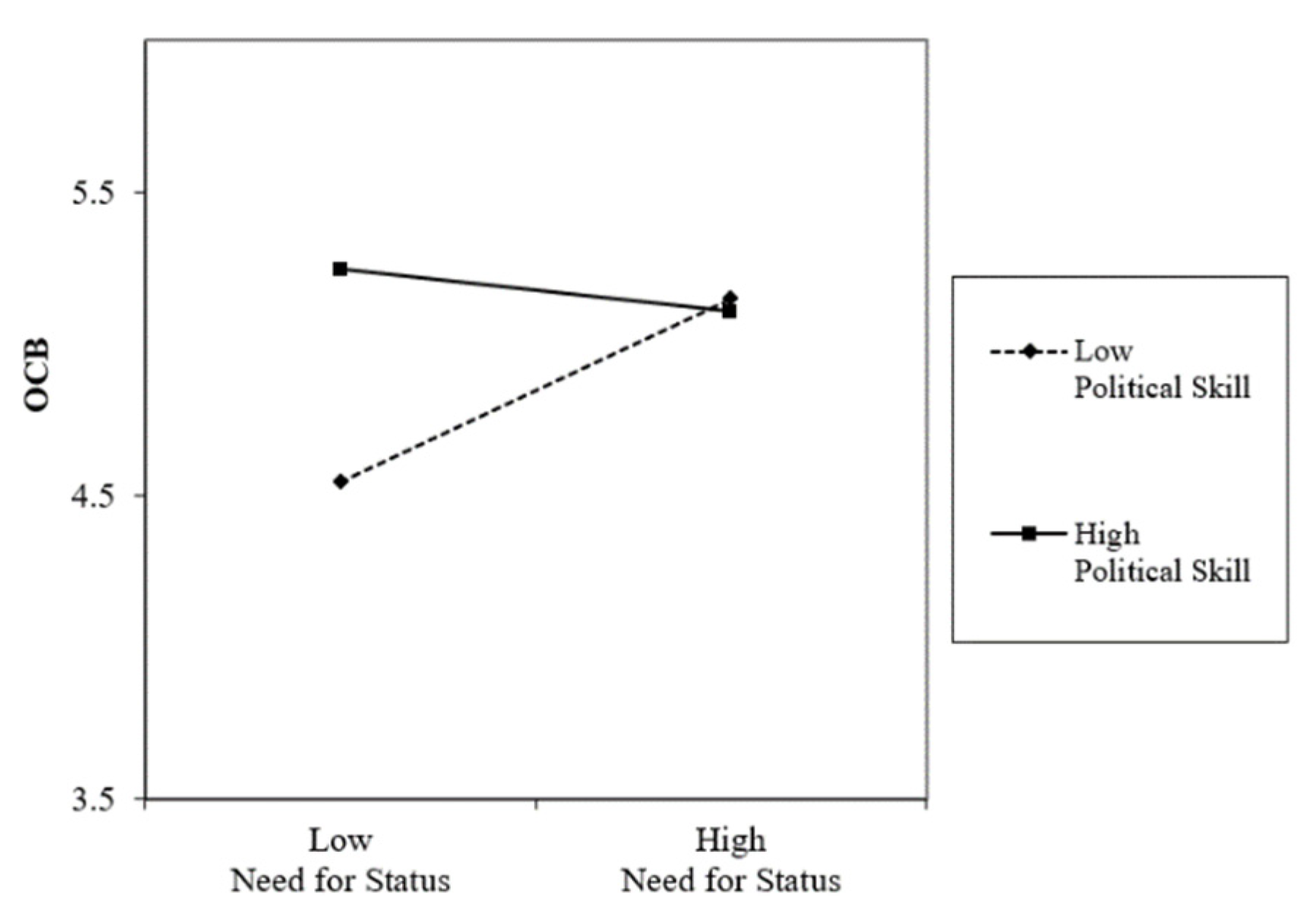
2.3. Moderating Role of Political Skill
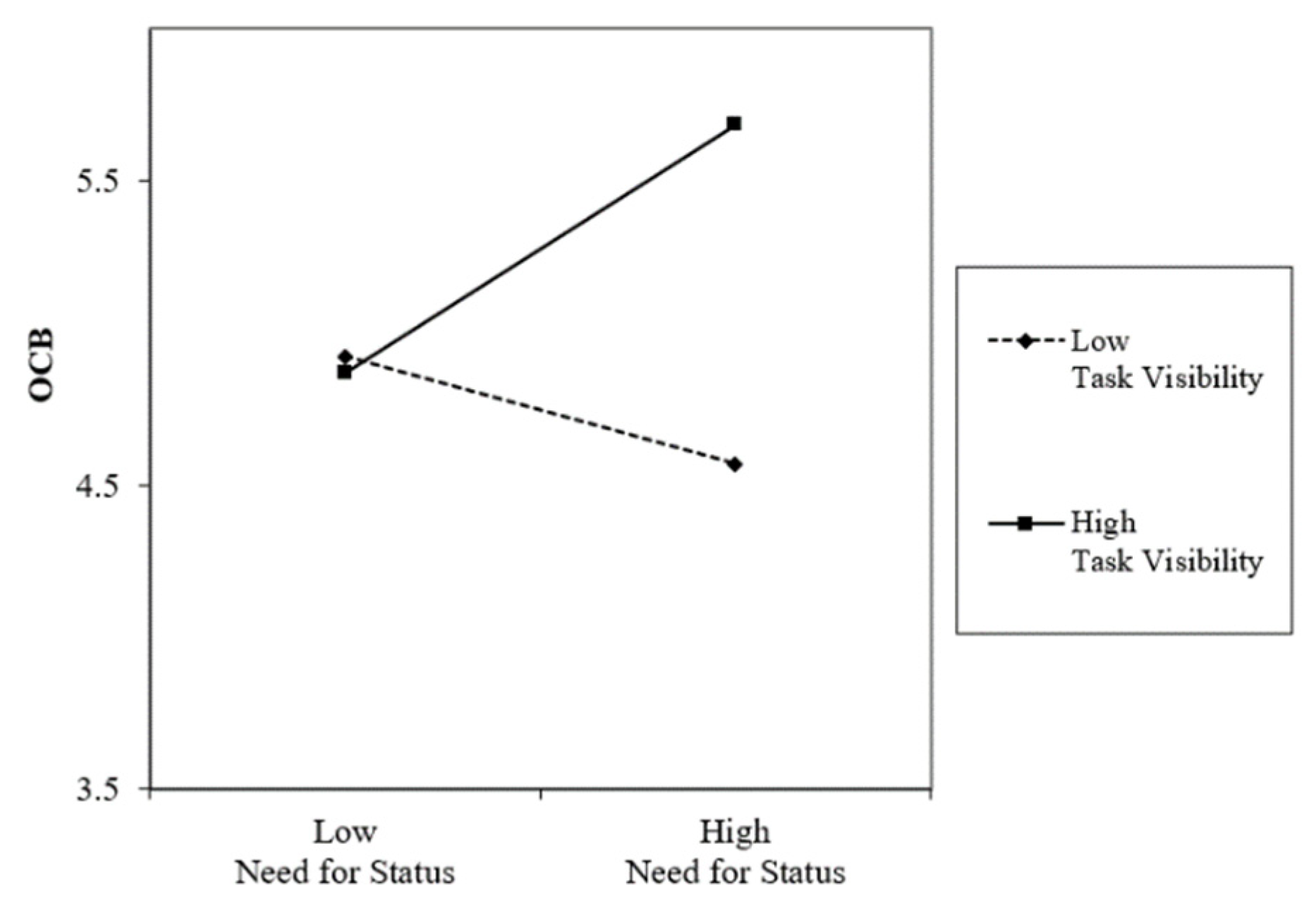
2.4. Moderating Role of Task Visibility
3. Methods
3.1. Sample and Procedures
3.2. Measures
3.3. Analysis Strategy
4. Results
4.1. Reliability and Validity Verification
4.2. Descriptive Statistics and Correlation Analysis
4.3. Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA)
4.4. Hypothesis Testing
5. Discussion
5.1. Overall Findings
5.2. Theoretical Implications
5.3. Managerial Implications
5.4. Limitations and Future Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bateman, T.S.; Organ, D.W. Job satisfaction and the good soldier: The relationship between affect and employee citizenship. Acad. Manag. J. 1983, 26, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organ, D.W. Organizational Citizenship Behavior: The Good Soldier Syndrome; Lexington Books/DC Heath and Com: Lexington, MA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Bolino, M.C.; Turnley, W.H.; Niehoff, B.P. The other side of the story: Reexamining prevailing assumptions about organizational citizenship behavior. Hum. Resour. Manag. Rev. 2004, 14, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organ, D.W.; Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B. Organizational Citizenship Behavior: Its Nature, Antecedents, and Consequences; SAGE: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Paine, J.B.; Bachrach, D.G. Organizational citizenship behaviors: A critical review of the theoretical and empirical literature and suggestions for future research. J. Manag. 2000, 26, 513–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo, L.; Acedillo, V.; Bacunador, A.M.; Balo, C.C.; Lagdameo, Y.J.; Tupa, N. S A historical review of the development of organizational citizenship behavior (OCB) and its implications for the twenty-first century. Pers. Rev. 2018, 47, 821–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioux, S.M.; Penner, L.A. The causes of organizational citizenship behavior: A motivational analysis. J. Appl. Psychol. 2001, 86, 1306–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolino, M.C. Citizenship and impression management: Good soldiers or good actors? Acad. Manag. Rev. 1999, 24, 82–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, A.M.; Mayer, D.M. Good soldiers and good actors: Prosocial and impression management motives as interactive predictors of affiliative citizenship behaviors. J. Appl. Psychol. 2009, 94, 900–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourdage, J.S.; Lee, K.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, K.H. Motives for organizational citizenship behavior: Personality correlates and coworker ratings of OCB. Hum. Perform. 2012, 25, 179–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoensukmongkol, P. The interaction of organizational politics and political skill on employees’ exposure to workplace cyberbullying: The conservation of resources theory perspective. Asi-Pac. J. Bus. Adm. 2023; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, D.; Singh, S.; Varma, A. Perceptions of politics and organizational citizenship behavior: Political skill and conscientiousness as moderators. J. Asia Bus. Stud. 2023, 17, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, M.A. Individualism/collectivism and organizational citizenship behavior: An integrative framework. Social Behav. Pers. 2012, 40, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Chae, H.; Choi, J.N. The need for status as a hidden motive of knowledge-sharing behavior: An application of costly signaling theory. Hum. Perform. 2017, 30, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly, B.L.; Certo, S.T.; Ireland, R.D.; Reutzel, C.R. Signaling theory: A review and assessment. J. Manag. 2011, 37, 39–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, P. Altruism as a courtship display: Some effects of third-party generosity on audience perceptions. Br. J. Psychol. 2010, 101, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.A.; Bliege Bird, R. Turtle hunting and tombstone opening: Public generosity as costly signaling. Evol. Hum. Behav. 2000, 21, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahavi, A. Altruism as a handicap: The limitations of kin selection and reciprocity. J. Avian Bio. 1995, 26, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, G.R.; Treadway, D.C.; Perrewe, P.L.; Brouer, R.L.; Douglas, C.J.; Lux, S. Political skill in organizations. J. Manag. 2007, 33, 290–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gintis, H.; Smith, E.A.; Bowles, S. Costly signaling and cooperation. J. Theor. Bio. 2013, 213, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, C.L.; Van Vugt, M. Nice guys finish first: The competitive altruism hypothesis. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2006, 32, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAndrew, F.T. New evolutionary perspectives on altruism: Multilevel-selection and costly-signaling theories. Curr. Dir. Soc. Psychol. Sci. 2002, 11, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukl, G.A. Leadership in Organizations, 8th ed.; Prentice Hall International: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ferris, G.R.; Treadway, D.C.; Kolodinsky, R.W.; Hochwarter, W.A.; Kacmar, A.; Douglas, C.J.; Frink, D.D. Development and validation of the political skill inventory. J. Manag. 2005, 31, 126–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyon, T.P.; Summers, J.K.; Thompson, K.M.; Ferris, G.R. Political skill and work outcomes: A theoretical extension, meta-analytic investigation, and agenda for the future. Pers. Psychol. 2015, 68, 143–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumura, T.A. review of political skill: Current research trend and directions for future research. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2015, 17, 312–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidwell, R.E.; Bennett, N. Employee propensity to withhold effort: A conceptual model to intersect three avenues of research. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1993, 18, 429–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.R. Task visibility, free riding, and shirking: Explaining the effect of structure and technology on employee behavior. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1984, 9, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latane, B.; Williams, K.D.; Harkins, S. Many hands make light the work: The causes and consequences of social loafing. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1979, 37, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liden, R.; Wayne, S.J.; Jaworski, R.A.; Benett, N. Social loafing: A field investigation. J. Manag. 2004, 30, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.Y.; Podsakoff, N.P. Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, F.J.; Reagans, R.E.; Amanatullah, E.T.; Ames, D.R. Helping one’s way to the top: Self-monitors achieve status by helping others and knowing who helps whom. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2006, 91, 1123–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Allen, N.J. Organizational citizenship behavior and workplace deviance: The role of affect and cognitions. J. Appl. Psychol. 2002, 87, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, T.D.; Rush, M.C. The effects of organizational citizenship behavior on performance judgments: A field study and a laboratory experiment. J. Appl. Psychol. 1998, 83, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preacher, K.J.; Rucker, D.D.; Hayes, A.F. Addressing moderated mediation hypotheses: Theory, methods, and prescriptions. Multivar. Behav. Res. 2007, 42, 185–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiken, L.S.; West, S.G. Multiple Regression: Testing and Interpreting Interactions; SAGE: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, P. An Easy Guide to Factor Analysis; Routledge: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Nunnally, J.C. Psychometric Theory; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Gravetter, F.J.; Wallnau, L.B. Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences, 10th ed.; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.T.; Bentler, P.M. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct. Equ. Model. 1999, 6, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Per. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hinrichs, K.T.; Prieto, L.; Howell, J.P. Five dimensions of organizational citizenship behavior: Comparing antecedents and levels of engagement in China and the US. Asia Pac. J. Manag. 2013, 30, 115–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basabe, N.; Ros, M. Cultural dimensions and social behavior correlates: Individualism-collectivism and power distance. Int. Rev. Soc. Psychol. 2005, 18, 189–225. [Google Scholar]
- To, C.; Leslie, L.M.; Torelli, C.J.; Stoner, J.L. Culture and social hierarchy: Collectivism as a driver of the relationship between power and status. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 2020, 157, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajcsák, Z.; Krajcsák, A. The moderating role of remote work in the relationship between organizational culture and OCB: Case studies from the financial sector. J. Adv. Manag. Res. 2022, 19, 300–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bret Becton, J.; Giles, W.F.; Schraeder, M. Evaluating and rewarding OCBs: Potential consequences of formally incorporating organisational citizenship behaviour in performance appraisal and reward systems. Empl. Relat. 2006, 30, 494–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chae, H. The Effect of the OCB Gap on Task Performance with the Moderating Role of Task Interdependence. Sustainability 2022, 14, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Items | Factor 1 (OE) | Factor 2 (PS) | Factor 3 (NS) | Factor 4 (TV) | Factor 5 (OCB) | Cronbach’s Alpha |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OE1 | 0.882 | −0.010 | 0.097 | −0.027 | 0.062 | 0.97 |
| OE2 | 0.896 | −0.010 | 0.067 | −0.064 | 0.019 | |
| OE3 | 0.910 | −0.043 | 0.093 | −0.051 | 0.053 | |
| OE4 | 0.863 | −0.023 | 0.105 | −0.030 | −0.015 | |
| OE5 | 0.871 | −0.003 | 0.074 | −0.026 | 0.056 | |
| PS1 | 0.184 | 0.600 | 0.169 | 0.210 | −0.052 | 0.90 |
| PS2 | 0.072 | 0.782 | 0.138 | 0.124 | 0.046 | |
| PS3 | 0.041 | 0.813 | 0.150 | 0.199 | 0.067 | |
| PS4 | −0.020 | 0.803 | 0.128 | 0.061 | 0.166 | |
| PS5 | 0.100 | 0.779 | 0.207 | 0.072 | 0.185 | |
| PS6 | 0.161 | 0.774 | 0.203 | 0.034 | 0.092 | |
| PS7 | 0.115 | 0.615 | 0.240 | 0.016 | 0.080 | |
| PS8 | 0.103 | 0.671 | 0.230 | −0.012 | −0.026 | |
| NS1 | 0.137 | 0.245 | 0.737 | 0.036 | 0.033 | 0.92 |
| NS2 | 0.222 | 0.382 | 0.670 | 0.090 | 0.042 | |
| NS3 | 0.183 | 0.188 | 0.791 | 0.059 | −0.089 | |
| NS4 | 0.226 | 0.217 | 0.755 | −0.013 | −0.065 | |
| NS5 | 0.154 | 0.214 | 0.817 | −0.051 | −0.021 | |
| NS6 | −0.046 | 0.183 | 0.749 | 0.036 | 0.211 | |
| NS7 | −0.040 | 0.082 | 0.781 | 0.013 | 0.214 | |
| NS8 | −0.035 | 0.141 | 0.716 | 0.041 | 0.263 | |
| TV1 | 0.040 | 0.246 | −0.031 | 0.650 | −0.034 | 0.88 |
| TV2 | 0.060 | 0.077 | −0.030 | 0.754 | 0.069 | |
| TV3 | −0.025 | 0.099 | 0.007 | 0.860 | 0.091 | |
| TV4 | 0.115 | 0.122 | 0.028 | 0.751 | −0.083 | |
| TV5 | 0.052 | 0.015 | 0.091 | 0.875 | 0.123 | |
| TV6 | 0.116 | −0.004 | 0.085 | 0.791 | 0.066 | |
| OCBI1 | 0.354 | 0.062 | 0.169 | 0.033 | 0.696 | 0.96 |
| OCBI2 | 0.384 | 0.105 | 0.140 | 0.029 | 0.640 | |
| OCBI3 | 0.316 | 0.144 | 0.079 | 0.097 | 0.640 | |
| OCBI4 | 0.322 | 0.166 | 0.196 | 0.038 | 0.679 | |
| OCBI5 | 0.328 | 0.061 | 0.117 | 0.145 | 0.658 | |
| OCBI6 | 0.300 | 0.227 | 0.133 | −0.006 | 0.640 | |
| OCBI7 | 0.375 | 0.173 | 0.156 | 0.076 | 0.566 | |
| OCBI8 | 0.297 | 0.142 | 0.134 | 0.086 | 0.676 | |
| OCBO1 | 0.366 | 0.017 | 0.053 | 0.117 | 0.668 | |
| OCBO2 | 0.280 | 0.104 | 0.103 | 0.125 | 0.756 | |
| OCBO3 | 0.230 | 0.124 | −0.065 | 0.183 | 0.729 | |
| OCBO4 | 0.135 | 0.179 | 0.018 | 0.176 | 0.786 | |
| OCBO5 | 0.110 | 0.173 | 0.085 | −0.030 | 0.809 | |
| OCBO6 | 0.116 | 0.198 | 0.040 | 0.158 | 0.759 | |
| OCBO7 | 0.183 | 0.189 | 0.098 | 0.109 | 0.785 | |
| OCBO8 | 0.107 | 0.187 | 0.058 | 0.102 | 0.719 | |
| Eigenvalues | 11.379 | 5.170 | 5.083 | 4.012 | 3.372 | |
| Variance explained (%) | 26.463 | 12.022 | 11.821 | 9.330 | 7.843 | |
| Accumulative variance explained (%) | 26.463 | 38.485 | 50.306 | 59.636 | 67.478 |
| Variable | Mean | S.D. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Age | 35.24 | 6.98 | ||||||||
| 2. Gender | 0.49 | 0.50 | 0.05 | |||||||
| 3. Tenure | 5.89 | 5.23 | 0.50 *** | 0.04 | ||||||
| 4. Education | 2.81 | 0.62 | −0.22 *** | 0.01 | −0.10 | |||||
| 5. Need for Status | 4.72 | 0.90 | −0.14 * | −0.03 | 0.05 | 0.18 ** | ||||
| 6. Political Skill | 4.73 | 0.86 | −0.08 | −0.21 *** | 0.10 | 0.22 *** | 0.49 *** | |||
| 7. Task Visibility | 4.55 | 0.61 | 0.09 | −0.03 | 0.06 | −0.01 | 0.11 | 0.24 *** | ||
| 8. OCB | 5.01 | 0.85 | −0.05 | −0.14 * | 0.13 * | 0.25 *** | 0.32 *** | 0.35 *** | 0.23 *** | |
| 9. Overall Evaluation | 4.98 | 1.17 | 0.04 | −0.12 * | 0.17 ** | 0.16 ** | 0.20 ** | 0.14 * | 0.06 | 0.76 *** |
| Model | No. of Factors | χ2 | df | Δχ2 | RMSEA | CFI | IFI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline model | Five factors: NS, PS, TV, OCB, OE | 1951.71 | 821 | 0.07 | 0.90 | 0.90 | |
| Model 1 | Four factors: (NS + PS), TV, OCB, OE | 2640.94 | 825 | 289.23 ** | 0.09 | 0.84 | 0.84 |
| Model 2 | Four factors: NS, PS, TV, (OCB + OE) | 2612.89 | 825 | 661.18 *** | 0.09 | 0.85 | 0.85 |
| Model 3 | Three factors: (NS + PS + TV), OCB, OE | 3397.10 | 828 | 1445.39 *** | 0.10 | 0.77 | 0.78 |
| Model 4 | Two factors: (NS + PS + TV), (OCB + OE) | 4050.36 | 830 | 2098.65 *** | 0.11 | 0.72 | 0.72 |
| Variable | OCB | Overall Evaluation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 | Model 7 | |
| Control variables | |||||||
| Age | −0.04 | −0.06 | −0.06 | 0.01 | 0.01 | −0.01 | 0.05 |
| Gender | −0.14 ** | −0.11 * | −0.10 | −0.12 * | −0.12 * | −0.10 | −0.02 |
| Tenure | 0.16 ** | 0.15 * | 0.11 | 0.18 ** | 0.18 * | 0.14 * | 0.05 |
| Education | 0.21 *** | 0.19 *** | 0.18 *** | 0.16 ** | 0.16 ** | 0.16 ** | 0.01 |
| Main effect | |||||||
| Need for status (NS) | 0.26 *** | 0.18 ** | 0.12 | 0.16 ** | 0.16 ** | 0.07 | −0.03 |
| Moderating variables | |||||||
| Political skill (PS) | 0.13 * | 0.17 ** | −0.03 | 0.01 | −0.11 | ||
| Task visibility (TV) | 0.17 ** | 0.19 *** | 0.04 | 0.05 | −0.10 | ||
| Interaction effects | |||||||
| NS ∗ PS | −0.18 ** | −0.14 * | 0.01 | ||||
| NS ∗ TV | 00.17 ** | 0.24 *** | 0.10 | ||||
| Mediating variable | |||||||
| OCB | 0.80 *** | ||||||
| R square | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.61 |
| R square change | 0.04 *** | 0.05 *** | 0.01 | 0.05 *** | 0.48 *** | ||
| Independent Variable | Mediator | Dependent Variable | Moderator | Moderator Level | Conditional Indirect Effect | Product of Coefficients | Bootstrapping Bias-Corrected 95% Confidence Interval | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SE | z | p | Lower | Upper | ||||||
| Need for status | OCB | Overall evaluation | Political skill | Lo (Mean − 1SD) | 0.292 | 0.111 | 2.63 | <0.01 | 0.070 | 0.495 |
| Mean | 0.193 | 0.072 | 2.68 | <0.01 | 0.051 | 0.331 | ||||
| Hi (Mean + 1SD) | 0.094 | 0.078 | 1.21 | ns. | −0.045 | 0.258 | ||||
| Task visibility | Lo (Mean − 1SD) | 0.190 | 0.098 | 1.94 | ns. | −0.010 | 0.380 | |||
| Mean | 0.227 | 0.066 | 3.44 | <0.01 | 0.091 | 0.347 | ||||
| Hi (Mean + 1SD) | 0.263 | 0.073 | 3.60 | <0.01 | 0.131 | 0.409 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.; Chae, H. The Need for Status, Organizational Citizenship Behavior, and Overall Evaluation: Focusing on the Moderating Effects of Political Skill and Task Visibility. Behav. Sci. 2024, 14, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14020105
Park J, Chae H. The Need for Status, Organizational Citizenship Behavior, and Overall Evaluation: Focusing on the Moderating Effects of Political Skill and Task Visibility. Behavioral Sciences. 2024; 14(2):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14020105
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jisung, and Heesun Chae. 2024. "The Need for Status, Organizational Citizenship Behavior, and Overall Evaluation: Focusing on the Moderating Effects of Political Skill and Task Visibility" Behavioral Sciences 14, no. 2: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14020105
APA StylePark, J., & Chae, H. (2024). The Need for Status, Organizational Citizenship Behavior, and Overall Evaluation: Focusing on the Moderating Effects of Political Skill and Task Visibility. Behavioral Sciences, 14(2), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14020105





