Age Weakens the Other-Race Effect among Han Subjects in Recognizing Own- and Other-Ethnicity Faces
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Participants
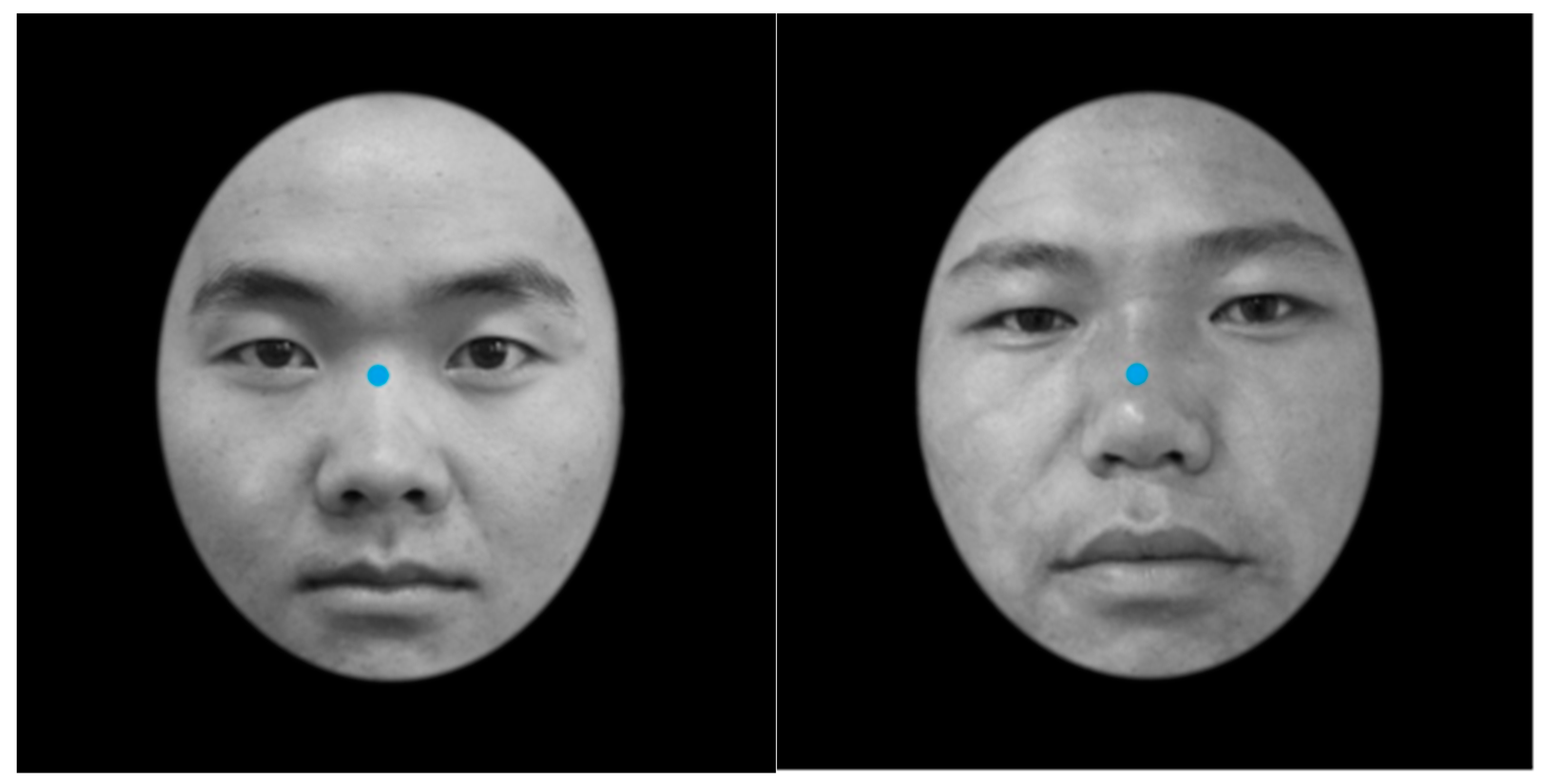
2.2. Experimental Materials
2.3. Equipment
2.4. Procedure
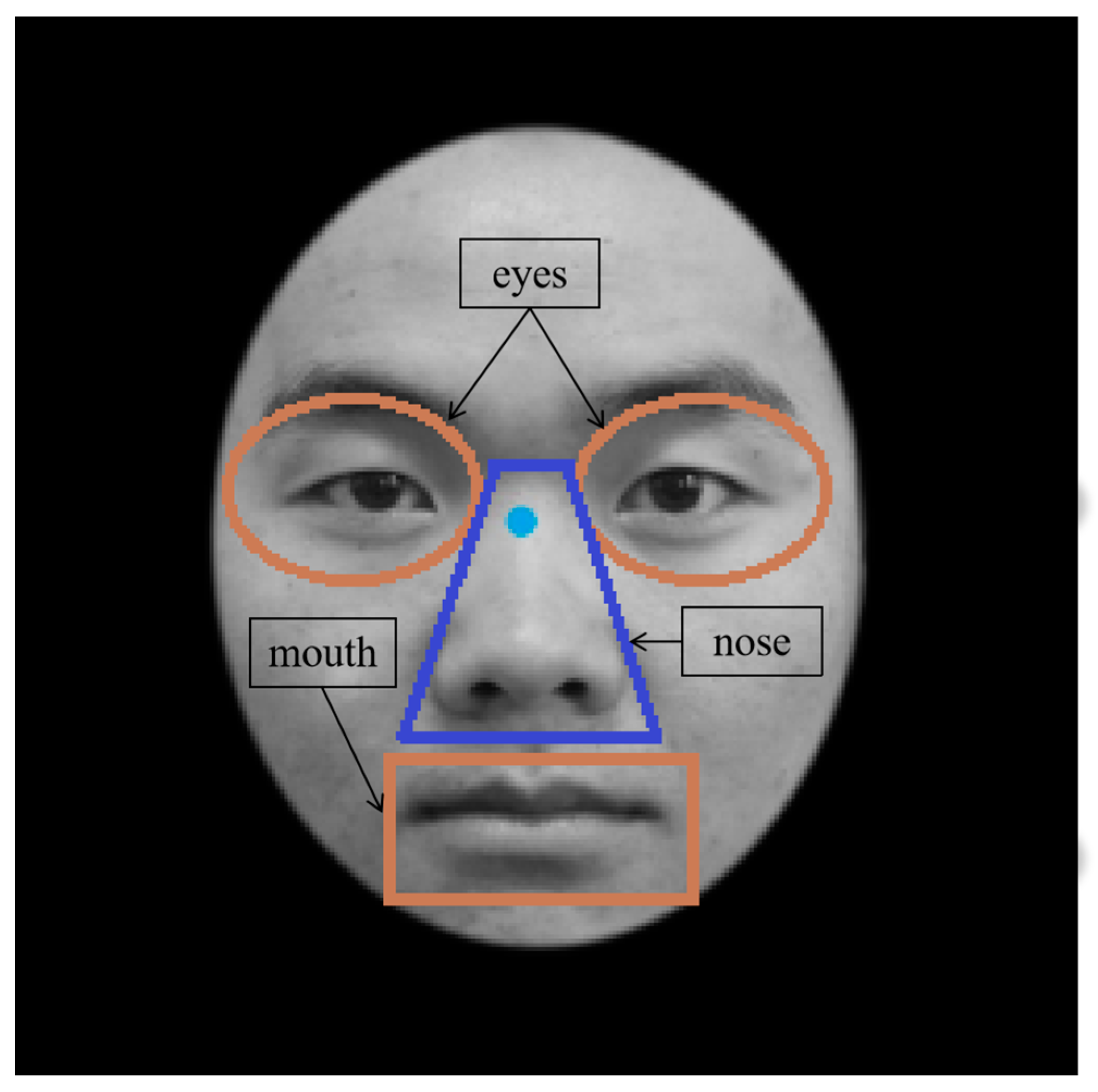
2.5. Research Design and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Data
Accuracy
3.2. Eye Movement Data
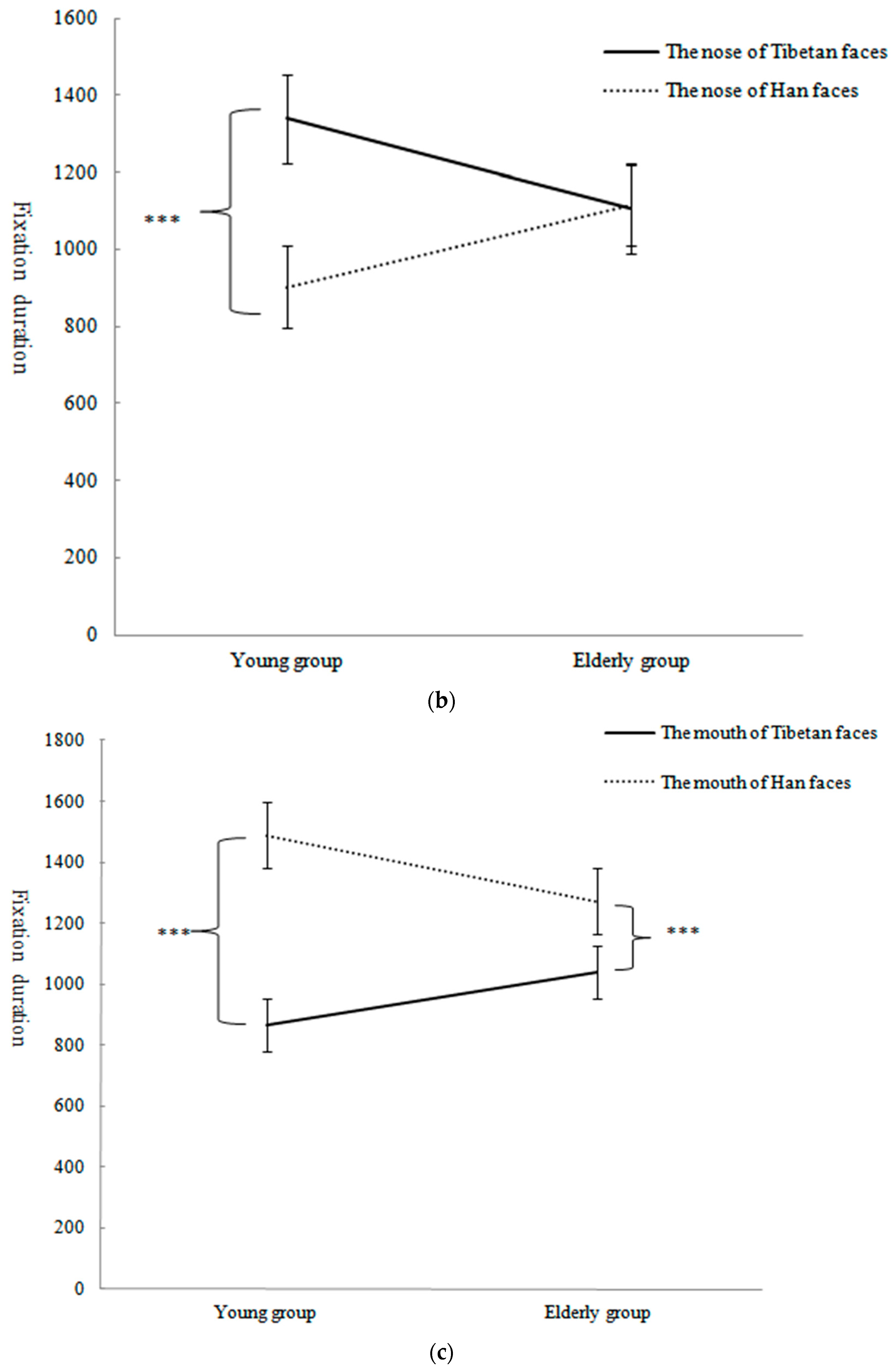
3.2.1. Fixation Duration for Facial AOIs
3.2.2. Fixation Counts for Facial AOIs
4. Discussion
4.1. ORE and Scanning Patterns of Cross-Ethnic Face Recognition
4.2. The Regulatory Effect of Age on the ORE and Visual Scanning Patterns of Cross-Ethnic Face Recognition
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malpass, R.S.; Kravitz, J. Recognition for faces of own and other race. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1969, 13, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jia, D.-M.; Liu, G.-X.; Long, C.-Q. Relationship between inter-ethnic friendship and cross-race effect in face recognition of Uygur and Han college students. Chin. Ment. Health J. 2017, 31, 406–411. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.L. The Lateralization Characteristics of Face Recognition of Tibetan Han and Hui Nationalities. Master Thesis, Northwest Normal University, LanZhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, D.J.; Miellet, S.; Caldara, R. Culture shapes eye movements for visually homogeneous objects. Front. Psychol. 2010, 1, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Quinn, P.C.; Wheeler, A.; Xiao, N.; Ge, L.; Lee, K. Similarity and difference in the processing of same-and other-race faces as revealed by eye tracking in 4-to 9-month-olds. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2011, 108, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, A.; Anzures, G.; Quinn, P.C.; Pascalis, O.; Omrin, D.S.; Lee, K. Caucasian infants scan own-and other-race faces differently. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassbender, I.; Lohaus, A. Fixations and fixation shifts in own-race and other-race face pairs at three, six and nine months. Infant Behav. Dev. 2019, 57, 101328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Hu, C.S.; Wang, Q.; Quinn, P.C.; Lee, K. Adults scan own-and other-race faces differently. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, R.; Kennett, S. Own-race and own-university biases in eye movements for face processing. Perception 2013, 42, 204. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Elshiekh, A.; Moulson, M.C. Lifetime perceptual experience shapes face memory for own-and other-race faces. Vis. Cogn. 2019, 27, 687–700. [Google Scholar]
- Miellet, S.; Vizioli, L.; He, L.; Zhou, X.; Caldara, R. Mapping face recognition information use across cultures. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brielmann, A.A.; Bülthoff, I.; Armann, R. Looking at faces from different angles: Europeans fixate different features in Asian and Caucasian faces. Vis. Res. 2014, 100, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Xiao, N.G.; Quinn, P.C.; Hu, C.S.; Qian, M.; Fu, G.; Lee, K. Visual scanning and recognition of Chinese, Caucasian, and racially ambiguous faces: Contributions from bottom-up facial physiognomic information and top-down knowledge of racial categories. Vis. Res. 2015, 107, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldinger, S.D.; He, Y.; Papesh, M.H. Deficits in cross-race face learning: Insights from eye movements and pupillometry. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 2009, 35, 1105–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, H.F.; Boland, J.E.; Nisbett, R.E. Cultural variation in eye movements during scene perception. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12629–12633. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Yang, B.; Li, Y. The left side of the face may be fixated on more often than the right side: Visual lateralization in recognizing own-and other-race faces. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardif, J.; Fiset, D.; Zhang, Y.; Estéphan, A.; Cai, Q.; Luo, C.; Sun, D.; Gosselin, F.; Blais, C. Culture shapes spatial frequency tuning for face identification. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2017, 43, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, G.P.; Bornstein, B.H.; Laub, C.E.; Mills, M.; Dodd, M.D. Perceptual processes in the cross-race effect: Evidence from eyetracking. Basic Appl. Soc. Psychol. 2014, 36, 478–493. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Luo, S.; Wu, B.; Wu, X.; Han, S. Mortality salience enhances racial in-group bias in empathic neural responses to others’ suffering. NeuroImage 2015, 118, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.Y.; Zhu, M.; Gao, X.P. Configural processing of faces in old adulthood. Adv. Psychol. Sci. 2017, 25, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Wang, Q.; Fu, G.; Quinn, P.C.; Lee, K. Both children and adults scan faces of own and other races differently. Vis. Res. 2014, 102, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzures, G.; Quinn, P.C.; Pascalis, O.; Slater, A.M.; Lee, K. Development of own-race biases. Vis. Cogn. 2013, 21, 1165–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.J.; Quinn, P.C.; Slater, A.M.; Lee, K.; Gibson, A.; Smith, M.; Ge, L.; Pascalis, O. Three-month-olds, but not newborns, prefer own-race faces. Dev. Sci. 2005, 8, F31–F36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bar-Haim, Y.; Ziv, T.; Lamy, D.; Hodes, R.M. Nature and nurture in own-race face processing. Psychol. Sci. 2006, 17, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.J.; Liu, S.; Ge, L.; Quinn, P.C.; Slater, A.M.; Lee, K.; Liu, Q.; Pascalis, O. Cross-race preferences for same-race faces extend beyond the African versus Caucasian contrast in 3-month-old infants. Infancy 2007, 11, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kelly, D.J.; Liu, S.; Lee, K.; Quinn, P.C.; Pascalis, O.; Slater, A.M.; Ge, L. Development of the other-race effect during infancy:Evidence toward universality? J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2009, 104, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.J.; Liu, S.; Rodger, H.; Miellet, S.; Ge, L.; Caldara, R. Developing cultural differences in face processing. Dev. Sci. 2011, 14, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Heering, A.; De Liedekerke, C.; Deboni, M.; Rossion, B. The role of experience during childhood in shaping the other-race effect. Dev. Sci. 2010, 13, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezdek, K.; Blandon-Gitlin, I.; Moore, C. Children’s face recognition memory: More evidence for the cross-race effect. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 760–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzures, G.; Wheeler, A.; Quinn, P.C.; Pascalis, O.; Slater, A.M.; Heron-Delaney, M.; Tanaka, J.W.; Lee, K. Brief daily exposures to Asian females reverses perceptual narrowing for Asian faces in Caucasian infants. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2012, 112, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, P.J.; Lewis, M.B. Reducing the own-race bias in face recognition by shifting attention. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 2006, 59, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, J.W.; Pierce, L.J. The neural plasticity of other-race face recognition. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2009, 9, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, G.; Locke, V.; Ewing, L.; Evangelista, E. Race coding and the other-race effect in face recognition. Perception 2009, 38, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argyle, M.; Cook, M. Gaze and Mutual Gaze; Cambridge University Press: Oxford, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Blais, C.; Jack, R.E.; Scheepers, C.; Fiset, D.; Caldara, R. Culture shapes how we look at faces. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Z. Culture and gaze direction in conversation. RASK 2004, 20, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Yang, B.; Luo, R.; Ding, X. Development of a facial-expression database of Chinese Han, Hui and Tibetan people. Int. J. Psychol. 2020, 55, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, M.G.; Fernández-Martín, A.; Nummenmaa, L. A smile biases the recognition of eye expressions: Configural projection from a salient mouth. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 2013, 66, 1159–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.; Chan, A.; Lee, T.; Hsiao, J. Eye movement patterns in face recognition are associated with cognitive decline in older adults: An hmm approach. J. Vis. 2018, 18, 2200–2207. [Google Scholar]
- Calvo, M.G.; Fernández-Martín, A. Can the eyes reveal a person’s emotions? Biasing role of the mouth expression. Motiv. Emot. 2013, 37, 202–211. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.; Song, L.; Bentin, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, L. Visual search for faces by race: A cross-race study. Vis. Res. 2013, 89, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ma, J.L.; Huang, J.Y. The Other-Race Effect of Tibetan and Han Face Recognition—Evidence from Behavioral and Eye Tracking Technology. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. under review.
- Cangöz, B.; Altun, A.; Aşkar, P.; Baran, Z.; Mazman, S.G. Examining the visual screening patterns of emotional facial expressions with gender, age and lateralization. J. Eye Mov. Res. 2013, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, S.; Ruffman, T.; Hutton, S.B. Age differences in emotion recognition skills and the visual scanning of emotion faces. J. Gerontol. Ser. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2007, 62, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
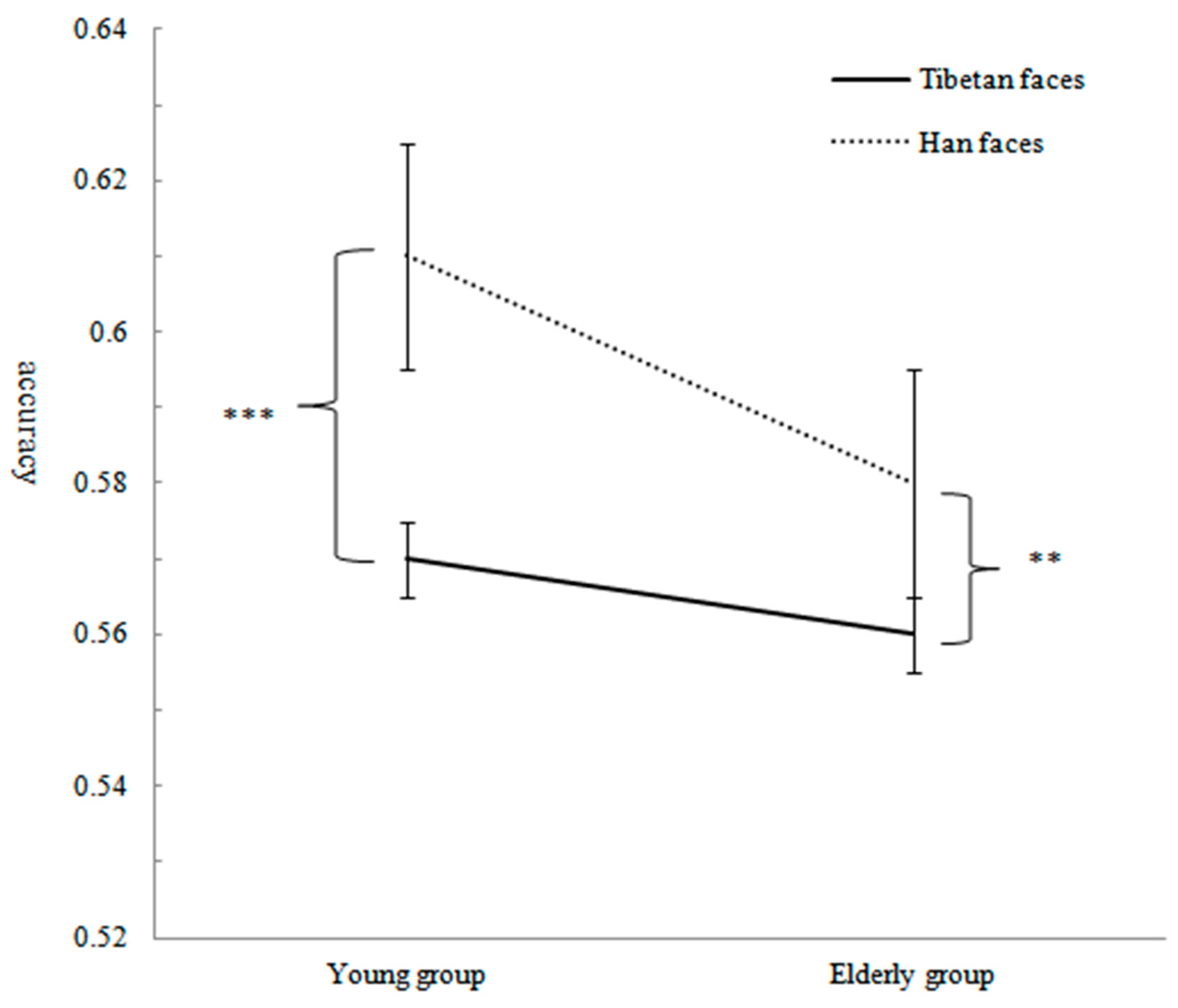



| Tibetan Face | Han Face | |
|---|---|---|
| Young group | 0.57 ± 0.16 | 0.61 ± 0.13 |
| Elderly group | 0.56 ± 0.15 | 0.58 ± 0.18 |
| AOI | Fixation Duration | Fixation Count | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tibetan Faces | Han Faces | Tibetan Faces | Han Faces | |
| Eyes | 1540.28 ± 521.51 | 1589.43 ± 472.66 | 6.36 ± 2.00 | 5.52 ± 1.39 |
| Nose | 1222.62 ± 402.46 | 1007.95 ± 454.69 | 4.37 ± 1.15 | 3.45 ± 1.25 |
| Mouth | 952.91 ± 475.28 | 1380.56 ± 506.70 | 3.17 ± 1.49 | 5.00 ± 1.37 |
| AOI | Young Group | Elderly Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tibetan Faces | Han Faces | Tibetan Faces | Han Faces | |
| Eyes | 1639.98 ± 525.24 | 1665.94 ± 487.42 | 1440.58 ± 506.80 | 1512.93 ± 454.09 |
| Nose | 1339.02 ± 408.51 | 903.00 ± 496.21 | 1106.22 ± 369.62 | 1112.90 ± 398.17 |
| Mouth | 865.12 ± 487.46 | 1488.68 ± 552.43 | 1040.70 ± 455.31 | 1272.42 ± 448.41 |
| AOI | Young Group | Elderly Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tibetan Faces | Han Faces | Tibetan Faces | Han Faces | |
| Eyes | 5.65 ± 1.93 | 5.76 ± 2.11 | 5.11 ± 2.05 | 5.32 ± 1.78 |
| Nose | 4.58 ± 1.45 | 3.04 ± 1.20 | 4.20 ± 1.14 | 3.80 ± 1.20 |
| Mouth | 2.63 ± 1.39 | 5.07 ± 1.39 | 3.63 ± 1.42 | 4.94 ± 1.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y. Age Weakens the Other-Race Effect among Han Subjects in Recognizing Own- and Other-Ethnicity Faces. Behav. Sci. 2023, 13, 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13080675
Ma J, Zhang R, Li Y. Age Weakens the Other-Race Effect among Han Subjects in Recognizing Own- and Other-Ethnicity Faces. Behavioral Sciences. 2023; 13(8):675. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13080675
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Jialin, Rui Zhang, and Yongxin Li. 2023. "Age Weakens the Other-Race Effect among Han Subjects in Recognizing Own- and Other-Ethnicity Faces" Behavioral Sciences 13, no. 8: 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13080675
APA StyleMa, J., Zhang, R., & Li, Y. (2023). Age Weakens the Other-Race Effect among Han Subjects in Recognizing Own- and Other-Ethnicity Faces. Behavioral Sciences, 13(8), 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13080675





